2 Installing OSO
Note:
For release version 23.4.5, OSO supports both fresh installation and upgrade from 23.4.x. For more information on how to upgrade OSO, see Upgrading OSO.- All the required OSO images, including opensource software as a tar file.
- All the required OSO Helm charts.
- A custom values.yaml file named
ocoso_23_4_5_0_0-custom-values.yaml.Note:
The README doc contains details to populate mandatory values in theocoso_23_4_5_0_0-custom-values.yamlfile. For more information about the configuration parameters, see OSO Configuration Parameters.
2.1 Prerequisites
Before installing and configuring OSO, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
- CSAR package is downloaded.
- Unzip and TAR utilities are installed.
- Docker or Podman is installed, and you must be able to run the docker or podman commands.
- Helm3 is installed.
- kubectl is installed.
- A central repository is available for all images, binaries, helm charts, and so on, before running this procedure.
- The following images are populated in the registry on the repo
server:
occne.io/oso/prometheus:v2.50.1occne.io/oso/alertmanager:v0.26.1occne.io/oso/configmapreload:v0.12.0occne.io/occne/23_4_common_pod:23.4.5
All the above images are packed into tar format and will be present in OSO CSAR under (Artifacts/Images) folder. You can use the following commands to load these images into your cluster's registry.$ docker/podman load -i <image-name>.tar $ docker/podman tag <image-url> <registryaddress>:<port>/image-url $ docker/podman push <registryaddress>:<port>/image-url
2.2 Installing OSO Using CSAR
Open Network Automation Platform (ONAP) compliant orchestrator uses CSAR format to onboard, validate, and install OSO. However, in the absence of an orchestrator, manual installation is possible using the CSAR file contents.
- Download the OSO CSAR zip file from My Oracle Support (MOS).
- Extract the CSAR zip
file:
$ unzip <OSO CSAR package> - Upload all the artifacts present in the
Artifacts/Imagesfolder to the configured repository. For more information about the artifacts, see the Prerequisites section. - Update the Prometheus and Alertmanager
ocoso_csar_23_4_5_0_0_custom_values.yamlfile insideArtifacts/Scriptsdirectory with the required values as mentioned in OSO Configuration Parameters. - Enable IPv6 Dualstack.
- Enable IPv6 Dualstack in the
ocoso_csar_23_4_5_0_0_custom_values.yaml. Search for the following comment in the yaml file and uncomment the following four lines after this comment.# Custom section to enable IPV6, Uncomment below section in order to enable Dualstack OSO having both Ipv4 and Ipv6 addresses #ipFamilies: #- IPv4 #- IPv6 #ipFamilyPolicy: PreferDualStackSave the file and proceed with the normal installation.
- Change the service type from
ClusterIP to LoadBalancer to assign IPv6.
- Extract the Helm charts tgz file
available in the
Artifacts/Scriptsdirectory.$ cd Artifacts/Scripts $ tar -xvzf ocoso_csar_23_4_5_0_0_chart.tgz - Install Prometheus and
AlertManager using Helm charts provided and
updated
ocoso_csar_23_4_5_0_0_custom_values.yamlfile with the following command.Use the following command for installation using Helm, if custom labels are given:
$ kubectl create namespace <deployment-namespace-name> $ helm install -f <ocoso_csar_23_4_5_0_0_custom_values.yaml> --namespace=<deployment-namespace-name> --name-template=<deployment-name> ./prometheus --disable-openapi-validationFor Example:
$ kubectl create namespace ns1 $ helm install -f <ocoso_csar_23_4_5_0_0_custom_values.yaml> --namespace=ns1 --name-template=ns1 ./prometheus --disable-openapi-validationNote:
Skip the flag (--disable-openapi-validation) if custom labels aren't given. - Run the following command to
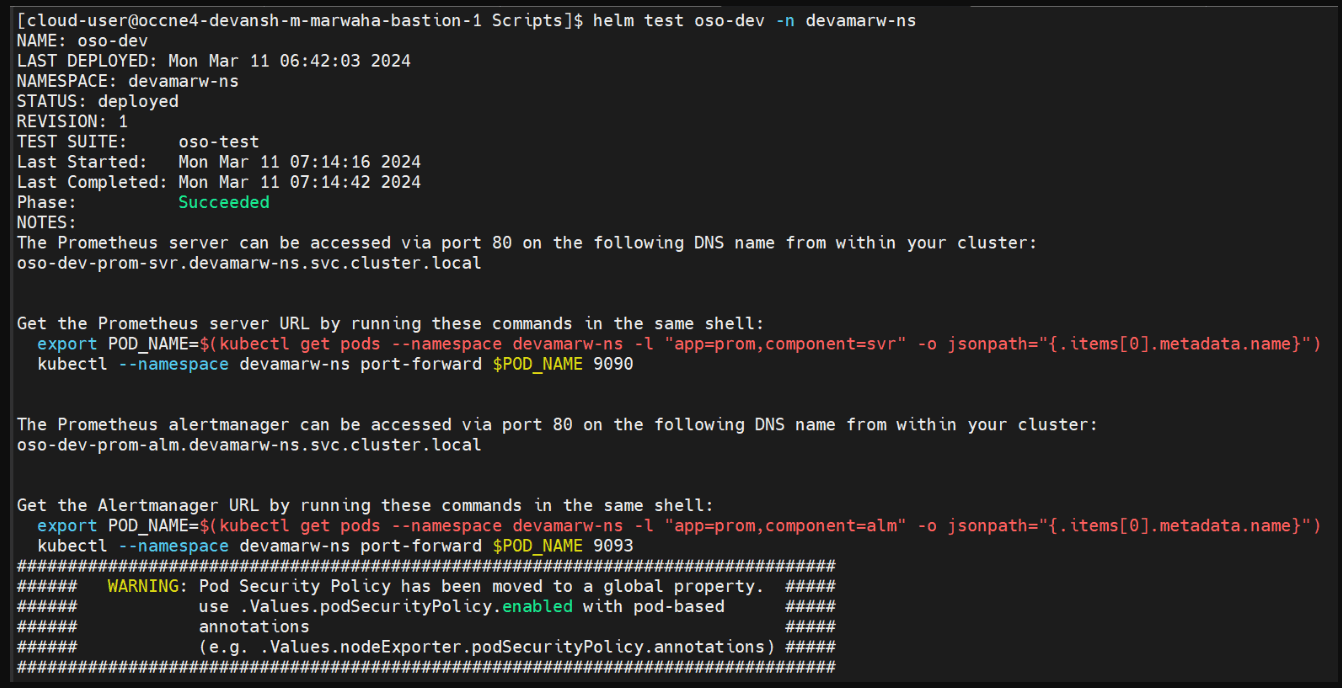
perform a Helm test. Populate the values in the
ocoso_csar__custom_values.yamlfile to run the Helm test.$ helm test <release-name> -n <namespace>Note:
Helm Test can be run for the first time smoothly, but if some issue occurs, and there's a need to re-run the helm test, first you will have to delete the existing test job and repeat the "helm test" command as shown above.$ kubectl get jobs.batch -n <namespace>$ kubectl delete jobs.batch oso-test -n <namespace>Figure 2-1 Helm Test
- Extract the Helm charts tgz file
available in the
- Enable IPv6 Dualstack in the
2.3 Postinstallation Tasks
This section explains the postinstallation tasks for OSO.
2.3.1 Verifying Installation
To verify if OSO is installed:
- Run the following commands to verify if pods are up and
running:
$ kubectl get pods --namespace <deployment-namespace-name>For Example:
$ kubectl get pods -n occne-infraSample output:NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE oso-prom-alm-0 2/2 Running 0 14h oso-prom-alm-1 2/2 Running 0 14h oso-prom-svr-84c8c7d488-qsnvx 2/2 Running 0 14h - Run the following commands to verify if services are up and running and
are assigned an EXTERNAL-IP (if LoadBalancer is being
used):
$ kubectl get service --namespace <deployment-namespace-name>For Example:$ kubectl get service -n occne-infraSample output:NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE oso-prom-alm ClusterIP 10.233.16.83 <none> 80/TCP 14h oso-prom-alm-headless ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP,6783/TCP 14h oso-prom-svr ClusterIP 10.233.46.136 <none> 80/TCP 14h - Verify that all the GUIs are accessible.
Note:
Prometheus and Alertmanager GUIs can be accessed only using the CNC Console. For more information about accessing Prometheus and Alertmanager GUIs using CNC Console, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console User Guide.If the service is of type LoadBalancer, use EXTERNAL-IP to open the Prometheus GUI. Refer to Step 2 to get the services and their EXTERNAL-IPs.
Example to access service IP address with output:
# kubectl get nodes -o wide NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME master Ready master 87d v1.17.1 10.75.226.13 <none> Oracle Linux Server 7.5 4.1.12-112.16.4.el7uek.x86_64 docker://19.3.11 slave1 Ready <none> 87d v1.17.1 10.75.225.177 <none> Oracle Linux Server 7.5 4.1.12-112.16.4.el7uek.x86_64 docker://19.3.11 slave2 Ready <none> 87d v1.17.1 10.75.225.47 <none> Oracle Linux Server 7.5 4.1.12-112.16.4.el7uek.x86_64 docker://19.3.11# kubectl get service -n ocnrf NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE oso-prom-alm ClusterIP 10.103.63.10 <none> 80/TCP 35m oso-prom-alm-headless ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP 35m oso-prom-svr ClusterIP 10.101.91.81 <none> 80/TCP 35mNote:
In case, Dualstack with IPv6 is enabled, change the service type to LoadBalancer in the custom values file. You can see both IPs when calling thekubectl get servicecommand, and the output is as follows:[root@master Scripts]# kubectl get service -n ocnrf NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE oso-prom-alm LoadBalancer 10.103.63.10 10.75.202.205,2606:b400:605:b809::2 80/TCP 35m oso-prom-alm-headless ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP 35m oso-prom-svr LoadBalancer 10.101.91.81 10.75.202.204,2606:b400:605:b809::1 80/TCP 35mFigure 2-2 Prometheus GUI

Figure 2-3 Alert Manager GUI
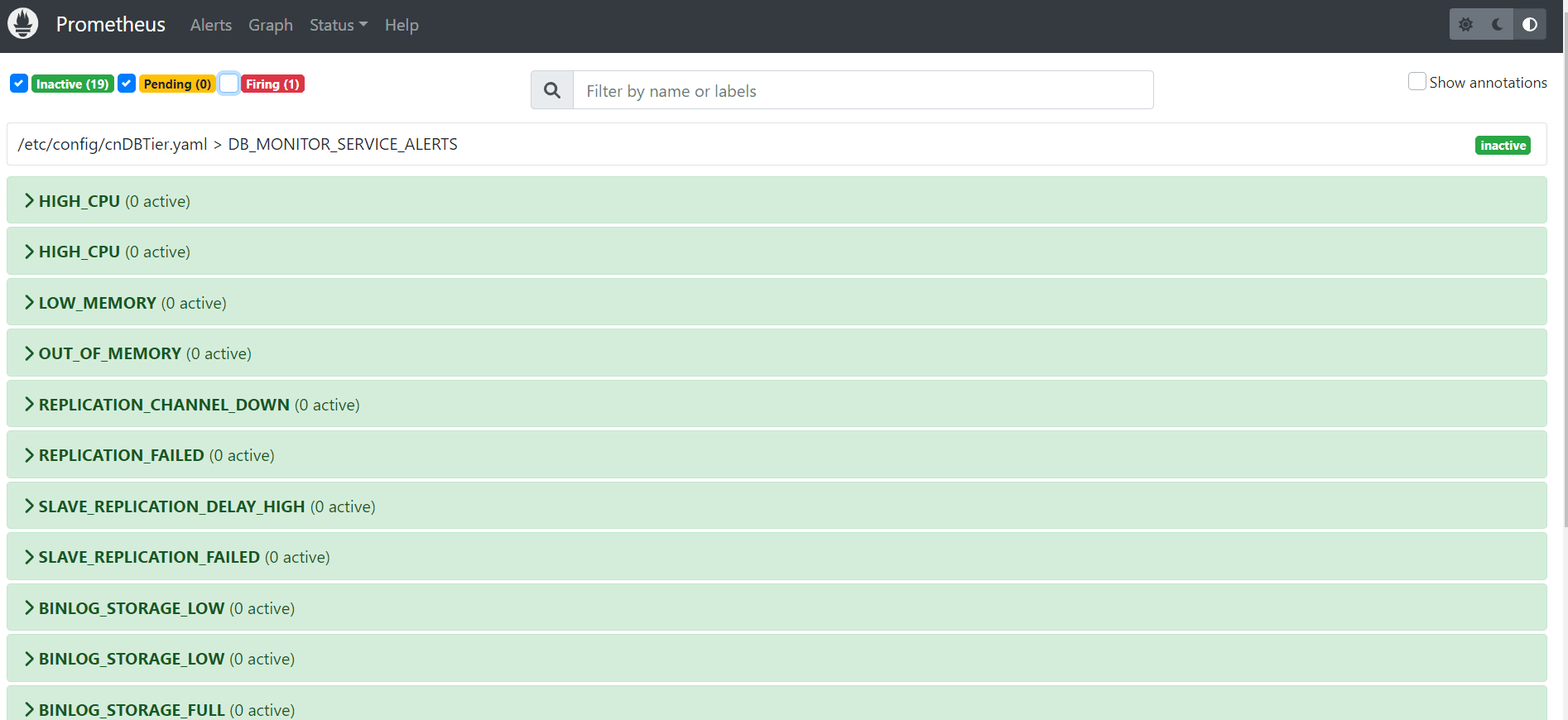
- On the Prometheus GUI, click Alerts to verify
that all the alerts (NF Alerts) are visible.
Note:
OSO Prometheus doesn't have any alerts of its own, therefore the GUI must appear empty initially. You can patch any NF alert rules in this section.The following image displays the alerts for cnDBTier:
Figure 2-4 Prometheus GUI
 After Alerts are raised, the GUI must display the triggered alerts as shown in the following image:
After Alerts are raised, the GUI must display the triggered alerts as shown in the following image:Figure 2-5 Prometheus GUI - Alerts

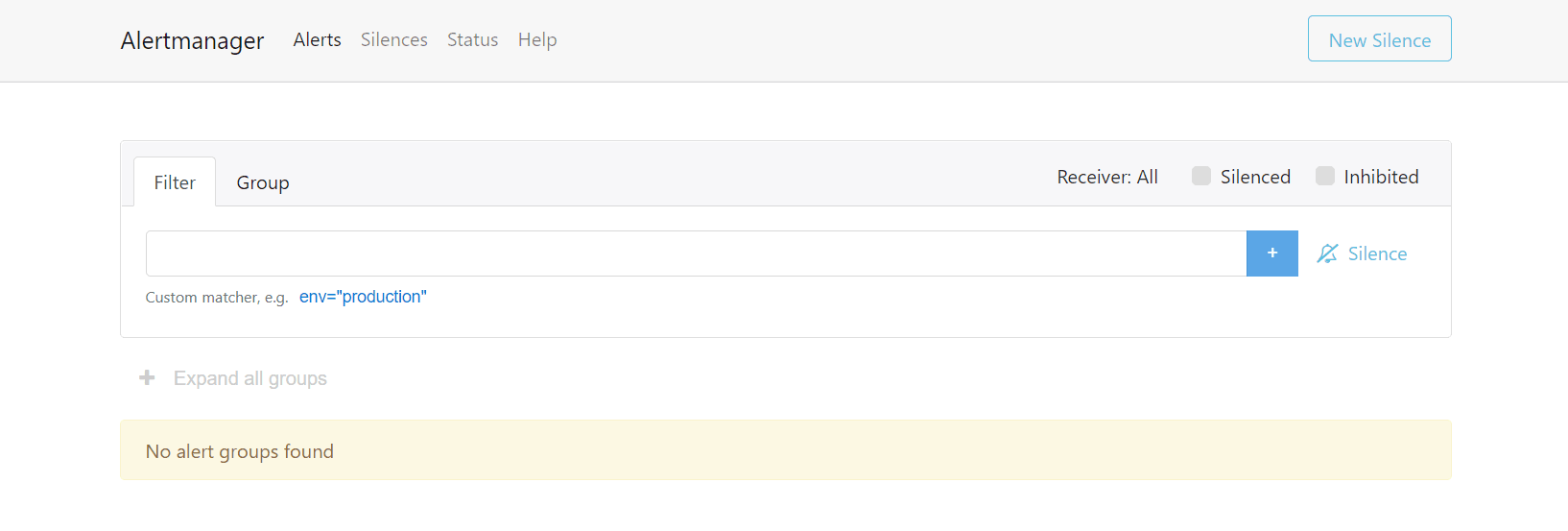
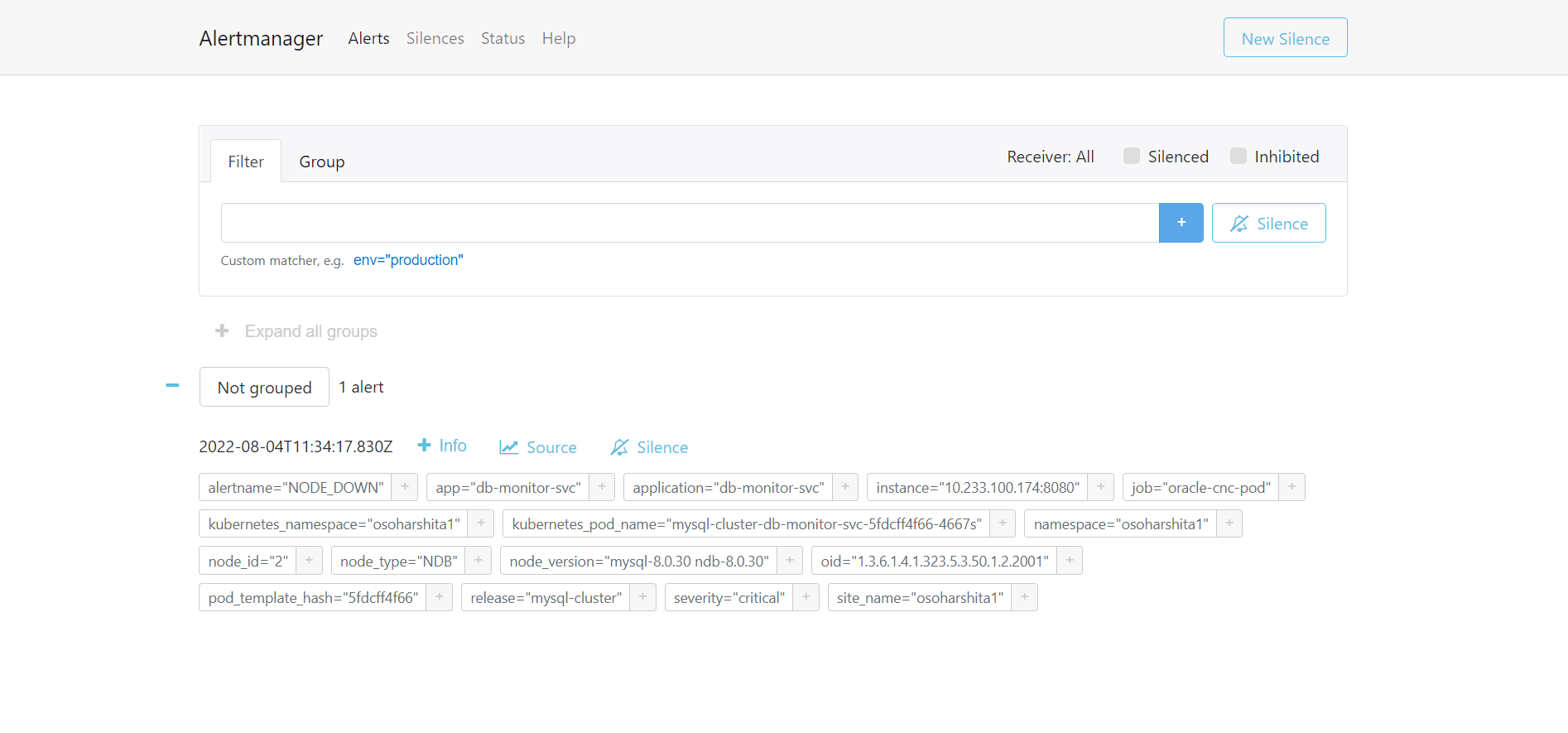
- Select Alerts tab on the Alertmanager GUI to
view the triggered alerts as shown in the following image:
Figure 2-6 Alertmanager - Alerts
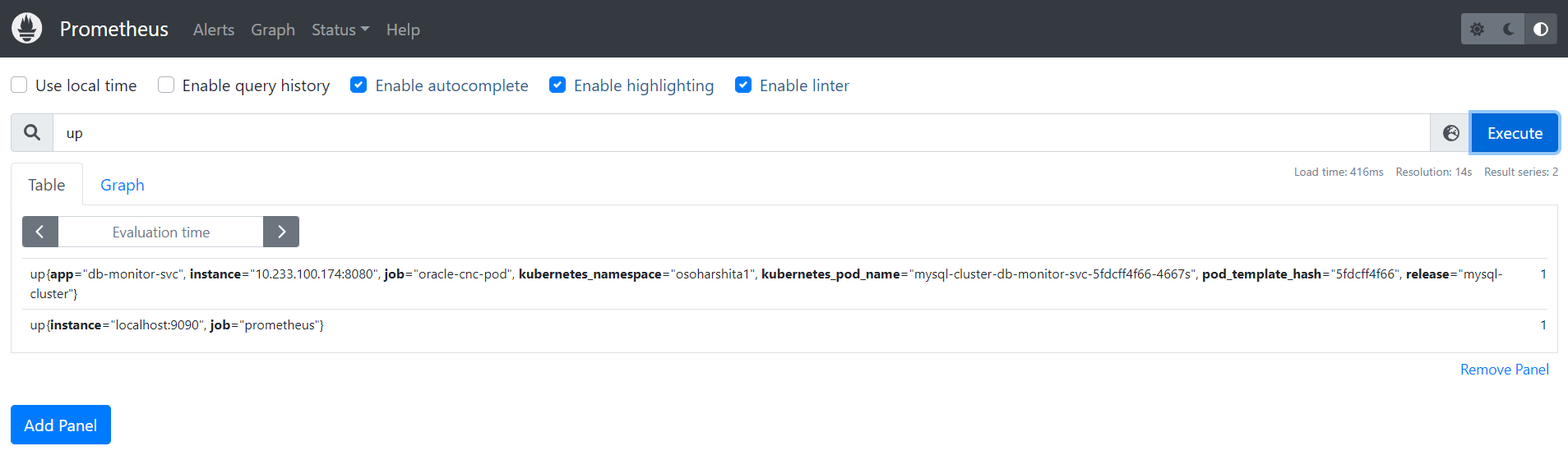
- On the Prometheus GUI, click Graph to verify if the expected
metrics (example, NF Metrics) are displayed. The following image displays a sample
Prometheus Graph with metrics:
Figure 2-7 Prometheus Graph
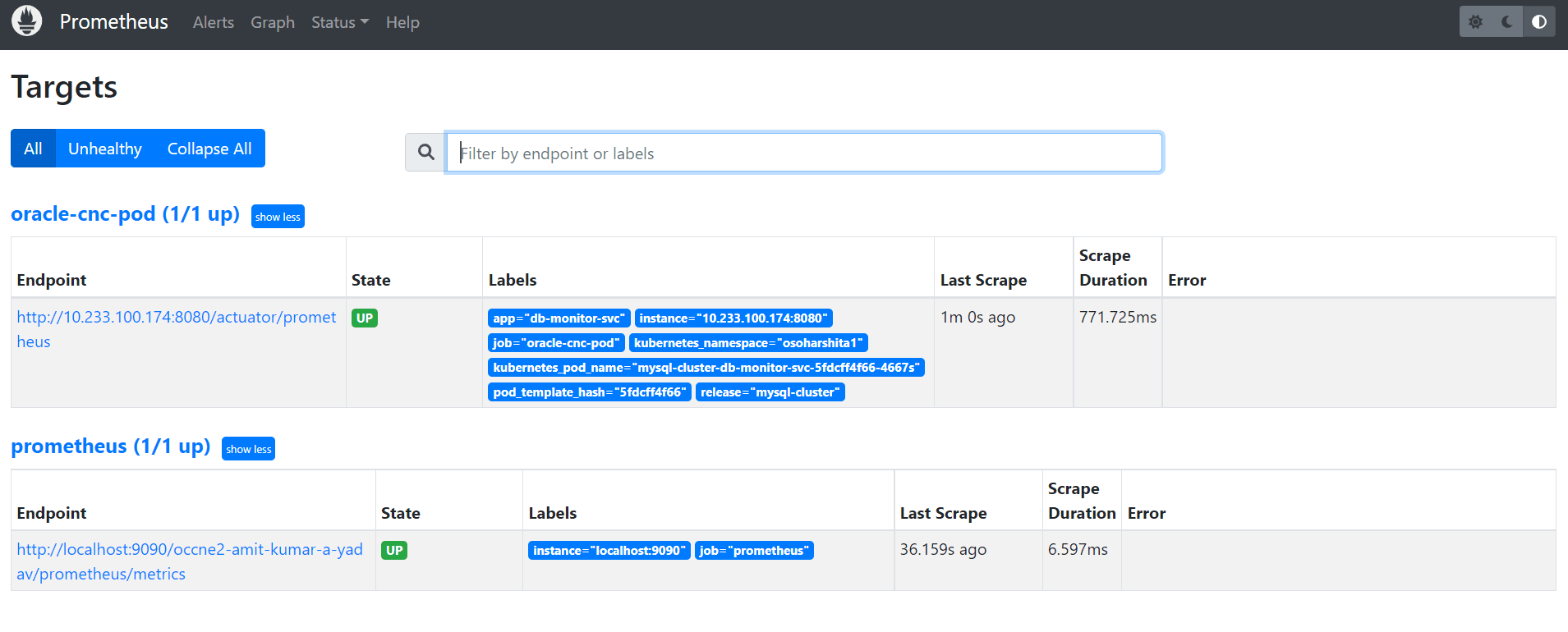
- On the Prometheus GUI, navigate to Status and
then click Target to verify if the configured targets are
displayed.
The following image shows Prometheus targets that are being extracted:
Figure 2-8 Prometheus Target