19 Implementing Recurring Charges
Learn how to implement and manage recurring charges in Pricing Design Center (PDC) for Oracle Communications Billing and Revenue Management (BRM).
Topics in this document:
See also "Advanced Configuration for Recurring Charges".
About Recurring Charges
Recurring charges are ongoing charges that are not generated or affected by usage, such as a charge for a monthly subscription fee. For example:
-
A 30-dollar monthly fee for a mobile phone service
-
A 5-dollar fee for an automatically renewing smartphone app
Recurring charges do not use Elastic Charging Engine (ECE) for rating. Instead, recurring charges are applied when you run BRM billing utilities.
There are three types of recurring charges:
-
A cycle forward charge applies a recurring charge in advance. The advantage of using a cycle forward charge is that you collect payments sooner.
-
A cycle arrears charge applies a recurring charge to the previous month. The advantage of using a cycle arrears charge is that all of the usage charges and recurring charges for a particular month are included in the same bill.
-
A cycle forward arrears charge applies a recurring charge to the previous month. identical to a cycle arrears charge. The advantage of using a cycle forward arrears charge is that the customer is not charged until the end of the month, but the balance impact is made at the beginning of the month, and can be recognized as unearned revenue at the beginning of the month.
About Cycle Forward Charges
To charge a fee in advance, create a charge offer that includes a cycle forward charge type, for example, Monthly Recurring Charge. You can charge fees in advance at any interval; for example, by using a Quarterly Recurring Charge or a Yearly Recurring Charge charge type. You can define your own recurring charge types; for example, weekly, or every five months (see "Configuring Flexible Cycle Forward Charges" for more information).
Monthly recurring charges are typically applied at the beginning of an accounting cycle, but they do not need to be synchronized to the start or end of an accounting cycle.
Cycle forward balance impacts are recorded in /item/cycle_forward bill items.
About the First Cycle Forward Charge in a New Account
A cycle forward fee incurred at account creation is included in the cycle forward item created when the account is created. Therefore, the first bill includes two cycle forward fees. Figure 19-1 shows an account created on May 15, with the first bill on June 15. The first cycle forward item includes the charge for the month from May 15 - June 15. The second cycle forward item includes the charge for June 15 - July 15. Both charges are included in the June 15 bill.
Figure 19-1 Cycle Forward Fees for New Account
Description of "Figure 19-1 Cycle Forward Fees for New Account"
About Cycle Arrears Charges
To charge a fee at the end of the month, create a charge offer that includes a cycle arrears charge type, for example, Monthly Recurring Charge Arrear. Cycle arrears charges apply a charge to the previous billing cycle; the customer pays for the month that has already occurred. Cycle arrears charges are always monthly.
In Figure 19-2, the customer is charged for a cycle forward fee and for a cycle arrears fee. The bill created on April 1 includes:
-
A $10 cycle arrears fee for March
-
A $10 cycle forward fee for April
Figure 19-2 Cycle Forward Charge and Cycle Arrears Charge
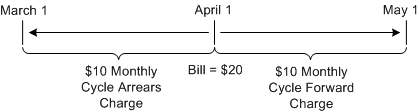
Description of "Figure 19-2 Cycle Forward Charge and Cycle Arrears Charge"
Cycle arrears balance impacts are recorded in /item/cycle_arrear bill items.
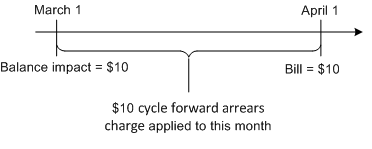
About Cycle Forward Arrears Charges
To charge a fee at the end of the month, and recognize unbilled revenue when you run general ledger reports, create a charge offer that includes a cycle forward arrears charge type, for example, Monthly Recurring Charge Forward Arrears.
Just like a cycle arrears charge, a cycle forward arrears charge charges the customer for the previous billing cycle. The difference between cycle arrears charges and cycle forward arrears charges is:
-
The balance impact for a cycle arrears charge is applied at the end of the accounting cycle.
-
The balance impact for a cycle forward arrears charge is applied at the beginning of the accounting cycle.
However, for both types of charges, the charge is not billed until the end of the billing cycle. Therefore, to the customer, there is no difference in how the charge is billed. The difference appears to your accounting department when you collect general ledger data. Cycle forward arrears charge types allow you to recognize unbilled revenue for the charge when you collect general ledger data before the end of the accounting cycle.
There is no multi-month cycle forward arrears fee.
Cycle forward arrears balance impacts are recorded in /item/cycle_forward_arrear bill items. However, the cycle forward arrears event is assigned to the item that belongs to the next accounting cycle. This way, the fee is tracked in the account balance for the current cycle, but it is not billed until the end of the cycle.
Figure 19-3 shows a cycle forward arrears charge applied on March 1, and billed on April 1. In this case, the balance impact occurs on March 1, but the charge is included in the bill item for April 1.
About Implementing Cycle Forward Arrears Charging
Cycle forward arrears events are standard in BRM. However, you must enable delayed billing if you charge for cycle forward arrears events. If you do not otherwise need delayed billing, you can enable delayed billing, but set the delayed billing period to 0.
For information about configuring delayed billing, see "Setting Up Delayed Billing" in BRM Configuring and Running Billing.
About Creating Recurring Charges in PDC
You create a recurring charge in PDC by assigning a recurring charge type to a charge offer. You then apply the same attributes as any charge, for example:
-
How the event is measured. Recurring charges are always measured by occurrence.
-
When to stop charging; for example, when the associated charge offer is inactivated or closed.
-
Tax calculation settings.
-
General Ledger (G/L) impacts. You can configure general ledger (G/L) reporting to report earned revenue and unearned revenue. Unearned revenue applies only to cycle forward events and cycle forward arrears events. It never applies to usage events or cycle arrears events.
-
Balance impact details, such as the amount to charge, balance element, and so on.
In addition, you can specify when the balance impact of a recurring charge is applied, and whether to prorate recurring charges. See:
Note:
A single charge offer cannot include multiple recurring charges that have the same frequency and type of balance impact, such as a cycle fee. For example, if you add a monthly cycle forward event to a charge offer, you cannot also add a monthly cycle arrears or monthly cycle forward arrears event to the same charge offer. Instead, Oracle recommends that you create separate charge offers for each cycle forward event.
Specifying When Recurring Charges are Charged
In PDC, you can configure the balance impact for recurring charges to occur at the following times:
- On the customer's current billing date. This is the default. If the recurring
charge is in a charge offer that is purchased mid-cycle, you can prorate a charge to
cover the time between the purchase date and the first billing date.
For example, if the billing date is the 1st of the month and the charge offer is purchased on January 10, the charge is prorated and applied on January 10 for the interval January 10 to February 1. For subsequent cycles, the charge is applied on the billing date (for the interval February 1 to March 1, March 1 to April 1, and so on).
- On the charge offer purchase date. For example, if the billing date is the 1st of the month and the charge offer is purchased on January 10, the charge is applied on the 10th of every month (for the interval January 10 to February 10, February 10 to March 10, and so on).
- At a specified time before the time period covered by the charge; for example, one
month in advance. For example:
- If you charge a one-month cycle forward fee one month in advance, and the billing day of month (DOM) is the 1st, the charge on May 1st applies to June 1 - June 30. Without in-advance billing, a cycle forward charge on May 1 applies to May 1 - May 31.
- If you charge a one-month cycle forward fee 15 days in advance, and the billing day of month (DOM) is the 1st, the charge on May 1 applies to May 15 - June 15, the charge on June 1 applies to June 15 - July 15, and so on.
When you charge cycle forward fees in advance, the first cycle forward charge might be larger than the subsequent charges. For example, if a charge offer is purchased on May 1 with in-advance billing of 15 days, the charge on May 1 includes one month in advance (May 15 - June 15) plus 15 days (May 1 - May 14). Subsequent charges are for June 15 - July 15, and so on.
If you create pricing components using the ImportExportPricing utility, you can also apply recurring charges on a specific day of the month. For example, you can apply the recurring charge on the 5th day of each month regardless of the billing or purchase date. This is useful for offers with validity that is defined in hours, minutes, and seconds rather than days, weeks, and months. See "Aligning Recurring Charges and Product Validity to a Specific Day of the Month" for more information.
Allowing Recurring Charges to Be Prorated
You can enable recurring charges to be prorated. A prorated charge typically charges a portion of the fee, based on how long it has been applied. You can also specify to apply no fee, or the full amount. You can specify to prorate charges in the following cases:
-
When a charge offer is purchased mid-cycle. This can occur at account creation or when a charge offer is purchased by an existing account.
-
When a charge offer that includes a recurring charge is canceled mid-cycle.
If a recurring charge includes more than one balance impact, you can specify which balance impacts should be prorated. For example, if the charge can be prorated, and there are two balance impacts, you can specify to prorate one of the balance impacts but not the other.
Figure 19-4 shows a cycle forward charge applied at account creation on May 1. The billing day of month is May 15, so the cycle forward charge is prorated for the two weeks between account creation and the first billing date.
Figure 19-4 Prorating Cycle Charges for a Monthly Fee
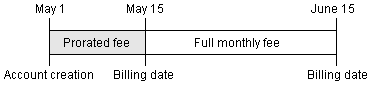
Description of "Figure 19-4 Prorating Cycle Charges for a Monthly Fee"
About Recurring Charges Events
Like all charges, recurring charges are rated by applying a balance impact to an event. Recurring charges are applied to cycle events. The cycle events are:
-
/event/billing/product/fee/cycle/cycle_forward_monthly
-
/event/billing/product/fee/cycle/cycle_forward_bimonthly
-
/event/billing/product/fee/cycle/cycle_forward_quarterly
-
/event/billing/product/fee/cycle/cycle_forward_semiannual
-
/event/billing/product/fee/cycle/cycle_forward_annual
-
/event/billing/product/fee/cycle/cycle_arrear
-
/event/billing/product/fee/cycle/cycle_forward_arrear
Cycle events are created when you run the pin_cycle_fees billing utility. The pin_cycle_fees utility is typically included in the pin_bill_day script that runs daily.