Overview of Updates and Upgrades
Your environment encounters challenges when trying to maintain databases at their latest version, leading to a dilemma where you either postpone your patching cycles or neglect to patch the databases altogether. This situation significantly heightens your vulnerability to potential threats.
| Unpatched Systems | Misconfiguration and Sprawl | Compromised Administrative Privileges |
|---|---|---|
| High risk of breaches | 45% of breaches were due to misconfiguration | 74% of breaches leveraged weak credentials |
| 21% of breaches are due to unpatched systems even though patches were available, but not applied | Preferred way to exploit are misconfigurations, insecure configuration changes, and sprawl. Home grown scripts increase vulnerability and maintenance cost | Lack of security policies with principles of least privileges to users contributes to breaches and security incidents |
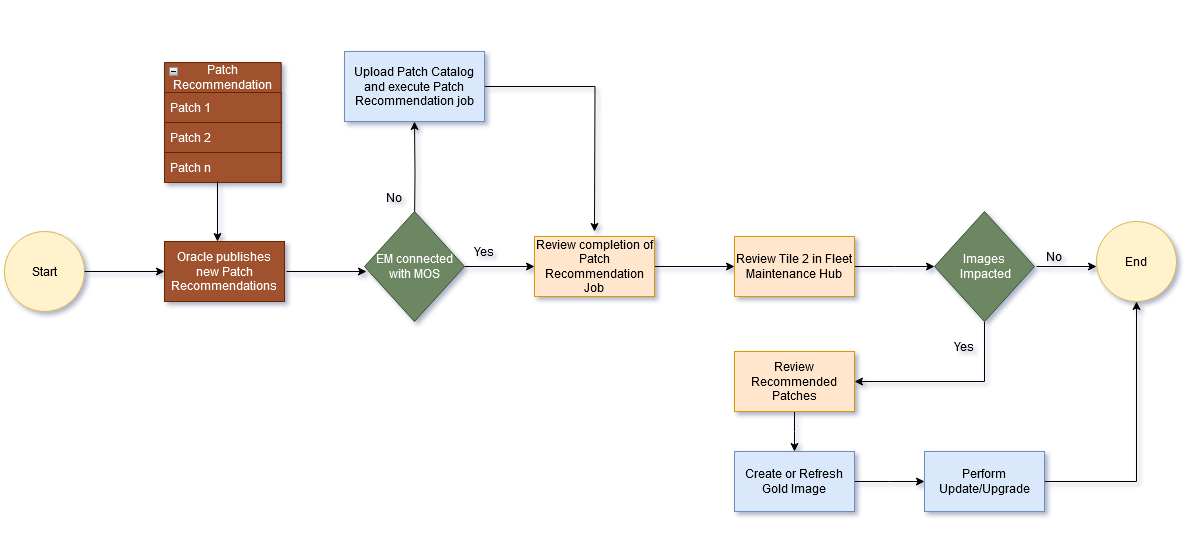
The following figure lists the steps required to perform database fleet maintenance. It covers various configurations such as RAC and Single Instance databases with or without Data Guard, Oracle Restart, RAC One-Node, and Grid Infrastructure Homes.
Figure 17-1 Fleet Maintenance Operations Lifecycle Overview
The video Patch Oracle Databases Using Oracle Enterprise Manager Fleet Maintenance, gives an overview of Oracle Database patching and features examples for single instance database patching: