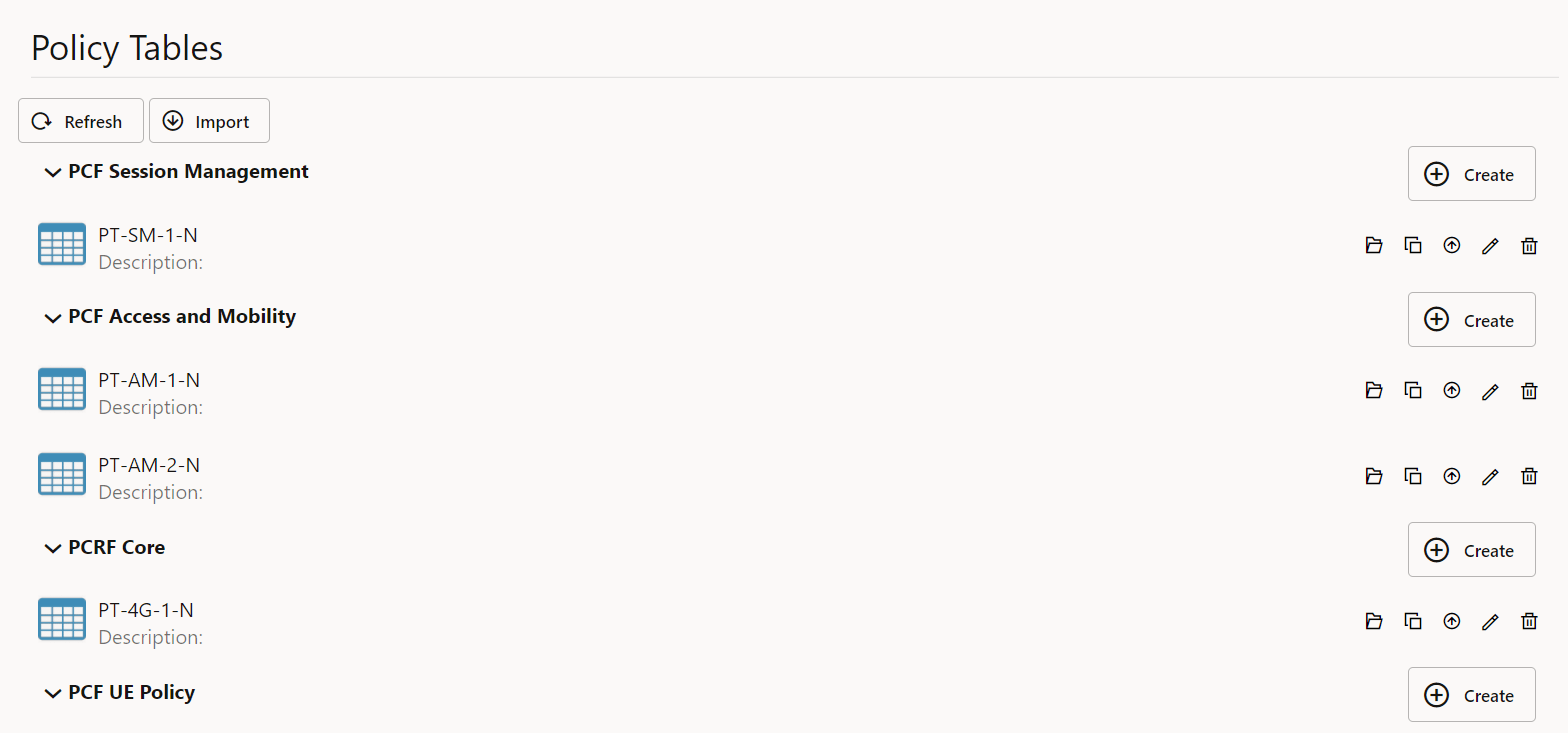
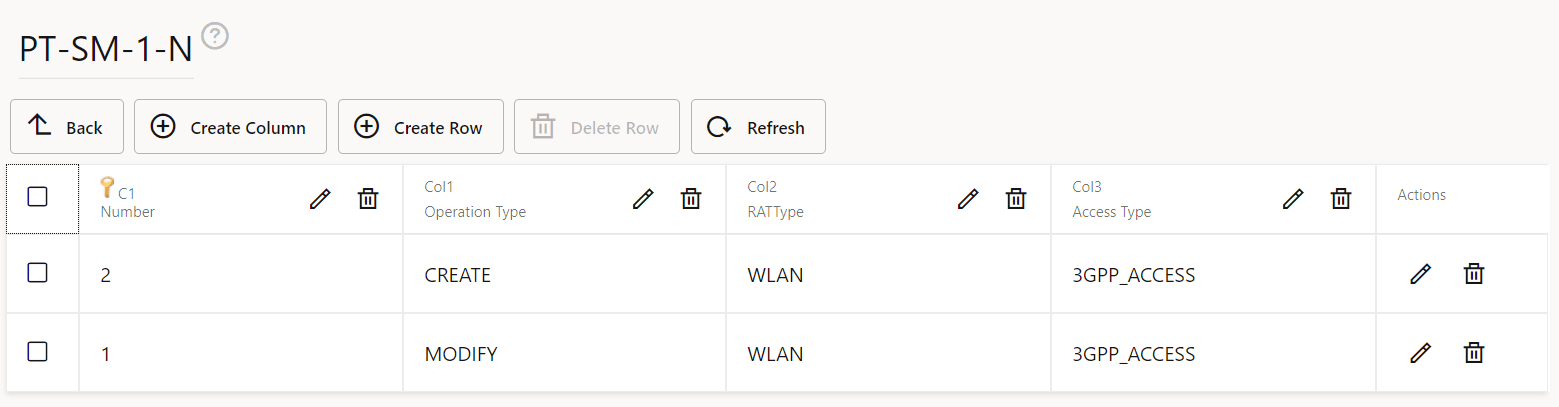
7 Configuring Policy Using CNC Console
This chapter describes how to configure different global and service parameters in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy using Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Configurations Console (CNC Console).
Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Configuration Console Interface
This section provides an overview of the CNC Console, which includes an interface to help in creating global and service parameters in Policy.
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc location.
-
In Windows system, open the hosts file in a notepad as an Administrator and append the following set of lines at the end:
<IP Address> cncc-iam-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local<IP Address> cncc-core-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.localwhere:
<IP Address> is the host address of the deployment cluster. It depends on the deployment cluster.
Example:
10.75.225.189 cncc-iam-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local10.75.225.189 cncc-core-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.localNote:
The IP Address can change when deployment cluster changes. -
Save and close the hosts file.
Note:
Before logging into CNC Console, create a CNC user and password. Using these user details, you can log in to the CNC Console application. For more information about creating a CNC Console user and password, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.- Open a web browser and enter the URL:
http://cncc-core-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local:port
number/ and press Enter.
Note:
port number is cncc-iam-ingress-port number.The login page opens.
- Enter the Username and Password.
- Click Log In.
- On the Welcome page, select the required NF instance from the
Please Select Instance drop-down field.
This opens the CNC Console home page for the selected NF instance:
Figure 7-1 CNC Console for Policy
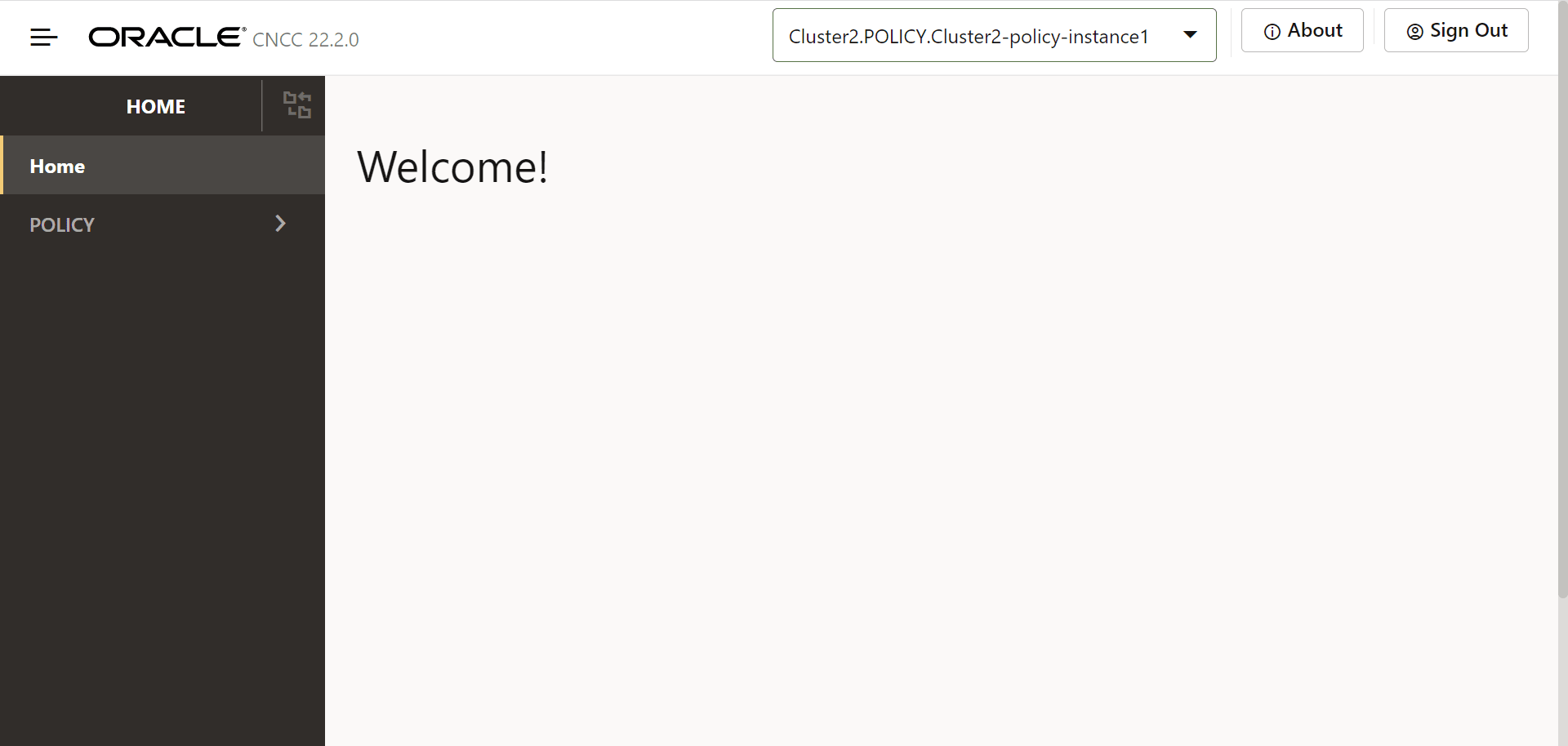
- To use Policy services integrated with CNC Console, click Policy in the left navigation pane.
7.1 General Configurations
This section describes how to customize the general settings in a Policy deployment using the General Configuration pages. The configurations include general settings, such as log levels settings, enabling or disabling metrics, subscriber activity logging settings, and so on.
7.1.1 General Settings
The General Settings page displays the General Settings related to the Policy setup. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, navigate to General
Configurations, and select General
Settings.
This opens the General Settings page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit General Settings page.
- Enter the following information:
Table 7-1 Edit General Settings
Field Name Description apiGatewayHost Specifies the name for the API gateway host . apiGatewayPort Specifies the port number of the API gateway . Enable Tracing Specifies whether to enable/disable tracing. The default value is true.
Enable Metrics Specifies whether to enable/disable system metrics. The default value is true.
Enable TLS Specifies whether to enable/disable TLS. The default value is false.
Enable Subscriber Activity Logging Specifies whether to enable/disable subscriber activity logging. The default value is false.
Enable Policy Event Record Specifies whether to enable/disable Policy Event Record (PER) feature. The default value is false.
Policy Event Record Host Specifies the valid URL of PER host to receive the PER record. The format of the url is: http://per-host:per-port, where per-host specifies the PER host and per-port specifies the PER port.
For example, http://localhost:8101/v1/echo
Enable SBI Correlation This specifies whether to enable/disable correlation-info header in PCF. The dafault value is false.
Enhanced Logging Configuration Enable Enhanced Logging Specifies whether to enable or disable enhanced logging for the PCF deployment. By default, this configuration is disabled. Enable UE Identifier Information Specifies whether to enable or disable UE Identifier information for the PCF deployment. By default, this configuration is disabled. - Click Save.
The page saves the General Settings.
7.1.2 Logging Configurations
This section describes how to customize the log level and subscriber logging activity settings in Policy using the Logging Configurations pages.
7.1.2.1 Logging Level
Note:
Default log level for each service is Warn.The Logging Level page displays the log level configured for different Policy services. The page allows you to edit the log level configurations.
To configure the log level:
- From the navigation menu, under Policy,
navigate to Logging Configuration, and select Logging
Level.
This opens the Logging Level Configuration page. You can add, edit, or delete the log level and package log level for each service type from this page.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Log Level page.
- From the Service Type drop-down list, select the service for which you need to view, edit, or delete the logs.
- From the Application Log Level drop-down list, select the root log level
of the application for the selected service type. Possible values are:
- TRACE
- DEBUG
- INFO
- WARN
- ERROR
Note:
The value for the Application Log Level field is the mandatory value, and the package log level is the optional value. - Expand the Package Log Level group to enter the package log level
information:
Note:
This section is only applicable when Oracle Engineering is trying to isolate an issue and requests one or more package names be added and logs collected after the reproduction of an issue.- Click
 .
.
The Add Package log Level dialog box opens.
- Enter the value in the Package field.
The value of Package field is dependent on the name of the package in each application. Before you set value of the Package field, you must know which package is available in that application.
- From the Log Level drop-down list, select the log level for the
package. Possible values are:
- TRACE
- DEBUG
- INFO
- WARN
- ERROR
- Click Save.
The Package log level information for the selected service is saved.
Note:
Use the or
or  icons available in the next column to update or delete the
package log level information.
icons available in the next column to update or delete the
package log level information.
- Click
- Click Save.
The page saves the log level information for the selected service type.
7.1.2.2 Subscriber Activity Logging
Subscriber Activity Logging allows you to define a list of the subscribers (identifier) that you are may require to troubleshoot the NFs and trace all the logs related to the subscribers separately to view. This functionality can be used to troubleshoot problematic subscribers without enabling logs or traces that can impact all subscribers. You can capture and monitor subscriber logs for UDR or CHF notifications, and associated call flow in Session Management (SM), Access and Mobility (AM), User Equipment (UE), PCRF Core, and Egress Gateway.
To enable the subscriber activity logging functionality, set value of the Enable Subscriber Activity Logging parameter to true on the General Configurations page. By default, this functionality remains disabled. For more information about enabling the functionality, see General Settings.
This procedure provides information about how to configure and manage subscriber logging.
The Subscriber Activity Logging page allows you to create new and manage existing subscribers. The page displays the list of defined subscribers and provides the options to import, export, or add lists.
You can configure the list of subscribers using the Subscriber Activity Logging page.
To configure a list of subscribers for logging:
To configure Subscriber Activity Logging:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to General
Configurations, click Logging Configurations,
and then select Subscriber Activity Logging.
This opens the Subscriber Activity Logging page. The page lists the existing configurations. You can add or import new subscriber activity logging configurations using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Subscriber Activity Logging page.
- On the Create Subscriber Activity Logging page, enter the
following information:
Table 7-2 Create Subscriber Activity Logging
Field Name Description Identifier Type Select the subscriber identifier type. Supported subscriber identifier type are: - GPSI
- SUPI
- IPV4
- IPV6
Note:
Subscriber Activity is supported for 64/128 prefix.
Note: AM and UE services do not support IPV4 or IPV6 identifiers.
Identifier Value The identifier value for the selected identifier type. Enable Use this switch to enable or disable the subscriber logging functionality for the selected subscriber. - Click Save.
The configuration gets listed on the Subscriber Activity Logging page. The page defines the Subscriber Activity Logging configuration in the Policy database and it is available to be used in a Policy.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the configuration.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the configuration.
Importing Subscriber Activity Logging
To import Subscriber Activity Logging configuration:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
Subscriber Identifiers
SUPI
In the 5G system, a globally unique Subscription Permanent Identifier (SUPI), known as IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) till 4G, is assigned for each subscription. The SUPIs are assigned in such a manner that it helps in identifying subscriptions and is independent of the user equipment.
imsi: <value>
supi: imsi-<value>
GPSI
General Public Subscription Identifier (GPSI), known as MSISDN (Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number) till 4G, is a 3GPP defined subscriber public identifier that can be used both inside and outside of the 3GPP system. The association between GPSI and its related SUPI are stored in the subscription data in a 5G system.
msisdn/e164:<value>
gpsi: msisdn-<value>
Limiting size of the Subscriber Activity Logging Mapping Table
Users can specify the number of sessions in the subscriber activity mapping table. By default, the number of sessions per subscriber is defined as 20 in the mapping table.
However, the users can modify the number of sessions by changing the value on the SUBS_ACT_MAPPINGTABLE_ENTRY_SIZE through CM service, Ingress Gateway deployment, or Diameter Gateway.
Limiting size of the mapping table helps in maintaining the network latency and size of the mapping table.
7.1.3 SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection
This procedure provides information about how to use the SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection page to create and manage SBI Ingress error code profiles collection in General Configurations.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click General
Configurations, and then select SBI Ingress Error
Code Profiles Collection.
This opens the SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection page.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Add SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 7-3 Error Code Profiles Configurations
Field Name Description Name Specifies a unique name to identify the error profile. Error Code Specifies the HTTP Code that is populated in the error response when a message request is rejected due to overload control. Error Cause Specifies the error cause that is populated in the error response when a message request is rejected due to overload control. Error Title Specifies the error title that is populated in the error response when a message request is rejected due to overload control. Error Description Specifies the error description that is populated in the error response when a message request is rejected due to overload control. - Click Save to save the error code
profile.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
The value gets listed on the SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
7.2 Error Handling
This section describes how to manage and view the error configurations in Policy, using the Error Handling Configurations page.
7.2.1 Error Configurations
The error handling framework allows the users to configure an error state and an action for it. The action contains two parts, an error rule and an error context. On the Console UI, the operator configures the error state specific to the PCF services and the list of actions for it.
The Error Configurations page displays the error configurations related to different Policy services.
To add error handler template for a Policy service:
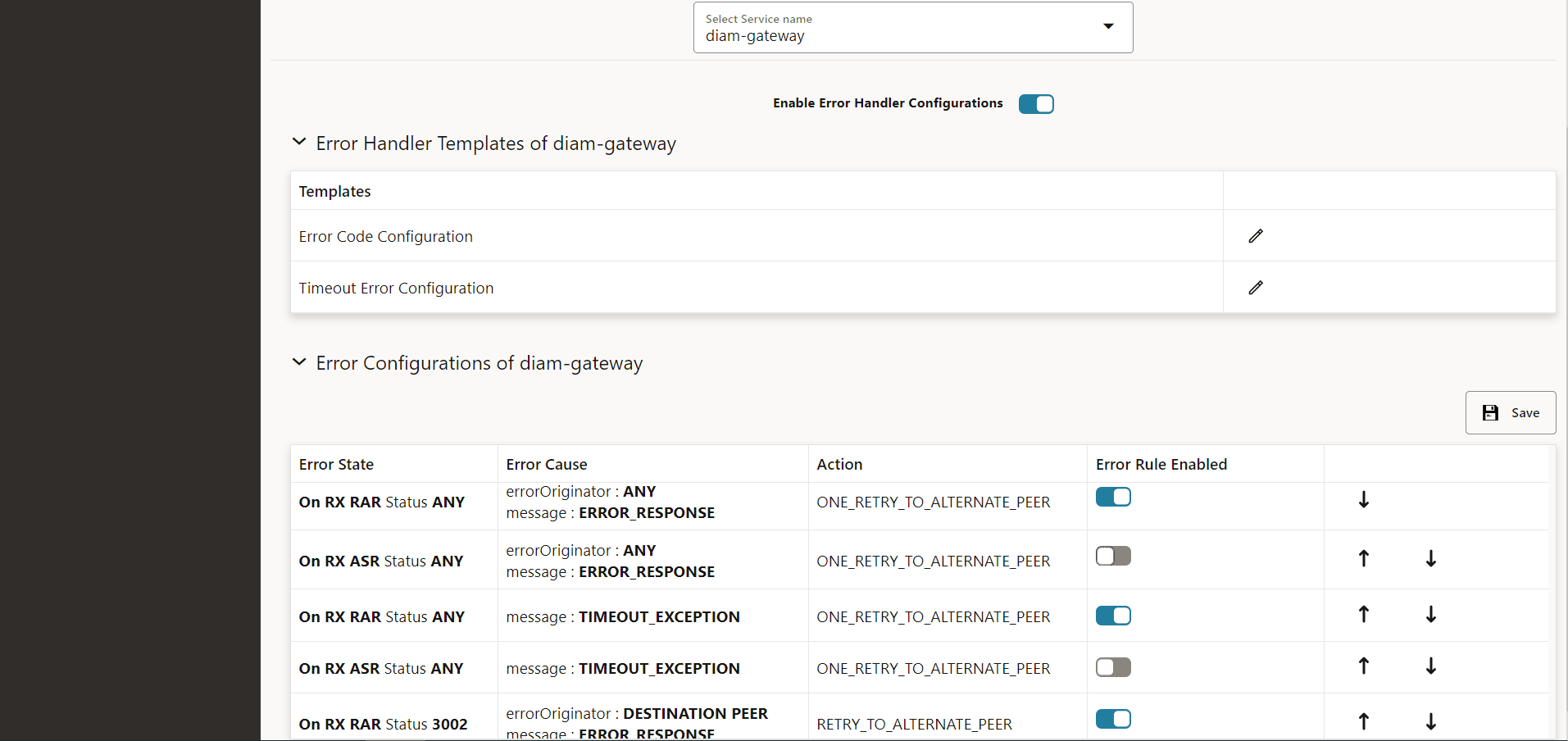
Error Configurations for Diameter Gateway Service
- From the navigation menu, under Policy, click Error Handling, and select Error Configurations page. This opens the Error Handling Configurations page.
- From the
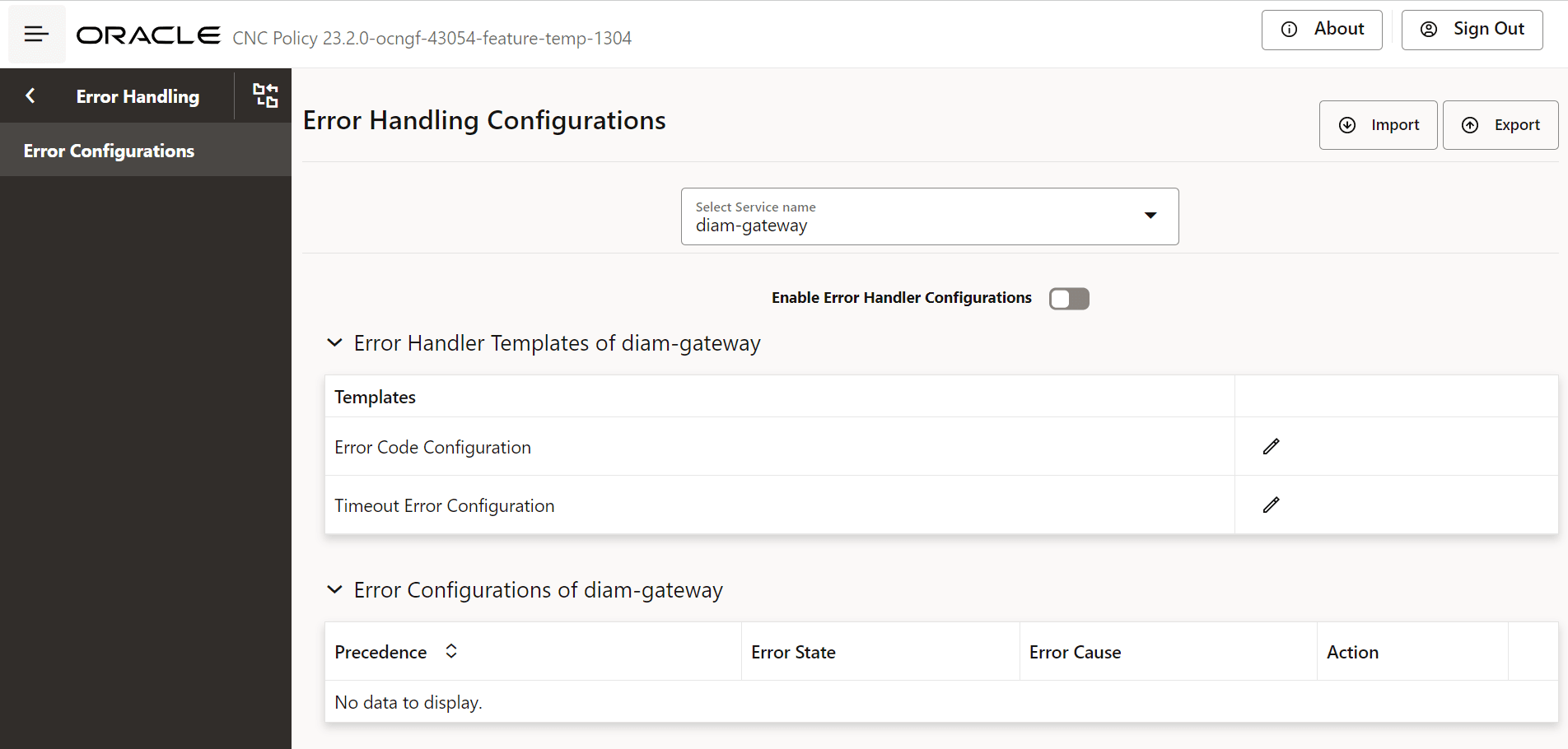
Select Service Namedrop-down list select the valuediam-gateway. The page allows you to add and edit configurations for diameter message retry for Rx RAA or Rx ASR. On the page Error Handler Templates of diam-gateway and Error Configurations of diam-gateway subsections are displayed. - Enable the error handler configurations using the Enable Error Handler Configurations toggle button.
- The Error Handler Templates of diam-gateway provides two
options:
- Error Code Configuration
- Timeout Error Configuration
Figure 7-2 Error Handling Configuration UI
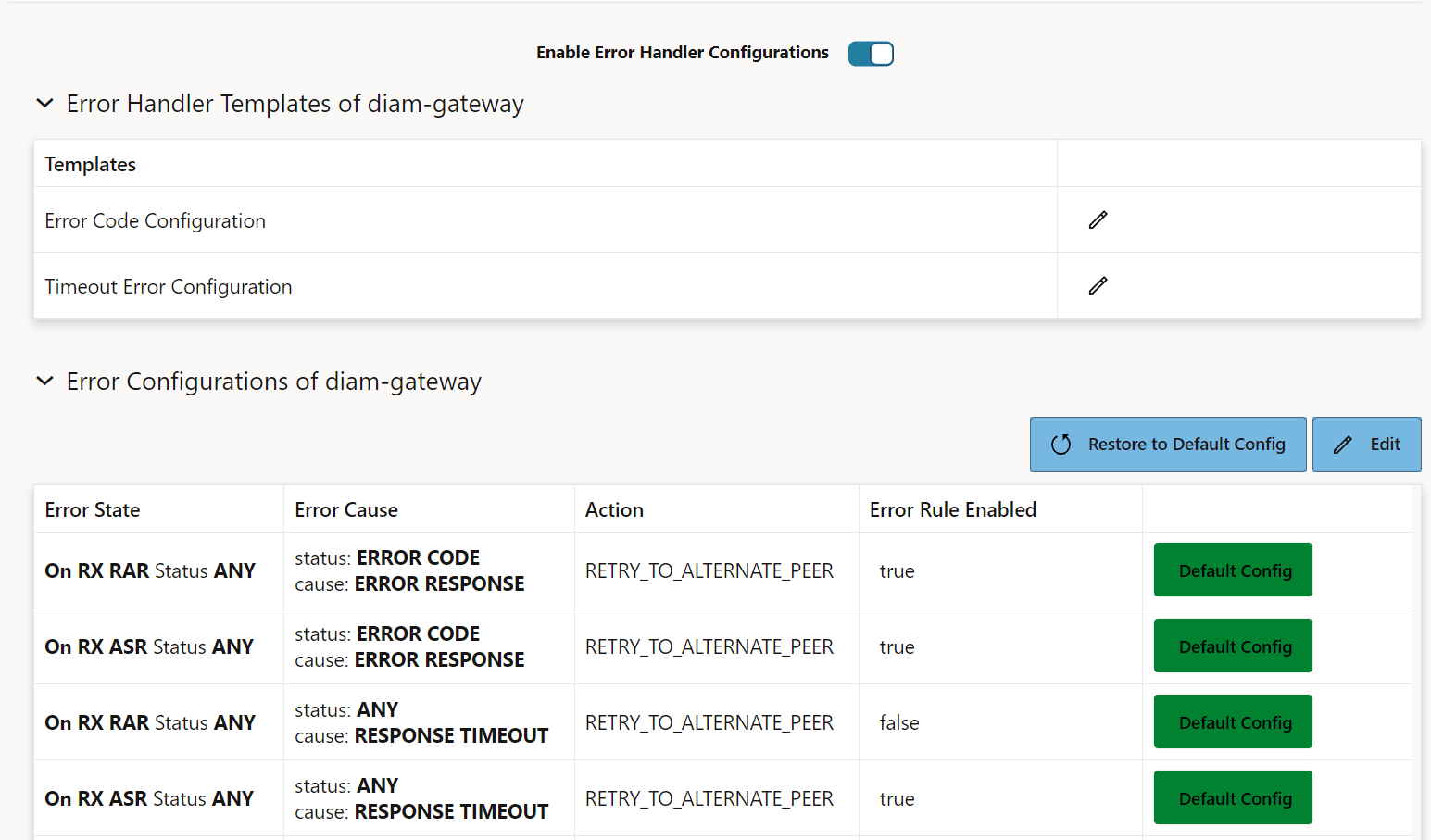
- The Error Configurations of diam-gateway provides default
error handling configurations to retry on all error codes (except diameter
result code 2xxx) and timeout for Rx RAA and Rx ASA failed diameter
messages.
Figure 7-3 Default Configurations
- To configure the Error Code Configuration in Error Handler
Templates of diam-gateway , Click
 .
.
This opens the Error Handler Template editing page.
-
Enter values for the available input fields. The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-4 Create Error Code Configuration - Edit
Field Name Description On Rx Specifies the list of diameter interfaces. The values are: - RAR
- ASR
Default value: RAR
Status Specifies the error status to be provided by the user. Error Cause Configure Error Cause Field Species to search for which error causing filed in the diameter answer message. Default value: ALL
Match Operator Species the match operator to search error section in the diameter answer message. Default value: ANY
Message Specifies the error message to search in the error section of diameter answer message. Default value: ANY
Status Specifies the error status code to search in the error section in the diameter answer message. Default value: ANY
Cause Specifies the field that matches the cause during error ends with 'not found'. User can choose from the following options: - ANY
- RESPONSE_TIMEOUT
Default value: ANY
Action Action The action to be performed in the event of failed diameter message on Rx interface. User can choose from the following options: - RETRY TO ALTERNATE PEER
- ONE RETRY TO ALTERNATE PEER
Error Originator The peer from which the error origination occurs. User can choose from the following options: - ANY
- INTERMEDIATE_PEER
- DESTINATION PEER
Figure 7-4 Edit Error Code Configuration:
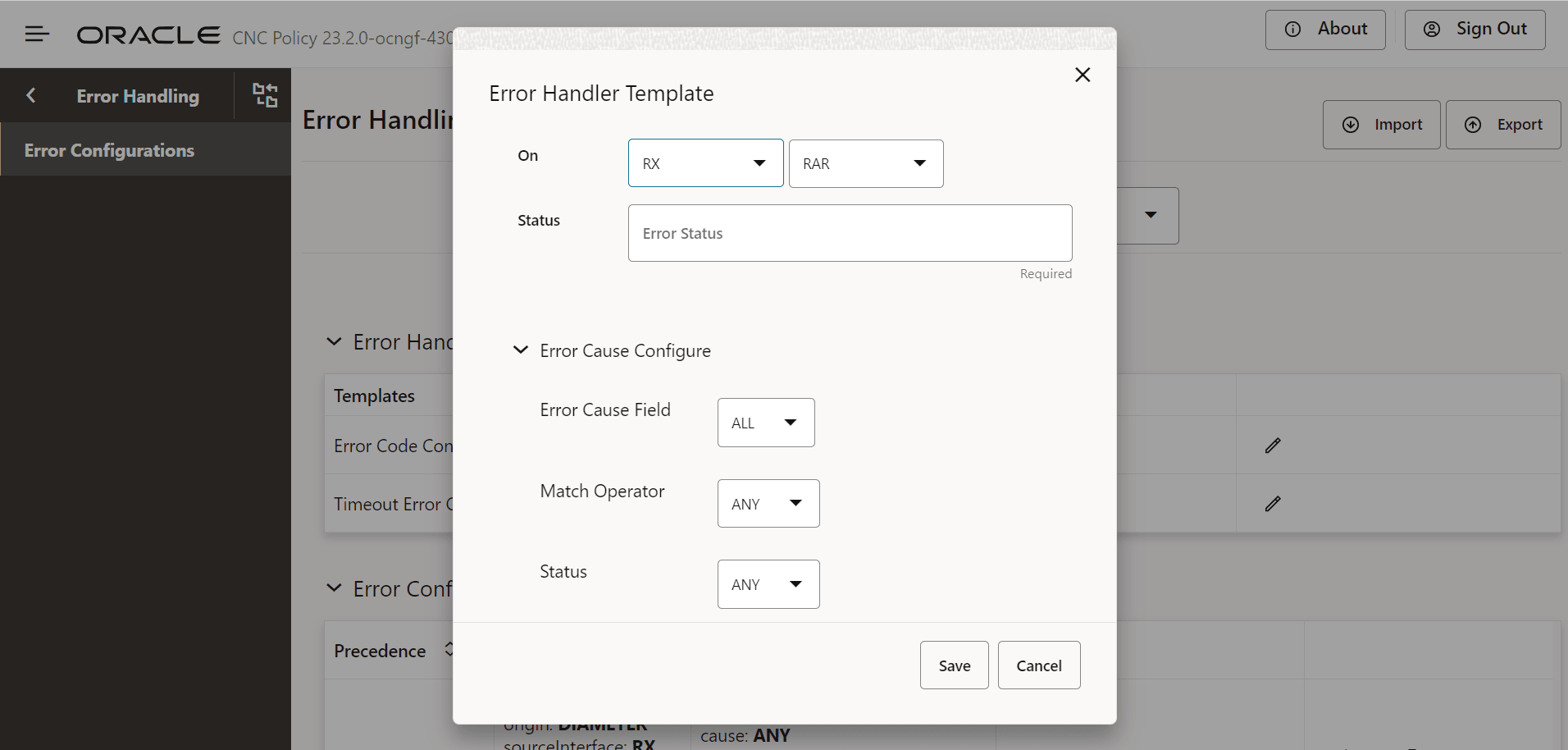
Figure 7-5 Edit Error Code Configuration continuation..

- Click Save to save the changes or Click Cancel to discard the changes.
- To configure Timeout Error Configuration in Error Handler
Templates of diam-gateway , Click
 .
.
This opens the Error Handler Template editing page
-
Enter values for the available input fields. The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-5 Create Timeout Error Configuration
Field Description On RX Specifies the list of diameter interfaces. Default value: RAR
Status Specifies the error status to be provided by the user. Default value: ANY
Error Cause Configure Error Cause Field Species to search for which error causing filed in the diameter answer message. Default value: MESSAGE
Match Operator Species the match operator to search error section in the diameter answer message. Default value: EQUALS
Message Specifies the error message to search in the error section of diameter answer message. Default value: TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION
Status Specifies the error status code to search in the error section in the diameter answer message. Default value: ANY
Cause Specifies the field that matches the cause during error ends with 'not found'. Default value: ANY
Instance Specifies the field that matches the instance during error contains the term 'Illegal'. Default value: ANY
resource Specifies the resource to search in the error section of diameter answer message. Default value: ANY
Action Action The action to be performed in the event of response timeout on Rx interface. User can choose from the following options: - RETRY TO ALTERNATE PEER
- ONE RETRY TO ALTERNATE PEER
Error Originator The peer from which the error origination occurs. User can choose from the following options: - ANY
- INTERMEDIATE_PEER
- DESTINATION PEER
Figure 7-6 Edit Timeout Error Configuration:
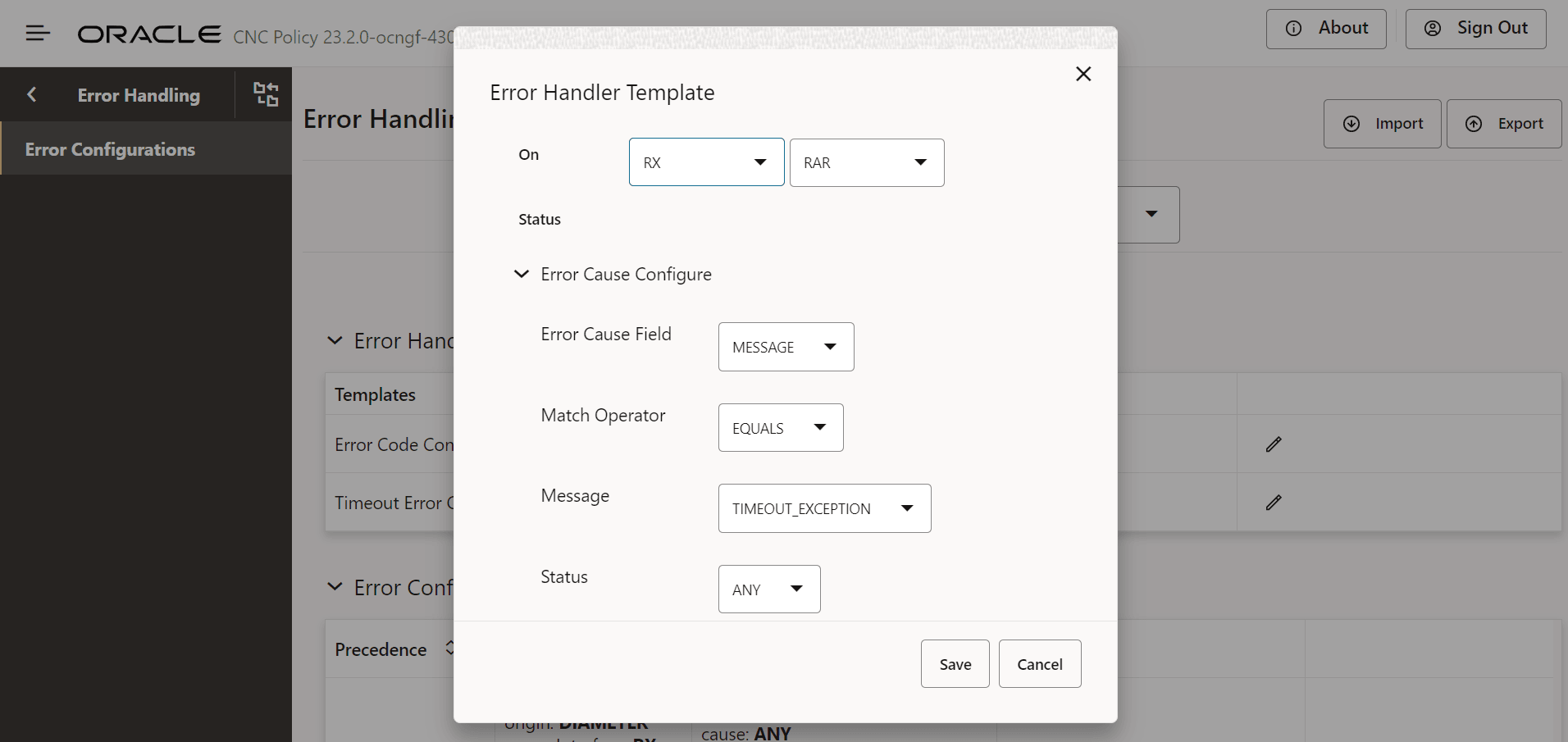
Figure 7-7 Edit Timeout Error Configuration Continuation:
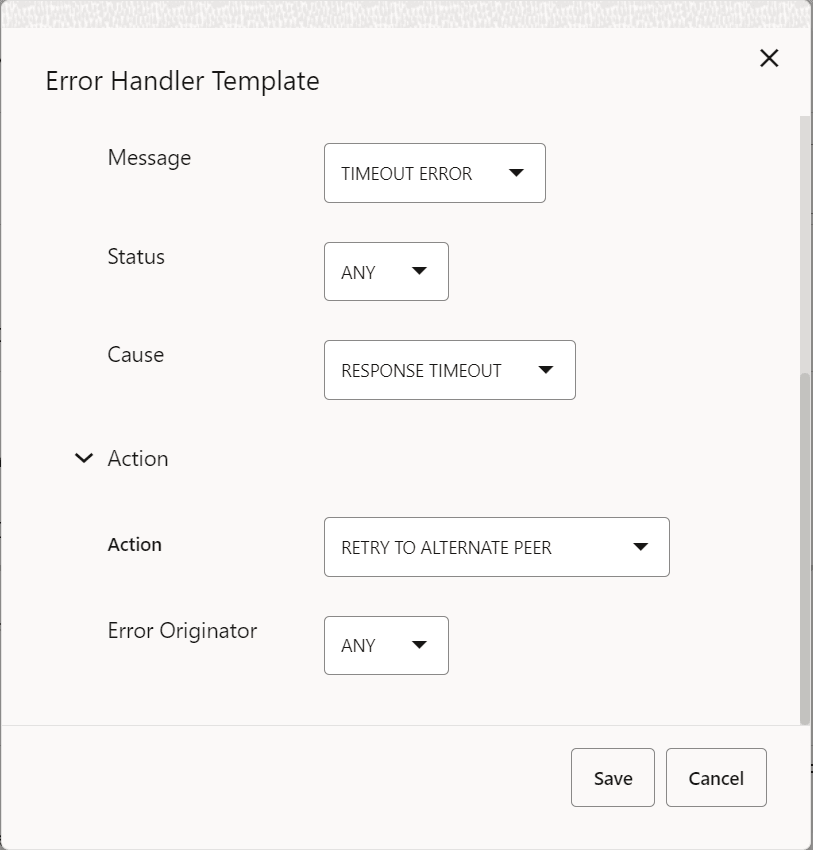
- Click Save to save the changes or Click Cancel to
discard the changes.
Using the edit error handling configuration option, you can enable or disable the configurations.
The priority for each error handling configuration can be set using the

and
arrow buttons.Figure 7-8 Error Handling User Saved Configuration with Priority:
Error Configurations for PA Service
- From the navigation menu, under Policy, click Error
Handling and select Error Configurations page.
This opens the Error Handling Configurations page.
- From the
Select Service Namedrop-down list, select the valueoccnp_pcf_pa. - Enable the error handler configurations using the Enable Error Handler Configurations toggle button.
- The Error Handler Templates of occnp_pcf_pa provide two
options:
- Diameter RAA Error Configuration
- Diameter Timeout Error Configuration
Figure 7-9 Error Handling Configuration

- To configure the Diameter RAA Error, Click
 .
.
This opens the Error Handler Template editing page for Diameter RAA Error.
-
Enter values for the available input fields. The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-6 Diameter RAA Error Configuration
Field Name Description On Rx Specifies the list of diameter interfaces. Default Value: RAR
Status Specifies the diameter error result code to be provided by the user. Error Cause Configure Error Cause Field Specifies the error causing filed in the diameter answer message. Default Value: Error Response Originator
Match Operator Specifies the match operator to search error section in the diameter answer message. Default Value: EQUALS
Error Response Originator Specifies the originator of the error response. Default Value: ANY
Action Action Either terminate the ongoing transaction related to RAA or cleanup the Rx/N5 session. Default Value: Terminate Transaction
Figure 7-10 Diameter RAA Error Configuration:

- Click Save to save the changes or Click Cancel to discard the changes.
-
- To configure Diameter Timeout Error Configuration, Click
 .
.
This opens the Error Handler Template page for Diameter Timeout Error Configuration.
-
Enter values for the available input fields. The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-7 Diameter Timeout Error Configuration
Field Description On RX Specifies the list of diameter interfaces. Default Value: RAR
Status Specifies the error status to be provided by the user. Default Value: NA
Error Cause Configure Error Cause Field Specifies the error causing filed in the diameter answer message. Default Value: MESSAGE
Match Operator Specifies the match operator to search for error section in the diameter answer message. Default value: EQUALS
Message Specifies the error message to search in the error section of diameter answer message. Default value: TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION
Action Action Either terminate the ongoing transaction related to RAA or cleanup the Rx/N5 session. Default value: Terminate Transaction
Figure 7-11 Diameter Timeout Error Configuration:

- Click Save to save the changes or Click Cancel to discard the changes.
-
Error Configurations for AM, SM, UE, CHF Connector, UDR Connector, and Binding Services
- From the navigation menu, under Policy, click Error Handling, and select Error Configurations page. This opens the Error Handling Configurations page.
- From the Select Service Name drop-down list, select the required service.
- Enable the error handler configurations using the Enable Error Handler Configurations toggle button.
- The error handler template provides Error Enhancement Configurations.
- To configure the Error Enhancement Configurations in Error
Handler Templates of the required service, Click
 . This opens the Error Handler Template editing page.
. This opens the Error Handler Template editing page.
- Enter values for the available input fields. The following table
describes the fields:
Table 7-8 Error Handler Template
Field Description On Specifies the Application Error. Default value: Application Error
Action Action Specifies the action to be performed in the event of failed message. Default value: Reject with Enhanced Detail
Exclude from error message Specifies exclusion of the provided components from detail error message. By default, "Error State and "Probelm Cause" are excluded. - Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
7.3 Service Configurations
Note:
The advanced settings keys should have a unique value without any duplicates. For example, CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_ENABLED_FOR_CHF_NOTIFICATION settings for PDS should have a single key with value either true or false. There should not be two keys for CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_ENABLED_FOR_CHF_NOTIFICATION, each of them holding different values.7.3.1 Common Data
This section includes the common data configurations for Policy services.
To access Common Data functionality from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Service Configurations and select Common Data.
7.3.1.1 Reattempts Profile
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the reattempts profiles for the binding registration.
The Reattempts Profile page allows you to create new and manage existing reattempt profiles. The page displays the list of defined reattempt profiles with the options to import, export, or add profiles.
To configure reattempt profile:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service Configurations,
click Common Data, and then select Reattempts
Profile.
This opens the Reattempts Profile page. The page lists the existing reattempt profiles. You can add or import new profiles using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Reattempts Profile page.
- On the Create Reattempts
Profile page, enter the following information:
Table 7-9 Create Reattempts Profile
Field Name Description Name The unique name for the reattempt profile. This name is used to refer to the reattempt profile in other service configuration screen, such as SM Service.
The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 255 characters.
Interface Type The interface for which a reattempt profile is being created. Note: Policy supports only the BSF Interface.
BSF Reattempts Settings Maximum Number of Attempts The maximum number of allowed recreate attempts. The number of reattempts that must be run when PCF Binding request fails.
Range: 0 to 50
Back-off timer configurations The amount of time that represents each back-off timer. The Back-off timer configurations table includes the following parameters:- Index: Represents the number of back-off timer
- Back-Off Timer: The timer value in seconds
- Max Random Number (Millisecond): Any random number that is added to the back-off timer.
Range: 0-5000 milliseconds
Note: In case the number of configured attempts in the Back-off timer configurations table is less than the set value for Maximum Number of Attempts, the remaining attempts uses the back off timer and max random number of the last configured attempt.
Note: Policy supports a maximum of 10 back-off timer configurations.
ThresHold Limit Level The threshold limit for the Pending Operations. Once this value is reached, no pending operations are added to the table. For information about pending operation configurations, see PCF Session Management.
Default Value: 1000
- Click Save.
The reattempt profile gets listed on the Reattempt Profile page. The page defines the reattempt profile in the Policy database and it is available to be used in a Policy.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update or delete
the reattempt profile.
available under the Actions column to update or delete
the reattempt profile.
Importing Reattempt Profiles
To import Reattempt Profile:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.3.1.2 Retry Profiles
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage retry profiles.
The Retry Profile page allows you to create new and manage existing retry profiles. The page displays the list of defined retry profiles with the options to import, export, or add profiles.
To configure retry profile:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations, click Common Data, and then
select Retry Profiles.
This opens the Retry Profiles page. The page lists the existing retry profiles. You can add or import new retry profile using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Retry Profile page.
- On the Create Retry Profile
page, enter the following information:
Table 7-10 Create Retry Profile
Field Name Description Name The unique name for the retry profile. This name is used to refer to the retry profile in other service configuration screen, such as SM Service, User Connector and so on.
The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 255 characters.
Retry on Internal Send Failure Specifies whether to enable or disable retry for failed messages between core microservices of Policy.
On enabling this switch, ensure that you configure the parameters under Retry Settings group. However, if the switch is disabled, the configurations in the Retry Settings group are not taken into consideration.
When enabled, retries are attempted when PCF encounters internal send failures for egress messages.
A failure to send egress messages internally indicates an exception in the core service, such as SM service, UDR or CHF connector, and so on. The exception can occur while connecting to the next microservice or a failure on the microservice itself. For example, egress message did not reach the egress gateway. This also includes the connection errors and timeouts on the core microservice.
Note: Since the failure is internal, the external NF and SCP (if applicable) remain the same during retry attempt.
Enable Alternate Routing Specifies whether to enable or disable alternate routing.
On enabling this switch, ensure that you configure the parameters under the Alternate Routing Settings group.
When enabled, alternate routing is attempted when the Policy messages are not delivered successfully to an external NF destination. It may happen because of an exception on the Egress Gateway, such as connection error, timeout, or a failure returned by the external NF or an intermediate router.
Server Header Support Specifies whether to enable or disable server header. The value configured in this parameter is used when PCF acts as a consumer and receives server header in error response messages.
Depending on the requirements, you can select any of the following values from the drop-down list:- Disabled (default) - Select this option to disable server header. On disabling server header, Policy as a consumer searches for alternate producer without considering the value of server header.
- Single Instance - Select this option to accept only one value in the server header. When the value is configured as Single Instance and server header contains multiple values, Policy rejects the header.
- Multi Instance - Select this option to accept multiple values in the server header.
Pattern To Ignore Server Header Value Specifies the pattern to ignore server header values. Note:
This field appears only when single Instance or Multi Instance is selected fron the drop-down of the Server Header Support field.Ignore Custom server header value This field appears on selection of either "Single Instance" or "Multi Instance" value for the field Server Header Support. In this field you can specify the string pattern that can be ignored in the server header value. This is provided in the form of regular expression. The regular expression evaluates the server header content to ignore the strings that match the pattern specified the regular expression. Retry Settings Provide Retry Settings details: Maximum Number Of Retries Specifies the number of retries that PCF attempts on encountering failure while sending egress messages from Policy core microservices.
Note: The value configured for this parameter does not include the initial attempt. For instance, if you set the value as 3, Policy performs the retry cycle three times after the initial attempt.
Alternate Routing Settings Provide Alternate Routing Settings details: Maximum Number Of Alternate Routing Attempts Specifies the number of retries that PCF attempts on receiving error response from Egress Gateway. The number of retry attempts can be in the range of 1 to 10.
Note: The value configured for this parameter does not include the initial attempt. For instance, if you set the value as 3, Policy performs the retry cycle three times after the initial attempt.
If the retry attempts are exhausted, CNC Policy fails the transaction with an exception. In certain cases, the number of retry attempts can be greater than the available alternate destinations to be tried. If such a situation arises, Policy fails the transaction when no alternate destination is available even if retry attempts are still available.
Attempt Alternate Route for Following Error Codes Allows to configure the HTTP error codes for which Policy reattempts the requests after the ARR request failures. Note: In Policy 22.1.0, Error Causes does not work for Notify Flows. Users are recommended to leave it blank.
To add a value, click Add and enter values for the following fields:
- Error Code - Specifies the HTTP error code. For example, 504
- Error Causes - Specifies the error cause. For example, GATEWAY_TIMEOUT, NF_TIMEOUT.
You can configure up to 32 error codes with each error code supporting up to five causes.
Priority Pool Specifies whether to enable or disable the load sharing between different NFs. Use Alternate SCP for Alternate Routing Specifies whether to enable or disable choosing alternate SCP to reach the alternate destination.
If you set the value for this parameter as true, Egress Gateway uses an alternate SCP for routing to an alternate NF destination. If there are fewer SCPs than alternate NF destinations, Egress Gateway tries sending the request through one of the previously used SCPs.
Note: Additional SCP configuration is required for egress gateway. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Policy Installation and Upgrade Guide.
Use Binding Information from Binding Header Specifies whether to enable or disable the use of information received in 3gpp-sbi-binding header. When Policy receives the unique NF Instance ID in the error response, it retrieves the 3gpp-sbi-binding header for that particular NF instance. It extracts the
SetIdto choose the alternate producer. This parameter is considered only for subsequent retry requests.By default, this switch is disabled.
Note: When this switch is enabled, the value of NFSet Preference is not taken into consideration.
Use Binding Information from NF Profile Specifies whether to enable or disable the use of information from the set NF Profile. When Policy receives the unique NF Instance ID in the error response, and it does not receive information from the 3gpp-sbi-binding header for that particular NF instance, it extracts the
SetIdto choose the alternate producer. This parameter is considered only for subsequent retry requests.By default, this switch is disabled.
Note: For subsequent requests, this field takes precedence only if the Use Binding Information from Binding Header flag is disabled or no NF binding is received in the initial request.
NF Set Resolution Specifies whether to enable the on demand discovery of subsequent messages based on the NFSet ID, in case of failure response.
The possible values are:-
NRF Discovery: If this value is selected, then PCF sends a request to NRF to get the list of NFs based on the
SetIdvalue from the 3gpp-Sbi-Binding header of the NF with a successful Initial Request. -
Cached NF Profiles: If this value is selected, then PCF selects the list of NFs from the already discovered NF list.
By default CachedNFProfiles remains selected.
Note: NRF discovery is applicable for subsequent messages functionality only. For the other retry requests, the NF list is provided through the cached NF profiles. If the Cached NF Profiles option is selected for the subsequent messages, then it uses the DNS-SRV configuration for session retry.
NF Set Preference Specifies the NF set preference when choosing the alternate producer for an initial request. Policy excludes the producer (received in the failed request) and selects an alternate producer based on the value you choose from the drop-down menu:- Same: Choose the next producer from the same NFSet as the previous request.
- Different: Choose the next producer from a different NFSet.
- None (default): NFSets filter does not apply.
Note: This parameter applies only to initial requests. For subsequent requests, the default behavior is to choose the same NFSet provided by Sbi-Binding Info (if enabled). Otherwise, it goes to the same NFSet as the the current NF. In case the current NF does not belong to any NFSet or NFSet is missing, it falls back to DNS-SRV.
Locality Preference Specifies the locality preference when choosing the alternate producer for a failed request.
Policy excludes the producer (received in the failed request) and selects an alternate producer based on the value you choose from the drop-down menu:
- Same: Choose the next producer from the same locality as the previous request.
- Different: Choose the next producer from a different locality.
- None (default): Locality filter does not apply.
Re-attempt to Same NF Specifies whether Policy shall send the request to the same NF that failed in the first attempt. If you enable this switch, Policy allows re-attempting to the same NF based on the following conditions: - If the server header in error-response has SCP host alone, Policy does not consider error code and error cause, and retries to the same NF.
- If the server header in error-response has instances with or without SCP or envoy, Policy checks error code and error cause to find out if retry to same NF is allowed.
By default, this switch is disabled.
Note: Make sure to configure the value for Re-attempt same NF for following Error Codes field.
Re-attempt Same NF for following Error Codes Specifies the HTTP error codes for which Policy does not look for alternate producer and retries the request to the same NF or SCP that failed in the first attempt.
To add a value, click Add and enter values for the following fields:
- Error Code - Specifies the HTTP error code. For example, 504
- Error Causes - Specifies the error cause. For example, GATEWAY_TIMEOUT, NF_TIMEOUT.
You can configure up to 10 error codes with each error code supporting up to five causes.
When the field is left empty (default), Policy does not send the request to the NF that failed in the first attempt.
NOTE: Policy considers this parameter only when Re-attempt to same NF switch is enabled.
Enable DNS Resolution Specifies whether to enable or disable falling back to DNS resolution.
When this flag is enabled, during subsequent requests, after the application of filters and flags if no alternate NFs are found, Policy falls back to DNS resolution (DNS SRV).
By default, this flag is disabled.
Note: Enable FallBack to Higher Priority Destination and Retry After Interval fields are considered only if Enable DNS Resolution field is enabled.
Enable Fallback to Higher Priority Destination Specifies whether to enable or disable falling back to the higher priority destination that failed earlier (after the retry interval). Policy attempts fallback even if the current destination is available. When you enable this switch, Policy attempts to fallback to a higher priority NF destination. The priority of NF destination is determined by Alternate Route service (either via DNS-SRV resolution or by static configuration).
Default Value: False
The following example illustrates a scenario when Fallback is enabled and Retry After Interval is set to 900 seconds:NRF returned profiles - UDR1 (priority-1), UDR2 (priority-2), UDR3 (priority-3), Alternate Route configuration for UDR1 - UDR1 (priority-1), UDR1.2 (priority-2), UDR1.3 (priority-3), Retry After Interval - 900 seconds, Fallback is enabled 9:00 AM PCF receives an SM Create request and establishes a session with UDR1 9:05 AM PCF receives an SM Modify request and routes to UDR1, UDR1 fails, PCF reroutes to UDR1.2 9:10 AM PCF receives an SM Modify request and routes to UDR1.2 9:20 AM PCF receives an SM Modify request and routes to UDR1 (fallback)Note: This configuration applies to subsequent message routing only.
Priority pool must be enabled to use Enable FallBack to Higher Priority Destination.
For multi-pod deployments where subsequent requests for a subscriber can be distributed across different pods, the fallback to higher priority destination will be effective only when there is sufficient traffic. The messages are distributed to all the pods such that they build up respective cache with failed destination info along with failed time stamp. If this cache is not present on a particular pod, the fallback to higher priority will not happen.
Retry After Interval (in seconds) Specifies the time in seconds after which Policy re-attempts a request to a higher priority destination.
In case of fallback, when a route is being determined while the current destination has not failed, PCF attempts to fallback to a higher priority NF destination. Priority of NF destination is determined by Alternate Route service, either through DNS-SRV resolution or static configuration.
You can set the value for retry after interval from 0 to 86,400 seconds.
By default, the value is set to 0, which means that a high priority destination is blocklisted.
Note:
- This configuration applies to subsequent message routing only.
- Blacklisting may still be done by Egress Gateway
- An NF destination (FQDN) is not re-attempted within the context of a single operation, such as SM Modification request
NRF returned profiles - UDR1 (priority-1), UDR2 (priority-2), UDR3 (priority-3), Alternate Route configuration for UDR1 - UDR1 (priority-1), UDR1.2 (priority-2), UDR1.3 (priority-3), UDR1.4 (priority-4) Retry After Interval - 900 seconds, Fallback is disabled 9:00 AM PCF receives an SM Create request and establishes a session with UDR1 9:05 AM PCF receives an SM Modify request and routes to UDR1, UDR1 fails, PCF reroutes to UDR1.2 9:10 AM PCF receives an SM Modify request and routes to UDR1.2 9:12 AM PCF receives an SM Modify request and routes to UDR1.2, UDR1.2 fails, PCF reroutes to UDR1.3 9:16 AM PCF receives an SM Modify request and routes to UDR1.3 (no fallback) 9:20 AM PCF receives an SM Modify request and routes to UDR1.3, UDR1.3 fails, PCF alternate routes to UDR1 (not UDR1.4)Retry again at end of alternate NF options When you set the value for this parameter to true, Policy initiates the retry cycle and sends request to the selected NF when the following conditions are true:
- Retry attempts made to all available NF instances
- Maximum Number of Alternate Routing Attempt is not exhausted
Figure 7-12 Create Retry Profile

- Click Save.
The retry profile gets listed on the Retry Profile page. The page defines the retry profile in the Policy database and it is available to be used in a Policy.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the retry profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the retry profile.
Importing Retry Profiles
To import Retry Profile:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.3.1.3 Timer Profiles
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage timer profiles.
The Timer Profile page allows you to create new and manage existing timer profiles. The page displays the list of defined timer profiles with the options to import, export, or add profiles.
To configure timer profile:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations, click Common Data, and then
select Timer Profiles.
This opens the Timer Profiles page. The page lists the existing timer profiles. You can add or import new profiles using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Timer Profile page.
- Select any of the following services from the
Service Type drop-down list and perform the required configurations.
- PCF User Connector
To configure the timer profile for PCF User Connector:
- Enter the timeout value for UDR:
Timeout Per Service.nudr-dr (in milliseconds): Specifies the maximum time for the response from the nudr-dr service.
Note:
You can enter timeout for specific messages. - Enter the timeout values for CHF:
Timeout Per Service.nchf-spendinglimitcontrol (in milliseconds): Specifies the maximum time for the response from the nchf-spendinglimitcontrol service.
- Enter the timeout value for UDR:
- PCF Session Management
To configure the timer profile for PCF Session Management:
- Enter the timeout values for SMF:
Timeout Per Service.notification (in milliseconds): Specifies the maximum time for the response from the notification service.
- Enter the timeout values for AF:
Timeout Per Service.notification (in milliseconds): Specifies the maximum time for the response from the notification service.
- Enter the timeout values for SMF:
- PCF Access and Mobility
To configure the timer profile for AMF:
- Enter the timeout values for AMF:
Timeout Per Service.notification (in milliseconds): Specifies the maximum time for the response from the notification service.
- Enter the timeout values for AMF:
- PCF UE Policy
To configure the timer profile for PCF UE Policy:
- Enter the timeout values for AMF:
Timeout Per Service.namf-comm (in milliseconds): Specifies the maximum time for the response from the namf-comm service.
Timeout Per Service.notification (Non N1N2 messages. In milliseconds): Specifies the maximum time for the response from the notification service. This will be used only if its value is less than the 3gpp-max-response-time header value.
- Enter the timeout values for AMF:
- PCF Binding Service
To configure the timer profile for Binding Service
- Enter the timeout values for BSF:
Timeout Per Service.nbsf-management (in milliseconds): Specifies the maximum time for the response from the BSF service.
- Enter the timeout values for BSF:
- PCF User Connector
- Click Save.
The timer profile gets listed on the Timer Profile page. The page defines the timer profile in the Policy database and it is available to be used in a Policy.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the timer profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the timer profile.
Importing Timer Profiles
To import Timer Profile:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.3.1.4 Site Takeover
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the sites for takeovers in case of failure scenarios.
The Site Takeover page allows you to create new and manage existing sites for takeover. The page displays the list of defined sites with the options to import, export, or add profiles.
To configure site:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service Configurations,
click Common Data, and then select Site
Takeover.
This opens the Site Takeover page. The page lists the existing sites. You can add or import new profiles using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Site Takeover page.
- On the Create Site
Takeover page, enter the following information:
Table 7-11 Create Site Takeover
Field Name Description Name The unique name for the site. This name is used to refer to the site in other service configuration screen, such as SM Service.
The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 255 characters.
Site ID The site ID for which the current site takes control of the pending binding records in case of binding registration failures. - Click Save.
The site gets listed on the Site Takeover page. The page defines the site in the Policy database and it is available to be used in a Policy.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update or delete
the site.
available under the Actions column to update or delete
the site.
Importing Site Takeover
To import site:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.3.1.5 NF Communication Profiles
The NF Communication Profiles page allows you to create new and manage existing NF communication profiles. The page displays the list of defined profiles with the options to import, export, or add profiles.
To configure NF communications profile, perform the following steps:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations, click Common Data, and then
select NF Communication Profiles.
This opens the NF Communication Profiles page. The page lists the existing profiles. You can add or import new profiles using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create NF Communication Profile page.
- On the Create NF Communication
Profile page, enter the following information:
Table 7-12 Create NF Communication Profile
Field Name Description NF Communication Profile Name The unique name for the NF communication profile. This name is used to refer to the profile in other service configuration screen, such as SM Service, User Connector, and so on.
The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 255 characters.
Policy NF Communication Model Indicates the communication model as defined in 3GPP Technical Specification 23.501 Annexue E, in which the Policy NF is deployed.
Select any of the following values from the drop down menu:
- Custom: Select this option to create a customized communication profile.
- Model B: Direct
communication with NRF interaction. In this model,
consumers perform discovery by querying the NRF.
Based on the discovery result, the consumer does the
selection and sends request to the selected
producer.
Selecting this option configures the communication profile according to Model B and populates data for the respective input fields.
- Model C:
Indirect communication without delegated discovery.
In this model, consumers perform discovery by
querying the NRF. Based on the discovery result, the
consumer does the selection of an NF set or a
specific NF instance of the NF set. The consumer
sends the request to the SCP containing the address
of the selected service producer pointing to a NF
service instance or a set of NF service instances.
In the latter case, the SCP selects an NF Service
instance. If possible, the SCP interacts with NRF to
get selection parameters such as location and
capacity. The SCP routes the request to the selected
NF service producer instance.
Selecting this option configures the communication profile according to Model C and populates data for the respective input fields.
- Model D: Indirect
communication with delegated discovery to SCP. In
this model, consumers such as PCF add discovery
parameters and delegate the discovery of the
producer to SCP. The delegated discovery applies to
both on-demand and autonomous discovery scenarios.
Selecting this option configures the communication profile according to Model D and populates data for the respective input fields.
NF Discovery Settings Provide NF Discovery Settings details: Initial Discovery Parameters Indicates the discovery parameter to be used in the 3gpp-sbi-discovery-<discovery-parameter> for all Policy Model D NF Communication. This parameter helps SCP to discover the suitable NF for discovery.
Policy supports the following discovery parameters for Model D NF Communication:supidata-set (may be included for UDR Discovery)preferred-localitydnn (may be included for BSF, SMF Discovery)snssaisguami (maybe included for AMF Discovery)group-id-list ( May be included for "UDR","CHF" discovery.)
Policy supports the following discovery parameters for Custom, Model B, and Model C NF Communications:target-nf-set-idsupigroup-id-list
Note: The Nbsf interface does not include SUPI as a discovery parameter that is, SUPI is not suppported for BSF interface.
Send Discovery Header in Initial Messages This switch indicates if PCF must include the 3gpp-sbi-discovery-<discovery-parameter> parameters in the initial SBI message.
By default the switch remains disabled.
Send Discovery Header in Subsequent Message This switch indicates if PCF must include the following 3gpp-sbi-discovery-<discovery-parameter> parameters in SBI messages: - Parameters to update a subscription, such as PUT messages when unable to fill in a 3gpp-sbi-routing-binding header.
- Parameters to delete a subscription, such as DELETE messages when unable to fill in a 3gpp-sbi-routing-binding header.
By default the switch remains disabled.
Send Target API Root Header in Initial Messages Indicates if PCF must include
3gpp-sbi-target-apirootin initial request messages.If the user selects Model D for Policy NF Communication Model, the value is set to false. For other Policy NF Communication Model values, the default value is true.
On Demand Discovery Caching Provide On Demand Discovery Caching details: Force Discovery Indicates whether to cache the NF profiles in NRF client or to skip caching and receive the response directly from NRF.
Value of this parameter can be 0 or 1.
- When the value of OC-Force-Rediscovery parameter is set to 0, global cache configuration is taken into account.
- When the value of OC-Force-Rediscovery parameter is set to 1, global cache configuration is ignored and NF profiles get retrieved directly from NRF while responding to the query from the backend services.
Default value: 0
Retention Period (in ms) Indicates the time a record is allowed to stay in database after expiry. This parameter accepts an integer value to indicate the retention period in milliseconds. When retention period is not configured or saved as null, backend will not send this header to NRF connector.
Default value: 0
NF Bindings Settings Provide NF Bindings Settings details: Binding Level Indicates the binding level that must to be included in the 3gpp-sbi-binding header when PCF adds this header in a message to another NF.
Select any of the following values from the drop down menu:
- NF Set
- NF Instance
Default Value: NF Set
Send Binding Header Indicates if PCF includes the 3gpp-sbi-binding header in SBI messages for the subscription creation, modification, or notification requests and responses, as applicable. By default the switch remains enabled.
Send PCF Service Name in Binding Header Indicates whether to include the service name in the binding header or not.
Possible values:- true: Includes
svcnamein the binding header sent towards NFs such as UDR, AMF, or BSF (customized) except for CHF, which contains the 3GPP defined PCF service name. - false: Does not include
svcnamein the binding header.
Default value : false
Send Routing Binding Header Indicates if PCF includes the 3gpp-sbi-routing-binding header in SBI messages for the subscription creation, modification, or notification requests, as applicable. By default the switch remains disabled.
Send Callback Header Indicates if PCF includes the 3gpp-sbi-callback header in SBI messages for the subscription creation, modification, or notification requests, as applicable. By default the switch remains disabled.
NF Server Settings Provide NF Server Settings details: Send Server Header Indicates if services Policy microservices include server header while sending an error response. Server Header Error Codes Specifies the error codes for which service header is generated. The error codes can be from 100 to 999. Note: If no error is specified, then Policy sends server header for all error responses.
Retry & Alternate Routing Settings Provide Retry & Alternate Routing Settings details: Retry Profile for Initial Messages Specifies the retry or alternate routing options when an SBI message is not delivered successfully in any of the following scenarios: - POST operation to create a subscription
- GET or PATCH request not belonging to a subscription
Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages Specifies the retry or alternate routing options when an SBI message that updates, deletes or notifies a subscription is not delivered successfully. NF Correlation Settings Provide NF Correlation Settings details: Send Correlation-info header This specifies if the PCF should send Subscriber identifier as sbi-header-info or not. By default the switch remains disabled.
Allowed Correlation-info Header Generation Type(s) Specifies that if correlation header is not received from Consumer NFs, PCF should generate the header. The Correlation-Type supported
- SUPI
- GPSI
- (Select either both or none)
Note:
If the Retry and Alternate Routing settings are configured on the NF Communication Profile page, these settings take precedence over the alternate routing settings configured on the service configurations page for each service. - Click Save.
The NF communication profile gets listed on the NF Communication Profiles page. The communication profile also get listed under the respective service configuration on the following pages:
- PCF Session Management
- PCF Access and Mobility
- PCF Policy Authorization
- PCF UE Policy Service
- Binding Service
- PCF User Connector
Note:
The NF Communication Profile must be deleted in the service configurations before deleting from this page. As cyclic references are not handled currently.Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the profile.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the profile.
Importing NF Communication Profiles
To import NF Communication Profile:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.3.1.6 Attribute Forwarding Profiles
The Attribute Forwarding Profiles page allows you to create new and manage existing Attriute Forwarding profiles. The page displays the list of defined profiles with the options to import, export, or add profiles.
For more details on Attribute Forwarding Profiles, see Attribute Forwarding Profiles section in Usage Monitoring on Gx Interface.
To configure Attribute Forwarding Profiles profile, perform the following steps:
- From the navigation menu under Policy, navigate to Service Configurations, click Common Data, and then select Attribute Forwarding Profiles.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Attribute Forwarding Profiles page.
- On the Create Attribute Forwarding Profiles page, enter the
following information:
Table 7-13 Create Attribute Forwarding Profiles
Field Name Description Name Enter the Attribute Forwarding Profile name. Forwarded Attributes Enter the list of attributes to be forwarded from one service to another. - To add new Forwarded Attributes, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Forwarded Attributes page.
- On Add Forwarded Attributes page, enter the following
details:
Table 7-14 Add Forwarded Attributes
Field Name Description Attribute Name Enter the name of the attribute. Attribute Source Specify the source of the attribute to be forwarded.
Attribute Source provides the following options:
- Request Message: The incoming request message such as Gx CCR message or SM Policy Association Create message.
- User Data: Data received from different data sources such as UDR and CHF.
- Session Data: Data saved in the session (association) previously, such as saved APN/DNN value.
Attribute Selection Attribute Selection can be:
- Predefined
- Custom
Request Message Type Request Message Type can be:
- Diameter Message
- HTTP Message
Note: Currently, Policy supports only Diameter Messages for Request Message Type.
Diameter This field appears when the Request Message Type is Diameter Message. Specifies the diameter message type such as 3GPP Gx and Gx CC Request.
Attribute Location CNC Console displays this field when the Attribute Selection is of Custom type.
It indicates the path/location at which this attribute can be found by the source (forwarder) micro-service.
- Click Save on Add Forwarded Attributes page to add the new Forwarded Attibute.
- Click Save on Create Attribute Forwarding Profiles page to add the new Attibute Forwarding Profile.
7.3.1.7 Rx Reauth Profiles
The Rx Reauth Profiles page allows you to create new and manage existing Rx Reauth Profiles. The page displays the list of defined profiles with the options to add profiles.
To configure Rx Reauth Profiles, perform the following steps:
- From the navigation menu under Policy, navigate to Service Configurations, click Common Data, and then select Rx Reauth Profiles.
- Click
 .
This opens the Create Rx Reauth Profiles page.
.
This opens the Create Rx Reauth Profiles page.Note:
Predefined Setting exists for ALL Media Type. Video user can edit these predefined settings based on the requirements and add new settings for additional Media Types. - On the Create Rx Reauth Profiles page, enter the
following information:
Table 7-15 Create Rx Reauth Profiles
Field Name Description Name Enter the Rx Reauth Profile name. Settings Enter the list of settings. - To add new settings, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Settings page.
- On the Add Settings page, enter the following
details:
Table 7-16 Add Settings
Field Name Description Media Type Enter the name of the media type. Allowed Values: ALL, AUDIO, DATA, APPLICATION, VIDEO, CONTROL, TEXT, MESSAGE, NOMEDIATYPE, OTHER
Default Value: All
Precedence When the Notify-Update triggered by Rx request towards SMF fails and if that respective Rx request had multiple media types resulting different Reauth Actions, then based on this precedence value Reauth Action will be finalised. Lowest Precedence will take the highest priority.
Allowed Values: 1-99
Default Value: Null
Accept All Errors If this field is true, Reauth Action is considered for any Error or Exception on Update Notify failure response from SMF triggered by Rx request.
Allowed Values: True, False
Default Value: False
Errors When the Notify-Update triggered by Rx request towards SMF fails with any error code or cause and the Accept All Errors field is set as False, check the Table 7-17 example table and match the ErrorCode and ErrorCause of the failure. To add ErrorCode and ErrorCause , click

Note: If the ErrorCode is configured and ErrorCause is left empty, PCF will compare only the ErrorCode and allow any ErrorCause for that specific error to match.
Default Value: Empty List
Exceptions When the Notify-Update triggered by Rx Request towards SMF fails with any exception, then match the exception of the failure. To add Exceptions , click

Default Value: Empty List
Reauth Action Given that all following conditions for current setting are met:
- MediaType specified matches
- Error matched successfully or Exception matches successfully
Then PCF will take one of the following Reauth Actions:
-
SEND_ASR: this means PCF will send continue to process as before the feature was implemented (send ASR to PCSCF/AF or RAR based on the pcc_rules removed).
- SUPPRESS_ASR: this means PCF will NOT send an ASR to PCSCF/AF
- SEND_RAR: this means PCF will send an RAR with
Failed Resource Allocation (FRA) to
PCSCF/AF
- The RAR will be sent with FRA irrespective if the AAR-I/U came with FRA AVP.
- In this case PCF will NOT send an ASR to PCSCF/AF.
Allowed Values: SEND_ASR, SUPPRESS_ASR, SEND_RAR
Default Value: SEND_ASR
The following table shows examples of the combinations configured in the Reauth Profile section in the CNC Console and Error/Exception received in UpdateNotify Response and the expected outcome from Reauth Profile configured logic:
Table 7-17 ErrorCode and ErrorCause Combination
Configuration mentioned in the CNC Console ErrorCode in Update Notify Response ErrorCause in Update Notify Response Expected outcome from Reauth Profile configured logic Nothing configured 5xx/4xx NA No match {"error code": 503, "error cause": ""}503 ... Match 503 SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE Match 503 CUSTOM_503 Match 404 ... No match { "error code": 503, "error cause": "SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE", "error code": 503, "error cause": "NF_CONGESTED", "error code": 503, "error cause": "CUSTOM_503", "error code": 404, "error cause": "NOT_FOUND", }503 ... Match 503 SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE Match 404 ... Match { "error code": 503, "error cause": "SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE", "error code": 404, "error cause": "NOT_FOUND", "error code": 503, "error cause": "", }503 SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE Match 503 CUSTOM_503 Match 404 NOT_FOUND Match - Click Save on Add Settings page to add the new settings.
- Click Save on Create Rx Reauth Profiles page to add the new Rx Reauth Profile.
7.3.2 PCF Session Management
This procedure provides information about configuring the PCF Session Management Service.
The PCF Session Management page displays the SM Service configurations. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations, and select PCF Session
Management.
This opens the PCF Session Management page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit PCF Session Management page displaying the default configuration for the fields available in respective groups.
- Expand the System group.
This group allows you to edit system configurations.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under the group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-18 Edit System Configurations
Field Name Description Component Tracing
Determines, if component tracing is enabled. Component tracing is used to evaluate system process latency in detail level.
By default, this switch remains disabled.
FQDN
The PCF FQDN used by the PCF to register Binding data to BSF. AF may use this FQDN to communicate with PCF on N5 reference point. FQDN needs to be in a standard FQDN format (RFC 1035).
Default Value: oc-diam-gateway
Note : If we have multiple PCF, Diameter identity and FQDN must be unique.Diameter Realm
The PCF Diameter realm used by the PCF to register Binding data to BSF. Diameter based AF may use this Diameter realm to communicate with PCF on Rx reference point.
Default Value: oracle.com
Diameter Identity
The PCF Diameter identity used by the PCF to register Binding data to BSF. Diameter based AF may use this Diameter identity to communicate with PCF on Rx reference point.
Default Value: oc-diam-gateway
Note : In case of multiple PCF, Diameter identity and FQDN must be unique.Snssai
Used to register Binding data to BSF by PCF.
AF or BSF may use this SNSSAI to discover proper PCF. Format is : sst,sd.
Default Value: 0,000000
Enable Metrics
This determines if system metrics is enabled. This takes priority on global metrics configuration. By default, this switch remains enabled. Default Value: true
Override Supported Features
Indicates a list of supported features that can be configured to override system embedded values. For example, SessionRuleErrorHandling, NetLoc, PolicyDecisionErrorHandling and so on. Note: If any supported feature is enabled in one site then the same needs to be enabled on all other sites at the same time.
By default, it is blank.
Enable Custom Json This determines if custom JSON is enabled. By default, this switch remains disabled. Default Value: false
SMF Notification Retry Profile Defines the retry profile configuration for session management. For more information on configuring retry profile, see Retry Profiles. SMF Communication Profile Specifies the NF communication profile used by SMF. For more information about configuring NF communication profiles, see NF Communication Profiles. Data Compression Scheme Specifies the data compression scheme used by SM. Following are the allowed values for this field: - Disabled
- MySQL_Compressed
- Zlib_Compressed
By default, this value remains disabled.
- Expand the User group.
This group allows you to edit the subscriber configurations.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under User group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-19 Edit User Configurations
Field Name Description Validate User If the User profile, for any of the User Data types given under the User Data Types group, are fetched successfully, the user is considered to be a known user. However, if the user profile lookup has failed on the discovered data source, the user profile is marked as Unknown. If this switch is enabled and user is marked as Unknown, the session creation requests are rejected.
If this switch is disabled and user is marked as Unknown, the session creation requests are handled and sessions are created successfully.
Query User Determines if user query from UDR is enabled. When this option is enabled, PCF queries the UDR about the subscriber contained in the SM Association create request by sending a GET request for “sm-data” resource on the nudr-dr service.
Note: The PDS service caches the subscriber profile when
Subscribe To Notifyoption is enabled, in that case, the PCF may not always reach the UDR when the subscriber profile is found in the local cache.By default, this switch remains enabled.
Query User on Update Determines if user query from UDR on update is enabled. When this option is enabled, PDS queries the UDR about the subscriber present in the SM Association update request by sending a GET request for
SmPolicyDataresource on thenudr-dr service.Note: If
Subscribe To Notifyis enabled for SM, then SM will not query the UDR during a Update requests.The PDS caches the subscriber profile when the
Subscribe To Notifyflag is enabled. In that case, Policy may not always reach the UDR when the subscriber profile is found in the local cache.When the
Subscribe To Notifyflag is enabled and previous subscription attempts failed, then along with the data query, PDS also sends a SUBSCRIBE request to UDR.By default, this option is disabled.
Query User on Terminate Determines if user query from UDR on delete is enabled. When this option is enabled, PCF queries the UDR about the subscriber present in the SM Association delete request by sending a GET request for “SmPolicyData” resource on the nudr-dr service.
Note: If
Subscribe To Notifyis enabled for SM, then SM will not query the UDR during a Terminate requests.The PDS caches the subscriber profile when the “Subscribe To Notify” option is enabled, in that case, the PCF may not always reach the UDR when the subscriber profile is found in the local cache.
By default, this option is disabled.
Query User on Reauth Determines if user query from UDR on reauth is enabled. When this option is enabled, PCF queries the UDR about the subscriber, when it receives a Reauthorization request, such as Rx or Policy Authorization request by sending a GET request for “SmPolicyData” resource on the nudr-dr service.
Note: The PDS caches the subscriber profile when the “Subscribe To Notify” option is enabled, in that case, the PCF may not always reach the UDR when the subscriber profile is found in the local cache.
By default, this option is disabled.Disable Subscriber Variables Determines if subscriber variables are stored or not in the PCF database. By default, the value is set to false. User Data Types SmPolicyData If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches SMPolicyData from nUDR. For information on configuring SMPolicyData attributes, see Table 7-20.
Operator Specific Data If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches OperatorSpecificData (imported using Custom Schema) from nUDR. For information on configuring SMPolicyData attributes, see Table 7-21.
Ldap Data If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches user profile from LDAP through PDS. CHF Data If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches policy counters from CHF. For information on configuring SMPolicyData attributes, see Table 7-22. OCS Data If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches policy counters from OCS. When this switch is enabled, PCF performs on-demand lookup of Policy Counters for a subscriber using the Fetch Policy Counters from OCS policy action.
By default, this option is disabled.
Note: It is possible to enable both CHF Data and OCS Data simultaneously. Based on PDS-PRE policy, PDS may make a choice between the two datasources.
For information on configuring SMPolicyData attributes, see Table 7-23.
The following table describes the SmPolicyData switches available in the Attributes column:
Table 7-20 SmPolicyData Attributes
Attribute Name Description Subscribe to Notify When this switch is enabled, Policy subscribes with the UDR to get notified on changes in subscriber profile.
By default, this option is enabled.
Ignore Subs Notification Check Ignore subscriber's notification check. By default, this option is false.
Note: Currently, this field is not used by the Policy application.
Include Snssai in User Query Determines if Snssai is included for SmPolicyData for PCF query and subscribe to UDR for Notification. Include Dnn in User Query Determines if Dnn is included for SmPolicyData for PCF query and subscribe to UDR for Notification. The following table describes the Operator Specific Data switches available in the Attributes column:Table 7-21 Operator Specific Data Attributes
Attribute Name Description Subscriber to Notify When this switch is enabled, Policy subscribes with the UDR to get notified on changes in subscriber profile. By default, this option is false.
The following table describes the CHF Data switches available in the Attributes column:
Table 7-22 CHF Data Attributes
Attribute Name Description Enable Async CHF Query When this button is enabled, PCF interacts with CHF in Asynchronous mode.
By default, this option is disabled.
The following table describes the OCS Data switches available in the Attributes column:
Table 7-23 OCS Data
Attribute Name Description Enable OCS Async Query When this button is enabled, PCF performs on demand lookup for Policy Counters to be fetched from OCS. By default, this option is disabled.
Enable force lookup on Update When this button is enabled, PCF performs force lookup for OCS Data. By default, this option is disabled.
- Expand the Policy group.
This group allows you to edit Policy configurations.
- Under the Policy group, enable or disable the
Evaluate switch.
This switch determines, if policy evaluation is enabled.
The default value is true.
- Expand the Policy Control Request Trigger group.
This group allows you to edit Policy Control Request Trigger configurations.
- Under the Policy Control Request Trigger group, select
values in the Default Policy Control Request Triggers
drop-down list.
This is the default Policy Control Request Trigger(s) to install on PDU session at SM Policy Association Establishment. You can select multiple values in a comma separated format.
- Expand the Binding Configuration group.
This group allows you to edit the Binding configurations.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under the group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-24 Edit Binding Configurations
Field Name Description Binding Operation
Determines if binding operation (register and deregister) to the BSF is enabled. This service level global configuration applies to all session creation requests (belonging to all DNN and/or S-NSSAI.
Default Value: TRUE
After performing necessary configurations on this screen, user may use the policy action - Set Binding Registration to to update configurations for specific policies. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy Design Guide.
Binding Use Local Configured Bsf Always
Whether to use local configured BSF without Always discovering.
Default Value: FALSE
Binding Use Local Configured Bsf When Not Discovered
Whether to use local configured (if having) BSF when not discovered or discover failed. Local configuration can be done using custom yaml.
Default Value: FALSE
Use HTTP2
Determines if using http/2 to communicate with BSF. Otherwise use http/1.1. Default Value : TRUE
Abort or Terminate Session on Binding Error Determines if PCF (SM service) should abort terminate session when binding error is received. BSF Retry Profile for Initial Messages Retry Profile to be used when PCF fails to send a create message to a producer node. For more information, see Retry Profiles. Note: This is a mandatory configuration to get the error codes from the Attempt Alternate Route for Following Error Codes option on the Retry Profiles page.
BSF Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages Retry Profile to be used when PCF fails to send an in-session message to a producer node. Note:- If both “Retry Profile for Initial Messages” and “Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages” are not configured (default case) no retry is attempted.
- If both “Retry Profile for Initial Messages” and “Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages” are configured, retries is attempted accordingly.
- If “Retry Profile for Initial Messages” is configured but “Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages” is not configured then the profile for initial messages is used for subsequent messages. (to be backward compatible with release 1.8.x)
- If “Retry Profile for Initial Messages” is not configured but “Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages” is configured then retry is not attempted for initial messages but is attempted for subsequent messages.
Default Binding Operation Mode Allows users to configure binding operation mode as synchronous or asynchronous. Default value: Synchronous
Note:- The mode chosen during the CREATE request remains same during UPDATE and TERMINATE operations for the same SM session.
- To ensure backward compatibility, if this attribute is not available in the database, the value is set to "Synchronous"
After performing necessary configurations on this screen, user may use the policy action - Set Binding Registration to under PCF-SM Category to update configurations for specific policies. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy Design Guide.
BSF Communication Profile Specifies the NF communication profile used by BSF. For more information about configuring NF communication profiles, see NF Communication Profiles. BSF Binding Recreate Attempt The switch to enable the BSF recreate attempts functionality. Possible values:- Enabled: The SM Service creates and
updates the PendingOperations if the response from
BSF applies for a reattempt and it updates the
PendingOperation table in Audit Service.
Audit Service sends notifications for retry timestamps that have been reached and SM Service triggers the Recreate attempt.
- Disabled: SM Service deregisters the PendingOperation table in Audit Service and it does not create nor update entries in the PendingOperation table.
- Disable and Cleanup: SM Service neither deregister the PendingOperation table in Audit Service nor it updates the table. Audit Service sends notifications to SM Service but the notifications does not get processed and SM service automatically deletes records from the PendingOperation table.
BSF Binding Recreate Attempt Profile The Reattempt profile to be used for binding recreate attempts. For more information, see Reattempts Profile. - Expand the QoS group.
This group allows you to edit the QoS configurations.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under the group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-25 Edit QoS Configurations
Field Name Description Qos Data Id Prefix
This is the prefix of qos data id used by PCF to generate qos data id. For example, prefix is "qosdata_", the generated qos data id is qosdata_0.
Default Value : qosdata_
update Default Pcf Rule With Auth Def Qos
This determines whether to update Qos of default PccRule with the authDefQos of session rule.
Default Value : TRUE
Install Default Qos If Not Requested
This determines whether to install default Qos to the PDU session if UE not requested. Default Value : TRUE
Default Qos 5qi
This is the 5Qi of default Qos which is applied if no default Qos is requested by UE. Default Value: 9
Default Qos Arp Preempt Cap
This is the ARP Preemption Capability of default Qos which is applied if no default Qos is requested by UE.
Default Value : MAY_PREEMPT
Default Qos Arp Preempt Vuln
This is the ARP PreemptionVulnerability of default Qos which is applied if no default Qos is requested by UE.
Default Value : NOT_PREEMPTABLE
Default Qos Arp Priority Level
This is the ARP Priority Level of default Qos which is applied if no default Qos is requested by UE. Default Value: 1
- Expand the Rule group.
This group allows you to edit the PCC Rule configurations.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under the group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-26 Edit Rule Configurations
Field Name Description Install Default Pcc Rule
This determines whether and how to install default pcc rule for a PDU session. Possible values are: - ALWAYS
- IF_NO_PROVISIONED_RULE only if no other provisioned rule is configured
- IF_NO_RULE only if no other rule (predefined or provisioned) is configured/installed
- NEVER
Default PCC Rule Profile (Optional) If a default PCC Rule Profile is configured by the user, it is applied to the chosen PCC Rule. Rule Id Prefix
This is the prefix of rule id of the pcc rule or session rule auto generated by PCF. for example, prefix is "0_", the generated rule id is 0_0, 0_1, etc. Default Pcc Rule 5qi
This is the 5Qi of default pcc rule. Default Value: 9
Default Pcc Rule Precedence
This is the precedence of default pcc rule.
Default Value : 3000
Default Pcc Rule Arp Preempt Cap
This is the ARP Preemption Capability of qos of default PCC rule.
Default Value : NOT_PREEMPT
Default Pcc Rule Arp Preempt Vuln
This is the ARP PreemptionVulnerability of qos of default pcc rule.
Default Value : PREEMPTABLE
Default PCC Rule Requested Rule Data Used to set the default Requested Rule Data for the PCC Rule.
Default Value: SUCC_RES_ALLO
App Rule Precedence Min
This value defines the minimum value for precedence of a PCC rule as authorized by the establishment of an application flow by the AF. If multiple rules are applied to the same packet flow or UE resource (i.e., overlapping rules) a rule with lower precedence value takes the priority over a rule with higher precedence value. The value of -1 is used to not set the precedence of a rule (NOT RECOMMENDED).
Default Value: 400
App Rule Precedence Max
This value defines the maximum value for precedence of a PCC rule as authorized by the establishment of an application flow by the AF. If multiple rules are applied to the same packet flow or UE resource (i.e., overlapping rules) a rule with lower precedence value takes the priority over a rule with higher precedence value. The value of -1 is used to not set the precedence of a rule (NOT RECOMMENDED).
Default Value: 899
Default Pcc Rule Arp Priority Level
This is the ARP Priority Level of qos of default pcc rule The range is 1 to 15. Values are ordered in decreasing order of priority, for example, with 1 as the highest priority and 15 as the lowest priority. Default Value : 15
Switch Flow In To Out Enabled
This determines whether to switch "in" to "out" in flow description. The src and desc is switched as well. For example, if enabled, "permit in ip from 2800:a00:cc01:c056:1c00:de10:c481:f193/128 to 2800:a00:800:7::1:3b/128 36004" is changed to "permit out ip from 2800:a00:800:7::1:3b/128 36004 to 2800:a00:cc01:c056:1c00:de10:c481:f193/128" Default Value: FALSE
Set PacketFilterUsage to true for Preliminary Service Info This determines whether the UE shall be provisioned with the packet filter for preliminary service.Default Value: FALSE Install/Remove Rule Conflicts Strategy When the remove action is Remove ALL(ALL, Predefined, Dynamic, Conditioned, non-conditioned):- INSTALL/MODIFY: SM Service removes all Session/PCC Rules previously installed and ignores all the remove actions for rules in conflict.
- REMOVE: SM Service removes all Session/PCC Rules previously installed and ignores all the install actions for rules in conflict.
- IGNORE: SM Service removes all Session/Pcc Rules previously installed and ignores all actions for rules in conflict, and does not run anything(install/remove).
- Default: SM Service processes the remove actions and then the INSTALL or MODIFY actions.
- Expand the Charging group.
This group allows you to edit the charging configurations.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under the group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-27 Edit Charging Configurations
Field Name Description Charging Data Id Prefix
This is the prefix of chg data id used by PCF to generate chg data id. For example, prefix is "chgdata_", the generated chg data id is chgdata_0, chgdata_1, etc. Default Value: chgdata_
Primary CHF Address
Address of the primary CHF Primary CHF Instance Id Instance ID of the primary CHF Primary CHF Set Id Set ID of the primary CHF Secondary CHF Address
Address of the secondary CHF Secondary CHF Instance Id Instance ID of the secondary CHF Secondary CHF Set Id Set ID of the secondary CHF Online
Indicates the online charging is applicable to the PDU session. Offline
Indicates the offline charging is applicable to the PDU session. Use Subscriber Default Charging Method
Indicates whether to use the online value defined in the PDU session. Default Value: true
- Expand the Traffic Control group.
This group allows you to edit Traffic Control configurations.
- Under the Traffic Control group, enter value of the
Traffic Control Id Prefix field.
This is the prefix of traffic control data ID used by PCF to generate tc data id. For example, if prefix is "tcdata_", the generated tc data ID is tcdata_0, tcdata_1, and so on.
Default Value: tcdata_
- Expand the IMS Emergency Session group.
This group allows you to edit IMS Emergency Session configurations.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under the group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-28 Edit IMS Emergency Session Configurations
Field Name Description Emergency DNNs
DNN included in the request from SMF to PCF to establish an emergency session. Priority Level
Defines the relative importance of a resource request.
Default Value: 1
Preemption Capability
Defines whether a service data flow may get resources that were already assigned to another service data flow with a lower priority level. Default Value: MAY_PREEMPT
Preemption Vulnerability
Defines whether a service data flow may lose the resources assigned to it in order to admit a service data flow with higher priority level. Default Value: NOT_PREEMPTABLE
- Expand the Audit group.
This group allows you to edit Audit configurations for SM Policy Association and Pending Operation DB tables.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under the SM Policy
Association group.
The following table describes the SM Policy Association fields:
Table 7-29 Edit SM Policy Association Configurations
Field Name Description Enabled Determines whether to send registration request to Audit service or not. Default Value: True
Notification Rate (per second) Defines the number of stale records which Audit service notifies to Session Management (SM) service in one second. Default and Recommended Value: 50
Note: To configure higher number than the recommended value, contact My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com)
Policy Association Age (in minutes) Defines the age of a SM policy association after which a record is considered to be stale on PCF and the SMF is queried for presence of such associations. Default Value: 1440
Policy Association Maximum Age (in minutes) Defines the maximum age of a SM policy association after which a record is purged from PCF SM database without sending further queries to SM. Default Value: 2880
Minimum Audit Attempts Specifies the minimum number of consecutive failed audit attempts until maxTTL / forceTTL is reached.
If maxTTL is reached and audit_attempts + 1 >= Minimum Audit Attempts for maxTTL, Audit service sends notification to SM service with maxTTL flag set to true. SM Service sends DELETE request to PDS and Binding Service.
Range: 0-99
Default Value: 0
Note: If maxTTL is not reached and if audit attempts are reached, the number of audit attempts are incremented until maxTTL is reached.
Minimum Audit Passes Interval (in minutes) Defines the time when next audit for the SM service table is done after delta time if auditing this table has been finished before this specified time. Default Value: 330
- Enter the values for the input fields, available
under the Pending Operation group.
The following table describes the Pending Operation fields:
Table 7-30 Edit Pending Operation Configurations
Field Name Description Notification Rate (per second) Defines the number of pending operation records which Audit service notifies to Session Management (SM) service in one second. Note: The notification rate for all the operations of Audit service remains the same. Policy does not allow to configure different values for different operations. Therefore, by default the notification rate configured for the SmPolicyAssociation section applies for Pending Operations.
Default Value: 50
Pending Operation Age (in minutes) Defines the age of a pending operation after which a record is considered to be stale. This is a non modifiable field. Default Value: 0
Pending Operation Maximum Age Defines the maximum age of a pending operation after which a record is purged from PCF SM database without sending further queries to SM. Default Value: 2880
Minimum Audit Passes Interval (in minutes) Defines the frequency with which the Audit service performs audit of the pending operation table for the Retry Timestamps that have been reached. Default Value: 10
Alternate Site The site takeover profile. For more information, see Site Takeover. Enable Alternate Site Specifies if the site takeover must be enabled in case of failure. - Enter the values for the input fields, available under the Pending
Transaction group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-31 Edit Pending Transaction Configurations
Field Name Description UpdateNotify Retry Backoff (in milliseconds) Indicates the time between two consecutive retry UpdateNotify messages when UpdateNotify message is held back from being sent to SMF. The default value for this field is 1000.
UpdateNotify Retry Count Indicates the count for UpdateNotify message to be retried when it is held back from sending to SMF. The default value for this field is 2.
Error Update Notify Handling Rx On Update Notify to SMF triggered by Rx, this configuration decides if it should RETRY (with UpdateNotifyRetryBackoff and UpdateNotifyRetryCount settings) or DISCARD when receiving 400 Pending Transaction response from SMF. The default value for this field is DISCARD. The allowed values are:- DISCARD (0)
- RETRY (1)
Error Update Notify Handling Subscription Notification On Update Notify to SMF triggered by Subscriber Notification, this configuration decides if it should RETRY (with UpdateNotifyRetryBackoff and UpdateNotifyRetryCount settings) or DISCARD when receiving 400 Pending Transaction response from SMF. The default value for this field is RETRY. The allowed values are:- DISCARD (0)
- RETRY (1)
- Under the NWDAF group, enable or disable the Enable NWDAF Data switch.
- Perform the following steps to configure
Advanced Settings that allows PCF to handle
concurrent requests:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following keys and respective values:
The following table describes the keys and values:Table 7-32 Add Advanced Settings Configurations
Key Value CONCURRENCY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION_FOR_CREATE The duration for which lock is kept once the acquisition is successful. After this duration, the lock gets released automatically.Default value: 6 seconds CONCURRENCY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION_FOR_CREATE Duration by which the SM service waits for the response to get a lock.
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT_FOR_CREATE Number of attempts the service make to request the lock.
CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_ENABLED_FOR_N7_CREATE Enables concurrency for create request.
Default value: FalseCONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF Defines the amount of time after which the service retries to gain the lock, incase of failure.
Default value: 750ms
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION_FOR_DELETE The duration for which lock is kept once the acquisition is successful. After this duration, the lock gets released automatically.Default value: 6 seconds CONCURRENCY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION_FOR_N7_DELETE Duration by which the SM service waits for the response to get a lock.
Default value: 3 secondsCONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT_FOR_DELETE Number of attempts the service make to request the lock.
Default value: 3 secondsCONCURRENCY.BULWARK_ENABLED_FOR_N7_DELETE Specifies if the concurrency has to be enabled for the SM Delete requests.
Default value: FalseCONCURRENCY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION_FOR_UPDATE The duration for which lock is kept once the acquisition is successful. After this duration, the lock gets released automatically.Default value: 6 seconds CONCURRENCY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION_FOR_UPDATE Duration by which the SM service waits for the response to get a lock.
Default value: 3 secondsCONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT_FOR_UPDATE Number of attempts the service can make to request the lock.
Default value: 3CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_ENABLED_FOR_N7_UPDATE Specifies if the concurrency has to be enabled for the SM Update requests.
Default value: FalseCONCURRENCY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION_FOR_CLEANUP The duration for which lock is kept once the acquisition is successful. After this duration, the lock gets released automatically.Default value: 6 seconds CONCURRENCY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION_FOR_CLEANUP Duration by which the SM service waits for the response to get a lock.
Default value: 3 secondsCONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT_FOR_CLEANUP Number of attempts the service can make to request the lock.
Default value: 3CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_ENABLED_FOR_N7_CLEANUP Specifies if the concurrency has to be enabled for the SM Clean requests.
Default value: FalseRESOURCEID.SUFFIX_LIST Select a subscriber value type from the drop down for which the lock must be requested: - SUPI
- GPSI
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF Defines the amount of time after which the service retries to gain the lock, incase of failure.
Default value: 750ms
BINDING-BSF_REATTEMPT_THRESHOLD Defines the frequency with which SM service calls the Audit service API for checking the Pending Operation threshold.
USER.RESET_CONTEXT_SM_POLICY_DATA_ON_SM_CREATE If this configuration is enabled, the sm-service on receiving the sm-create for a SUPI, checks if there is no other
smPolicyAssociationfor the same SUPI and setsresetContextflag for the SM policy on the request towards PDS.Default Value: False
USER.RESET_CONTEXT_OSD_ON_SM_CREATE If this configuration is enabled, the sm-service on receiving the sm-create for a SUPI, checks if there is no other
smPolicyAssociationfor the same SUPI and setsresetContextflag for the OSD on the request towards PDS.Default Value: False
USER.RESET_CONTEXT_CHF_DATA_ON_SM_CREATE If this configuration is enabled, the sm-service on receiving the sm-create for a SUPI, checks if there is no other
smPolicyAssociationfor the same SUPI and setsresetContextflag for the CHF on the request towards PDS.Default Value: False
USER.RESET_CONTEXT_LDAP_DATA_ON_SM_CREATE If this configuration is enabled, the sm-service on receiving the sm-create for a SUPI, checks if there is no other
smPolicyAssociationfor the same SUPI and setsresetContextflag for the LDAP on the request towards PDS.Default Value: False
USER.RESET_CONTEXT_SSV_ON_SM_CREATE If this configuration is enabled, the sm-service on receiving the sm-create for a SUPI, checks if there is no other
smPolicyAssociationfor the same SUPI and setsresetContext flagfor the SSV on the request towards PDS.Default Value: False
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION_FOR_UPDATE_NOTIFY Duration for which lock is held once it is acquired. After this duration, the lock will be released automatically.
Default Value: 6 Seconds
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION_FOR_UPDATE_NOTIFY Duration for which the Policy service will wait for the response to get a lock. The same duration is used by Bulwark service to poll for the lock if a lock is not available.
Default Value: 3 Seconds
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT_FOR_UPDATE_NOTIFY The number of retries when a request to Bulwark service fails.
Default Value: 3
CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_ENABLED_FOR_N7_UPDATE_NOTIFY Determines whether to enable Bulwark service for SM notification flow.
Default Value: false
CONCURRENCY.UPDATE_USERDATA_IN_ASSOCIATION_ON_LOCKFAILURE Facilitates the user to update user data in the database in the case of lock failure.
Default Value: false
NWDAF.EVENT Allow to add one or more Events to be send in the request towards NWDAF. Default value: SLICE_LOAD_LEVEL
NWDAF.REQUEST_TIMEOUT Allow to control the timeout of the request from SM towards NWDAF. Default value: 3000 (ms)
SYSTEM.PA_MAX_APP_SESSIONS Specifies the limit on the number of AppSessions per SM session. Default value: 4
USER.excludeDnnSet.<dnnSetId> List of Data Network Names (DNNs) for which all the requests or sessions will be excluded for all the User Data Types.
The DNN list can include the comma separated values.
Regular expressions (regex) are allowed for the DNN names with the following conditions:- must not contain white spaces.
- must be case insensitive.
- can not be an empty string.
- '\' (backslash) must be specified as '/d'.
- the names must be separated only with commas (,).
USER.smPolicyData.excludeDnn.<Snssai> Specify the Snssai corresponding to the DNNs for which all the requests or sessions will be excluded for smPolicyData.
Snssai corresponding to the DNN must be the dnnSetId configured in the key from
USER.excludeDnnSet.<dnnSetId>.There is no regex applied to the snssai value.
USER.ldapData.excludeDnn.<Snssai> Specify the Snssai corresponding to the DNNs for which all the requests or sessions will be excluded for the given Ldap Data.
USER.operatorSpecificData.excludeDnn.<Snssai> Specify the Snssai corresponding to the DNNs for which all the requests or sessions will be excluded for the given Operator Specific Data.
USER.chfData.excludeDnn.<Snssai> Specify the Snssai corresponding to the DNNs for which all the requests or sessions will be excluded for the given CHF Data.
USER.ocsData.excludeDnn.<Snssai> Specify the Snssai corresponding to the DNNs for which all the requests or sessions will be excluded for the given OCS Data.
USER.CREATE_CONTEXT_ON_FAILURE_OCS_DATA When the value of this key is true, PCRF core sends this flag as part request parameters to PDS. PDS creates a dummy context for OCS in case of getting error while performing OCS lookup. This will support the PDS when it receives notificaiton from UDR to fetch OCS data. This is applicable for SM Create and SM Update. This is applicable for SmCreate and SmUpdate with Asynchronous flow either set as true or false.
Default Value: false
SYSTEM.SMF_MAX_WAIT_DURATION_FOR_DELETE Specify the wait time for SMF to trigger delete request on receiving successful response for terminateNotify request. The allowed value range from 0 to 30000 milliseconds. Note: If value is either less than 0ms or more than 30000ms, by default 30000ms is considered.
The default value for this parameter is 30000ms.
USE_TGPP_SBI_MSG_PRIORITY Specify the use of 3gpp-sbi-message-priorityheader for lock requests. Allowed values aretrueorfalse.Default value: true
REQUEST_PRIORITY_FOR_SM_DELETE Specify the setting request priority for delete requests. Allowed integer number ranging from 0-100. Default value: 16
REQUEST_PRIORITY_FOR_SM_UPDATE Specify the setting request priority for update requests. Allowed integer number ranging from 0-100. Default value: 18
REQUEST_PRIORITY_FOR_SM_UPDATE_NOTIFY Specify the setting request priority for update notify requests. Allowed integer number ranging from 0-100. Default value: 18
REQUEST_PRIORITY_FOR_SM_CLEANUP Specify the setting request priority for cleanup requests. Allowed integer number ranging from 0-100. Default value: 18
REQUEST_PRIORITY_FOR_SM_CREATE Specify the setting request priority for cleanup requests. Allowed integer number ranging from 0-100. Default value: 24
ENABLE_SM_POLICY_ASSOCIATION_TABLE_SLICING Indicates whether to enable/disable the database operations on sliced tables. That is, whenever ENABLE_SM_POLICY_ASSOCIATION_TABLE_SLICING flag is set to
Default value: falsetrue, the create/retrieve/update/delete operations are performed on the database slices instead of the main database.AUDIT_SMPOLICY_ASSOCIATION.MAX_TTL.TERMINATE_NOTIFY.ENABLED When SM service receives a MaxTTL notification from Audit service, and if the value of this advanced settings key is set to
true, SM service sends Terminate Notify to SMF.Default value: false
SYSTEM.COLLISION_DETECTION.TERMINATE_NOTIFY.ENABLED When a collision is detected and the existing session is older than the new one, and if the value of this advanced settings key is set to
true, SM service sends TerminateNotify to SMF.Default value: false
AUDIT.HTTP2_ENABLED Determines whether to use http/2 or http/1.1 to communicate with Audit service for threshold polling task.
Possible values:- true: http/2 is used to communicate with Audit service
- false: http/1.1 is used to communicate with Audit service
Default value: true
USER.CREATE_CONTEXT_ON_FAILURE_SM_POLICY_DATA If this flag is enabled the SM service sends this as a request parameter toward PDS.
At PDS, if it receives an error during SmPolicyData-UDR lookup, then PDS creates a dummy context for SmPolicyData. This creation of dummy context helps, when PDS receives next request for a UDR lookup and this time it is successful, then both the sessions will have the latest SmPolicyData.
This is applicable for SmCreate and SmUpdate.
Default value: false
USER.CREATE_CONTEXT_ON_FAILURE_CHF_DATA If this flag is enabled the SM service sends this as a request parameter toward PDS.
PDS creates a dummy context for CHF in case of getting error while performing CHF lookup. This creation of dummy context helps, when PDS receive next request for a CHF lookup and this time it is successful, then both the sessions will have the latest information.
This is applicable for SmCreate and SmUpdate with Asynchronous flow either set as true or false.
Default value: false
USER.CREATE_CONTEXT_ON_FAILURE_OPERATOR_SPECIFIC_DATA If this flag is enabled the SM service sends this as a request parameter toward PDS.
At PDS, if it receives an error during operatorSpecificData-UDR lookup, then PDS creates a dummy context for operatorSpecificData. This creation of dummy context helps, when PDS receives next request for a UDR lookup and this time it is successful, then both the sessions will have the latest operatorSpecificData.
This is applicable for SmCreate and SmUpdate.
Default value: false
RULE.ENABLE_PCC_RULE_REMOVE_ON_FAILURE If this flag is enabled and the updatenotify request fails for PCC rule remove with any HTTP error, then the association will be updated with rule removed.
Default value: false
ENABLE_LATE_PROCESSING Indicates whether the stale request cleanup functionality for SM service is enabled or disabled. To enable the stale request cleanup functionality for SM service, set the value of this key to
true.Default value: false
USER.allDataTypes.excludeDnns Specifies the comma separated list of DNNs. For any request that matches one of the DNNs in the list, the communication with PDS will be excluded. Regular expressions (regex) are applied as supported by regex from java Pattern class with the following special cases:- All whitespaces should be removed before processing any values in the arrays.
- Every dnn should contain regex characters '^' at the start and '$' at the end. The dnn can not be an empty string.
- dnn exclude settings are case insensitive
- For security reasons '\' (backslash) is not supported, to interpret regex conditions like '\d' it will need to be written as '/d',. Internally all '/' will be translated to '' for java to handle backslash regex conditions.
- { n, m } repetitions are not supported as ',' will be used to separate each dnn.
BINDING.excludeDnns Specifies the comma separated list of DNNs. For any request that matches one of the DNNs in the list, the communication with Binding Service will be excluded. Regular expressions (regex) are applied as supported by regex from java Pattern class with the following special cases:- All whitespaces should be removed before processing any values in the arrays.
- Every dnn should contain regex characters '^' at the start and '$' at the end. The dnn can not be an empty string.
- dnn exclude settings are case insensitive
- For security reasons '\' (backslash) is not supported, to interpret regex conditions like '\d' it will need to be written as '/d',. Internally all '/' will be translated to '' for java to handle backslash regex conditions.
- { n, m } repetitions are not supported as ',' will be used to separate each dnn.
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_RETRY_MODE Indicates whether the lock retry must be triggered under SM service.
Possible valures are:- CLIENT_ONLY: lock retry is triggered only in client services.
- SERVER_ONLY: lock retry is triggered only in bulwark.
- CLIENT_AND_SERVER: lock retry is triggered by both server and client.(server will retry to acquire the lock till the lockWaitTimeout is expired and client will retry after the configured request backOff timer is expired)
- Consumer services's advance settings should be updated with the non-zero lockWaitTimeOut.
BULWARK.excludeDnns Specifies the comma separated list of DNNs. For any request that matches one of the DNNs in the list, the communication with Bulwark Service will be excluded. Regular expressions (regex) are applied as supported by regex from java Pattern class with the following special cases:- All whitespaces should be removed before processing any values in the arrays.
- Every dnn should contain regex characters '^' at the start and '$' at the end. The dnn can not be an empty string.
- dnn exclude settings are case insensitive
- For security reasons '\' (backslash) is not supported, to interpret regex conditions like '\d' it will need to be written as '/d',. Internally all '/' will be translated to '' for java to handle backslash regex conditions.
- { n, m } repetitions are not supported as ',' will be used to separate each dnn.
SYSTEM.ENABLE_CLEANUP_DELAY_AFTER_FAILED_REQUEST During SM create, when request is rejected or an exception occurred, this flag lets the user decide if unsubscribe request to UDR and CHF should be send immediately or after a certain delay. Default value: false
SYSTEM.CLEANUP_DELAY_AFTER_FAILED_REQUEST When there is a delay on unsubscribe request after failure flag is enabled, this flag lets the user configure the delay before sending unsubscribe request to UDR and CHF. Value in miliseconds. Default value: 2000
Table 7-33 Add Advanced Settings Configurations
Key Value SM.UPDATE.EVENT.SUBS.PRIORITY Set request priority for creation or modification of an event subscription request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 18
SM.CREATE.PRIORITY Set request priority for SM create request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 24
SM.SUB.FAIL.NOTIFY.PRIORITY Set request priority for UDR subscription failure notification request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 26
SM.USER.SERVICE.NOTIFY.PRIORITY Set request priority for User Data change notification request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 18
SM.UPDATE_PRIORITY Set request priority for SM update request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 18
SM.REAUTH_PRIORITY Set request priority for SM reauthorization request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 20
SM.DELETE.PRIORITY Set request priority for SM delete request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 16
SM.POLICY.CLEANUP.PRIORITY Set request priority for clean up SM policies request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 20
SM.APP.SESSION.CREATE.PRIORITY Set request priority for Policy authorization create request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 24
SM.APP.SESSION.DELETE.PRIORITY Set request priority for Policy authorization delete request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 16
SM.APP.SESSION.CLEANUP.PRIORITY Set request priority for cleanup App sessions request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 20
SM.AUDIT.NOTIFY.PRIORITY Set request priority for Audit notification request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 30
SM.GET.APP.SESSION.PRIORITY Set request priority for Retrieve App Session request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 28
SM.GET.ASSOC.PRIORITY Set request priority for retrieve Policy association request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 28
SM.GET.SUBSCRIBER.SESSIONS.PRIORITY Set request priority configured retrieve any type of session for rest api endpoint. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 28
SM.GET.ASSOC.QUERY.PRIORITY Set request priority for advanced search of Policy Association request. Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 28
CONGESTION_RESPONSE_CODE Configure the response code of any rejected requests by SM service due to congestion state. By default, SM service sends 503 as response code. If configured then it shall be 5xx only. Allowed Values: 503
Default Value: 5xx
- Click the
- Click Save to save the PCF Session Management configurations.
7.3.2.1 UDR Subscriber Delete Resource Support
The PCF call flow has been updated to support terminating an active subscriber session by the deployed policy when the subscriber resources are deleted on the UDR.
The following figure describes a call flow for UDR subscriber resource deletion:
Figure 7-13 Call Flow for UDR Subscriber Resource Deletion
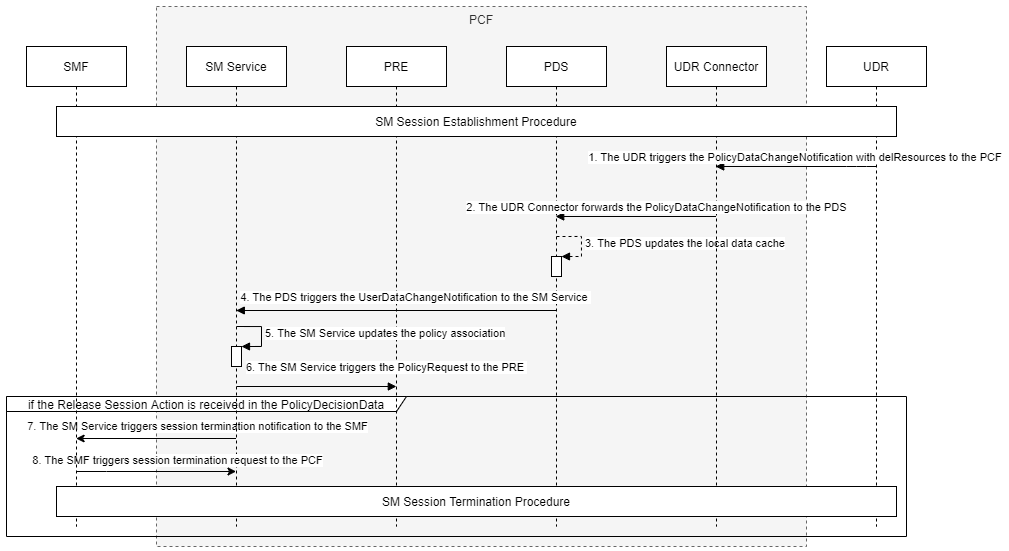
- The UDR triggers the PolicyDataChangeNotification with the attribute "delResources" to the PCF.
- The UDR connector forwards the received PolicyDataChangeNotification to the PDS.
- After receiving the UDR notification, PDS calls UDR-Notify
workflow, in this workflow, PDS compares the PolicyDataChangeNotification with
the existing data in database and perform database update or delete, if needed,
and notify the SM service (with the attribute "delResources"), if needed.
If delResources exists in PolicyDataChangeNotification and the delResources URL meet the condition "contains '/policy-data/ues/{ueId}/operator-specific-data' or 'policy-data/ues/{ueId}/sm-data/' ", the existing subscriber information in database is be deleted.
- After the data updates, the PDS triggers an UserDataChangeNotification with received PolicyDataChangeNotification to the SM service.
- The related resources (smPolicyData or operatorSpecificData) within
the SmPolicyAssociation are deleted when the delResources of the
PolicyDataChangeNotification is received.
The smPolicyData is deleted if the resource URL contains "sm-data".
The operatorSpecificData is deleted if the resource URL contains "operator-specific-data".
- The SM Service triggers the PolicyRequest with the
UserDataChangeNotification to the PRE to get the PolicyDecisionData, if the
"Release Session" action is received, Step 7 is triggered. New conditions and action have been
added to support this.
For more information on these conditions and action, see PCF-SM Category section in Oracle Communcations Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy Design Guide.
The following screen capture illustrates an example of how to use these conditions and action to release a policy association:
- The SM Service triggers session termination notification to the SMF if the "Release Session" action is received in the PolicyDecisionData.
- The SMF triggers a session termination request to the PCF.
7.3.3 PCF Access and Mobility
This procedure provides information about configuring the Access and Mobility Service.
The Access and Mobility page displays the AM Service configurations. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations and select PCF Access and
Mobility.
This opens the PCF Access and Mobility page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the PCF Access and Mobility page.
- Check the default configuration for the
fields available in respective groups and edit as necessary.
The following table describes the fields along with their valid input values under each group:
Table 7-34 Edit PCF Access and Mobility
Field Name Description System AMF Notification Retry Profile Defines the retry profile configuration for Access and Mobility service. For more information about configuring retry profile, see Retry Profiles. AMF Communication Profile Specifies the NF communication profile used by AMF. For more information about configuring NF communication profiles, see NF Communication Profiles. Enable Max Session Limit Specifies whether to enable the Limiting the Number of Sessions functionality. Max Session Limit Per User Specifies the maximum number of sessions to be limited per user if Enable Max Session Limit flag is enabled. Range: 1-2
Default value: 1
Override Supported Features This configuration enables the pending transactions along with the Advanced Settings. User Validate User When this button is enabled , and the subscriber is not found in the UDR, or PCF is not able to query an available/eligible UDR, PCF sends an HTTP '400 USER_UNKNOWN' error to AMF. However, when you disable Validate User button, PCF continues policy processing even after the subscriber is not found in the UDR, or PCF is unable to query an available/eligible UDR. Default value: false.
Enable Subscriber State Variables If this switch is enabled, AM Service controls the querying and saving of local and remote subscriber state variables (SSV) on PDS.
Default value: false.
User Data Types AMPolicyData If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches AMPolicyData from nUDR.
For information on configuring AMPolicyData attributes, see
AMPolicyData Attributes table.CHF Data If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches policy counters from CHF.
For information on configuring CHF Data attributes, see
CHF Attributes table.AMPolicyData Attributes Subcribe to Notify When Subscribe to Notify flag is enabled (default behavior), Policy subscribes with the UDR to receive notifications whenever a change is made to a subscriber profile. Further, AM service notifies PDS, which in turn looks for an existing subscription for that subsciber and do any of the following:- If a subscription already exists
and
monitoredResourceUrisalready contains "am-data", no action is taken by PDS. - If a subscription does not exist, PDS subscribes with the UDR using the POST method with monitoredResourceUris set to "am-data".
By default, this option is disabled.
Query User on Create When this parameter is enabled (default behavior), PDS queries the UDR about the subscriber contained in the AM Association create request. It is done by sending a GET request for "am-data" resource on the nudr-dr service. Note: If you enable the Subscribe to Notify parameter for AM service configurations, the Policy service may look up for the requested subscriber profile in its local cache before querying UDR.
By default, this option is enabled.
Query User on Update When this parameter is enabled, PDS queries the UDR about the subscriber present in the AM Association update request by sending a GET request for “am-data” resource on the nudr-dr service. By default, this parameter is disabled.
Note:
If you enable the
Subscribe To Notifyflag for AM service configurations, the Policy service may look up for the requested subscriber profile in its local cache before querying UDR.When the
Subscribe To Notifyflag is enabled and previous subscription attempts failed, then along with the data query, PDS also sends a SUBSCRIBE request to UDR.Query User on Terminate When this parameter is enabled, PDS queries the UDR about the subscriber present in the AM Association delete request by sending a GET request for “am-data” resource on the nudr-dr service. Note: If you have enabled Subscribe to Notify button for AM service configurations, the PCF user service may look up for the requested subscriber profile in its local cache before querying UDR.
By default, this button is disabled.
CHF Data Attributes CHF Data If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches policy counters from CHF. Async CHF Query Enabled When this button is enabled, PCF interacts with CHF in Asynchronous mode. Policy Evaluate This determines if policy evaluate is enabled. By default, this button is enabled. Rules Default Service Area Restriction
This field shows the default Service Area Restriction (SAR). To update your default Service Area Restriction, click Edit and select any one from the drop-down list of preconfigured SARs. For more information on how to create or configure SAR, see Service Area Restriction.
Default RFSP Index
The RFSP Index refers to a particular UE information used locally by the Access Network for implementing specific radio resource management strategies. This field shows the default value for RFSP Index, which can be a number between 1 and 256. Default Triggers
This field shows the default triggers. To update the default triggers, click Edit and select desired value(s) from drop-down list values. The supported values are:- LOC_CH, that is, change in location
- PRA_CH, that is, change of UE presence in PRA
Audit Enabled Determines whether to send registration request to Audit service or not. Default Value: True
Query AMF When this flag is set to true, audit service sends notification to AMF to check the presence of a stale session. If a stale session is present, AMF sends a 404 response to audit service. Then, audit service deletes the AM Policy association from the database. Default Value: False
Note: When Minimum Audit Attempts is 1 and Query AMF is false, Audit service removes the AM session after the maxTTL expiry and the Minimum Audit Attempts remains 0 in Audit database.
Notification Rate (per second) Defines the number of stale records which Audit service notifies to AM service in one second. Value of this parameter ranges between 20 and 700.
Default and Recommended Value: 50
Note: To configure higher number than the recommended value, contact My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com)
Policy Association Age (in minutes) Defines the age of an AM policy association after which a record is considered to be stale on PCF and the AMF is queried for presence of such associations. Value of this parameter ranges between 1 and 10080.
Default Value: 1440
Policy Association Maximum Age (in minutes) Defines the maximum age of an AM policy association after which a record is purged from PCF AM d Value of this parameter ranges between 1 and 20160.
Default Value: 2880
Minimum Audit Attempts Specifies the minimum number of consecutive failed audit attempts until maxTTL / forceTTL is reached.
If maxTTL is reached and audit_attempts >= Minimum Audit Attempts for maxTTL, Audit service sends notification to AM service with maxTTL flag set to true. AM Service sends DELETE request to PDS.
Range: 0-255
Default Value: 0
Note: If maxTTL is not reached and if audit attempts are reached, the number of audit attempts are incremented until maxTTL is reached.
Minimum Audit Passes Interval (in minutes) Defines the time when next audit for the AM service table begins after delta time if auditing this table has been finished before this specified time. Default Value: 330
Pending Transaction UpdateNotify Retry Backoff (in milliseconds) Defines the retry backoff for UpdateNotify in milliseconds. Default Value: 0 - 10000 milliseconds
UpdateNotify Retry Count Defines the total number of retries for UpdateNotify. Default Value: 0 - 5
- If a subscription already exists
and
- Perform the following steps to configure
Advanced Settings:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following keys and respective values:
The following table describes the keys and values:Table 7-35 Add Advanced Settings Configurations
Key Value CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_SERVICE_ENABLED Enables the communication to Bulwark service, if it is set to true. Default value: False
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION The duration for which lock is kept once the acquisition is successful. After this duration, the lock gets released automatically. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Duration by which the UE service waits for the response to get a lock.
Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT Number of attempts the service make to request the lock.
Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF Defines the amount of time after which the service retries to gain the lock, incase of failure.
Default value: 1000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE Enables the communication to Bulwark service during UPDATE request flow. Default value: False
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION The duration for which lock is kept once the acquisition is successful. After this duration, the lock gets released automatically. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Duration for which the Policy service will wait for the response. Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT Number of attempts the service can make to request the lock.
Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF Number of retries to acquire the lock upon Failure response from Bulwark service for such a request. Default value: 1000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY Enables the communication to Bulwark service during update-notify request flow.
Default value: False
BULWARK.SERVICE_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT Allows to control the connection timeout of a Bulwark service. Default value: 3000
PENDING_TRANSACTION.NOTIFICATION_ERROR_HANDLING_APP Allows to notify the pending transactions. Default value: 1
USER.RESET_CONTEXT_CHF_DATA_ON_AM_CREATE Sets resetContext flag for the CHF on the request towards PDS. Default value: false
USER.RESET_CONTEXT_AM_POLICY_DATA_ON_AM_CREATE Sets resetContext flag for the AM policy on the request towards PDS. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_SERVICE_ENABLED Enables the concurrency functionality. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.ENABLED Enables concurrency feature for AM-create call flow. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Lease duration for which lock will be acquired. After this time, Bulwark will automatically release the lock. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Wait time out for lock acquisition if not acquired. Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT Wait time out for lock acquisition if not acquired. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF This is the duration for which AM service will wait once it receives ALREADY_LOCKED Response from Bulwark for the AM Update flow. Default value: 1000
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.ENABLED Enables concurrency feature for AM-Delete call flow. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Lease duration for which lock will be acquired. After this time, Bulwark will automatically release the lock. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF This is the duration for which AM service will wait once it receives ALREADY_LOCKED Response from Bulwark for the AM Delete flow. Default value: 1000
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT If lock acquisition failed from Bulwark due to lock request failed. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Wait time out for lock acquisition if not acquired. Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.ENABLED Enable concurrency feature for AM-Update call flow. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Lease duration for which lock will be acquired. After this time, Bulwark will automatically release the lock. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF This is the duration for which AM service will wait once it receives ALREADY_LOCKED Response from Bulwark for the AM Update flow. Default value: 1000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT If lock acquisition failed from Bulwark due to lock request failed. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Wait time out for lock acquisition if not acquired. Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.ENABLED Enable concurrency feature for AM-Update-Notify call flow. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Lease duration for which lock will be acquired. After this time, Bulwark will automatically release the lock. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF This is the duration for which AM service will wait once it receives ALREADY_LOCKED Response from Bulwark for the AM Update Notify flow. Default value: 1000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT If lock acquisition failed from Bulwark due to lock request failed. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Wait time out for lock acquisition if not acquired. Default value: 0
RESOURCEID.SUFFIXLIST ResourceId because this is generic to all resources like AM or other service..Like in our case for AM we need this for association id which is a resource identifier.Hence ResourceId.
Suffix because we are going to concatenate it with association id which will be after generated uuid.
Default value: SUPI
ENABLE.ASSOCIATIONID.ENCODING Enables the encoding of the Association ID in the format:
PolicyAssociationId_versionNo_encoded(featureName1:value1)_encoded(featureName2:value2)where:
versionNo: is the value which will decide about the encoding version being used. If the value is 0, it indicates that it will be base64 encrypted.
encoded: indicates the encoded value for each feature, hence each feature will be separated by an underscore, that is "_". An encoded value consists of a number that will mean the name of the feature, in this case 0 will be for Concurrency and value separated by ":"
featureName: represents the feature for which the coding is, in the format it will be represented as a number that will have a feature assigned to it. For example,
value: is key value pair of SUPI/GPS
Default value: false
- Click the
- Click Save.
The page saves the PCF Access and Mobility configurations.
7.3.4 PCF Policy Authorization
This procedure provides information about configuring the PCF Policy Authorization Service.
The PCF Policy Authorization page displays the authorization service configurations. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations, and select PCF Policy
Authorization.
This opens the PCF Policy Authorization page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit PCF Policy Authorization page.
- Check the default configuration for all the fields
in all groups and edit as necessary.
The following table describes the input fields displayed under each group:
Table 7-36 Edit PCF Policy Authorization
Field Name Description System Provide System details: Af Direct Reply
Determines, if reply must be sent to AF before the PCF that sends the policy decision to SMF, after successful session binding.Default Value: true Override Supported Features
Defines the supported features that can be configured to override system embedded values. Represent a string separated by comma. For example, "InfluenceOnTrafficRouting,SponsoredConnectivity". The "" means an empty supported feature set.
AF Terminate Uri Segment
Specifies AF notify to terminate uri segment appended to AF notify uri. For example, {NotificationUri}/termination. "termination" is the terminate uri segment.Default Value: terminate AF Subscriber Notify Segment
Specifies AF subscription notify uri segment appended to AF subs notify uri. For example, {NotificationUri}/notify. "notify" is the subscription notify uri segment.Default Value: terminate Rx Resource Allocation Partial Failure Report Prefence After PCF triggers a notification to Diameter Connector, the connector generates a RAR message. The partial failed specific action in the RAR message depends on the priority of the action subscribed in the AAR message. The priority of the actions is INDICATION_OF_FAILED_RESOURCES_ALLOCATION > INDICATION_OF_RELEASE_OF_BEARER > INDICATION_OF_LOSS_OF_BEARER. If you want to assign the action not depend on the priority, you can assign the action in this field. The default configuration is empty, you can choose one action from the following options. Once the value is defined in this field, the connector uses the configured action not depend on the priority.
Valid Options are:- INDICATION_OF_FAILED_RESOURCES_ALLOCATION
- INDICATION_OF_RELEASE_OF_BEARER
- INDICATION_OF_LOSS_OF_BEARER
AF Notifications Retry Profile Defines the retry profile configuration for Policy Authorization. For more information on configuring retry profile, see Retry Profiles. AF Communication Profile Specifies the NF communication profile used by AF. For more information about configuring NF communication profiles, see NF Communication Profiles. Data Compression Scheme Specifies the data compression scheme that can be used. Enable Authorization Lifetime Specifies whether to enable feature negotiation for Authorization Lifetime of Rx Sessions.
Default Value: false
IMS Emergency Session Provide IMS Emergency Session details: Emergency Service URNs
Defines the Uniform Resource Name (URN) values for emergency and other well-known services. Reservation Priority Types
Detemines the IMS Signalling Priority.Default Value: PRIO_6 NWDAF Provide NWDAF details: Enable NWDAF Data Enables or disables the Enable NWDAF Data switch. Audit Provide Audit details: Audit Enabled Specifies whether to enable or disable the stale Rx session audit and deletion.
When this parameters is enabled, SM Service registers with Audit service for monitoring Rx sessions.
Default Value: false
App Session Age (in minutes) Specifies the Time To Live (TTL) of Rx sessions.
Range: 0-21600
Default Value: 1440
App Session Maximum Age (in minutes) Specifies the maximum Time To Live (TTL) of Rx sessions.
Default Value: 4320
Range: 0-21600
Notification Rate (per second) Maximum amount of app session cleanup requests per second.
Default and Recommended Value: 50
Note: To configure higher number than the recommended value, contact My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com)
Minimum Audit Passes Interval (in minutes) Specifies how long the Audit Service waits for next audit cycle.
Default Value: 10
Handle NULL As Stale If
EXPIRY_TIMESTAMPorSITEIDcontainsNULLvalue, (legacy stale records after upgrade) they will be considered in the next audit cycle as TTL expired.Default Value: false
- Perform the following steps to configure
Advanced Settings:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following keys and respective values:
The following table describes the keys and values:Table 7-37 Add Advanced Settings Configurations
Key Value PA.NWDAF.EVENT Allow to add one or more Events to be send in the request towards NWDAF. Default value: SLICE_LOAD_LEVEL
PA.NWDAF.REQUEST_TIMEOUT Allow to control the timeout of the request from SM towards NWDAF. Default value: 3000 (ms)
SYSTEM.PA_ERROR_HANDLER_ENABLED Allows to enable the RAA error handling feature. Default value: False
SYSTEM.PA.EVENT_TRIGGERS This is a comma separated list of Event-Trigger names that are installed on SMF by PCF upon PA session establishment. Default value: Empty ("")
SYSTEM.RX.EVENT_TRIGGERS This is a comma separated list of Event-Trigger names that are installed on SMF by PCF upon Rx session establishment. Default value:- ACCESS_TYPE_CHANGE
- FAILED_RESOURCES_ALLOCATION
- PLMN_CHG
- QOS_NOTIF
- SUCCESSFUL_RESOURCES_ALLOCATION
- USAGE_REPORT
- ANI_REPORT
SYSTEM.PA_TERMINATE_NOTIFY_TIMEOUT_TRIGGER_PA_DELETE When the value of this key is set to
true, Policy Authorization service cleans up the AppSession as soon as the ASR request times out, irrespective of whether it receives ASA or not.Default value:
false - Click the
- Click Save.
The page saves the PCF Policy Authorization configurations.
7.3.5 PCF UE Policy Service
This procedure provides information about configuring the PCF UE Policy Service.
The PCF UE Policy page displays the UE Service configurations. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy navigate to Service
Configurations and select PCF UE Policy.
This opens the PCF UE Policy page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit PCF UE Policy page.
- Check the default configuration for the fields
available in the respective groups and edit as necessary.
The following table describes each field present under PCF UE policy along with the default configurations.
Table 7-38 Edit PCF UE Policy
Field Name Description System Notification URI Root
Specifies the URI Root where the PCF (UE Policy service) is expected to receive notifications from AMF. Example: http://localhost:8080
Note: Include the API prefix required by the API Gateway (if any). For example,
https://api-gateway.pcf.com/uepolicyserviceEnable Max Session Limit Specifies whether to enable the Limiting the Number of Sessions functionality. Max Session Limit Per User Specifies the maximum number of sessions to be limited per user if Enable Max Session Limit flag is enabled. Range: 1-2
Default value: 1
Override Supported Features This configuration enables the pending transactions along with the Advanced Settings. AMF AMF Discovery Criteria Specifies the criteria to discover producer AMFs based on the AMF Set ID and the AMF Region ID.
Valid options are:GUAMISetID and RegionID.
When this parameter is set to GUAMI, Policy parses the GUAMI to fetch the AMF SetID and AMF RegionID and uses these IDs to discover the producer AMF.
AMF Communication Profile Specifies the NF communication profile used by AMF. For more information about configuring NF communication profiles, see NF Communication Profiles. AMF Notification Retry Profile Specifies the retry profile used by AMF. For more information about configuring retry profiles, see Retry Profiles. NAS Communication Profile Specifies the NF communication profile used by NAS. For more information about configuring NF communication profiles, see NF Communication Profiles. NAS Retry Profile for Initial Messages Specifies the retry profile used by NAS. For more information about configuring NF retry profiles, see Retry Profiles. NAS Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages Specifies the retry profile for subsequent messages used by NAS. For more information about configuring NF retry profiles, see Retry Profiles. Send SBI Binding Header For N1N2 Transfer Requests Indicates when to send the SBI binding information for N1N2Transfer request. The options can be:- When binding information changes
- Always
- Never
Default Value: When binding information changes
Send Routing Binding Header For N1N2 Transfer Requests Indicates when to send the routing binding information for N1N2Transfer request. The options can be:- Always
- Never
Default (no value)
Send Discovery Header For N1N2 Transfer Requests Indicates when to send the discovery binding information for N1N2Transfer request. The options can be:- Always
- Never
Default (no value)
User Validate User
When Validate User is enabled, and the subscriber is not found in the UDR, or PCF is not able to query an available/eligible UDR, PCF fails the UE Association creation request with a 400 USER_UNKNOWN error.
On the contrary when you disable Validate User, and the subscriber is not found in the UDR, or PCF is not able to query an available/eligible UDR, PCF does not fail the UE Association creation request, but continue policy processing.
Default Value: disabledEnable Subscriber State Variables If this switch is enabled, UE Policy Service controls the querying and saving of local and remote subscriber state variables (SSV) on PDS.
Default value: false
User Data Types UEPolicyData If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches UEPolicyData from nUDR.
For information on configuring UEPolicyData attributes, see UEPolicyData Attributes table.CHF Data If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches policy counters from CHF.
For information on configuring CHF Data attributes, see CHF Attributes table.UEPolicyData Attributes Subscribe to Notify When Subscribe to Notify is enabled, Policy subscribes with the UDR to get notified on changes in subscriber profile. UE Policy notifies PDS, which in turn looks for an existing subscription for that subscriber and do any of the following:- If a subscription already exists
and the
monitoredResourceUrisalready contains "ue-policy-set", no action is taken by PDS. - If a subscription does not exist, PDS subscribes with the UDR using the POST method with monitoredResourceUris set to "ue-policy-set".
Default Value: The button is enabled by default.
Query User on Create
Determines if user query from UDR is enabled. When this option is enabled, PDS queries the UDR about the subscriber contained in the UE Association create request by sending a GET request for “ue-policy-set” resource on the nudr-dr service. Note: The Policy Service caches the subscriber profile when Subscribe To Notify option is enabled. In that case, Policy may not always reach the UDR when the subscriber profile is found in the local cache.
Default Value: The parameter is enabled by default.
Query User on Update Determines if user query from UDR on update is enabled. When this option is enabled, PDS queries the UDR about the subscriber present in the UE Association update request by sending a GET request for “ue-policy-set” resource on the nudr-dr service. Default Value: This parameter is disabled by default.
Note:
The Policy Service caches the subscriber profile when the
Subscribe To Notifyoption is enabled. In that case, Policy may not always reach the UDR when the subscriber profile is found in the local cache.When the
Subscribe To Notifyflag is enabled and previous subscription attempts failed, then along with the data query, PDS also sends a SUBSCRIBE request to UDR.Query User on Terminate Determines if user query from UDR on delete is enabled. When this option is enabled, PCF queries the UDR about the subscriber present in the UE Association delete request by sending a GET request for “ue-policy-set” resource on the nudr-dr service. Note: The PCF User Service caches the subscriber profile when the Subscribe To Notify option is enabled, in that case, the PCF may not always reach the UDR when the subscriber profile is found in the local cache.
Default Value: The button is disabled by default.
CHF Data Attributes CHF Data If this switch is enabled, PCF fetches policy counters from CHF. Async CHF Query Enabled When this button is enabled, PCF interacts with CHF in Asynchronous mode. Home PLMN MCC The Mobile Country Code and Mobile Network Code of the Home PLMN Default Value: NA
MNC The Mobile Country Code and Mobile Network Code of the Home PLMN Default Value: NA
N1 Message Transfer Settings N1 Message Maximum Size Maximum number of URSP Rules to be encoded in a single UE Policy Section (UPSI) container. Default Value: 2000
UE Policy Section Maximum Size The maximum size in bytes of a "MANAGE UE POLICY COMMAND" after encoding to send out to AMF for delivery to UE. Default Value: 2000
Maximum Number of URSP Rules per UE Policy Section Maximum number of URSP Rules to be encoded in a single UE Policy Section (UPSI) container. Default Value: 4
UE Policy Section Code (UPSC) Start This fields indicate the range of UPSC allocation by PCF and can be used to maintain a dedicated range of UPSCs used by PCF generated UPSIs. Configuring these fields avoids the conflict of UPSCs between the UE built-in UPSC and the PCF delivered UPSC.
Note: If the UPSI based policy action is also used for non-fragmented URSP delivery, then the range of UPSCs used by that method should be outside the range configured here.
Default Value: Start: 0
UE Policy Section Code (UPSC) End This fields indicate the range of UPSC allocation by PCF and can be used to maintain a dedicated range of UPSCs used by PCF generated UPSIs. Configuring these fields avoids the conflict of UPSCs between the UE built-in UPSC and the PCF delivered UPSC.
Note: If the UPSI based policy action is also used for non-fragmented URSP delivery, then the range of UPSCs used by that method should be outside the range configured here.
Default Value: End: 65535
Timer Settings T 3501 Timer Duration If it's value is zero, T 3501 Timer handling functionality will be disabled. If a non-zero value is configured, then the timer will be initiated after every N1 transfer receives success response from AMF. PCF will be expecting N1N2-notify to be received before the timer gets expired.
Default Value: 5000
Range: 0 to 60000
Back-off Timer Duration The action to be taken by PCF when the AMF notifies the PCF that it could not deliver the "MANAGE UE POLICY COMMAND" message to UE. Default Value: 15000
N1 Message Retransmission Settings On T 3501 Timer Expiry Action The action to be taken by PCF when N1 notification is not received within configured duration defined in T 3501 Timer Duration.
Default Value: Abort N1 Delivery
Max Number of Re-transmissions Maximum number of retransmissions to be attempted (excluding the initial attempt) after which UE service shall not try further to resend the same fragment to AMF.
Default Value: 2
Re-transmission Failure Behaviour The behavior of PCF UE service if the N1 message is not delivered to the UE after a maximum number of re-transmissions have been tried.
Default Value: Abort N1 Delivery
On Transaction Failure Notification Action The action to be taken by PCF when the AMF notifies the PCF that it could not deliver the "MANAGE UE POLICY COMMAND" message to UE. Default Value: Abort N1 Delivery
Max Number of Re-transmissions Maximum number of re-transmissions to be attempted (excluding the initial attempt) after which UE service shall not try further to re-send the same fragment to AMF.
Default Value: 2
Re-transmission Failure Behaviour The behavior of PCF UE service if the N1 message is not delivered to the UE after a maximum number of re-transmissions have been tried.
Default Value: Abort N1 Delivery
On UE Policy Command Reject Action The action to be taken by PCF when the UE notifies the PCF that it could not process the "MANAGE UE POLICY COMMAND" message. Default Value: Abort N1 Delivery
Maximum Number of Re-transmissions Maximum number of re-transmissions to be attempted (excluding the initial attempt) after which UE service shall not try further to re-send the same fragment to AMF Default Value: 2
Re-transmission Failure Behaviour The behavior of PCF UE service if the N1 message is not delivered to the UE after a maximum number of re-transmissions have been tried. Default Value: Abort N1 Delivery
Audit Enabled If this flag is enabled, UE service registers with Audit service for auditing the records in
UEPolicyAssociationtable. Once the registration is successful, a record for UE service is created in theAuditRegistrationtable.Default Value: False
Query AMF If this flag is enabled, the UE service sends the stale session notification received from Audit service to AMF to check if the session is present in AMF. If a stale session is present, AMF sends a 404 response to audit service. Then, audit service deletes the UE Policy association from the database.
Default Value: False
Note: When Minimum Audit Attempts is 1 and Query AMF is false, Audit service removes the UE Policy session after the maxTTL expiry and the Minimum Audit Attempts remains 0 in Audit database.
Notification Rate (per second) Defines the maximum number of stale records, which Audit Service notifies to UE service in one second.
Value of this parameter ranges between 20 and 700.
Default and Recommended Value: 50
Note: To configure higher number than the recommended value, contact My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com)
Policy Association Age (in minutes) Defines the age of the UE Policy Association, after which a record is considered to be stale on PCF and the AMF is queried (if query AMF is set to TRUE) for presence of such associations.
Value of this parameter ranges between 1 and 10080.
Default Value: 1440
Policy Association Maximum Age (in minutes) Defines the maximum age of a UE Policy Association, after which a record is considered as stale and is purged from PCF UE database without sending further queries to AMF.
Value of this parameter ranges between 1 and 20160.
Default Value: 2880
Minimum Audit Attempts Specifies the minimum number of consecutive failed audit attempts until maxTTL / forceTTL is reached.
If maxTTL is reached and audit_attempts >= Minimum Audit Attempts for maxTTL, Audit service sends notification to UE Policy service with maxTTL flag set to true. UE Policy service sends DELETE request to PDS.
Range: 0-255
Default Value: 0
Note: If maxTTL is not reached and if audit attempts are reached, the number of audit attempts are incremented until maxTTL is reached.
Minimum Audit Passes Interval (in minutes) Defines the time when next audit for the UE service table is done after delta time if auditing this table has been finished before this specified time.
Value of this parameter ranges between 1 and 1440.
Default Value: 10
Pending Transaction UpdateNotify Retry Backoff (in milliseconds) Defines the retry backoff for UpdateNotify in milliseconds. Default Value:
UpdateNotify Retry Count Defines the total number of retries for UpdateNotify. Default Value:
- Perform the following steps to configure
Advanced Settings:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following keys and respective values:
The following table describes the keys and values:Table 7-39 Add Advanced Settings Configurations
Key Value CONCURRENCY.ENABLED Enables the communication to Bulwark service, if it is set to true. These will override Bulwark service enabled flag set during deployment using deployment yaml files. Default value: False
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION The duration for which lock is kept once the acquisition is successful. After this duration, the lock gets released automatically. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Duration by which the UE service waits for the response to get a lock.
Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT Number of attempts the service make to request the lock.
Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.ENABLED Enables the communication to Bulwark service during CREATE request flow if these flag and Bulwark service flag in deployment yaml file are set to True. Default value: False
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.ALLOW_ON_SERVICE_FAILURE Allows the UE service to continue with the processing of CREATE request even if the response get from Bulwark service to lock/unlock was a failure. Default value: True
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Duration of the lock is kept once the block is successful. After this duration the lock will be released automatically. The duration is set only for UPDATE request flow. It can be set to 0 to indicate no release lock timeout. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Duration which consumer service will wait for the lock response. The duration is set only for UPDATE request flow. It can be set to 0 to indicate no release lock timeout. Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT Number of retries when a request to bulwark service fails. The duration is set only for UPDATE request flow. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.ENABLED Enables the communication to Bulwark service during UPDATE request flow. IF pendingtransaction feature is enabled then this Advance setting is avoided. Default value: False
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.ALLOW_ON_SERVICE_FAILURE Allows the UE service to continue with the processing of UPDATE request even if the response get from Bulwark service to lock/unlock was a failure. Default value: True
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Duration of the lock is kept once the block is successful. After this duration the lock will be released automatically. The duration is set only for TERMINATE request flow. It can be set to 0 to indicate no release lock timeout. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Duration of the lock is kept once the block is successful. After this duration the lock will be released automatically. The duration is set only for TERMINATE request flow. It can be set to 0 to indicate no release lock timeout. Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT Number of retries when a request to bulwark service fails. The duration is set only for TERMIANATE request flow. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.ENABLED Enables the communication to Bulwark service during TERMINATE request flow if theseflag and Bulwark service flag in deployment yaml file are set to True. Default value: False
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.ALLOW_ON_SERVICE_FAILURE Allows the UE service to continue with the processing of TERMINATE request even if the response get from Bulwark service to lock/unlock was a failure Default value: True
CONCURRENCY.N15.NOTIFICATION.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Duration of the lock is kept once the block is successful. After this duration the lock will be released automatically. The duration is set only for NOTIFY request flow. It can be set to 0 to indicate no release lock timeout. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.NOTIFICATION.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Duration which consumer service will wait for the lock response. The duration is set only for NOTIFY request flow. It can be set to 0 to indicate no release lock timeout. Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.NOTIFICATION.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Duration which consumer service will wait for the lock response. The duration is set only for NOTIFY request flow. It can be set to 0 to indicate no release lock timeout. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.NOTIFICATION.ENABLED Set it to True will enable the communication to Bulwark service during NOTIFY request flow. IF pendingtransaction feature is enabled then this Advance setting is avoided. Default value: False
CONCURRENCY.N15.NOTIFICATION.ALLOW_ON_SERVICE_FAILURE Allows the UE service to continue with the processing of NOTIFY request even if the GET response from Bulwark service to lock/unlock was a failure. Default value: True
BULWARK.SERVICE_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT Duration which consumer service will wait for Bulwark response. Default value: 3000
USER.RESET_CONTEXT_SSV_ON_UE_CREATE Sets resetContext flag for the SSV on the request towards PDS. Default value: false
USER.RESET_CONTEXT_CHF_DATA_ON_UE_CREATE Sets resetContext flag for the CHF on the request towards PDS. Default value: false
USER.RESET_CONTEXT_UE_POLICY_DATA_ON_UE_CREATE Sets resetContext flag for the UE policy on the request towards PDS. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_SERVICE_ENABLED Enables the concurrency functionality. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.ENABLED Enables concurrency feature for AM-create call flow. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Lease duration for which lock will be acquired. After this time, Bulwark will automatically release the lock. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Wait time out for lock acquisition if not acquired. Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT Wait time out for lock acquisition if not acquired. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.CREATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF This is the duration for which AM service will wait once it receives ALREADY_LOCKED Response from Bulwark for the AM Update flow. Default value: 1000
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.ENABLED Enables concurrency feature for AM-Delete call flow. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Lease duration for which lock will be acquired. After this time, Bulwark will automatically release the lock. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF This is the duration for which AM service will wait once it receives ALREADY_LOCKED Response from Bulwark for the AM Delete flow. Default value: 1000
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT If lock acquisition failed from Bulwark due to lock request failed. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.TERMINATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Wait time out for lock acquisition if not acquired. Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.ENABLED Enable concurrency feature for AM-Update call flow. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Lease duration for which lock will be acquired. After this time, Bulwark will automatically release the lock. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF This is the duration for which AM service will wait once it receives ALREADY_LOCKED Response from Bulwark for the AM Update flow. Default value: 1000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT If lock acquisition failed from Bulwark due to lock request failed. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Wait time out for lock acquisition if not acquired. Default value: 0
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.ENABLED Enable concurrency feature for AM-Update-Notify call flow. Default value: false
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Lease duration for which lock will be acquired. After this time, Bulwark will automatically release the lock. Default value: 2000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF This is the duration for which AM service will wait once it receives ALREADY_LOCKED Response from Bulwark for the AM Update Notify flow. Default value: 1000
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT If lock acquisition failed from Bulwark due to lock request failed. Default value: 2
CONCURRENCY.N15.UPDATE_NOTIFY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Wait time out for lock acquisition if not acquired. Default value: 0
RESOURCEID.SUFFIXLIST ResourceId because this is generic to all resources like AM or other service..Like in our case for AM we need this for association id which is a resource identifier.Hence ResourceId.
Suffix because we are going to concatenate it with association id which will be after generated uuid.
Default value: SUPI
ENABLE.ASSOCIATIONID.ENCODING Enables the encoding of the Association ID in the format:
PolicyAssociationId_versionNo_encoded(featureName1:value1)_encoded(featureName2:value2)where:
versionNo: is the value which will decide about the encoding version being used. If the value is 0, it indicates that it will be base64 encrypted.
encoded: indicates the encoded value for each feature, hence each feature will be separated by an underscore, that is "_". An encoded value consists of a number that will mean the name of the feature, in this case 0 will be for Concurrency and value separated by ":"
featureName: represents the feature for which the coding is, in the format it will be represented as a number that will have a feature assigned to it. For example,
value: is key value pair of SUPI/GPS
Default value: false
Table 7-40 Advanced Settings for Congestion Control
Key Value Description UE.GET.SUBSCRIBER.SESSIONS.PRIORITY 24 Retrieve any type of subscriber session priorities. Allowed Values: 0- 31
UE.GET.POLICY.ASSOCIATION.PRIORITY 18 Retrieve the individual UE policy association priority. Allowed Values: 0- 31
UE.CREATE.PRIORITY 24 Create a new individual UE policy association. Allowed Values: 0- 31
UE.UPDATE.PRIORITY 18 Report observed event triggers and possibly obtain updated policies for the individual UE policy association Allowed Values: 0- 31
UE.UPDATE.NOTIFICATION.PRIORITY 18 Update notification from PDS Allowed Values: 0- 31
UE.DELETE.PRIORITY 16 Delete the individual UE policy association. Allowed Values: 0- 31
UE.AUDIT.NOTIFY.PRIORITY 30 To handle Audit notification. Allowed Values: 0- 31
UE.N1.NOTIFICATION.MESSAGE.PRIORITY 18 To handle UE N1 notification messages. Allowed Values: 0- 31
UE.N1.FAILURE.NOTIFICATION.MESSAGE.PRIORITY 18 To handle UE N1 Failure notification messages. Allowed Values: 0- 31
CONGESTION.HTTP.RESPONSE.CODE 503 Configure the response code of any rejected requests by UE service due to congestion state. By default, the service sends 503 as response code. If configured then it shall be 5xx only. - Click the
- Click Save.
The page saves the PCF UE Policy configurations.
7.3.6 PCF User Connector
This procedure provides information about configuring the PCF User Connector Service.
The PCF User Connector page displays the User Connector Service configurations. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations and select PCF User
Connector.
This opens the PCF User Connector page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit PCF User Connector page.
- Check the default configuration for all the fields
in all groups and edit as necessary.
The following table describes the input fields displayed under each group:
Table 7-41 Edit PCF User Connector
Field Name Description System Server Root URL
Specifies the callback URI for notifications to be received by the User service. For example, while creating a subscription for the user with UDR.
Common Request Timeout
Request timeout in milliseconds for: - AmPolicyData change notification request sent to AM service
- UePolicySet change notification request sent to UE service
- SmPolicyData change notification request sent to SM service
- SpendingLimit status change notification/terminate request sent to SM service
- On demand discovery request sent to NRF client for dynamic discovery of UDR
UDR Base Uri
Base Uri specifies the part of resource uri, which follows apiRoot. The Base Uri is common to all Policy Data resources. For example – In the Resource Uri
Default Value: /nudr-dr/v1{apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/policy-data/ues/{ueId}/sm-data,nudr-dr/{apiVersion}is the base Uri.Supported Features
Refers to the value set to supportedFeatures field in PolicyDataSubscription while sending subscriptions request to UDR for notifying changes in policy data. Default Value: f
SM Data VSA Names
Indicates to provision subscriber name from Vendor Specific Attribute (VSA) data in SM Policy data for subscriber profile.
Example: VendorSpecific-000111
Note: This field must be configured for Cloud Native Core PCRF deployments that have Usage Monitoring enabled that interacts with UDR to fetch Subscriber Profile Data over 3GPP N36 interface. This field indicates a list of Vendor Specific Attribute names that are provisioned in the SessionManagementPolicyData Resource on UDR that needs to be fetched by the Cloud Native PCRF Function to be used in PCRF Core and Usage Monitoring.
AM Data Uri
It refers to the section of resource uri that represents all UE related access and mobility policy attributes in the UDR for a given "ueId". AM Data Uri follows base uri part of the resource uri. Default Value: /policy-data/ues/{ueId}/am-data
UE Policy Set Uri
It refers to the section of resource uri that represents UE policy set attributes in the UDR for a given "ueId". UE Policy Set Uri follows base uri part of the resource uri. Default Value: /policy-data/ues/{ueId}/ue-policy-set
SM Data Uri
It refers to the section of resource uri that represents all PDU session related subscription attributes in the UDR for a given "ueId". SM Data Uri follows base uri part of the resource uri. Default Value: /policy-data/ues/{ueId}/sm-data
Usage Mon Uri
It refers to the section of resource uri that represents an individual usage monitoring resource created in the UDR and associated with a ueId and a usageMonId. Usage Mon Uri follows base uri part of the resource uri. Default Value: /policy-data/ues/{ueId}/sm-data/{usageMonId}
Subs To Notify Uri
It refers to the section of resource uri that represents subscriptions to notification of policy data modification. Subs To Notify Uri follows base uri part of the resource uri. Default Value: /policy-data/subs-to-notify
Subs To Notify Subs Id Uri
It refers to the section of resource uri that represents an individual subscription to notification of policy data modification. Subs To Notify Subs Id Uri follows base uri part of the resource uri. Default Value: /policy-data/subs-to-notify/{subsId}
SM Data Subscription Resource Default value would be 1 on selection of "Sm-data" and other value is 2 on selection of "As requested by SM service". Discover UDR with Policy as Supported Data Set Indicates whether to send "POLICY" as data-set to be supported by the UDR during NRF discovery procedure. In turn, this configuration helps NRF filter and responds with only those UDR NF Profiles which support "POLICY" as one of the data-sets. By default, the value for this parameter is set to false.
Request Timeout
Specifies the timeout interval in milliseconds in which a request to UDR fails if UDR fails to respond within this value of timeout. Default Value: 1000 milliseconds Enable Discovery On Demand
When this field is set to true, UDR discovery from NRF takes place for each UeId. Default Value: false
Retry Profile for Initial Messages Retry Profile to be used when PCF fails to send a create message to a producer node. Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages Retry Profile to be used when PCF fails to send an in-session message to a producer node. Retry Subscription Message as: Retry Subscription Message enables the operator to choose Retry Logic for SUBSCRIBE/POST towards UDR from the follow possible options: - Initial Message: PCF will treat POST as Initial message and apply Initial Retry Logic for Session Retry.
- Subsequent Message: PCF will treat POST as Subsequent message and apply Subsequent Retry Logic for Session Retry.
NF Communication Profile The NF communication profile created for the service. This profile is created using the NF Communication Profiles page. Send Target API Root Header in Subscribe to Notify Request Specifies whether to include Target API Root header in the subscribe to notify request sent by PCF towards UDR. Note: If the user selects Model D for Policy NF Communication Model, the value for this field can be set to true or false. For other Policy NF Communication Model values, the value for this field must be set to true.
By default, the value for this parameter is set to true.
Send Initial Discovery Parameters in Subscribe to Notify Request Specifies whether to include initial discovery parameters in the subscribe to notify request sent by PCF towards UDR. By default, the value for this parameter is set to false.
Send Producer Id in Discovery Header in Subscribe to Notify Request Specifies whether to include Producer ID in discovery header in the subscribe to notify request sent by PCF towards UDR. By default, the value for this parameter is set to false.
CHF Retry Profile for Initial Messages Retry Profile to be used when PCF fails to send a create message to a producer node. Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages Retry Profile to be used when PCF fails to send an in-session message to a producer node. NF Communication Profile The NF communication profile created for the service. This profile is created using the NF Communication Profiles page. PCF Service name in Binding Header Specifies the custom/3GPP defined PCF service name to be included in the binding header in the subscription request or notification responses sent towards CHF.
Possible values:- Aggregate or custom service name
that represents a group of PCF services with
aggregated service level information.
For example:
npcf-custom-service - Any of the 3GPP defined PCF service
names such as
npcf-smpolicycontrolornpcf-am-policy-control
There is no default value configured for this field.
Note:
- If both Retry Profile for Initial Messages and Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages are not configured (default case) no retry is attempted.
- If both Retry Profile for Initial Messages and Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages are configured, retries is attempted accordingly.
- If Retry Profile for Initial Messages is configured but Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages is not configured then the profile for initial messages is used for subsequent messages. (to be backward compatible with release 1.8.x)
- If Retry Profile for Initial Messages is not configured but Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages is configured, then retry is not attempted for initial messages. But it is attempted for the subsequent messages.
-
If Send PCF Service Name in Binding Header parameter under NF Bindings Setting section in NF communication profile page is enabled for CHF interface , the aggregate custom Service name or a 3gpp defined pcf service name must be defined in PCF Service name in Binding header parameter. This service name will be included in the binding header towards CHF sent over N28/Nchf interface.
- Perform the following steps to configure Advanced Settings that sets the
key precendence on user connector:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following key and respective value:
Table 7-42 Parameters for Advanced Settings
Keys Value UDR.KeyPrecedence It is used to set the Key Precedence given on User Connector. Default Value: SUPI, GPSI
CONCURRENCY_LOCK_FAILURE_ERROR_CODE Indicates an error in PDS Service in acquiring a lock from Bulwark Service to process a notification from UDR or CHF.
Default Value: 500
RETAIN_ORIGINAL_MONITORED_RESOURCE_URI_ON_REVALIDATION If the flag is set to true the monitoredResourceUri sent in the POST will be retained for the subsequent PUT request.
Default Value: false
UDR_errorHandlerEnabled This flag enables error handling configuration with UDR connector service. Default Value: false
CHF_errorHandlerEnabled This flag enables error handling configuration with CHF connector service. Default Value: false
UDR_NF_PROFILE_COOKIE_ENABLED This flag indicates whether the UDR profiles discovered during UDR-GET needs to be cached till UDR-POST is completed (success/failure). Default Value: false
UDR_NF_PROFILE_COOKIE_COMPRESS This flag indicates whether to compress the UDR profiles cached between GET and POST request. Default Value: false
UDR_NF_PROFILE_COOKIE_LIMIT This flag indicates the number of UDR profiles between GET and POST that can be cached. Default Value: 10
Note: It is recommended to enable UDR_NF_PROFILE_COOKIE_COMPRESS to true so that we can support caching of upto 10 UDR profiles. For supporting lesser number of UDR profile caching (like 3-4), we can disable the compression. Caching of more than 10 profiles is not supported.
UDR_GET_USE_RELATED_RESOURCE This flag allows GET for related resources (for example, amPolicyData and uePolicySet) from the same UDR where previous GET was done. Default Value: false
- Click the
- Click Save.
The page saves the PCF User Connector configurations.
7.3.7 Configuring Usage Monitoring
This procedure provides information about managing configurations for Usage Monitoring service.
The Usage Monitoring page allows you to edit default Usage Monitoring configurations.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Service
Configurations, and select Usage
Monitoring.
This opens the Usage Monitoring page with the default configurations.
-
Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Usage Monitoring page.
- Enter values for the input fields, described in the following
table:
Table 7-43 Usage Monitoring Configurations
Field Name Description Enable PRE Specifies whether to enable or disable interaction with PRE for Policy evaluation as per the match list. Minimum Volume Grant (bytes) Enter the minimum grant value (in bytes) that can be approved for volume based usage monitoring. If the grant value published by PRE is less than the value for this field, then Policy considers the minimum grant value out of the two. After deducting the current grant, if the remaining grant value is less than the minimum grant value, then the remaining grant is also added to the current grant.
Default value: 2048
Range: 512 - 1048576 (1MB)
Maximum Volume Grant (bytes) Enter the maximum grant value (in bytes) that can be approved for volume based usage monitoring. If the grant value published by PRE is greater than the value for this field, then Policy considers the maximum grant value out of the two. Default value: 2048
Range: 1024- 1000,000,000,000
Minimum Time Grant (seconds) Enter the minimum grant value (in seconds) that can be approved for time based usage monitoring. If the grant value published by PRE is less than the value for this field, then Policy considers the minimum grant value out of the two. After deducting the current grant, if the remaining grant value is less than the minimum grant value, then the remaining grant is also added to the current grant.
Default value: 300
Range: 30 - 3600 (1 hour)
Maximum Time Grant (seconds) Enter the maximum grant value (in seconds) that can be approved for time based usage monitoring. If the grant value published by PRE is greater than the value for this field, then Policy considers the maximum grant value out of the two. Default value: 300
Range: 60 - 86400 (24 hours)
Inactivity Time (seconds) Enter the time interval (in seconds) during which if no packets are received for a given monitoring key, PGW or SMF stops measuring the time. Default value: 86400
Range: 0 - 604800 (7 Days)
Usage Accumulation Start Date and Time Select the start time and date from when the Usage Monitoring service starts counting the usage reset periodicity. The values are: - Plan Start Date and Time: Counted from the plan start date and time as provisioned on the UDR.
- Plan Activation Date and Time: Counted from the plan activation date and time as provisioned on the UDR.
- Period Start Date and Time: Counted from the period start date and time.
Week Start Day Enter the starting day of the week. Default value: Sunday
Default Data Rollover Profile Indicates the default data rollover profile to use for UDR provided data limits for which rollover is applicable. That is, "Data Rollover" attribute is set to "true" and a separate "Data Rollover Profile" attribute is not provided. Enable Quota Migration Indicates whether to enable retrieval of OCPM data from CnUDR. If enabled, CnPCRF interacts with CnUDR to collect the quota details of the OCPM (4G) subscribers.
Default value: false
Note: Disabling this flag while Subscriber Data Migration from OCUDR (4G) to CnUDR (5G) is incomplete may result in Quota loss. It is recommended to not fallback to OCPM PCRF once this flag is disabled as after this, the data provided to OCPM PCRF may NOT be up to date.
Reverse Priority Indicates the priority consideration order. When this flag is enabled: Higher number indicates lower priority
When this flag is disabled: Higher number indicates higher priority
Default value:
falseEnable Pro-rated Data at The Time of Activation Iindicates whether pro-rated data calculation should be applied to the selected plan at a time of activation or not.
Default value: false
Enable Pro-rated Data at The Time of Billing Day Change Iindicates whether pro-rated data calculation should be applied to the selected plan at a time obilling day change .
Default value: false
Apply Billing Day / Data Plan Change Indicates if the flexible billing cycle option is enabled.
The accepted values are:- Current Billing Cycle
- Next Billing Cycle
Default value: Next Billing Cycle
Data Compression Scheme Used to configure the data compression in UmContext table. This flag accepts the following values:Disabled: Indicates that the data will not be compressed and will be stored in the column in uncompressed format. The value ofCOMPRESSION_SCHEMEfor that row is set to the default value 0.MySQL Compressed: Indicates that the data will be compressed using MySQL and will be stored in the column in compressed format. The value ofCOMPRESSION_SCHEMEfor that row is set to 1.Application Compressed: Indicates that the data will be compressed using Zlib and will be stored in the column in compressed format. The value ofCOMPRESSION_SCHEMEfor that row is set to 2.
Default value: Disabled
When accessing the data from
UmContext .v, the application determines the compression status based on the value ofCOMPRESSION_SCHEMEand does the decompression accordingly.For more details on data compression, see Data Compression in Usage Monitoring section in Usage Monitoring on Gx Interface.
Default Volume Grant Grant Unit Select a value from the drop-down list: - Percent: Grant volume is calculated as a percentage.
- Bytes: Grant volume is calculated as an absolute value.
Default value: Percent
Grant Value (Percent) Note: This field becomes active when you select Grant Unit as percent. Enter the default Grant Volume in percentage, which is considered when PRE is not invoked or PRE does not return a decision.
This value is applied to the Total Volume and divided equally among the Uplink and Downlink Volumes when available.
Default value: 10
Range: 1-100
When the grant value is 0 and Grant is not calculated by PRE, then volume based Usage Monitoring is disabled for the session.
Grant Value (Bytes) Note: This field becomes active when you select Grant Unit as Bytes. Enter the default Grant Volume in Bytes, which is considered when PRE is not invoked or PRE does not return a decision.
This value is applied to the Total Volume and divided equally among the Uplink and Downlink Volumes when available.
Default value: 2048
Range: 512 - 1048576 (1 MB)
When the grant value is 0 and Grant is not calculated by PRE, then volume based Usage Monitoring is disabled for the session.
Grant Source Note: This field becomes active when you select Grant Unit as Percent. Select a value from the drop-down list:
- Initial Volume: Calculate grant volume from the initial volume.
- Used Volume: Calculate grant volume from the used volume.
- Remaining Volume: Calculate grant volume from the remaining volume.
Default value: Initial Volume
Default Time Grant Grant Unit Select a value from the drop-down list: - Percent: Grant time is calculated as a percentage.
- Seconds: Grant time is calculated as an absolute value.
Default value: Percent
Grant Value (Percent) Note: This field becomes active when you select Grant Unit as percent. Enter the default Grant time in percentage, which is considered when PRE is not invoked or PRE does not return a decision.
Default value: 10
Range: 1-100
When the grant value is 0 and grant is not calculated by PRE, then time based Usage Monitoring is disabled for the session.
Grant Value (seconds) Note: This field becomes active when you select Grant Unit as seconds. Enter the default Grant time in seconds, which is considered when PRE is not invoked or PRE does not return a decision.
Default value: 3600
Range: 30 - 86400 (1 day)
When the grant value is 0 and grant is not calculated by PRE, then time based Usage Monitoring is disabled for the session.
Grant Source Note: This field becomes active when you select Grant Unit as Percent. Select a value from the drop-down list:
- Initial Duration: Calculate grant time from the initial duration.
- Used Duration: Calculate grant time from the used duration.
- Remaining Duration: Calculate grant time from the remaining duration.
Default value: Initial Volume
Default Usage Levels Minor Usage Level (%) Enter threshold value in percentage indicating minor usage. Default value: 50
Major Usage Level (%) Enter threshold value in percentage indicating major usage. Default value: 75
Critical Usage Level (%) Enter threshold value in percentage indicating critical usage. Default value: 95
Exhausted Usage Level (%) Enter threshold value in percentage indicating usage level has exhausted allowed limit. Default value: 100
Custom Attribute Mapping Reset Day & Time Enter a string identifying the custom attribute in UDR response that represents the usage reset day. Example: SmPolicyData/umDataLimits/{limitId}/billingDay
Data Plan Name To map the custom attribute available in the UDR provided data limit to name. A "name" associated with the data limit can be used in a Selection Profile to select the plan to apply when multiple active plans are found. Default vlaue: SmPolicyData/umDataLimits/{limitId}/name
Data Plan Priority To map the custom attribute available in the UDR provided data limit to priority. A "priority" associated with the data limit would help to select the plan to apply when multiple active plans are found. Possible values allowed in this field in UDR Data Limit are: any integer.
Default value: SmPolicyData/umDataLimits/{limitId}/priority
Data Plan Type To map the custom attribute available in the UDR provided data limit to type. A "type" associated with the data limit would help to order the selection of the plan. Possible values are: "base", "pass", "top-up".
A separate configuration would order the selection, for example: Pass > Base Plan > Top-up.
Default: SmPolicyData/umDataLimits/{limitId}/type
Default value: base
Note: The Plan Type, Priority within that Plan Type and the Selection Order of Plan Types together decide the order of selection of Data Plans.
Data Rollover To map the custom attribute available in the UDR provided data limit to indicate whether rollover is enabled for this data limit. Possible values allowed in this field in UDR Data Limit are: "true" and "false".
Default value: SmPolicyData/umDataLimits/{limitId}/rollover
Default value to apply if this mapped attribute is absent: false
Data Rollover Profile To map the custom attribute available in the UDR provided data limit to a pre-configured rollover profile. See "Data Rollover Profile" for more information. Possible values allowed in this field in UDR Data Limit are: A "Data Rollover Profile" name pre-configured on Policy.
Default value: SmPolicyData/umDataLimits/{limitId}/rolloverProfile
Parent Plan Name To map the custom attribute available in the UDR provided data limit to parent plan name. Attributes not present in the UmDataLimit shall be picked up from the "parent" (if present). The parent plan name may be a configured Data Limit Profile Name. Default value: SmPolicyData/umDataLimits/{limitId}/parent
Parent Plan Source To map the custom attribute available in the UDR provided data limit to parent plan source. A parent plan source "parent" (if present). The parent plan name may be a configured Data Limit Profile Name. Possible values allowed in this field in UDR Data Limit are: "data-limit-profile", "um-data-limit".
Default value: SmPolicyData/umDataLimits/{limitId}/parentSource
Default value to apply if this mapped attribute is absent: "data-limit-profile"
-
To add selection profles for the Data Limit Selection, perform the following configurations:
Field Name Description Default Data Limit Profile Indicates the default data limit profile to apply when no (usable) data limits were obtained from UDR and no (usable) data limits were applied by policy. Default Data Limit Selection Profile Indicates the default data limit selection profile to use while selecting a data limit among more than one active data limits provided by UDR. Default Data Limit Sorting Profile Indicates the default data limit sorting profile to use while selecting a data limit among more than one active data limits provided by UDR. Selection Order 1 Selection Order determines the order/priority of selection of different types of plans.
Default Value of Selection Order 1 : Pass
Selection Order 2 Default Value of Selection Order 2 : Base Plan Selection Order 3 Default Value of Selection Order 3: Top-Up - Enter values for the input fields, described in the following
table:
Table 7-44 Conflict Resolution Configurations
Field Name Description Enable ETag / If-Match headers Indicates if the ETag functionality is enabled or disabled between PDS and UDR. By default, this is disabled. Following scenarios may occur if it is enabled: - When the Usage Monitoring service sends a GET request for the first time, then PDS will fetch latest ETag details from UDR and update it in THE pdssubscriber table.
- when the Usage Monitoring service sends PATCH request to PDS, PDS sends the request to UDR using if-match header. UDR matches the ETag of PDS with UDR. If it matches, then UDR replies with the latest ETag that gets udpated on PDS.
- If the If-Match headers failS, it means ETag on PDS does not match with UDR. UDR replies with 412 error response and based on the response code, Usage Monitoring service sends a force request to PDS to get the latest ETag from UDR and update it on PDS database.
Maximum Number of Conflict Resolution Attempts Specifies the number of retry the Usage Monitoring service will do when if-match will fail on UDR. Default value: 5
- Enter values for as described in the
following table to configure audit cycles for Usage Monitoring Gx sessions:
Table 7-45 Audit Configurations
Field Name Description Enable Used to enable or disable the Audit registration for Usage Monitoring service.
When this field is enabled, Usage Monitoring sends registration request to Audit service.
When this field is disabled, Usage Monitoring sends de-registration request to Audit service.
Default value: true
Notification Rate (per second) Indicates the number of stale records that Audit service notifies to Usage Monitoring service in one second.
Value of this parameter ranges between 20 and 700.
Default and Recommended Value: 50
Note: To configure higher number than the recommended value, contact My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com)
Policy Association Age (in minutes): Indicates the age of a Usage Monitoring session, after which the session is considered to be stale and the PCRF Core service is queried for the presence of such associations.
Note: This value should be higher than the Gx session audit.
Value of this parameter ranges between 1 and 10080.
Default Value: 1440
Policy Association Maximum Age (in minutes): Indicates the maximum age of a UMPolicyAssociation, after which the session is purged from UMContext database without sending further queries.
Note: This value should be higher than the Gx session audit.
Value of this parameter ranges between 1 and 20160.
Default Value: 2880
Minimum Audit Attempts Indicates the minimum number of queries to PCRF Core service before deleting a session.
Range: 0-255
Default Value: 0
Minimum Audit Passes Interval (in minutes) Defines the time when next audit for the Usage Monitoring service table is done after delta time if auditing this table has been finished before this specified time.
Default Value: 330
- Enter values for the input fields, described in the following table to
configure message priorities for Congestion Control in Usage
Monitoring:
Table 7-46 Message Default Priority for Congestion Control Configurations
Field Name Description UM Session Create API Set request priority for UM session creation (CCR-I) request.
Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 20
UM Session Update API Set request priority for UM session update (CCR-U) request.
Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 17
UM Session Terminate API Set request priority for UM session terminate (CCR-T) request.
Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 15
UM Session Notify API Set request priority for UM session notification request.
Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 17
UM Session Audit Subscriber API Set request priority for UM session audit subscriber request.
Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 31
UM Session Search Subscriber API Set request priority for UM session search for subscriber request.
Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 30
UM Session Audit Notify API Set request priority for terminate session (CCR-T) request.
Allowed Values: 0-31
Default Value: 31
Congestion Error Code Configure the response code of the any rejected requests by Usage Monitoring due to congestion state. By default, Usage Monitoring sends 503 as response code. If configured then it shall be 5xx only. Allowed Values: 5xx
Default Value: 503
- Perform the following steps to configure Advanced
Settings for Usage Monitoring:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following keys and respective values:
The following table describes the keys and values:Table 7-47 Add Advanced Settings Configurations
Key Value PREVIOUS_UM_CONTEXT_TABLE_SLICING_COUNT Used to configure the previous slicing count for UMContext table.
If
UM_CONTEXT_TABLE_SLICING_COUNTHelm parameter is changed and the Usage Monitoring service cannot find the data with the current slicing count, it usesPREVIOUS_UM_CONTEXT_TABLE_SLICING_COUNTto search for the data.If there are multiple values for
PREVIOUS_UM_CONTEXT_TABLE_SLICING_COUNT, the Usage Monitoring service uses the latest previous count and if the data is still not found, it uses the next previous count. That is, ifPREVIOUS_UM_CONTEXT_TABLE_SLICING_COUNTcontains two values such as 0,5, the Usage Monitoring service first uses the previous count as 5 to search for the data. If it is still not found, the service uses the previous count as 0 to search for the data.Default value: 0
- Click the
- Click Save to save Usage Monitoring service configurations.
7.3.8 PCRF Core Service Configurations
This section describes how to configure the PCRF Core service.
To access PCRF Core service configurations from CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Service Configurations and select PCRF Core.
7.3.8.1 Settings
This procedure provides information about configuring the PCRF Core settings.
The Settings page under PCRF Core displays the PCRF Core service settings. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations, click PCRF Core, and
select Settings.
This opens the Settings page. The page displays the existing settings for PCRF Core service.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Settings page.
- Expand the User group, to enable or disable switches,
described in the following table:
Table 7-48 User Group Settings
Field Name Description Validate User If the User profile, for any of the User Data types given under the User Data Types group, are fetched successfully, the user is considered to be a known user. However, if the user profile lookup has failed on all the configured data sources, the user profile is marked as Unknown. If this switch is enabled and user is marked as Unknown, the session creation requests are rejected.
If this switch is disabled and user is marked as Unknown, the session creation requests are handled and sessions are created successfully.
Enable Subscriber Variables If this switch is enabled, PCRF Core controls the querying and saving of remote subscriber state variables (SSV) on PDS.
When CCR message is received by PCRF Core, then it queries PDS to fetch SSV for the user, instead of retrieving it locally.
By default, the switch remains disabled.
User Data Types SmPolicyData If this switch is enabled, PCRF-Core fetches SMPolicyData from nUDR. To configure the SMPolicyData attributes, see Table 7-49.
Operator Specific Data If this switch is enabled, PCRF fetches OperatorSpecificData (imported using Custom Schema) from nUDR. To configure the SMPolicyData attributes, see Table 7-50.
Ldap Data If this switch is enabled, PCRF-Core fetches user profile from LDAP through PDS. OCS Spending Limit If this switch is enabled, PCRF-Core fetches policy counters for a subscriber from 4G OCS. Irrespective of whether OCS is configured as primary datasource or on-demand datasource, this switch must be enabled to retrieve policy counters. To configure the OCS spending limit attributes, see Table 7-51.
Sh Data If this switch is enabled, PCRF-Core fetches user profile from 4G UDR. Note: Sh interface is not supported for Converged Policy mode of deployment.
The following table describes the SmPolicyData switches available in the Attributes column:
Table 7-49 SmPolicyData Attributes
Attribute Name Description Subscribe to Notify When this switch is enabled, PCRF Core subscribes with the UDR to get notified on changes in subscriber profile.
Note: When this switch is disabled, Usage Monitor feature cannot be tested. It will not be functional.
By default, this option is enabled.
Query User on Update Determines if user query from UDR on update is enabled. When this option is enabled, PCRF Core queries the UDR about the subscriber present in the CCR request or GX message by sending a GET request for “SmPolicyData” resource on the nudr-dr service.
Note: If
Subscribe To Notifyis enabled for PCRF Core, then PCRF services will not query the UDR during a Update requests.The PDS caches the subscriber profile when the “Subscribe To Notify” option is enabled, in that case, the PCRF core may not always reach the UDR when the subscriber profile is found in the local cache.
By default, this option is disabled.
Query User on Terminate Determines if user query from UDR on delete is enabled. When this option is enabled, PCRF Core queries the UDR about the subscriber present in the CCR request or the GX message by sending a GET request for “SmPolicyData” resource on the nudr-dr service.
Note: If
Subscribe To Notifyis enabled for PCRF Core, then PCRF service will not query the UDR during a Terminate requests.The PDS caches the subscriber profile when the “Subscribe To Notify” option is enabled, in that case, the PCRF Core may not always reach the UDR when the subscriber profile is found in the local cache.
By default, this option is disabled.Query User on Reauth Determines if user query from UDR on reauth is enabled. When this option is enabled, PCRF Core queries the UDR about the subscriber, when it receives a Reauthorization request, such as Rx or Policy Authorization request by sending a GET request for “SmPolicyData” resource on the nudr-dr service.
Note: The PDS caches the subscriber profile when the “Subscribe To Notify” option is enabled, in that case, the PCRF Core may not always reach the UDR when the subscriber profile is found in the local cache.
By default, this option is disabled.Auto Enrollment on UDR To specify whether to enable or disable the autoprovisioning of the subscriber profile at UDR when the subscriber profile is not available. Default-S-NSSAI To configure a default S-NSSAI, which will be used when a subscriber is auto-enrolled on the UDR. This parameter is applicable only when Auto-Enrollment on UDR is set to
true. The value configured here must match the Default S-NSSAI configured on UDR.The following table describes the Operator Specific Data switch available in the Attributes column:
Table 7-50 Operator Specific Data Attributes
Attribute Name Description Subscribe to Notify When this switch is enabled, PCRF Core subscribes to get notified of any changes in the profile.
By default, this option is true.
The OCS Spending Limit switches available in the Attributes column:
Table 7-51 OCS Spending Limit Attributes
Attribute Name Description Async Query When this switch is enabled, PCRF Core performs on-demand lookup of Policy Counters for a subscriber using the Fetch Policy Counters from OCS policy action.
By default, this option is disabled.
Enable force lookup on Update When this switch is enabled, the core services (PCRF Core and SM) sends OCS request skipping the PDS optimiziations. By default, this option is disabled.
- Under the Usage Monitoring group, update the
values for the fields, described in the following table:
Table 7-52 Usage Monitoring Settings
Field Name Description Enabled Specifies whether to enable or disable Usage Monitoring service for PCRF. By default, this switch is disabled.
APN List Specifies the list of APNs for which usage monitoring is enabled. If you leave this field empty, Usage Monitoring is enabled for all APNs. Attribute Forwarding Interface Type Indicates the interface type for which the profile applies. For more details on Attribute Forwarding Profiles, see Attribute Forwarding Profiles section in Usage Monitoring on Gx Interface.
Message Type Indicates the message type for which the profile applies. Forwarding Profile Refers to the configured Attribute Forwarding Profile. -
Under MCPTT group, apply the configurations to set the default ARP and default preemption control.
Table 7-53 MCPTT Settings
Parameter Description Default ARP Settings Priority Level Indicates the priority level.
Range: 1-15
Default Value: 1
Preemption Capability Indicates if the preemption cabaility is enabled or disabled. It can take the following values:
PREEMPTION_CAPABILITY_ENABLEDPREEMPTION_CAPABILITY_DISABLED
Default Value:
PREEMPTION_CAPABILITY_ENABLEDPreemption Vulnerability Indicates if the preemption vulnerability is enabled or disabled. It can take the following values:
PREEMPTION_VULNERABILITY_ENABLEDPREEMPTION_VULNERABILITY_DISABLED
Default Value:
PREEMPTION_VULNERABILITY_DISABLEDDefault Preemption Control Default Preemption Control info Includes the Default Preemption Control information:
LEAST_RECENT_ADDED_FLOWMOST_RECENT_ADDED_FLOWHIGHEST_BANDWIDTH_FLOW
Default Value:
LEAST_RECENT_ADDED_FLOW - Expand the Audit group, and update the values for the
fields described in the following table:
Table 7-54 Audit Group Settings
Field Name Description Enabled Determines whether to send registration request to Audit service or not. By default, this switch is enabled.
Notification Rate (per second) Defines the number of stale records which Audit service notifies to PCRF Core service in one second. Default and Recommended Value: 50
Note: To configure higher number than the recommended value, contact My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com)
Policy Association Age (in minutes) for Gx Session Defines the age of a Gx session after which a record is considered to be stale on PCRF Core and the PGW is queried for presence of such associations. Default Value: 1440
Policy Association Maximum Age (in minutes) for Gx Session Defines the maximum age of a Gx session after which a record is purged from PCRF Core database (Gx Session table) without sending further queries to PGW. Default Value: 2880
Minimum Audit Attempts for Gx session Specifies the minimum number of consecutive failed audit attempts until maxTTL / forceTTL is reached.
If maxTTL is reached and audit_attempts >= Minimum Audit Attempts for maxTTL, Audit service sends notification to PCRF Core service with maxTTL flag set to true. PCRF Core service triggers the TERMINATE (CCR-T) leg.
Range: 0-255
Default Value: 0
Note: If maxTTL is not reached and if audit attempts are reached, the number of audit attempts are incremented until maxTTL is reached.
Policy Association Age (in minutes) for Rx Session Defines the age of an Rx session after which a record is considered to be stale on PCRF Core. When the maxTTL flag is TRUE, Rx sessions are cleaned.
Note:The cleanup functionality is not implemented for Rx sessions, if themaxTTL flag is false
Default Value: 1440
Policy Association Maximum Age (in minutes) for Rx Session Defines the maximum age of an Rx session after which a record is purged from PCRF Core database (Rx Session table) without sending further queries to PGW. Default Value: 2880
Policy Association Age (in minutes) for Sd Session Defines the age of an Sd session after which a record is considered to be stale on PCRF Core. Default Value: 1440
Policy Association Maximum Age (in minutes) for Sd Session Defines the maximum age of an Sd session after which a record is purged from PCRF Core database (Sd Session table) without sending further queries to PGW. Default Value: 2880
Minimum Audit Attempts for Sd session Specifies the minimum number of consecutive failed audit attempts until maxTTL / forceTTL is reached.
If maxTTL is reached and audit_attempts >= Minimum Audit Attempts for maxTTL, Audit service sends notification to PCRF Core service with maxTTL flag set to true. PCRF Core service triggers the TERMINATE (CCR-T) leg.
Range: 0-255
Default Value: 0
Note: If maxTTL is not reached and if audit attempts are reached, the number of audit attempts are incremented until maxTTL is reached.
Minimum Audit Passes Interval (in minutes) Defines the time when next audit for the PCRF Core service table begins after delta time if auditing this table has been finished before this specified time. Default Value: 330
- Enter
the values for the input fields, available under the Pending
Transaction group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-55 Edit Pending Transaction Configurations
Field Name Description Enabled Specifies whether to enable or disable Pending Transaction. By default, this switch is disabled.
RAR Retry Backoff (in milliseconds) Indicates the time gap between the consecutive retry RAR messages when PGW is sending error response with cause of DIAMETER_PENDING_TRANSACTION and RAR message is triggered by PDS/AF/PRE. Default Value: 1000
RAR Retry Count Indicates the count for RAR messages when PGW is sending error response with cause of DIAMETER_PENDING_TRANSACTION and RAR message is triggered by Notification message from PDS/AF/PRE. Default Value: 2
User Notify Reauth Error Handling Indicates if an RAR initiated by User Notification message need to be discarded or retried when it is responded by P-GW with an error of DIAMETER_PENDING_TRANSACTION. Default Value: RETRY
AF Reauth Error Handling Indicates if an RAR initiated by AF message should be discarded or retried when it is responded by PGW with an error of DIAMETER_PENDING_TRANSACTION. Default Value: RETRY
Reauth Error Handling: Indicates if an RAR initiated by any message should be discarded or retried when it is responded by PGW with an error of DIAMETER_PENDING_TRANSACTION. Default Value: RETRY
- Perform the following steps to configure Advanced Settings that allows PCRF Core
to handle concurrent requests:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following keys and respective values:
The following tables describe the keys and values:Table 7-56 General
Key Default Value CONCURRENCY.ENABLED false Gx.DisableSupportedFeatures false Rx.DisableSupportedFeatures false DISTRIBUTE_GX_TRAFFIC_USING_TABLE_SLICING When this key is enabled, traffic for GxSessions are distributed across all the new tables. PCRF Core service will register the new tables with Audit Service and also distributes the new sessions to the new slices.
Default value: false
USER.ocsSpendingLimit.resetContextOnGxCreate When the value of this key is set to
true, PCRF Core setsresetContexttotruein PDS request reqParam for the first Gx session and PDS will revalidate the Sy session.Default value: false
sbi.timer.enabled When the value of this key is set totrue, PCRF-Core handles the following HTTP SBI headers at incoming and outgoing requests:- 3gpp-Sbi-Origination-Timestamp
- 3gpp-Sbi-Max-Rsp-Time
- 3gpp-Sbi-Sender-Timestamp
RESOURCEID.SUFFIX_LIST When both IMSI and GPSI keys are present in the request/session, and if bulwark.service.enabledis enabled for that request,RESOURCEID.SUFFIX_LISTsetting allows to choose the userID key(s) which will be sent to make the lock request.Possible values:
- " " (<empty string>): This is the default setting which sends IMSI key if available and GPSI key if available.
IMSI: If both IMSI and GPSI keys are present it will only send IMSI key.GPSI: If both IMSI and GPSI keys are present it will only send GPSI key.IMSI, GPSI: Same as empty string, this sends IMSI key if available and GPSI key if available
Default value: empty string
Table 7-57 Add Advanced Settings Configurations for Gx CCR-I
Key Default Value CONCURRENCY.GX.CREATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT 2 CONCURRENCY.GX.CREATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF 1000 CONCURRENCY.GX.CREATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION 2000 CONCURRENCY.GX.CREATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION 3000 CONCURRENCY.GX.CREATE.ENABLED True CONCURRENCY.GX.CREATE.ALLOW_ON_SERVICE_FAILURE True USER.ocsSpendingLimit.resetContextOnGxCreate false When the value of this key is true, the resetContext flag is set to true in PDS request reqParam for the first Gx session and PDS will revalidate the sy session.
USER.ocsSpendingLimit.createContextOnFailure If this flag is enabled the PCRF Core sends this as a request parameter toward PDS.
PDS creates a dummy context for OCS in case of getting error while performing OCS lookup. This will support the PDS when it receives notificaiton from UDR to fetch OCS data.
This is applicable for CCR-I and CCR-U messages with Asynchronous flow either set as true or false.
Default Value: false
USER.smPolicyData.createContextOnFailure If this flag is enabled the PCRF Core sends this as a request parameter toward PDS.
At PDS, if it receives an error during SmPolicyData-UDR lookup, then PDS creates a dummy context for SmPolicyData. This creation of dummy context helps, when PDS receives next request for a UDR lookup and this time it is successful, then both the sessions will have the latest SmPolicyData.
This is applicable for CCR-I and CCR-U Messages too.
Default value: false
USER.operatorSpecificData.createContextOnFailure If this flag is enabled the PCRF Core sends this as a request parameter toward PDS.
At PDS, if it receives an error during operatorSpecificData-UDR lookup, then PDS creates a dummy context for operatorSpecificData. This creation of dummy context helps, when PDS receives next request for a UDR lookup and this time it is successful, then both the sessions will have the latest operatorSpecificData.
This is applicable for CCR-I and CCR-U Messages too.
Default value: false
Table 7-58 Add Advanced Settings Configurations for Gx CCR-U
Key Default Value CONCURRENCY.GX.MODIFY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT 2 CONCURRENCY.GX.MODIFY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF 1000 CONCURRENCY.GX.MODIFY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION 2000 CONCURRENCY.GX.MODIFY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION 3000 CONCURRENCY.GX.MODIFY.ENABLED True CONCURRENCY.GX.MODIFY.ALLOW_ON_SERVICE_FAILURE True Table 7-59 Add Advanced Settings Configurations for Gx CCR-T
Key Default Value CONCURRENCY.GX.DELETE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT 2 CONCURRENCY.GX.DELETE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF 1000 CONCURRENCY.GX.DELETE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION 2000 CONCURRENCY.GX.DELETE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION 3000 CONCURRENCY.GX.DELETE.ENABLED True CONCURRENCY.GX.DELETE.ALLOW_ON_SERVICE_FAILURE True Table 7-60 Add Advanced Settings Configurations for Gx RAR
Key Default Value CONCURRENCY.GX.REAUTH.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT 2 CONCURRENCY.GX.REAUTH.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF 1000 CONCURRENCY.GX.REAUTH.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION 2000 CONCURRENCY.GX.REAUTH.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION 3000 CONCURRENCY.GX.REAUTH.ENABLED True CONCURRENCY.GX.REAUTH.ALLOW_ON_SERVICE_FAILURE True Table 7-61 Add Advanced Settings Configurations for SD TSR
Key Default Value CONCURRENCY.SD.CREATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT 2 CONCURRENCY.SD.CREATE.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_BACKOFF 1000 CONCURRENCY.SD.CREATE.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION 2000
CONCURRENCY.SD.CREATE.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION 3000 CONCURRENCY.SD.CREATE.ENABLED True CONCURRENCY.SD.CREATE.ALLOW_ON_SERVICE_FAILURE True Table 7-62 Bulwark Serivce Advanced Settings for Http Client and Request Timeout Configurations.
Key Default Value bulwark.service.enabled true BULWARK.REQUEST.URL http://10.75.241.7:30900/v1/locks BULWARK.REQUEST.TIMEOUT 3000 BULWARK.CONNECTION.HTTP2.ENABLED true BULWARK.CONNECTION.HTTP2.IDLE.TIMEOUT 600000 BULWARK.CONNECTION.HTTP2.CONNECT.TIMEOUT 3000 BULWARK.CONNECTION.HTTP2.MAX.CONNECTIONS.PER.DESTINATION 6 BULWARK.CONNECTION.HTTP2.MAX.REQUESTS.QUEUED.PER.DESTINATION 5000 BULWARK.CONNECTION.HTTP2.INITIAL.SESSION.RECV.WINDOW 16777216 Table 7-63 PDS Service Advanced Settings for Http Client and Request Timeout Configurations.
Key Default Value POLICYDS.REQUEST.URL http://localhost:8084/pds/v2/user-data POLICYDS.REQUEST.TIMEOUT 3000 POLICYDS.CONNECTION.HTTP2.ENABLED false POLICYDS.CONNECTION.HTTP2.IDLE.TIMEOUT 600000 POLICYDS.CONNECTION.HTTP2.CONNECT.TIMEOUT 3000 POLICYDS.CONNECTION.HTTP2.MAX.CONNECTIONS.PER.DESTINATION 6 POLICYDS.CONNECTION.HTTP2.MAX.REQUESTS.QUEUED.PER.DESTINATION 5000 POLICYDS.CONNECTION.HTTP2.INITIAL.SESSION.RECV.WINDOW 16777216 Table 7-64 PRE Service Advanced Settings for Http Client and Request Timeout Configurations.
Key Default Value Policy.PREEngineEnabled true PRE.REQUEST.URL http://localhost:5806/v1/policy/engine/pcrf-core PRE.REQUEST.TIMEOUT 2000 PRE.CONNECTION.HTTP2.ENABLED false PRE.CONNECTION.HTTP11.IDLE.TIMEOUT 600000 PRE.CONNECTION.HTTP11.CONNECT.TIMEOUT 3000 PRE.CONNECTION.HTTP11.MAX.CONNECTIONS.PER.DESTINATION 6 PRE.CONNECTION.HTTP11.MAX.REQUESTS.QUEUED.PER.DESTINATION 5000 PRE.CONNECTION.HTTP11.INITIAL.SESSION.RECV.WINDOW 16777216 Table 7-65 Binding Service Advanced Settings for Http Client and Request Timeout Configurations.
Key Default Value BindingService.Enabled true BINDING.REQUEST.URL http://localhost:8080/binding/v1 BINDING.REQUEST.TIMEOUT 3000 BINDING.CONNECTION.HTTP2.ENABLED false BINDING.CONNECTION.HTTP2.IDLE.TIMEOUT 600000 BINDING.CONNECTION.HTTP2.CONNECT.TIMEOUT 3000 BINDING.CONNECTION.HTTP2.MAX.CONNECTIONS.PER.DESTINATION 6 BINDING.CONNECTION.HTTP2.MAX.REQUESTS.QUEUED.PER.DESTINATION 5000 BINDING.CONNECTION.HTTP2.INITIAL.SESSION.RECV.WINDOW 16777216 Table 7-66 Usage Monitoring Service Advanced Settings for Http Client and Request Timeout Configurations.
Key Default Value USAGEMON.REQUEST.URL http://localhost:1080/occnp-usage-mon/v1/um-sessions USAGEMON.REQUEST.TIMEOUT 3000 USAGEMON.CONNECTION.HTTP2.ENABLED true USAGEMON.CONNECTION.HTTP2.IDLE.TIMEOUT 600000 USAGEMON.CONNECTION.HTTP2.CONNECT.TIMEOUT 3000 USAGEMON.CONNECTION.HTTP2.MAX.CONNECTIONS.PER.DESTINATION 6 USAGEMON.CONNECTION.HTTP2.MAX.REQUESTS.QUEUED.PER.DESTINATION 5000 USAGEMON.CONNECTION.HTTP2.INITIAL.SESSION.RECV.WINDOW 16777216 Table 7-67 Advanced Settings to exclude specific APNs for the User Data Types
Key Description USER.allDataTypes.excludeApns List the Access Point Names (APNs) for which all the requests or sessions from the PDS requests will be excluded for all the User Data Types (even if they are enabled).
The list can include the comma separated values.
Regular expressions are allowed for the APN names with the following conditions:- must not contain white spaces.
- must be case insensitive.
- can not be an empty string.
- '\' (backslash) must be specified as '/d'.
- the names must be separated only with commas (,).
USER.smPolicyData.excludeApns List the APNs for which all the requests or sessions from the PDS requests will be excluded for the given SmPolicyData (even if they are enabled).
USER.ldapData.excludeApns List the APNs for which all the requests or sessions from the PDS requests will be excluded for the given Ldap Data (even if they are enabled).
USER.ocsSpendingLimit.excludeApns List the APNs for which all the requests or sessions from the PDS requests will be excluded for the given OCS Spending Limit (even if they are enabled).
USER.operatorSpecificData.excludeApns List the APNs for which all the requests or sessions from the PDS requests will be excluded for the given Operator Specific Data (even if they are enabled).
Table 7-68 Advanced Key/Values for configuring congestion response codes
Key Value Description CONGESTION.HTTP.RESPONSE.CODE 503 Configure the response code of any rejected requests by PCRF Core service due to congestion state. By default, the service sends 503 as response code. If configured then it shall be 5xx only. PDS.NOTIFY.REQUEST.PRIORITY 18 Set request priority for post PDS notification request.
Allowed Values: 0-100
UM.NOTIFY.REQUEST.PRIORITY 18 Set request priority for post Usage monitoring notification request.
Allowed Values: 0-100
PCRF.SESSION.DELETE.REQUEST.PRIORITY 30 Set request priority for deleting PCRF session request.
Allowed Values: 0-100
PCRF.SESSION.GET.REQUEST.PRIORITY 30 Set request priority for fetching PCRF session request.
Allowed Values: 0-100
AUDIT.NOTIFY.REQUEST.PRIORITY 30 Set request priority for post Audit notification request.
Allowed Values: 0-100
Table 7-69 Advanced Key/Values for configuring congestion response codes
Key Value Description CONGESTION.USE.EXPERIMENTAL.RESULT.CODE false To set if user wants to use experimental result code when rejecting diameter messages. Allowed values are true or false. By default it will be false. CONGESTION.VENDOR.ID 0 To set the vendor id when user wants to send experimental response code. To use experimental result code, set CONGESTION.USE.EXPERIMENTAL.RESULT.CODEas true, and setCONGESTION.VENDOR.IDas non-zero positive integer.CONGESTION.DIAMETER.RESPONSE.CODE 3004 To set response code when rejecting diameter messages. Only valid 3xxx, 4xxx, 5xxx response codes are allowed. GX.CREATE.REQUEST.PRIORITY 24 Set message priority for Diameter message Gx CCR-I. If user provides invalid value then the default request priority shall be considered.
Allowed Values: 0-100
GX.MODIFY.REQUEST.PRIORITY 18 Set message priority for Diameter message Gx CCR-U. If user provides invalid value then the default request priority shall be considered.
Allowed Values: 0-100
GX.DELETE.REQUEST.PRIORITY 16 Set message priority for Diameter message Gx CCR-T. If user provides invalid value then the default request priority shall be considered.
Allowed Values: 0-100
RX.CREATE.REQUEST.PRIORITY 24 Set message priority for Diameter message Rx AAR-I. If user provides invalid value then the default request priority shall be considered.
Allowed Values: 0-100
RX.MODIFY.REQUEST.PRIORITY 18 Set message priority for Diameter message Rx AAR-U. If user provides invalid value then the default request priority shall be considered.
Allowed Values: 0-100
RX.DELETE.REQUEST.PRIORITY 16 Set message priority for Diameter message Rx STR. If user provides invalid value then the default request priority shall be considered.
Allowed Values: 0-100
SD.MODIFY.REQUEST.PRIORITY 18 Set message priority for Diameter message Sd CCR-U. If user provides invalid value then the default request priority shall be considered.
Allowed Values: 0-100
SD.DELETE.REQUEST.PRIORITY 16 Set message priority for Diameter message Sd CCR-T. If user provides invalid value then the default request priority shall be considered.
Allowed Values: 0-100
Table 7-70 Advanced Settings Configurations for handling the race condition between Gx and Sy over two sites for CCR-U.
Key Default Value DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RaceModeratorEnabled This is used to enable or disable race condition detection on CCR-U. If this flag is enabled, on detecting the race condition the following settings are used to decide the actions to take:- DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryOnRarRaceEventTriggers
- DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryAttemptsOnRarRace
- DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryWaitTimeOnRarRace
- DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RejectionErrorCodeOnRarRace
Supported values: true/false
Default value: false
DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryOnRarRaceEventTriggers If
DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RaceModeratorEnabledis true, then a validation is made for all of the EventTriggers in the CCR-U request that are also included in this setting.Note: There must be at least one
registeredHandlerpresent in the Gx session that will make use of this event.If the validation fails for at least one of them, then the CCR-U will be put on hold, read the session again, and retry based on these settings:- DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryAttemptsOnRarRace
- DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryWaitTimeOnRarRace
- DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RejectionErrorCodeOnRarRace
Supported values: These values can be provided as comma separated list.
Rx Triggers:- ACCESS_NETWORK_INFO_REPORT
- SUCCESSFUL_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION
- LOSS_OF_BEARER
Sd Triggers:- APPLICATION_START
- APPLICATION_STOP
Default value: ACCESS_NETWORK_INFO_REPORT
DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryAttemptsOnRarRace The maximum number of retries when
DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryOnRarRaceEventTriggersvalidation fails.Supported values: integer (0-n)
Default value: 1
DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryWaitTimeOnRarRace The amount of delay in milliseconds between retries when
DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryOnRarRaceEventTriggersvalidation fails.Supported values: integer (0-n)
Default value: 100
DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RejectionErrorCodeOnRarRace The error code response for the CCA-U when
DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryOnRarRaceEventTriggersvalidation fails, andDIAMETER.Gx.Update.RetryAttemptsOnRarRaceretries are exhausted.Supported values: Diameter Error codes- 5012 (DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY)
- 3002 (DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER)
Default value: 5012
Note: If invalid value is provided, fallback will be the default value 5012.
Table 7-71 Advanced Settings Configurations for handling the race condition between Gx and Sy over two sites for CCR-T.
Key Default Value DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RaceModeratorEnabled This is used to enable or disable race condition detection on CCR-T. If this flag is enabled, on detecting the race condition the following settings are used to decide the actions to take:- DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryOnRarRaceEventTriggers
- DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryAttemptsOnRarRace
- DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryWaitTimeOnRarRace
- DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RejectionErrorCodeOnRarRace
Supported values: true/false
Default value: false
DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryOnRarRaceEventTriggers If
DIAMETER.Gx.Update.RaceModeratorEnabledis true, then a validation is made for all of the EventTriggers in the CCR-T request that are also included in this setting.Note: There must be at least one
registeredHandlerpresent in the Gx session that will make use of this event.If the validation fails for at least one of them, then the CCR-T will be put on hold, read the session again, and retry based on these settings:- DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryAttemptsOnRarRace
- DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryWaitTimeOnRarRace
- DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RejectionErrorCodeOnRarRace
Supported values in comma separated list:
Rx Triggers:- ACCESS_NETWORK_INFO_REPORT
- SUCCESSFUL_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION
- LOSS_OF_BEARER
Sd Triggers:- APPLICATION_START
- APPLICATION_STOP
Default value: ACCESS_NETWORK_INFO_REPORT
DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryAttemptsOnRarRace The maximum number of retries when
DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryOnRarRaceEventTriggersvalidation fails.Supported values: integer (0-n)
Default value: 1
DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryWaitTimeOnRarRace The amount of delay in milliseconds between retries when
DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryOnRarRaceEventTriggersvalidation fails.Supported values: integer (0-n)
Default value: 100
DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RejectionErrorCodeOnRarRace The error code response for the CCA-T when
DIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryOnRarRaceEventTriggersvalidation fails, andDIAMETER.Gx.Terminate.RetryAttemptsOnRarRaceretries are exhausted.Supported values: Diameter Error codes- 5012 (DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY)
- 3002 (DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER)
Default value: 5012
Note: If invalid value is provided, fallback will be the default value 5012.
- Click the
- (Optional) To avoid sending stale session notification to PGW for
Gx sessions when maxTTL value is reached, user can add Override Cleanup
Audit parameter as AVP with its value set to true. To do so, perform the
following steps:
- Expand the Advanced Settings group
and click

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- On the Add Advanced Settings dialog box, enter the
follwing Keys and respective values:
Table 7-72 Add Advanced Settings Key and Value
Key Default Value Description DIAMETER.Cleanup.OverrideCleanupAudit True This parameter is used along with
maxTTLflag.If true along with
maxTTLis also true, deletes the Gx and Rx stale sessions and no notification is sent to PGW.If false, notification is sent to PGW and stale sessions are not deleted.
DIAMETER.ENF.DUPLICATE.UPDATE.MESSAGE.HANDLING false Specifies if the duplicate message handling feature should be enabled or disabled. DIAMETER.MsgBufferThreadCount 60 Specifies the number of threads to process read-diameter-messages. DIAMETER.MsgBufferQueueSize 8192 Specifies the size of the queue for holding pending read-diameter-messages. DIAMETER.AF.MaxAFReportHandler The minimum valid value for this parameter is 1.
The maximum valid value of this setting is defined according to the following criteria:- For an Rx session with 2 media components (Audio, video) and 2 media sub components for each media component, the maximum value allowed is 2.
- For an Rx session with 1 media component (Audio) and 2 media sub components, the maximum value allowed is 4.
Note:
To enable the feature flag, Enter the value as true in the Value field.Specifies the number of the Rx session to establish. Note: These minimum and maximum values are only valid with data compression disabled.
DIAMETER.ENF.AFDirectReply True Note: Allowed value True or False
If true, PCRF responds immediatly to AAR request with AAA answer to AF, and at the same time RAR request is sent to PGW.
If false, PCRF awaits until RAA is received from PGW and then responds with AAA answer to AF.
DIAMETER.AF.MaxWaitForInfoOnTermination 3000 milliseconds Note: Allowed value 0 - 10000 milliseconds.
The PCRF maximum wait time in milliseconds to receive the information from PCEF before responding to the AF with STR request. On not receiving the awaited information within the configured waiting period, PCRF resoponds to AF with successful STA answer without the requested information.
DIAMETER.AF.IgnorePartialCodec false It specifies wheather to ignore QoS calculation if the uplink and downlink codec values are received in separate Rx messages. For example, uplink codec data in AAR-I and downlink codec data in AAR-U.
POLICYDS_REQUEST_TIMEOUT 3000 milliseconds Note: Allowed value 0 - 10000 milliseconds.
The PCRF maximum wait time for receiving response from PDS. On not receiving the awaited information from PDS within the configured waiting period, PCRF times out.
DB.GX.DATA.ENCODING.Enabled false When the value of this key is set to true, PCRF Core gxsession data is encoded. The JSON parameters are encoded based on the version indicated byDB.GX.ENCODING.MAP.Versionvalue. IfDB.GX.ENCODING.MAP.Versionis not configured, its default version will be "gx0" and the parameter is encoded by default mapping.The PCRF Core gxsession data is decoded based version value in the session.
DB.RX.DATA.ENCODING.Enabled false When the value of this key is set to true, PCRF Core rxsession data encoding is enabled. The JSON parameters are encoded based on the version indicated byDB.RX.ENCODING.MAP.Versionvalue. IfDB.RX.ENCODING.MAP.Versionis not configured, its default version will be "rx0" and the parameter is encoded by default mapping.The PCRF Core rxsession data is decoded based version value in the session.
DB.SD.DATA.ENCODING.Enabled false When the value of this key is set to true, PCRF Core sdsession data is encoded. The JSON parameters are encoded based on the version indicated byDB.SD.ENCODING.MAP.Versionvalue. IfDB.SD.ENCODING.MAP.Versionis not configured, its default version will be "sd0" and the parameter is encoded by default mapping.The PCRF Core sdsession data is decoded based version value in the session.
DB.GX.ENCODING.MAP.Version 0 Indicates the mapping version name for gxsession encoding. To set this use a "unique string" such as "gx0". The encoding version is used for decoding. When value of this key is set to "0", or this key is not configured, the encoding/decoding uses default map.
DB.RX.ENCODING.MAP.Version 0 Indicates the mapping version name for rxsession encoding. To set this use a "unique string" such as "rx0". The encoding version is used for decoding. When value of this key is set to "0", or this key is not configured, the encoding/decoding uses default map.
DB.SD.ENCODING.MAP.Version 0 Indicates the mapping version name for sdsession encoding. To set this use a "unique string" such as "sd0". The encoding version is used for decoding. When value of this key is set to "0", or this key is not configured, the encoding/decoding uses default map.
DB.ENCODING.MAP.LIST 0 Indicates the mapping list keyMap and valueMap in JSON format. When this value is set to "0" the default map is referred for encoding and decoding.
To set this to cusomized map in the form of JSON format containing keyMap and valueMap.
enable.late.arrival Disabled Indicates whether the stale request cleanup functionality for PCRF Core is enabled or disabled. Default value: false
late.arrival.max.resp.time Specifies the maximum time (in miliseconds) to wait until the request is processed. skip.late.processing.for.terminate false
When enabled, PCRF-Core will not check if Terminate requests have gone stale.
- Click Save.
This saves the advanced settings and the details get listed on Edit Settings page under Advanced Settings.
- Expand the Advanced Settings group
and click
- Click Save.
The page saves the PCRF Core service settings.
7.3.8.2 Serving Gateway
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage serving gateways.
The Serving Gateway page allows you to create new and manage existing serving gateways. The page displays the list of defined serving gateways and provides the options to import, export, or add gateways.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations, click PCRF Core, and
then select Serving Gateway.
This opens the Serving Gateway page. The page lists the existing gateway details. You can add or import new serving gateways using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Service Gateway page.
- On the Create Service Gateway page,
enter the following information:
Table 7-73 Create Service Gateway
Field Name Description Name The customized name for serving gateway Description The customized description for serving gateway MCC-MNC The Mobile country code (3-digit number) or Mobile network code (2- or 3-digit number) Serving Gateway IP Address/Subnet IP address or subnet for the serving gateway - Click Save.
The serving gateway gets listed on the Serving Gateway page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the serving gateway.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the serving gateway.
Importing Serving Gateway
To import Serving Gateway:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.3.8.3 Network Element
This section describes how to configure network elements.
To access network elements configurations from CNC Console home page, under Policy, navigate to Service Configurations, click PCRF Core, and then select Network Elements.
7.3.8.3.1 PGW
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage PDN Gateway (PGW) network element.
The PGW page allows you to create new and manage existing PGWs. The page displays the list of defined PGWs with the options to import, export, or add profiles.
- From the navigation menu under
Network Elements, select
PGW.
This opens the PGW page. The page lists the existing PGWs. You can add or import new PGWs using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create PGW page.
- On the Create PGW page, enter the
following information:
Table 7-74 Create PGW
Field Name Description Name Use this field to add a customized name for PGW. Description/Location Use this field to add a customized description or location for network element. Backup Host Name/IP Address Registered domain name, or IP address in IPv4 or IPv6 format, assigned to the network element. Host Name/IP Address Alternate address that is used if communication between the CNC Policy and the primary address for the network element fails. Capability Specifies the capability for the network element. PGW network elements are compatible with usage_report event trigger value 26. Capacity Specifies the bandwidth allocated to the network element. IP Domain ID Specifies the IPv4 domain identity. This value uniquely identifies the network element if the same IPv4 address is assigned in multiple networks. Diameter Realm Specifies the realm to be sent in the diameter message. MIP6 Host Identity Specifies the Mobile IPv6 (MIPv6) host. Diameter Identity Specifies the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the network element - Click Save.
The PGW gets listed on the PGW page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the PGW.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the PGW.
Importing PGW
To import PGW:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.3.8.3.2 GGSN
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage PDN Gateway (GGSN) network element.
The GGSN page allows you to create new and manage existing GGSNs. The page displays the list of defined GGSNs with the options to import, export, or add profiles.
- From the navigation menu under
Network Elements, select
GGSN.
This opens the GGSN page. The page lists the existing GGSNs. You can add or import new GGSNs using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create GGSN page.
- On the Create GGSN page, enter the
following information:
Table 7-75 Create GGSN
Field Name Description Name Use this field to add a customized name for GGSN Description/Location Use this field to add a customized description or location for network element Backup Host Name/IP Address Registered domain name, or IP address in IPv4 or IPv6 format, assigned to the network element Host Name/IP Address Alternate address that is used if communication between the CNC Policy and the primary address for the network element fails Capability Specifies the capability for the network element. Usually, GGSN network elements are compatable with usage_report event trigger value 26 Capacity Specifies the bandwidth allocated to the network element IP Domain ID Specifies the IPv4 domain identity. This value uniquely identifies the network element if the same IPv4 address is assigned in multiple networks Diameter Realm Specifies the realm to be sent in the diameter message Diameter Identity Specifies the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the network element - Click Save.
The GGSN gets listed on the GGSN page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the GGSN.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the GGSN.
Importing GGSN
To import GGSN:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.3.9 Audit Service
This procedure provides information about configuring the Audit Service.
The Audit Service page displays the Audit Service configurations. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations, and select Audit Service.
This opens the Audit Service page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Audit Service page.
- Make sure that the value of the Audit Enabled switch is
enabled.
This field determines if auditing must be enabled for all the registered Policy services. By default, this switch remains disabled.
-
Expand the Forced Deletion group and configure the Minimum Audit Attempts parameter.
Minimum Audit Attempts specifies the minimum number of audit attempts until ForceTTL is reached.
If ForceTTL is reached and audit_attempts >= Minimum Audit Attempts of ForceTTL, then Audit service deletes the identified stale records from its respective database.
For example, it deletes the stale SM sessions from SMPolicyAssociation table.
The default value of this parameter is 0 and the value can range between 0 to 255.
- Click Save.
The page saves the Audit service configurations.
Note:
-
Perform the Audit configurations at the individual service level (SM service and Binding service), for Audit service and notifications to work appropriately.
Important considerations during Audit configurations:
In situations where the number of stale records (records that are eligible to be audited) at any given point of time in the system (for a given microservice database) is expected to be high (for example, > 1M), then the Policy Session Age and/or the Notification Rate parameters should be set appropriately such that at least 2 audit cycles can be finished before the records that were assessed by the first cycle fall stale again. The Audit procedure having a Policy Association Age less than this recommendation, may not be able to assess all stale records as the already assessed ones will be stale again too soon. It is recommended to keep a minimum of 24 hours for the Policy Association Age and a minimum of 48 hours for Max Policy Association Age.
The time taken to complete an Audit Cycle and begin the next one can be calculated as below:
Audit Cycle Time = S / (N*60) + I minutes, where,
S = expected number of stale sessions at any given time,
N = notification rate (per second),
I = minimum Audit Interval
-
When table slicing feature is enabled, and audit is running on a set of sliced tables, the audit notification rate would be expected to reach no of sliced tables * configured notification rate if audit is running for some/all the sliced tables concurrently.
Audit Schedule Data
Figure 7-14 Audit Scheduled Service List Data
Table 7-76 Audit Schedule Data Fields
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Name | Name of the service that had registerd for audit service. |
| Table Name | Name of the database table that has requested for the audit service |
| Next Schedule | Next schedule availability time |
| Status | Scheduler job status |
| Start Time | Audit start time of pod. |
| End Time | Audit end time of pod. |
| Last Polled Time | Pod and associated scheduler details. |
| Schedular Details | Last time at which pod updated this table. |
| Is Service Dependent | If this is true, notification will be triggered for one table in the service, for all table’s in the service, notifications will be sent parallelly based on the notificationRate set for each table. |
| Priority | Priority set by customer to audit certain records or group of records in some order |
| Version | For JPA optimization |
Audit Schedule task can be in one of the state described below:
Figure 7-15 Audit Schedule Job Work Flow
Table 7-77 Audit Schedule Job Status
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| QUEUED | When a registered request is received it is added to the schedule table, the job status is set to Queued. |
| INITIALISING | When polling task is complete and is initialising for AuditTaskManager to audit, the job status is set to Initialising. |
| RUNNING | When Audit task manager starts the task, the job status is set to Running. |
| COMPLETE | When Audit TaskManager completes the Audit, the status is set to Complete. |
| INTERRUPTED |
When the audit process is paused from GUI, then the job status is set to Interrupted. When resumed from GUI, job status is set to Queued When deregistered, the job data will be removed from the table. when a service is register, it is set to Queued. |
| DEREGISTERED |
When deregistered, the job status is set to Deregistered for Initialising or Running and the entry will be deleted for any other status(except Initialising or Running). In case the a service register request is received before AuditTaskManager deletes the table entry for deregistered job statuses, the status would be moved to Queued. |
For more information on Audit Service and Audit Schedule REST API details, see the section Audit Service in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy REST Specification Guide.
7.3.10 Configuring Notifier Service
This section provides information on how to configure Notifier service.
7.3.10.1 Notifier Configurations
This procedure provides information about managing Notifier Service Settings.
The Notifier Service Settings page allows you to edit Advanced Settings for Notifier service.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Service
Configurations, click Notifier, and
then select Notifier Configurations.
This opens the Notifier Service Settings page.
-
Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Notifier Service Settings page.
-
Edit the SMPP Configuration:
Table 7-78 SMPP Configuration
Attribute Name Description Enable SMPP Enables the Subscriber Notification using SMPP Protocol.
Default Value: false
Default SMS Gateway Group All the SMS Gateways that are created in SMS GATEWAY CONFIGURATION page.
ESME Source Address External Short Messaging Entity (ESME) Source Address.
By default this field is empty.
ESME Source Address TON Indicates the ESME Source address type of number:- UNKNOWN
- INTERNATIONAL
- NATIONAL
- NETWORK_SPECIFIC
- SUBSCRIBER_NUMBER
- ALPHANUMERIC
- ABBREVIATED
Default Value: UNKNOWN
ESME Source Address NPI ESME Source Address Number Plan Indicator:- UNKNOWN
- ISDN (E163/E164)
- DATA (X, 121)
- TELEX
- LAND_MOBILE
- NATIONAL
- PRIVATE
- ERMES
- INTERNET
- WAP
Default Value: UNKNOWN
Connection Timeout (in milliseconds) Indicates the SMS Gateway Connection Timeout in milliseconds.
Range: 1-60000
Default Value: 30000
Response Timeout (in milliseconds) Indicates the timeout (in milliseconds) for the response going towards SMS Gateway.
Range: 1-60000
Default Value: 10000
- Click Add to add the advanced settings.
Table 7-79 Advanced Settings
Key Value smpp.bindType Bind type of the SMPP server.
Allowed values:- BIND_TX
- BIND_RX
- BIND_TRX
Default value: BIND_TRX
smpp.systemType System type. This key can accept null values.
smpp.addrTon Address type of number of the SMPP server. Allowed values:- UNKNOWN
- INTERNATIONAL
- NATIONAL
- NETWORK_SPECIFIC
- SUBSCRIBER_NUMBER
- ALPHANUMERIC
- ABBREVIATED
Default value: UNKNOWN
smpp.addrNpi Address Number Plan Indicator: - UNKNOWN
- ISDN (E163/E164)
- DATA (X, 121)
- TELEX
- LAND_MOBILE
- NATIONAL
- PRIVATE
- ERMES
- INTERNET
- WAP
Default value: UNKNOWN
smpp.addrRange Set of SME addresses.
Address range can accept null values.smpp.serviceType Service type can be either null or CMT. smpp.encodingScheme SMPP Encoding Scheme. Default value: UTF-8
smpp.destAddrTon Destination address type of number: - UNKNOWN
- INTERNATIONAL
- NATIONAL
- NETWORK_SPECIFIC
- SUBSCRIBER_NUMBER
- ALPHANUMERIC
- ABBREVIATED
Default value: UNKNOWN
smpp.destAddrNpi Destination Address Number Plan Indicator: - UNKNOWN
- ISDN (E163/E164)
- DATA (X, 121)
- TELEX
- LAND_MOBILE
- NATIONAL
- PRIVATE
- ERMES
- INTERNET
- WAP
Default value: ISDN
smpp.validatePeriodInDays Validity period of the SMS (in days) Default value: 3 days
smpp.esmClassValue The message mode and type, indicating any special message attributes associated with the SMS.
Default value: 0
smpp.reconnectMinDelayMillis Minimum delay in milliseconds after the consumer/producer tries to reconnect to the SMSC, after the connection was lost. Default value: 500
smpp.reconnectMaxDelayMillis Maximum delay in milliseconds after the consumer/producer tries to reconnect to the SMSC, after the connection was lost. Default value: 10000
smpp.smDefaultMsgId Short message default message identifier. Default value: 0
smpp.protocolId Protocol ID. Default value: 0
smpp.priorityFlag Priority Flag. Default value: 0
smpp.packedGSM7Encoding Indicates whether to apply GSM-7 character encoding. Default value: false
smpp.sarSegmentSize SMS Segment size. Default value: 134
- Click Save to save the advanced
settings.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
- Click Save to save the Notifier Service
Settings.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
7.3.10.2 Notification Server
7.3.10.2.1 HTTP Server
This procedure provides information on how to add and manage HTTP Server.
The HTTP Server page allows you to add and edit HTTP servers.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Service
Configurations, click Notifier, click
Notification Server, and then select HTTP
Server.
This opens the HTTP Server page.
-
Click Add.
This opens the Add HTTP Server page.
- Enter values for the following input fields, as described in the
following table:
Table 7-80 Add HTTP Server
Field Name Description Name Enter the name of the HTTP server. The name can only contain the characters A through Z, a through z, 0 through 9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_).
Description/Location Free-form text that identifies the HTTP server within the network. Enter up to 250 characters. Scheme Select the scheme. The available values are: - HTTP
- HTTPS
Host Enter the Host Name of the HTTP server. Alt Host Enter the Alternate Host Name of the HTTP server. URI Path Enter the URI path. HTTP Version Select the HTTP version. The available values are: - 1.1
- 2
HTTP Header Header Key Enter the header key. Header Value Enter the value for the header key. - Click Save. The HTTP server is displayed on
the HTTP Server page.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
Use pencil icon or trash bin icon available in the next column to edit or update the created HTTP server.
7.3.10.2.2 SMS Gateway Group
The SMS Gateway Group page allows you to configure the SME Gateways.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Service
Configurations, click Notifier, click
Notification Server, and then select SMS
Gateway Group.
This opens the SMS Gateway Group page.
-
Click Add.
This opens the Add SMS Gateway Group page.
- Enter values for the following input fields, as described in the
following table:
Table 7-81 Add SMS Gateway Group
Field Name Description Name Enter the name of the SMS Gateway server. The name can be Maximum 40 characters consisting of alphabets, numbers, period, hyphen and underscore (_).
By default, the value is left empty.
Description Free-form text that identifies the SMS Gateway server within the network. Enter up to 250 characters. By default, the value is left empty.
Primary SMSC Host Enter the Host Name of the primary SMSC Host server. By default, the value is left empty.
Request Delivery Receipt Specify the mode of delivery receipt.
This field accepts the following integer values:- 0 to indicate REQUEST_DELIVERY_RECEIPT_NO
- 1 to indicate REQUEST_DELIVERY_RECEIPT_SUCCESS_FAILURE
- 2 to indicate REQUEST_DELIVERY_RECEIPT_FAILURE
Default Value: 0
Maximum Byte Length Maximum number of bytes allowed for the message.
The length of the message can range between 1 to 254 bytes.
Default Value: 140
Long Message Enabled Enables the long messages.
Default Value: true
Long Message maximum Byte Length Specifies the maximum number of bytes allowed in the long message.
Maximum length of the long messages can range between 1 to 999 bytes.
Default Value: 500
For details on the long message scenarios, see Long Message Scenarios
Long Message Delivery Method Specify the long message delivery method. It can take the following integer values: - 0 to indicate SEGMENTATION AND REASSEMBLY (SAR) to deliver the long messages in segments
- 1 to indicate the MESSAGE_PAYLOAD to deliver the long messages in payload
Default Value: 0
Truncate Long Messages Indicates whether to truncate messages longer than the specified length.
Default Value: false
Fail Max Message Size Specify the maximum length of the message after which the message fails.
Default Value: true
Table 7-82 Long Message Scenarios
Scenario Fail Max Message Size Long Message Enabled Truncate Long Messages Result Message with 165 charactersLength > 140 and < 254 Enabled Disabled Disabled - Message failed with cause: SmsLengthExceeded
- "message":"rejecting message because longMsgEnabled: false, messageLen: 165 > maxBytesLen: 140, failMsgOnMaxMsgSize: true",
Message with 165 charactersLength > 140 and < 254 Disabled Disabled Disabled Message has been successfully sent to the SMSC server without any error. Message with 260 characters Length > 140 and > 254 Disabled Disabled Disabled - Messaged failed with cause: SmsLengthExceeded
- "message":"rejecting message because longMsgEnabled: false, messageLen: 140 > 254, truncateOnLongMsg: false"
Message with 165 characters Length > 140 and < 254 Disabled Disabled Enabled Message has been truncated to 140 characters and sent to the SMSC server without any error. Message with 260 charactersLength > 140 and > 254 Disabled Disabled Enabled Message has been truncated to 140 characters and sent to the SMSC server without any error. - Click Save. The SMS Gateway details are
displayed on the SMS Gateway Group page.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
-
You can use pencil icon or trash bin icon available in the next column to edit or delete the created SMS Gateway server.
7.3.10.2.3 SMSC Host Info
The SMSC Host Info page allows you to add and edit SMSC host configuration.
- From the navigation menu, under Policy, click
Service Configurations, click
Notifier, click Notification
Server, and then select SMSC Host Info.
This opens the SMSC Host Info page.
-
Click Add.
This opens the Add SMSC Host Info page.
- Enter values for the following input fields, as described in the
following table:
Table 7-83 Add SMSC Host Info
Field Name Description Name Enter the name of the SMSC Host server. The name can be lower case alphanumeric characters, '-' or '.', and must start and end with an alphanumeric character.
By default, the value is left empty.
SMSC Host Enter the Host Name of the SMSC server. The host can be Ipv4, Ipv6 or FQDN with optional port value.
By default, the value is left empty.
SMSC Port Enter the Port number of the SMSC server. Range: 0-65535
By default, the value is left empty.
- Click Save. The SMSC Host server is
displayed on the SMSC Host Info page.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
Use pencil icon or trash bin icon available in the next column to edit or delete the SMSC Host details.
7.3.11 PDS
This section includes the Policy Data Service (PDS) configurations.
To access PDS configurations from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Service Configurations and select PDS.
- PDS Settings
- PDS Workflow
7.3.11.1 PDS Settings
This procedure provides information about configuring the PDS settings.
The PDS Settings page under PDS displays the PDS settings. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations, click PDS, and then
select PDS Settings.
This opens the PDS Settings page. The page displays the existing settings for PDS.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit PDS Settings page.
- Expand the Remote Subscriber State Variable Root Path
group.
Remote Subscriber State Variable Root Path defines the root path of the remote subscriber state variables block corresponding to each datasources. For example, SMPolicyData, AMPolicyData, OperatorSpecificData, UEPolicyData, SpendingLimitData, and so on.
For information about subscriber state variables block, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy Design Guide. This information is written back (PATCH Request) to UDR as soon as the values are updated or when the last session of the subscriber terminates.
- Under the Remote Subscriber State Variable Root Path
group, enter values for the following parameters:
Table 7-84 Remote Subscriber State Variable Root Path Group Settings
Field Name Description SM Policy Data Defines the path of subscriber state variables under SMPolicyData. You can provide multiple paths separated by commas.
UE Policy Set Defines the path of subscriber state variables under UEPolicyData. You can provide multiple paths separated by commas. Enable End Session SSV Remote to UDR Determines if the dynamic write should happen at time of policy execution or at the end of the last session for subscriber. Figure 7-16 PDS Settings: Remote Subscriber State Variable Root Path

Figure 7-17 Sample UE Policy Set Configured

- Expand the Common group and enter values for the following parameters:
Table 7-85 Common Group Settings
Field Name Description Enable HTTP2 If this switch is enabled, the HTTP2 remains enabled. By default, the switch remains disabled. Request Timeout If PDS Setting is updated then set the timeout as 3000 for the initial flow to succeed. Type of Search Specifies a key preference for PDS search query used to look up for a Pdsprofile record. The value can be Multi-UE ID Search or Preferential Search . When Multi-UE ID Search is selected the search query uses OR criteria and the search time will be higher. When Preferential Search is selected, Preference Order field is displayed. By default, the value for this parameter is set to Multi-UE ID Search.
Preference Order Specifies a list of PDS search indexes that user can select in any order of their preference. From drop-down menu, user can select from: SUPI, GPSI, GPSI/SUPI, SUPI/GPSI. If the PDS search happens using the search key SUPI, it will look up for Pdsprofile record based on SUPI. In case the request does not have SUPI, the request will be rejected.
If the PDS search happens using the search key SUPI/GPSI, it will look up for Pdsprofile record based on SUPI. In case the request does not have SUPI, it will use GPSI as the search index.
Note: If Preferential Search is selected, but Preference Order is not set, then default preference order will be: GPSI,SUPI.
Enable Fetch and Resubscribe If this switch is set to true, PDS refetches the data and revalidates the subscription when the number of sessions exceeds the configured limit at PDS. PDS revalidates each subsequent request received after the configured limit. If the revalidation is successful, PDS does not perform any further action. However, if PDS fails to revalidate subscriptions (with error status 404), then it resubscribes with the datasource.
By default, the value for this parameter is set to false.
For
smPolicyData, the limit for the number of sessions is defined per SNSSAI:DNN.Note: For user data type
smPolicyData, the attributes Include Snssai in User Query and Include Dnn in User Query on the PCF Session Management page must be set to false.For
spendingLimitData, the limit is defined per DNN:SNSSAI.Data Compression Scheme Specifies the data compression scheme used by PDS. Following are the allowed values for this field: - Disabled
- Zlib_Compressed
By default, this value remains disabled.
When the Enable Fetch and Resubscribe switch is set to true, you are required to configure the parameters described in this table.Table 7-86 Session Count per DNN/APN List Settings
Field Name Description DNN Displays the Data Network Name. The allowed expression for DNN is [^[A-Za-z0-9-.]+$] and NA. Note: Do not add spaces to this field.
SST Displays the Slice or Service Type name in the S-NSSAI. You can enter a number from 0 to 255 or NA. SD Displays the Slice Differentiator Name. The allowed expression for SD is ^([A-Fa-f0-9]+|NA)$. Note: Do not add spaces or any other characters to this field.
Max Sessions Count Displays the number of sessions after which PDS refetches and revalidates subscriptions. You can enter a number from 1 to 20. - Under the Audit group, enter values for the following parameters:
Table 7-87 Configurable Parameters for Audit group
Field Name Description Enabled Determines whether to send registration request to Audit service or not. Default Value: false
Notification Rate (per second) Defines the number of stale records which Audit service notifies to PDS service in one second. Default and Recommended Value: 50
Note: To configure higher number than the recommended value, contact My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com)
Subscriber Session Age (in minutes) Defines the age of PDS subscriber entry after which a record is considered to be stale on Policy and services (SM, AM, UE, and PCRF Core) are queried for presence of such associations. Default Value: 1500
Subscriber Session Max Age (in minutes) Defines the age of PDS subscriber entry after which a record is purged from the database and no query requests are sent to services for presence of such associations. Default Value: 2940
Subscriber Min Audit Pass Interval (in minutes) Defines the minimum interval between start times of two consecutive audit passes for the pdssubscriber table. Default Value: 390
PDS Profile Age (in minutes) Defines the age of PDS profile (GPSI-SUPI-NAI mapping) after which the profile is considered to be stale in Policy and PDS subscriber table is queried for presence of such associations. Default Value: 4500
PDS Profile Max Age (in minutes) Defines the age of PDS profile (GPSI-SUPI-NAI mapping) after which the profile is purged from the database without sending any queries to PDS subscriber table. Default Value: 8820
PDS Profile Min Audit Pass Interval (in minutes) Defines the minimum interval between start times of two consecutive audit passes for the pdssubscriber table. Default Value: 1170
Note:
At the time of fresh installation, check and save PDS settings configuration even if there is no change to the configuration.- Click Edit.
- Update the values if required.
- Click Save (even if there is no change to the configuration).
The Audit Service starts auditing with the default/updated configuration.
- Perform the following steps to configure Advanced
Settings that allows PDS to handle concurrent requests:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following keys and respective values:
Table 7-88 Parameters for Advanced Settings
Keys Value NOTIFICATION_DATA_COMPARE_FLAG When enabled, this flag compares the incoming notification content with existing data in the database for a subscriber. If there is any change identified, PDS notifies the context owner, otherwise notification will not be forwarded to core service (context-owner).
Default Value:
falseCONCURRENT_REQUEST_GUARD_TIME On receiving resetContext flag for a resource from core-service, PolicyDS keeps the association per subscriber resource that are within the time period (in milliseconds). Any other associations which are beyond this time period are cleaned up. Default Value: 10000 milisec
Note: When Usage Monitoring feature is enabled and Concurrency Control is enabled in Usage Monitoring settings, set the value of CONCURRENT_REQUEST_GUARD_TIME=0.
OPTIMISTIC_RETRY_MAX_ATTEMPT In case of concurrent DB transactions, if DB operation failed then for these many number of times the DB operation can be re-attempted. Default Value: 2
ACTION_ON_SSV_REMOTE_IN_REVALIDATION_OR_NOTIFICATION Used to control the behavior (IGNORE/OVERRIDE) of Subscriber Remote section during:- revalidation of subscription for N+ sessions
- UDR notification
This parameter can take the following values:- OVERRIDE: To override the Subscriber Remote section if Revalidation limit reached and a new SM data is received.
- IGNORE: To retain/preserve old Subscriber Remote section even if the Revalidation limit is reached and a new SM data is received.
Default Value: OVERRIDE
PDS_SEARCH_USING_All_UEIDS Used when typeOfSearch field is set to Preferential Search. When set to true, the preference order will be ignored. PDS will use all the UE Ids available in the request as search indexes and use them one by one to search for Pdsprofile record.
Default Value: false
Note: When typeOfSearch field is set to Multi-UE Id search this configuration is not considered.
CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_ENABLED_FOR_CHF_NOTIFICATION Determines whether to enable Bulwark service for CHF notification flow.
Default Value: false
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT_FOR_CHF_NOTIFICATION The number of retries when a request to Bulwark service fails for CHF notification flow.
Default Value: 3
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION_FOR_CHF_NOTIFICATION Duration in (milliseconds) for which the lock can be held for CHF Notification.
Default Value: 2000 (ms)
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION_FOR_CHF_NOTIFICATION Duration in (milliseconds) for which the CHF can wait to acquire a lock once it sends a request to Bulwark service.
Default Value: 3000 (ms)
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_KEY_TYPE_FOR_CHF_NOTIFICATION Determines the key value that is used to acquire the lock for CHF Notification.
Default Value: SUPI
CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_ENABLED_FOR_OCS_NOTIFICATION Determines whether to enable Bulwark service for OCS notification flow.
Default Value: false
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT_FOR_OCS_NOTIFICATION The number of retries when a request to Bulwark service fails for OCS notification flow.
Default Value: 3
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION_FOR_OCS_NOTIFICATION Duration in (milliseconds) for which the lock can be held for OCS Notification.
Default Value: 2000 (ms)
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION_FOR_OCS_NOTIFICATION Duration in (milliseconds) for which the OCS can wait to acquire a lock once it sends a request to Bulwark service.
Default Value: 3000 (ms)
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_KEY_TYPE_FOR_OCS_NOTIFICATION Determines the key value that is used to acquire the lock for OCS Notification.
Default Value: SUPI
CONCURRENCY.BULWARK_ENABLED_FOR_UDR_NOTIFICATION Determines whether to enable Bulwark service for UDR notification flow.
Default Value: false
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT_FOR_UDR_NOTIFICATION The number of retries when a request to Bulwark service fails for UDR notification flow.
Default Value: 3
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION_FOR_UDR_NOTIFICATION Duration in (milliseconds) for which the lock can be held for UDR Notification.
Default Value: 2000 (ms)
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION_FOR_UDR_NOTIFICATION Duration in (milliseconds) for which the UDR can wait to acquire a lock once it sends a request to Bulwark service.
Default Value: 3000 (ms)
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_KEY_TYPE_FOR_UDR_NOTIFICATION Determines the key value that is used to acquire the lock for UDR Notification.
Default Value: SUPI
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_REQUEST_RETRY_COUNT The number of retries when a request to Bulwark service fails.
Default Value: 3
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_LEASE_DURATION Duration for which lock is held once it is acquired. After this duration, the lock will be released automatically.
Default Value: 6000 (ms)
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_WAIT_DURATION Duration for which the Policy service will wait for the response to get a lock. The same duration is used by Bulwark service to poll for the lock if a lock is not available.
Default Value: 3000 (ms)
BULWARK_ERROR_CODES Error codes from Bulwark Service for which Notification can be rejected by PDS.
ENABLE_CUSTOM_ATTRIBUTES_IN_UDR_NOTIFICATION Determines whether to disable customAttributes in UDR-Notification. That is:
If the value of the key is
true, UDR notification with unmapped variables parsed inside customAttributes are forwarded to core service.If the value of the key is
false, UDR notification with unmapped variables are forwarded to core service as it is received from UDR, without customAttributes.Default value:
trueNote: For PCRF Core to forward the custom attributes to Usage Monitoring service, you must set the value of ENABLE_CUSTOM_ATTRIBUTES_IN_UDR_NOTIFICATION to
false.CREATE_PDSPROFILE_ON_REQUESTPC Determines whether to create a PDS profile if it is not present.
If the value is
true, create request is sent if PDS Profile is empty.If the value is
false, delete request is sent if PDS Profile is empty.Default value:
truePDS_ERROR_HANDLER_ENABLED This flag enables error handling library integration with PDS service. Default Value: false
UPDATE_SSV_DATASOURCE_INFO_ON_CHANGE This flag is used to avoid additional database operations (SEARCH and UPDATE) required to update the latest data source information received in the PATCH response.
Possible values:true: PDS updates the latest data source information in the database received in the PATCH response for SSV entry.false: PDS skips updating the latest data source information in the database received in the PATCH response.
When the value of this key is set to
true, this flag updates SSV's subscription information following each PATCH call. The PATCH call returns updated subscription information.Default value:
falseUSER.ocsSpendingLimit.resetContextOnGxCreate When the value of this key is set to
true, PCRF Core setsresetContexttotruein PDS request reqParam for the first Gx session and PDS will revalidate the Sy session.Default value:
falseUDR_FETCH_RELATED_RESOURCE This flag fetches related UDR resource and forwards to UDR connector. Default Value: false
NOTIFY_PCF_SM_ON_SUBSCRIPTION_FAILURE Indicates whether to notify the SM service if there is a subscription failure.
Default Value: true
NOTIFY_PCF_UE_ON_SUBSCRIPTION_FAILURE Indicates whether to notify the UE Policy service if there is a subscription failure.
Default Value: true
NOTIFY_PCF_AM_ON_SUBSCRIPTION_FAILURE Indicates whether to notify the AM service if there is a subscription failure.
Default Value: true
SUBSCRIPTION_FAILURE_NOTIFICATION_DELAY Indicates the delay for the initial subscription failure notification (in milliseconds).
Default Value: 3000
SUBSCRIPTION_FAILURE_NOTIFICATION_RETRY_COUNT Indicates the retry count for subscription failure notification (if value is 3 then maximum 3 calls will be done including first web call).
Default Value: 3
SUBSCRIPTION_FAILURE_NOTIFICATION_RETRY_DELAY Indicates the delay between retry of subscription failure notification.
Default Value: 3000
PDS_NOTIFY_USER_DATA_REQUEST_PRIORITY Set request priority for Notify user data requests.
Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 18
PDS_GET_DEFAULT_WORKFLOW_REQUEST_PRIORITY Set request priority to default PDS workflow request.
Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 30
PDS_GET_USER_DATA_REQUEST_PRIORITY Set request priority to fetch User data request.
Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 18
PDS_UPDATE_USER_DATA_REQUEST_PRIORITY Set request priority to update User data for request.
Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 18
PDS_DELETE_USER_DATA_REQUEST_PRIORITY Set request priority to delete User data request.
Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 16
PDS_AUDIT_NOTIFY_REQUEST_PRIORITY Set request priority to Audit notify request.
Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 27
CONGESTION_RESPONSE_CODE Configure the response code of the rejected requests by PDS due to congestion state. By default, PDS sends 503 as response code. If configured then it shall be 5xx only. Allowed Values: 5xx
Default Value: 503
ENABLE_STACK_TRACE_FOR_DB_OPS This flag helps to prevent the flooding of stack trace logs in case of Optimistic exception or other DB exceptions. When this flag is enabled, it prints the complete exception stack trace.
When this flag is disabled, it prints the exception message rather than the complete stack trace.
Default Value: false
CONCURRENCY.LOCK_RETRY_MODE Indicates whether the lock retry must be triggered under PDS.
Possible valures are:- CLIENT_ONLY: lock retry is triggered only in client services.
- SERVER_ONLY: lock retry is triggered only in bulwark.
- CLIENT_AND_SERVER: lock retry is triggered by both server and client.(server will retry to acquire the lock till the lockWaitTimeout is expired and client will retry after the configured request backOff timer is expired)
- Consumer services's advance settings should be updated with the non-zero lockWaitTimeOut.
PRIMARYKEY_LOOKUP_ENABLEDFoot 1 When this flag is enabled, PDS performs primary key based search in its DB during delete, query on update and query on terminate call flows.
Currently, this is supported for AM, UE and PCRF Core services only.
Note: When this flag is enabled, it is suggested to enable Bulwark in the core services to get the better performance and reduce concurrency.
Default Value: false
CONCURRENCY_DETECTION_CURRENT_FLOW_ENABLED This flag is used only when
PRIMARYKEY_LOOKUP_ENABLEDflag is enabled. If not then the optimistic merge is performed in the existing call flow.When this flag is enabled, PDS ensures concurrency handling using optimistic merge in the existing call flow.
When this flag is disabled, PDS handles the optimistic merge in the subsequent create/notify call flows.
Default Value: false
USE_SAVE_METHOD_TO_INSERT When this flag is enabled, JPA uses save instead of saveAll to improve the performance.
Default Value:
trueENABLE_PDS_PROFILE_ENTITY_DELETE When this flag is disabled, PDS DB profile deletion is not be done when all the sessions are deleted, instead audit service handles its deletion.
Default Value:
trueNOTIFICATION_RETRY_COUNT The number of tries performed by PDS to respective context owner for PDS location information notification after optimistic merge in case of non 2xx and non 404.
Default Value:
3NOTIFICATION_RETRY_DELAY The delay between the retries performed for PDS location information notification to the context owners. The delay value is provided in milliseconds.
Default Value:
3000Footnote 1
Note:
Assumptions/Limitations, when PRIMARYKEY_LOOKUP_ENABLED is enabled:- When the revalidation fails in the subsequent create requests and if the entry is deleted in the PDSSUBSCRIBER table, the older associations in core services for that user are not updated with latest PDS Location Information.
- SSV-GET and SSV-UPDATE request triggered by N1N2 Notification from UE service does not handle the pds location information header.
- If parameters,
PRIMARYKEY_LOOKUP_ENABLEis enabled andCONCURRENCY_DETECTION_CURRENT_FLOW_ENABLEDis disabled, then the concurrency handling/optimistic merge gets triggered in the subsequent CREATE requests and not for REQUEST-PC.
- Click the
- Click Save.
The page saves the PDS settings.
7.3.11.2 PDS Workflow
Using the PDS Workflow page, you can alter the behavior of PDS to suit the network requirements where you are deploying Policy. This page displays the call flow, depending on the value you select for Workflow type and the mode of deployment.
On upgrading to Policy, the system comes up with the default workflow.
- On the PDS Workflow page, click Edit.
- Select any of the following values from the drop-down list:
Table 7-89 Workflow Type
Value Description Default On selecting this option, the default PDS behavior applies. Charging Profile selection based on User Profile On selecting this option, you can configure whether to select user profile from LDAP or UDR. Note: For Sy selection per subscriber on the basis of LDAP attribute, select the value LDAP for user profile.
Charging Profile selection based on Notification On selecting this option, you can configure to select user profile based on Notification from UDR. Datasource selection based on PRE On selecting this option, you can configure to select datasource based on PRE. Custom For a custom workflow, contact Oracle Policy engineering team and paste the workflow in JSON format provided by the team. Figure 7-18 PDS Workflow
- Click Save to save your updates.
7.3.12 Binding Service
This procedure provides information about configuring the Binding Service.
The Binding Service Configuration page displays the configurations for the Binding Service. You can edit the existing configurations using this page.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Service
Configurations, and select Binding
Service.
This opens the Binding Service Configuration page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Binding Service Configuration page.
- Check the default configuration for all the fields
in all groups and edit as necessary.
The following table describes the input fields displayed under each group:
Table 7-90 Edit Binding Service Configuration
Field Name Description BSF Enabled Determines if BSF is enabled or disabled. When the the value of the Binding Operation field is set to false, BSF cannot be enabled. Binding Use Local Configured Bsf Always Specifies whether to use local configured BSF without Always discovering.
Default Value: FALSE
Binding Use Local Configured Bsf When Not Discovered Whether to use local configured (if having) BSF when not discovered or discover failed. Local configuration can be done using custom yaml.
Default Value: FALSE
Use HTTP2 Determines if using http/2 to communicate with BSF. Otherwise use http/1.1.
Default Value : TRUE
Abort or Terminate Session on BSF Error Determines if PCF (SM service) should abort terminate session when binding error is received.
Note: This works for Create, Modify, and Pending Transactions requests only.
Session Limit By User This parameter can be used to enable or disable user level limiting for bindings at Binding service. Binding service only marks the sessions as stale, and then notifies either SM or PCRF Core to perform the clean-up. The default value for this parameter is true.
Max Session Limit By User This parameter can be used to specify the maximum session limit for a particular user. The default value for this parameter is 10.
Max Session Limit By APN This parameter can be used to enable or disable limiting of number of bindings at DNN + SNSSAI + IP domain level at Binding service. The default value for this parameter is true.
Max Session Cleanup Mode Binding service uses this flag to send request to SM service for either local or remote session clean up. The allowed values for this flag are: LocalRemote
On choosing the flag to
Local, PCF deletes the session locally and does not send notify terminate request toward SMF.Default Value: Local
Max Session Force Delete On Expiry Of Wait Timer For Remote Cleanup On Max Session Cleanup Modeset toRemotethis toggle flag appears. It makesforceDeleteOnExpiryOfWaitTimerflag to true or false which is used in SM service request for remote cleanup.Default Value: false
Max Session Force Delete On Error For Remote Cleanup On Max Session Cleanup Modeset toRemotethis toggle flag appears. It makesforceDeleteOnErrorflag to true or false which is used in SM service request for remote cleanup.On SM service notify terminate request failure and based on
forceDeleteOnErrorflag, the session with 4xx and 5xx response status codes are deleted except for the 404 status code.Default Value: false
Apn Filter By Snssai This parameter can be used to specify the maximum session limit for DNN + SNSSAI + IP domain level. The default value for this parameter is 2.
BSF Retry Profile For Initial Messages Retry Profile to be used when PCF fails to send a create message to a producer node. BSF Retry Profile For Subsequent Messages Retry Profile to be used when PCF fails to send an in-session message to a producer node. Note:- If both “Retry Profile for Initial Messages” and “Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages” are not configured (default case) no retry is attempted.
- If both “Retry Profile for Initial Messages” and “Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages” are configured, retries is attempted accordingly.
- If “Retry Profile for Initial Messages” is configured but “Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages” is not configured then the profile for initial messages is used for subsequent messages. (to be backward compatible with release 1.8.x)
- If “Retry Profile for Initial Messages” is not configured but “Retry Profile for Subsequent Messages” is configured then retry is not attempted for initial messages but is attempted for subsequent messages.
BSF Communication Profile Specifies the NF communication profile used by BSF. For more information about configuring NF communication profiles, see NF Communication Profiles. Enable Vendor Specific Attribute in Register Request Determines if PCF sends Vendor-Specific-Attribute in the Binding Create or Register request. By default, the value is set to false. Vendor ID Note: This field becomes active only when Enable Vendor Specific Attribute in Register Request switch is enabled. Specifies the VendorI ID that is mapped to the
vendorIdin the Vendor-Specific-Attribute.Data Compression Scheme Specifies the data compression scheme used by Binding Service. Following are the allowed values for this field: - Disabled
- Zlib_Compressed
By default, this value remains disabled.
- Expand the
Audit group.
This group allows you to edit Audit configurations.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under the group.
Table 7-91 Edit Audit Configurations
Field Name Description Enabled Determines whether to send registration request to Audit service or not. Default Value: True
Notification Rate (per second) Defines the number of stale records which Audit service notifies to Binding service in one second. Default and Recommended Value: 50
Note: To configure higher number than the recommended value, contact My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com)
Binding Age (in minutes) Defines the age of the binding entry after which Binding service queries the SM service or the PCRF Core service to check the staleness. Default Value: 1500
Maximum Binding Age (in minutes) Defines the age of the binding entry after which records are deleted from the binding without querying the SM or PCRF Core services. Default Value: 2940
Minimum Audit Attempts Specifies the minimum number of consecutive failed audit attempts until maxTTL / forceTTL is reached.
If maxTTL is reached and audit_attempts + 1 >= Minimum Audit Attempts for maxTTL, Audit service sends notification to Binding Service with maxTTL flag set to true. Binding Service deletes the corresponding contextbinding information from its database.
Range: 0-255
Default Value: 0
Note: If maxTTL is not reached and if audit attempts are reached, the number of audit attempts are incremented until maxTTL is reached.
Minimum Audit Passes Interval (in minutes) Defines the time when next audit for the Binding service table is done after delta time if auditing this table has been finished before this specified time. Default Value: 15
- Click Save.
The page saves the Binding Service configurations.
- Perform the following steps to configure Advanced Settings that sets the
key for configuring congestion response code and message priority to various
rest api end points:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following key and respective value:
Table 7-92 Parameters for Advanced Settings
Keys Value CONGESTION_RESPONSE_CODE Configure the response code of the any rejected requests by Usage Monitoring due to congestion state. By default, Binding service sends 503 as response code. If configured then it shall be 5xx only. Allowed Values: 5xx
Default Value: 503
AUDIT_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for Audit notification request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 30
BSF_AUDIT_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for BSF Audit request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 27
DEPENDENT_CONTEXT_BINDING_REGISTER_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for registring binding contextbinidng request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 24
DEPENDENT_CONTEXT_BINDING_DEREGISTER_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for deregistering binding contextbinding request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 16
DEPENDENT_CONTEXT_BINDING_FIND_CONTEXT_OWNER_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for finding dependent contextbinidng owner request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 16
SESSION_BINDING_REGISTER_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for session binding register request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 24
SESSION_BINDING_UPDATE_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for session binding update request . Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 20
SESSION_BINDING_DEREGISTER_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for deregistering session binding request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 16
SESSION_BINDING_SEARCH_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for searcing session binding request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 30
SESSION_BINDING_FIND_CONTEXT_OWNER_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for finding binding context owner request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 16
SESSION_BINDING_CLEANUP_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for session binding cleanup request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 30
BSF_SESSION_UPDATE_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for binding session update. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 20
STALE_SESSION_TRACKER_REFRESH_MESSAGE_PRIORITY Set request priority for tracking stale session request. Allowed Values: 0-100
Default Value: 30
- Click the
7.3.13 Policy Engine
This section provides information about viewing the Policy service details.
The Policy Engine page displays the list of the services available on the Policy deployment.
Note:
This page must only be used for adding the Policy Data Source (PDS) service. Rest of the services must not be added or edited using this page.The following screen capture shows an illustrations of the Policy Engine page:
Figure 7-19 Policy Engine
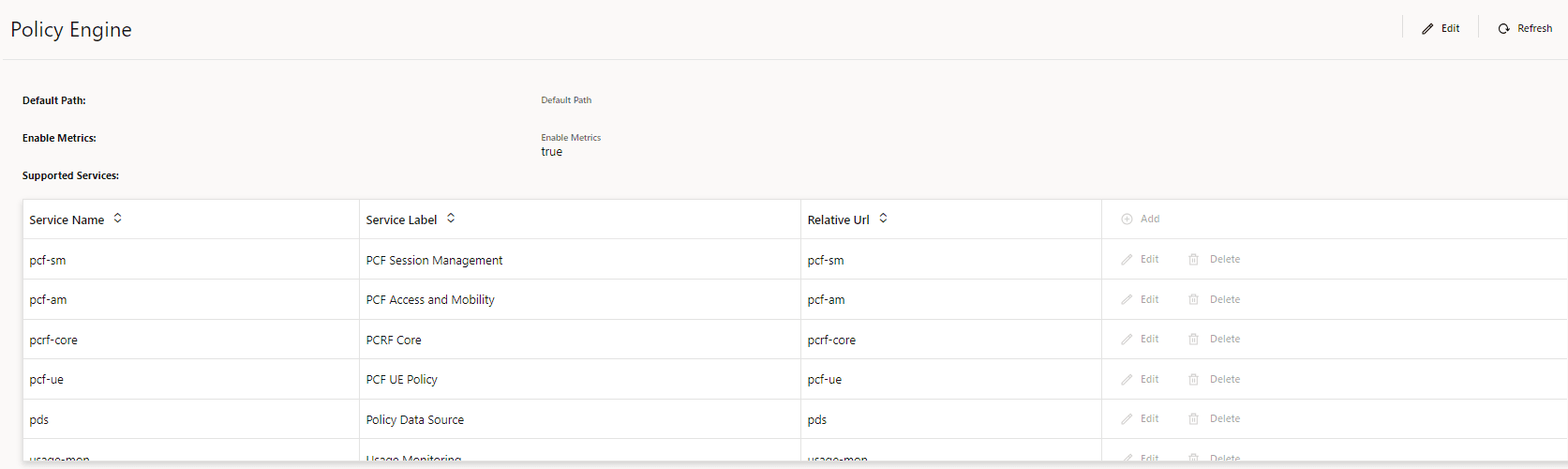
Configuring PDS Service
- On the Policy Engine page, click
 .
.
This opens the Edit PDS Service page displaying the supported services in a tabular format, under the Supported Services group.
- Make sure that the Enable Metrics switch is enabled. This field specifies whether to enable the metrics for this functionality. By default, this switch remains disabled.
- Click
 available in the table.
available in the table.
The page opens the Add Supported Services dialog box.
- Enter the following information:
Table 7-93 Add Supported Services Configuration
Field Name Description Service Name The name of the service. For PDS, enter the value: pds
Service Label The service label. Enter Policy Data Source
Relative Url Enter pds - Click Save on the dialog box.
The pds service gets listed on the Edit PDS Service page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the pds service details.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the pds service details.
- On the Edit PDS
Service page, click Save.
The page saves PDS as the supported service.
7.3.14 Configuring NWDAF Agent
This section provides information on how to configure NWDAF Agent.
7.3.14.1 Settings
This procedure provides information about managing NWDAF Agent Settings
The Settings page allows you to edit Advanced Settings for NWDAF Agent service.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Service
Configurations, click NWDAF Agent,
and then select Settings.
This opens the Settings page.
-
Click Edit.
This opens the Edit NWDAF Agent Settings page.
- Click Add.
- On the Add Advanced Settings dialog box,
enter values for the following input fields:
- Key - Specify the name of the key.
- Value - Specify the value for the key.
- Click Save to save the advanced
settings.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
- Click Save to save the NWDAF Agent
Settings.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
7.3.14.2 Slice Load Level
This procedure provides information on how to add and manage Slice Load Level.
The Slice Load Level page allows you to add and edit Slice Load Levels.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Service
Configurations, click NWDAF Agent, click
Autonomous Subscription, and then select
Slice Load Level.
This opens the Slice Load Level Configuration page.
-
Click Add.
This opens the Config Slice Load Level page.
- Enter values for the following input fields, as described in the
following table:
Table 7-94 Config Slice Load Level
Field Name Description SNSSAI Identification of network slice to which the subscription applies. Threshold Indication of slice load level in percentage. ImmRep Indication of immediate reporting. - Click Save. The Slice Load Level is
displayed on the Slice Load Level Configuration page.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
Importing Slice Load Level
To import Slice Load Level :
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.3.15 NRF Agent
Most of the PCF services discovery requests(On Demand Discovery) towards NRF do not use UE identifiers for NF discovery. Hence the requests do not carry correlation-info header. But On Demand Discovery of UDRs requests have the UE identifiers like SUPI or GPSI. These UDR discovery request with UE identifier toward NRF is updated to support correlation-info header.
- From the navigation menu under Policy, navigate to Service Configurations, and then select NRF Agent. This opens the NRF Agent page.
- Click Edit. This opens Edit NRF Agent page.
- On the Edit NRF Agent page, enter the following
information:
Table 7-95 Edit NRF Agent
Field Name Description NRF Agent Communication Profile Specifies the NRF Communication Profile to handle correlation info header toward NRF. On Demand Discovery Caching Provide details about On Demand Discovery Caching Enable Caching Indicates NRF Client to cache the profile data and use it to process the future discovery on demand requests.
Default value: false
Query Parameters Accepts the list of parameters that NRF Client uses to fetch the profile data from cache.
Note: The query parameters in the request from SM service, AM service, UE Policy service must match and must be in the same order as the data received from NRF. Otherwise, NRF Client can not process the request.
Supported values:
- data-set
- target-nf-type
- requester-nf-type
- target-nf-set-id
- service-names
- amf-region-id
- amf-set-id
- GUAMI
- target-nf-instance-id
- group-id-list
Retention Period (in ms) Indicates the time a record is allowed to stay in database after expiry and before any clean process is executed.
Default value: 864000000
Refresh Before Expiry Time (in ms) Indicates the time in milliseconds before expiration when a rediscovery must be performed for the requested discovery parameters.
Default value: 4500
Cached entry limit Parameter to set the upper bound of cache registries allowed to be retained.
Default value: 2000
Auditor Scheduler Interval (in ms) Parameter to set time in milliseconds to activate the Discovery Cache auditor service to clean stale records.
Default value: 1800000
Auditor Purge Percentage Parameter to set the percentage of the cached discovery requests that will be pruned once the threshold has been passed.
Default value: 20
- Click Save to save the changes
target-nf-type and
requester-nf-type parameters are selected along with other query
parameters. If they are not selected then the configurations are not saved and error
message is displayed on the NRF Agent page.
Figure 7-20 NRF Agent Error Message

7.3.16 IGW
Note:
Use the Edit icon or Delete available in the next column of the specific entry to update or delete the error code series information.Table 7-96 Error Code Series
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Profile | Specifies the name for error code series list profile. |
| Error Code Series |
Lists the error codes for a specific service. |
Table 7-97 Error Code Series Configuration
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Error Set | Possible values for "errorSet" attribute: 5xx, 4xx, 3xx, 2xx, 1xx |
| Error Codes |
Possible values include all error codes in the respective HttpSeries value assigned for "errorSet". Note: Use single value of "-1" if all error codes in that HttpSeries are to be considered. |
7.3.17 Bulwark
This section describes how to configure Bulwark service.
7.3.17.1 Bulwark Settings
This procedure provides information about managing Bulwark service settings.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Service
Configurations, click Bulwark, and then
select Settings.
This opens the Bulwark Settings page.
-
Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Bulwark Settings page.
- Under Server Retry On Already Locked Keys section,
configure the following fields:
Table 7-98 Server Retry On Already Locked Keys
Field Description Enable Indicates whether to enable or disable server retry on already locked keys.
To enable the feature, set the value of this field to
true.Default value:
falseMaximum Pending Lock Requests allowed per Key Indicates the maximum number of pending lock requests allowed per key.
Default value: 5
- Click Save to save the settings.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
7.3.18 Diameter Connector
The Diameter Connector page allows to configure Diameter Connector.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Service
Configurations and select Diameter
Connector.
This opens the Diameter Connector page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Diameter Connector page.
- Enter the following information
under the respective groups:
Table 7-99 Edit Diameter Connector
Field Name Description Stale Request Cleanup Enable Late Arrival Indicates whether to validate an incoming request if it is stale during arrival.
Enable this field to stop processing the incoming requests to Diameter Connector if it already stale.
Default value: false
Enable Late Processing Indicates whether to validate a request at Diameter Connector if it is stale during processing.
Enable this field to stop processing the requests at Diameter Connector if it becomes stale during processing.
Default value: false
Skip Late Processing For Terminate Indicates whether to skip validating requests of type DELETE if the request becomes stale during arrival and processing.
Default value: false
SBI Timer Enabled Indicates whether to handle HTTP SBI headers that are attached to incoming request.
Default value: false
- Click Save to save the configuration.
7.4 Policy Data Configurations
This section describes how to create the manageable objects (MOs) in Policy, using the Policy Data Configurations pages.
7.4.1 Common
This section includes the common services configurations for Policy services.
To access Common Data functionality from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Policy Data Configurations and select Common.
7.4.1.1 Policy Table
Policy Tables are the independent objects that can be used to capture differences in policy structures.
Most of the policies are very similar with small differences between them. A policy table abstracts the differences between related policies. Instead of creating many similar policies, using a policy table makes the tasks of adding new policies, modifying existing sets of policies, and checking consistency among related policies simpler and less prone to error.
- Table name
- Table description
- Column
definitions
Every column has a definition that contains a name, data type, and indication if the column is a key column. Every entry in the column is of the same data type as the column. Every policy table must have at least one key column.
- Data
The contents of the table cells. Blank cells are not allowed in a policy table.
Each row in a policy table can be thought of as a scenario. Substitutions in policy condition and action parameters can include the values in a specified policy table.
Note:
CNC Policy supports Policy Table for the following services:- SM
- AM
- UE Policy
- PCRF Core
- Usage Monitoring
You can manage multiple policies with small differences by abstracting the differences into tables. This makes the process of modifying the policies, or creating new or similar policies a matter of modifying the policy table, which is simpler and less prone to error.
Managing Policy Tables
This section describes how to create, modify, delete, and view policy tables.
To access Policy Table configurations from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Policy Data Configurations and select Policy Table.
7.4.1.1.1 Configure Policy Table
This procedure provides information on how to create and manage Policy Tables.
The Policy Tables page allows you to create new and manage existing policy tables. The page displays the list of available policy tables and provides the options to create, configure, import, export, clone, modify, or delete the tables.
Important:
When you define a policy table, it must contain at least one key column and one row, and you must populate every cell in the table.To create and configure a policy table, perform the following steps:
7.4.1.1.2 Associating a Policy Table with a Policy
This procedure provides information on how to associate a policy table with a new or existing policy.
To associate a policy table with a policy, the policy table must already be configured. For information about configuring Policy Tables, see Configure Policy Table.
Note:
When a user creates or updates a Policy Table through CNC Console or REST API, it may take up to 30 seconds for the changes to reflect in the policy rule associated with that Policy Table.To associate a policy table with a policy rule:
- From the navigation menu, under Policy Management, click
Policy Projects.
This opens the Policy Projects page displaying all the existing policies.
- Click
 corresponding to the policy to be associated.
corresponding to the policy to be associated.
This opens a new page for the selected policy.
- On the policy page, expand Public, and select
Policy Table.
This provides you the access to the Policy Table blocks.
The following screen capture shows an example of Policy Table blocks for a PCF Session Management policy:
Figure 7-23 Example of Policy Table Blocks for SM Policy
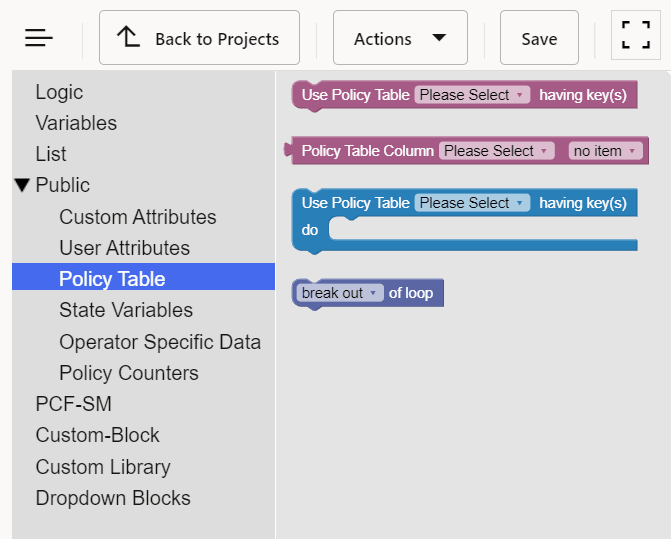
- In the first block, select the policy table from the Policy Table
drop-down list.
The corresponding key columns are displayed in key(s).
The following screen capture shows an example in which Policy Table T1 is selected and the OperationType and RatType are the corresponding key columns in the table T1:
Note:
This block is being deprecated. Use the third block on the Policy Tables page to achieve the functionality of the deprecated block. For more information, see Step 7.Figure 7-24 Example of Policy Table First Block

- Select the operator from the operator drop-down list and associate the value or
policy condition with the key column. You can select the value or policy
condition from Public and PCF-SM topics. .
The following screen capture shows an example of associating policy conditions with the key columns, OperationType and RatType:
Figure 7-25 Example of Associating Policy Conditions with Key Columns
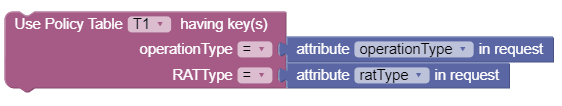
If all the values associated with the key columns match its column data from the policy table based on the used operator ("="), then it returns the complete row data.
Note:
This block can return only single row. - In the second block, select the policy table from the Policy Table
Column drop-down and the corresponding non-key columns are displayed in
no item drop-down list.
The following screen capture shows an example in which policy table T1 is selected and the non-key column, pccRule is displayed in the drop-down list:
Figure 7-26 Example of Policy Table with non-key Column

This block returns the value of the non-key column selected by taking row data as input from the first block.
- In the third block, select the policy table from the Policy Table drop-down
list and the corresponding key and non-key columns are displayed in
key(s).
The following screen capture shows an example in which Policy Table REGEXPT has been selected and the rat and supi are the corresponding columns in the table REGEXPT.
Figure 7-27 Example of Policy Table with Corresponding Columns
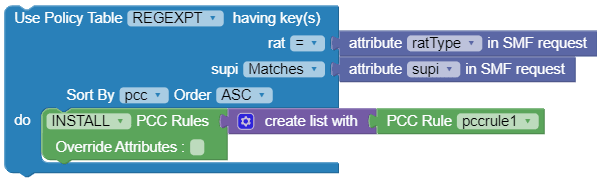
Select the operator from the operator drop-down and associate the value or policy condition with the columns. You can select the value or policy condition from Public and PCF-SM topics. The following screen capture shows an example of associating policy conditions with the columns, RAT and SUPI.
If all the values associated with the columns match its column data from policy table based on the operator used ("=") and Matches, then it returns the complete row data.
Note:
- This block can return multiple rows.
- For this block, "=", "!=", Matches, and Ignore opearotrs are supported.
- Click Save.
7.4.1.2 Dropdown Blocks
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage dropdown blocks for policy projects.
The Dropdown Blocks page allows you to create new and manage existing blocks. The page displays the list of defined dropdown blocks with the options to import, export, or add blocks.
To configure the Dropdown blocks:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click Common, and select
Dropdown Blocks.
This opens the Dropdown Blocks page. The page lists the existing dropdown blocks. You can add or import new dropdown block using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Dropdown Blocks page.
- On the Create Dropdown
Blocks page, enter the following information:
Table 7-100 Create Dropdown Blocks
Field Name Description Attribute Name Name of the attribute Description Description of the attribute Type Select from the following values: - static
- dynamic
- Expand the Block Options group.
This group allows you to add multiple block options.
- To add block options:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Block Options dialog box.
- On the dialog box, enter the
following values:
Table 7-101 Add Block Options
Field Name Description Label Name Name of the block Value Specify the value for the block option. - Click Save.
The block option gets listed under the Block Option group on the Create DropDown Blocks page.
- Click
- On the Create DropDown Blocks
page, click Save.
The page lists the dropdown block.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the dropdown block.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the dropdown block.
Importing Dropdown Blocks
To import Dropdown Blocks:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.1.3 PCF Presence Reporting Area
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage PCF Presence Reporting Area (PRA).
The PCF Presence Reporting Area page allows you to create new and manage existing PRAs. The page displays the list of defined PRAs and provides the options to import, export, or add PRAs.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click Common, and
then select PCF Presence Reporting Area.
This opens the PCF Presence Reporting Area page. The page lists the existing PRAs listed in a tabular format. You can add or import new PRAs using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create PCF Presence Reporting Area page.
- On the Create PCF Presence Reporting
Area page, enter the following information:
Table 7-102 Create PCF Presence Reporting Area
Field Name Description Pra Id The unique identifying number of the PRA list. The ID must be a number between 0 and 16777125. This field is present if the Area of Interest subscribed or reported is a Presence Reporting Area. Name The unique name assigned to the PRA. - Expand the Tracking Area List group.
This group allows you to add multiple Tracking Area List
- To add the Tracking Area Lists:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Tracking Area List dialog box.
- On the dialog box, enter the following values:
Table 7-103 Add Tracking Area List
Field Name Description PLMN Id MNC Defines the Mobile Network Code. It can be two or three digit number. MCC Defines the Mobile Country Code. It should be a 3-digit number. TAC 28-bit string identifying an E-UTRAN Cell Id as specified, in hexadecimal representation. Each character in the string takes a value of "0" to "9" or "A" to "F" and represents 4 bits. The most significant character representing the 4 most significant bits of the Cell Id appears first in the string, and the character representing the 4 least significant bit of the Cell Id appears last in the string. Pattern: '^[A-Fa-f0-9]{7}$'
Example: An E-UTRAN Cell Id 0x5BD6007 be encoded as "5BD6007".
- Click Save.
The TAC gets listed under the Tracking Area List group on the Create PCF Presence Reporting Area page.
- Click
- On the Create PCF Presence Reporting Area page, expand
the ECGI List group.
This group allows you to add multiple ECGI Lists.
- To add the ECGI Lists:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add ECGI List dialog box.
- On the dialog box, enter the following values:
Table 7-104 ECGI List
Field Name Description MNC Defines the Mobile Network Code of the PLMN. It can be two or three digit number. MCC Defines the Mobile Country Code of the PLMN. It should be a 3-digit number. Eutra Cell Id 28-bit string identifying an E-UTRA Cell Id as specified in hexadecimal representation. Each character in the string takes a value of "0" to "9" or "A" to "F" and represents 4 bits. The most significant character representing the 4 most significant bits of the Cell Id appears first in the string, and the character representing the 4 least significant bit of the Cell Id appears last in the string. Pattern: '^[A-Fa-f0-9]{7}$'
Example: An E-UTRA Cell Id 0x5BD6007 be encoded as "5BD6007".
- Click Save.
The ECGI List gets listed under the ECGI List group on the Create PCF Presence Reporting Area page.
- Click
- On the Create PCF Presence Reporting Area page, expand
the NCGI List group.
This group allows you to add multiple NCGI Lists.
- To add the NCGI Lists:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add NCGI List dialog box.
- On the dialog box, enter the following values:
Table 7-105 NCGI List
Field Name Description MNC Defines the Mobile Network Code of the PLMN. It can be two or three digit number. MCC Defines the Mobile Country Code of the PLMN. It should be a 3-digit number. NR Cell Id 36-bit string identifying an NR Cell Id as specified in hexadecimal representation. Each character in the string takes a value of "0" to "9" or "A" to "F" and represents 4 bits. The most significant character representing the 4 most significant bits of the Cell Id appears first in the string, and the character representing the 4 least significant bit of the Cell Id appears last in the string. Pattern: '^[A-Fa-f0-9]{9}$'
Example: An NR Cell Id 0x225BD6007 is encoded as "225BD6007".
- Click Save.
The NCGI List gets listed under the NCGI List group on the Create PCF Presence Reporting Area page.
- Click
- On the Create PCF Presence Reporting Area page, expand
the Global RAN NodeId List group.
This group allows you to add multiple RAN Node ID Lists.
- To add the Global RAN NodeId Lists:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Global RAN NodeId List dialog box.
- On the dialog box, enter the following values:
Field Name Description PLMN Id MNC Defines the Mobile Network Code of the PLMN. It can be a 2- or 3-digit number. MCC Defines the Mobile Country Code of the PLMN. It should be a 3-digit number. N3 lwf Id This field is included if the RAN node belongs to non 3GPP access (i.e a N3IWF). It contains the FQDN of the N3IWF. gNb Id Bit Length Unsigned integer representing the bit length of the gNB ID within the range 22 to 32. gNb Value Specifies the gNb identifier. The value of the gNB ID is encoded in hexadecimal representation. Each character in the string takes a value of "0" to "9" or "A" to "F" and represents 4 bits. The most significant character representing the 4 most significant bits of the gNB ID appears first in the string, and the character representing the 4 least significant bit of the gNB ID appears last in the string. The string is formatted with following pattern:'^[A-Fa-f0-9]{6,8}$'
Example: "382A3F47" indicates a gNB ID with value 0x382A3F47
Nge Nb Id This field is included if the RAN Node Id represents a NG-eNB. It contains the identifier of an NG-eNB. - Click Save.
The Global RAN NodeId List gets listed under the Global RAN NodeId List group on the Create PCF Presence Reporting Area page.
- Click
- On the Create PCF Presence
Reporting Area page, click Save.
The PRA gets listed on the PCF Presence Reporting Area page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the PRA.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the PRA.
Importing PCF Presence Reporting Area
To import PRA:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.1.4 Policy Counter Id
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage Policy Counter Ids.
The Policy Counter Id page allows you to create new and manage existing IDs. The page displays the list of defined Policy Counter Ids and provides the options to import, export, or add new IDs.
To configure the Policy Counter Id:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click Common, and then select
Policy Counter Id.
This opens the Policy Counter Id page. The page lists the existing policy counter IDs listed in a tabular format. You can add or import new IDs using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Policy Counter Id page.
- On the Create Policy Counter Id
page, enter values for the following input fields:
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-106 Create Policy Counter Id
Field Name Description Policy Counter Id
Policy Counter Id's Name. Name The unique name of the counter ID. Description
Policy Counter Id's description. Default Status
- Click Save.
The policy counter ID gets listed on the Policy Counter Id page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the counter ID.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the counter ID.
Importing Policy Counter Id Data
To import Policy Counter Ids:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.1.5 Match Lists
In a wireless network, a match list is a set of values in various categories, including Access Point Names (APNs), subscriber IMSIs, Location Area Codes (LACs), Service Area Codes (SACs), Internet addresses, and user equipment identities. Match lists provide allowlist (listing items to be included) and blocklist (listing items to be excluded) functions in policy rules. Match lists support wildcards. Using wild cards, a range of values can be specified compactly.
By using a match list, you can apply a policy to all subscribers in a set of LACs, block access to a list of Internet addresses known to be high risk, and so on.
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage Match Lists.
The Match List page allows you to create new and manage existing lists. The page displays the list of defined match lists and provides the options to import, export, or add lists.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click Common, and
then select Match List.
This opens the Match List page. The page lists the existing match lists. You can add or import new lists using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Match List page.
- Enter values for the input fields available on the page:
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-107 Create Match List
Field Name Description ID
The ID assigned to the match list. Name The name assigned to the match list.
The name can only contain the characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 40 characters.
Description
Free-form text Type
Select from the following: - String (default) - The list consists of strings.
- Wildcard String - The list consists of wildcard match patterns that use an asterisk (*) to match zero or more characters or a question mark (?) to match exactly one character.
- IPv4 Subnet - IP address in IPv4 subnet.
- IPv6 Subnet - IP address in IPv6 subnet.
- Regular Expression - Regular Expression to match the IP address.
Items
Item list to either include or exclude. - Click Save.
The match list gets listed on the Match List page. It is is defined in the database and can now be used in a policy.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the match list.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the match list.
Importing the Match Lists
To import match lists:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.1.6 Schemas
Schemas enable operators to accept data in custom format instead of the standard format. This data can then be used to construct conditions and actions.
This section describes how to configure Schemas for Policy.
To access Schemas configurations from CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Policy Data Configurations, click Common, and select Schemas.
7.4.1.6.1 Yaml Schema
This procedure provides information about how to view, import, and configure the custom schemas.
The Yaml Schema page allows you to import and manage existing Yaml Schemas. The page displays the list of defined Yaml schemas and provides the options to import, export, update, or delete the schemas.
Note:
Custom schema yaml file must follow Open API standards.To import a custom Yaml schema:
- From the navigation menu under
Schemas, select Yaml Schemas.
This opens the Yaml Schemas page.
The page lists the details including schema name, Schema Tag, and Actions for the following previsioned schema yaml files:AmPolicyDataSmPolicyDataUePolicyData
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Select the tags to tag the schemas in the selected files. The page supports only User tag.
- Click Import.
Note:
-
To update any existing schema, click
 , make changes to the exported yaml file, and save it on your system. Then,
import the file again.
, make changes to the exported yaml file, and save it on your system. Then,
import the file again.
-
To delete any existing service area restriction, click the
 under the Action column.
under the Action column.
When a schema is tagged as User during import, CNC Policy allows you to access and configure the schema using the User Attributes blocks, available under the Public category. When a schema is not tagged, you may access and configure it using the Custom Attributes blocks, available under the Public category. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Policy Design Guide.
Sample Yaml Schema
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
description: Customer
version: 0.0.1
title: Customer
paths:
/:
get:
operationId: get
summary: get
tags:
- get
responses:
'200':
description: OK
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Customer'
components:
schemas:
Customer:
type: object
properties:
phones:
type: array
items:
type: string
name:
type: string
address:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Address'
Address:
type: object
properties:
house:
type: string
street:
type: string
city:
type: string7.4.1.6.2 Diameter Schemas
This section describes the diameter schemas for user data configurations.
To access Schemas configurations under Schemas, select Diameter Schemas.
7.4.1.6.2.1 Custom AVP
An attribute-value pair (AVP) is used to encapsulate protocol specific information supported by CNC Policy. Diameter messages, such as RAA, CCA, CCR, and RAR are supported by third-party AVP policy conditions. The supported outgoing Diameter messages set or remove the third-party AVPs. For more information, see Custom AVP to Support Third-Party Vendor Specific AVPs.
- From the navigation menu, under Diameter
Schemas, select Custom AVP.
This opens the Custom AVP page. The page lists the existing AVPs. You can add or import new AVPs using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Custom AVP page.
- Enter values for the input fields available on the page:
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-108 Create Custom AVP
Field Name Description AVP Name
The name you assign to the AVP.
This is a mandatory field.
The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 255 characters.
Description Free-form text that identifies the AVP. Enter up to 250 characters. AVP Code
A unique numeric value assigned to the new AVP. This is a mandatory field.
Vendor
Select a vendor from the vendor list. To add a vendor to the list, see Custom Vendor. Mandatory Flag Protect Flag When checked, specifies the protected AVP values. May Encrypt Flag The AVP is encrypted if the checkbox is specified. Vendor Specific Flag The AVP is encrypted if the checkbox is specified. AVP Type Select the data type from the list: - address
- enumerated
- float32
- float64
- grouped
- id
- int32
- int64
- ipFilterRule
- octetString
- time
- uint32
- uint64
- uri
- utf8String
Parent AVP If the AVP is a member of a grouped AVP, then the parent AVP must be specified. Select one of the following from the list: - ADC-Rule-Definition:10415
- ADC-Rule-Install:10415
- ADC-Rule-Remove:10415
- ADC-Rule-Report:10415
- AF-Correlation-Information:10415
- Acceptable-Service-Info:10415
- Access-Network-Charging-Identifier-Gx:10415
- Access-Network-Charging-Identifier:10415
- Access-Network-Physical-Access-ID:10415
- Allocation-Retention-Priority:10415
- Application-Detection-Information:10415
- CC-Money
- Charging-Information:10415
- Charging-Rule-Definition-3GPP2:5535
- Charging-Rule-Definition:10415
- Charging-Rule-Event-Cisco:9
- Charging-Rule-Event-Trigger-Cisco:9
- Charging-Rule-Install-3GPP2:5535
- Charging-Rule-Install:10415
- Charging-Rule-Remove:10415
- Charging-Rule-Report-3GPP2:5535
- Charging-Rule-Report:10415
- Codec-Data-Tmp:10415
- Click Save.
- If the AVP name matches the name of a standard AVP, a confirmation message displays. Click OK to overwrite the existing AVP.
Note:
UseImporting Custom AVP
To import the custom AVP:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.1.6.2.2 Custom Vendor
A custom vendor is used to define a vendor in the the PCRF system. This dictionary includes vendor IDs and text descriptions. You can define custom vendors and add them to the dictionary.
- From the navigation menu, under Diameter
Schemas, select Custom Vendor.
This opens the Custom Vendor page. The page lists the existing vendors. You can add or import new vendors using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Custom Vendor page.
- Enter values for the input fields available on the page:
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-109 Create Custom Vendor
Field Name Description Vendor Name
The name you assign to the vendor.
This is a mandatory field.
The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 255 characters.
Description Free-form text that identifies the vendor. Enter up to 250 characters. Vendor Code
A unique numeric value assigned to the new vendor. This is a mandatory field.
- Click Save.
The Custom Vendor gets listed on the Custom Vendor page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the vendor.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the vendor.
Importing Custom Vendor
To import custom vendor:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.2 PCF Session Management
This section includes the configurations for PCF Session Management service.
To access PCF Session Management configurations from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Policy Data Configurations and select PCF Session Management.
The PCF Session Management configurations includes:
7.4.2.1 Session Rule
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the session rules in CNC Policy.
The Session Rule page allows you to create new and manage existing session rule configurations. The page displays the list of defined rules and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure the session rules:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF Session Management,
and then, select Session Rule.
This opens the Session Rule page. The page lists the existing session rules data. You can add or import new rules using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Session Rule page.
- On the Create Session Rule page,
enter the information common to all the groups available on the page.
The following table describes the common input fields:
Table 7-110 Create Session Rule
Field Name Description Session Rule ID Specifies the Session Rule ID. Name Specifies the name assigned to the session rule. Description Free-form text that identifies the session rule. - Expand the Authorized Session AMBR group.
This group allows you to add authorized session AMBR information.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available
under the Authorized Session AMBR group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-111 Authorized Session AMBR
Field Name Description Uplink Bandwidth Specifies the bandwidth in uplink. Downlink Bandwidth Specifies the bandwidth in downlink. Note:
Click the Remove button to remove the Authorized Session AMBR details from the page. - Select value for Condition Data from the drop-down list.
- Select value for Authorize Default
Qos from the drop-down list.
Note:
The drop-down list data is configured from the QoS Information. For more information about QoS Data configuration, see QoS Data. - Click Save.
The session rule data gets listed on the Session Rule page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the session rule data configurations.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the session rule data configurations.
Importing Session Rules
To import session rules:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.2.2 Session Rule Profile
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the session rule profiles that can be assigned to session rule profiles.
The Session Rule Profile page allows you to create new and manage existing session rule profile configurations. The page displays the list of defined rules and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure the session rule profiles:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF Session Management,
and then, select Session Rule Profile.
This opens the Session Rule Profile page. The page lists the existing session rule profiles. You can add or import new profiles using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Session Rule Profile page.
- On the Create Session Rule Profile
page, enter the information common to all the groups available on the page.
The following table describes the common input fields:
Table 7-112 Create Session Rule Profile
Field Name Description Session Rule Profile NAME Specifies the name assigned to the session rule profile. Description Free-form text that identifies the session rule profile. - Expand the Authorized Session AMBR group.
This group allows you to add authorized session AMBR information.
- Enter the values for the input fields,
available under the Authorized Session AMBR group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-113 Authorized Session AMBR
Field Name Description Uplink Bandwidth Specifies the bandwidth in uplink. Downlink Bandwidth Specifies the bandwidth in downlink. Note:
Click the Remove button to remove the Authorized Session AMBR details from the page. - Select value for Condition Data from the drop-down list.
- Select value for Authorize
Default Qos from the drop-down list.
Note:
The drop-down list data is configured from the QoS Information. For more information about QoS Data configuration, see QoS Data. - Click Save.
The profile data gets listed on the Session Rule Profile page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the session rule profile configurations.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the session rule profile configurations.
Importing the Session Rule Profiles
To import session rule profiles:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.2.3 QoS Information
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the Quality of Service (QoS) information in CNC Policy.
The QoS Information page allows you to create new and manage existing information related to QoS configurations. The page displays the list of defined QoS identifiers and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure QoS Information data:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF Session Management,
and then, select QoS Information.
This opens the QoS Information page. The page lists the existing session QoS data. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create QoS Information page.
- On the Create QoS Information
page, enter values for the input fields common to all the groups available on the
page.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-114 Common Configuration on Create QoS Information
Field Name Description Name Specifies the name assigned to the QOS information. Description Free-form text that identifies the QOS information. Default 5G QoS Identifier Identifier for the authorized QoS parameters for the service data flow. It is included when the QoS information decision is initially provisioned. Priority Level Unsigned integer indicating the 5QI Priority Level, within a range of 1 to 127. Average Window Represents the duration over which the guaranteed and maximum bitrate is calculated (NOTE). Max DataBurstVol Denotes the largest amount of data that is required to be transferred within a period of 5GAN PDB (NOTE). - Expand the ARP group.
This group allows you to add Allocation and Retention Priority (ARP) information.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available
under the ARP group.
The following table describes the fields:
Field Name Description Priority Level Unsigned integer indicating the ARP Priority Level, within the range 1 to 15. Preemption Capability Defines whether a service data flow may get resources that were already assigned to another service data flow with a lower priority level. Possible values are: - NOT_PREEMPT : Does not trigger pre-emption.
- MAY_PREEMPT : May trigger pre-emption.
Preemption Vulnerability Defines whether a service data flow may lose the resources assigned to it in order to admit a service data flow with higher priority level. Possible values are: - NOT_PREEMPTABLE : Does not be pre-empted.
- PREEMPTABLE : May be pre-empted.
Note:
Click the Remove button to remove the ARP fields from the page. - Click Save.
The QoS information data gets listed on the QoS Information page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the QoS information.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the QoS information.
Importing the QoS Information
To import the QoS Information:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.2.4 PCC Rule
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the PCC Rules in Policy.
The PCC Rule page allows you to create new and manage existing PCC Rule configurations. The page displays the list of defined rules and provides the options to import, export, or add rules.
To configure the PCC rule:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF Session Management,
and then, select PCC Rule.
This opens the PCC Rule page. The page lists the existing session PCC rules data. You can add or import new rules using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create PCC Rule page.
- On the Create PCC Rule page, enter
values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-115 Create PCC Rule
Field Name Description PCC Rule Id Specifies the PCC Rule ID. Name Specifies the name assigned to the PCC rule. Description Free-form text that identifies the PCC rule. Type Select the required type. Possible values are: Use Custom QoS Class Identifier When this flag is enabled, you can use the custom QCI values.
Defalut Value: Disabled
QoS Class Identifier (1-254) When Use Custom QoS Class Identifier flag is enabled, you can use a custom value for this parameter. The value ranges between 1 and 254.
When Use Custom QoS Class Identifier flag is disabled, you can select one of the QCIs from the dropdown list box:
- 4=Streaming
- 5-Interactive with Priority 1 Signalling
- 6=Interactive with Priority 1
- 7=Interactive with Priority 2
- 8=Interactive with Priority 3
- 9=Background
- 65=MC-PTT Voice
- 66-PTT Voice
- Expand the Flow Information group.
The expanded group displays the available flow information and allows you to add new information.
To add flow information:- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Flow Information dialog box.
- On the dialog box, enter values for the following input
fields:
Table 7-116 Add Flow Information
Field Name Description Name
Indicates the name for the flow. Pack Filt Id
An identifier of packet filter. Packet Filter Usage
The packet is sent to the UE. The default value "FALSE" applies, if the attribute is not present and has not been supplied previously. Tos Traffic Class
Contains the IPv4 Type-of-Service and mask field or the IPv6 Traffic-Class field and mask field. Spi The security parameter index of the IPSec packet. Flow Label
The IPv6 flow label header field. - Click Save.
The Flow Information gets listed under the Flow Information group on the Create PCC Rule page.
- Click
- On the Create PCC Rule page, enter the values for the following
input fields:
Table 7-117 Create PCC Profile Common Configurations
Field Name Description App Id
A reference to the application detection filter configured at the UPF. Content Version
Indicates the content version of the PCC rule. Precedence
Determines the order in which this PCC rule is applied relative to other PCC rules within the same PDU session. It is included if the "flowInfos" attribute is included or may be included if the "appId" attribute is included when the PCF initially provisions the PCC rule. AF Signalling Protocol
Indicates the protocol used for signaling between the UE and the AF. The default value "NO_INFORMATION" applies, if the attribute is not present and has not been supplied previously. --QoS Flow Usage Indicates the QoS flow usage. The default value is not applicable for this field. Users can select GENERAL or IMS_SIG from the drop down list as per the requirement. Application Relocation
Indication of application relocation possibility. The default value "NO_INFORMATION" is applicable, if the attribute is not present and has not been supplied previously. Qos Data
A reference to the QoSData policy type decision type. Traffic Control Data
A reference to the TrafficControlData policy decision type. Charging Data
A reference to the ChargingData policy decision type. Usage Monitoring Data
A reference to UsageMonitoringData policy decision type. Condition Data
A reference to the condition data. - On the Create PCC
Rule page, click Save.
The PCC profile data gets listed on the PCC Rule page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the rule data.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the rule data.
Importing the PCC Rules
To import the pcc rules:
- Click
Import.
The File Upload window appears on the screen.
- Upload the files in required format by clicking Drop Files here or click to upload.
7.4.2.5 PCC Rule Profile
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the PCC Rule Profiles in Policy.
The PCC Rule Profile page allows you to create new and manage existing PCC Rule Profile configurations. The page displays the list of defined profiles and provides the options to import, export, or add profiles.
To configure PCC Rule Profile:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF Session Management,
and then, select PCC Rule Profile.
This opens the PCC Rule Profile page. The page lists the existing session PCC rule profile data. You can add or import new profiles using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create PCC Rule Profile page.
- On the Create PCC Rule Profile page,
enter values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-118 Create PCC Rule Profile
Field Name Description Name Specifies the name assigned to the PCC rule profile. Description Free-form text that identifies the PCC rule profile. Type Select the required type. Possible Values are: - Predefined PCC Rule
- Dynamic PCC Rule
If you have selected Dynamic PCC Rule, then perform Step 4 else, perform Step 5.
Use Custom QoS Class Identifier When this flag is enabled, you can use the custom QCI values.
Defalut Value: Disabled
QoS Class Identifier (1-254) When Use Custom QoS Class Identifier flag is enabled, you can use a custom value for this parameter. The value ranges between 1 and 254.
When Use Custom QoS Class Identifier flag is disabled, you can select one of the QCIs from the dropdown list box:
- 4=Streaming
- 5-Interactive with Priority 1 Signalling
- 6=Interactive with Priority 1
- 7=Interactive with Priority 2
- 8=Interactive with Priority 3
- 9=Background
- 65=MC-PTT Voice
- 66-PTT Voice
- Expand the Flow Information group.
The expanded group displays the available flow information and allows you to add new information.
To add flow information:- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Flow Information dialog box.
- On the dialog box, enter values for the following input
fields:
Table 7-119 Add Flow Information
Field Name Description Name
Indicates the name for the flow. Pack Filt Id
An identifier of packet filter. Packet Filter Usage
The packet is sent to the UE. The default value "FALSE" is applicable, if the attribute is not present and has not been supplied previously. Tos Traffic Class
Contains the IPv4 Type-of-Service and mask field or the IPv6 Traffic-Class field and mask field. Spi The security parameter index of the IPSec packet. Flow Label
The IPv6 flow label header field. - Click Save.
The Flow Information gets listed under the Flow Information group on the Create PCC Rule Profile page.
- Click
- On the Create PCC Rule Profile page, enter the values for the
following input fields:
Table 7-120 Create PCC Rule Profile Common Configurations
Field Name Description App Id
A reference to the application detection filter configured at the UPF. Content Version
Indicates the content version of the PCC rule. Precedence
Determines the order in which this PCC rule is applied relative to other PCC rules within the same PDU session. It is included if the "flowInfos" attribute is included or may be included if the "appId" attribute is included when the PCF initially provisions the PCC rule. AF Signalling Protocol
Indicates the protocol used for signaling between the UE and the AF. The default value "NO_INFORMATION" is applicable, if the attribute is not present and has not been supplied previously. --QoS Flow Usage Indicates the QoS flow usage. The default value is not applicable for this field. Users can select GENERAL or IMS_SIG from the drop down list as per the requirement. Application Relocation
Indication of application relocation possibility. The default value "NO_INFORMATION" is applicable, if the attribute is not present and has not been supplied previously. Qos Data
A reference to the QoSData policy type decision type. Traffic Control Data
A reference to the TrafficControlData policy decision type. Charging Data
A reference to the ChargingData policy decision type. Usage Monitoring Data
A reference to UsageMonitoringData policy decision type. Condition Data
A reference to the condition data. - On the Create PCC Rule
Profile page, click Save.
The PCC profile data gets listed on the PCC Rule Profile page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the profile data.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the profile data.
Importing PCC Rule Profiles
To import PCC Rule Profiles:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.2.6 QoS Data
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the QoS data in Policy.
The QoS Data page allows you to create new and manage existing data related to QoS configurations. The page displays the list of defined QoS details and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure QoS data:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF Session Management,
and then, select QoS Data.
This opens the QoS Data page. The page lists the existing session QoS data. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create QoS Data page.
- On the Create QoS Data page,
enter values for the input fields common to all the groups available on the page.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-121 Create QoS Data Common Configurations
Field Name Description QoS ID Specifies the QoS ID. Name
Specifies the name assigned to the QOS data. Description
Free-form text that identifies the QOS data. Default 5G QoS Identifier
Identifier for the authorized QoS parameters of the service data flow. It is included when the QoS data decision is initially provisioned. Maximum Bit Rate UL
Indicates the max bandwidth in uplink. Maximum Bit Rate DL
Indicates the max bandwidth in downlink. Guaranteed Bit Rate UL
Indicates the guaranteed bandwidth in uplink Guaranteed Bit Rate DL
Indicates the guaranteed bandwidth in downlink. QoS Notification Control
Reflective QoS
Indicates whether the QoS information is reflective for the corresponding service data flow. Default value is "FALSE", if not present and has not been supplied previously.
Sharing Key Ul
Indicates, by containing the same value, what PCC rules may share resource in uplink direction. Sharing Key Dl
Indicates, by containing the same value, what PCC rules may share resource in downlink direction. Priority Level
Defines the relative importance of a resource request. Averaging Window
Represents the duration over which the guaranteed and maximum bitrate is calculated (NOTE). Maximum Data Burst Volume
Denotes the largest amount of data that is required to be transferred within a period of 5GAN PDB (NOTE). Maximum Packet Loss Rate Dl
Indicates the uplink maximum rate for lost packets that can be tolerated for the service data flow. Max Packet Loss Rate Ul
Indicates the uplink maximum rate for lost packets that can be tolerated for the service data flow. Default QoS Flow Indication
Indicates that the dynamic PCC rule always have its binding with the QoS Flow associated with the default QoS rule. Default value is "FALSE", if not present and has not been supplied previously.
- Expand the ARP group.
This group allows you to add Allocation and Retention Priority (ARP) information.
- Enter the values for the input fields,
available under the ARP group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-122 ARP Configurations
Field Name Description Priority Level Defines the relative importance of a resource request. Preemption Capability Defines whether a service data flow may get resources that were already assigned to another service data flow with a lower priority level. Possible values are: - NOT_PREEMPT
- MAY_PREEMPT
Preemption Vulnerability Defines whether a service data flow may lose the resources assigned to it in order to admit a service data flow with higher priority level. Possible values are: - NOT_PREEMPTABLE
- PREEMPTABLE
- Click Save.
The QoS data gets listed on the QoS Data page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete theQoS data.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete theQoS data.
Importing QoS Data
To import QoS data:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.2.7 Charging Data
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the charging data in Policy.
The Charging Data page allows you to create new and manage existing charging data configurations. The page displays the list of defined charging details and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure charging data:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF Session Management,
and then, select Charging Data.
This opens the Charging Data page. The page lists the existing charging data. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Charging Data page.
- On the Create Charging Data page,
enter values for the following input fields:
:
Table 7-123 Create Charging Data Configurations
Field Name Description Charging id Specifies the charging ID Name
A unique of the Charging data Description
Brief description of the Charging data Metering Method
The following options are available
- DURATION
- VOLUME
- DURATION_VOLUME
- EVENT
Defines. which parameters must be metered for offline charging.
If the attribute is not present, but it has been supplied previously, the previous information remains valid.
If the attribute is not present and it has not been supplied previously or the attribute has been supplied previously but it is set to NULL, the metering method preconfigured at the SMF is applicable as the default metering method.
Offline
Indicates that offline charging is applicable to the PDU session or PCC rule.
The default value is false, if the attribute is not present and it has not been supplied previously.
Online
Indicates that online charging is applicable to the PDU session or PCC rule.
The default value is false, if the attribute is not present and it has not been supplied previously.
Rating Group
The charging key for the PCC rule used for rating purposes. Reporting Level
The following options are available:
- SER_ID_LEVEL
- RAT_GR_LEVEL
- SPON_CON_LEVEL
Defines, on which level the SMF reports the usage for the related PCC rule.
If the attribute is not present but it has been provided previously, the previous information remains valid.
If the attribute is not present and it has not been supplied previously or the attribute has been supplied previously but it is set to NULL, the reporting level preconfigured at the SMF is applicable as the default reporting level.
Service Id
Indicates the identifier of the service or the service component in the service data flow of a PCC rule. Sponsor Id
Indicates the sponsor identity. App Svc Prov Id
Indicates the application service provider identity. Af Charging Identifier
Identifies the charging control policy data within a PDU session. sdfHandl
sdfHandl attribute send to SMF to indicate whether the service data flow is allowed to start, while the SMF is waiting for the response of the credit request from CHF. - Click Save.
The Charging data gets listed on the Charging Data page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the charging data.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the charging data.
Importing Charging Data
To import charging data:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.2.8 Traffic Control Data
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the Traffic Control data in Policy.
The Traffic Control Data page allows you to create new and manage existing traffic control configurations. The page displays the list of defined traffic control configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure traffic control data:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF Session Management,
and then, select Traffic Control Data.
This opens the Traffic Control Data page. The page lists the existing traffic control data. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Traffic Control Data page.
- On the Create Traffic Control Data
page, enter the information common to all the groups available on the page.
The following table describes the common input fields:
Table 7-124 Create Traffic Control Data Common Input Fields
Field Name Description Traffic Control id Specifies the traffic control policy data id Name
The name of the Traffic Control policy data Description
The description of the Traffic Control policy data Flow Status
The following options are available:- ENABLED-UPLINK
- ENABLED-DOWNLINK
- ENABLED
- DISABLED
- REMOVED
Enum determining what action to perform on traffic.
Possible values are: [enable, disable, enable_uplink, enable_downlink] . The default value "ENABLED" is applicable, if the attribute is not present and has not been supplied previously.
- Expand the Redirect Information group.
This group allows you to add traffic redirect information.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available
under Redirect Information group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-125 Redirect Information
Field Name Description Redirect Enabled Indicates the redirect is enabled. This is an optional field.
Redirect Address Type This string provides forward-compatibility with future extensions to the enumeration but is not used to encode content defined in the present version of this API. Redirect Server Address Indicates the address of the redirect server. Note:
Click the Remove button to remove the Redirect Information details from the page. - Enter the values for the following input fields:
Table 7-126 Create Traffic Control Data Common Input Fields
Field Name Description Mute Notification Indicates whether application's start or stop notification is to be muted. The default value "FALSE" is applicable, if the attribute is not present and has not been supplied previously.
Traffic Steering Pol Id Dl Reference to a preconfigured traffic steering policy for downlink traffic at the SMF. Traffic Steering Pol Id Ul Reference to a preconfigured traffic steering policy for uplink traffic at the SMF.
- Expand the Route To Locs group.
The expanded group displays the available routes and allows you to create new routes.
To create new routes:- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Route to Locs dialog box.
- Enter the value for the DNAI.
The DNAI value identifies the location of the application.
- Expand the Route Information group.
This group allows you to add the traffic routing information.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under Route
Information group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-127 Redirect Information
Field Name Description Ipv6 Addr Ipv6 address of the tunnel end point in the data network. Port Number UDP port number of the tunnel end point in the data network. Ipv4 Addr Ipv4 address of the tunnel end point in the data network. Note:
Click the Remove button to remove the Route Information details from the dialog box. - Enter the value for Route Profile
Id.
This value identifies the routing profile Id.
- Click Save.
The Route Information gets listed under the Route to Locs group on the Create Traffic Control Data page.
- Click
- On the Create Traffic Control Data page, expand the Up Path Chg Event group.
- Enter the values for the input fields, available under Up Path Chg
Event group.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-128 Up Path Chg Event
Field Name Description Notification Uri Defines the notification Uri sent by the SMF. Notification Correlation Id It is used to set the value of Notification Correlation ID in the notification sent by the SMF.
Dnai Change Type The following options are available:
- EARLY
- EARLY_LATE
- LATE
Possible values are
EARLY: Early notification of UP path reconfiguration. -
EARLY_LATE: Early and late notification of UP path reconfiguration. This value is present in the subscription to the DNAI change event.
LATE: Late notification of UP path reconfiguration. This string provides forwardcompatibility with future extensions to the enumeration but is not used to encode content defined in the present version of this API.
Note:
Click the Remove button to remove the Redirect Information details from the page. - On the Create Traffic Control
Data page, click Save.
The traffic control data gets listed on the Traffic Control Data page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the traffic control data configurations.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the traffic control data configurations.
Importing Traffic Control Data
To import the traffic control data:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.2.9 Condition Data
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the Condition data in Policy.
The Condition Data page allows you to create new and manage existing conditions that can be applied for Policy services. The page displays the list of defined conditions and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure condition data:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF Session Management,
and then, select Condition Data.
This opens the Condition Data page. The page lists the existing conditions. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Condition Data page.
- On the Create Condition Data page,
enter values for the following input fields:
:
Table 7-129 Create Condition Data Configurations
Field Name Description Condition id Specifies the condition data policy data id. Name
The name of the Condition Data policy data. Description
The description of the Condition Data policy data. Activation Time
The time when the decision data is activated. Deactivation Time
The time when the decision data is deactivated. - Click Save.
The condition gets listed on the Condition Data page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the condition data.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the condition data.
Importing Condition Data
To import condition data:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.3 PCF Access and Mobility
This section includes the configurations for PCF Access and Mobility service.
To access PCF Access and Mobility configurations from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Policy Data Configurations and select PCF Access and Mobility.
The PCF Access and Mobility configuration includes Managing Service Area Restriction.
7.4.3.1 Service Area Restriction
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the Service Area Restriction (SAR) in Policy.
The Service Area Restriction page allows you to create new and manage existing restrictions. The page displays the list of defined rules and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF Access and
Mobility, and then, select Service Area
Restriction.
This opens the Service Area Restriction page. The page lists the details of existing service area restrictions including their name and restriction type in a tabular format. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Service Area Restriction page.
- On the Create Service Area Restriction
page, enter the information common to all the groups available on the page.
The following table describes the common input fields:
Table 7-130 Create Service Area Restriction Configurations
Field Name Description Name Use this field to add a customized name for service area restriction. Description Use this field to add a customized description for service area restriction. Restriction Type Use this field to specify the restriction type. Possible values are: - ALLOWED_AREAS
- NOT_ALLOWED_AREAS
Note: Set a restriction type for service area restriction only when Areas attribute is available.
- Expand the Areas group.
This group lists the existing area details and allows you to configure new areas.
- To add new areas:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Areas dialog box.
- Enter the value for the following fields:
Table 7-131 Add Areas Configurations
Field Name Description Tacs The value for Type Allocation Codes (Tacs) can be defined as a hexa decimal number between 0 and 65535. Area Codes Enter the value of area codes. - Click Save.
The areas gets listed under the Areas group on the Create Service Area Restriction page.
- Click
- Enter value for the Max Number of TAs field.
- Click Save.
The SAR data gets listed on the Service Area Restriction page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the SAR data.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the SAR data.
Importing Service Area Restrictions
To import the Service Area Restrictions:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.4 PCF UE Policy
This section includes the configurations for PCF UE Policy service.
To access PCF UE Policy configurations from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Policy Data Configurations and select PCF UE Policy.
The PCF UE Policy configurations includes:
7.4.4.1 URSP Rule
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the UE Route Selection Policy (URSP) Rules in Policy.
The URSP Rule page allows you to create new and manage existing reules. The page displays the list of defined URSP rule configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add rules.
To configure URSP Rules:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF UE Policy, and
then, select URSP Rule.
This opens the URSP Rule page. The page lists the existing URSP rules data. You can add or import new rules using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create URSP Rule page.
- On the Create URSP Rule page, enter
the information common to all the groups available on the page.
The following table describes the common input fields:
Table 7-132 Create URSP Rule Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the URSP rule. Precedence Precedence value of the URSP rule. Note:
Name can not be the substring of any other configured URSP rule Name.
- Expand the Traffic Descriptor group.
The expanded group allows you to create new descriptors.
To create new traffic descriptors:- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Traffic Descriptor dialog box.
- Select a value from the Type drop-down list and
then, enter corresponding values, if applicable. The following table
lists the traffic descriptor types and their corresponding values:
Table 7-133 Traffic Descriptor Type and Values
Traffic Descriptor Type Value MATCH_ALL NA OS_ID_OS_APP_ID - OS ID
- OS APP ID
IPV4_REMOTE_ADDRESS - IPv4 Address
- Subnet Mask
IPV6_REMOTE_ADDRESS - IPv6 Address
- IPv6 Prefix Length
PROTOCOL_IDENTIFIER Protocol Number SINGLE_REMOTE_PORT Remote Port REMOTE_PORT_RANGE - Start Port
- End Port
SECURITY_PARAMETER_INDEX IPSec Security Parameter Index TYPE_OF_SERVICE_CLASS - Type of Service
- Mask
FLOW_LABEL IPv6 Flow Label DESTINATION_MAC_ADDRESS MAC Address T_802_1Q_C_TAG_VID Customer VLAN ID T_802_1Q_S_TAG_VID Service VLAN ID T_802_1Q_C_TAG_PCP_DEI - Priority Code Point (PCP)
- Drop Eligible Indicator (DEI)
T_802_1Q_S_TAG_PCP_DEI - Priority Code Point (PCP)
- Drop Eligible Indicator (DEI)
ETHERTYPE Ethertype DNN DNN CONNECTION_CAPABILITIES Connection Capabilities DESTINATION_FQDN FQDN OS_APP_ID OS APP ID - Click Save.
The Route Information gets listed under the Traffic Descriptor group on the Create URSP Rule page.
- Click
- Expand the Route Selection Descriptor List group.
The expanded group allows you to create new descriptors.
To create new route selection descriptors:- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Route Selection Descriptor List dialog box.
- Enter the value in the Precedence field.
- Expand Route Selection Descriptor Components
group.
The expanded group allows you to create new descriptors components.
- To add new components:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Route Selection Descriptor Components dialog box.
- Select a value from the Type drop-down
list and then, enter corresponding values, if applicable. The
following table lists the route selection descriptor component
types and their corresponding values:
Table 7-134 Route Selection Descriptor Components Configurations
Type Value SSC_MODE Select any of the following values for SSC Mode: - SSC Mode 1
- SSC Mode 2
- SSC Mode 3
SNSSAI Enter the values for the following fields: - SST
- SD
- Mapped SST
- Mapped SD
DNN Enter the value of DNN in the provided field. PDU_SESSION_TYPE Select any of the following values for PDU Session Type: - IPV4
- IPV6
- IPV4V6
- Unstructured
- Ethernet
PREFERRED_ACCESS_TYPE Select any of the following values for Preferred Access Type: - 3GPP Access
- Non 3GPP Access
NON_SEAMLESS_NON_3GPP_OFFLOAD_INDICATION NA - Click Save on the Add Route Selection Descriptor Components dialog box.
- Click
- Click Save on the on the Add Route Selection Descriptor Lists dialog box.
- Click
- On the Create URSP
Rule page, click Save.
The URSP rule data gets listed on the URSP Rule page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the URSP rule configurations.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the URSP rule configurations.
Importing URSP Rule
To import the URSP rules:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.4.2 UPSI
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage the UE Policy Section Identifier (UPSI) in Policy.
The UPSI page allows you to create new and manage existing UPSI configurations. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure UPSI:
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Policy Data
Configurations, click PCF UE Policy, and
then, select UPSI.
This opens the UPSI page. The page lists the existing UPSI data. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on your
system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create UPSI page.
- On the Create UPSI page, enter
values for the input fields common to all the groups available on the page.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-135 Create UPSI Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the UPSI. UPSC Defines UE Policy Section Code. Enter a number between 0 and 65,535. URSP Rules Defines URSP rules. Note:
Name can not be the substring of any other configured URSP rule Name.
- Expand the PLMN group.
This group allows you to add PLMN information.
The following table describes the fields:Table 7-136 PLMN Configurations
Field Name Description MCC Defines the Mobile Country Code. Enter a number between 0 and 999. MNC Defines the Mobile Network Code. Enter a number between 0 and 999. - Click Save.
The UPSI data gets listed on the UPSI page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to update
or delete the session UPSI configurations.
available under the Actions column to update
or delete the session UPSI configurations.
Importing UPSI
To import UPSIs:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5 PCRF Core
This section includes the configurations for PCRF Core.
To access PCRF Core configurations from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Policy Data Configurations and select PCRF Core.
7.4.5.1 Charging Server
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage charging servers within the PCRF Core in Policy. A charging server is an application that calculates billing charges.
The Charging Server page allows you to create new and manage existing charging server configurations. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
7.4.5.2 Media Profile
Note:
Media Profiles is a function that is applicable to Cable mode only.The Media Profile page allows you to create new and manage existing media profile configurations. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure media profile:
7.4.5.3 Presence Reporting Area
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage Presence Reporting Area (PRA) under PCRF Core in Policy.
The Presence Reporting Area page allows you to create new and manage existing PRA configurations. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure PCRF PRA:
- From the navigation menu under Policy, navigate to
Policy Data Configurations, click PCRF
Core, and then, select Presence Reporting
Area.
This opens the Presence Reporting Area page. The page lists the existing PRAs. You can add or import new PRAs using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Presence Reporting Area page.
- On the Create Presence Reporting Area page, enter values
for the input fields common to all the groups available on the page.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-139 Create Presence Reporting Area Configurations
Field Name Description ID The unique identifying number of the PRA list. The ID must be a number between 0 and 16777125. This field is present if the Area of Interest subscribed or reported is a Presence Reporting Area. Name The unique name assigned to the PRA. Description Description of the PRA. Type Select the PRA type from the drop-down list. The available options are: - predefined: Select this to create a core network pre-configured PRA.
- ue_dedicated: Select this to create a ue dedicated PRA.
- Expand the PRA Items group.
The expanded group allows you to add PRA items.
- To add new items:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add PRA Items dialog box.
- Select a value from the Type
drop-down list and then, enter corresponding values. The available
options with value combination are:
- TAI: Tracking Area Identity (MCC,MNC,TAC)
- RAI: Routing Area Identity (MCC,MNC,LAC,RAC)
- Macro eNodeB: (MCC,MNC,MENB)
- Home eNodeB: (MCC,MNC,HENB)
- ECGI: E-UTRAN Cell Global Identifier (MCC,MNC,ECI)
- SAI: Service Area Identity (MCC,MNC,LAC,SAC)
- CGI: Cell Global Identity (MCC,MNC,LAC,CI)
The input fields differ for each Type, based on the components applicable for that PRA item type. The following table describes each field:Table 7-140 PRA Items Components Based on Type
Field Name Description MNC Applicable for All
Defines the Mobile Network Code. It can be a 2- or 3-digit number. MCC Applicable for All
Defines the Mobile Country Code. It should be a 3-digit number. TAC Applicable for All
28-bit string identifying an E-UTRAN Cell Id as specified, in hexadecimal representation. Each character in the string takes a value of "0" to "9" or "A" to "F" and represents 4 bits. The most significant character representing the 4 most significant bits of the Cell Id appears first in the string, and the character representing the 4 least significant bit of the Cell Id appears last in the string. Pattern: '^[A-Fa-f0-9]{7}$'
Example: An E-UTRAN Cell Id 0x5BD6007 is encoded as "5BD6007".
LAC Applicable for Type: RAI/SAI/CGI
16-bit number that forms part of the Local Area Identifier (LAI) which includes the Mobile Country Code (MCC0 the Mobile Network Code (MNC) and the Local area code. Pattern: A decimal number between 0 and 65535.
RAC Applicable for Type: RAI
The routing area code for calling and differing of various RAs. Pattern: A decimal number between 0 and 65535.
MENB Applicable for Type: Macro eNodeB
Master eNodeB. Pattern: A decimal number between 0 and 268435455.
HENB Applicable for Type: Macro eNodeB
Home eNodeB Pattern: A decimal number between 0 and 268435455.
ECI Applicable for Type: ECGI
E-UTRAN Cell Identifier Pattern: A decimal number between 0 and 268435455.
SAC Applicable for Type: SAI
Service area code Pattern: A decimal number between 0 and 65535.
CI Applicable for Type: CGI
Cell identification Pattern: A decimal number between 0 and 65535.
- Click Save on the on the Add PRA Items dialog box.
- Click
- On the Create Presence
Reporting Area page, click Save.
The PRA gets listed on the Presence Reporting Area page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the PRA configurations.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the PRA configurations.
Importing Presence Reporting Area
To import PRA:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.4 Time Periods
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage Time Periods under PCRF Core in Policy.
- Specific time of day
- Different days of the week
- Different days of a month
- Specific years
- Specific day and time in a specific year
- Specific day and time in every year
- Every Monday at 2 o'clock
- On the last day of the month
- On every Valentines day
- On May 17, 2016
- The first three days of March, July, and September
To configure time period:
- From the navigation menu under Policy,
navigate to Policy Data Configurations, click
PCRF Core, and then, select Time
Periods.
This opens the Time Periods page. The page lists the existing time periods. You can add or import new periods using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Time Period page.
- On the Create Time Period page, enter values for the
input fields common to all the groups available on the page.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-141 Create Time Periods Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the time period. The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_).
Description A descriptive phrase. Prcendence A positive integer. The lower the number, the higher the precedence. If time periods overlap, the time period with the highest precedence (lowest number) applies.
- Expand the Time Slot group.
The expanded group allows you to add time slots.
- To add time slots:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Time Slot dialog box.
- Enter the values for the following input fields:
Table 7-142 Add Time Slot Configurations
Field Name Description Years Number of years. Months of year Number of months of the year. Days of Month Days of the month. Days of Week Days of the week. Start Time Starting time. End Time End time. Note:
The fields in the time slot configuration must have certain value. It must not be left empty. - Click Save on the Add Time Slot dialog box.
- Click
- On the Create Time
Period page, click Save.
The time period gets listed on the Time Period page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the time period configurations.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the time period configurations.
Importing Time Periods
To import time periods:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.5 Retry Profile
This section describes how to configure Retry Profiles for PCRF Core.
To access Retry Profile configurations from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Policy Data Configurations, click PCRF Core, and select Retry Profile.
7.4.5.5.1 PCC Retry Profile
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage PCC Retry Profile under PCRF Core in CNC Policy.
The PCC Retry Profile page allows you to create new and manage existing profiles. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure PCC Retry Profile:
- From the navigation menu under Retry Profile,
select PCC Retry Profile.
This opens the PCC Retry Profile page. The page lists the existing PCC Retry Profiles. You can add or import new profiles using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create PCC Retry Profile page.
- On the Create PCC Retry Profile page, enter
values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-143 Create PCC Retry Profile Configurations
Field Name Description Name Enter the Name for the profile. The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 255 characters.
Description Enter the Description/Location. Free-form text describing the profile.
Maximum Retry Attempt (per Retry Cycle) The maximum number of retry attempts during a retry cycle in the range from 1 to 10. The default is 5. Initial Retry Interval Enter the Initial Retry Interval. The length of time to wait, in seconds, after a reported failure or the end of the Back Off Interval before retrying. Enter a value from 0 to 30 seconds. The default is 10 seconds.
Maximum Retry Interval Enter the Maximum Retry Interval. The maximum wait, in seconds, after a reported failure or the end of the Back Off Interval before retrying during a retry cycle. Enter a value from 1 to 180 seconds. The default is 60 seconds.
Back Off Interval Enter the Back Off Interval. The interval from 1 to 86400 seconds between successive retry cycles. The default is 300 seconds.
Maximum Retry Cycles Enter the Maximum Retry Cycles. The number of retry cycles ranging from 1 to 4. The default value is 1 cycle.
Rule Filure Code Rule Failure Code The upper box lists available rule failure codes. The lower box lists rule failure codes installed in the profile.
- Click Save.
The PCC Retry Profile gets listed on the PCC Retry Profile page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the PCC Retry Profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the PCC Retry Profile.
Importing PCC Retry Profile
To import PCC Retry Profile:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.5.2 ADC Retry Profile
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage ADC Retry Profile under PCRF Core in CNC Policy.
The ADC Retry Profile page allows you to create new and manage existing profiles. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To configure ADC Retry Profile:
- From the navigation menu under Retry Profile,
select ADC Retry Profile.
This opens the ADC Retry Profile page. The page lists the existing ADC Retry Profiles. You can add or import new profiles using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create ADC Retry Profile page.
- On the Create ADC Retry Profile page, enter
values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-144 Create ADC Retry Profile Configurations
Field Name Description Name Enter the Name for the profile. The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 255 characters.
Description Enter the Description/Location. Free-form text describing the profile.
Maximum Retry Attempt (per Retry Cycle) The maximum number of retry attempts during a retry cycle in the range from 1 to 10. The default is 5. Initial Retry Interval Enter the Initial Retry Interval. The length of time to wait, in seconds, after a reported failure or the end of the Back Off Interval before retrying. Enter a value from 0 to 30 seconds. The default is 10 seconds.
Maximum Retry Interval Enter the Maximum Retry Interval. The maximum wait, in seconds, after a reported failure or the end of the Back Off Interval before retrying during a retry cycle. Enter a value from 1 to 180 seconds. The default is 60 seconds.
Back Off Interval Enter the Back Off Interval. The interval from 1 to 86400 seconds between successive retry cycles. The default is 300 seconds.
Maximum Retry Cycles Enter the Maximum Retry Cycles. The number of retry cycles ranging from 1 to 4. The default value is 1 cycle.
Rule Filure Code Rule Failure Code The upper box lists available rule failure codes. The lower box lists rule failure codes installed in the profile.
- Click Save.
The ADC Retry Profile gets listed on the ADC Retry Profile page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the ADC Retry Profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the ADC Retry Profile.
Importing ADC Retry Profile
To import ADC Retry Profile:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.6 Traffic Profile
This section describes how to configure Traffic Profiles for PCRF Core.
To access Retry Profile configurations from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Policy Data Configurations, click PCRF Core, and select Traffic Profile.
7.4.5.6.1 ADC Rule
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage ADC Rules under Traffic Profiles in PCRF Core.
The ADC Rule page allows you to create new and manage existing ADC Rules. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To confifure ADC Rule:
- From the navigation menu under Traffic
Profile, select ADC Rule.
This opens the ADC Rule page. The page lists the existing ADC Rules. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create ADC Rule page.
- On the Create ADC Rule page, enter values for the
available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-145 Create ADC Rule Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the Profile. Rule Name Uniquely identifies the ADC rule. Used to reference an ADC rule in communication between the CNC Policy and a PCEF within one IP-CAN session. Description Description of the profile. Uplink Max Authorized Rate (bps) Maximum authorized bandwidth in bits per second for uplinks (user equipment to network). Downlink Max Authorized Rate (bps) Maximum authorized bandwidth in bits per second for downlinks (network to user equipment). Monitoring Key Monitoring key that may apply to the ADC rule. Flow Status Indicates whether the application traffic is enabled or disabled in either the uplink or downlink direction. Select from the following: - ENABLED_UPLINK
- ENABLED_DOWNLINK
- ENABLED
- DISABLED
TDF Application Identifier Identifies the traffic that belongs to the application to which the rule applies. TDF Redirect Support Indicates whether the application traffic should be redirected to another controlled address. Select from the following: - REDIRECTION_DISABLED
- REDIRECTION_ENABLED
TDF Redirect Address Type Specifies the format for the redirect address. Select from the following: - IPv4
- IPv6
- URL
- SIP_URI
TDF Redirect Server Address The address of the TDF redirect server in the specified address type. Mute Notification Notification to disable application detection notifications from the TDF device. Select MUTE_REQUIRED from the drop-down list. By default, mute remains disabled.
Service Identifier Credit-control service identifier associated with the traffic defined by this rule. Only applicable if online charging is enabled. Rating Group Credit-control rating group associated with the traffic defined by this profile. Only applicable if online charging is enabled. Reporting Level Select from the following: - SERVICE_IDENTIFIER_LEVEL
- RATING_GROUP_LEVEL
Online Charging Specifies whether or not online charging is enabled in this profile. Select from the following: - DISABLE_ONLINE
- ENABLE_ONLINE
Offline Charging Specifies whether or not offline charging is enabled in this profile. Select from the following:: - DISABLE_OFFLINE
- ENABLE_OFFLINE
Metering Method Defines how service data-flow traffic is metered for offline charging. Select from the following: - DURATION
- VOLUME
- DURATION_VOLUME
- EVENT
Precedence Precedence value of the profile. The lower the precedence, the higher the priority. - Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the ADC Rule page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
Importing ADC Rule
To import ADC Rule:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.6.2 Diameter QoS
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage Diameter QoSs under Traffic Profiles in PCRF Core.
The Diameter QoS page allows you to create new and manage existing Diameter QoSs. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To confifure Diameter QoS:
- From the navigation menu under Traffic
Profile, select Diameter QoS.
This opens the Diameter QoS page. The page lists the existing Diameter QoSs. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Diameter QoS page.
- On the Create Diameter QoS page, enter
values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-146 Create Diameter QoS Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the Profile. Description Description of the profile. QoS Class Identifier (1-254) Identifies the QoS class. Enter a value between 1 and 254 or select from the following: - 1 = Conversational speech
- 2 = Conversational
- 3 = Streaming speech
- 4 = Streaming
- 5 = Interactive with priority 1 signalling
- 6 = Interactive with priority 1
- 7 = Interactive with priority 2
- 8 = Interactive with priority 3
- 9 = Background
- 65 = MC-PTT Voice
- 66 = PTT Voice
- 69 = MC-PTT Signaling
- 70 = MC Data
Note: QCI values between 1 and 254 are supported. Values other than 1 through 9, 65, 66, 69, and 70 are undefined.
Uplink Max Authorized Rate (bps) Maximum authorized bandwidth in bits per second for uplinks (user equipment to network). Downlink Max Authorized Rate (bps) Maximum authorized bandwidth in bits per second for downlinks (network to user equipment). Uplink Min Guranteed Rate (bps) Minimum guaranteed bandwidth in bits per second for uplinks (user equipment to network). Only applicable if the QoS class identifier is between 1 and 4. Downlink Min Guranteed Rate (bps) Minimum guaranteed bandwidth in bits per second for downlinks (network to user equipment). Only applicable if the QoS class identifier is between 1 and 4. ARP Priority Level Allocation and Retention Priority level of the service flows associated with this profile. Highest: 1
Lowest: 15
ARP Preemption Capability Enable or disable the ARP Preemption Capability. Select from the following: - PREEMPTION_CAPABILITY_ENABLED
- PREEMPTION_CAPABILITY_DISABLED
ARP Preemption Vulnerability Enable or disable the ARP Preemption Vulnerability. Select from the following: - PREEMPTION_VULNERABILITY_ENABLED
- PREEMPTION_VULNERABILITY_DISABLED
Resource Allocation Notification Resource Allocation Notification Indicates that the allocation of resources for the related Diameter QoSs are confirmed. Select ENABLE_NOTIFICATION to enable. - Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the Diameter QoS page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
Importing Diameter QoS
To import Diameter QoS:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.6.3 PCC Profile
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage PCC Profiles under Traffic Profiles in PCRF Core.
The PCC Profile page allows you to create new and manage existing PCC Profiles. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To confifure PCC Profile:
- From the navigation menu under Traffic
Profile, select PCC Profile.
This opens the PCC Profile page. The page lists the existing PCC Profiles. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create PCC Profile page.
- On the Create PCC Profile page, enter
values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-147 Create PCC Profile Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the Profile. Description Description of the profile. QoS Class Identifier (1-254) Identifies the QoS class. Enter a value between 1 and 254 or select from the following: - 1 = Conversational speech
- 2 = Conversational
- 3 = Streaming speech
- 4 = Streaming
- 5 = Interactive with priority 1 signalling
- 6 = Interactive with priority 1
- 7 = Interactive with priority 2
- 8 = Interactive with priority 3
- 9 = Background
- 65 = MC-PTT Voice
- 66 = PTT Voice
- 69 = MC-PTT Signaling
- 70 = MC Data
Note: QCI values between 1 and 254 are supported. Values other than 1 through 9, 65, 66, 69, and 70 are undefined.
Bearer Usage Indicates the Bearer usage. The default value is not applicable for this field. Users can select GENERAL or IMS_SIGNALLING from the drop down list as per the requirement. Uplink Max Authorized Rate (bps) Maximum authorized bandwidth in bits per second for uplinks (user equipment to network). Downlink Max Authorized Rate (bps) Maximum authorized bandwidth in bits per second for downlinks (network to user equipment). Uplink Min Guranteed Rate (bps) Minimum guaranteed bandwidth in bits per second for uplinks (user equipment to network). Downlink Min Guranteed Rate (bps) Minimum guaranteed bandwidth in bits per second for downlinks (network to user equipment). ARP Priority Level Allocation and Retention Priority level of the service flows associated with this profile. Highest: 1
Lowest: 15
ARP Preemption Capability Enable or disable the ARP Preemption Capability. Select from the following: - PREEMPTION_CAPABILITY_ENABLED
- PREEMPTION_CAPABILITY_DISABLED
ARP Preemption Vulnerability Enable or disable the ARP Preemption Vulnerability. Select from the following: - PREEMPTION_VULNERABILITY_ENABLED
- PREEMPTION_VULNERABILITY_DISABLED
Service Identifier Credit-control service identifier associated with the traffic defined by this rule. Only applicable if online charging is enabled. Rating Group Credit-control rating group associated with the traffic defined by this profile. Only applicable if online charging is enabled. Monitoring Key Monitoring key that may apply to the PCC Rule. Reporting Level The reporting level. Select from the following: - SERVICE_IDENTIFIER_LEVEL
- RATING_GROUP_LEVEL
- SPONSORED_CONNECTIVITY_LEVEL
Online Charging Specifies whether or not online charging is enabled in this profile. Select from the following: - DISABLE_ONLINE
- ENABLE_ONLINE
Offline Charging Specifies whether or not offline charging is enabled in this profile. Select from the following:: - DISABLE_OFFLINE
- ENABLE_OFFLINE
Metering Method Defines how service data-flow traffic is metered for offline charging. Select from the following: - DURATION
- VOLUME
- DURATION_VOLUME
- EVENT
Precedence Precedence value of the profile. The lower the precedence, the higher the priority. Flow Status Indicates whether the application traffic is enabled or disabled in either the uplink or downlink direction. Select from the following: - ENABLED_UPLINK
- ENABLED_DOWNLINK
- ENABLED
- DISABLED
Resource Allocation Notification Resource Allocation Notification Indicates that the allocation of resources for the related PCC rules are confirmed. Select ENABLE_NOTIFICATION to enable. Required Access Info Select from the following: - USER_LOCATION — the subscriber’s location
- MS_TIME_ZONE — the mobile subscriber’s time zone
- USER_LOCATION and MS_TIME_ZONE — the (mobile) subscriber’s location and time zone
TDF Application Identifier Identifies the traffic that belongs to the application to which the rule applies. TDF Redirect Support Indicates whether the application traffic should be redirected to another controlled address. Select from the following: - REDIRECTION_DISABLED
- REDIRECTION_ENABLED
TDF Redirect Address Type Specifies the format for the redirect address. Select from the following: - IPv4
- IPv6
- URL
- SIP_URI
TDF Redirect Server Address The address of the TDF redirect server in the specified address type. Mute Notification Notification to disable application detection notifications from the TDF device. Select MUTE_REQUIRED from the drop-down list. By default, mute remains disabled.
Sponsor Identity Name identifying a connectivity sponsor. Application Service Provider Identity Name identifying an application service provider. Flow Descriptions(s) IP flows associated with this profile. A comma-separated list of Diameter IP Filter rules following the format specified in RFC 3588 section 4.3. Used in the following cases:- An old traffic profile is imported, and the flow description is not an empty string.
- An upgrade from an older version is in process and the existing traffic profile flow description is not an empty string.
- Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the PCC Profile page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
Importing PCC Profile
To import PCC Profile:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.6.4 PCC Rule
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage PCC Rules under Traffic Profiles in PCRF Core.
The PCC Rule page allows you to create new and manage existing PCC Rules. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To confifure PCC Rule:
- From the navigation menu under Traffic
Profile, select PCC Rule.
This opens the PCC Rule page. The page lists the existing PCC Rules. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create PCC Rule page.
- On the Create PCC Rule page, enter values for the
available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-148 Create PCC Rule Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the Profile. Rule Name Uniquely identifies the PCC Rule. Used to reference an PCC Rule in communication between the CNC Policy and a PCEF within one IP-CAN session. Note: The Name and the Rule Name fields must have the same values. It helps in proper installation of PCC rules.
Description Description of the profile. QoS Class Identifier (1-254) Identifies the QoS class. Enter a value between 1 and 254 or select from the following: - 1 = Conversational speech
- 2 = Conversational
- 3 = Streaming speech
- 4 = Streaming
- 5 = Interactive with priority 1 signalling
- 6 = Interactive with priority 1
- 7 = Interactive with priority 2
- 8 = Interactive with priority 3
- 9 = Background
- 65 = MC-PTT Voice
- 66 = PTT Voice
- 69 = MC-PTT Signaling
- 70 = MC Data
Note: QCI values between 1 and 254 are supported. Values other than 1 through 9, 65, 66, 69, and 70 are undefined.
Bearer Usage Indicates the Bearer usage. The default value is not applicable for this field. Users can select GENERAL or IMS_SIGNALLING from the drop down list as per the requirement. Uplink Max Authorized Rate (bps) Maximum authorized bandwidth in bits per second for uplinks (user equipment to network). Downlink Max Authorized Rate (bps) Maximum authorized bandwidth in bits per second for downlinks (network to user equipment). Uplink Min Guranteed Rate (bps) Minimum guaranteed bandwidth in bits per second for uplinks (user equipment to network). Only applicable if the QoS class identifier is between 1 and 4. Downlink Min Guranteed Rate (bps) Minimum guaranteed bandwidth in bits per second for downlinks (network to user equipment). Only applicable if the QoS class identifier is between 1 and 4. ARP Priority Level Allocation and Retention Priority level of the service flows associated with this profile. Highest: 1
Lowest: 15
ARP Preemption Capability Enable or disable the ARP Preemption Capability. Select from the following: - PREEMPTION_CAPABILITY_ENABLED
- PREEMPTION_CAPABILITY_DISABLED
ARP Preemption Vulnerability Enable or disable the ARP Preemption Vulnerability. Select from the following: - PREEMPTION_VULNERABILITY_ENABLED
- PREEMPTION_VULNERABILITY_DISABLED
Service Identifier Credit-control service identifier associated with the traffic defined by this rule. Only applicable if online charging is enabled. Rating Group Credit-control rating group associated with the traffic defined by this profile. Only applicable if online charging is enabled. Reporting Level The reporting level. Select from the following: - SERVICE_IDENTIFIER_LEVEL
- RATING_GROUP_LEVEL
- SPONSORED_CONNECTIVITY_LEVEL
Online Charging Specifies whether or not online charging is enabled in this profile. Select from the following: - DISABLE_ONLINE
- ENABLE_ONLINE
Offline Charging Specifies whether or not offline charging is enabled in this profile. Select from the following:: - DISABLE_OFFLINE
- ENABLE_OFFLINE
Metering Method Defines how service data-flow traffic is metered for offline charging. Select from the following: - DURATION
- VOLUME
- DURATION_VOLUME
- EVENT
Precedence Precedence value of the profile. The lower the precedence, the higher the priority. Flow Status Indicates whether the application traffic is enabled or disabled in either the uplink or downlink direction. Select from the following: - ENABLED_UPLINK
- ENABLED_DOWNLINK
- ENABLED
- DISABLED
Resource Allocation Notification Resource Allocation Notification Indicates that the allocation of resources for the related PCC rules are confirmed. Select ENABLE_NOTIFICATION to enable. Required Access Info Select from the following: - USER_LOCATION — the subscriber’s location
- MS_TIME_ZONE — the mobile subscriber’s time zone
- USER_LOCATION and MS_TIME_ZONE — the (mobile) subscriber’s location and time zone
TDF Application Identifier Identifies the traffic that belongs to the application to which the rule applies. TDF Redirect Support Indicates whether the application traffic should be redirected to another controlled address. Select from the following: - REDIRECTION_DISABLED
- REDIRECTION_ENABLED
TDF Redirect Address Type Specifies the format for the redirect address. Select from the following: - IPv4
- IPv6
- URL
- SIP_URI
TDF Redirect Server Address The address of the TDF redirect server in the specified address type. Mute Notification Notification to disable application detection notifications from the TDF device. Select MUTE_REQUIRED from the drop-down list. By default, mute remains disabled.
Sponsor Identity Name identifying a connectivity sponsor. Application Service Provider Identity Name identifying an application service provider. PS to CS Session Connectivity Indicates that the service data flow carries video and allows for packet switch (PS) to circuit switch (CS) session continuity. Select VIDEO_PS2CS_CONT_CANDIDATE from the drop-down list. Flow Descriptions(s) IP flows associated with this profile. A comma-separated list of Diameter IP Filter rules following the format specified in RFC 3588 section 4.3. Used in the following cases:- An old traffic profile is imported, and the flow description is not an empty string.
- An upgrade from an older version is in process and the existing traffic profile flow description is not an empty string.
- Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the PCC Rule page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
Importing PCC Rule
To import PCC Rule:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.6.5 Predefined ADC Rule
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage Predefined ADC Rules under Traffic Profiles in PCRF Core.
The Predefined ADC Rule page allows you to create new and manage existing Predefined ADC Rules. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To confifure Predefined ADC Rule:
- From the navigation menu under Traffic
Profile, select Predefined ADC Rule.
This opens the Predefined ADC Rule page. The page lists the existing Predefined ADC Rules. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Predefined ADC Rule page.
- On the Create Predefined ADC Rule page,
enter values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-149 Create Predefined ADC Rule Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the Predefined ADC Rule. Rule-Base Name Uniquely identifies the Predefined ADC Rule. Used to reference an Predefined ADC Rule in communication between the CNC Policy and a PCEF within one IP-CAN session. Description Description of the ADC Rule. - Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the Predefined ADC Rule page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
Importing Predefined ADC Rule
To import Predefined ADC Rule:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.6.6 Predefined ADC Rule Base
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage Predefined ADC Rule Bases under Traffic Profiles in PCRF Core.
The Predefined ADC Rule Base page allows you to create new and manage existing Predefined ADC Rule Bases. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To confifure Predefined ADC Rule Base:
- From the navigation menu under Traffic
Profile, select Predefined ADC Rule Base.
This opens the Predefined ADC Rule Base page. The page lists the existing Predefined ADC Rule Bases. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Predefined ADC Rule Base page.
- On the Create Predefined ADC Rule Base
page, enter values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-150 Create Predefined ADC Rule Base Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the Predefined ADC Rule Base. Rule-Base Name: Uniquely identifies the Predefined ADC Rule Base. Used to reference an Predefined ADC Rule Base in communication between the CNC Policy and a PCEF within one IP-CAN session. Description Description of the Predefined ADC Rule Base. - Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the Predefined ADC Rule Base page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
Importing Predefined ADC Rule Base
To import Predefined ADC Rule Base:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.6.7 Predefined PCC Rule
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage Predefined PCC Rules under Traffic Profiles in PCRF Core.
The Predefined PCC Rule page allows you to create new and manage existing Predefined PCC Rules. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To confifure Predefined PCC Rule:
- From the navigation menu under Traffic
Profile, select Predefined PCC Rule.
This opens the Predefined PCC Rule page. The page lists the existing Predefined PCC Rules. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Predefined PCC Rule page.
- On the Create Predefined PCC Rule page, enter values
for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-151 Create Predefined PCC Rule Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the Predefined PCC Rule. Rule Name Uniquely identifies the Predefined Predefined PCC Rule. Used to reference an Predefined Predefined PCC Rule in communication between the CNC Policy and a PCEF within one IP-CAN session. Note: The Name and the Rule Name fields must have the same values. It helps in proper installation of PCC rules.
Description Description of the Predefined PCC Rule. - Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the Predefined PCC Rule page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
Importing Predefined PCC Rule
To import Predefined PCC Rule:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.5.6.8 Predefined PCC Rule Base
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage Predefined PCC Rule Bases under Traffic Profiles in PCRF Core.
The Predefined PCC Rule Base page allows you to create new and manage existing Predefined PCC Rule Bases. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
To confifure Predefined PCC Rule Base:
- From the navigation menu under Traffic
Profile, select Predefined PCC Rule Base.
This opens the Predefined PCC Rule Base page. The page lists the existing Predefined PCC Rule Bases. You can add or import new data using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Predefined PCC Rule Base page.
- On the Create Predefined PCC Rule Base
page, enter values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-152 Create Predefined PCC Rule Base Configurations
Field Name Description Name Name of the Predefined PCC Rule Base. Rule Name Uniquely identifies the Predefined PCC Rule Base. Used to reference an Predefined PCC Rule Base in communication between the CNC Policy and a PCEF within one IP-CAN session. Note: The Name and the Rule Name fields must have the same values. It helps in proper installation of PCC rules.
Description Description of the Predefined PCC Rule Base. Monitoring Key Monitoring key that may apply to the Predefined PCC Rule Base. - Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the Predefined PCC Rule Base page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
Importing Predefined PCC Rule Base
To import Predefined PCC Rule Base:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.4.6 Usage Monitoring
This section includes the configurations for Usage Monitoring.
To access Usage Monitoring configurations from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Policy Data Configurations, and select Usage Monitoring.
- Data Limit Profiles
- Data Limit Selection Profiles
- Data Limit Sorting Profiles
- Data Rollover Profiles
7.4.6.1 Data Limit Profiles
To configure the data limit profiles:
- Navigate to Data Limit Profiles page under Usage Monitoring in Policy Data Configurations.
- Click
 .
.
The Create Data Limit Profile page appears.
- On Create Data Limit Profile page, add the
following details:
Field Name Description Profile Name Uniquely identifies the UM Data Limit Profile by a name. This field is for configuration purpose only and not transmitted over the network. Limit Identifier Specifies the limit identifier. Multiple limit identifiers may have the same priority. Monitoring Key Uniquely identifies the UM Data Limit Profile by a Monitoring Key. If its value is not explicitly provided, then the data limit profile's limitId will be used as the monitoring Key of that profile.
Profile Type Specifies the type of the Data Limit Profile.
Default value: SUBSCRIBER
Note: Striked-out entries are for future.
Plan Type Specifies the type of Plan such as Base, Top-up, and Pass. This helps to determine the priority in selecting the plan over other types. The priority is configurable in service configuration screen.
Default value: Base
Parent Plan Identifies a Data Limit Profile as a parent data plan. Any attribute that is not explicitly configured in this plan shall be taken from the parent plan (if present). Priority A Priority is used to weigh it with other Data Limit Profiles and UDR provisioned Data Limits of the same Plan Type. The priority can be used by Policy or Data Limit Selection Profile for choosing among different candidate profiles.
The Plan Type, Priority within that Plan Type and the Selection Order of Plan Types together decide the order of selection of Data Plans.
Validity Duration Indicates the length of usage time in seconds. Range: 3600 - 31536000 (1 Year)
Note: Validity Duration is applicable only for plans, which has Periodicity as
NEVER. There is no validity for the recurring plans.UM Level Indicates the level of the usage monitoring instance (PDU Session level or per Service).
Default value: Session Level
Inactivity Time (seconds) Time interval in seconds after which the PGW or SMF shall stop time measurement for the Monitoring Key, if no packets are received belonging to the corresponding Monitoring Key
Range: 0 - 604800 (7 Days)
Default value: 86400 ( 1 Day)
Data Rollover Profile A reference to a Data Rollover Profile. If not configured, Data Rollover will be disabled for this Data Plan. Allow Excess Usage Indicates whether or not excess usage is allowed for this Data Limit Profile. When Excess Usage is allowed, Usage Monitoring shall continue to grant and accumulate usage even after consuming 100% of allocated volume/time. The QoS, Charging etc. parameters can be controlled at PCRF Core Policy on account of the consumed usage.
Default value: False
Usage Limit Duration Indicates the length of time in seconds.
Range: 3600 - 31536000 (1 Year)
Volume Total Specifies the total data octets for both downlink and uplink
Range: 512 - 1073741824000 (1000 GB)
Volume Uplink Specifies the uplink data octets.
Range: 512 - 1073741824000 (1000 GB)
Volume Downlink Specifies the downlink data octets.
Range: 512 - 1073741824000 (1000 GB)
Reset Period Period Indicates whether the periodicity is "YEARLY", "MONTHLY", "WEEKLY", "DAILY" or "HOURLY".
Default value: Monthly
Maximum Number Of Periods Indicates the maximum number of periods after which the usage monitoring instance does not apply. If omitted, there is no limit in the number of periods. Billing Day Type Indicates which day of the period to reset the usage limit.
Default value: LAST_DAY
Note: If this configuration is updated, the new configuration shall be applied in the next billing cycle.
Day Indicates the the specific day of the period. Day count starts from 1. If the Day entered is beyond the last day of a period (for example 31 for the month of April), the last day shall be considered.
Required when "SPECIFIC_DAY" is selected in the Type field.
Note: If this configuration is updated, the new configuration shall be applied in the next billing cycle.
Time Indicates the specific time of day in "HH:MM:SS"
Default value: "00:00:00"
Note: If this configuration is updated, the new configuration shall be applied in the next billing cycle.
Excess Usage Limit Percentage Indicates the percentage of base volume/time up to which excess usage is allowed.
Range: 100 - 1500
Note: If this field is applicable for Excess Usage Limit, the value of the field should not be left empty. Otherwise, excess usage beyond the usage limit duration will not be allowed.
Duration Indicates the length of time in seconds. This is inclusive of the base duration. That is, the value in this field indicates the total duration to be consumed including base + excess.
Range: 3600 - 31536000 (1 Year)
Note: If this field is applicable for Excess Usage Limit, the value of the field should not be left empty. Otherwise, excess usage beyond the usage limit duration will not be allowed.
Volume Total Specifies the total data octets for both downlink and uplink. This is inclusive of the base total volume.
Range: 512 - 1073741824000 (1000 GB)
Note: If this field is applicable for Excess Usage Limit, the value of the field should not be left empty. Otherwise, excess usage limit for both uplink and downlink data octets will not be considered.
Volume Uplink Uplink data octets. This is inclusive of the base uplink volume.
Range: 512 - 1073741824000 (1000 GB)
Note: If this field is applicable for Excess Usage Limit, the value of the field should not be left empty. Otherwise, excess usage limit for uplink data octets will not be considered.
Volume Downlink Downlink data octets. This is inclusive of the base downlink volume.
Range: 512 - 1073741824000 (1000 GB)
Note: If this field is applicable for Excess Usage Limit, the value of the field should not be left empty. Otherwise, excess usage limit for downlink data octets will not be considered.
- Click Save to save the Data Limit Profile.
7.4.6.2 Data Limit Selection Profiles
This page allows you to select, create, and configure Data Limit Selection Profiles.
Data Limit Selection is a set of rules to select one or more Data Limits based on certain conditions.
To create and configure the Data Limit Selection Profiles:
- Navigate to Data Limit Selection Profiles page under Usage Monitoring in Policy Data Configurations.
- Click
 .
.
The Create Data Limit Selection Profile page appears.
- Enter the a unique name to identify the Data Limit Selection Profile.
- Click
 to create new selection rules.
to create new selection rules.
The Add Selection Rules dialog box appears.
- Enter values for the available input fields described in the following
table:
Table 7-153 Selection Rules Configurations
Field Name Description Priority Indicates the selection rule priority. Type Indicates the selection rules type. Data Limit Profile Name This field is displayed when Type is "Data Limit Profile". This field should match the name configured in the Data Limit Profile. UDR Data Limit Name This field is displayed when Type is "UDR Data Limit". This field should match the Limit Identifier or the name of the plan if configured in Custom Attribute mapping and present in the UM Data Limit. Always Match When this is true, no conditions shall be evaluated. This can be used as a CATCH ALL Selection Rule.
Default value: false
- Under Conditions, click
 .
.
The Add Conditions dialog box appears.
Enter values for the available input fields described in the following table:
Table 7-154 Conditions Configurations
Field Name Description Parameter Type Indicates the type of parameter on which the condition will be applied.
- Forwarded Attribute - Am attribute forwarded by the core service, for e.g. Serving Gateway MCCMNC / IP Address, APN etc.
- Policy Decision Tag - A Tag applied by the policy.
Attribute Name This field is displayed when Parameter Type is "Forwarded Attribute". Operator Accepts the following values: - Equals
- Not Equals
- Less Than
- Greater Than
- Matches
Value Displays the list of configured Match Lists when the Operator is "Matches". Click Save to save the conditions.
- Click Save to save selection rules.
7.4.6.3 Data Limit Sorting Profiles
This page allows you to select, create, and configure Data Limit Sorting Profiles.
Data Limit Sorting Rule is a set of rules to sort Data Limits. If Sorting Rules are configured, Sorting rules are applied after applying Selection Rules and when the output of Selection Rules results in more than one Data Limit.
To configure Selection and/or Sorting Rules to select one Usage Monitoring Data Limit out of many data limits provided by UDR or out of those configured in Data Limit Profiles, perform the following configurations:
- Navigate to Data Limit Sorting Profiles page under Usage Monitoring in Policy Data Configurations.
- Click
 .
.
The Create Data Limit Sorting Profile page appears.
- On the Create Data Limit Sorting Profile
page:
- Enter the name of the Data Limit Sorting Profile.
- Under Sorting Rules, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Sorting Rules dialog box.
- In Add Sorting Rules dialog box, perform
the following configurations:
Table 7-155 Sorting Rules Configurations
Field Name Description Index Specifies the index. The sorting rules are applied in the order of index. Parameter Type Specifies the type of the parameter. Attribute Name Specifies the name of the attribute Order Specifies the order. - Click Save to save sorting rules.
- Click Save on the Create Data Limit Sorting Profile page to save the Data Limit Sorting Profile.
7.4.6.4 Data Rollover Profiles
- Navigate to Data Rollover Profiles page under Usage Monitoring in Policy Data Configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens Create Data Rollover Profile page.
-
In the Create Data Rollover Profile page, add the following configurations:
Field Name Description Profile Name A unique to identify the Data Rollover Profile. Data Rollover Enabled Indicates whether to enable or disable Data Rollover. Rollover Data Consumption Indicates when to consume the rollover data. Rollover data to be consumed before or after a base plan. Note: As of now, Policy does not support consumption of the rollover data after the parent plan.
Maximum Number of Rollovers Indicates how many cycles the data plan can rollover. A value of 0 means there is no limit to the number of cycles the left over data can rollover.
Range: 0 to 24
Default value: 0 (No limit)
Data Rollover Percentage Indicates the percentage of left over data volume/time to rollover to the next cycle.
Range: 0 to 100
Default value: 100.
Data Limit Cap Enabled Indicates whether to enable or disable a cap (maximum limit) on the total data volume/time to be allotted for the next billing cycle or period. The maximum cap is applied on the total of base plan volume/time and total accumulated rolled over volume/time. Maximum Rollover Threshold (To configure the maximum amount of data volume/time that can roll over from one cycle to another) Base Data Percentage Indicates the percentage of base plan data volume/time that is allowed as rollover data volume/time.
Range: 0 to 100
Duration Indicates the length of time in seconds.
Range: 3600 - 2592000 (30 Days)
Volume Total Specifies the total data octets for both downlink and uplink.
Range: 512 - 107374182400 (100 GB)
Volume Uplink Specifies the uplink data octets.
Range: 512 - 107374182400 (100 GB)
Volume Downlink Specifies the downlink data octets.
Range: 512 - 107374182400 (100 GB)
Minimum Rollover Threshold Duration Indicates the length of time in seconds. The remaining duration if applicable shall be rolled over to the next period if it is greater than the threshold value configured here.
Range: 0 - 2592000 (30 Days)
Volume Total Specifies the total data octets for both downlink and uplink. The remaining total volume if applicable shall be rolled over to the next period if it is greater than the threshold value configured here.
Range: 0 - 107374182400 (100 GB)
Volume Uplink Specifies the uplink data octets. The remaining uplink volume if applicable will be rolled over to the next period if it is greater than the threshold value configured here.
Range: 0 - 107374182400 (100 GB)
Volume Downlink Specifies the downlink data octets. The remaining downlink volume if applicable will be rolled over to the next period if it is greater than the threshold value configured here.
Range: 0 - 107374182400 (100 GB)
Data Limit Cap Settings Data Limit Cap Settings is used to configure the data threshold across all roll-overs. The rollover data should not exceed the limits configured under Data Limit Cap Settings.
Duration Indicates the length of time (duration) in seconds for which the data cap must be imposed.
Range: 3600 - 2592000 (30 Days)
Volume Total Indicates the maximum limit on the total volume of data octets for both downlink and uplink.
Range: 512 - 107374182400 (100 GB)
Volume Uplink Indicates the maximum volume of data that must be allowed for the uplink data octets.
Range: 512 - 107374182400 (100 GB)
Volume Downlink Indicates the maximum volume of data that must bbe allowed for the downlink data octets.
Range: 512 - 107374182400 (100 GB)
- Click Save to save the Data Rollover Profile.
7.5 Policy Management
- Session Management and Policy Authorization
- Access and Mobility Management
- UE Management
- PCRF Core
- Policy Data Source
- Usage Monitoring
This section describes how to create, manage, and deploy policies using the Policy Management pages.
- Policy Projects
- Policy Library
- Policy Tests
The following section describes the configurations on the Policy Projects page.
For information on Policy Library and Policy Tests functionalities, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy Design Guide.
7.5.1 Policy Projects
You can create and deploy a Policy project using Policy Projects page. There are two possible states for the Policy project, Prod and Dev.
- From the navigation pane under
Policy, navigate to Policy
Management and select Policy Projects.
This opens the Policy Projects page, displaying the existing Policy projects for the respective Policy service.
The following screen capture shows an illustration of the Policy Projects page:
Figure 7-28 Policy Projects
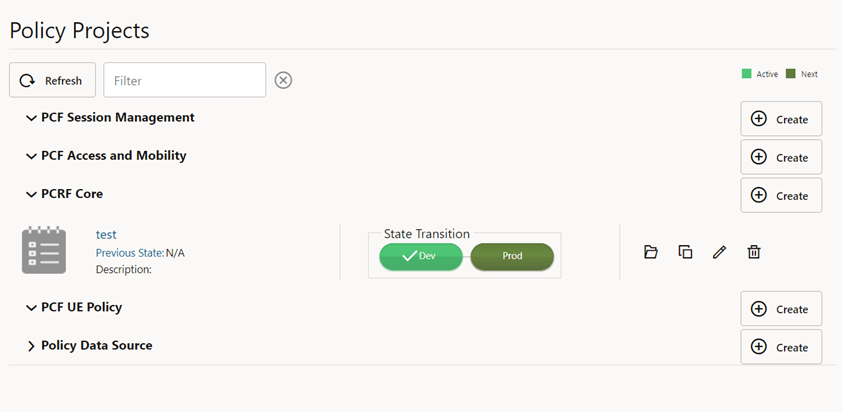
You can filter the existing projects based on Project Name and Active State using the Filter box available at the top of the page.
- To create new project, click
 for the service group, for which the Policy project is to be created.
The page opens the Create Policy Project dialog box.
for the service group, for which the Policy project is to be created.
The page opens the Create Policy Project dialog box.Note:
Policy supports 10 projects per service type. An error message is displayed on clicking , if the number of projects created for a selected service type
has reached maximum limit.
, if the number of projects created for a selected service type
has reached maximum limit.
- In the Create Policy Projects dialog box,
enter the following information:
Field Name Description Name The unique name you assign to the policy project
This is a mandatory field.
The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underscore (_). The maximum length is 32 characters.
Description Free-form text that identifies the Policy project.
The maximum length is 255 characters.
- Click Save.
This creates the Policy Project. The project is listed under the respective service name group.
Note:
- Policy allows you to perform unit test for a
project. For more information on testing the projects, see
Test Policy Projectssection in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy Design Guide. - The Policy Project page
allows you to clone projects. Use the
 icon available with the Policy project listing to clone
the project. The cloned project contains the data similar to the
project from which it is cloned.
icon available with the Policy project listing to clone
the project. The cloned project contains the data similar to the
project from which it is cloned.
- Use
 or
or  to update or delete the Policy project.
to update or delete the Policy project.
- Policy allows you to perform unit test for a
project. For more information on testing the projects, see
- To configure the Policy project, click
 corresponding to the project name.
This opens the Blockly editor. The editor allows you to construct one or more policies using the building blocks provided in the left hand side panel of the editor.
corresponding to the project name.
This opens the Blockly editor. The editor allows you to construct one or more policies using the building blocks provided in the left hand side panel of the editor.Note:
The projects in Prod state are not editable. You can only view these projects and the associated policies, but cannot modify them.For more information on configuring Policy blocks using Blockly editor, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy Design Guide.
- Change the state of a the Policy project, if required.
Policy Projects can have any of the following states:
- Dev: By default, the Dev state is assigned to a Policy project. Dev projects do not process any traffic in PRE.
- Prod: The projects in Prod state processes traffic in PRE.
The current state of any project can be identified with a tick mark and light green colored button as displayed at the upper right hand corner of the Policy Projects page.
The following screen capture illustrates the different states of a project.
Figure 7-29 Policy Project States

Note:
At any point of time there can be only one project in Prod state for a service. If you change the state of the project to Prod and there is already a project with the Prod state for that service, the Prod state for the existing project automatically gets updated to Dev state and the project in Dev state is updated to Prod state.
Note:
When a user creates or updates (for example project states) a Policy project through CNC Console or REST API, it may take up to 10 seconds for the changes to reflect in the Policy rule.Viewing Policy Project States
- Example 1:
The following screen capture shows an example, displaying a project in Prod state:
Figure 7-30 Example 1

The following details are highlighted in the above example:
Current State: Prod
Previous State: Dev
Timestamp when the state changed from Dev to Prod: 02 Jul 2020 15:08 UTC
- Example 2:
The following screen capture shows an example, displaying a newly created project in Dev state:
Figure 7-31 Example 2

The following points lists the details highlighted in the above example:
Current State: Dev
Previous State: N/A
Since it is a new project, there is no previous state.
- Example 3:
The following screen capture shows an example of getting the complete history of the previous states of a Policy project by clicking the Previous States:
Figure 7-32 Example 3
7.6 Diameter Configurations
This section describes how to manage and view the Diameter Configurations in Policy using the Diameter Configurations pages.
7.6.1 Settings
The Settings page displays the general configurations related to the Diameter node. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Diameter
Configurations and select Settings.
This opens the Settings page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Settings page.
- Enter the following information
under the respective groups:
Table 7-156 Edit Settings
Field Name Description Timer Reconnect Delay (sec) Enter the time frame to delay before attempting to reconnect after a connection failure in seconds. The default value is 3 seconds.
Response Timeout (ms) Enter the response timeout interval in milliseconds. The default value is 5000 ms.
Note: The response timeout interval can have a decimal value. It helps to put the value in milliseconds.
Connection Timeout (sec) Enter the connection timeout interval in seconds. The default value is 3 seconds.
WatchDog Interval (sec) Enter the watchdog interval in seconds. The default value is 6 seconds.
Transport Protocol The protocol supported is TCP. Congestion Control Load Shedding Profile Select any one of the configured load shedding profiles from the drop-down menu. Message Priority Profile Select any of the configured message priority profiles from the drop-down menu. Overload Control Load Shedding Profile Select any one of the configured load shedding profiles from the drop-down menu. Message Priority Profile Select any of the configured message priority profiles from the drop-down menu. Note:
The following message priority data that was exported prior to Policy 23.2.0 cannot be imported as the data may be corrupt:- message containing Sd as interface
- Sy-SLR as condition message
The data with Sd interface or Sy-SLR condition messages that are exported only with Policy 23.2.0 or later versions can be imported.
Topology Hiding Topology Hiding Enable or disable the topology hiding feature using this switch. When this feature is disabled, no changes are made to the orgin-host in the message. On enabling this feature, origin-host is updated in all or specific messages. Apps to Hide Specifies the application names for which topology hiding feature needs to be enabled. Users can select one or many values from the following list using the drop-down: - Rx
- Gx
- Sy
- All
When Topology Hiding feature is enabled with value All for Apps to Hide field, origin-host is replaced for all the diameter interface outgoing messages.
Enhanced Timer Configuration Application Name Request Timer configuration for applications name like Rx, Gx, Sy, Sd.
Application Response Timeout (milliseconds) Enter the application response timeout in milliseconds. The range of this value is between between 3 seconds to 2147483647. Command Code Response Timeout AAR (milliseconds) The command code response timeout value for AAR. The allowed value ranges from 3 to 2147483647.
Default Value: 5000
STR (milliseconds) The command code response timeout value for STR. The allowed value ranges from 3 to 2147483647.
Default Value: 5000
RAR (milliseconds) The command code response timeout value for RAR. The allowed value ranges from 3 to 2147483647.
Default Value: 5000
ASR (milliseconds) The command code response timeout value for ASR. The allowed value ranges from 3 to 2147483647.
Default Value: 5000
The order of precedence (from highest to lowest) of response timeout configurations is:- Command Code Response Timeout (ms) - Message level configurations i.e at AAR, STR etc.
- Application Response Timeout (ms) - Interface level configurattion i.e at Gx, Rx etc.
- Response Timeout (ms) - General level configutation
Figure 7-33 Add Enhanced Timer Configuration in the edit mode
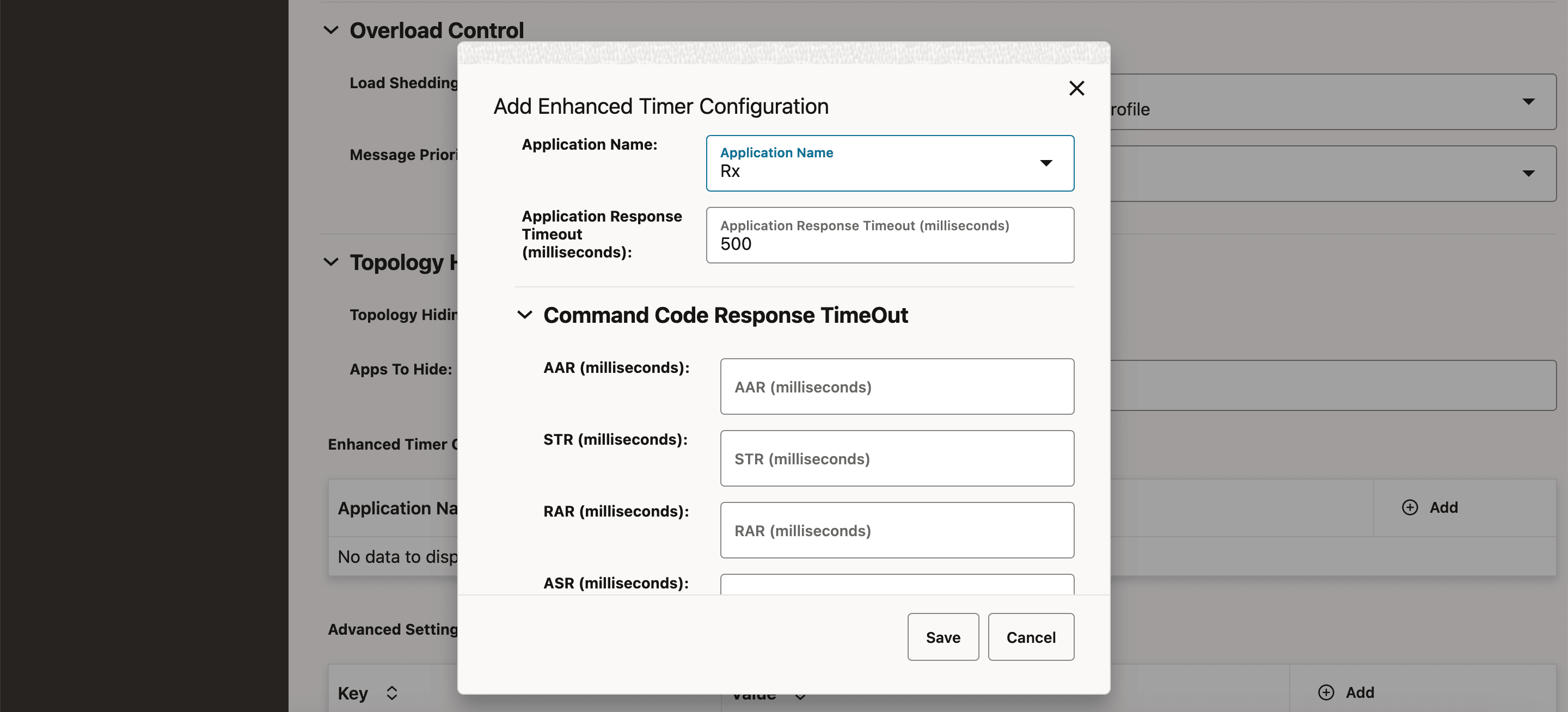
- Click Save to save the settings.
- Perform the following
steps to configure Advanced Settings:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following
key and respective
value:
Table 7-157 Parameters for Advanced Settings
Keys Value DIAMETER.ErrorHandler.MaxRetryCount.Rx.RAR It is used to set the maximum retries that can be performed for failed RAR messages. The retry attempt value can be any positive integer number between 1 to 2147483647. Note: If retry attempt value configured is a zero or negative number, then the default retry attempt value shall be considered.
Default Value: 1
DIAMETER.ErrorHandler.CycleBackRetry.Rx.RAR It is used to set if peers can be cycled back for retries or not. Default Value: false
DIAMETER.ErrorHandler.MaxRetryCount.Rx.ASR It is used to set the maximum retries that can be performed for failed ASR messages. The retry attempt value can be any positive integer number between 1 to 2147483647. Note: If retry attempt value configured is a zero or negative number, then the default retry attempt value shall be considered.
Default Value: 1
DIAMETER.ErrorHandler.CycleBackRetry.Rx.ASR It is used to set if peers can be cycled back for retries or not. Default Value: false
DIAMETER.gateway.binding.lookup.failure.forcerouting.enabled This is used to enable force routing to PCRF Core and/or Diameter Connector on receiving Rx Commands along with Binding error response.
Default Value: false
DIAMETER.gateway.binding.lookup.failure.forcerouting.service.list This is used to set the force routing to PCRF Core and/or Diameter Connector. The possible list of values:- PCRF_CORE
- DIAMETER_CONNECTOR
DIAMETER.gateway.binding.lookup.failure.forcerouting.exceptions This is used to identify the exceptions for which force routing needs to be set.
The possible list of values:- java.net.UnknownHostException
- java.net.ConnectException
- java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException
But any class exception can be placed as a value of the list.
DIAMETER.gateway.binding.lookup.failure.forcerouting.responsecodes This is used to identify the response error codes for which force routing needs to be set.
The possible list of values:- 404
- 503
But any http status code can be placed as a value of the list.
- Click Save.
The page saves the Error Handling configurations.
- Click the
7.6.2 Peer Nodes
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage Peer Nodes in Diameter Configurations.
The Peer Nodes page allows you to create new and manage existing Peer Nodes. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Diameter
Configurations, and select Peer
Nodes.
This opens the Peer Nodes page. The page lists the existing Peer Nodes. You can add or import new nodes using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Peer Node page.
- On the Create Peer Node page, enter
values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-158 Create Peer Node Configurations
Field Name Description Name Unique name of the peer node. Example value: ocs
Type Defines which type of diameter service must be selected. The values can be - PCF
- Application function (AF)
- Backend
- Diameter Routing Agent (DRA)
- Online Charging System (OCS)
- TDF
- UDR
You can choose a specific type if a particular NF can be directly connected. If NF is behind the DRA, then DRA must be chosen.
Backend is a special type used by the engineering team to connect to the backend core services.
Reconnect Limit (sec) The reconnect limit. This value must be configured as the Diameter peer configuration. Currently, all the Gateway pods reconnect for infinite time for the cloud native environment. Hence, this variable is of no use. This value can be kept as it is.
Initiate Connection Initiate connection has two options: - True: diameter-gateway initiates a connection.
Note: Each diameter-gateway pod initiates one connection.
- False: diamteter-gateway acts as a responder. It waits for other peers to initiate a connection.
Note: When the diameter gateway is the connection initiator, then each diameter gateway pod would initiate 1 diameter connection with a network peer. For an example, if there are three diameter gateway pods and two external peers, then a mesh would be created with 6 diameter connections.
Port Enter the port number. Enter a number from 0 to 65535. Example value: 8007
Transport Defines the type of transport ways for configuring a peer. The values can be: - TCP
- TLSv1.2
- TLSv1.3
- TLSv1.2_OR_TLSv1.3
Host Enter the host name. Enter a FQDN or IP address available for establishing diameter transport connections to the peer node. Note: It is mandatory if Initiate Connection is set to true.
Realm Enter the Realm of the peer to which diameter-gateway needs to be connected. For example,to add the realm detail of the OCS peer, enter oracle.com .
Identity Enter an identity of the peer to which diameter-gateway needs to be connected. For example, to add the identity detail of the OCS peer, provide value enter ocs.
- Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the Peer Node page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
Importing Peer Node
To import peer node:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.6.3 Routing Table
Configuration allows the routing of Diameter request messages to next hop peer based on Diameter application-id, Destination-Realm, and Destination-Host using Diameter routing table.
- Host-Based Routing: The destination-host of incoming message is checked in the routing table, and then the message is routed to the top priority of the matching route's peer.
- Realm-Based Routing: The destination-realm of incoming message is checked in the routing table, and then the message is routed to the top priority of the matching route's peer.
Routing decision at Diameter-Gateway
- If the incoming request message has destination-host and the specified peer is directly connected with the gateway pod, then the message is routed to the peer specified in destination-host.
- If the incoming request message has destination-host and is not directly connected via any other diameter-gateway pods in cluster, then the message will be inter-pod routed.
- The routing table is scanned for a matching route:
- If the host is reachable, message is sent.
- If the host is not reachable directly, find if it can be reached by another diameter gateway pod, message is sent using inter-pod route.
- If the host is not reachable directly or indirectly, look up the routing table again for the next priority matching route.
Note:
In the routing table, if any peers are not matched then the default route peer will be selected if it is configured.
The Diameter Routing Table Configurations page displays the Diameter routing table configurations. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Diameter
Configurations and select Routing Table.
This opens the Diameter Routing Table Configurations page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
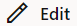 .
.
This opens the Edit Diameter Routing Table Configurations page.
- Expand the Diameter Route Table Table
group.
The expanded group allows you to add route table entries.
- To add routing table:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Diameter Route Table dialog box.
- Enter the values for the following input fields:
Table 7-159 Add Diameter Route Table Configuration
Field Name Description Priority Defines the order of use when one or more routes have overlapping criteria. Note: If there are more than one routing table entry with same priority, it will consider only first row from multiple rows with same priority.
The range is 0-65535.
Example value: 1
Name Configure Name as the value specified in Server Identifier. Starting with release 1.11.1, for the data sources configured as peer nodes in diameter gateway for Sy interface, the diameter routing table configurations must be added. While configuring, ensure that the given name is same as the value specified in the Server Identifier field.
Type Route type. The value can be Realm or Host. - When the Realm is selected in the Type field, Realms field is displayed.
- When the Hosts is selected in the Type field, Hosts field is displayed.
Realms The realm detail of the route. Example value: oracle.com
Application ID Select Rx , Gx, Sy, or All.
Example value: SyServer Identifier Specifies the server to which the message is to be routed. This identity must also be present in the Identity field of the peer node. Note: If multiple server identifiers are configured one after the other separated by (,) comma, it considers the first value and ignores the rest of the values which were added with the comma separator.
- Click Save on the Add Diameter Routing Table dialog box.
- Click
- On the Edit Diameter Routing Table Configurations page, expand the Default Route group.
- Enter value for the Server Identifier
drop-down list.
The server identifier drop-down list shows the list of the configured peer nodes on the Peer Nodes configuration page. For more information on configuring Peer Nodes, see Peer Nodes.
On selecting any of the value, ensure that the name is same as the values of server identifier.Note:
* (asterisk) wild card character is allowed in Hosts, Realms, and Server Identifier fields. - Click Save.
The configuration gets listed on the Diameter Routing Table Configurations page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the Diameter Routing Table configurations.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the Diameter Routing Table configurations.
7.6.4 Peer Node Sets
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Diameter
Configurations and select Peer Node
Sets.
This opens the Peer Node Sets page. The page lists the existing Peer Node Sets. You can add or import new nodes using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Peer Node Sets page.
- On the Create Peer Node Sets page, enter
values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the fields:
Table 7-160 Create Peer Node Sets Configurations
Field Name Description Name Unique name of the peer node. Example value: ocs
Description Type Defines which type of diameter service must be selected. The values can be - PCF
- Application function (AF)
- backend
- diameter routing agent (dra)
- online charging system (ocs)
- tdf
- udr
Realm Enter the realm name, that is, FQDNs to all of that computers that transact diameter traffic. For example,to add the realm detail of the OCS peer, enter oracle.com .
Primary Server The primary server for a TDF client. Secondary Server The secondary server for a TDF client. Tertiary Server The teritiary server for a TDF client. Quaternary Server The quatenary server for a TDF client. - Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the Peer Node Sets page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
7.6.5 Diameter Error Configurations
This section describes how to customize the Diameter error codes according to the network requirements using the Diameter Error Codes page.
The Diameter Error Codes page on CNC Console allows users to view and edit conditions defined by default for the Policy network function. This page also provides the options to import and export Diameter error codes.
Table 7-161 Error Codes and Responses
| Condition ID and Name | Error Message | Diameter Error Code/Experimental Result Code | Application Error Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Invalid AVP Value |
The request contained an AVP with an invalid value in its data portion. | 5004 | DIAMETER_INVALID_AVP_VALUE |
|
Missing AVP |
The request did not contain an AVP that is required by the Command Code definition. | 5005 | DIAMETER_MISSING_AVP |
|
Unsupported Command Code |
The Request contained a Command-Code that the receiver did not recognize or support. | 3001 | DIAMETER_COMMAND_UNSUPPORTED |
|
Loop Detected |
The Request contained a Command-Code that the receiver did not recognize or support. | 3005 | DIAMETER_LOOP_DETECTED |
|
Invalid Diameter Error |
A request was received whose bits in the Diameter header were either set to an invalid combination, or to a value that is inconsistent with the command code definition. Note: Strict parsing must be enabled. |
3008 | DIAMETER_INVALID_HDR_BITS |
|
Invalid AVP Bits |
A request was received that included an AVP whose flag bits are set to an unrecognized value, or that is inconsistent with the AVP definition. Note: Strict parsing must be enabled. |
3009 | DIAMETER_INVALID_AVP_BITS |
|
Unsupported AVP |
The peer received a message that contained an AVP that is not recognized or supported and was marked with the Mandatory bit. Note: Strict parsing must be enabled. |
5001 | DIAMETER_AVP_UNSUPPORTED |
|
AVP Occurs Too Many Times |
A message was received that included an AVP that appeared more often than permitted in the message definition. Note: Strict parsing must be enabled. |
5009 | DIAMETER_AVP_OCCURS_TOO_MANY_TIMES |
|
Unsupported Version |
A request was received, whose version number is unsupported. | 5011 | DIAMETER_INVALID_AVP_LENGTH |
|
Invalid AVP Length |
The request contained an AVP with an invalid length. Note: Strict parsing must be enabled. |
5014 | DIAMETER_INVALID_AVP_LENGTH |
|
IP-CAN Session Not Available |
A request is received without associated PDU session for a binding. | 5065 | IP-CAN_SESSION_NOT_AVAILABLE |
|
Unknown Session ID |
A request is received with unknown session ID. | 5002 | DIAMETER_UNKNOWN_SESSION_ID |
|
Internal Error |
An internal failure occurred. | 5012 | DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY |
Table 7-162 Error Codes and Responses
| Condition ID and Name | Error Message | Diameter Error Code | Application Error Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
No common security |
CER message is received, and there are no common security mechanisms supported between the peers. | 5017 | DIAMETER_NO_COMMON_SECURITY |
|
No common security |
CER message is received, and there are no common applications supported between the peers. | 5010 | DIAMETER_NO_COMMON_APPLICATION |
|
No common security |
Received the diameter request for unsupported application. | 3007 | ERROR_COND_APPLICATION_UNSUPPORTED |
Editing Diameter Error Codes
- From the navigation menu, click Policy,
then select Diameter Configurations, and click
Diameter Error Codes.
This opens the Diameter Error Codes page that lists the CapEx and Rx application ID.
- Click Edit against the
application ID that you need to customize.
This opens the Edit Diameter Error Codes page for the selected application ID.
- Update the required values for the
fields as described in the following table:
Table 7-163 Parameters for Edit Diameter Error Codes
Parameter Description Applicable for Condition Name Specifies the description for a defined condition. It is recommended to use descriptions that clearly explain the condition. Rx and CapEx Result Code Specifes the Diameter result code for a defined condition. When Use Experimental Result switch is disabled, this field cannot be left blank. Note: The value must be a standard diameter result code as defined in the RFC 6733.
Rx and CapEx Use Experimental Result Indicates whether to use the Result Code AVP (268) or Experimental Result AVP (297) when an error result is generated by Policy. Vendor ID Specifies the Vendor ID of the operator or governing body that manages the code entered by the user in the Experimental Result Code field. When Use Experimental Result switch is enabled, this field cannot be left blank. Rx Experimental Error Code Specifies the custom Diameter result code for a defined condition. When Use Experimental Result switch is enabled, this field cannot be left blank. Note: The value must be a standard diameter result code, from 3000 to 9999, as defined in the 3GPP Technical Specification 29.230.
Rx Error Message A message that explains the nature of the error. This error message is only for user understanding and must not be parsed by network entities. Rx and CapEx Use
 available under the Actions column to
update the error code.
available under the Actions column to
update the error code.
- Click Save.
Unsupported Diameter Error Codes
Table 7-164 Unsupported Diameter Error Codes
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 3006 | DIAMETER_REDIRECT_INDICATION |
| 3010 | DIAMETER_UNKNOWN_PEER |
| 4001 | DIAMETER_AUTHENTICATION_REJECTED |
| 4002 | DIAMETER_OUT_OF_SPACE |
| 4003 | ELECTION_LOST |
| 5006 | DIAMETER_RESOURCES_EXCEEDED |
| 5007 | DIAMETER_CONTRADICTING_AVPS |
| 5013 | DIAMETER_INVALID_BIT_IN_HEADER |
| 5015 | DIAMETER_INVALID_MESSAGE_LENGTH |
| 5016 | DIAMETER_INVALID_AVP_BIT_COMBO |
| 5061 | INVALID_SERVICE_INFORMATION |
| 5062 | FILTER_RESTRICTIONS |
| 5063 | REQUESTED_SERVICE_NOT_AUTHORIZED |
| 5064 | DUPLICATED_AF_SESSION |
| 5066 | UNAUTHORIZED_NON_EMERGENCY_SESSION |
| 5067 | UNAUTHORIZED_SPONSORED_DATA_CONNECTIVITY |
| 5068 | TEMPORARY_NETWORK_FAILURE |
| 5198 | DIAMETER_OVERLOAD_RETRY_NOT_ALLOWED_TO_ANY |
| 5199 | DIAMETER_NEWER_SESSION_DETECTED |
| 5999 | ALLOWED_SERVICE_NO_POLICIES_REQUIRED |
| 5003 | DIAMETER_AUTHORIZATION_REJECTED |
| 3003 | DIAMETER_REALM_NOT_SERVED |
7.7 Data Source Configurations
Policy establishes connections with data sources to retrieve information about subscribers from the database. It queries a data source using a key attribute that uniquely identifies a subscriber and stores the results in the cache. A data source uses this key attribute, such as the phone or account number of the subscriber to index the information available in the database.
This section describes how to manage and view the Policy datasource configurations in Policy, using the Data Source Configurations pages.
7.7.1 Data Sources
This procedure provides information about how to configure and manage the Policy data sources.
The Data Sources page allows you to create new and manage existing data sources. The page displays the list of defined data source configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, navigate to Data Source
Configurations, and select Data
Sources.
This opens the Data Sources page. The page lists the existing data source configurations. You can add or import new data sources using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Data Source page.
- On the Create Data Source page, enter the information
specific to the available groups:
Table 7-165 Create Data Source Configuration
Field Name Description Name Specifies the name of the data source. Example value: ocs
Description Specifies additional information about the data source. Type Specifies the type of data source. Users can select any of the following valid values from the drop-down menu:- LDAP
- Sy
If
LDAPdata source is selected then see the "Setting Up LDAP as Policy Data Source" section.If
Sydata source is selected then see the "Setting Up OCS as Policy Data Source" section. - Click Save.
The Data source gets listed on the Data Sources page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the data source configuration.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the data source configuration.
Setting Up LDAP as Policy Data Source
To set LDAP as the data source:
- On the Create Data Source page, in the Type drop-down list, select LDAP.
- Following fields will become available on selecting LDAP as data
source
Type:Table 7-166 Create LDAP Data Source Configuration
Field Name Description Read Connection It is used to specify the number of read connections established with the data source. Primary Server: The primary data source server details. Identity Primary server identity. Example value: oc-diam-gateway
Addr Load balancer IP of Diameter gateway. Port Primary server Port. Secondary Server The secondary data source server details. If primary server is not reachable, then data source connection is established with secondary (if available). You can add or remove the secondary data source server.
Identity Secondary server identity. Example value: oc-diam-gateway
Addr Load balancer IP of Diameter gateway. Port Secondary server Port. Tertiary Server The tertiary data source server details. If primary and secondary are not reachable, then LDAP connection is established with tertiary (if available). You can add or remove the tertiary data source server.
Identity Tertiary server identity. Addr Load balancer IP of Diameter gateway. Port Tertiary server Port. Quaternary Server Quaternary data source server. If primary, secondary, and tertiary are not reachable then LDAP connection is established with Quaternary (if available). You can add or remove the quaternary data source server.
Identity Quaternary server identity. Addr Load balancer IP of Diameter gateway. Port Quaternary server Port. Search Criteria The criteria on which the data source search is performed. You can add or remove the Search Criteria settings.
Base DN Base DN Attribute - Enter the Primary Server configurations.
The following screen capture shows an example on how to create LDAP data source with name LDAP1:
Figure 7-34 LDAP Configuration using Edit Data Sources Page
- Click Save.
This creates the LDAP1 data source.
- Create the pds service type in PCF
system using the Policy Engine page.
For more information about creating pds service type, see Policy Engine.
Note:
On the Policy Engine page, the service name must be entered as pds. - Create a Policy Project for the PDS service
type.
For information about creating Policy Projects, see Adding PDS Service using Policy Engine.
- Create policy action and condition in the newly
created policy project for PDS service type.
For detailed information about configuring the policy blocks for PDS service type, see Oracle Communication Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy Design Guide.
Setting Up OCS as Policy Data Source
To set OCS as the data source, perform the following steps:
- On the Create Data Source page, in the Type drop-down list, select Sy.
- Following fields will become available on selecting Sy as data
source
Type:Table 7-167 Create Sy Data Source Configuration
Field Name Description admin state Enable this switch for data source (Sy) interaction to happen. When the admin state switch is disabled, the data source becomes unavailable temporarily. Realm Specifies the realm of the primary and optional secondary servers to connect. In case of Sy data sources, the DestinationRealm AVPin request message to Diameter Gateway is set using this value.Select OCS from Peer Configurations When this switch is enabled, the user can configure primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary servers by selecting diameter peer nodes using the drop-down menu. For the peer nodes to be made available while configuring a data source, the user must have performed the configurations on Peer Nodes page under Diameter Configurations. Primary Server: The primary data source server details. Identity Primary server identity. Example value: oc-diam-gateway
Addr Load balancer IP of Diameter gateway. Port Primary server Port. Secondary Server The secondary data source server details. If primary server is not reachable, then data source connection is established with secondary (if available). You can add or remove the secondary data source server.
Identity Secondary server identity. Example value: oc-diam-gateway
Addr Load balancer IP of Diameter gateway. Port Secondary server Port. Tertiary Server The tertiary data source server details. Tertiary data source server. If primary and secondary are not reachable, then LDAP connection is established with tertiary (if available). You can add or remove the tertiary data source server.
Identity Tertiary server identity. Addr Load balancer IP of Diameter gateway. Port Tertiary server Port. Quaternary Server Quaternary data source server.
If primary, secondary and tertiary are not reachable then LDAP connection is established with tertiary (if available). You can add or remove the quaternary data source server.
Identity Quaternary server identity. Addr Load balancer IP of Diameter gateway. Port Quaternary server Port. Search Criteria The criteria on which the data source search is performed. You can add or remove the Search Criteria settings.
Type Users can select any of the following valid values from the drop-down menu:- NAI
- MSISDN
- IMSI
Search Filter The search filter during the data source search. You can add or remove the Search Fiter settings.
Id Filters Type Users can select any of the following valid values from the drop-down menu:- NAI
- MSISDN
- IMSI
- Select the Primary Server using the drop-down menu. The
peer nodes are configured using the Peer Nodes
page under Diameter Configurations.
The following screen capture shows an example on how to create OCS data source with name OCS datasource:
Figure 7-35 OCS Configuration using Edit Data Sources Page
- Click Save.
This creates the OCS datasource .
- Create the pds service type in PCF system using the Policy
Engine page.
For more information about creating pds service type, see Policy Engine.
Note:
On the Policy Engine page, the service name must be entered as pds. - Create a Policy Project for the PDS service type.
For information about creating Policy Projects, see Adding PDS Service using Policy Engine.
- Create policy action and condition in the newly created policy project for
PDS service type.
For detailed information about configuring the policy blocks for PDS service type, see Oracle Communication Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy Design Guide.
7.8 Administration
This section describes how to perform administration tasks, such as bulk import and bulk export of configurable objects into the Policy system.
7.8.1 Export & Import
This section describes how to perform the bulk export or bulk import of the managed objects (MOs) configured on Policy.
- Using CNC Console for Policy:
Policy provides the GUI to perform bulk export and import of Policy data.
To access the export and import functionality from the CNC Console home page, expand Policy, navigate to Administration, and select Export & Import.
The page displays the Export and Import tabs. By default, the Export tab remains selected. The following screen capture illustrates an example of the Export & Import page:
Figure 7-36 Export and Import

On initiating either bulk import or export for managed objects (MO's), a detailed progress information is displayed in the UI. Information like managed object type being imported or exported, total number of processes or tables, current number of managed object type being processed, managed object name like table name or rule name, number of records processed for managed Object, total number of managed object records present and progress messages. The following screen capture illustrates an example of the Export & Import page with detailed progress description:
Figure 7-37 Import showing Managed Object count progress status
Note:
- Importing the Overload Threshold Profile will be rejected if the
CPU validation mentioned under
Configure Threshold Valuessection in Overload Control Threshold fails for any of the three threshold levels. - The service names mentioned in the json file used to import the Overload Threshold Profile must be same as mentioned in the exported json file.
- The default Overload Threshold Profile cannot be exported or imported. The default Overload Threshold Profile must be customized with a different profile name before exporting.
Figure 7-38 Export showing Managed Object count progress status
Note:
Currently this detailed progress information display is supported for export/import of records from Policy Table MO only.You can perform the following operations using the Export & Import page:Note:
The following message priority data that was exported prior to Policy 23.2.0 cannot be imported as the data may be corrupt:- message containing Sd as interface
- Sy-SLR as condition message
The data with Sd interface or Sy-SLR condition messages that are exported only with Policy 23.2.0 or later versions can be imported.
- Importing the Overload Threshold Profile will be rejected if the
CPU validation mentioned under
- Using REST API for Policy:
Policy provides REST APIs to bulk export and import of Policy data. For more information about REST API configuration, see Using REST API for Policy Export & Import.
7.8.1.1 Exporting Policy Data
7.8.1.1.1 Exporting Policy Projects with Dependencies
The Export & Import page provides an option to export only the Policy Projects and Policies with their dependencies, without any MO configurations. The Policy Projects export is aligned with Policy services. You can export either all the Policy Projects or the projects of the selected services.
7.8.1.2 Importing Policy Data
To import Policy data in ZIP file format:
7.8.1.3 Using REST API for Policy Export & Import
Policy provides an option to perform the bulk export or import of Policy configurations and Policy Data using REST APIs. For more information about Bulk Import REST APIs, see "Bulk Import Export Controller" in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy REST Specification Guide.
7.9 Status and Query
This section describes how to retrieve status of Policy profile registration and query sessions using the Session Viewer page.
7.9.1 Session Viewer
The Session Viewer page displays the detailed session information of subscribers. You can use this page to enter query parameters to render session data for specific subscribers.
This procedure provides information about how to view session details and perform different operations for a single, multiple, or all subscribers of a specific session type.
- From the navigation menu, click
Policy, select Status and
Query, and then click Session Viewer.
This opens the Session Viewer page.
- Select the session type for which you
want to view the subscriber details. Select any of the following services from
the Session Type drop-down list:
- SM Policy Association
- AM Policy Association
- PA Policy Association
- PCRF-Core Session
- Binding Session
- User Data
- Usage Monitoring
- UE Policy Association
- ALL
- From the Identifier
Type drop-down menu, select the required identifier type.
The following table lists the identifier types supported for each session type:
Table 7-168 Supported values for Identifier type
Session Type Identifier Type SM Policy Association - SUPI
- GPSI
- IPV4
- IPV6
- POLICY_ASSOC_ID
AM Policy Association - SUPI
- GPSI
- POLICY_ASSOC_ID
- PEI
PA Policy Association - SUPI
- GPSI
- IPV4
- IPV6
- POLICY_ASSOC_ID
PCRF-Core Session - DIAMETER_SESSION_ID
- IMSI
- MSISDN
- IPV4
- IPV6
Note: For the PCRF-Core Session type, the page displays the Session Subtype dropdown containing the session type that can be used. The dropdown values depends on the Identifier Type value. For more details of the Session Subtype field, see Step 4.
Binding Session - SUPI
- GPSI
- IPV4
- IPV6
- POLICY_ASSOC_ID
- MAC
User Data - SUPI
- GPSI
UE Policy Association - SUPI
- GPSI
- PEI
- POLICY_ASSOC_ID
Usage Monitoring - SUPI
- GPSI
ALL - SUPI
- GPSI
Note: On selecting ALL as the session type, the following sessions are impacted:- SM session
- PA session
- UE session
- AM session
- Binding session
- Diameter session
- Usage Monitoring
- <Optional> In case of PCRF-Core
Session type, the page displays the Session
Subtype dropdown containing the session type that can be used.
The dropdown values depends on the Identifier Type
value.
The following table lists the session subtypes supported for different identifier types:
Table 7-169 Supported values for Identifier type
Session Type Identifier Type - IMSI
- MSISDN
- IPV4
- IPV6
- All sessions
- Gx Session
- Rx Session
- Sd Session
DIAMETER_SESSION_ID - Gx Session
- Rx Session
- Sd Session
- Enter the value in the
Identifier Value field for the selected identifier
type.
For more information on identifier values, see Subscriber Identifiers in Subscriber Activity Logging.
- Enable the User Data switch to get the user data from the Policy directory.
- Click the Query
button.
The page displays the subscriber information according to the selected session type.
The following image displays the query results for session type as SM Policy Association with SUPI as the identifier type:
Figure 7-46 Query Results on Session Viewer
 The query results are displayed in tabular form with each row displaying the following details:
The query results are displayed in tabular form with each row displaying the following details:- Identifier: The selected session identifier.
- Type: Type of the session.
- Creation Time: The session creation time.
- Action: Provides the buttons to perform the
following actions:
- View Session Details: Click the

icon to view the selected session details in the JSON editor. - Download Session Details: Click the

icon to download the selected file containing the details of the session on your system.Note:
To download multiple session files in single instance, select the sessions and click the Download button at the bottom of the page. - Delete Sessions: Click the

icon to delete the selected session manually.Note:
- To delete multiple sessions in a single instance, select the sessions and click the Delete button at the bottom of the page.
-
For remote delete, enable

box. When this option is enabled, Policy sends delete subscriptions to remote NFs when any previous subscriptions are enabled with remote NFs.Note:
Initiate Remote Session Cleanup is applicable only for SM Service.
In case of AM_Policy_Association and UE_Policy_Association, when a session is deleted, the corresponding context information in PDS is cleaned. If all the PDS context for UDR data are deleted, the subscription data in the UDR is also deleted.
- View Session Details: Click the
Note:
Use the Modify Search button to modify the search criteria.
Policy also provides an option to configure session viewer using REST APIs. For more information, see "Session Viewer" in Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy REST Specification Guide.
7.9.2 NF Status
This section provides information on NF status.
7.9.2.1 PCF Registration Profile
This page lists the PCF profile registered with NRF.
- Click Edit button.
- Update the values of the required parameters.
- Click Save.
To dowload the BSF profile, click
Download button. A file named
pcfRegistrationProfile.json is
saved on your system.
7.9.2.2 NRF Status
On the NRF Status page, you can view the status of PCF and the NRFs deployed in the cluster.
For PCF
You can view the following details for PCF:
- PCF status with NRF - It shows whether the PCF instance is registered, suspended, or deregistered with NRF.
- FQDN - It shows the FQDN of the PCF registered with NRF.
- Instance ID - It shows the unique Instance ID of PCF registered with NRF.
- Registered with - It shows the FQDN of the NRF with which PCF is registered.
- Registration Time - It shows the time at which PCF registered with NRF.
If you want to view more details of the PCF instance such as its registration profile, click View More Details. It opens the NF Registration Profile page.
For NRF
You can view the following details for NRF:
- Health Status - This ribbon-styled badge shows the health status of the NRF instance. It could be in either healthy or unhealthy state.
- Primary NRF - The circular icon with the label P indicates that the NRF is primary.
- Active Status - The pulsating green circular icon shows that the NRF is currently active.
- FQDN - It shows the FQDN of the NRF.
- Priority - It shows the priority of the NRF instances. An NRF instance with priority 1 is treated as primary NRF.
- Last Connected Time - It shows the time when PCF last connected with primary NRF.
- Last Status Change Time - It shows the time when the NRF status changed.
When the status of an NRF instance changes from healthy to unhealthy, the error reason is also displayed on the page.
To reload the data on the page at any time, click the Refresh button.
Based on when the data refreshes, the Last Refresh Time on the page is also updated.
The number of NRFs displayed on the page are dynamic, and get updated according to the NRFs configured in the network.
Figure 7-47 NRF Status
Note:
Currently, the page is known to display the status of up to 8 NRF Instances.In case of any network error, the page displays an error - Unable to load NRF data.
7.9.2.3 Discovered NF Instances
This page displays the list of discovered NF Instances.
On the Discovered NF Instances page, you can view the autonomously discovered NF profiles for BSF, CHF, UDR, and NWDAF.
Based on the value you select from the drop-down list, the following details are populated on the page:
- NF Instance ID - It shows the unique instance ID of the discovered NF.
- FQDN - It shows the FQDN of the discovered NF.
- Priority - It shows the priority assigned to the NF.
- Status - It shows whether the NF is registered or suspended.
- View Details - Click to view the NF profile.
If no profile is discovered or in case of any network error, the page shows "No data to display" along with 404-Not Found.
7.10 Overload and Congestion Control Configurations
This section describes how to perform overload and congestion control configurations.
To use the Error Code Profiles page to create and manage error code profiles in Overload Control Configurations for Diameter Gateway and SBI interface, see SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection section.
Note:
When overload control feature is enabled, it should be enabled for both Diameter gateway and SBI interface. The overload control manager needs data from both Ingress Gateway and Diameter Gateway to determine the overall load on BSF management. It is not possible to enable overload control for Diameter Gateway and disable the same in Ingress Gateway.
7.10.1 Diameter
This section describes configuring the Load Shedding Profiles and the Message Priority Profiles for Diameter Gateway.
To use the Error Code Profiles page to create and manage error code profiles in Overload Control Configurations for Diameter Connector, see SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection.
7.10.1.1 Load Shedding Profiles
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage load shedding profiles in Diameter Configurations.
The Load Shedding Profiles page allows you to create new and manage existing load shedding profiles. The page displays the list of defined profiles and provides the options to import and export data as well.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Diameter
Configurations, and select Load Shedding
Profiles.
This opens the Load Shedding Profiles page.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Load Shedding Profiles page.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described in the
following table:
Table 7-170 Load Shedding Profiles Configurations
Field Name Description Name Unique name of the load shedding profile. Scheme Allows to configure the discard policy based on - Priority: to discard messages based on priority range
- Priority and Percentage: to discard messages based on priority range and percentage for each range
Type Defines the type of load shedding profile. You can select any of the following values from the drop-down list: - Congestion Control
- Overload Control
To add load shedding rules for the profile type congestion control, perform the following steps:
- Under Load Shedding Rules, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Load Shedding Rules dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described
in the following table:
Table 7-171 Load Shedding Rules Configurations When the Selected Scheme is "Priority"
Field Name Description State This field appears when the Type of load shedding profile is
Specifies the type of state for which the rule is being defined. Select any of the following values using the drop-down:Congestion Control.- Danger of Congestion
- Congested
Discard Priority This field appears when the Scheme of load shedding profiles is
Priority.Specifies the discard priority for the load shedding rule. The discard priority value can be a number from 0 to 15. Any request message with equal or greater priority is rejected.
Answer with Result Code Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of congestion control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down menu: - DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE
Note: When the EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE value is selected, the following two fields are populated on the page:- Result Code: Enter a custom result code.
- Vendor ID: Enter a valid value to specify vendor ID.
Table 7-172 Load Shedding Rules Configurations When the Selected Scheme is "Priority and Percentage"
Field Name Description State This field appears when the Type of load shedding profile is
Specifies the type of state for which the rule is being defined. Select any of the following values using the drop-down:Congestion Control.- Danger of Congestion
- Congested
Discard Priority Percentage Allows to configure the Discard Priority Percentage as explained in the following step.
- To configure discard
Priority Percentage, perform the following steps:
- Under Discard Priority
Percentage, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Discard Priority Percentage dialog box.
Enter values for the available input fields, described in the following table:
Table 7-173 Adding Discard Priority Percentage
Field Name Description Priority Range Specifies the discard priority range for the load shedding rule. The discard priority value can be a number from 0 to 15. Any request message with equal or greater priority will be rejected based on the percentage discard configured.
Note: For Priority added as percentage type, when a single digit number is provided in the priority range then those many numbers of priority messages will be rejected. For example: If Priority is 9, only 9 priority messages will be rejected.
Discard Percentage Specifies the discard percentage for the specified priority range. Answer with Result Code Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of congestion control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down menu: - DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE
Note: When the EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE value is selected, the following two fields are populated on the page:- Result Code: Enter a custom result code.
- Vendor ID: Enter a valid value to specify vendor ID.
- Click Save to save the discard priority percentage.
- Under Discard Priority
Percentage, click
- Click Save to save the load shedding rule.
OR
To add load shedding rules for the profile type overload control, perform the following steps:
- Under Load Shedding Rules, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Load Shedding Rules dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described
in the following table:
Table 7-174 Load Shedding Rules Configurations When the Selected Scheme is "Priority"
Field Name Description Level Specifies the name of the level. The name specified in this parameter must match the level name in Ingress Gateway's ocdiscardpolicies. Select any of the following values using the drop-down list: - L1
- L2
- L3
Note: Any existing L4 level data will be removed, as L4 is not supported.
Discard Priority Specifies the discard priority for the load shedding rule. The discard priority value can be a number from 0 to 15. Any request message with equal or greater priority is rejected. Answer with Result Code Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of overload control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down menu: - DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE
Note: When the EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE value is selected, the following two fields are populated on the page:- Result Code: Enter a custom result code.
- Vendor ID: Enter a valid value to specify vendor ID.
Table 7-175 Load Shedding Rules Configurations When the Selected Scheme is "Priority and Percentage"
Field Name Description Level Specifies the name of the level. The name specified in this parameter must match the level name in Ingress Gateway's ocdiscardpolicies. Select any of the following values using the drop-down list: - L1
- L2
- L3
Note: Any existing L4 level data will be removed, as L4 is not supported.
Discard Priority Percentage Configure the discard priority percentage as explained in the following step.
- To configure Discard
Priority Percentage, perform the following steps:
- Under Discard Priority
Percentage, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Discard Priority Percentage dialog box.
Enter values for the available input fields, described in the following table:
Table 7-176 Adding Discard Priority Percentage
Field Name Description Priority Range Specifies the discard priority range for the load shedding rule. The discard priority value can be a number from 0 to 15. Any request message with equal or greater priority will be rejected based on the percentage discard configured. Note: For Priority and Percentage type, when we give single number in the priority range, for example 9, only 9 priority messages will be rejected.
Discard Percentage Specifies the discard percentage for the specified priority range. Answer with Result Code Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of congestion control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down menu: - DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE
Note: When the EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE value is selected, the following two fields are populated on the page:- Result Code: Enter a custom result code.
- Vendor ID: Enter a valid value to specify vendor ID.
- Click Save to save the discard priority percentage.
- Under Discard Priority
Percentage, click
- Click Save to save the load shedding rule.
- Click Save to save the load shedding
profile.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
The value gets listed on the Load Shedding Profiles page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
Note:
While Diameter Gateway enters overload situation, messages only from network peer will be considered for load shedding. That is, messages from backed peers will not be considered for load shedding.
For example, during overload Sy-SLR / Rx-RAR will not be considered for load shedding as they are generated by backend microservices.
Importing Load Shedding Profiles
To import load shedding profiles, perform the following steps:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
Exporting Load Shedding Profiles
To export load shedding profiles, click Export. A
json file is saved to your device.
7.10.1.2 Message Priority Profiles
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage message priority profiles in Diameter Configurations.
The Message Priority Profiles page allows you to create new and manage existing message priority profiles. The page displays the list of defined profiles and provides the options to import and export data as well.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Diameter
Configurations, and select Message Priority
Profiles.
This opens the Message Priority Profiles page.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Message Priority Profiles page.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described in the
following table:
Table 7-177 Message Priority Profiles Configurations
Field Name Description Name Unique name of the message priority profile. To add message priority rules for the profile, perform the following steps:
- Under Message Priority Rules, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Message Priority Rules dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described in the
following table:
Table 7-178 Message Priority Rules Configurations
Field Name Description Name Specifies the unique name of the message priority rule. Message Priority Specifies the priority assigned to the message. It can be a number from 0 to 15. Note: The default message priority is 10, if no rule is available. For setting a different default message priority, a rule must be added with lowest rule priority(higher number) to match all the messages(application set to "any", message type set to "any"). This will ensure that, this rule will be run at the last i.e., when no other rules match.
Rule Priority Specifies the priority assigned to the message priority rule. The range for this field is 0 to 65535.
Note: During Import and Export, if the old data has rule priority value greater than the specified range, then the Rule Priority might be impacted.
Use DRMP Priority When this switch is enabled, the priority for the message rule is assigned from DRMP AVP. Conditions Application Specifies the type of application. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down: - Gx
- Sd
- Rx
- Sy
- Any
Message Specifies the type of message for the selected application. The supported message values for each application type are as follow: - For Gx application, choose a value from CCR, RAR, and Any.
- For Sd application, choose CCR.
- For Rx application, choose a value from AAR, ASR, RAR, STR, and Any.
- For Sy application, choose a value from Sy-SLR, STR, Sy-SNR, and Any.
- For application type selected as Any, choose a value from the drop-down list of Message.
- To add pre-defined AVP conditions, click
 under Pre Defined AVP Conditions. On
the Add Pre Defined AVP Conditions dialog
box, select Name and enter values as described in the following
table:
under Pre Defined AVP Conditions. On
the Add Pre Defined AVP Conditions dialog
box, select Name and enter values as described in the following
table:
Table 7-179 Pre Defined AVP Conditions Configurations
Name Values Called-Station-Id This AVP can be used only when the application type is specified as Gx and Rx. Users can enter multiple comma-separated values. Note: CNC Policy supports wildcard format for this AVP.
CC-Request-Type This AVP can be used for Gx application with message specified as CCR. You can select any of the following valid values from the drop-down list: - INITIAL_REQUEST
- UPDATE_REQUEST
- TERMINATION_REQUEST
- EVENT_REQUEST
Rx-Request-Type This AVP can be used for Rx application with message specified as AAR. You can select any of the following valid values from the drop-down list: - INITIAL_REQUEST
- UPDATE_REQUEST
- PCSCF_RESTORATION_REQUEST
Service-URN This AVP indicates that an AF session is used for emergency traffic. It is of type OctetString. Examples: "sos", "sos.fire", "sos.police" and "sos.ambulance".
Note: CNC Policy supports wildcard format for this AVP.
MPS-Identifier This AVP indicates that an AF session relates to an MPS session and contains the national variant for MPS service name. It is of type OctetString. Example: NGN GETS
MCPTT-Identifier This AVP includes either one of the namespace values used for MCPTT and may include the name of the MCPTT service provider. It is of type OctetString. MCVideo-Identifier This AVP includes the name of the MCVideo service provider. It is of type OctetString. Reservation-Priority This AVP is of type Enumerated and is specified in an AA-Request as the main AVP to associate a priority with a resource reservation or modification request. You can specify a value from 0 to 7 for this AVP. SN-Request-Type This AVP informs the PCRF about the type of the Spending-Status-Notification-Request (SNR).You can select any of the following valid values from the drop-down list: - ABORT_SESSION_REQUEST
- NORMAL_REQUEST
Click Save to save the pre-defined AVP conditions for the message priority rule.
- Click Save to save the message priority rule.
- Under Message Priority Rules, click
- Click Save to save the message priority
profile.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
The value gets listed on the Message Priority Profiles page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
Importing Load Shedding Profiles
To import message priority profiles, perform the following steps:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
Exporting Message Priority Profiles
To export load shedding profiles, click Export. A
json file is saved to your device.
7.10.2 SBI
This section describes the Rate Limiting and overload control for SBI.
To use the Error Code Profiles page to create and manage error code profiles in Overload Control Configurations for SBI interface, see SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection.
7.10.2.1 Rate Limiting
This section describes Rate Limiting Policy and Route Level Mapping for SBI.
Note:
As of now if the system requires overload configuration for both rate limiting and failure count, it is suggested to do these configuration using API's only. For more details, see Rate Limiting at Ingress Gateway and Failure Count at Ingress Gateway sections in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy REST Specification Guide7.10.2.1.1 Rate Limiting Policy
This procedure provides information about how to use the Rate Limiting Policy page to manage rate limiting policies for overload control on SBI interface.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Overload Control
Configurations, select SBI, then
select Rate Limiting, and then select Rate
Limiting Policy.
This opens the Rate Limiting Policy page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Rate Limiting Policy page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the following
table:
Table 7-180 Rate Limiting Policy Configurations
Field Name Description Enable Rate Limiting Specifies whether to enable or disable rate limiting. Sampling Period (in milliseconds) Specifies the time frame for each cycle of rate limiting per service. Its default value is 200 ms. -
Under Rate Limit Policy, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Rate Limit Policy dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 7-181 Rate Limit Policy Configurations
Field Name Description Name Specifies the name of the rate limit policy that is further used to determine a mapping between route and discard policy name per route. Discard Priority Specifies the discard priority for the rate limiting policy. Any request with message priority higher in value than the discard priority is rejected. Action Specifies the action taken when when requests are discarded. Currently, the only supported value is RejectWithErrorCode. Scheme Specifies the scheme for applying rate limiting. Currently, the only supported value is PriorityBased. Error Code Profile Specifies the list of error code profiles configured on the Error Code Profiles page. - Click Save to save the rate limit
policy. The value gets listed under the Rate Limit
Policy group.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
- Click Save to save the rate limiting
policy.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
7.10.2.2 Overload Control
This section describes the Discard Policy Mapping and Discard Policy for SBI interface.
7.10.2.2.1 Discard Policy Mapping
This procedure provides information about how to use the Discard Policy Mapping page to manage discard policy mapping in Overload Control Configurations for SBI interface.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Overload Control
Configurations, select SBI, then
select Overload Control, and then select
Discard Policy Mapping.
This opens the Discard Policy Mapping page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Discard Policy Mapping page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the following
table:
Table 7-182 Discard Policy Mapping Configurations
Field Name Description Enable Overload Control Specifies whether to enable or disable overload control. Sampling Period (in milliseconds) Specifies the time frame for each cycle of overload control per service. Its default value is 200 ms. -
Under Mappings, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Mappings dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 7-183 Mappings Configurations
Field Name Description Service Name Specifies the name of the microservice that is further used to determine a mapping between service and discard policy name per service. Policy Name Specifies the name of the discard policy that is used to determine a mapping between service and discard policy name per service. The drop-down list shows the policies configured using the Discard Policy page. - Click Save to save the mappings.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
The value gets listed under the Mappings group on the Discard Policy Mapping page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the mappings.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the mappings.
- Click Save to save the discard policy
mapping.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
7.10.2.2.2 Discard Policy
This procedure provides information about how to use the Discard Policy page to manage discard policies for overload control for SBI interface.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Overload Control
Configurations, select SBI, then
select Overload Control, and then select
Discard Policy.
This opens the Overload Control Discard Policy page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Overload Control Discard Policy page.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Add Discard Policies page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 7-184 Discard Policy Configurations
Field Name Description Name Specifies the unique name of the discard policy. Scheme Specifies the criteria of dropping requests for a microservice. It could be either priority based or percentage based. If you select the value as Priority Based, configure the values of the parameters under Priority Based Policies. For Percentage Based scheme, configure the parameters under Percentage Based Policies. To add priority based policies, perform the following steps:
- Under Priority Based Policies,
click
 .
.
This opens the Add Priority Based Policies dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields as
described in the following table:
Table 7-185 Priority Based Policies Configurations
Field Name Description Level Specifies the name of the level. The name specified in this parameter must match the level name in Ingress Gateway's ocdiscardpolicies. Select any of the following values using the drop-down list: - L1 (Load Level 1)
- L2 (Load Level 2)
- L3 (Load Level 3)
Discard Priority Specify the discard priority for the discard policy rule. Any request message with equal or lower message priority is rejected. Note:
1 is considered as the highest message priority.Error Code Profile Select an error code profile from the drop-down list. It displays the list of error profiles configured using the Error Code Profile page. Action Specifies the action taken when selected requests are rejected. Currently, it only supports the action to reject requests based on error code. OR
Table 7-186 Percentage Based Policies Configurations
Field Name Description Level Specifies the name of the level. The name specified in this parameter must match the level name in Ingress Gateway's ocdiscardpolicies. Select any of the following values using the drop-down list: - L1 (Load Level 1)
- L2 (Load Level 2)
- L3 (Load Level 3)
Discard Percentage Specify the discard percentage for the policy rule. The specified percentage of the calculated rate for service in previous sampling period is discarded in current sampling period. Error Code Profile Select an error code profile from the drop-down list. It displays the list of error profiles configured using the Error Code Profile page. Action Specifies the action taken when selected requests are rejected. Currently, it only supports the action to reject requests based on error code. - Click Save to save the discard
policy.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
- Under Priority Based Policies,
click
- Click Save to save the overload control
discard policy.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
The value gets listed on the Overload Control Discard Policy page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
7.10.2.3 Route Level Mapping
This procedure provides information about how to use the Route Level Mapping page to manage route level mapping for overload control on SBI interface.
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Overload Control
Configurations, select SBI, then
select Rate Limiting, and then select
Route Level Mapping.
This opens the Route Level Mapping page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Route Level Mapping page.
-
Under Route Configuration, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Route Configuration dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the following
table:
Table 7-187 Rate Limiting Policy Configurations
Field Name Description Id Specifies the list of route IDs available for Policy.
-
Under Rate Limiting, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Method dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 7-188 Method Configurations
Field Name Description Http Method Specifies the HTTP method. Depending on the value select for Id, you can select any of the following values from the drop-down list: - POST
- PUT
- GET
- DELETE
- PATCH
Message Rate (per sampling period) Specifies the message rate per sampling period for a given method. Rate Limit Policy Select a rate limit policy from the drop-down list. It displays the list of rate limit policies configured using the Rate Limiting Policy page. - Click Save to save the method. The value
gets listed under the Rate Limiting group.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
- Click Save to save the route
configuration.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
- Click Save to save the route level
mapping.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
7.10.2.4 Failure Count
Note:
Currently, all the configurations for failure count can be performed only using REST APIs.
Only the failure count threshold can be configured using CNC Console. Configuring the error codes and mapping the respective routes must be done only through REST APIs.
Also, if the system requires overload configuration for both rate limiting and failure count, it is suggested to perform these configuration using API's only.
For more details, see Rate Limiting and Failure Count at Ingress gateway sections in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy REST Specification Guide.
From 24.1.0 release, you can configure failure count using CNC Console. For more details, see IGW .
7.10.3 Congestion Control
7.10.3.1 Settings
The Settings page displays the general configurations related to the Congestion Control. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, click Overload and Congestion
Control and select Settings.
This opens the Settings page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Settings page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 7-189 Edit Configurations
Field Name Description Service Name Specifies the Policy service name. You can check the default configuration for the all fields and edit as necessary. Enable Specifies whether to enable or disable Congestion Control for the selected Policy service. Default value: False
State Change Sample Count This specifies after how many continuous intervals, the pod state can be changed. This count can range from 1 to 2147483647.
Default Value:
Bulwark Service: 2
Binding, PDS, Usage Monitoring, SM Service, PCRF Core Service, UE Service: 5
State Calculation Interval (in milliseconds) This specifies that after this time duration or interval, the pod congestion state will be re-verified. This inverval in milliseconds can range from 50 to 2147483647.
Default Value
Bulwark Service: 5000
Binding , PDS, Usage Monitoring, SM Service, PCRF Core Service, UE Service: 200
Figure 7-48 Edit Congestion Control Settings for Bulwark Service

- Click Save to save the congestion
control configuration.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
The value gets listed on the Settings page.Figure 7-49 Congestion Control Settings

7.10.3.2 Thresholds
-
From the navigation menu under Policy navigate to Overload and Congestion Control, select Congestion Control and select Thresholds.
This opens the Congestion Control Thresholds page. The page shows the existing configurations for a specific Policy service. You can add a new threshold profile configuration or copy the existing profile and modify it.
- Select from the drop down list fields, as described in the
following table:
Table 7-190 Thresholds Configuration
Field Name Description Service Name Provides a drop down lists of Policy services. You can select the service for which the congestion control thresholds are to be configured. Threshold Profiles Provides a drop down lists of all the configured threshold profiles. A default congestion control threshold profile is provided during PCF deployment. You cannot either edit or delete this profile. If the selected profile is already active, you can see
Activebutton in green color next to the profile name. - Click Go To Active button. The current active profile from the Threshold Profile drop down list is selected.
- Click
 .
This opens the Create Profile window and allows you to create a new profile.
.
This opens the Create Profile window and allows you to create a new profile.- Enter values for the available input fields, described
in the following table:
Table 7-191 Create Profile Configurations
Field Name Description Service Name Specifies the selected PCF service for which a new threshold profile is to be created.
Name of the profile Provide a unique name for the threshold profile to be created.
The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 255 characters.
- Click Create to create the
threshold profile.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
- The value gets listed on the Congestion Control Thresholds page.
By default, the newly created profile has the same values as the default profile configuration values.
Figure 7-50 Bulwark Default Threshold
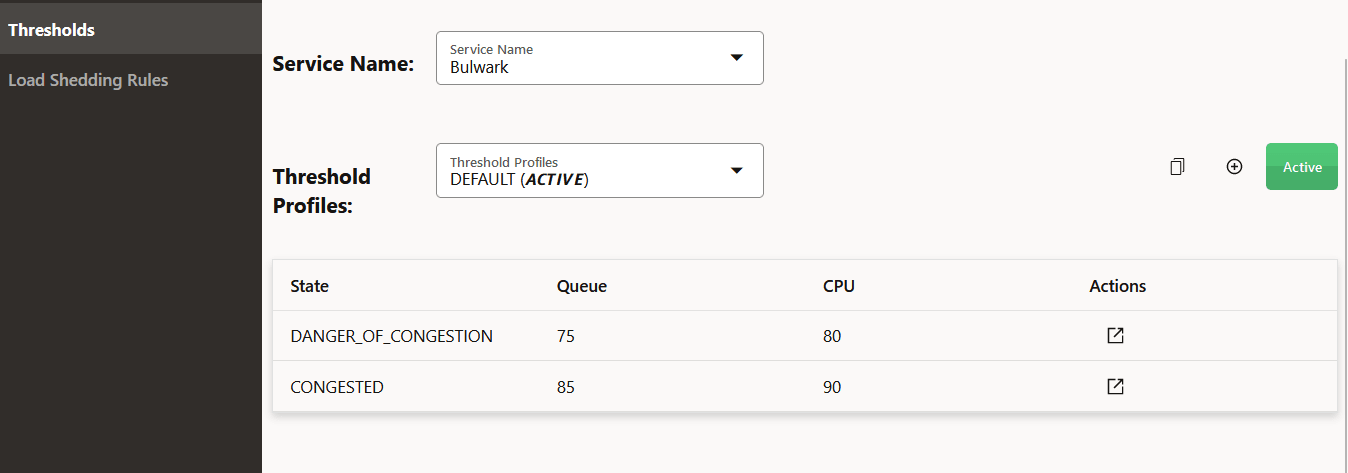
- Click
 to view the Queue and CPU values for the various congested
states.
to view the Queue and CPU values for the various congested
states.
- Click
 to edit each of the various congested states
Queue and CPU
values. This opens the Edit <Congestion
States> page, where <Congestion States>
will be different for different services.
The Bulwark pod's can be in following Congestion states:
to edit each of the various congested states
Queue and CPU
values. This opens the Edit <Congestion
States> page, where <Congestion States>
will be different for different services.
The Bulwark pod's can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-192 Bulwark Congestion States
Congestion States CPU Percentage Queue Percentage DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 80 75 CONGESTED 90 85 Note:
If user either adds or updates the Threshold configurations for Bulwark service, then Congestion Control feature gets disabled for Bulwark service. The user will have to enable the congestion control feature again for Bulwark service using the Settings menu in CNC Console, and the new/updated Threshold configurations will be applied.The Binding service pod's can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-193 Binding Service Congestion States
Congestion States CPU Percentage Queue (Pending Requests) DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 70 30 CONGESTION_L1 75 36 CONGESTION_L2 80 42 CONGESTED 85 48 The SM Service pods can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-194 SM Services Pod Congestion States
Congestion States CPU Percentage Queue (Pending Requests) DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 77 140 CONGESTION_L1 78 160 CONGESTION_L2 79 180 CONGESTED 80 200 The Policy Services pods can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-195 Usage Monitoring and PDS Services Pod Congestion States
Congestion States CPU Percentage Queue (Pending Requests) DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 65 50 CONGESTION_L1 70 100 CONGESTION_L2 75 150 CONGESTED 80 200 The PCRF Core Services pods can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-196 PCRF Core Service Congestion States
Congestion States CPU Percentage Queue (Pending Requests) DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 60 250 CONGESTION_L1 65 300 CONGESTION_L2 75 350 CONGESTED 85 400 The UE Services pods can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-197 UE Service Congestion States
Congestion States CPU Percentage Queue (Pending Requests) DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 77 140 CONGESTION_L1 78 160 CONGESTION_L2 79 180 CONGESTED 80 200 - Enter the following information:
Table 7-198 Edit <Congestion State> Fields
Field Name Description Service Name Specifies the selected service for which threshold profile configurations are to be edited. Profile Name Specifies the selected threshold profile for which DOC type queue and CPU values are to be edited. Queue Specifies the Queue percentage for Bulwark and Queue (pending requests) for all other Policy services across all the congestion levels. For Bulwark the range is 1 to 100 and for other services the range is between 1 to 2147483647. CPU Specifies the CPU percentage across all the congestion levels. The number can be between 1 to 100. - Click Save to save the
configurations.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
The updated value gets listed on the Congestion Control Thresholds page.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described
in the following table:
- Click
 . This opens the Copy Profile window to copy an
existing profile.
. This opens the Copy Profile window to copy an
existing profile.
While using the copy profile option, whichever profile is selected in the Threshold Profile dropdown, the values are copied from that profile.
- Click
 . This deletes the selected threshold profile. User cannot delete the
default and active threshold profiles.
. This deletes the selected threshold profile. User cannot delete the
default and active threshold profiles.
7.10.3.3 Load Shedding Rules
The Congestion Load Shedding Rules page allows you to create new and manage existing congestion load shedding rules.
- From the navigation menu under
Policy navigate to Overload and Congestion
Control, select Congestion Control and
then select Load Shedding Rules.
This opens the Congestion Load Shedding Rules page. The page shows the existing configurations for a specific Policy service. You can add a new congestion control load shedding rule or copy the existing rule and modify it.
- Select from the drop down list fields, as described in the
following table:
Table 7-199 Congestion Load Shedding Rules
Field Name Description Service Name Provides a drop down lists of Policy services. You can select the service for which the congestion load shedding rules are to be configured. Load Shedding Rules Provides a drop down lists of all the configured load shedding rules. A default load shedding rule is provided during PCF deployment. You cannot either edit or delete this rule.
If the selected profile is already active, you can see
Activebutton in green color next to the profile name. - Click Go To Active button. The current ACTIVE rule from the Load Shedding Rules drop down list is selected.
- Click
 .
This opens the Create rule window and allows you to create a new rule.
.
This opens the Create rule window and allows you to create a new rule.- Enter values for the available input fields, described
in the following table:
Table 7-200 Create Rule Configurations
Field Name Description Service Name Specifies the selected PCF service for which a new load shedding rule is to be created.
Name of the rule Provide a unique name for the load shedding rule to be created.
The name can only contain the characters A–Z, a–z, 0–9, period (.), hyphen (-), and underline (_). The maximum length is 255 characters.
- Click Create to create the load
shedding rule.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
- The value gets listed on the Congestion Load Shedding Rules page.
By default, the newly created rule has the same values as the default rule configuration values.
Figure 7-51 Bulwark Default Load Shedding Rule
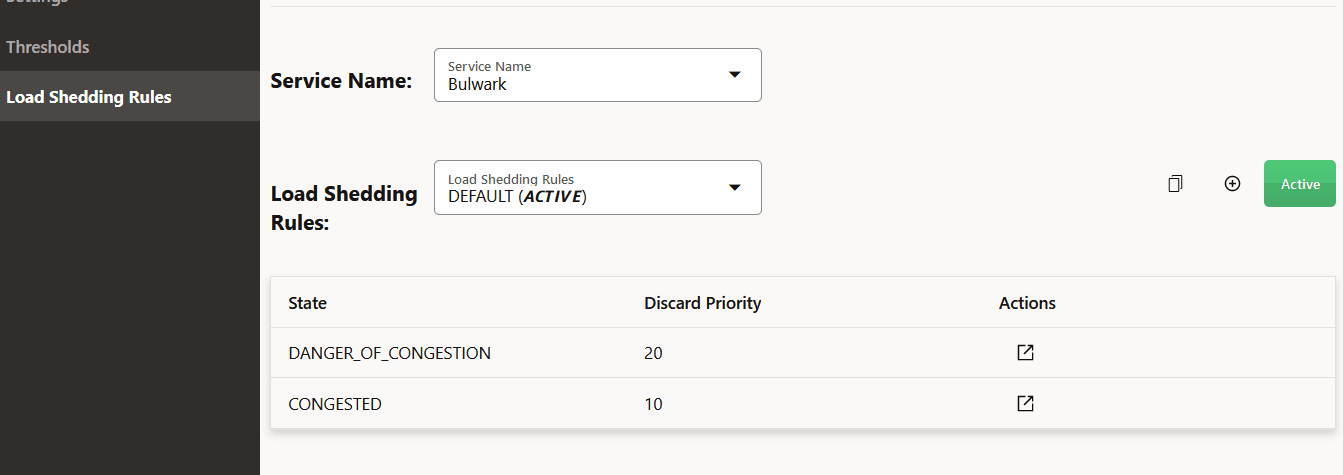
- Click
 to view the Discard Priority values for the various
congested states.
The Bulwark pod's can be in following Congestion states:
to view the Discard Priority values for the various
congested states.
The Bulwark pod's can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-201 Bulwark Congestion States
Congestion States Discard Priority DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 20 CONGESTED 10 The Binding service pod's can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-202 Binding Service Congestion States
Congestion States Discard Priority DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 30 CONGESTION_L1 27 CONGESTION_L2 24 CONGESTED 20 The SM service pod's can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-203 SM Services Pod Congestion States
Congestion States Discard Priority DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 27 CONGESTION_L1 19 CONGESTION_L2 17 CONGESTED 15 The Policy service pod's can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-204 Usage Monitoring and PDS Pod Congestion States
Congestion States Discard Priority DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 28 CONGESTION_L1 20 CONGESTION_L2 17 CONGESTED 15 The PCRF Core service pod's can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-205 PCRF Core Service Congestion States
Congestion States Discard Priority DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 29 CONGESTION_L1 23 CONGESTION_L2 17 CONGESTED 15 The UE service pods can be in following Congestion states:Table 7-206 UE Service Congestion States
Congestion States Discard Priority DANGER_OF_CONGESTION (DOC) 28 CONGESTION_L1 25 CONGESTION_L2 20 CONGESTED 17 - Click
 to edit each of the various congested states
Discard Priority value. This opens the
Edit <Congestion States> page, where
<Congestion States> will be different for different services.
to edit each of the various congested states
Discard Priority value. This opens the
Edit <Congestion States> page, where
<Congestion States> will be different for different services.
- Enter the following information:
Table 7-207 Edit <Congestion State> Fields
Field Name Description Service Name Specifies the selected PCF service for which the load shedding rule is edited. Rule Name Specifies the selected load shedding rule for the chosen Congestion state. Discard Priority Specifies the discard priority that can be configured for the selected Congestion state.
This number can be between 1 to 100 for Bulwark, Binding and PDS services.
This number can be between 1 to 31 for Usage Monitoring and SM services.
- Click Save to save the
configurations.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
The updated value gets listed on the Congestion Load Shedding Rules page.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described
in the following table:
- Click
 . This opens the Copy Rule window to copy an
existing profile.
. This opens the Copy Rule window to copy an
existing profile.
While using the copy rule option, whichever rule is selected in the Load Shedding Rules drop down, the values are copied from that rule.
- Click
 . This deletes the selected load shedding rule. User cannot delete the
default and active load shedding rules.
. This deletes the selected load shedding rule. User cannot delete the
default and active load shedding rules.
7.10.4 Overload Control Threshold
-
From the navigation menu under Policy, navigate to Overload Control Configurations, and select Overload Control Threshold.
Overload Control Threshold page is displayed. The page shows the existing configurations.
-
Policy allows you to configure the threshold values using a profile. You can either use a default or custom profile or create a new profile. You must activate one of the profiles to use the values. At a time, you can activate only one profile.
Note:
If there are no profiles activated, Policy calculates the load level based onoverloadLevelThresholdconfigured incustom-values.yamlfile.If you are upgrading from an older version of Policy to 23.1.0 or later, the following message appears at the top of the page:
System looks to be using old configuration (Not profile based). Request you to please migrate the data or activate one of the profile- Click Migrate.
Migrate Data window opens.
- Enter the name of the profile.
- Either click Migrate to migrate
the data from the previous version of Policy or click
Migrate and Activate to migrate the data
and activate the profile.
Note:
Migrate button will only migrate the existing threshold data to profile. It does not activate the profile. Until one of the profile is not active , the UI will continue to show the above message to migrate the data.
In case of fault recovery, the active profile details are recovered and used from the database. No need to migrate again.
- Click Migrate.
Table 7-208 Create and Manage Threshold Profiles
| Button/icon | Action |
|---|---|
| Opens the Create Profile window
and allows you to create a new profile.
By default, the values of the
default profile are associated with the new profile. Click |
|
| Deletes the selected threshold profile.
Note: You cannot delete the default system provided profile. |
|
| Opens the Copy Profile window to
copy an existing profile.
While using the copy profile option, whichever profile is selected in the Threshold Profile dropdown, the values are copied from that profile. |
|
| Threshold Profile | Lists all the threshold profiles. You can select any of
the profiles from the list to activate.
If the selected
profile is already active, you can see
|
| Activate | Activates the profile selected from Threshold
Profile list.
At a time, you can have only one active profile. |
| Go To Active |
Go To Active button selects the current active profile from the Threshold Profile drop down list. Note: If none of the profiles are active, the Go To Active button does not appear. |
Table 7-209 Configure Threshold Values
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Name | You can configure the threshold values for the following
services:
Note: Irrespective of PCF or PCRF mode of deployment, this list of services remains the same. For PCRF-CORE deployment mode, configuring overload level threshold for SM Service, AM Service, and UE Policy Service is not required. For PCF deployment mode, configuring the overload level threshold for PCRF Core is not required. |
| CPU |
Click The onset and abatement values for CPU are calucalted in percentage (%) and the range is from 1 to 100. Click Note: Make sure that the onset value of L1 is less than the abatement value of L2 and the onset value of L2 is less than the abatement value of L3. You can click Note: If the above mentioned CPU validation fails for any of the threshold levels, importing of the Overload Threshold Profile will be rejected. |
| Pending Message Count |
Click Pending message count accepts an integer value between 1 to 1000000. |
| Failure Count |
Click The failure count accepts an integer value between 1 to 1000000. |
| Memory |
Click Memory details are calculated in Percentage (%) and ranges between 1 to 100. |
7.11 Controlled Shutdown Configurations
This section describes how to perform Controlled Shutdown configurations for Diameter and Ingress interface.
7.11.1 Operational State
- From the navigation menu, under Policy,
click Controlled Shutdown, and then select
Operational State.
This opens the page displaying the two groups, Switch Operational State and Operational State History:
Figure 7-52 Operational State

- Switch Operational State
It displays the following operational states:
- NORMAL: NF instance is discoverable and services all requests.
- PARTIAL SHUTDOWN: NF instance is non discoverable and no new session creation requests accepted.
- COMPLETE SHUTDOWN: NF instance is non discoverable and no new session creation requests accepted.
Note:
By default, NORMAL state is assigned to a site. The current state of any site can be identified with a tick mark.Note:
The operational state is stored in configuration server. The service instances (pod) detects the state change only after the configuration refresh is performed. Hence if the config refresh interval is set at 5 seconds then te pods recognise the operational state change after 5 seconds.
You can switch to a different operational state by clicking the NORMAL, PARTIAL SHUTDOWN, or COMPLETE SHUTDOWN button.
- Operational State History:
It displays the history of the operational states along with the
timestamp.
Note:
It displays maximim of ten records at a time. On scrolling further, another set of ten records is displayed. The maximum number of record maintained is hundred.
- Switch Operational State
It displays the following operational states:
7.11.2 Diameter Error Mapping
- From the navigation menu under
Policy, click Controlled
Shutdown and then select Diameter Error
Mapping.
This opens the Diameter Error Mapping page. The page lists the existing configurations. You can add or import new diameter error mapping configurations using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Diameter Error Mapping page.
- On the Create Diameter Error Mapping
page, enter the following information:
Table 7-210 Create Diameter Error Mapping
Field Name Description Message Type Type of the request Answer with Result Code Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of congestion control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down menu: - DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- CUSTOM_RESULT_CODE
Note: When the CUSTOM_RESULT_CODE value is selected, the following two fields are populated on the page:- Result Code: Enter a custom result code.
- Use Experimental Result
Code: This is disabled by default. You can
enable it by clicking the icon against it. When it
is enabled, Vendor ID field is poplulated on the
page:
- Vendor ID: Enter a valid value to specify vendor ID.
- Click Save.
The configuration gets listed on the Diameter Error Mapping page. The page defines the Diameter Error Mapping configuration in the Policy database and it is available to be used in a Policy.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the configuration.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the configuration.
Importing Diameter Error Mapping
To import Diameter Error Mapping configuration:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
7.11.3 SBI Ingress Error Mapping
- From the navigation menu, under
Policy, click Controlled
Shutdown, and then select SBI Ingress Error
Mapping.
This opens the SBI Ingress Error Mapping page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit SBI Ingress Error Mapping page.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Add SBI Ingress Error Mapping page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 7-211 Ingress Error Mapping Configurations
Field Name Description Id Specifies the list of IDs available for Policy. Error Code Profile Select an error code profile from the dropdown list. It displays the list of error profiles configured using the SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection. - Click Save to save the Ingress error
mapping.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
The value gets listed on the SBI Ingress Error Mapping page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
7.12 NF Scoring Configurations
You can configure the NF Scoring feature using the CNC Console. To navigate to NF Scoring, click NF Scoring, under Policy. It shows Settings and Calculated Score, which are described as follows:
Table 7-212 CNC Console NF Scoring Settings
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable NF Scoring | Specifies whether to enable or disable the NF Scoring |
| TPS | |
| Enable | Enables the TPS. |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the TPS. |
| Max TPS | Specifies the maximum TPS. |
| Service Health | Specifies the service health of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Service Health. |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the Service Health. |
| Signaling Connections | Specifies the Signaling Connections of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Signaling Connections. |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the Signaling Connections. |
| Max Connections | Specifies the maximum connections. |
| Replication Health | Specifies the Replication Health of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Replication Health. |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the Replication Health. |
| Locality/Site Preference | Specifies the Locality or Site Preference. |
| Enable | Enables the Locality or Site Preference. |
| Score | Specifies the score of the Locality or Site Preference. |
| Active Alert | Specifies the Active Alerts of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Active Alert. |
| Critical Alert Weightage | The site with more critical alerts is unhealthy. |
| Major Alert Weightage | The site with more major alerts is unhealthy. |
| Minor Alert Weightage | The site with more minor alerts is unhealthy. |
Calculated Score:
To check the calculated Score of a site:
Figure 7-53 NF Scoring Disabled
Figure 7-54 NF Scoring Enabled

Note:
If app-info pod is down, you will not be getting the NF Score. You will get an error message that "Data can't be fetched due to internal server error".Calculated Score shows the total score along with the Instance ID. The total score is shown in either Green or Orange color. If the NF Score is shown in green color there are no failed factors. And, if the NF Score is shown in Orange color there are one or more failed factors. You can click on Detailed information to view different criteria and their Max Score, Evaluated Score, and More Info. The criteria in the detailed information tab show the evaluated score. The failed factors are shown with a warning symbol under the evaluated score.
On the top-right of the screen, the Last Refresh Time information is available. Moreover, a Refresh button is given to refresh the NF Score of a site.
7.13 Viewing cnDBTier APIs in CNC Console
Note:
The following cnDBTier functionalities are read only and is available only through CNC Console.7.13.1 Backup List
- From the left navigation pane, click the Policy tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the Backup List to view the list of
completed backups along with Backup ID, Backup size, and Creation Timestamp.
The Backup List screen is displayed.
Table 7-213 Backup List
Fields Description Backup Details This field displays information such as backup Id, backup size, and backup creation timestamp. Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which Policy is connected. Backup Id This field displays the ID of the stored backup. Backup Size (bytes) This field displays the size of the stored backup. Creation TimeStamp This field displays the time recorded when the backup was stored.
7.13.2 Database Statistics Report
- From the left navigation pane, click the Policy tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the Database Statistics Report to view
the available database.
Table 7-214 Database Statistics Report
Fields Description Database Count This field displays the number of available database. Database Tables Count This field displays the available database names and their table count. Database Name This field displays the database name. Table Count This field displays the table count for each database. Database Table Rows Count This field displays the table rows present in each table. -
Click the View icon available next to the database name to view the View Database Table Rows Count screen.
Table 7-215 View Database Table Rows Count
Fields Description Database Name This field displays the database name. Tables This field displays the table names and the corresponding rows in each table. Table Name This field displays the table name. Row Count This field displays the table rows present in each table.
-
7.13.3 Georeplication Status
- From the left navigation pane, click the Policy tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the Georeplication Status to view the
local site and remote site name to which Policy is connected.
Table 7-216 GeoReplication Status
Fields Description Local Site Name This field displays the local site name to which Policy is connected. Remote Site Name This field displays the remote site name. Replication Status This field displays the replication status with corresponding sites. Seconds Behind Remote Site This field displays the number of seconds that the last record read by the local site is behind the latest record written by the remote site for all the replication groups. - Click the View icon in the
Actions menu to view the View
Georeplication Status screen.
Table 7-217 Georeplication Status
Fields Description Replication Group Delay This field displays the number of seconds that the last record read by the local site is behind the latest record written by the remote site for individual replication groups. Replication Channel Group Id This field displays the ID of the replication channel group. - Click the View icon to view the
Replication Group Delay attributes.
Table 7-218 View Replication Group Delay
Fields Description Channel Details This field displays the channel details such as Remote Replication IP and Role. Remote Replication IP This field displays the IP of the remote replication channel. Role This field displays the role of the replication channel IP.
- Click the View icon in the
Actions menu to view the View
Georeplication Status screen.
7.13.4 Heartbeat Status
- From the left navigation pane, click the Policy tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the HeartBeat Status to view the
connectivity between local site and remote site to which Policy is
connected.
Table 7-219 HeartBeat Status Details
Fields Description Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which Policy is connected. HeartBeat Details This field displays information such as the remote site name, heartbeat status, heartbeat lag, and replication channel group id. Remote Site Name This field displays the remote site name. Heartbeat Status This field displays the connectivity status with corresponding sites. Heartbeat Lag This field displays the lag or latency in seconds it took to syncronize between sites. Replication Channel Group Id This field displays the ID of the replication channel group.
7.13.5 Georeplication Recovery
Note:
- Currently, if a site is used for georeplication recovery has failures, then it should not be marked as failed. Instead, the user must troubleshoot the issues and resolve it manually rather than mark it as failed.
- All the georeplication sites must be on the same cnDBTier version as 24.2.x to perform georeplication recovery. However, you can perform georeplication recovery on a different cnDBTier version if it is newer than 24.2.x.
- User must wait until all the GRR process is complete before selecting the same site for another site's georeplication recovery.
- From the left navigation pane, click the Policy tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click Georeplication Recovery to access the
Georeplication Recovery Status of the cnDBTier cluster. This includes options
such as Update Cluster As Failed, Start Georeplication Recovery, and
Georeplication Recovery Status.
- Click the Update Cluster As Failed to mark the
cluster as FAILED.
The Update Cluster As Failed page is displayed.
Table 7-220 Update Cluster As Failed
Fields Description Cluster Names This attribute lists the names of cnDBTier clusters. It allows you to select a cluster from the available list to mark as failed. Failed Cluster Names This attribute displays the list of names of cnDBTier clusters that are marked as failed. Update Cluster Click the Update Cluster to mark the cluster as FAILED. Cancel Click the Cancel to cancel the process. - Click the Start Georeplication
Recovery to start the georeplication recovery process
for a failed site.
The Start Georeplication Recovery page is displayed.
Table 7-221 Start Georeplication Recovery
Attribute Description Failed Cluster Name This attribute displays a list of cnDBTier clusters that have been marked as failed. Backup Cluster Name (Optional) This attribute displays the list of active cnDBTier clusters designated for georeplication recovery. Start Georeplication Recovery Click the Start Georeplication Recovery to start the georeplication recovery process for a failed site. Cancel Click the Cancel to cancel the process. - Click the Georeplication Recovery
Status to view the status of georeplication recovery for
cnDBTier clusters.
The Georeplication Recovery Status page is displayed.
Table 7-222 Georeplication Recovery Status
Attribute Description Local Cluster Name This attribute displays the name of the local cluster. Georeplication Recover Status Details This attribute displays the details of the georeplication recovery status for cnDBTier clusters. Cluster Name This attribute displays the names of all the clusters. Georeplication Recovery Status This attribute displays the current status of georeplication recovery for a cluster. Refresh Click Refresh to view the most current data.
The following are the states of Georeplication Recovery:Table 7-223 Georeplication Recovery States
Georeplication Recovery State Description ACTIVE The cluster is in a healthy state, and replication is up and running with its respective mate cluster. REINSTALLED The cluster enters this state during fatal error recovery when the end user reinstalls the cluster. STARTDRRESTORE When Georeplication recovery is started, the cluster will transition into this state. INITIATEBACKUP Once Georeplication recovery is started, the cluster will identify a healthy cluster for backup initiation and transition into this state. CHECKBACKUP Once the backup is initiated, the georeplication recovery cluster will monitor the progress of the backup until its completion. If the backup fails, the cluster will restart the backup. COPY_BACKUP Upon completion of the backup, the georeplication recovery cluster will request the transfer of the backup from the healthy cluster to the georeplication recovery cluster. CHECK_BACKUP_COPY Once backup copy is started georeplication recovery cluster will monitor for the backup transfer progress till it's completion and if it's fails the cluster will re-initiates the backup transfer. BACKUPCOPIED Once the backup copy is started, the georeplication recovery cluster will monitor the progress of the backup transfer until its completion. If the transfer fails, the cluster will restart the backup transfer. BACKUPEXTRACTED This state indicates that the backup has been successfully extracted at the georeplication recovery cluster, allowing the restoration of the backup to start. FAILED This state is used by end user to mark specific cluster as failed and hence georeplication recovery is essential to recover the cluster.This state can also indicates that georeplication recovery started and the database is restored using the healthy cluster backup. UNKNOWN This state is used by the end user to mark a specific cluster as failed, necessitating georeplication recovery for cluster recovery. Additionally, this state can indicate that georeplication recovery has started and the database has been restored using the backup from the healthy cluster. RECONNECTSQLNODES This state is used to instruct SQL nodes to be offline during backup restoration to prevent any records from entering the binlog of the georeplication recovery cluster. BACKUPRESTORE This state indicates that the backup, successfully copied from the healthy cluster, is currently being used to restore the georeplication recovery cluster. RESTORED Once the backup is successfully restored in the georeplication recovery cluster, the cluster will enter this state to start the reestablishment of replication channels. BINLOGINITIALIZED This state indicates the start of binlogs for the restoration of replication channels, necessary to start the restore process RECONFIGURE Once the binlog is restarted, the georeplication recovery cluster will reestablish the replication channels with respect to all its mate clusters. - Click the Update Cluster As Failed to mark the
cluster as FAILED.
7.13.6 Local Cluster Status
- From the left navigation pane, click the Policy tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the Local Cluster Status to view the
local cluster status for the current site:
Table 7-224 Local Cluster Status
Fields Description Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which Policy is connected. Cluster Status This field displays the local cluster status for the current site.
7.13.7 On Demand Backup
- From the left navigation pane, click the Policy tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the On Demand Backup to create a new
backup and view the status of initiated on-demand backups.
Note:
On Demand Backup can be initiated on both single site and multi-site cnDBTier cluster and can be used to restore the first standalone site. DB Backup will not be initiated if sites are not properly configured.Table 7-225 On Demand Backup Details
Fields Description Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which Policy is connected. DR Status This field displays the status of DR. Backup Id This field displays the ID of the stored backup. Backup Status This field displays the status of backup. Remote Transfer Status The field displays the status of remote transfer. Initiate Backup The field displays whether the backup is initiated or not. - Click the Edit icon.
The Edit On Demand Backup screen appears.
Note:
The Edit mode is available only for Initiate Backup. - To enable the Initiate Backup option, click
Save.
A confirmation message "Save successfully" appears.
- Click Cancel to navigate back to the On Demand Backup screen.
- Click Refresh to reload the On Demand Backup screen.
- Click the Edit icon.
7.13.8 Version
- From the left navigation pane, click the Policy tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the cnDBTier Version to view the
version.
Table 7-226 cnDBTier Version Attributes
Fields Description cnDBTier Version This field displays the cnDBTier version. NDB Version This field displays the network database (NDB) version.