6 Provisioning Oracle Grid Infrastructure for Oracle Real Application Clusters Databases
This chapter explains how you can mass-deploy Oracle Grid Infrastructure and Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) for clustered environments in an unattended, repeatable, and reliable manner. In particular, this chapter covers the following:
-
Getting Started with Provisioning Grid Infrastructure for Oracle RAC Databases
-
Provisioning Oracle Real Application Clusters Database with File System on an Existing Cluster
-
Provisioning Oracle Real Application Clusters Database with File System on a New Cluster
-
Using No Root Credentials for Provisioning Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) Databases
Getting Started with Provisioning Grid Infrastructure for Oracle RAC Databases
This section helps you get started with this chapter by providing an overview of the steps involved in provisioning Oracle Grid Infrastructure and Oracle RAC. Consider this section to be a documentation map to understand the sequence of actions you must perform to successfully provision Oracle Grid Infrastructure and Oracle RAC. Click the reference links provided against the steps to reach the relevant sections that provide more information.
Table 6-1 Getting Started with Provisioning Oracle Grid Infrastructure and Oracle RAC Databases
| Step | Description | Reference Links |
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
Understanding Oracle RAC Topology Understand the Oracle Real Application Clusters Database topology provisioned by Cloud Control. |
To learn about the topology, see Oracle Real Application Clusters Database Topologyand Oracle Flex Clusters and Flex ASM. |
|
Step 2 |
Selecting the Use Case This chapter covers a few use cases for provisioning Oracle Grid Infrastructure and Oracle RAC. Select the use case that best matches your requirements. |
|
|
Step 3 |
Meeting the Prerequisites Before you run any Deployment Procedure, you must meet the prerequisites, such as setting up of the provisioning environment, applying mandatory patches, and setting up of Oracle Software Library. |
|
|
Step 4 |
Running the Deployment Procedure Run the Deployment Procedure to successfully provision Oracle Grid Infrastructure and Oracle RAC. |
|
Oracle Real Application Clusters Database Topology
Oracle Enterprise Manager enables standardized gold image-based deployments of Oracle RAC databases with provisioning profiles, input lock down in designer role, and associating compliance standards with databases. Figure 6-1 shows a typical Oracle RAC database topology that you can provision using Enterprise Manager.
Figure 6-1 Oracle RAC Database Topology
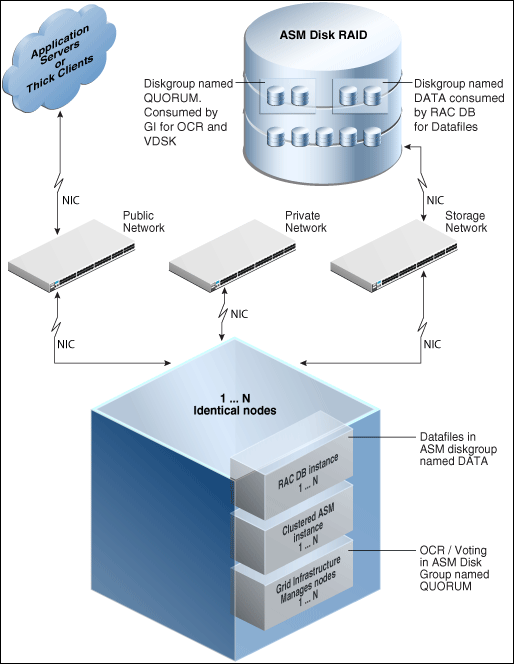
The topology shows a N-node setup using Grid Infrastructure, clustered ASM, and policy-managed Oracle RAC database. An ASM disk array is shared thorough the cluster setup. The Grid Infrastructure uses an ASM diskgroup named QUORUM for Oracle Cluster Registry (OCR) and Voting Disk (Heartbeat). The Oracle RAC database uses another diskgroup named DATA. This stores database datafiles. The nodes are multihomed such that a high speed internal network between nodes facilitates cluster operation, and a public network is used for external connectivity. The networks are public, private, and storage network between nodes and the ASM disk array.
Oracle Flex Clusters and Flex ASM
Oracle Flex Clusters
Oracle Grid Infrastructure installed in an Oracle Flex Cluster configuration is a scalable, dynamic, robust network of nodes. Oracle Flex Clusters provide a platform for a variety of applications, including Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) databases with large numbers of nodes. Oracle Flex Clusters also provide a platform for other service deployments that require coordination and automation for high availability.
All nodes in an Oracle Flex Cluster belong to a single Oracle Grid Infrastructure cluster. This architecture centralizes policy decisions for deployment of resources based on application needs, to account for various service levels, loads, failure responses, and recovery.
Oracle Flex Clusters contain two types of nodes arranged in a hub and spoke architecture: Hub Nodes and Leaf Nodes. The number of Hub Nodes in an Oracle Flex Cluster can be as many as 64. The number of Leaf Nodes can be many more. Hub Nodes and Leaf Nodes can host different types of applications.
Hub Nodes are similar to Oracle Grid Infrastructure nodes in an Oracle Clusterware standard Cluster configuration: they are tightly connected, and have direct access to shared storage. In an Oracle Flex Cluster configuration, shared storage can be provisioned to Leaf Nodes independent of the Oracle Grid Infrastructure.
Leaf Nodes are different from standard Oracle Grid Infrastructure nodes, in that they do not require direct access to shared storage, but instead request data through Hub Nodes. Hub Nodes can run in an Oracle Flex Cluster configuration without having any Leaf Nodes as cluster member nodes, but Leaf Nodes must be members of a cluster that includes at least one Hub Node.
Oracle Flex ASM
Oracle Flex ASM enables an Oracle ASM instance to run on a separate physical server from the database servers. With this deployment, larger clusters of Oracle ASM instances can support more database clients while reducing the Oracle ASM footprint for the overall system.
For more information on Oracle Flex Clusters and Flex ASM see the links below:
- Oracle Database documentation
- Overview of Oracle Flex ASM in Automatic Storage Management Administrator's Guide.
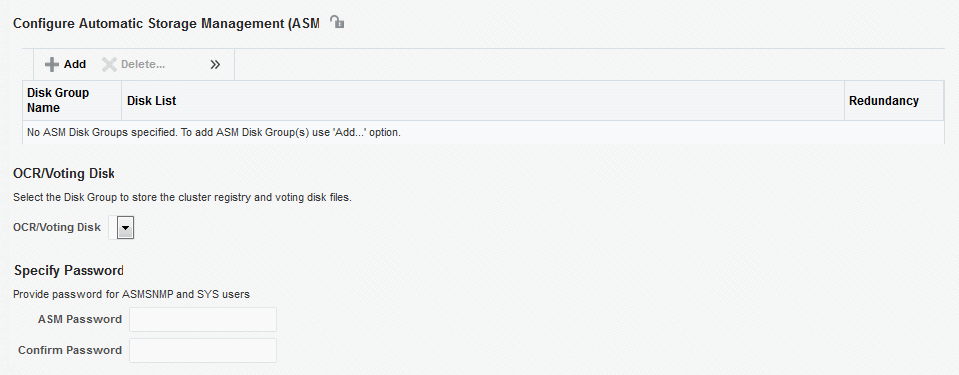
Provisioning Grid Infrastructure with Oracle Real Application Clusters Database and Configuring Database with Oracle Automatic Storage Management
This section describes how you can provision Grid Infrastructure with Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) Database and configure Database with Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM).
In particular, this section covers the following:
Prerequisites for Provisioning Grid Infrastructure with Oracle RAC Database
Before running the Deployment Procedure, meet the prerequisites listed in Setting Up Database Provisioning.
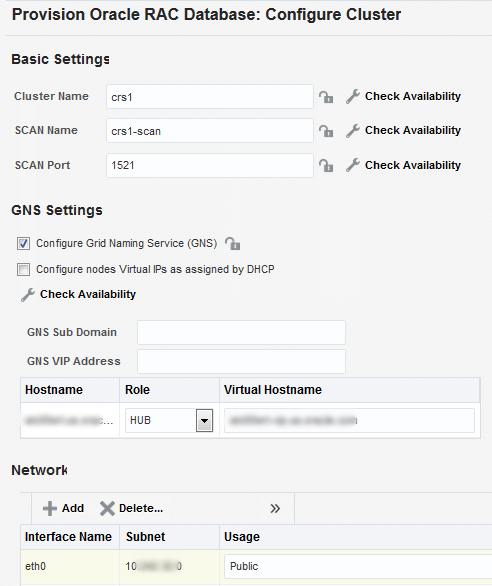
Procedure for Provisioning Grid Infrastructure with Oracle RAC Database and ASM
To provision the grid infrastructure with Oracle RAC database, and to configure the database with Oracle ASM, follow these steps:
Note:
If the Deployment Procedure fails, then review log files described in Reviewing Log Files.
Requirements for Grid Infrastructure Software Location Path
Meet the following requirements while specifying a directory path for the Oracle Grid Infrastructure home to deploy the Oracle Grid Infrastructure binaries. These requirements are suggested as the GI configuration changes the ownership of the GI home and all parent directories to be owned by root.
-
It should be created in a path outside existing Oracle homes.
-
It should not be located in a user home directory.
-
It should be created either as a subdirectory in a path where all files can be owned by root, or in a unique path.
-
Before installation, it should be owned by the installation owner of Oracle Grid Infrastructure (typically,
oracle, for a single installation owner for all Oracle software, or grid for role-based Oracle installation owners), and set to 755 permissions.
Provisioning Oracle Real Application Clusters Database with File System on an Existing Cluster
This section describes how you can provision Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) database with a file system on an existing cluster. In particular, this section covers the following:
Prerequisites for Provisioning Oracle RAC Database with File System on an Existing Cluster
Before running the Deployment Procedure, meet the prerequisites listed in Setting Up Database Provisioning.
Procedure for Provisioning Oracle RAC with ASM or File System on an Existing Cluster
To provision Oracle RAC databases with file system on an existing cluster, follow these steps:
Note:
If the Deployment Procedure fails, then review log files described in Reviewing Log Files.
Provisioning Oracle Real Application Clusters Database with File System on a New Cluster
This section describes how to provision Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) Database with file system on a new cluster. In particular, this section covers the following:
Prerequisites for Provisioning Oracle RAC Database with File System on a New Cluster
Before running the Deployment Procedure, meet the prerequisites listed in Setting Up Database Provisioning.
Procedure for Provisioning Oracle RAC Database with File System on a New Cluster
Note:
If the Deployment Procedure fails, then review log files described in Reviewing Log Files.