2 Troubleshooting Service Communication Proxy
This section provides information to troubleshoot common errors that occur while installing and upgrading Service Communication Proxy (SCP).
Note:
kubectl commands might vary based on the platform
deployment. Replace kubectl with Kubernetes environment-specific
command line tool to configure Kubernetes resources through kube-api server. The
instructions provided in this document are as per the Oracle Communications Cloud
Native Environment (OCCNE) version of kube-api server.
2.1 Generic Checklist
The following sections provide a generic checklist for troubleshooting tips.
Deployment Related Tips
- Are OCSCP deployment, pods, and services created, running, and
available?
To check this, run the following command:
# kubectl -n <namespace> get deployments,pods,svcInspect the output and check the following columns:- READY, STATUS, and RESTARTS
- PORT(S)
- Is the correct image used and the correct environment variables
set in the deployment?
To check this, run the following command:
# kubectl -n <namespace> get deployment <deployment-name> -o yaml - Check if the microservices can access each other through REST
interface.
To check this, run the following command:
# kubectl -n <namespace> exec <pod name> -- curl <uri>Example:kubectl exec -it ocscp-scpc-subscription-6bf9b7d69f-qvcnn -n ocscp curl http://ocscp-scpc-notification:8082/ocscp/scpc-notification/v2/compositecustomobjectskubectl exec -it ocscp-scpc-notification-dd5c74869-cswkb -n ocscp curl http://ocscp-scpc-configuration:8081/ocscp/scpc-configuration/v1/systemoptions/sseNote:
These commands are in their simplest form and display the logs only if scpc-notification and scpc-configuration pods are deployed.
The list of URIs for all the microservices:
- scp-worker:
http://ocscp-scp-worker:8000/hostNFMapper - scpc-configuration:
http://ocscp-scpc-configuration:8081/ocscp/scpc-configuration/v1/systemoptions/sseOr any other configuration URI from SWAGGER-UI - scpc-notification:
http://ocscp-scpc-notification:8082/ocscp/scpc-notification/v2/compositecustomobjects - scpc-subscription:
http://ocscp-scpc-subscription:8080/ocscp/scpc-subscription/v1/appstate
Application Related Tips
# kubectl -n <namespace> logs -f <pod name>You can use '-f' to follow the logs or 'grep' for specific pattern in the log output.
Example:
# kubectl -n scp-svc logs -f $(kubectl -n scp-svc get pods -o name|cut -d'/' -f 2|grep nfr)Note:
These commands are in their simple form and display the logs only if there is 1 scp<registration> and nf<subscription> pod deployed.2.2 Helm Install Failure
This section describes Helm installation failure scenarios.
2.2.1 Incorrect Image Name in the ocscp-custom-values Files
Problem
helm install might fail if incorrect image name is
provided in the ocscp_values.yaml file.
Error Code or Error Message
When you run kubectl get pods -n
<ocscp_namespace>, the status of the pods might be
ImagePullBackOff or ErrImagePull.
Solution
- Edit the
ocscp_values.yamlfile and provide release specific image name and tags. - Run the
helm installcommand. - Run the
kubectl get pods -n <ocscp_namespace>command to verify if the status of all the pods is Running.
2.2.2 Docker Registry is Incorrectly Configured
Problem
helm install might fail if docker registry is not
configured in all primary and secondary nodes.
Error Code or Error Message
When you run kubectl get pods -n
<ocscp_namespace>, the status of the pods might be ImagePullBackOff
or ErrImagePull.
Solution
Configure docker registry on all primary and secondary nodes.
For information about docker registry configuration, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
2.2.3 Continuous Restart of Pods
Problem
helm install might fail if MySQL primary and secondary
hosts may not be configured properly in ocscp-custom-values.yaml.
Error Code/Error Message
When you run kubectl get pods -n
<ocscp_namespace>, the pods restart count increases continuously.
Solution
MySQL servers may not be configured properly. For more information about the MySQL configuration, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Service Communication Proxy Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
2.3 Custom Value File Parse Failure
custom-values.yaml file.
Problem
Unable to parse the ocscp_values-x.x.x.yaml file while
running Helm install.
Error Code or Error Message
Error: failed to parse ocscp_values-x.x.x.yaml: error converting YAML to JSON: yaml
Symptom
ocscp-custom-values-x.x.x.yaml file, if
the above mentioned error is received, it indicates that the file is not parsed because
of the following reasons:
- The tree structure may not have been followed
- There may be a tab spaces in the file
Solution
Download the ocscp_csar_23_2_0_0_0.zip folder from
MOS and complete the steps as described in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Service Communication Proxy
Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
2.4 Curl HTTP2 Not Supported
Problem
curl http2 is not supported on the system.
Error Code or Error Message
Unsupported protocol error is thrown or connection is established with HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Symptom
If unsupported protocol error is thrown or connection is established with http1.1, it is an indication that curl http2 support may not be present on your machine.
Solution
Note:
You must check the software platform policies before executing the following procedure.Following is the procedure to install curl with HTTP2 support:
- Run the following command to ensure that Git is
installed:
$ sudo yum install git -y - Run the following commands to install
nghttp2:
$ git clone https://github.com/tatsuhiro-t/nghttp2.git $ cd nghttp2$ autoreconf -i $ automake $ autoconf$ ./configure $ make $ sudo make install$ echo '/usr/local/lib' > /etc/ld.so.conf.d/custom-libs.conf$ ldconfig - Run the following commands to install the latest Curl:
$ wget http://curl.haxx.se/download/curl-7.46.0.tar.bz2 (NOTE: Check for latest version during Installation) $ tar -xvjf curl-7.46.0.tar.bz2 $ cd curl-7.46.0$ ./configure --with-nghttp2=/usr/local --with-ssl$ make$ sudo make install$ sudo ldconfig - Run the following command to ensure that HTTP2 is added in
features:
$ curl --http2-prior-knowledge -v "<http://10.75.204.35:32270/nscp-disc/v1/nf-instances?requester-nf-type=AMF&target-nf-type=SMF>"
2.5 SCP DB goes into the Deadlock State
Problem
MySQL locks get struck.
Error Code/Error Message
ERROR 1213 (40001): Deadlock found when trying to get lock; try restarting transaction.
Symptom
Unable to access MySQL.
Solution
- Run the following command on each SQL node:
SELECT CONCAT('KILL ', id, ';') FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PROCESSLIST WHERE `User` = <DbUsername> AND `db` = <DbName>;This command retrieves the list of commands to kill each connections.
Example:select CONCAT('KILL ', id, ';') FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PROCESSLIST where `User` = 'scpuser' AND `db` = 'ocscpdb'; +--------------------------+ | CONCAT('KILL ', id, ';') | +--------------------------+ | KILL 204491; | | KILL 200332; | | KILL 202845; | +--------------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) - Run the kill command on each SQL node.
2.6 Helm Test Error Scenarios
Note:
You must clean up any residual job from the SCP deployment before performing the following procedure.- Run the following command to retrieve the Helm Test pod
name:
kubectl get pods -n <deployment-namespace> - Check for the Helm Test pod that is in the error state:
Figure 2-1 Helm test pod

- Run the following command to retrieve the
logs:
kubectl logs <podname> -n <namespace>
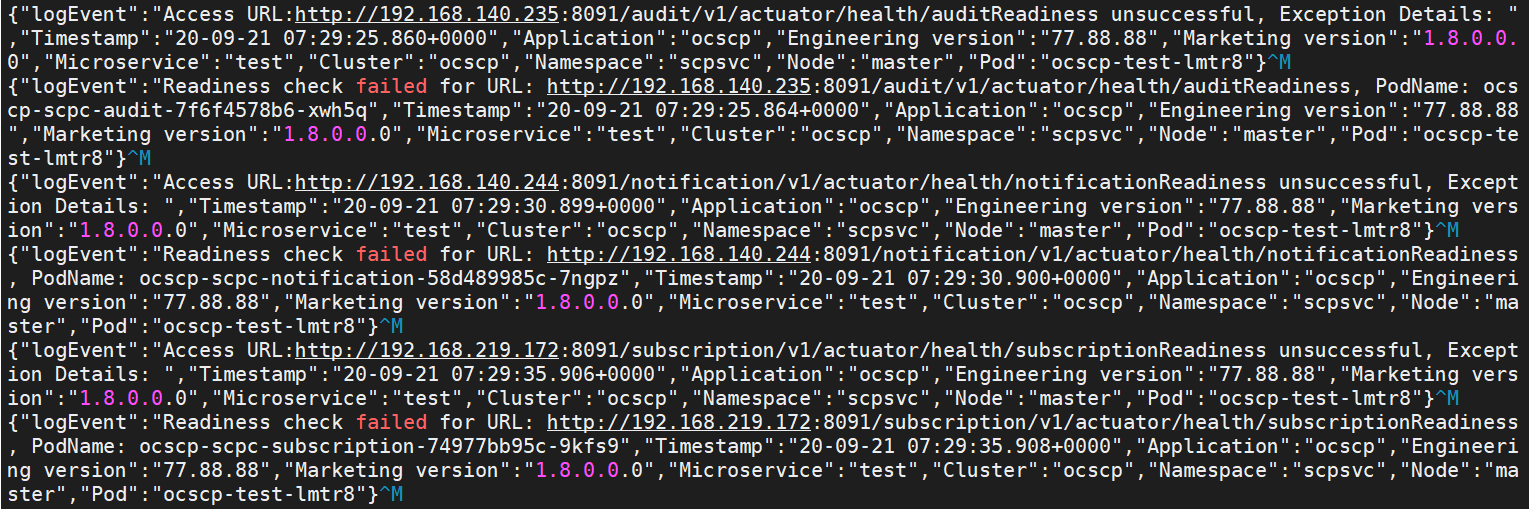
Readiness Probe Failure
Helm install might fail due to the readiness probe URL failure.
Figure 2-2 Readiness Probe Failure
Low Resources
Figure 2-3 Low Resource

In this case, check the CPU and memory availability in the Kubernetes cluster.
2.7 Using Debug Tool
The Debug Tool provides third-party troubleshooting tools for debugging the runtime issues for lab environment. The following tools are available:
- tcpdump
- ip
- netstat
- curl
- ping
- nmap
- dig
2.7.1 Prerequisites to Use the Debug Tool
Note:
- For CNE 23.2.0 and later versions, follow Step 1.
- For CNE versions prior to 23.2.0, follow Step 2.
- The debug tool requires security context with the following
permissions:
securityContext: allowPrivilegeEscalation: true capabilities: drop: - ALL add: - NET_RAW - NET_ADMIN runAsUser: <user-id> volumeMounts: - mountPath: /tmp/tools name: debug-tools-dirFor OpenShift environment, security context constraint must exist to allow above permissions to enable debug tool deployment.
2.7.3 Debug Tool Configuration Parameters
Following are the parameters used to configure the debug tool.
CNE Parameters
Table 2-1 CNE Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| apiVersion | Defines the version schema of this representation of an object. |
| kind | Indicates a string value representing the REST resource this object represents. |
| metadata | Indicates the metadata of Standard object. |
| metadata.name | Indicates the metadata name that must be unique within a namespace. |
| spec | Defines the policy enforced. |
| spec.readOnlyRootFilesystem | Controls whether the containers run with a read-only root filesystem, that is, no writable layer. |
| spec.allowPrivilegeEscalation | Gates whether or not a user is allowed to set the security context of a container to allowPrivilegeEscalation=true. |
| spec.allowedCapabilities | Provides a list of capabilities that are allowed to be added to a container. |
| spec.fsGroup | Controls the supplemental group applied to some volumes. RunAsAny allows any fsGroup ID to be specified. |
| spec.runAsUser | Controls which user ID the containers are run with. RunAsAny allows any runAsUser to be specified. |
| spec.seLinux | RunAsAny allows any seLinuxOptions to be specified. |
| spec.supplementalGroups | Controls which group IDs containers add. RunAsAny allows any supplementalGroups to be specified. |
| spec.volumes | Provides a list of allowed volume types. The allowed values correspond to the volume sources that are defined when creating a volume. |
Role Creation Parameters
Table 2-2 Role Creation
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| apiVersion | Defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object. |
| kind | Indicates a string value representing the REST resource this object represents. |
| metadata | Indicates the metadata of Standard object. |
| metadata.name | Indicates the name of metadata that must be unique within a namespace. |
| metadata.namespace | Defines the space within which each name must be unique. |
| rules | Manages all the PolicyRules for this Role. |
| apiGroups | Indicates the name of the APIGroup that contains the resources. |
| rules.resources | Indicates the list of resources this rule applies to. |
| rules.verbs | Indicates the list of Verbs that applies to ALL the ResourceKinds and AttributeRestrictions contained in this rule. |
| rules.resourceNames | Indicates an optional white list of names that the rule applies to. |
Table 2-3 Role Binding Creation
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| apiVersion | Defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object. |
| kind | Indicates the string value representing the REST resource this object represents. |
| metadata | Indicates the metadata of Standard object. |
| metadata.name | Indicates the name that must be unique within a namespace. |
| metadata.namespace | Defines the space within which each name must be unique. |
| roleRef | References a Role in the current namespace or a ClusterRole in the global namespace. |
| roleRef.apiGroup | Indicates the group for the resource being referenced. |
| roleRef.kind | Indicates the type of resource being referenced. |
| roleRef.name | Indicates the name of resource being referenced. |
| subjects | Manages references to the objects the role applies to. |
| subjects.kind | Indicates the type of object being referenced. Values defined by this API group are "User", "Group", and "ServiceAccount". |
| subjects.apiGroup | Manages the API group of the referenced subject. |
| subjects.name | Indicates the name of the object being referenced. |
Debug Tool Configuration Parameters
Table 2-4 Debug Tool Configuration Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| command | Indicates the string array used for container command. |
| image | Indicates the docker image name. |
| imagePullPolicy | Indicates the Image Pull Policy. |
| name | Indicates the name of the container. |
| resources | Indicates the Compute Resources required by this container. |
| resources.limits | Describes the maximum amount of compute resources allowed. |
| resources.requests | Describes the minimum amount of compute resources required. |
| resources.limits.cpu | Indicates the CPU limits. |
| resources.limits.memory | Indicates the Memory limits. |
| resources.limits.ephemeral-storage | Indicates the Ephemeral Storage limits. |
| resources.requests.cpu | Indicates the CPU requests. |
| resources.requests.memory | Indicates the Memory requests. |
| resources.requests.ephemeral-storage | Indicates the Ephemeral Storage requests. |
| securityContext | Indicates the Security options the container should run with. |
| securityContext.allowPrivilegeEscalation | AllowPrivilegeEscalation controls whether a process can gain more privileges than its parent process. It directly controls whether the no_new_privs flag to be set on the container process. |
| secuirtyContext.readOnlyRootFilesystem | Indicates whether this container has a read-only root filesystem. The default value is false. |
| securityContext.capabilities | Indicates the capabilities to add or drop when running containers. It defaults to the default set of capabilities granted by the container runtime. |
| securityContext.capabilities.drop | Indicates the removed capabilities. |
| secuirtyContext.capabilities.add | Indicates the added capabilities. |
| securityContext.runAsUser | Indicates the UID to run the entrypoint of the container process. |
| extraContainersTpl.volumeMounts | Indicates that the parameter is used for mounting the volume. |
| extraContainersTpl.volumeMounts.mountPath | Indicates the path for volume mount. |
| extraContainersTpl.volumeMounts.name | Indicates the name of the directory for debug tool logs storage. |
| extraContainersVolumesTpl.name | Indicates the name of the volume for debug tool logs storage. |
| extraContainersVolumesTpl.emptyDir.medium | Indicates where the emptyDir volume is stored. |
| extraContainersVolumesTpl.emptyDir.sizeLimit | Indicates the emptyDir volume size. |
2.7.4 Tools Tested in Debug Container
The following tables describe the list of debug tools that are tested.
Table 2-5 tcpdump
| Options Tested | Description | Output | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| -D | Print the list of the network interfaces available on
the system and on which tcpdump can capture
packets.
|
tcpdump -D
|
NET_ADMIN, NET_RAW |
| -i | Listen on interface.
|
tcpdump -i eth0tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decodelistening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes12:10:37.381199 IP cncc-core-ingress-gateway-7ffc49bb7f-2kkhc.46519 > kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local.https: Flags [P.], seq 1986927241:1986927276, ack 1334332290, win 626, options [nop,nop,TS val 849591834 ecr 849561833], length 3512:10:37.381952 IP cncc-core-ingress-gateway-7ffc49bb7f-2kkhc.45868 > kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local.domain: 62870+ PTR? 1.0.96.10.in-addr.arpa. (40) |
NET_ADMIN, NET_RAW |
| -w | Write the raw packets to file rather than parsing and printing them out. | tcpdump -w capture.pcap -i
eth0 |
NET_ADMIN, NET_RAW |
| -r | Read packets from file, which was
created with the -w option.
|
tcpdump -r capture.pcapreading from file /tmp/capture.pcap, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet)12:13:07.381019 IP cncc-core-ingress-gateway-7ffc49bb7f-2kkhc.46519 > kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local.https: Flags [P.], seq 1986927416:1986927451, ack 1334332445, win 626, options [nop,nop,TS val 849741834 ecr 849711834], length 3512:13:07.381194 IP kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local.https > cncc-core-ingress-gateway-7ffc49bb7f-2kkhc.46519: Flags [P.], seq 1:32, ack 35, win 247, options [nop,nop,TS val 849741834 ecr 849741834], length 3112:13:07.381207 IP cncc-core-ingress-gateway-7ffc49bb7f-2kkhc.46519 > kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local.https: Flags [.], ack 32, win 626, options [nop,nop,TS val 849741834 ecr 849741834], length 0 |
NET_ADMIN, NET_RAW |
Table 2-6 ip
| Options Tested | Description | Output | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| addr show | Look at the protocol addresses. |
ip addr show1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group defaultlink/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lovalid_lft forever preferred_lft forever2: tunl0@NONE: <NOARP> mtu 1480 qdisc noop state DOWN group defaultlink/ipip 0.0.0.0 brd 0.0.0.04: eth0@if190: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1440 qdisc noqueue state UP group defaultlink/ether aa:5a:27:8d:74:6f brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0inet 192.168.219.112/32 scope global eth0valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever |
- |
| route show | List routes. | ip route showdefault via 169.254.1.1 dev eth0 169.254.1.1 dev eth0 scope link |
- |
| addrlabel list | List address labels |
ip addrlabel listprefix ::1/128 label 0 prefix ::/96 label 3 prefix ::ffff:0.0.0.0/96 label 4 prefix 2001::/32 label 6 prefix 2001:10::/28 label 7 prefix 3ffe::/16 label 12 prefix 2002::/16 label 2 prefix fec0::/10 label 11 prefix fc00::/7 label 5 prefix ::/0 label 1 |
- |
Table 2-7 netstat
| Options Tested | Description | Output | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| -a | Show both listening and non-listening sockets. For TCP, this means established connections. | netstat -aActive Internet connections (servers and established)Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address Statetcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:tproxy 0.0.0.0:* LISTENtcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:websm 0.0.0.0:* LISTENtcp 0 0 cncc-core-ingress:websm 10-178-254-194.ku:47292 TIME_WAITtcp 0 0 cncc-core-ingress:46519 kubernetes.defaul:https ESTABLISHEDtcp 0 0 cncc-core-ingress:websm 10-178-254-194.ku:47240 TIME_WAITtcp 0 0 cncc-core-ingress:websm 10-178-254-194.ku:47347 TIME_WAITudp 0 0 localhost:59351 localhost:ambit-lm ESTABLISHEDActive UNIX domain sockets (servers and established)Proto RefCnt Flags Type State I-Node Pathunix 2 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 576064861 |
- |
| -l | Show only listening sockets. | netstat -lActive Internet connections (only servers)Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address Statetcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:tproxy 0.0.0.0:* LISTENtcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:websm 0.0.0.0:* LISTENActive UNIX domain sockets (only servers)Proto RefCnt Flags Type State I-Node Path |
- |
| -s | Display summary statistics for each protocol. | netstat -sIp:4070 total packets received0 forwarded0 incoming packets discarded4070 incoming packets delivered4315 requests sent outIcmp:0 ICMP messages received0 input ICMP message failed.ICMP input histogram:2 ICMP messages sent0 ICMP messages failedICMP output histogram:destination unreachable: 2 |
- |
| -i | Display a table of all network interfaces. | netstat -iKernel Interface tableIface MTU RX-OK RX-ERR RX-DRP RX-OVR TX-OK TX-ERR TX-DRP TX-OVR Flgeth0 1440 4131 0 0 0 4355 0 0 0 BMRUlo 65536 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 LRU |
- |
Table 2-8 curl
| Options Tested | Description | Output | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| -o | Write output to <file> instead of stdout. |
curl -o file.txt http://abc.com/file.txt |
- |
| -x | Use the specified HTTP proxy. |
curl -x proxy.com:8080 -o
http://abc.com/file.txt |
- |
| --http2 | Use the specified HTTP/2 | curl --http2 -v
http://cncc-iam-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local:30085/cncc/auth/admin |
- |
Table 2-9 ping
| Options Tested | Description | Output | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| <ip> | Run a ping test to see whether the target host is reachable or not. |
ping 10.178.254.194 |
NET_ADMIN, NET_RAW |
| -c | Stop after sending 'c' number of ECHO_REQUEST packets. |
ping -c 5 10.178.254.194 |
NET_ADMIN, NET_RAW |
| -f (with non zero interval) | Flood ping. For every ECHO_REQUEST sent a period ''.'' is printed, while for every ECHO_REPLY received a backspace is printed. |
ping -f -i 2 10.178.254.194 |
NET_ADMIN, NET_RAW |
Table 2-10 nmap
| Options Tested | Description | Output | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| <ip> | Scan for Live hosts, Operating systems, packet filters, and open ports running on remote hosts. |
nmap
10.178.254.194 |
- |
| -v | Increase verbosity level |
nmap -v
10.178.254.194 |
- |
| -iL | Scan all the listed IP addresses in a file. Sample file |
nmap -iL
sample.txt |
- |
Table 2-11 dig
| Options Tested | Description | Output | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| <ip> | It performs DNS lookups and displays the answers that are returned from the name servers that were queried. | dig 10.178.254.194Note:
The IP should be reachable from inside the
container. |
- |
| -x | Query DNS Reverse Look-up. | dig -x 10.178.254.194 |
- |
2.8 Logs
This chapter explains the process to retrieve the logs and status that can be used for effective troubleshooting. SCP provides various sources of information that may be helpful in the troubleshooting process.
Log Levels
Logs register system events along with their date and time of occurrence. They also provide important details about a chain of events that could have led to an error or problem.
Supported Log Levels
For SCP, the log level for a microservice can be set to any of the following valid values:
- DEBUG: A log level used for events considered to be useful during software debugging when more granular information is required.
- INFO: The standard log level indicating that something happened, the application entered a certain state, and so on.
- WARN: Indicates that something unexpected happened in the application, a problem, or a situation that might disturb one of the processes. But that doesn’t mean that the application has failed. The WARN level should be used in situations that are unexpected, but the code can continue the work.
- ERROR: The log level that should be used when the application reaches an issue preventing one or more functionalities from properly functioning.
Configuring Log Levels
To view logging configurations and update logging levels, use the Logging Config option on the Cloud Native Configuration Console. For more information, see "Configuring Global Options" in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Service Communication Proxy User Guide.
2.8.1 Collecting Logs
- Run the following command to get the pods
details:
$ kubectl -n <namespace_name> get pods - Run the following command to collect the logs from the specific
pods or containers:
$ kubectl logs <podname> -n <namespace>Example:$ kubectl logs ocscp-scp-worker-xxxxx -n ocscp - Run the following command to store the log in a
file:
$ kubectl logs <podname> -n <namespace> > <filename>Example:$ kubectl logs ocscp-scp-worker-xxxxx -n ocscp > logs.txt - (Optional) Run the following command for the log stream with file
redirection starting with last 100 lines of
log:
$ kubectl logs <podname> -n <namespace> -f --tail <number of lines> > <filename>Example:$ kubectl logs ocscp-scp-worker-xxxxx -n ocscp -f --tail 100 > logs.txt
2.8.2 Understanding Logs
This section explains the logs required to look into, to handle different SCP debugging issues.
The log level attributes of SCP services are as follows:
- SCPC-Subscription
- SCPC-Notification
- SCP-Worker
Sample Logs
Sample log statement for SCPC-Subscription:
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1614521111,"nanoOfSecond":908545000},"thread":"main","level":"INFO","loggerName":"com.oracle.cgbu.cne.scp.soothsayer.subscription.processor.SubscriptionDataConsumer","message":"{logMsg=Subscription consumer cycle completed.Thread Will now sleep for given time, cycle=232, threadSleepTimeInMs=100}","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":30,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"21-06-07 12:38:56.784+0000","application":"ocscp","microservice":"scpc-subscription","engVersion":"1.12.0","mktgVersion":"1.12.0.0.0","vendor":"oracle","namespace":"scpsvc","node":"master","pod":"ocscp-scpc-subscription-7f5b7c8ccd-z89wb","subsystem":"subscription","instanceType":"prod","processId":"1"}Sample log statement for SCPC-Notification:
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1623069485,"nanoOfSecond":496630558},"thread":"main","level":"INFO","loggerName":"com.oracle.cgbu.cne.scp.soothsayer.Process","message":"{logMsg=Successfully processed notification, nfInstanceId=6faf1bbc-6e4a-2828-a507-a14ef8e1bc5b, nfType=NRF}","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":1,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"21-06-07 12:38:05.496+0000","application":"ocscp","microservice":"scpc-notification","engVersion":"1.12.0","mktgVersion":"1.12.0.0.0","vendor":"oracle","namespace":"scpsvc","node":"master","pod":"ocscp-scpc-notification-76597b5b7-wfmxb","subsystem":"notification","instanceType":"prod","processId":"1"}Sample log statement for SCP-Worker
{"instant":\{"epochSecond":1623069702,"nanoOfSecond":672444454},"thread":"scp-upstream-worker-7","level":"WARN","loggerName":"com.oracle.cgbu.cne.scp.router.routelayer.MsgRouteChain","message":"MsgRouteChain::sendRsp(): SCP generated Response, Response Code = 503, body = {\"title\":\"Service Unavailable\",\"status\":\"503\",\"detail\":\"Service Unavailable:: Service Unavailable\"}, error category = Destination webclient Connection Failure, ingress request host = ocscp-scp-worker.scpsvc.svc.cluster.local:8000, ingress request path = /nnrf-nfm/v1/subscriptions, ingress 3gpp-sbi-target-apiRoot = http://nrf1svc.scpsvc.svc.cluster.local:8080, egress request Uri = http://nrf2svc.scpsvc.svc.cluster.local:8080/nnrf-nfm/v1/subscriptions, egress request Destination = nrf2svc.scpsvc.svc.cluster.local","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":139,"threadPriority":5,"messageId":"c49b3b48-afc1-4058-83e8-b719ee181ed8","messageTimestamp":"21-06-07 12:41:42.672+0000","application":"ocscp","microservice":"scp-worker","engVersion":"17.17.17","mktgVersion":"1.12.0.0.0","vendor":"oracle","namespace":"scpsvc","node":"master","pod":"ocscp-scp-worker-9567767dc-7bqg9","subsystem":"router","instanceType":"prod","processId":"1"}The following table describes different log attributes:
Table 2-12 Log Attribute Details
| Log Attribute | Details | Sample Value | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| instant | Epoch time
Note: It is a group of two values such as epochSecond and nanoOfSecond. |
{"epochSecond":1614521244,"nanoOfSecond":775702000} | Object |
| thread | Logging Thread Name | "pool-4-thread-1" | String |
| level | Log Level of the log printed | "ERROR" | String |
| loggerName | Class or Module which printed the log | "com.oracle.cgbu.cne.scp.soothsayer.audit.process.AuditMaster" | String |
| message | Message related to the log providing brief details
Note: WARN log level indicates that SCP connection with NRF is established. |
{logMsg=NRF health check did not complete successfully. Next health check will start in given interval, timeIntervalInSec=2} | String |
| endOfBatch |
Log4j2 Internal |
false | boolean |
| loggerFqcn |
Log4j2 Internal |
org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger | String |
| threadId | Thread Id generated internally by Log4j2 | 31 | Integer |
| threadPriority | Thread Priority set internally by Log4j2 | 5 | Integer |
| messageTimestamp | Timestamp when log was printed | "21-06-07 12:41:15.277+0000" | String |
| application | Application name | "ocscp" | String |
| scpFqdn | SCP FQDN | ocscp-scp-worker.ocscp-thrust5-06.svc.thrust5 | String |
| microservice | Name of the microservice | "scpc-audit" | String |
| engVersion | Engineering version of the software | "1.12.0" | String |
| mktgVersion | Marketing version of the software | "1.12.0.0.0" | String |
| vendor | Vendor of the software | "oracle" | String |
| namespace | Namespace where application is deployed | "scpsvc" | String |
| node | Node where the pod resides | "master" | String |
| pod | Pod name of deployed application | "ocscp-scpc-audit-6c5ddb4c54-hf8kr" | String |
| subsystem | Subsystem inside microservice group | "audit" | String |
| instanceType | Instance type | "prod" | String |
| processId | Process ID internally assigned | 1 | Integer |
2.9 Verifying the Availability of Multus Container Network Interface
Note:
Ensure that Multus Container Network Interface configuration is completed as described in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Service Communication Proxy Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.- To verify whether the pod contains signaling network, go to Kubernetes
cluster and run the following
command:
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n <namespace> - Check whether the pod output contains the "net1"
interface.
Sample pod output:
k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/network-status: [{ "name": "", "ips": [ "192.168.219.111" ], "default": true, "dns": {} },{ "name": "scpsvc/macvlan-siga", "interface": "net1", "ips": [ "192.68.3.78" ], "mac": "b6:41:f9:a6:c8:8e", "dns": {} }] k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: [{ "name": "macvlan-siga"}]
2.10 Upgrade or Rollback Failure
When Service Communication Proxy (SCP) upgrade or rollback fails, perform the following procedure.
- Check the pre or post upgrade or rollback hook logs in Kibana as
applicable.
Users can filter upgrade or rollback logs using the following filters:
- For upgrade: lifeCycleEvent=9001 or 9011
- For rollback: lifeCycleEvent=9002
{"time_stamp":"2021-11-22 10:28:11.820+0000","thread":"main","level":"INFO","logger":"com.oracle.cgbu.cne.scp.soothsayer.hooks.releases.ReleaseHelmHook_1_14_1","message":"{logMsg=Starting Pre-Upgrade hook Execution, lifeCycleEvent=9001 | Upgrade, sourceRelease=101400, targetRelease=101500}","loc":"com.oracle.cgbu.cne.scp.soothsayer.common.utils.EventSpecificLogger.submit(EventSpecificLogger.java:94)" - Check the pod logs in Kibana to analyze the cause of failure.
- After detecting the cause of failure, do the following:
- For upgrade failure:
- If the cause of upgrade failure is database or network connectivity issue, contact your system administrator. When the issue is resolved, rerun the upgrade command.
- If the cause of failure is not related to database or network connectivity issue and is observed during the preupgrade phase, do not perform rollback because SCP deployment remains in the source or older release.
- If the upgrade failure occurs during the postupgrade phase, for example, post upgrade hook failure due to target release pod not moving to ready state, then perform a rollback.
- For rollback failure: If the cause of rollback failure is database or network connectivity issue, contact your system administrator. When the issue is resolved, rerun the rollback command.
- For upgrade failure:
- If the issue persists, contact My Oracle Support.
2.11 Error Messages for Mediation Rule Configuration
This section allows you to troubleshoot and resolve problems in Mediation Rules using Drools Rule Language (DRL).
- Custom Errors
- Errors specific to Drool library
- Value not valid for type: This error is shown in cases where a field in the request body contains a value that is not expected.
- Fields are required and missing for rules with state: This error is shown in cases where a required field file is missing in the request.
- Rule name already exists in the database: When cloning a rule and the new name exists in the database, this error appears.
- Rule cannot be deleted on status: An APPLIED rule cannot be deleted. In the case of a delete request with APPLIED status, this exception will appear.
- Request body ruleName does not match with param ruleName: If the value of the rule name in the URL does not match the value in the "name" field in the request body, this exception will appear.
- Rule was not found: This error is shown when a get or delete request has a rule name that doesn’t exist in the database.
- The State field is not valid at the creation of the rule; it must be SAVE state: The rule is not going to be created if the value of state in the request body is different from SAVE state.
- State transition is not valid for status: For more information, refer "Mediation Rule API Migration" section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Service Communication Proxy User Guide.
- The APPLIED Status is not valid at the creation of the rule, it must be in the DRAFT status.
Note:
Once a rule is generated, ruleName, Format, and Status fields cannot be changed. Some fields are dependent on Status fields to be able to modify. For more information, refer "Mediation Rule API Migration" section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Service Communication Proxy User Guide.- 1st Block: Indicates the error code.
- 2nd Block: Indicates the DRL source line and column where the problem occurred.
- 3rd Block: Indicates the description of the problem.
- 4th Block: Indicates the Components in the DRL source where the issue occurred, such as rules, functions, and queries.
- 5th Block: Indicates the DRL source pattern where the issue occurred.
Figure 2-4 Error Message Format

-
101: no viable alternative
Indicates that the parser reached a decision point but was unable to find an alternative.
Example rule with incorrect spelling//incorrect spelling //incorrect syntax package com.oracle.cgbu.ocmediation.nfmediation; import com.oracle.cgbu.ocmediation.factdetails.Request; dialect "mvel" rule "ruleTest" when  req : Request(headers.has("header") == true) //special character then req.headers.add("newHeader","132465") endNote:
The parser reported an invalid token due to a special character. -
102: mismatched input
Indicates that the parser expects a specific input that is not present at the current input point.
Example rule with an incomplete rule statement//incomplete rule statement // incorrect syntax package com.oracle.cgbu.ocmediation.nfmediation; import com.oracle.cgbu.ocmediation.factdetails.Request; dialect "mvel" //Must have a rule name when req : Request(headers.has("header1") == true) then req.headers.add("TEST","132465") endNote:
The parser encountered an incomplete construct due to a missing rule name. -
103: failed predicate
Indicates that a validating semantic predicate is evaluated as false. These semantic predicates are commonly used in DRL files to identify component terms such as declare, rule, exists, not, and others.
Example rule with an invalid keywordpackage com.oracle.cgbu.ocmediation.nfmediation; import com.oracle.cgbu.ocmediation.factdetails.Request; dialect "mvel" fdsfdsfds rule "ruleTest" when req : Request(headers.has("header") == true) then req.headers.add("newHeader","132465") endNote:
This text line is not a DRL keyword construct, hence the parser cannot validate the rest of the DRL file. -
105: did not match anything
Indicates the parser reached a grammar sub-rule that must match an alternative at least once but did not match anything.
Example rule with invalid text in an empty conditionpackage com.oracle.cgbu.ocmediation.nfmediation; import com.oracle.cgbu.ocmediation.factdetails.Request; dialect "mvel" rule "ruleTest" when None // Must remove `None` if condition is empty then req.headers.add("TEST","132465") endNote:
The condition should be empty, but the wordNoneis used. This error is resolved by removingNone, which is not a valid DRL keyword.
For more information on the list of errors specific to the Drool library, see Drools User Guide.
2.12 Errors Observed on Grafana and OCI Dashboards
This section provides information to troubleshoot errors observed on Grafana and OCI dashboards. These errors occur when the number of records fetched by a query, which is an expression that uses application metrics and dimensions, exceeds the configured limit, due to which charts or widgets are invisible on dashboards.
The following sample error messages are displayed on the:
- Grafana dashboard: execution: execution: query processing would load too many samples into memory in query execution.
- OCI dashboard: Query cannot result in more than 2000 streams
To resolve this issue, perform the following tasks to view the data on these dashboards:
- On the Grafana or OCI dashboard, minimize the query interval to
check if the data appears.
- To debug an issue, check the error logs and select the interval on the dashboard based on the timestamp of the observed error logs to minimize the search results.
This task fetches only records within that query interval and reduces the number of records on the dashboard.
- You can add more filters using the metric dimensions (as per the traffic being run) to the query to minimize the search results. For more information about metric dimensions, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Service Communication Proxy User Guide. To query a particular metric, these dimensions act as filter keys as defined in Table 2-13 and Table 2-14.
- Ensure that the metric used in the query is pegged by the SCP application.
The following tables describe examples of queries on Grafana and OCI dashboards:
Table 2-13 Examples of Query on Grafana Dashboard
| Metric Used | Default Query on Dashboard | Query after Applying Additional Filters |
|---|---|---|
| ocscp_metric_http_rx_req_total | sum(irate(ocscp_metric_http_rx_req_total{namespace="scpsvc"}[2m])) by (pod) | sum(irate(ocscp_metric_http_rx_req_total{namespace="scpsvc",ocscp_nf_service_type="nausf-auth"}[2m])) by (pod) |
| ocscp_metric_http_tx_req_total | sum(irate(ocscp_metric_http_tx_req_total{namespace="ocscp"}[5m])) by (ocscp_nf_type,ocscp_producer_service_instance_id) | sum(irate(ocscp_metric_http_rx_req_total{namespace="ocscp",,ocscp_nf_service_type="nausf-auth"}[5m])) by (ocscp_nf_type,ocscp_producer_service_instance_id) |
Table 2-14 Examples of Query on OCI Dashboard
| Metric Used | Default Query on Dashboard | Query after Applying Additional Filters |
|---|---|---|
| ocscp_metric_http_rx_req_total | ocscp_metric_http_rx_req_total[10m]{k8Namespace="ocscp-2"}.rate().groupBy(podname).sum() |
|
| ocscp_metric_http_tx_res_total | ocscp_metric_http_tx_res_total[10m]{k8Namespace="ocscp-2"}.rate().groupBy(ocscp_consumer_info).sum() |
|
2.13 TLS Connection Failure
This section describes the TLS related issues and their resolution steps. It is recommended to attempt the resolution steps provided in this guide before contacting Oracle Support:
Problem: Ingress Connection Failure Due to TLS 1.3 Version Mismatch Between Consumer NF and SCP Server
Scenario: The Consumer NF has requested a connection using TLS 1.3, but the SCP server is currently configured to support only TLS 1.2. This version mismatch prevents successful communication between the client and server.
The client supported protocol versions [TLSv1.3] are not accepted by server preferences [TLSv1.2]Received fatal alert: protocol_version- Update the
ocscp-custom-values.yamlfile on the SCP server to set thesbiProxySslConfigurations.server.tlsVersionparameters to include TLS 1.3 and TLS 1.2. This configuration applies to fresh installations. For fixing issues or changing the version, you can use the REST API for configuration. - Verify TLS 1.3 for secure communication between the consumer NF and SCP to ensure that the issue has been resolved.
Problem: Egress Connection Failure Due to Cipher Mismatch: SCP Client and Producer Server for TLS v1.3.
Scenario: The SCP client is configured to request a connection using TLSv1.3 with specific ciphers that are not supported by the Producer server. As a result, the connection fails due to the cipher mismatch, preventing secure communication between the client and server.
No appropriate protocol(protocol is disabled or cipher suites are inappropriate)Received fatal alert: handshake failure- Ensure that the following cipher suites are configured for the
SCP client to use with TLS 1.3:
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
- Verify TLS 1.3 for secure communication between the SCP client and the Producer server to ensure that the issue has been resolved.
Problem: Egress Connection Failure for TLS v1.3 Due to Expired Certificates.
Scenario: The SCP client is attempting to establish an egress connection using TLSv1.3, but the connection fails due to expired certificates. Specifically, the SCP client is presenting TLSv1.3 certificates that have passed their validity period, which causes the Producer server to reject the connection.
Service Unavailable for producer due to Certificate ExpiredReceived fatal alert: handshake failure- Verify the validity of the current certificate
(
client_ocscp.cer). - If the certificate has expired, renew it or extend its validity.
- Attempt to establish a connection between the SCP client and the Producer server to confirm that the issue has been resolved.
- Verify the TLSv1.3 for secure communication.
Problem: Pods are not available after populating the
clientDisabledExtension or
serverDisabledExtension parameter.
- Check the value of the
clientDisabledExtensionorserverDisabledExtensionparameters. The following values cannot be added to these parameters:- supported_versions
- key_share
- supported_groups
- signature_algorithms
- certificate_authorities
If any of the above values are present, remove them or revert to the default configuration for the pod to start properly.
Note:
Thecertificate_authoritiesvalue can be added to theclientDisabledExtensionparameter but cannot be added to theserverDisabledExtensionparameter.
Problem: Pods are not available after populating the
clientAllowedSignatureSchemes parameter.
- Check the value of the
clientAllowedSignatureSchemesparameter. - The following values should be present for this parameter:
- ecdsa_secp521r1_sha512
- ecdsa_secp384r1_sha384
- ecdsa_secp256r1_sha256
- ed448
- ed25519
- rsa_pss_rsae_sha512
- rsa_pss_rsae_sha384
- rsa_pss_rsae_sha256
- rsa_pss_pss_sha512
- rsa_pss_pss_sha384
- rsa_pss_pss_sha256
- rsa_pkcs1_sha512
- rsa_pkcs1_sha384
- rsa_pkcs1_sha256