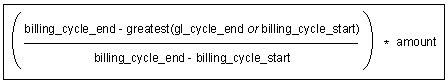11 About Event-Based Revenue Recognition
Learn how to set up revenue recognition based on the event schedule in Oracle Communications Billing and Revenue Management (BRM).
Topics in this document:
About Event-Based Revenue Recognition
In event-based revenue recognition, BRM recognizes revenue based on the event schedule:
-
Revenue from one-time purchases, cancellation charges, and usage charges is earned immediately.
-
Revenue from recurring charges is earned over the cycle period, such as over the month or over the quarter, as services are rendered. For example, a monthly cycle charge is considered only partially earned if the customer hasn't used the entire month of service yet.
In event-based revenue recognition, BRM can report these revenue types:
-
Billed
-
Unbilled
-
Billed earned revenue
-
Billed unearned revenue
-
Unbilled earned revenue
-
Unbilled unearned revenue
-
Previously billed earned revenue
Examples of Billed and Unbilled Revenue
If your company uses immediate revenue recognition, BRM reports all revenue as billed or unbilled.
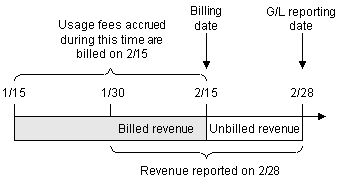
Billed and Unbilled Usage Fees
In Figure 11-1, the last billing date for the customer was 2/15, and the G/L report was run on 2/28. Usage fees occurring between 2/15 and 2/28 are reported as unbilled.
Figure 11-1 Billed and Unbilled Usage Fees
Description of "Figure 11-1 Billed and Unbilled Usage Fees"
Billed and Unbilled Purchase and Cancellation Fees
In Figure 11-2, a purchase fee made on 1/20 was billed during the scheduled billing cycle that ran on 2/15. Another purchase fee was made on 2/20. Since the scheduled billing date (2/15) has passed, the revenue for the second purchase fee is recorded as unbilled.
Figure 11-2 Billed and Unbilled Purchase and Cancellation Fees
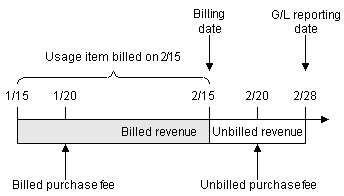
Description of "Figure 11-2 Billed and Unbilled Purchase and Cancellation Fees"
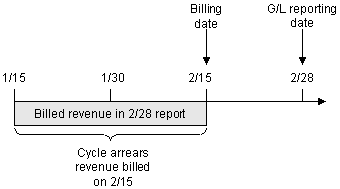
Billed Cycle Arrears Fees
Cycle arrears fees are always billed. In the example illustrated in Figure 11-3, the cycle arrears fee billed on 2/15 is included in the 2/28 report as billed.
Billed and Unbilled Cycle Forward Arrears Fees
In Figure 11-4, the last billing date for the customer was 2/15, and the G/L report was run on 2/28. Cycle forward arrears fees occurring between 2/15 and 2/28 are reported as unbilled:
Figure 11-4 Billed and Unbilled Cycle Forward Arrears Fees
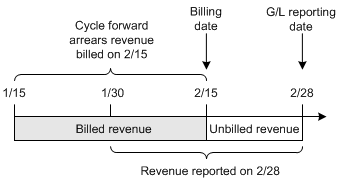
Description of "Figure 11-4 Billed and Unbilled Cycle Forward Arrears Fees"
Billed and Unbilled Nonrated Events
Revenue from nonrated events that are not included in bill items, such as payments and refunds, is always recorded as billed if the event occurs before the G/L report. The billing date has no effect on whether a payment or refund is reported as billed. If a payment or refund event occurs after a G/L reporting date, it is not included in the report.
In Figure 11-5, the payments made on 1/31 and 2/20 are included as billed revenue in the 2/28 G/L report. The payment made on 3/20 is not included in the 2/28 G/L report.
Figure 11-5 Billed and Unbilled Nonrated Events
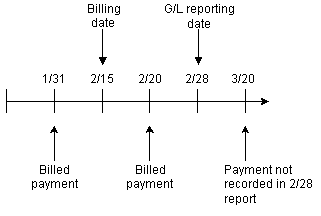
Description of "Figure 11-5 Billed and Unbilled Nonrated Events"
Billed and Unbilled Cycle Forward Fees
Cycle forward fees are always billed except when the cycle forward fee is for a new account. In Figure 11-6, the cycle forward fee billed on 2/28 is reported as billed in the G/L report on 3/15.
Figure 11-6 Billed and Unbilled Cycle Forward Fees
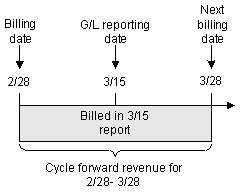
Description of "Figure 11-6 Billed and Unbilled Cycle Forward Fees"
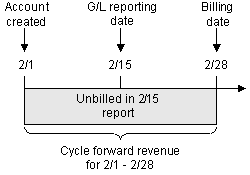
About Unbilled Cycle Forward Fees
Cycle forward fees can be unbilled when the fee is for a new account.
In Figure 11-7, the cycle forward fee charged when the account is created is not billed until 2/28. Therefore, the G/L report run on 2/15 reports the revenue as unbilled.
About Earned and Unearned Revenue
If your company uses accrual–based revenue recognition, BRM reports revenue as earned and unearned. BRM reports these revenue types:
-
Billed earned
-
Unbilled earned
-
Billed unearned
-
Unbilled unearned
-
Previously billed earned
Earned revenue is earned at the time that a G/L report is run. Usage, purchase, and cancellation fees are always earned.
Unearned revenue is not earned at the time the G/L report is run. Unearned revenue only applies to revenue from cycle forward fees and cycle forward arrears fees.
Figure 11-8 shows the earned and unearned revenue for a cycle forward fee.
Figure 11-8 Earned and Unearned Revenue in a Cycle Forward Fee
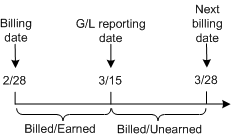
Description of "Figure 11-8 Earned and Unearned Revenue in a Cycle Forward Fee"
In a cycle forward arrears fee, the revenue is recognized at the start of the cycle, but not billed until the end of the cycle. Figure 11-9 shows earned and unearned revenue for a cycle forward arrears fee.
Figure 11-9 Earned and Unearned Cycle Forward Arrears Fees
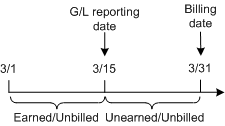
Description of "Figure 11-9 Earned and Unearned Cycle Forward Arrears Fees"
Figure 11-10 shows the first cycle forward fee when the account is not billed at account creation.
Figure 11-10 Cycle Forward Fee at Account Creation
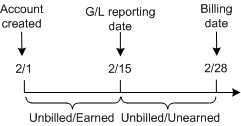
Description of "Figure 11-10 Cycle Forward Fee at Account Creation"
About Previously Billed Earned Revenue
Previously billed revenue is revenue that was billed in the previous billing cycle but recognized in the current G/L cycle. For example, if a portion of a cycle event, such as a cycle fee, is earned across two G/L cycles, BRM reports the earned portion of this revenue as previously billed earned revenue.
About Incremental Reports and Cumulative Revenue
When you export G/L reports for the following revenue types, the reports include cumulative revenue across reporting periods:
-
Unbilled
-
Unbilled earned
-
Unbilled unearned
-
Billed unearned
Part of the total revenue reported for the current period may have been included in the same report for the previous period. The export operation determines the cumulative revenue amounts by calculating the difference between the revenue reported in the current reporting period for a G/L segment and the revenue reported in the previous reporting period for the same G/L segment. (The end date for the previous report is the start date for the current report.) The G/L reports contain the incremental revenue amounts.
When you export G/L reports for nested segments and the revenue type is unbilled, unbilled unearned, unbilled earned, or billed unearned revenue (cumulative revenue), the segment you report on must be the same from reporting period to reporting period. For example, if a January G/L report calculates unbilled revenue for the .westcoast.california G/L segment, the February G/L report must calculate Unbilled revenue for the .westcoast.california G/L segment. If, instead, the February report calculates unbilled revenue for the .westcoast G/L segment or .westcoast.california.sf G/L segment, the G/L data overlaps and invalid revenue is reported.
Note:
You can specify overlapping segments for snapshot reports; however, it is not recommended.
About Reversing G/L Entries
An amount reported as unbilled should be reversed in your company's general ledger in the period following the one in which it was reported. For example, an entry made for unbilled revenue in the month of January should be reversed if it is billed in February. BRM automatically reverses its general ledger data when it changes from unbilled to billed; however, you might need to reverse the data in your company's accounting software.
About Adjustments and G/L Reporting
By default, adjustments made to an open bill item or a pending bill item are always considered billed. The BRM system creates an /event/billing/adjustment/event object and records the adjustment amount as billed in the adjustment item (/item/adjustment). The adjusted amount is reported in the billed G/L report.
In addition, when adjustments are made to a pending bill item, the original amount in the bill item is considered unbilled and is reported in the unbilled G/L report, and the adjustment amount in the adjustment item (item/adjustment) is considered billed and reported in the billed G/L report. When the pending bill items are eventually billed, the billed amount is reported in the billed G/L report.
You can change this behavior to create shadow event objects instead of adjustment event objects. Creating shadow event objects has the following advantages:
-
For pending bill item adjustments, both the original amount and the adjustment amount are associated with the same bill item and are recorded in the unbilled G/L report until billing is run.
-
Adjustment amounts do not show up in customers' bills as line items that modify the total due because the events have already been adjusted. You can specify whether shadow event adjustment details are displayed in invoices. See the discussion on customizing information included in invoices in BRM Configuring and Running Billing.
Note:
Shadow events are created for event-level adjustments only. BRM creates shadow events only for events that are adjusted before they are billed.
To specify whether to generate a shadow event or adjustment event, you modify the input list of the PCM_OP_AR_EVENT_ADJUSTMENT opcode. For more information, see the chapter about accounts receivable opcode workflows in BRM Opcode Guide.
How BRM Calculates Earned and Unearned Revenue
BRM uses formulas to calculate earned and unearned revenue. You can use these formulas to determine if revenue is calculated as expected.
Each event in BRM is associated with an item. The status of an item can be pending, open, or closed.
Each item starts in the pending state, gathering events that accrue revenue for the duration of the billing cycle. At the time of billing, the item changes status from pending to open. An open item indicates that payment for the item is due and a bill has been generated. Once payment is received, the status of the item changes to closed.
-
Revenue for events associated with a pending item is unbilled revenue.
-
Revenue for events associated with an open or closed item is billed revenue.
The PIN_FLD_EFFECTIVE_T field in the /item object holds the date on which an item goes from pending (unbilled) to open (billed) status. This date is used by BRM to determine whether revenue is billed or unbilled.
When BRM creates a cycle event (/event/billing/cycle), the cycle dates for the cycle fee are saved in fields called PIN_FLD_EARNED_START_T and PIN_FLD_EARNED_END_T. The equations in this chapter use the values in those fields. The fields are represented in the equations as shown in Table 11-1:
Table 11-1 Fields and Equations
| Field Name | Equation Name |
|---|---|
|
PIN_FLD_EARNED_START_T |
billing_cycle_start |
|
PIN_FLD_EARNED_END_T |
billing_cycle_end |
Calculating Billed Earned Revenue
BRM uses the equation in Figure 11-11 to calculate billed earned revenue:
Figure 11-11 Billed Earned Revenue Equation
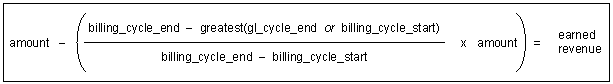
Description of "Figure 11-11 Billed Earned Revenue Equation"
For example, you run the G/L report on the first of every month. A new customer account is created on 7/3, after the G/L report is run on 7/1. Because the new customer's billing cycle runs from 7/3 to 8/3, the monthly cycle fee covers the period from 7/3 to 8/3. Since G/L is posted on the first of every month, the report run on 8/1 shows the revenue earned for the monthly cycle fees for the period 7/3 to 8/1 in the billed_earned category as shown in Figure 11-12.
Figure 11-12 Calculating Billed Earned Revenue
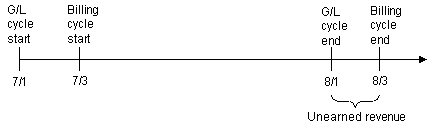
Description of "Figure 11-12 Calculating Billed Earned Revenue"
If the monthly fee is $100, BRM calculates the earned revenue for the period 7/1 to 8/1 as shown in Figure 11-13:
Figure 11-13 Sample Earned Revenue Calculation
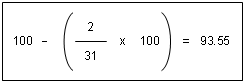
Description of "Figure 11-13 Sample Earned Revenue Calculation"
Calculating Previously Billed Earned Revenue
BRM uses the equation in Figure 11-14 to calculate previously billed revenue:
Figure 11-14 Previously Billed Revenue Equation

Description of "Figure 11-14 Previously Billed Revenue Equation"
For example, if a new customer account is created on 7/3 with a bimonthly cycle fee, then the new customer is billed for the next bimonthly cycle fee on 9/3. Since your company requires you to run the G/L report on the first of every month and the cycle fee was created and billed on 7/3, the G/L report run on 8/1 reports the earnings in the prev_billed_earned revenue category. This is because the cycle fee was billed before the G/L run on 8/1.
If the bimonthly fee is $120, BRM calculates the previously billed earned revenue as shown in Figure 11-15:
Figure 11-15 Sample Previously Billed Earned Revenue Calculation
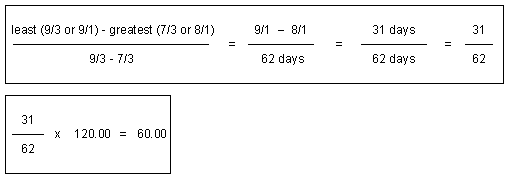
Description of "Figure 11-15 Sample Previously Billed Earned Revenue Calculation"
Calculating Unearned Revenue
BRM calculates unearned revenue for cycle fees only. BRM uses the equation in Figure 11-16 to calculate unearned revenue:
For example, if an account is created on 7/3, then the billing cycle will run on the third day of each subsequent month, or on 8/3 as shown in Figure 11-17. If the G/L cycle runs on the first of each month, then the timeline for the billing and G/L cycles is as follows:
For a monthly cycle fee of $19.95, the calculation for unearned revenue is completed as shown in Figure 11-18:
Figure 11-18 Sample Unearned Revenue Calculation
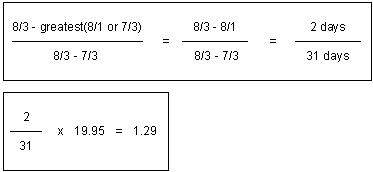
Description of "Figure 11-18 Sample Unearned Revenue Calculation"
BRM always calculates cumulative unearned revenue. For every successive G/L run, BRM continues to decrease the unearned portion and increase the earned portion. This continues until all revenue is earned by the end date.
If a customer starts a service on 7/3 with a bimonthly cycle fee, then the timeline is as shown in Figure 11-19:
Figure 11-19 Cumulative Unearned Revenue Timeline
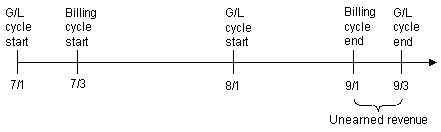
Description of "Figure 11-19 Cumulative Unearned Revenue Timeline"
The unearned revenue for August is also reported as unearned in July. The unearned revenue for July and August is calculated as shown in Figure 11-20:
Figure 11-20 Sample Unearned Revenue Calculations
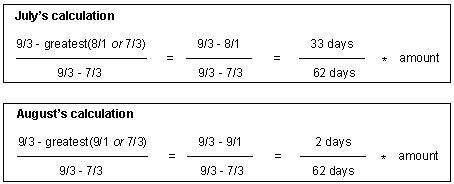
Description of "Figure 11-20 Sample Unearned Revenue Calculations"