5 Writing Policy Conditions
The policy wizard supports a large number of conditions that can be used for constructing policy rules. To help you find the conditions you want, the conditions are organized into different categories, which are summarized in
The conditions that are included within each of these categories are described in the sections that follow. Within each category, conditions are listed in alphabetical order. The parameters that can be modified within each condition are also detailed.
Policy Condition Categories
- Variable Name
- Description
- Mobility
- Conditions that are based on information associated with wireless networks that include mobile subscribers. See Mobility Conditions.
- Network Devices
- Conditions related to the specific network device for which the policy rule is being evaluated. This includes conditions based on the network device type, as well as those that refer to specific unique identifiers for network devices. See Network Device Conditions .
- Policy SDP Properties
- Conditions related to SDP properties that are used to check the codec type (offer/answer) for the device (remote/local). See Policy SDP Properties Conditions .
- Request
- Conditions that are based on information that is explicitly contained within or related to the protocol message (request) that triggered the policy rule execution. See Request Conditions .
- Time of Day
- Conditions related to the time at which the policy rules are being executed. See Time of Day Conditions .
Mobility Conditions
Mobility conditions are based on information associated with networks that include mobile subscribers (such as a wireless network).
where the mobile session supports sponsored connectivity
Syntax
where the mobile
session
support sponsored
connectivity
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Triggers a policy that evaluates whether or not the mobile session supports sponsored data connectivity. This condition supports sponsored data connectivity for both Gx and Rx requests.
Example 5-1 Example
where the mobile session supports sponsored connectivitywhere the Cell Identifier matches one of specified CI value(s)
Syntax
where the Cell
Identifier
matches-op
match-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
- matches-op
- One of the following:
- matches one of (default)
- does not match any of
- match-list
- A comma-separated list of values, where each value is a wildcard match pattern that uses the * (asterisk) character to match zero or more characters and the ? (question mark) character to match exactly one character.
Description
Triggers a policy that is only evaluated for one or more specific Cell Identifier values (based on matching wildcard patterns). A valid Cell Identifier is an integer between 0 and 65535.
where the IP address of the Serving Gateway matches one of specified value(s)(es)
Syntax
where the IP
address of the Serving Gateway
matches-op
match-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
- matches-op
- One of the following:
- matches one of (default)
- does not match any of
- match-list
- A comma-separated list of values, where each value is a wildcard match pattern that uses the * (asterisk) character to match zero or more characters and the ? (question mark) character to match exactly one character.
Description
Triggers a policy that is only evaluated for one or more specific Serving Gateway addresses (based on matching wildcard patterns).
where the IP-CAN type specified
Syntax
where the IP-CAN
type
ip-can-type
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Triggers a policy that is only evaluated for a protocol message with a specific IP-CAN type.
where the E-UTRAN Cell Identifier matches one of specified ECI value(s)
Syntax
where the
E-UTRAN Cell Identifier
matches-op
match-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
- matches-op
- One of the following:
- matches one of (default)
- does not match any of
- match-list
- A comma-separated list of values, where each value is a wildcard match pattern that uses the * (asterisk) character to match zero or more characters and the ? (question mark) character to match exactly one character.
Description
Triggers a policy that is only evaluated for one or more specific E-UTRAN Cell Identifier values (based on matching wildcard patterns).
where the subscribed PRA area matches one of PRA area(s)
Syntax
where the
subscribed PRA area
matches-op
pra-areas
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
- matches-op
- One of the following:
- matches one of (default)
- does not match any of
- pra-areas
- A single area or multiple specific PRA areas
selected from the defined PRA areas, manually input, or Default.
- CMP defined PRA
lists
Select one or more defined PRA lists
- Manual
Input
Enter the identifier for the PRA in hexadecimal format or a custom PRA from a subscriber profile in the format {User.CustomField}.
The manual input format for multiple PRAs is:PRA identifier1 [;PRA element list1],PRA identifier2 [; PRA element list2],…The format of PRA identifier and PRA Element List is according to section 8.108 of TS 29.274[9]. It is specified in Hexadecimal format. If only has a PRA identifier then the PRA area is a predefined PRA area. If both PRA identifier and PRA Element List exists then it is a UE-dedicated PRA Area. The manual input is typically used to input a temporally PRA area. The manual input can also be used to get a PRA area from Custom field of subscriber. For example, {User.Custom4}. If the operator wants to manually input a PRA area they need to get the Hexadecimal value for each. Different vendors/operators should interact or exchange PRA info using the Hexadecimal representation as defined in section 8.108 of TS 29.274[9].
The manual input format for a single PRA is:PRA identifier [, PRA element list] - Default
The PRA to which the user equipment is already subscribed, if any.
The Default option specifies using the default PRA area. The default PRA is the PRA area subscribed or provisioned by the PCRF for the UE during IP-CAN session life cycle. It is either a UE- dedicated or predefined PRA area. It can be a PRA area that is retrieved from the subscriber profile (normally UE-dedicated) or a PRA area defined in the CMP (normally predefined). When used , this Default option means to check whether the UE has subscribed to a PRA area but does not care what the PRA area is.
- CMP defined PRA
lists
Description
Triggers a policy that is only evaluated for one or more specific PRA values. If default area is selected as the definition for the parameter pra-areas, the policy is only evaluated if the user equipment is already subscribed to a PRA.
where the UE is inside/outside/inactive for any one of PRA Area
Syntax
where the UE is
location subscribed PRA area
PRA areas
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
- location
- One of the following:
- inside
- outside
- inactive
- pra-areas
- A single area or multiple specific PRA areas
selected from the defined PRA areas, manually input, or Default.
- CMP defined PRA
lists
Select one or more defined PRA lists
- Manual
Input
Enter the identifier for the PRA in hexadecimal format or a custom PRA from a subscriber profile in the format {User.CustomField}.
The manual input format for multiple PRAs is:PRA identifier1 [;PRA element list1],PRA identifier2 [; PRA element list2],…The format of PRA identifier and PRA Element List is according to section 8.108 of TS 29.274[9]. It is specified in Hexadecimal format. If only has a PRA identifier then the PRA area is a predefined PRA area. If both PRA identifier and PRA Element List exists then it is a UE-dedicated PRA Area. The manual input is typically used to input a temporally PRA area. The manual input can also be used to get a PRA area from Custom field of subscriber. For example, {User.Custom4}. If the operator wants to manually input a PRA area they need to get the Hexadecimal value for each. Different vendors/operators should interact or exchange PRA info using the Hexadecimal representation as defined in section 8.108 of TS 29.274[9].
The manual input format for a single PRA is:PRA identifier [, PRA element list] - Default
The PRA to which the user equipment is already subscribed, if any.
The Default option specifies using the default PRA area. The default PRA is the PRA area subscribed or provisioned by the PCRF for the UE during IP-CAN session life cycle. It is either a UE- dedicated or predefined PRA area. It can be a PRA area that is retrieved from the subscriber profile (normally UE-dedicated) or a PRA area defined in the CMP (normally predefined). When used , this Default option means to check whether the UE has subscribed to a PRA area but does not care what the PRA area is.
- CMP defined PRA
lists
Description
Triggers a policy that is only evaluated when the user equipment is or is not inside the subscribed PRA.
where the APN matches one of specified APN value(s)
Syntax
where the APN
matches-op
match-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
- matches-op
- One of the following:
- matches one of (default)
- does not match any of
- match-list
- A comma-separated list of values, where each value is a wildcard match pattern that uses the * (asterisk) character to match zero or more characters and the ? (question mark) character to match exactly one character.
Description
Triggers a policy that is only evaluated for one or more
specific access point name (APN) values (based on matching wildcard patterns).
A valid APN value is any domain name; for example:
network.operator.com.
Network Device Conditions
Network Device conditions are related to the specific network device for which the policy rule is being evaluated. This includes conditions based on the network device type, as well as those that refer to specific unique identifiers for network devices.
where the User Equipment IMEISV matches one of specified IMEISV value(s)
Syntax
where the User
Equipment IMEISV
matches-op
match-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:

Description
Triggers a policy that is only evaluated for one or more specific IMEISV values (based on matching wildcard patterns). A valid IMEISV value has 16 decimal digits. If the IMEISV value matches with IMEISV value present in event, enfsession and then session then the condition returns true, otherwise false.
Policy SDP Properties Conditions
Session Description Protocol (SDP) properties conditions identify any specific SDP attributes and evaluate their value. This includes setting proper bandwidth values on related PCC rules. The following conditions are available.
where the local codec data is an offer
Syntax
where the
sdp_capabilities
codec data is an
codec-type
Parameters
- sdp_capabilities
- Specifies where to search for the SDP property:
- Local—The capabilities of the device for the subscriber.
- Remote—The capabilities of the device for the remote party.
- Common—The capabilities that the local and remote devices have in common.
- codec-type
- Specifies the Codec type. The options are:
- offer (default)
- answer
Description
Checks the Codec type (offer or answer) for a subscribers device (remote, local or both).
where the local specified SDP property exists
Syntax
where the
sdp_capabilities
SDP property
accessibility
Parameters
- sdp_capabilities
- Specifies where to search for the SDP property:
- Local—The capabilities of the device for the subscriber.
- Remote—The capabilities of the device for the remote party.
- Common—The capabilities that the local and remote devices have in common.
- SDP property
- A comma-delimited list of SDP properties. Specify
the SDP properties using one of the following methods:
- Generic descriptor
sdp.[option] - Media descriptor
sdp.[m.option] - rtpmap
sdp.[codec-name(codec-name).rtpmap.OPTION] - fmtp
sdp.[codec-name(codec-name).fmtp.OPTIONS]Where:Examples using fmtp:where the common sdp.[codec-name(AMR-WB).fmtp.fmt] exists
- Generic descriptor
- accessibility
- One of the following:
- exists (default)
- does not exist
Description
Checks for the existence or non-existence of any SDP property.
where the local specified SDP property is numerically equal to value
Syntax
where the
sdp_capabilities
sdp_capabilities
is numerically
operator
value
Parameters
- sdp_capabilities
- Specifies where to search for the SDP property:
- Local—The capabilities of the device for the subscriber.
- Remote—The capabilities of the device for the remote party.
- Common—The capabilities that the local and remote devices have in common.
- SDP property
- A comma-delimited list of SDP properties. Specify
the SDP properties using one of the following methods:
- Generic descriptor
Syntax:
sdp.[option]Examples using an SDP generic descriptor:where the common sdp.[a=ptime] is numerically equal to 20where the common sdp.[f=hello] is numerically equal to 20
- Media descriptor
Syntax:
sdp.[m.option]Example using an SDP media descriptor:where the local sdp.[m.numberofports] is numerically equal to 2
- rtpmap
Syntax:
sdp.[codec-name(codec-name).rtpmap.OPTION]Examples using rtpmap:-
where the local sdp.[codec-name(AMR-WB).rtpmap.clockrate] is numerically less than or equal to 16000
-
- fmtp
Syntax:
sdp.[codec-name(codec-name).fmtp.OPTIONS]Where:Example using fmtp:-
where the local sdp.[codec-name(AMR-WB).fmtp.mode-set] is numerically less than or equal to 4
-
- Generic descriptor
- operator
- One of the following:
- greater than or equal to
- greater than
- less than or equal to
- less than
- equal to
- not equal to
- value
- String.
Description
Compares a numerical SDP property value against a specified number.
where the local specified SDP property matches one of value(s)
Syntax
where the
sdp_capabilities
SDP property
matches-op
value-list
Parameters
- sdp_capabilities
- Specifies where to search for the SDP property:
- Local—The capabilities of the device for the subscriber.
- Remote—The capabilities of the device for the remote party.
- Common—The capabilities that the local and remote devices have in common.
- SDP property
- A comma-delimited list of SDP properties. Specify
the SDP properties using one of the following methods:
- Generic descriptor
Syntax:
sdp.[option]Examples using an SDP generic descriptor:where the local sdp.[i] matches one of *recvonly*where the common sdp.[a=ptime] matches one of 20where the common sdp.[a] matches one of ptime: 20where the common sdp.[u] matches one of http://www.oracle.com:8080/hr/one.htmwhere the common sdp.[u=http://www.oracle.com] matches one of 8080/hr/one.htmwhere the common sdp.[u=http] matches one of //www.oracle.com:8080/hr/one.htmwhere the remote sdp.[xy] matches one of zwhere the remote sdp.[xy=z] matches one of 80
- Media descriptor
Syntax:
sdp.[m.option]Examples using an SDP media descriptor:where the common sdp.[m.fmt] matches one of 102-
where the common sdp.[m.port] does not match any of 41000,41002 where the remote sdp.[m.media] matches one of audio,video-
where the local sdp.[m.proto] matches one of RTP/AVP
- rtpmap
Syntax:
sdp.[codec-name(codec-name).rtpmap.OPTION]Examples using rtpmap:where the common sdp.[ codec-name(AMR-WB).rtpmap] matches one of 104 AMR-WB/160000where the common sdp.[ codec-name(AMR-WB).rtpmap.encodingparameters] matches one of 2-
where the common sdp.[ codec-name(AMR-WB).rtpmap.payloadtype] matches one of 104,102
- fmtp
Syntax:
sdp.[codec-name(codec-name).fmtp.OPTIONS]Where:Examples using fmtp:where the common sdp.[codec-name(AMR-WB).fmtp.fmt] matches one of 104,102where the common sdp.[codec-name(AMR-WB).fmtp.mode-set] matches one of 2,4-
where the commonsdp.[codec-name(H264).fmtp.profile-level-id] matches one of42e00c
- Generic descriptor
- matches-op
- One of the following:
- matches one of (default)
- does not match any of
- value-list
- A comma-delimited list of values to compare against.
Description
Checks the Codec type (offer or answer) for a subscribers device (remote, local or both) for specific values.
Request Conditions
Request conditions are based on information that is explicitly contained within, or related to, the protocol message (request) that triggered the policy rule execution.
where the requested QCI is specified QCI
Mode
Cable, Wireless
Syntax
where the
requested QCI is create list with
specified QCI
Parameters
The following screen capture displays the sample policy condition:
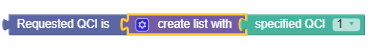
- specified QCI
- One or more of the following:
- 1 (Conversational speech)
- 2 (Conversational)
- 3 (Streaming speech)
- 4 (Streaming)
- 5 (Interactive with priority 1 signalling)
- 6 (Interactive with priority 1)
- 7 (Interactive with priority 2)
- 8 (Interactive with priority 3)
- 9 (Background)
- 65 (Mission critical push-to-talk voice)
- 66 (Push-to-talk voice)
- 69 (Mission critical push-to-talk signalling)
- 70 (Mission critical data)
Description
Selects protocol messages based on the QoS class identifier (QCI).
where the request supports feature name
Syntax
where the
request
supports feature
value-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:

Description
Determines whether the request supports a specified feature.
where the session is an enforcement session
Syntax
where the
session is
session-type
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:

Description
Distinguishes between protocol messages that are operating on different sessions.
where the request AVP name exists
Syntax
where the
request AVP
avp
accessibility
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
![]()
Description
Checks for the presence or absence of the third-party AVP in an incoming Diameter message.
Note:
The condition supports both loaded base Diameter AVPs and third-party AVPs.where the request AVP namevalue matches one of value(s)
Syntax
where the
request AVP
avp
matches-op
value-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Compares the specified AVP value with the values or variables from the specified list. The condition is where the request AVP name value matches one of the values. The values can be evaluated for equality as well as inequality. To evaluate an AVP value for inequality, the variable matches one of must be changed to does not match any of.
Note:
The condition supports both loaded base Diameter AVPs and third-party AVPs.where the request AVP name value is numerically equal to value
Syntax
where the
request AVP
avp value is numerically
operator
value
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
![]()
Description
Compares a numerical AVP value against a specified number or policy context number variable value.
Note:
The condition supports both loaded base Diameter AVPs and third-party AVPs.where the request AVP name value is contained in Match Lists select lists
Syntax
where the
request AVP
avp value
operator-binary
contained in Match Lists
match-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
- avp
- AVP in one of the following formats:
or a full pathname:vendorID
for the members of the grouped AVPs[avp_name1]:vendorID.[avp_name2]:vendorID… - operator-binary
- One of the following:
- is (default)
- is not
- match-list
- A comma-separated list of values, where each value is a wildcard match pattern that uses the * (asterisk) character to match zero or more characters and the ? (question mark) character to match exactly one character.
Description
Compares the specified AVP value with the values or variables from the specified match list. The condition is where the request AVP name value matches one of the values. The values can be evaluated for equality as well as inequality. To evaluate an AVP value for inequality, the condition matches one of must be changed to does not match any of.
Note:
The condition supports both loaded base Diameter AVPs and third-party AVPs.where the request AVP name value contains one of value(s)
Syntax
where the
request AVP
avp value
containment
value-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Performs a lookup of the sub-strings in the AVP value. It is possible to check multiple sub-string entries at on time. If the operation type is changed, you can check the opposite scenario, which would not include any of the provided sub-strings.
Note:
The condition supports both loaded base Diameter AVPs and third-party AVPs.where at least one flow has media type that matches specified type(s)
Syntax
where at least
one flow has media type that matches
media-type
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
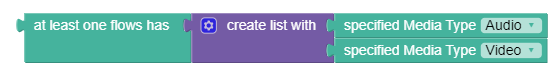
Description
Triggers a policy based on whether at least one flow matches one or more of the specified media types.
Example 5-2 Example
where at least one flow has media type that matches Video,Applicationwhere the AF-Application-ID matches one of specified value(s)
Syntax
where the
AF-Application-ID matches one of
value-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Selects protocol messages based on the Diameter AF Application Identifier field. A valid AF Application identifier is any string describing the application, for example VoIP or streaming.
Example 5-3 Example
where the AF-Application-ID matches one of ptt-application-id
apply PTT to all flows in the request
continue processing messagewhere the corresponding enforcement session supports feature name
Syntax
where the
corresponding enforcement session
action feature
value-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Evaluates the feature name in the enforcement session that correlates to the corresponding application (Rx) request.
Example 5-4 Example
where the corresponding enforcement session supports feature GroupComService.where the flow media type is one of specified type(s)
Syntax
where the
flow(s) media type is one of
media-type
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Selects protocol messages based on the media type of the flow or flows.
where the request is creating a new flow
Syntax
where the
request is
change-type
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Distinguishes between protocol messages based on the type of operation being performed on the flow.
where the specific action is one of specified action(s)
Syntax
where the
specific action is one of
action
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
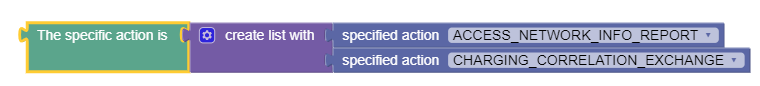
- action
- One or more of the following actions:
- SERVICE_INFORMATION_REQUEST
- CHARGING_CORRELATION_EXCHANGE
- INDICATION_OF_LOSS_OF_BEARER
- INDICATION_OF_RECOVERY_OF_BEARER
- INDICATION_OF_RELEASE_OF_BEARER
- INDICATION_OF_ESTABLISHMENT_OF_BEARER
- INDICATION_OF_IP_CAN_CHANGE
- INDICATION_OF_OUT_OF_CREDIT
- INDICATION_OF_SUCCESSFUL_RESOURCES_ALLOCATION
- INDICATION_OF_FAILED_RESOURCES_ALLOCATION
- USAGE_REPORT
- ACCESS_NETWORK_INFO_REPORT
- INDICATION_OF_RECOVERY_FROM_LIMITED_PCC_DEPLOYMENT
- INDICATION_OF_ACCESS_NETWORK_INFO_REPORTING_FAILURE
Description
This condition lets you take action based on the value of the Specific-Action AVP field within an Rx RAA message.
where the rule report contains one of specified rule name(s) and the rule status is active
Syntax
where the rule
report contains one of
value-list
and the rule status is
field
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
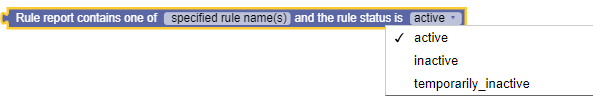
Description
Selects protocol messages based on whether a rule name and a status was received in a rule report.
where the request MPS Identifier matches one of value(s)
Syntax
where the MPS
Identifier
matches-op
value-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Determines whether the MPS Identifier matches a specified value(s).
where the requested media component description reservation priority is one of specified
Syntax
where the
requested media component description reservation priority is one of
priority
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Selects Rx protocol messages based on the requested media component description reservation priority.
where the requested session reservation priority is one of specified
Syntax
where the
requested session reservation priority is one of
priority
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:

Description
Selects Rx protocol messages based on the requested session reservation priority.
where the flow media type matches one of user defined media type(s)
Syntax
where the flow
media type
matches-op
value-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Selects one or more protocol messages that match one or more user-defined media types.
where the Sponsor-Identity matches one of specified Sponsor Identity(s)
Syntax
where the
Sponsor-Identity matches one of
value-list
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Selects protocol messages based on whether the Sponsored-Identity AVP matches a list of sponsors. This condition supports sponsored data connectivity.
Example 5-5 Example
where the Sponsor-Identity matches one of ESPN,FIFAwhere the AF-Application-ID is available
Syntax
where the
AF-Application-ID
operator-binary
available
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
Description
Checks for the presence or absence of the AF Application Identifier field. A valid AF Application identifier is any string describing the application, for example VoIP or streaming.
where the requested APN aggregate maximum bitrate upstream is greater than # bps
Syntax
where the requested APN aggregate maximum bitrate flow-direction is operator
bandwidthThe following screen
capture displays the sample policy condition: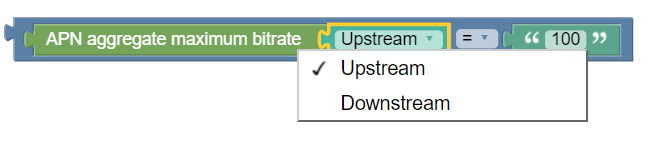
Parameters
- flow-direction
- One of the following:
- upstream
- downstream
- upstream or downstream (default)
- operator
- One of the following:
- greater than or equal to
- greater than
- less than or equal to
- less than
- equal to
- not equal to
bandwidth
A numeric value that specifies the bandwidth. The unit of bandwidth is compatible with the Cedit Control Request (CCR) meesage.
Description
Selects protocol messages based on the maximum bitrate being requested for an access point name (APN) in a specific direction relative to a numeric value.
Time of Day Conditions
Time-of-Day conditions are related to the time at which the policy rules are being executed.
Configuring Local Time
- From the navigation menu,
under
PCRF, then
under
Services, click
Core Service.
The Core Service screen appears.
- Click Edit to edit the core service configurations.
- In
Advance
Settings, click
Create.
The Create page appears.
- Enter DB.User.DefaultLocalTimeMode in the Key field.
- Enter True in the Value field.
- Click Save.
If no configuration is provided, the SYSTEM_LOCAL_TIME is considered as default local time.
where the current time is between start time and end time using configured local time
Syntax
where the
current time
operator-binary
between
time-of-day and
time-of-day using
time-zone
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:

Parameters
- operator-binary
- One of the following:
- is (default)
- is not
- time-of-day
- A time, in the format of hh:mm, where hh is a number in the range from 0 to 23.
- time-zone
- One of the following:
- CONFIGURED LOCAL TIME (default)—Calculate the time from the location configured for this MPE device
- SYSTEM LOCAL TIME—Calculate the time from the location of this MPE device
- USER LOCAL TIME—Calculate the time from the location configured for the user equipment's location
Description
Triggers a policy based on time. If the present time is between start time and end time then the condition returns true, otherwise false. If start time is greater than end time then the condition is evaluated, where the end time is considered as the next day.
where the current time is within the specified time period(s)
Syntax
where the
current time
operator-binary
within the
time-period time periods
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition
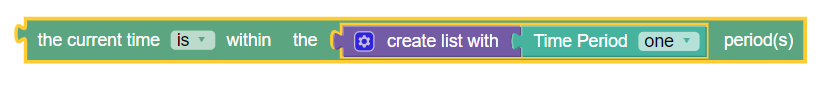
- operator-binary
- One of the following:
- is (default)
- is not
- time-period
- Names of one or more time periods that are defined in the cnPCRF GUI.
Description
Triggers a policy based on the time period. This condition gets time slots of all the time periods, and compares current time with these time slots. If the current time falls within the range of time slots configured in these time periods then the condition returns true, otherwise false.
where today is a week day using configured local time
Syntax
where today is a
week day using
time-zone
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:

- time-zone
- One of the following:
- CONFIGURED LOCAL TIME (default)—Calculate the time from the location configured for this MPE device
- SYSTEM LOCAL TIME—Calculate the time from the location of this MPE device
- USER LOCAL TIME—Calculate the time from the location configured for the user equipment's location
Description
Triggers a policy based on the day of the week. If today is week day using the system time then the condition returns true, otherwise false.
where today is a weekend day using configured local time
Syntax
where today is a
weekend day using
time-zone
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:

- time-zone
- One of the following:
- CONFIGURED LOCAL TIME (default)—Calculate the time from the location configured for this MPE device
- SYSTEM LOCAL TIME—Calculate the time from the location of this MPE device
- USER LOCAL TIME—Calculate the time from the location configured for the user equipment's location
Description
Triggers a policy based on the day of the week. If today is weekend according to configured time then the condition returns true, otherwise false.
where today is day using configured local time
Syntax
where today
operator-binary
day-of-week
using
time-zone
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:
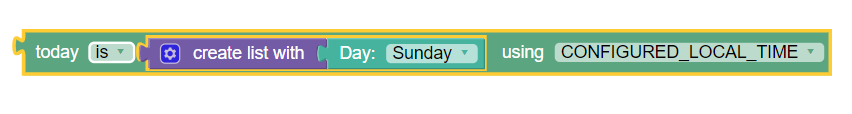
- operator-binary
- One of the following:
- is (default)
- is not
- day-of-week
- One of the following:
- Sunday
- Monday
- Tuesday
- Wednesday
- Thursday
- Friday
- Saturday
- time-zone
- One of the following:
- CONFIGURED LOCAL TIME (default)—Calculate the time from the location configured for this MPE device
- SYSTEM LOCAL TIME—Calculate the time from the location of this MPE device
- USER LOCAL TIME—Calculate the time from the location configured for the user equipment's location
Description
Triggers a policy based on the day of the week. If today is day within specified days then the condition returns true, otherwise false.
where today is the specified number(s) th day(s) of Any Month in natural order using configured local time
Syntax
where today
operator-binary
the
value-list
th days of
month in
order using
time-zone
Parameters
The following screen capture shows a sample policy condition:

- operator-binary
- One of the following:
- is (default)
- is not
- value-list
- A comma-delimited list of values to compare against.
- month
- One or more of the following:
- January
- February
- March
- April
- May
- June
- July
- August
- September
- October
- November
- December
- order
- Specifies the order to evaluate the value list. The
options are:
- natural order
- reverse order
- time-zone
- One of the following:
- CONFIGURED LOCAL TIME (default)—Calculate the time from the location configured for this MPE device
- SYSTEM LOCAL TIME—Calculate the time from the location of this MPE device
- USER LOCAL TIME—Calculate the time from the location configured for the user equipment's location
Description
Triggers a policy based on a day in a month. If current date matches specified number th day of specified months in natural/reverse order as per the configured time then the condition returns true, otherwise false.
Example 5-6 Example
where today is the 1,2,3,4 th days of March,April,May in natural order using USER LOCAL TIME