4 Configuring BSF Using CNC Console
This chapter describes how to configure different global and service parameters in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Binding Service Function (BSF) using Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console (CNC Console).
Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console (CNC Console)
This section provides an overview of the CNC Console, which includes an interface to help in creating global and service parameters in BSF.
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc location.
-
In Windows system, open the hosts file in a notepad as an Administrator and append the following set of lines at the end:
<IP Address> cncc-iam-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local<IP Address> cncc-core-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.localwhere:
<IP Address> is the host address of the deployment cluster. It depends on the deployment cluster.
Example:
10.75.225.189 cncc-iam-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local10.75.225.189 cncc-core-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.localNote:
The IP Address can change when deployment cluster changes. -
Save and close the hosts file.
Note:
Before logging into CNC Console, create a CNC user and password. Using these user details, you can log in to the CNC Console application. For more information about creating a CNC Console user and password, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console (CNC Console) Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.- Open a web browser and enter the URL:
http://cncc-core-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local:port
number/ and press Enter.
Note:
port number is cncc-iam-ingress-port number.The login page opens.
- Enter the Username and Password.
- Click Log In.
- On the Welcome page, select the required NF instance from the
Please Select Instance drop-down field.
This opens the CNC Console home page for the selected NF instance:
Figure 4-1 CNC Console for BSF
- To use BSF services integrated with CNC Console, click BSF in the left navigation pane.
4.1 General Configurations
This section describes the general configurations for Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Binding Support Function (BSF).
To access the General Configurations page from the CNC Console home page, click BSF, and then click General Configurations.
4.1.1 General Settings
This section describes the general settings, which can be configured using Cloud Native Core Console for Binding Support Function (BSF).
To access the General Settings page from the CNC Console home page, click BSF, select General Configurations, and click General Settings.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit General Settings page.
- Enter the values for the following
fields:
Table 4-1 General Settings
Field Name Description Enable Tracing Specifies whether to enable or disable tracing for the BSF deployment. By default, this configuration is enabled. Enable Metrics Specifies whether to enable or disable system metrics for the BSF deployment. By default, this configuration is enabled. Enable Collision Detection Specifies whether to enable or disable collision detection for the BSF deployment. By default, this configuration is disabled. Binding Discovery Request Timeout Specifies the request timeout value for the discovery request sent by the BSF Diameter Gateway towards the BSF Management Service. Enable Subscriber Activity Logging Specifies whether to enable or disable subscriber activity logging. The default value is false. Enable SBI Correlation Specifies whether to enable or disable correlation-info header in BSF. The dafault value is false. Table 4-2 General Settings - Enhanced Logging Configuration
Field Name Description Enable Enhanced Logging Specifies whether to enable or disable enhanced logging for the BSF deployment. By default, this configuration is disabled. Enable UE Identifier Information Specifies whether to enable or disable UE Identifier information for the BSF deployment. By default, this configuration is disabled. Figure 4-2 General Setting Console Page
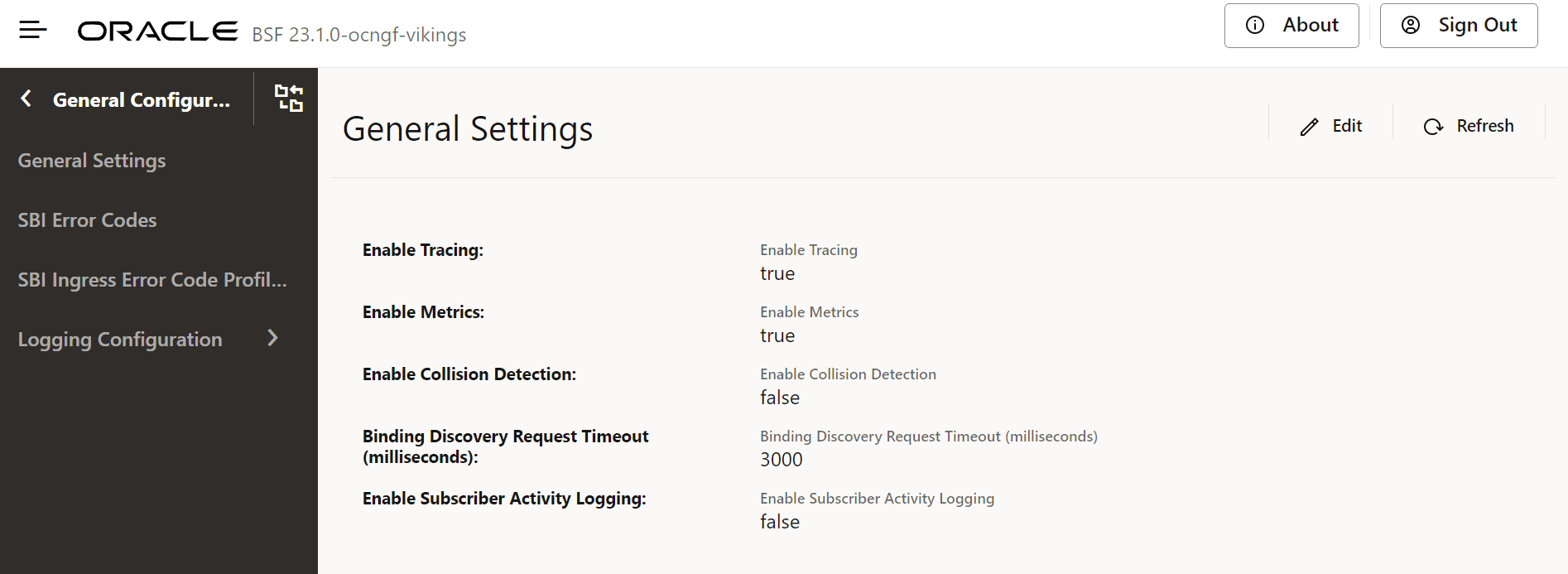
- Click Save to save the chosen general settings.
4.1.2 SBI Error Codes Configurations
This section describes how to customize the SBI error codes according to the network requirements using the SBI Error Codes page.
The SBI Error Codes page on CNC Console allows users to view and edit conditions defined by default for the Binding Support Function (BSF) network function. This page also provides the options to import and export SBI error codes.
Table 4-3 Error Codes and Responses
| Condition ID and Name | Error Description | HTTP Status Code | Application Error Code |
|---|---|---|---|
ERROR_CODE_RESOURCE_URI_STRUCTURE_NOT_FOUND
Binding resource URI is invalid |
This error is returned when bindingId is missing in the request URI or when the request URI is invalid. | 404 | RESOURCE_URI_STRUCTURE_NOT_FOUND |
ERROR_CODE_BINDING_NOT_FOUND
Binding key not found |
This error is returned when binding data is not found in the database. | 404 | NOT_FOUND |
ERROR_CODE_INVALID_QUERY_PARAM
Parameters in binding key are not acceptable |
This error is returned when parameters such as multiple UE addresses are sent in the request. | 400 | INVALID_QUERY_PARAM |
ERROR_CODE_MANDATORY_QUERY_PARAM_INCORRECT
Required parameter in binding key is not acceptable |
This error is returned when the mandatory query parameter is invalid. | 400 | MANDATORY_QUERY_PARAM_INCORRECT |
ERROR_CODE_OPTIONAL_QUERY_PARAM_INCORRECT
Optional parameter in binding key is invalid |
This error is returned when the optional query parameter is invalid. | 400 | OPTIONAL_QUERY_PARAM_INCORRECT |
ERROR_CODE_MANDATORY_QUERY_PARAM_MISSING
Required parameter in binding key is missing |
This error is returned when the mandatory query parameter is missing in the URI request. | 400 | MANDATORY_QUERY_PARAM_MISSING |
ERROR_CODE_INVALID_MSG_FORMAT
Parameter(s) in binding data is not supported |
This error is returned in case of invalid binding data is sent as payload. For instance, when an IP domain is present without an IPv4 address, this error is reported. | 400 | INVALID_MSG_FORMAT |
ERROR_CODE_MANDATORY_IE_INCORRECT
Required parameter in binding data is invalid |
This error is returned when the mandatory parameter such as SNSSAI is assigned a semantically incorrect value. | 400 | MANDATORY_IE_INCORRECT |
ERROR_CODE_MANDATORY_IE_MISSING
Required parameter in binding data is missing |
This error is returned when the mandatory parameter such as SNSSAI is missing. | 400 | MANDATORY_IE_MISSING |
ERROR_CODE_OPTIONAL_IE_INCORRECT
Optional parameter in binding data is invalid |
This error is returned when the Information Element (IE) in the request is invalid. | 400 | OPTIONAL_IE_INCORRECT |
ERROR_CODE_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR
Unexpected server error |
This error is returned in the following
situations:
|
500 | INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR |
ERROR_CODE_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED
Request method not supported |
This error is returned when the requested method is not supported. For instance, if the user sends a PUT request instead of a POST request to register PCFBinding, BSF returns error 405 in response to the request. | 405 | METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED |
Editing SBI Error Codes
- From the navigation menu, click BSF,
then select General Configurations, and click
SBI Error Codes.
This opens the SBI Error Codes page that lists the condition names along with their HTTP Status code and Application Error Code.
- Click Edit against the condition
that you need to customize.
This opens the Edit SBI Error Codes page.
- Update the required values for the
fields as described in the following table:
Table 4-4 Parameters for Edit SBI Error Codes
Parameter Description Error Description Specifies the description for a defined condition. It is recommended to use descriptions that clearly explain the condition. HTTP Status Code Specifies the HTTP Status code for a defined condition. This is a mandatory field and cannot be left blank. Note: Currently, the value for HTTP status code can be selected only from the supported set of values. To view the values, see Table 4-3.
Application Error Code Specifies the application error code for a defined condition. Users can customize application error codes as per their requirements. This is a mandatory field and cannot be left blank. - Click Save.
Supported HTTP Status Codes
Table 4-5 1xx Informational Series
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 100 | CONTINUE |
| 101 | SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS |
| 102 | PROCESSING |
| 103 | CHECKPOINT |
Table 4-6 2xx Success Series
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | OK |
| 201 | CREATED |
| 202 | ACCEPTED |
| 203 | NON_AUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION |
| 204 | NO_CONTENT |
| 205 | RESET_CONTENT |
| 206 | PARTIAL_CONTENT |
| 207 | MULTI_STATUS |
| 208 | ALREADY_REPORTED |
| 226 | IM_USED |
Table 4-7 3xx Redirection Series
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 300 | MULTIPLE_CHOICES |
| 301 | MOVED_PERMANENTLY |
| 302 | FOUND |
| 302 | MOVED_TEMPORARILY |
| 303 | SEE_OTHER |
| 304 | NOT_MODIFIED |
| 305 | USE_PROXY |
| 307 | TEMPORARY_REDIRECT |
| 308 | PERMANENT_REDIRECT |
Table 4-8 4xx Client Error Series
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 400 | BAD_REQUEST |
| 401 | UNAUTHORIZED |
| 402 | PAYMENT_REQUIRED |
| 403 | FORBIDDEN |
| 404 | NOT_FOUND |
| 405 | METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED |
| 406 | NOT_ACCEPTABLE |
| 407 | PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED |
| 408 | REQUEST_TIMEOUT |
| 409 | CONFLICT |
| 410 | GONE |
| 411 | LENGTH_REQUIRED |
| 412 | PRECONDITION_FAILED |
| 413 | PAYLOAD_TOO_LARGE |
| 413 | REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE |
| 414 | URI_TOO_LONG |
| 414 | REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG |
| 415 | UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE |
| 416 | REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE |
| 417 | EXPECTATION_FAILED |
| 418 | I_AM_A_TEAPOT |
| 419 | INSUFFICIENT_SPACE_ON_RESOURCE |
| 420 | METHOD_FAILURE |
| 421 | DESTINATION_LOCKED |
| 422 | UNPROCESSABLE_ENTITY |
| 423 | LOCKED |
| 424 | FAILED_DEPENDENCY |
| 425 | TOO_EARLY |
| 426 | UPGRADE_REQUIRED |
| 428 | PRECONDITION_REQUIRED |
| 429 | TOO_MANY_REQUESTS |
| 431 | REQUEST_HEADER_FIELDS_TOO_LARGE |
| 451 | UNAVAILABLE_FOR_LEGAL_REASONS |
Table 4-9 5xx Server Error Series
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 500 | INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR |
| 501 | NOT_IMPLEMENTED |
| 502 | BAD_GATEWAY |
| 503 | SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE |
| 504 | GATEWAY_TIMEOUT |
| 505 | HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED |
| 506 | VARIANT_ALSO_NEGOTIATES |
| 507 | INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE |
| 508 | LOOP_DETECTED |
| 509 | BANDWIDTH_LIMIT_EXCEEDED |
| 510 | NOT_EXTENDED |
| 511 | NETWORK_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED |
4.1.3 SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection
This procedure provides information about how to use the SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection page to create and manage SBI Ingress error code profiles collection in General Configurations.
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click General
Configurations, and then select SBI Ingress Error
Code Profiles Collection.
This opens the SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection page.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Add SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 4-10 Error Code Profiles Collection Configurations
Field Name Description Name Specifies a unique name to identify the error profile. Error Code Specifies the HTTP Code that is populated in the error response when a message request is rejected due to overload control. Error Cause Specifies the error cause that is populated in the error response when a message request is rejected due to overload control. Error Title Specifies the error title that is populated in the error response when a message request is rejected due to overload control. Error Description Specifies the error description that is populated in the error response when a message request is rejected due to overload control. - Click Save to save the error code
profile.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
The value gets listed on the SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
4.2 Error Handling
This section describes how to manage and view the error configurations in BSF, using the Error Handling Configurations page
4.2.1 Error Configurations
The error handling framework allows the users to configure an error state and an action for it. The action contains two parts, an error rule and an error context. On the Console UI, the operator configures the error state specific to the BSF services and the list of actions for it.
The Error Configurations page displays the error configurations related to different BSF services.
To add error handler template for a BSF service:
Error Configurations for Diameter Gateway Service
- From the navigation menu, under BSF, click Error Handling, and select Error Configurations page. This opens the Error Handling Configurations page.
- From the
Select Service Namedrop-down list select the valuediam-gateway. This page displays diameter message retry configurations for AAR messages.. On the page Error Handler Templates of diam-gateway and Error Configurations of diam-gateway subsections are displayed. - The Error Handler Templates of diam-gateway provides two
options:
- Error Code Configuration
- Timeout Error Configuration
- The Error Configurations of diam-gateway provides default error handling configurations to retry on all error codes (except diameter result code 2xxx) and timeout for Rx AAR failed diameter messages.
- To configure the Error Code Configuration in Error Handler
Templates of diam-gateway , Click
 .
.
This opens the Error Handler Template editing page.
- Enter values for the available input fields. The following table
describes the fields:
Table 4-11 Create Error Code Configuration - Edit
Field Name Description On Rx Specifies the list of diameter interfaces. The values are: - AAR
Status Specifies the error status to be provided by the user. Table 4-12 Error Cause Configure
Field Name Description Error Cause Field Species to search for which error causing filed in the diameter answer message. Default value: ALL
Match Operator Species the match operator to search error section in the diameter answer message. Default value: ANY
Error Response Originator The peer from which the error origination occurs. User can choose from the following options: - ANY
- INTERMEDIATE_PEER
- DESTINATION PEER
Message Specifies the error message to search in the error section of diameter answer message. Default value: ANY
Status Specifies the error status code to search in the error section in the diameter answer message. Default value: ANY
Cause Specifies the field that matches the cause during error ends with 'not found'. User can choose from the following options: - ANY
- RESPONSE_TIMEOUT
Table 4-13 Action
Field Name Description Action The action to be performed in the event of failed diameter message on Rx interface. User can choose from the following options: - RETRY TO ALTERNATE PEER
- ONE RETRY TO ALTERNATE PEER
- Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes. - To configure Timeout Error Configuration in Error Handler
Templates of diam-gateway , Click
 .
.
This opens the Error Handler Template editing page.
- Enter values for the available input fields. The following table
describes the fields:
Table 4-14 Create Timeout Error Configuration
Field Description On Rx Specifies the list of diameter interfaces. Default value: AAR
Status Specifies the error status to be provided by the user. Default value: ANY
Table 4-15 Error Cause Configure
Field Description Error Cause Field Species to search for which error causing filed in the diameter answer message. Default value: MESSAGE
Match Operator Species the match operator to search error section in the diameter answer message. Default value: EQUALS
Message Specifies the error message to search in the error section of diameter answer message. Default value: TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION
Status Specifies the error status code to search in the error section in the diameter answer message. Default value: ANY
Cause Specifies the field that matches the cause during error ends with 'not found'. Default value: ANY
Instance Specifies the field that matches the instance during error contains the term 'Illegal'. Default value: ANY
resource Specifies the resource to search in the error section of diameter answer message. Default value: ANY
Table 4-16 Action
Field Description Action The action to be performed in the event of response timeout on Rx interface. User can choose from the following options: - RETRY TO ALTERNATE PEER
- ONE RETRY TO ALTERNATE PEER
Error Originator The peer from which the error origination occurs. User can choose from the following options: - ANY
- INTERMEDIATE_PEER
- DESTINATION PEER
- Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes. - Perform the following steps to configure Advanced
Settings:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following
key and respective
value:
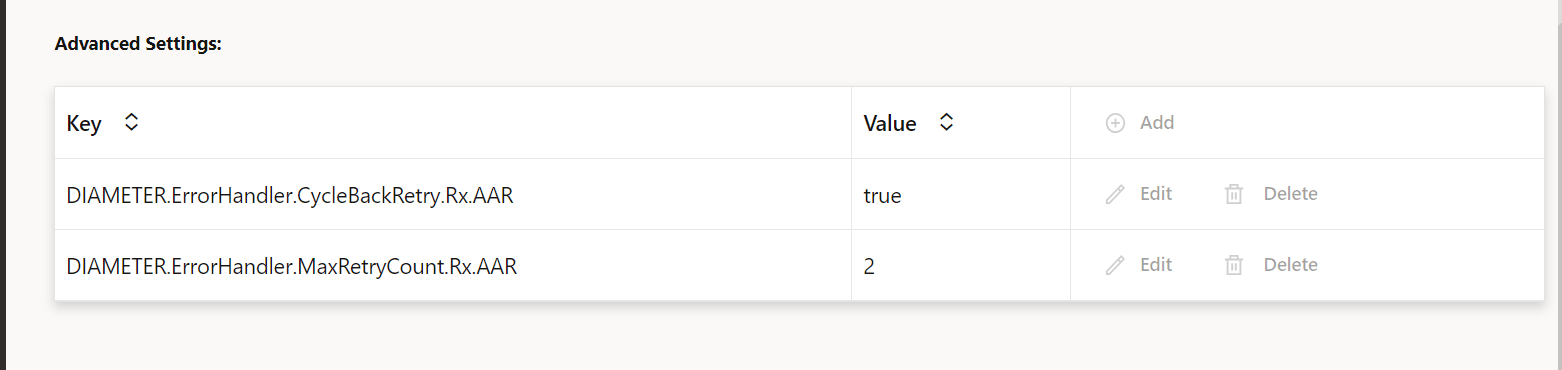
Table 4-17 Parameters for Advanced Settings
Keys Value DIAMETER.ErrorHandler.MaxRetryCount.Rx.AAR It is used to set the maximum retries that can be performed for failed AAR messages. Default Value: 1
DIAMETER.ErrorHandler.CycleBackRetry.Rx.AAR It is used to set if peers can be cycled back for retries or not. Default Value: false
Figure 4-3 Advance Setting Configurations Screen
- Click Save.
The page saves the Error Handling configurations.
- Click the
Error Configurations for BSF Management Service
- From the navigation menu, under BSF, click Error Handling, and select Error Configurations page. This opens the Error Handling Configurations page.
- From the
Select Service Namedrop-down list select the valueBSF Management Sevice. This page displays BSF Management Sevice. - Enable the error handler configurations using the Enable Error Handler Configurations toggle button.
- The error handler template provides Error Enhancement Configurations.
- To configure the Error Enhancement Configurations in Error
Handler Templates of the required service, Click
 . This opens the Error Handler Template editing page.
. This opens the Error Handler Template editing page.
- Enter values for the available input fields. The following table
describes the fields:
Table 4-18 Error Handler Template
Field Description On Specifies the Application Error. Default value: Application Error
Table 4-19 Action
Field Description Action Specifies the action to be performed in the event of failed message. Default value: Reject with Enhanced Detail
Exclude from error message Specifies exclusion of the provided components from detail error message. By default, "Error State and "Probelm Cause" are excluded. - Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
- Click the Import icon.
The File Upload dialog box opens.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
4.3 Logging Configurations
This section describes how to customize the log level and subscriber logging activity settings in BSF using the Logging Configurations pages.
4.3.1 Logging Level
Note:
The default log level for each service is Warn.The Logging Level page displays the log level configured for different services. The page allows you to edit the log level configurations.
To configure the log level:
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Logging Level.
This opens the Logging Level Configuration page. You can add or edit the log level and package log level for each service type from this page.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Log Level page.
- From the Service Type drop-down list, select the service for which you need to view, edit, or delete the logs.
- From the Application Log Level drop-down list, select the root log level
of the application for the selected service type. Possible values are:
- TRACE
- DEBUG
- INFO
- WARN
- ERROR
Note:
The value for the Application Log Level field is the mandatory value, and the Package Log Level is the optional value. - Expand the Package Log Level group to enter the package log level
information:
Note:
This step is only applicable when Oracle Engineering is trying to isolate an issue and requests one or more package names be added and logs collected after the reproduction of an issue.- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Package log Level dialog box.
- Enter the value in the Package field. The value of Package field is dependent on the package's name in each application. Before you set the value of Package field, you need to know what package is existed in that application.
- From the Log Level drop-down menu, select the log level
for the package. Possible values are:
- TRACE
- DEBUG
- INFO
- WARN
- ERROR
- Click Save.
The Package log level information for the selected service is saved.
Note:
Use or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the package
log level information.
available in the next column to update or delete the package
log level information.
- Click
- Click Save.
The log level information for the selected service type is saved.
4.3.2 Subscriber Activity Logging
Subscriber Activity Logging allows you to define a list of the subscribers (identifier) that you may require to troubleshoot the NFs and trace all the logs related to the subscribers separately to view. This functionality can be used to troubleshoot problematic subscribers without enabling logs or traces that can impact all subscribers. You can capture and monitor subscriber logs for Binding Register and Deregister call flow between Ingress Gateway and BSF Management Service and Binding Discovery call flow between Diameter Gateway and BSF Management Service.
To enable the subscriber activity logging functionality, set value of the Enable Subscriber Activity Logging parameter to true on the General Configurations page. By default, this functionality remains disabled. For more information about enabling the functionality, see General Settings
This procedure provides information about how to configure and manage subscriber logging.
The Subscriber Activity Logging page allows you to create new and manage existing subscribers. The page displays the list of defined subscribers and provides the options to import, export, or add lists.
You can configure the list of subscribers using the Subscriber Activity Logging page.
To configure a list of subscribers for logging:
To configure Subscriber Activity Logging:
- From the navigation menu under
BSF, navigate to General
Configurations, click Logging
Configurations, and then select Subscriber Activity
Logging.
This opens the Subscriber Activity Logging page. The page lists the existing configurations. You can add or import new subscriber activity logging configurations using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format on
your system.
Figure 4-4 Adding Subscriber Activity Logging
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Subscriber Activity Logging page.
- On the Create Subscriber Activity Logging
page, enter the following information:
Table 4-20 Create Subscriber Activity Logging Field Description
Field Name Description Identifier Type Select the subscriber identifier type. Supported subscriber identifier type are: - GPSI
- SUPI
- IPV4
- IPV6
Identifier Value The identifier value for the selected identifier type. Enable Use this switch to enable or disable the subscriber logging functionality for the selected subscriber. Figure 4-5 Creation of Subscriber for Logging with Identifier Console
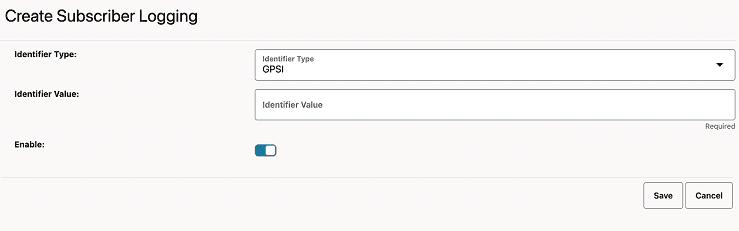
- Click Save.
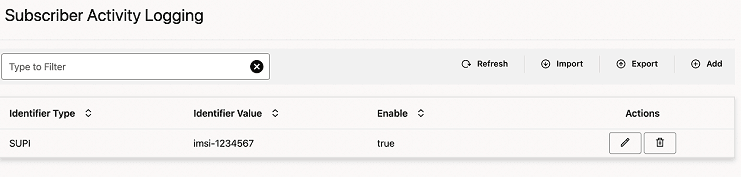
The configuration gets listed on the Subscriber Activity Logging page. The page defines the Subscriber Activity Logging configuration in the BSF database.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the configuration.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the configuration.
Figure 4-6 Added List of Subscribers
To import Subscriber Activity Logging configuration:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
Subscriber Identifiers
SUPI
In the 5G system, a globally unique Subscription Permanent Identifier (SUPI), known as IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) till 4G, is assigned for each subscription. The SUPIs are assigned in such a manner that it helps in identifying subscriptions and is independent of the user equipment.
imsi: <value>
supi: imsi-<value>
GPSI
General Public Subscription Identifier (GPSI), known as MSISDN (Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number) till 4G, is a 3GPP defined subscriber public identifier that can be used both inside and outside of the 3GPP system. The association between GPSI and its related SUPI are stored in the subscription data in a 5G system.
msisdn/e164:<value>
gpsi: msisdn-<value>
4.4 Service Configurations
This section describes how to customize the BSF Management Service and Audit Service according to the network requirements using the Service Configuration page.
4.4.1 Management Service
You can view and edit configurations for BSF Management Service on the Management Service page using the CNC Console.
To access this screen from the Home screen of CNC Console, under BSF, click Service Configurations and then Management Service.
- From the navigation menu, under BSF. click
Service Configurations, and select
Management Service.
This opens the Management Service page.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Management Service page.
- Update the required values for the
parameters as described in the following table:
Table 4-21 Parameters for Edit Management Service Configurations
Parameter Description Server Root URL Specifies the callback URI for notifications to be received by the user. Table 4-22 NF Bindings Settings
Parameter Description Send Binding Header Indicates if BSF includes the 3gpp-sbi-binding header in SBI messages for the registration creation, modification, or notification responses, as applicable. By default, the switch remains disabled.
Binding Level Indicates the binding level to be included in the 3gpp-sbi-binding header when BSF adds this header in a message to another NF. Select any of the following values from the drop-down menu:- NF Set
- NF Instance (Default)
Table 4-23 NF Server Settings
Parameter Description Send Server Header Indicates if BSF management service includes server header while sending an error response. Server Header Error Codes Indicates the error codes for which service header is generated. The error codes can be from 100 to 999. Note: If you do not specify an error code in this field, BSF management service sends server headers for all error codes.
Table 4-24 Audit
Parameter Description Enabled Use this flag to enable or disable stale session handling feature. By default, the feature is disabled.
Notification Rate (per second) Specifies the number of notifications that Audit service sends to the BSF Management service in one second. The recommended value is 50.
Default and Recommended Value: 50
Note: To configure higher number than the recommended value, contact My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com)
Binding Age (in minutes) Specifies the binding age for binding records. Once the binding age for a record exceeds the configured value, audit service marks the record as suspected stale.
The recommended value is 3600.
Maximum Binding Age (in minutes) Specifies the maximum binding age for binding records. Once the binding age for a record exceeds the configured value, audit service marks the record as stale and BSF removes the record from its local database. The recommended value is 7200.
Minimum Audit Attempts Specifies the minimum number of consecutive failed audit attempts until maxTTL / forceTTL is reached.
If maxTTL is reached and audit_attempts + 1 >= Minimum Audit Attempts for maxTTL, Audit service sends notification to Management Service with maxTTL flag set to true. Management Service deletes the record.
Range: 0-255
Default Value: 0
Note: If maxTTL is not reached and if audit attempts are reached, the number of audit attempts are incremented until maxTTL is reached.
Minimum Audit Passes Interval (in minutes) Specifies the minimum interval between two consecutive audits. The recommended value is 10.
Answer with Result Code Configuration Choose the value that BSF compares with the result code in the AAA-I answer. If both the values match, BSF Management service initiates stale record notification. To add the result code, perform the following steps:- Click Add.
The Add Answer with Result Code Configuration dialog box opens.
- For the Answer with
Result Code, select any of the
following valid values from the drop-down list:
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE
Note: If you select
EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE, enter the required values for Result Code and Vendor ID.
- Click Save on the dialog box.
Query to PCF Indicates whether BSF management service queries PCF to confirm the status of a PcfBinding record, which is suspected as stale by the audit service. Default value: false
Note: When Query to PCF parameter is set to false, the value of "Minimum Audit Attempts" parameter in Service Configurations of Management Service, and "Forced Deletion - Minimum Audit Attempts" parameter in Service configurations of Audit Service should be set to 0.
Vendor ID Specifies the vendor ID that BSF retrieves from the Vendor Specific Attribute to send query requests towards PCF. The vendor ID should be 6-digit long. Note: PCF sends the Vendor Specific Attribute in the request body at the time of binding registration.
Table 4-25 Active Bindings Counting
Parameter Description Count Active Binding Enables or disables the active sessions counting. By default, the active sessions counting is disabled. To enable the feature, set the value of this parameter to
true.Bindings Count Interval (in minutes) Specifies the time interval (in minutes) for which maximum active sessions are reported as a metric. Default value is 15 minutes.
You can set the time interval to any value between 1 to 60 minutes.
Root Log Level Specifies the log level of BSF Management service. The available values for this field are as follows:- Trace
- Debug
- Information
- Warn (Default)
- Error
- Always
Log Levels To add the log levels, perform the following steps:- You can add log levels using the Log Levels group on this page.
- To add log level:
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Add Log Levels dialog box.
- On the dialog box, enter the values shown in Table 4-26.
- Click Save
on the dialog box.
The log level information for the selected service type is saved.
- Click
Table 4-26 Parameters for Add Log Levels Configurations
Parameter Description Logger Name Specifies the name of the logger. Level Specifies the log level of BSF Management service. Select any of the following valid values:- Trace
- Debug
- Information
- Warn (Default)
- Error
- Always
Table 4-27 NF Correlation Settings
Parameter Description Send Correlation-Info Header Specifies an option to forward the received or generated headers to the Produce NFs. By default the switch remains disabled.
Allowed Correlation-info Header Generation Type(s) Specifies that if correlation header is not received from consumer NFs, BSF should generate the header. The Correlation-Type supported
- SUPI
- GPSI
- (Select either both or none)
Enable Binding Revalidation When this field is enabled, BSF checks if the binding information for the PDU session is present in BSF. Existence of the binding association for the PDU session in BSF confirms the binding association being valid in BSF. If the binding association is missing in BSF, it is restored by creating the association in BSF.
Default value: false
- Click Save on the Edit Management Service page to save your changes.
4.4.2 Audit Service
This section provides information about configuring the Audit Service.
4.4.2.1 Audit
The Audit Service page displays the Audit Service configurations. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu under
BSF, navigate to Service
Configurations, and select Audit Service
and browse to Audit page.
This opens the Audit page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Audit page.
- Make sure that the value of the Audit
Enabled switch is enabled.
This field determines if auditing is enabled for BSF Management Service. By default, this switch is enabled.
-
Expand the Forced Deletion group and configure the Minimum Audit Attempts parameter.
Minimum Audit Attempts specifies the minimum number of audit attempts until ForceTTL is reached.
If ForceTTL is reached and audit_attempts + 1 >= Minimum Audit Attempts of ForceTTL, then Audit service deletes the identified stale records from its respective database.
The default value of this parameter is 0 and the value can range between 0 to 255.
- Click Save.
The page saves the Audit service configurations.
Note:
Important considerations during Audit configurations:
In situations where the number of stale records (records that are eligible to be audited) at any given point of time in the system (for a given microservice database) is expected to be high (for example, > 1M), then the Session Age and/or the Notification Rate parameters should be set appropriately such that at least 2 audit cycles can be finished before the records that were assessed by the first cycle fall stale again. The Audit procedure having a Session Age less than this recommendation, may not be able to assess all stale records as the already assessed ones will be stale again too soon. It is recommended to keep a minimum of 24 hours for the Session Age and a minimum of 48 hours for Max Binding Age.
The time taken to complete an Audit Cycle and begin the next one can be calculated as below:
Audit Cycle Time = S / (N*60) + I minutes, where,
S = expected number of stale sessions at any given time,
N = notification rate (per second),
I = minimum Audit Interval
4.4.2.2 Audit Schedule Data
Figure 4-7 Audit Scheduled Service List Data

Table 4-28 Audit Schedule Data Fields
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Name | Name of the service that had registerd for audit service. |
| Table Name | Name of the database table that has requested for the audit service |
| Next Schedule | Next schedule availability time |
| Status | Scheduler job status |
| Start Time | Audit start time of pod. |
| End Time | Audit end time of pod. |
| Last Polled Time | Pod and associated scheduler details. |
| Schedular Details | Last time at which pod updated this table. |
| Is Service Dependent | If this is true, notification will be triggered for one table in the service, for all table’s in the service, notifications will be sent parallelly based on the notificationRate set for each table. |
Audit Schedule task can be in one of the state described below:
Figure 4-8 Audit Schedule Job Work Flow

Table 4-29 Audit Schedule Job Status
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| QUEUED | When a registered request is received it is added to the schedule table, the job status is set to Queued. |
| INITIALISING | When polling task is complete and is initialising for AuditTaskManager to audit, the job status is set to Initialising. |
| RUNNING | When Audit task manager starts the task, the job status is set to Running. |
| COMPLETE | When Audit TaskManager completes the Audit, the status is set to Complete. |
| INTERRUPTED |
When the audit process is paused from GUI, then the job status is set to Interrupted. When resumed from GUI, job status is set to Queued When deregistered, the job data will be removed from the table. when a service is register, it is set to Queued. |
| DEREGISTERED |
When deregistered, the job status is set to Deregistered for Initialising or Running and the entry will be deleted for any other status(except Initialising or Running). In case the a service register request is received before AuditTaskManager deletes the table entry for deregistered job statuses, the status would be moved to Queued. |
For more information on Audit Service and Audit Schedule REST API details, see the section Audit Service in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Binding Support Function REST Specification Guide.
4.5 Diameter Configurations
This section describes how to manage and view the Diameter Configurations in BSF using the Diameter Configurations pages.
4.5.1 Settings
The Settings page displays the general configurations related to the Diameter Gateway. The page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Diameter
Configurations and select Settings.
This opens the Settings page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Settings page.
- Enter the following information
under the respective groups:
Table 4-30 Timer
Field Name Description Reconnect Delay (sec) Enter the time frame to delay before attempting to reconnect after a connection failure in seconds. The default value is 3 seconds.
Response Timeout (sec) The amount of time Diameter Gateway waits for the answer to come from the sent request. It is a global value applicable for all the interfaces messages. Enter the response timeout interval in seconds. Note: To enable Application or Command code Response timeout value, see Enhanced Timer Configuration.
The default value is 5 seconds.
Connection Timeout (sec) Enter the connection timeout interval in seconds. The default value is 3 seconds.
WatchDog Interval (sec) Enter the watchdog interval in seconds. The default value is 6 seconds.
Table 4-31 Transport
Field Name Description Protocol The protocol supported is TCP. Table 4-32 Congestion Control
Field Name Description Load Shedding Profile Select any one of the configured load shedding profiles for congestion control on Diameter interface from the drop-down list. Message Priority Profile Select any one of the configured message priority profiles for congestion control on Diameter interface from the drop-down list. Table 4-33 Overload Control
Field Name Description Load Shedding Profile Select any one of the configured load shedding profiles for overload control on Diameter interface from the drop-down list. Message Priority Profile Select any one of the configured message priority profiles for overload control on Diameter interface from the drop-down list. Note:
The following message priority data that was exported prior to BSF 23.2.0 cannot be imported as the data may be corrupt:- message containing Sd as interface
- Sy-SLR as condition message
The data with Sd interface or Sy-SLR condition messages that are exported only with BSF 23.2.0 or later versions can be imported.
Table 4-34 Enhanced Timer Configuration
Field Name Description Application Name Request Timer configuration for applications name like Rx, Gx, Sy, Sd.
Application Response Timeout (milliseconds) Enter the application response timeout in milliseconds. The range of this value is between between 3 seconds to 2147483647. Table 4-35 Command Code Response TimeOut
Field Name Description AAR (milliseconds) The command code response timeout value for AAR. The allowed value ranges from 3 to 2147483647.
Default Value: 5000
STR (milliseconds) The command code response timeout value for STR. The allowed value ranges from 3 to 2147483647.
Default Value: 5000
RAR (milliseconds) The command code response timeout value for RAR. The allowed value ranges from 3 to 2147483647.
Default Value: 5000
ASR (milliseconds) The command code response timeout value for ASR. The allowed value ranges from 3 to 2147483647.
Default Value: 5000
The order of precedence (from highest to lowest) of response timeout configurations is:- Command Code Response Timeout (ms) - Message level configurations i.e at AAR, STR etc.
- Application Response Timeout (ms) - Interface level configurattion i.e at Gx, Rx etc.
- Response Timeout (ms) - General level configutation
- Perform the following steps to configure
Advanced Settings:
- Click the

The page opens the Add Advanced Settings dialog box.
- In the dialog box, enter the following keys and respective values:
The following table describes the keys and values:Table 4-36 Add Advanced Settings Configurations
Key Value DIAMETER.Enable.Validate.Realm Used to validate the destination-realm received in the AAR-I message against the destination-realm in BSF's Diameter Gateway host realm.
Default value: false
DIAMETER.BSF.Enable.Validate.Binding.Realm Used to validate the destination-realm of AAR-I against the discovered pcfBinding's realm.
Default value: false
DIAMETER.BSF.Enable.Overwrite.Realm Used to configure whether to overwrite the pcfBinding's realm and identity information in AAR-I destination-realm AVP.
Default value: false
DIAMETER.ErrorHandler.Enable.UpdateDestinationHost By default, BSF Diameter Gateway keeps the Destination-Host AVP to the retry message same as originally recieved request message.
There is an option to change the Destination-Host for retry message with respective destination peer (Retry Peer) found using the error handling configuration.
If DIAMETER.ErrorHandler.Enable.UpdateDestinationHost value is set to true, then change the Destination-Host with respective destination peer (retry peer).
Default value: false
- Click the
- Click Save to save the settings.
4.5.2 Peer Nodes
This procedure provides information about how to define and manage Peer Nodes in Diameter Configurations.
The Peer Nodes page allows you to create new peer nodes and manage existing peer nodes. The page displays the list of defined configurations and provides the options to import, export, or add data.
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Diameter
Configurations, and select Peer
Nodes.
This opens the Peer Nodes page. The page lists the existing Peer Nodes. You can add or import new nodes using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Peer Node page.
- On the Create Peer Node page, enter
values for the available input fields.
The following table describes the various field names:
Table 4-37 Create Peer Node Configurations
Field Name Description Name Unique name of the peer node. Example value: ocs
Type Defines which type of diameter service must be selected. The values can be - PCF
- Application function (AF)
- backend
- diameter routing agent (dra)
- online charging system (ocs)
- tdf
- udr
Reconnect Limit (sec) Defines the reconnect limit. Configure this value as the Diameter peer configuration. Example value: 10
Initiate Connection Set to true to initiate the connection with peer node. Transport Defines the type of transport ways for configuring a peer. The values can be: - TCP
- TLSv1.2
- TLSv1.3
- TLSv1.2_OR_TLSv1.3
Port Enter the port number. Enter a number from 0 to 65535. Example value: 8007
Host Enter the host name. Enter an FQDN, ipv4, or ipv6 address available for establishing diameter transport connections to the peer node. Realm Enter the realm name, that is, FQDNs to all of the computers that transact diameter traffic. For example, to add the realm detail of the OCS peer, enter xxx.com.
Identity Enter an identity to define a node in a realm. For example, to add the identity detail of the OCS peer, provide value enter ocs.
- Click Save to save the changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The value gets listed on the Peer Node page. Use
 or
or  available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
available in the next column to update or delete the
listing.
Importing Peer Nodes
To import peer node:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
4.5.3 Diameter Routing Table
Configuration allows routing Diameter request messages to next hop peer based on Diameter application-id, Destination-Realm, and Destination-Host.
- Host-Based Routing: The destination-host of incoming message is checked in the routing table, and then the message is routed to the top priority matching route's peer.
- Realm-Based Routing: The destination-realm of incoming message is checked in the routing table, and then the message is routed to the top priority matching route's peer.
Routing decision at Diameter-Gateway
- If the incoming request message has destination-host and the specified peer is directly connected with gateway pod, then the message is routed to the peer specified in destination-host.
- If the incoming request message has destination-host and is not directly connected via any other diameter-gateway pods in the cluster, then the message will be inter-pod routed.
- The routing table is scanned for a matching route by:
- If the host is reachable, message is sent.
- If the host is not reachable directly, find if it can be reached by another diameter gateway pod, message is sent using inter-pod route
- If the host is not reachable directly or indirectly, lookup the routing table again for the next matching route.
The Diameter Routing Table Configurations page displays the Diameter routing configurations. This page allows you to edit the configurations.
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Diameter
Configurations, and select Routing Table.
This opens the Diameter Routing Table Configurations page. The page displays the existing configurations.
- Click
 .
.
This opens the Edit Diameter Routing Table Configurations page.
- Expand the Diameter Route Table Table
group.
The expanded group allows you to add route table entries.
- To add routing table:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the Add Diameter Route Table dialog box.
- Enter the values for the following input fields:
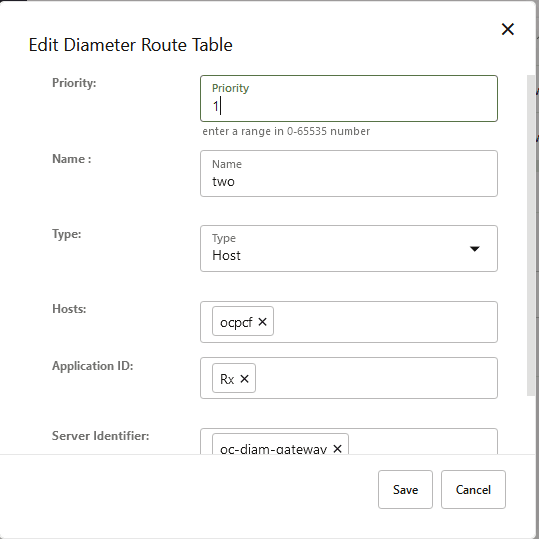
Table 4-38 Add Diameter Route Table Configuration
Field Name Description Priority Defines the order of use when one or more routes have overlapping criteria. It can be a number in the range of 0 to 65535. The lowest priority value indicates the highest priority. Note: If there are more than one routing table entry with same priority, it will consider only first row from multiple rows with same priority.
Name Specifies the unique name of the diameter routing table. Type Specifies whether the diameter route table is Host or Realm based. Realms/Hosts Specifies the value of the Realms or Hosts depending on the Type selected by the user. For Realms, you can add multiple FQDNs to this field. Application ID Specifies the type of application or interface. The available values are - Rx
- Gx
- Sh
- Sy
- All
Users can select multiple values for this parameter.
Server Identifier Specifies the server to which the message is to be routed. This identity must also be present in the Identity field of the peer node. Note: If multiple server identifiers are configured one after the other separated by (,) comma, it considers the first value and ignores the rest of the values which were added with the comma separator.
An example of adding the diameter routing details is shown below:
Figure 4-9 Adding first Diameter Routing Element
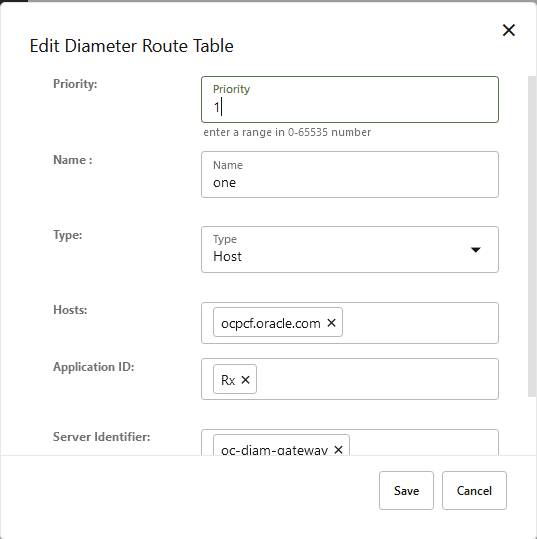
Figure 4-10 Adding Second Diameter Routing Element
- Click Save on the Add Diameter Routing Table dialog box.
- Click
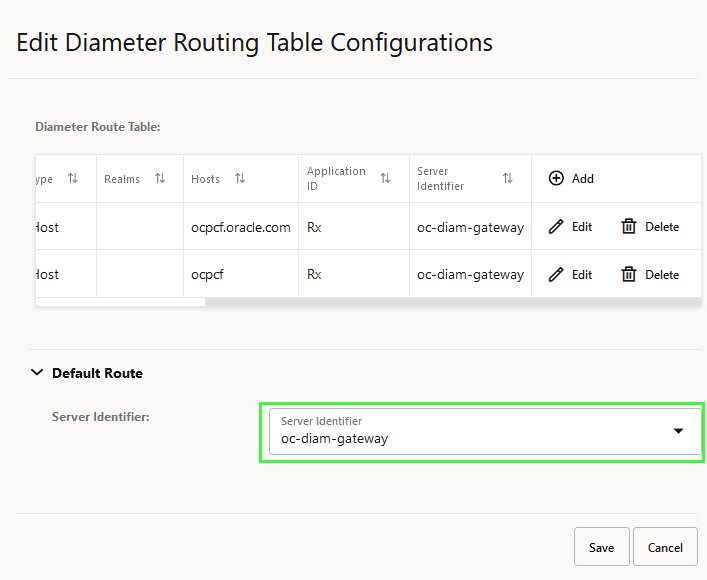
- On the Edit Diameter Routing Table Configurations page, expand the Default Route group.
- Enter a value for the Server Identifier drop-down list.
The server identifier drop-down list shows the list of the configured peer nodes on the Peer Nodes configuration page. For more information on configuring Peer Nodes, see Peer Nodes.
On selecting any of the values, make sure that the name is the same as the value of server identifier.Note:
* (asterisk) wildcard character is allowed in Hosts, Realms, and Server Identifier fields.Figure 4-11 Diamter Routing Table Configurations
- Click Save.
The configuration gets listed on the Diameter Routing Table Configurations page.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the Diameter Routing Table configurations.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the Diameter Routing Table configurations.
4.5.4 Diameter Error Codes Configurations
This section describes how to customize the Diameter error codes according to the network requirements using the Diameter Error Codes page.
The Diameter Error Codes page on CNC Console allows users to view and edit conditions, which are defined by default for the Binding Support Function (BSF) network function. This page also provides the options to import and export diameter error codes.
Table 4-39 Error Codes and Responses
| Condition Name | Error Message | Diameter Result Code |
|---|---|---|
| Unable to Route Diameter Message | BSF cannot route a diameter message to the selected destination. | 3002 DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER |
| Diameter Request Message Timeout | BSF sent a diameter request message to the selected destination but did not receive a response in the specified time. | 3002 DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER |
| Unsupported Diameter Interface Received | A diameter message was received for a diameter interface that is not supported by BSF. | 3007 DIAMETER_APPLICATION_UNSUPPORTED |
| AVP Value Invalid | A diameter message was received containing an AVP with a value that is invalid (indicated in FailedAVP) | 5004 DIAMETER_INVALID_AVP_VALUE |
| Required AVP Not Present | A diameter message was received that did not have a required AVP (indicated in FailedAVP) | 5005 DIAMETER_MISSING_AVP |
| Binding Not Found | A binding record was not found for the subscriber key(s) present in the Diameter AAR Initial message | 5065 IP-CAN_SESSION_NOT_AVAILABLE |
| Internal Error | An internal failure occurred | 5012 DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY |
Table 4-40 Error Codes and Responses
| Condition Name | Error Message | Diameter Result Code |
|---|---|---|
| Unable to Route Diameter Message | BSF cannot route a diameter message to the selected destination. | 3002 DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER |
| Diameter Request Message Timeout | BSF sent a diameter request message to the selected destination but did not receive a response in the specified time. | 3002 DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER |
| Unsupported Diameter Interface Received | A diameter message was received for a diameter interface that is not supported by BSF. | 3007 DIAMETER_APPLICATION_UNSUPPORTED |
| AVP Value Invalid | A diameter message was received containing an AVP with a value that is invalid (indicated in FailedAVP) | 5004 DIAMETER_INVALID_AVP_VALUE |
| Required AVP Not Present | A diameter message was received that did not have a required AVP (indicated in FailedAVP) | 5005 DIAMETER_MISSING_AVP |
| Binding Not Found | A binding record was not found for the subscriber key(s) present in the Diameter AAR Initial message | 5065 IP-CAN_SESSION_NOT_AVAILABLE |
| Internal Error | An internal failure occurred | 5012 DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY |
Table 4-41 Error Codes and Responses
| Condition Name | Error Message | Diameter Result Code |
|---|---|---|
| Unable to Route Diameter Message | BSF cannot route a diameter message to the selected destination. | 3002 DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER |
| Diameter Request Message Timeout | BSF sent a diameter request message to the selected destination but did not receive a response in the specified time. | 3002 DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER |
| Unsupported Diameter Interface Received | A diameter message was received for a diameter interface that is not supported by BSF. | 3007 DIAMETER_APPLICATION_UNSUPPORTED |
| AVP Value Invalid | A diameter message was received containing an AVP with a value that is invalid (indicated in FailedAVP) | 5004 DIAMETER_INVALID_AVP_VALUE |
| Required AVP Not Present | A diameter message was received that did not have a required AVP (indicated in FailedAVP) | 5005 DIAMETER_MISSING_AVP |
| Binding Not Found | A binding record was not found for the subscriber key(s) present in the Diameter AAR Initial message | 5065 IP-CAN_SESSION_NOT_AVAILABLE |
| Internal Error | An internal failure occurred | 5012 DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY |
Editing Diameter Error Codes
- From the navigation menu, click BSF,
then select Diameter Configurations, and click
Diameter Error Codes.
This opens the Diameter Error Codes page that lists the condition names along with their Result code, Vendor Id, and Application Error Code.
- Click Edit
against the condition that you need to customize.
This opens the Edit Diameter Error Codes page.
- Update the required values for the
fields, described in the following table:
Table 4-42 Parameters for Edit Diameter Error Codes
Parameter Description Use Experimental Result Indicates whether to use the Result Code AVP (268) or Experimental Result AVP (297) when an error result is generated by BSF. Result Code Specifes the Diameter result code for a defined condition. When Use Experimental Result switch is disabled, this field cannot be left blank. Note: The value must be a standard diameter result code as defined in the RFC 6733.
Experimental Result Code Specifies the custom Diameter result code for a defined condition. When Use Experimental Result switch is enabled, this field cannot be left blank. Note: The value must be a standard diameter result code, from 3000 to 9999, as defined in the 3GPP Technical Specification 29.230
Vendor Id Specifies the Vendor ID of the operator or governing body that manages the code entered by the user in the Experimental Result Code field. When Use Experimental Result switch is enabled, this field cannot be left blank.
Error Message A message that explains the nature of the error. This error message is only for user understanding and must not be parsed by network entities.
- Click Save.
Importing Diameter Error Codes
- Click Import.
The File Upload dialog box opens.
- Using the Drag and Drop button, upload the file in JSON format.
- Click Import.
Exporting Diameter Error Codes
To export Diameter error codes, click Export. A
file named bsf.diameter.errorcodes.json is saved to your
device.
4.6 Status and Query
This section describes how to retrieve status of BSF profile registration and query sessions using the Session Viewer page.
4.6.1 Session Viewer
- SUPI
- GPSI
- UE Address
To access this screen from the Home screen of CNC Console, click BSF and then Session Viewer.
- On the Session Viewer page, enter the value of SUPI,
GPSI, or UE Address.
Query Parameters Session Viewer
Table 4-43 Address
Parameter Description IPv4 Address Specifies the IP addresses in IPv4 format IPv6 Prefix Specifies the IPv6 Address Prefix. Note: When you use IPv6 prefix to query a session, ensure that you provide the full notation value.
Example:
2011:db8:3c4d:0:0:0:0:0/48IP Domain Specifies the IPv4 address domain identifier MAC Address Specifies the MAC address, which is formatted as six groups of two hexadecimal digits separated by colons (:) or hyphens (-). For example, in the format hh:hh:hh:hh:hh:hh. Table 4-44 User
Parameter Description SUPI Specifies the Subscription Permanent Identifier. For example - imsi-450081100100001.GPSI Specifies the Generic Public Subscription Identifier. For example - msisdn-9192503899.Table 4-45 Slice Information/DNN
Parameter Description DNN Specifies the Data Network Name (DNN). S-NSSAI_SST Specifies the Slice or Service type for a given S-NSSAI (Single Network Slice Selection Assistance Information). S-NSSAI_SD Specifies the Slice Differentiator (SD) for a given S-NSSAI (Single Network Slice Selection Assistance Information). This optional information is used to difference slice or service type across multiple network slices. - Click Query.
The page displays all the PCF binding records of the UE. For georedundant BSF deployments, the query results include PCF binding data across all sites.
The following screenshot shows the binding IDs when the user searches with GPSI as 9192503855:Figure 4-12 Query Results using Session Viewer
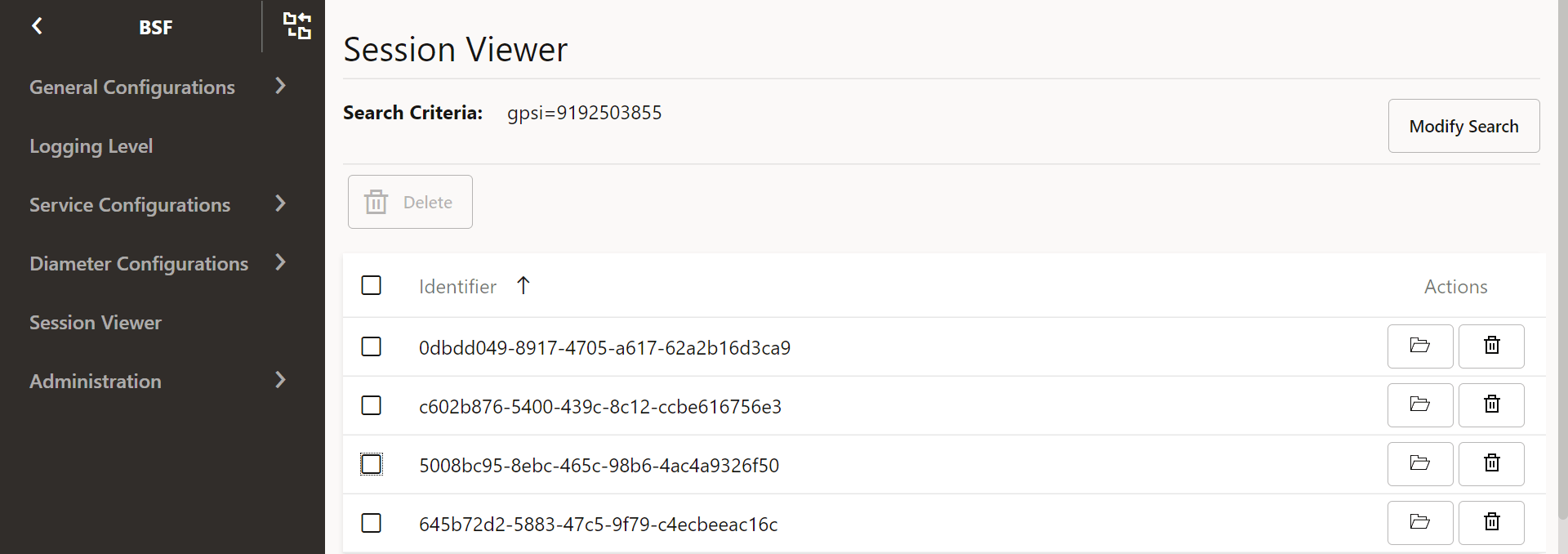
Note:
As SUPI and GPSI are optional parameters, PCF may not add these values when sending a query request. In such cases, BSF returns a No session found message despite binding data being available in the database.Delete Bindings in Session Viewer
Upon receiving the search results for a query, user may want to delete one or multiple PCF binding IDs on the Session Viewer page.
To delete PCF binding IDs individually, click delete under Actions against the required binding ID.
To delete multiple or all the binding records for a subscriber, select binding IDs, then click Delete button, and select YES on the dialog box.
For georedundant BSF deployments, user can delete PCF binding data across all sites by selecting the binding records from the query results.
4.6.2 BSF NF Data
This section provides information on NF status.
4.6.2.1 BSF Registration Profile
This page lists the BSF profile registered with NRF.
- Click Edit button.
- Update the values of the required parameters.
- Click Save.
To dowload the BSF profile, click Download button. A file named
bsfRegistrationProfile.json is saved on your system.
4.6.2.2 BSF NRF Status
This page provides the consolidated status of BSF instances registered with NRF.
On the BSF NRF Status page, you can view the status of BSF and the NRFs deployed in the cluster.
- From the navigation menu under BSF navigate to
Status and Query. Click BSF NRF
Data and select BSF NRF Status.
This opens the BSF NRF Status page.
- The page displays the registered BSF instances and current NRF
health status.
Figure 4-13 BSF Registration Status at NRF
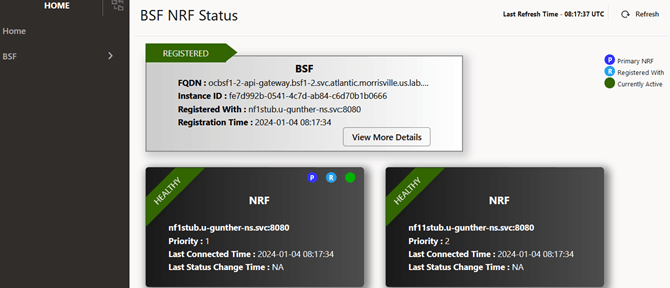
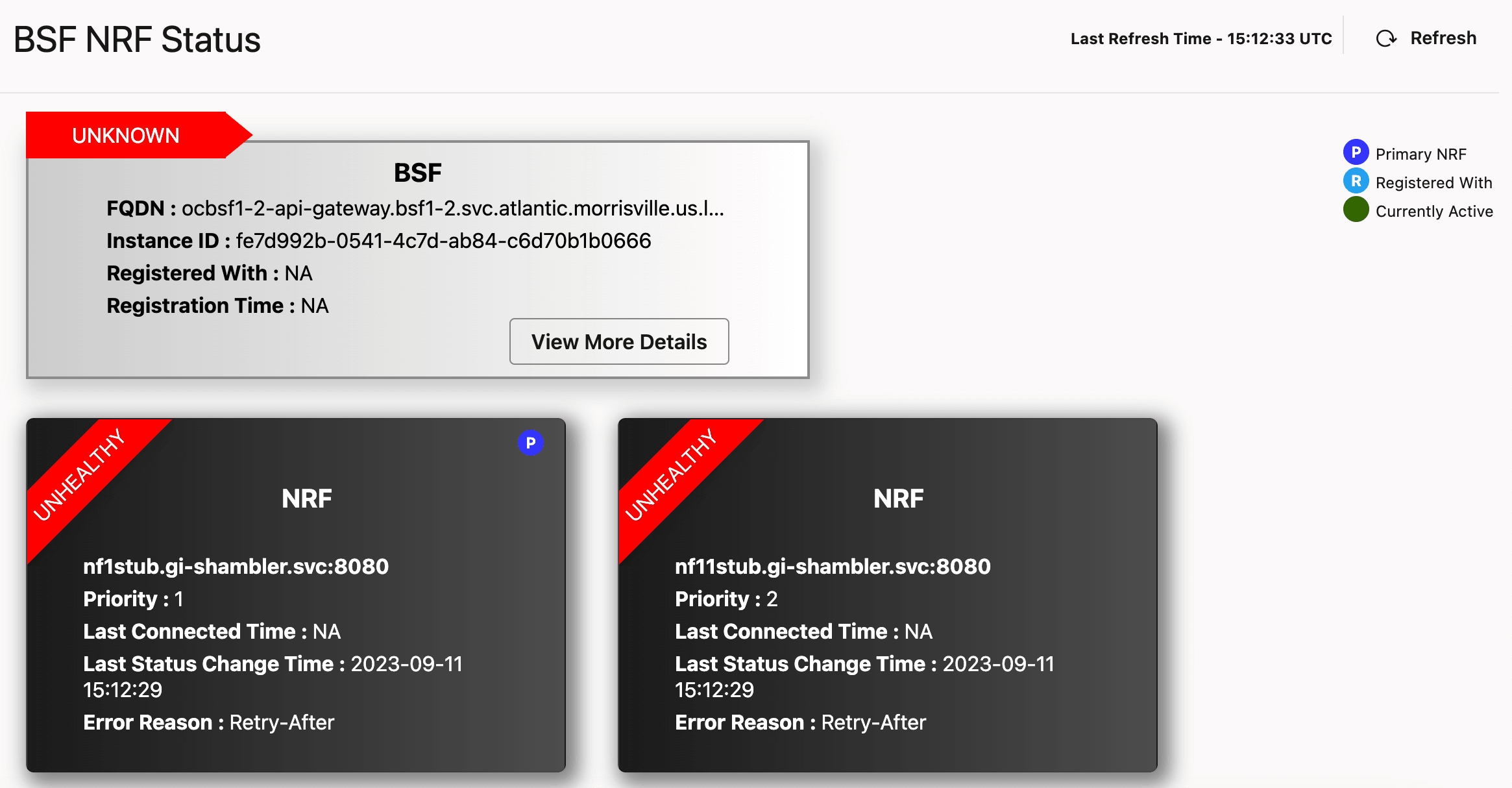
Figure 4-14 BSF NRF Health Status
-
For BSF
You can view the following details for BSF:- BSF status with NRF - It shows whether the BSF instance is REGISTERED, SUSPENDED, or DEREGISTERED with NRF.
- FQDN - It shows the FQDN of the BSF registered with NRF.
- Instance ID - It shows the unique Instance ID of BSF was registered with NRF.
- Registration Time - It shows the time at which BSF was registered with NRF.
If you want to view more details of the BSF instance such as its registration profile, click View More Details. It opens the NF Registration Profile page.
-
For NRF
You can view the following details for NRF:- Health Status - This ribbon-styled badge shows the health status of the NRF instance. It could be in either healthy or unhealthy state.
- Primary NRF - The circular icon with the label P indicates that the NRF is primary.
- Active Status - The pulsating green circular icon shows that the NRF is currently active.
- FQDN - It shows the FQDN of the NRF.
- Priority - It shows the priority of the NRF instances. An NRF instance with priority 1 is treated as primary NRF.
- Last Connected Time - It shows the time when BSF last connected with primary NRF.
- Last Status Change Time - It shows the time when the NRF status changed.
When the status of an NRF instance changes from healthy to unhealthy, the error reason is also displayed on the page.
The number of NRF's displayed on the page are dynamic and get updated according to the NRF's configured in the network.
- Based on when the data refreshes, the Last Refresh Time on the page is also updated.
In case of any network error, the page displays Unable to load NRF data error.
4.6.3 Active Session Query
This section describes the Active Session Query tab under Status and Query in CNC Console.
This page allows you to query active sessions count instantly.
To get the active sessions count, click Query Active Sessions.
Count: 7032
DateTime: 07-07-2022 11:42:284.7 Administration
This section describes how to perform administration tasks, such as bulk import and bulk export of configurable objects into the BSF system.
4.7.1 Import and Export
This section describes how to perform the bulk export or bulk import of the managed objects (MOs) configured on BSF.
- Using CNC Console for BSF:
BSF provides the GUI to perform bulk export and import of BSF data.
To access the export and import functionality from the CNC Console home page, expand BSF, navigate to Administration, and select Import & Export.
The page displays the Export and Import tabs. By default, the Export tab remains selected. The following screen capture illustrates an example of the Import & Export page:
Figure 4-15 Import & Export
 You can perform the following operations using the Import & Export page:
You can perform the following operations using the Import & Export page:Note:
- Importing the Overload Threshold Profile will be rejected if the
CPU validation mentioned under
Configure Threshold Valuessection in Overload Control Threshold fails for any of the three threshold levels. - The service names mentioned in the json file used to import the Overload Threshold Profile must be same as mentioned in the exported json file.
- The default Overload Threshold Profile cannot be exported or imported. The default Overload Threshold Profile must be customized with a different profile name before exporting.
- Importing the Overload Threshold Profile will be rejected if the
CPU validation mentioned under
- Using REST API for BSF:
BSF provides REST APIs to bulk export and import BSF data. For more information about REST API configuration, see Using REST API for BSF Import & Export.
Note:
- message containing Sd as interface
- Sy-SLR as condition message
The data with Sd interface or Sy-SLR condition messages that are exported only with BSF 23.2.0 or later versions can be imported.
4.7.1.1 Exporting BSF Configurations
The export functionality allows you to export BSF configurations with the respective data.
The BSF data export is aligned with the left navigation menu options under BSF on the CNC Console. You can export either all the configurations or the configurations of the selected menu options.
- From BSF, navigate to
Administration, and select Import &
Export.
This opens the Import & Export page, displaying the Export and Import tabs. By default, the Export tab remains selected.
- Click
.

This opens the Objects to be Exported dialog box, displaying the list of BSF configurations in a menu tree structure. The dialog box allows you to select the configurations to be exported. The following screen capture displays an illustration of the Objects to be Exported dialog box:
Figure 4-16 Objects to be Exported dialog box

- In the dialog box, select the configurations according to the export
requirement. Selecting or deselecting a parent folder automatically selects or deselects
all the child nodes respectively.
Note:
To select or deselect all the configurations, click Selection and perform the required operation. - Click Export.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the export operation.This starts the export of all the selected configurations. A row is created in the export status table on the Import & Export page, displaying the export status with the following details:- Export ResourceId: A new export resource ID is generated for each export operation. You can use this ID to get the export status.
- Creation TimeStamp: The timestamp of generation of Export ResourceId.
- Progress (%): Shows the export progress in form of a percentage bar. The page auto refreshes the status until the progress reaches 100 percent.
- Status: The status of the export operation. It can be any of
the following:
- INIT: The validation of policies is in progress, and the export of the configurations has not yet started.
- IN_PROGRESS: The export is running.
- DONE: The export is complete.
- Actions: Provides the buttons to download the following:
- Export configuration files in ZIP file format: The
exported configurations in ZIP file format. The ZIP file contains the
configuration data in JSON file format. You can download the exported data by
clicking
under the Action column.
- Export report in TEXT file format: The export report
provides results for each JSON file present in the exported ZIP file. It also
provides the reason for failure in case the export of any of the
configurations fails.
You can download the export report by clicking
 under the Action column.
under the Action column.
Note:
The buttons remain enabled only for the export operation with DONE status.
- Export configuration files in ZIP file format: The
exported configurations in ZIP file format. The ZIP file contains the
configuration data in JSON file format. You can download the exported data by
clicking
- Result: Provides the result of an export operation. This
result is available only for the export operations with DONE status.
Following are the possible values:
- SUCCESS: The export is successful
- FAILED: The export fails
- PARTIAL_SUCCESS: The export is partially successful
4.7.1.2 Importing BSF Configurations
To import BSF data in JSON or ZIP file format:
4.7.1.3 Using REST API for BSF Import & Export
This section describes how to perform the bulk export or import of BSF configurations and BSF Data using REST APIs. BSF provides cURL commands for export and import.
cURL Commands for Bulk Import
curl -X POST "http://<ipAddress>:<port>/oc-bsfconfiguration/v1/administration/import"-H "accept: */*" -H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" -F "importFile=@<exported zip file name>;type=application/x-zip-compressed"
where,
<exported zip file name> specifies the name of the zip file to be imported.
<ipAddress>:<port> is the host and port where CNC BSF is running.
curl -X GET "http://<ipAddress>:<port>/oc-bsfconfiguration/v1/administration/import/{importResourceId}/report" -H "accept: application/octet-stream" where, <importResourceId> is the resource id generated in response to the POST request for import. The ResourceId is the background task id for the POST operations. This id can be used to track the import requests, and download the data.
curl -X GET "http://<ipAddress>:<port>/oc-bsfconfiguration/v1/administration/import/{importResourceId}/status/<importResourceId>/status" -H "accept: application/json"For more information about Bulk Import REST APIs, see "Bulk Import Export Controller" in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core BSF REST Specification Guide.
cURL Commands for Bulk Export
curl -X POST "http://<ipAddress>:<port>/oc-bsf-configuration/v1/administration/export" -H "accept: */*" -d""
where, <ipAddress>:<port> is the host and port where CNC BSF is running.
curl -X POST "http://<ipAddress>:<port>/oc-bsf-configuration/v1/administration/export/?managedObjects=PCF%20Session%20Management" -H "accept: */*" -d""
curl -X GET "http://<ipAddress>:<port>/oc-bsf-configuration/v1/administration/export/<exportResourceId>/download" -H "accept: application/octet-stream"
where, <exportResourceId> is the resource id generated in response to the POST request for export. The ResourceId is the background task id for the POST operations. This id can be used to track the export requests, and download the data.
curl -X GET "http://<ipAddress>:<port>/oc-bsf-configuration/v1/administration/export/<exportResourceId>/report" -H "accept: application/octet-stream"
curl -X GET "http://<ipAddress>:<port>/oc-bsf-configuration/v1/administration/export/<exportResourceId>/status" -H "accept: application/json"
For more information about Bulk Export REST APIs, see "Bulk Import Export Controller" in Cloud Native Binding Support Function REST Specification Guide.
4.8 Controlled Shutdown Configurations
This section describes how to perform Controlled Shutdown configurations for Diameter and Ingress interface.
4.8.1 Operational State
- From the navigation menu, under BSF, click
Controlled Shutdown, and then select
Operational State.
This opens the page displaying the two groups, Switch Operational State and Operational State History:
Figure 4-20 Operational State

- Switch Operational State
It displays the following operational states:
- NORMAL: NF instance is discoverable and services all requests.
- PARTIAL SHUTDOWN: NF instance is non discoverable and no new session creation requests accepted.
- COMPLETE SHUTDOWN: NF instance is non discoverable and no new session creation requests accepted.
Note:
By default, NORMAL state is assigned to a site. The current state of any site can be identified with a tick mark.You can switch to a different operational state by clicking the NORMAL, PARTIAL SHUTDOWN, or COMPLETE SHUTDOWN button.
- Operational State History:
It displays the history of the operational states along with the
timestamp.
Note:
It displays maximim of ten records at a time. On scrolling further, another set of ten records is displayed. The maximum number of record maintained is hundred.
- Switch Operational State
It displays the following operational states:
4.8.2 Diameter Error Mapping
- From the navigation menu under
BSF, click Controlled
Shutdown and then select Diameter Error
Mapping.
This opens the Diameter Error Mapping page. The page lists the existing configurations. You can add or import new diameter error mapping configurations using this page.
Note:
Click to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
to download the available listings in the JSON file format
on your system.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Diameter Error Mapping page.
- On the Create Diameter Error Mapping
page, enter the following information:
Table 4-46 Create Diameter Error Mapping
Field Name Description Message Type Type of the request Answer with Result Code Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of congestion control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down menu: - DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- CUSTOM_RESULT_CODE
Note: When the CUSTOM_RESULT_CODE value is selected, the following two fields are populated on the page:- Result Code: Enter a custom result code.
- Use Experimental Result
Code: This is disabled by default. You can
enable it by clicking the icon against it. When it
is enabled, Vendor ID field is poplulated on the
page:
- Vendor ID: Enter a valid value to specify vendor ID.
- Click Save.
The configuration gets listed on the Diameter Error Mapping page. The page defines the Diameter Error Mapping configuration in the BSF database and it is available to be used in a BSF.
Note:
Use or
or  available under the Actions column
to update or delete the configuration.
available under the Actions column
to update or delete the configuration.
Importing Diameter Error Mapping
To import Diameter Error Mapping configuration:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
4.8.3 SBI Ingress Error Mapping
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Controlled
Shutdown, and then select SBI Ingress Error
Mapping.
This opens the SBI Ingress Error Mapping page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit SBI Ingress Error Mapping page.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Add SBI Ingress Error Mapping page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 4-47 Ingress Error Mapping Configurations
Field Name Description Id Specifies the list of IDs available for BSF. Error Code Profile Select an error code profile from the dropdown list. It displays the list of error profiles configured using the SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection. - Click Save to save the Ingress error
mapping.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
The value gets listed on the SBI Ingress Error Mapping page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
4.9 Overload and Congestion Control Configurations
This section describes how to perform overload and congestion control configurations.
To use the Error Code Profiles page to create and manage error code profiles in Overload Control Configurations for Diameter Gateway and SBI interface, see SBI Ingress Error Code Profiles Collection section.
Note:
When overload control feature is enabled, it should be enabled for both Diameter gateway and SBI interface. The overload control manager needs data from both Ingress Gateway and Diameter Gateway to determine the overall load on BSF management. It is not possible to enable overload control for Diameter Gateway and disable the same in Ingress Gateway.
4.9.1 Load Shedding Profiles
This procedure provides information about how to create and manage load shedding profiles in Diameter Configurations.
The Load Shedding Profiles page allows you to create new and manage existing load shedding profiles. The page displays the list of defined profiles and provides the options to import and export data as well.
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Diameter
Configurations, and select Load Shedding
Profiles.
This opens the Load Shedding Profiles page.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Load Shedding Profiles page.
- Enter values for the available input fields described in the
following table:
Table 4-48 Load Shedding Profiles Configurations
Field Name Description Name Unique name of the load shedding profile. Scheme Allows to configure the discard policy based on - Priority: to discard messages based on priority range
- Priority and Percentage: to discard messages based on priority range and percentage for each range
Type Defines the type of load shedding profile. You can select any of the following values from the drop-down list: - Congestion Control
- Overload Control
To add load shedding rules for the profile type congestion control, perform the following steps:
- Under Load Shedding Rules, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Load Shedding Rules dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described
in the following table:
Table 4-49 Load Shedding Rules Configurations When the Selected Scheme is "Priority"
Field Name Description State This field appears when the Type of load shedding profile is
Specifies the type of state for which the rule is being defined. Select any of the following values using the drop-down:Congestion Control.- Danger of Congestion
- Congested
Discard Priority This field appears when the Scheme of load shedding profiles is
Priority.Specifies the discard priority for the load shedding rule. The discard priority value can be a number from 0 to 15. Any request message with equal or greater priority is rejected.
Answer with Result Code Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of congestion control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down menu: - DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE
Note: When the EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE value is selected, the following two fields are populated on the page:- Result Code: Enter a custom result code.
- Vendor ID: Enter a valid value to specify vendor ID.
Table 4-50 Load Shedding Rules Configurations When the Selected Scheme is "Priority and Percentage"
Field Name Description State This field appears when the Type of load shedding profile is
Specifies the type of state for which the rule is being defined. Select any of the following values using the drop-down:Congestion Control.- Danger of Congestion
- Congested
Discard Priority Percentage Allows to configure the Discard Priority Percentage as explained in the following step.
- To configure discard
Priority Percentage, perform the following steps:
- Under Discard Priority
Percentage, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Discard Priority Percentage dialog box.
Enter values for the available input fields, described in the following table:
Table 4-51 Adding Discard Priority Percentage
Field Name Description Priority Range Specifies the discard priority range for the load shedding rule. The discard priority value can be a number from 0 to 15. Any request message with equal or greater priority will be rejected based on the percentage discard configured. Discard Percentage Specifies the discard percentage for the specified priority range. Answer with Result Code Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of congestion control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down menu: - DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE
Note: When the EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE value is selected, the following two fields are populated on the page:- Result Code: Enter a custom result code.
- Vendor ID: Enter a valid value to specify vendor ID.
- Click Save to save the discard priority percentage.
- Under Discard Priority
Percentage, click
- Click Save to save the load shedding rule.
OR
To add load shedding rules for the profile type overload control, perform the following steps:
- Under Load Shedding Rules, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Load Shedding Rules dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described
in the following table:
Table 4-52 Load Shedding Rules Configurations When the Selected Scheme is "Priority"
Field Name Description Level Specifies the name of the level. The name specified in this parameter must match the level name in Ingress Gateway's ocdiscardpolicies. Select any of the following values using the drop-down list: - L1
- L2
- L3
Note: If the load levels are not configured, then level transitions will not happen and it will stay at the same level.
Also, any existing L4 level data will be removed, as L4 is not supported.
Discard Priority Specifies the discard priority for the load shedding rule. The discard priority value can be a number from 0 to 15. Any request message with equal or greater priority is rejected. Answer with Result Code Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of overload control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down menu: - DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE
Note: When the EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE value is selected, the following two fields are populated on the page:- Result Code: Enter a custom result code.
- Vendor ID: Enter a valid value to specify vendor ID.
Table 4-53 Load Shedding Rules Configurations When the Selected Scheme is "Priority and Percentage"
Field Name Description Level Specifies the name of the level. The name specified in this parameter must match the level name in Ingress Gateway's ocdiscardpolicies. Select any of the following values using the drop-down list: - L1
- L2
- L3
Note: If the load levels are not configured, then level transitions will not happen and it will stay at the same level.
Also, any existing L4 level data will be removed, as L4 is not supported.
Discard Priority Percentage Configure the discard priority percentage as explained in the following step.
- To configure Discard
Priority Percentage, perform the following steps:
- Under Discard Priority
Percentage, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Discard Priority Percentage dialog box.
Enter values for the available input fields, described in the following table:
Table 4-54 Adding Discard Priority Percentage
Field Name Description Priority Range Specifies the discard priority range for the load shedding rule. The discard priority value can be a number from 0 to 15. Any request message with equal or greater priority will be rejected based on the percentage discard configured. Discard Percentage Specifies the discard percentage for the specified priority range. Answer with Result Code Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of congestion control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down menu: - DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY
- DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER
- EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE
Note: When the EXPERIMENTAL_RESULT_CODE value is selected, the following two fields are populated on the page:- Result Code: Enter a custom result code.
- Vendor ID: Enter a valid value to specify vendor ID.
- Click Save to save the discard priority percentage.
- Under Discard Priority
Percentage, click
- Click Save to save the load shedding rule.
Note:
You can not edit or delete the load shedding rule for an existing load shedding profile. As a workaround, you must create a new load shedding profile with the updated load shedding rule and delete the old load shedding profile. - Click Save to save the load shedding
profile.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
The value gets listed on the Load Shedding Profiles page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
Importing Load Shedding Profiles
To import load shedding profiles, perform the following steps:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
Exporting Load Shedding Profiles
To export load shedding profiles, click Export. A
json file is saved to your device.
4.9.2 Message Priority Profiles
This procedure provides information about creating and managing message priority profiles in Diameter Configurations.
The Message Priority Profiles page allows you to create new and manage existing message priority profiles. The page displays the list of defined profiles and provides the options to import and export data.
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Overload Control
Configurations, select Diameter, and
then select Message Priority Profiles.
This opens the Message Priority Profiles page.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Create Message Priority Profiles page.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described in the
following table:
Table 4-55 Message Priority Profiles Configurations
Field Name Description Name Unique name of the message priority profile. To add message priority rules for the profile, perform the following steps:
- Under Message Priority Rules, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Message Priority Rules dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields, described
in the following table:
Table 4-56 Message Priority Rules Configurations
Field Name Description Name Specifies the unique name of the message priority rule. Message Priority Specifies the priority assigned to the message. It can be a number from 0 to 15. Rule Priority Specifies the priority assigned to the message priority rule. Use DRMP Priority When this switch is enabled, the priority for the message rule is assigned from DRMP AVP. Table 4-57 Message Priority Rules Configurations - Conditions
Field Name Description Application Specifies the type of application. Users can select the following value from the drop-down: - Rx
Message Specifies the type of message for the selected application. The supported message values for each application type are as follow: - For Rx application, choose a value from AAR, STR, RAR, and ASR.
- To add pre-defined AVP conditions, click
 under Add Pre Defined AVP Conditions.
On the Add Pre Defined AVP Conditions dialog
box, select Name and enter values as described in the following
table:
under Add Pre Defined AVP Conditions.
On the Add Pre Defined AVP Conditions dialog
box, select Name and enter values as described in the following
table:
Table 4-58 Pre Defined AVP Conditions Configurations
Name Values Called-Station-Id This AVP can be used only when the application type is specified a Rx. Users can enter multiple comma-separated values. Note: BSF supports wildcard format for this AVP.
Rx-Request-Type This AVP can be used for Rx application with message specified as AAR. You can select any of the following valid values from the drop-down list: - INITIAL_REQUEST
- UPDATE_REQUEST
- PCSCF_RESTORATION_REQUEST
Service-URN This AVP indicates that an AF session is used for emergency traffic. It is of type OctetString. Examples: "sos", "sos.fire", "sos.police" and "sos.ambulance".
Note: BSF supports wildcard format for this AVP.
MPS-Identifier This AVP indicates that an AF session relates to an MPS session and contains the national variant for MPS service name. It is of type OctetString. Example: NGN GETS
MCPTT-Identifier This AVP includes either one of the namespace values used for MCPTT and may include the name of the MCPTT service provider. It is of type OctetString. MCVideo-Identifier This AVP includes the name of the MCVideo service provider. It is of type OctetString. Reservation-Priority This AVP is of type Enumerated and is specified in an AA-Request as the main AVP to associate a priority with a resource reservation or modification request. You can specify a value from 0 to 7 for this AVP. Click Save to save the pre-defined AVP conditions for the message priority rule.
- Click Save to save the message priority rule.
- Under Message Priority Rules, click
- Click Save to save the message priority
profile.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
The value gets listed on the Message Priority Profiles page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the profile.
Importing Load Shedding Profiles
To import message priority profiles, perform the following steps:
- Click
 .
.
The page opens the File Upload dialog box.
- Upload the file in JSON format by using the Drag and Drop button.
- Click Import.
Exporting Message Priority Profiles
To export load shedding profiles, click Export. A
json file is saved to your device.
4.9.3 Rate Limiting Policy
This procedure provides information about how to use the Rate Limiting Policy page to manage rate limiting policies for overload control on SBI interface.
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Overload Control
Configurations, select SBI, then
select Rate Limiting, and then select Rate
Limiting Policy.
This opens the Rate Limiting Policy page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Rate Limiting Policy page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the following
table:
Table 4-59 Rate Limiting Policy Configurations
Field Name Description Enable Rate Limiting Specifies whether to enable or disable rate limiting. Sampling Period (in milliseconds) Specifies the time frame for each cycle of rate limiting per service. Its default value is 200 ms. -
Under Rate Limit Policy, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Rate Limit Policy dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 4-60 Rate Limit Policy Configurations
Field Name Description Name Specifies the name of the rate limit policy that is further used to determine a mapping between route and discard policy name per route. Discard Priority Specifies the discard priority for the rate limiting policy. Any request with message priority higher in value than the discard priority is rejected. Action Specifies the action taken when when requests are discarded. Currently, the only supported value is RejectWithErrorCode. Scheme Specifies the scheme for applying rate limiting. Currently, the only supported value is PriorityBased. Error Code Profile Specifies the list of error code profiles configured on the Error Code Profiles page. - Click Save to save the rate limit
policy. The value gets listed under the Rate Limit
Policy group.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
- Click Save to save the rate limiting
policy.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
4.9.4 Route Level Mapping
This procedure provides information about how to use the Route Level Mapping page to manage route level mapping for overload control on SBI interface.
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Overload Control
Configurations, select SBI, then
select Rate Limiting, and then select
Route Level Mapping.
This opens the Route Level Mapping page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Route Level Mapping page.
-
Under Route Configuration, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Route Configuration dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the following
table:
Table 4-61 Rate Limiting Policy Configurations
Field Name Description Id Specifies the list of route IDs available for BSF. Choose any value from the drop-down list:
- BSF Management Register
- BSF Management Deregister
- BSF Management Discovery
-
Under Rate Limiting, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Method dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 4-62 Method Configurations
Field Name Description Http Method Specifies the HTTP method. Depending on the value select for Id, you can select any of the following values from the drop-down list: - POST
- PUT
- GET
- DELETE
- PATCH
Message Rate (per sampling period) Specifies the message rate per sampling period for a given method. Rate Limit Policy Select a rate limit policy from the drop-down list. It displays the list of rate limit policies configured using the Rate Limiting Policy page. - Click Save to save the method. The value
gets listed under the Rate Limiting group.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
- Click Save to save the route
configuration.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
- Click Save to save the route level
mapping.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
4.9.5 Discard Policy Mapping
This procedure provides information about how to use the Discard Policy Mapping page to manage discard policy mapping in Overload Control Configurations for SBI interface.
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Overload Control
Configurations, select SBI, then
select Overload Control, and then select
Discard Policy Mapping.
This opens the Discard Policy Mapping page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Discard Policy Mapping page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the following
table:
Table 4-63 Discard Policy Mapping Configurations
Field Name Description Enable Overload Control Specifies whether to enable or disable overload control. Sampling Period (in milliseconds) Specifies the time frame for each cycle of overload control per service. Its default value is 200 ms. -
Under Mappings, click
 .
.
This opens the Add Mappings dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 4-64 Mappings Configurations
Field Name Description Service Name Specifies the name of the microservice that is further used to determine a mapping between service and discard policy name per service. BSF Management is the only supported value for this field.
Policy Name Specifies the name of the discard policy that is used to determine a mapping between service and discard policy name per service. The drop-down list shows the policies configured using the Discard Policy page. - Click Save to save the mappings.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
The value gets listed under the Mappings group on the Discard Policy Mapping page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete the mappings.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete the mappings.
- Click Save to save the discard policy
mapping.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
4.9.6 Discard Policy
This procedure provides information about how to use the Discard Policy page to manage discard policies for overload control for SBI interface.
- From the navigation menu, under
BSF, click Overload Control
Configurations, select SBI, then
select Overload Control, and then select
Discard Policy.
This opens the Overload Control Discard Policy page.
- Click Edit.
This opens the Edit Overload Control Discard Policy page.
-
Click
 .
.
This opens the Add Discard Policies page.
- Enter values for the available input fields as described in the
following table:
Table 4-65 Discard Policy Configurations
Field Name Description Name Specifies the unique name of the discard policy. Scheme Specifies the criteria of dropping requests for a microservice. It could be either priority based or percentage based. If you select the value as Priority Based, configure the values of the parameters under Priority Based Policies. For Percentage Based scheme, configure the parameters under Percentage Based Policies. To add priority based policies, perform the following steps:
- Under Priority Based Policies,
click
 .
.
This opens the Add Priority Based Policies dialog box.
- Enter values for the available input fields as
described in the following table:
Table 4-66 Priority Based Policies Configurations
Field Name Description Level Specifies the name of the level. The name specified in this parameter must match the level name in Ingress Gateway's ocdiscardpolicies. Select any of the following values using the drop-down list: - L1 (Load Level 1)
- L2 (Load Level 2)
- L3 (Load Level 3)
Discard Priority Specify the discard priority for the discard policy rule. Any request message with equal or lower message priority is rejected. Note: 1 is considered as the highest message priority.
Error Code Profile Select an error code profile from the drop-down list. It displays the list of error profiles configured using the Error Code Profile page. Action Specifies the action taken when selected requests are rejected. Currently, it only supports the action to reject requests based on error code. OR
Table 4-67 Percentage Based Policies Configurations
Field Name Description Level Specifies the name of the level. The name specified in this parameter must match the level name in Ingress Gateway's ocdiscardpolicies. Select any of the following values using the drop-down list: - L1 (Load Level 1)
- L2 (Load Level 2)
- L3 (Load Level 3)
Discard Percentage Specify the discard percentage for the policy rule. The specified percentage of the calculated rate for service in previous sampling period is discarded in current sampling period. Error Code Profile Select an error code profile from the drop-down list. It displays the list of error profiles configured using the Error Code Profile page. Action Specifies the action taken when selected requests are rejected. Currently, it only supports the action to reject requests based on error code. - Click Save to save the discard
policy.
To discard the changes, click Cancel.
- Under Priority Based Policies,
click
- Click Save to save the overload control
discard policy.
To discard the changes, click Cancel
The value gets listed on the Overload Control Discard Policy page. Use
 or
or  available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
available under the Actions column to
update or delete any given policy.
4.9.7 Overload Control Threshold
-
From the navigation menu under BSF, navigate to Overload Control Configurations, and select Overload Control Threshold.
Overload Control Threshold page is displayed. The page shows the existing configurations.
-
BSF allows you to configure the threshold values using a profile. You can either use a default or custom profile or create a new profile. You must activate one of the profiles to use the values. At a time, you can activate only one profile.
Note:
If there are no profiles activated, Policy calculates the load level based onoverloadLevelThresholdconfigured incustom-values.yamlfile.If you are upgrading from an older version of BSF to 23.1.0 or later, the following message appears at the top of the page:
System looks to be using old configuration (Not profile based). Request you to please migrate the data or activate one of the profile- Click Migrate.
Migrate Data window opens.
- Enter the name of the profile.
- Either click Migrate to migrate
the data from the previous version of BSF or click
Migrate and Activate to migrate the data
and activate the profile.
Note:
Migrate button will only migrate the existing threshold data to profile. It does not activate the profile. Until one of the profile is not active , the UI will continue to show the above message to migrate the data.
In case of fault recovery, the active profile details are recovered and used from the database. No need to migrate again.
- Click Migrate.
Table 4-68 Create and Manage Threshold Profiles
| Button/icon | Action |
|---|---|
| Opens the Create Profile window
and allows you to create a new profile.
By default, the values of the
default profile are associated with the new profile. Click |
|
| Deletes the selected threshold profile.
Note: You cannot delete the default system provided profile. |
|
| Opens the Copy Profile window to
copy an existing profile.
While using the copy profile option, whichever profile is selected in the Threshold Profile dropdown, the values are copied from that profile. |
|
| Threshold Profile | Lists all the threshold profiles. You can select any of
the profiles from the list to activate.
If the selected
profile is already active, you can see
|
| Activate | Activates the profile selected from Threshold
Profile list.
At a time, you can have only one active profile. |
| Go To Active |
Go To Active button selects the current active profile from the Threshold Profile drop down list. Note: If none of the profiles are active, the Go To Active button does not appear. |
Table 4-69 Configure Threshold Values
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Name | You can configure the threshold values for BSF Management Services: |
| CPU |
Click The onset and abatement values for CPU are calucalted in percentage (%) and the range is from 1 to 100. Click Note: Make sure that the onset value of L1 is less than the abatement value of L2 and the onset value of L2 is less than the abatement value of L3. You can click |
| Pending Message Count |
Click Pending message count accepts an integer value between 1 to 1000000. |
| Failure Count |
Click The failure count accepts an integer value between 1 to 1000000. |
| Memory |
Click Memory details are calculated in Percentage (%) and ranges between 1 to 100. |
4.10 NF Scoring Configurations
Table 4-70 NF Scoring
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable NF Scoring | Specifies whether to enable or disable the NF Scoring |
| TPS | Traffic |
| Enable | Enables the TPS. |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the TPS. |
| Max TPS | Specifies the maximum TPS. |
| Service Health | Specifies the service health of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Service Health. |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the Service Health. |
| Signaling Connections | Specifies the Signaling Connections of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Signaling Connections. |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the Signaling Connections. |
| Max Connections | Specifies the maximum connections. |
| Replication Health | Specifies the Replication Health of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Replication Health. |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the Replication Health. |
| Locality/Site Preference | Specifies the Locality or Site Preference. |
| Enable | Enables the Locality or Site Preference. |
| Score | Specifies the score of the Locality or Site Preference. |
| Active Alert | Specifies the Active Alerts of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Active Alert. |
| Critical Alert Weightage | The site with more critical alerts is unhealthy. |
| Major Alert Weightage | The site with more major alerts is unhealthy. |
| Minor Alert Weightage | The site with more minor alerts is unhealthy. |
Calculated Score:
To check the calculated Score of a site:
Figure 4-21 NF Scoring Disabled

Figure 4-22 NF Scoring Enabled
Note:
If app-info pod is down, you will not be getting the NF Score. You will get an error message that "Data can't be fetched due to internal server error".Calculated Score shows the total score along with the Instance ID. The total score is shown in either Green or Orange color. If the NF Score is shown in green color there are no failed factors. And, if the NF Score is shown in Orange color there are one or more failed factors. You can click on Detailed information to view different criteria and their Max Score, Evaluated Score, and More Info. The criteria in the detailed information tab show the evaluated score. The failed factors are shown with a warning symbol under the evaluated score.
On the top-right of the screen, the Last Refresh Time information is available. Moreover, a Refresh button is given to refresh the NF Score of a site.
4.11 Viewing cnDBTier functionalities in CNC Console
Note:
The following cnDBTier functionalities are read only and is available only through CNC Console.4.11.1 Backup List
- From the left navigation pane, click the BSF tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the Backup List to view the list of
completed backups along with Backup ID, Backup size, and Creation Timestamp.
The Backup List screen is displayed.
Table 4-71 Backup List
Fields Description Backup Details This field displays information such as backup Id, backup size, and backup creation timestamp. Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which BSF is connected. Backup Id This field displays the ID of the stored backup. Backup Size (bytes) This field displays the size of the stored backup. Creation TimeStamp This field displays the time recorded when the backup was stored.
4.11.2 Database Statistics Report
- From the left navigation pane, click the BSF tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the Database Statistics Report to view
the available database.
Table 4-72 Database Statistics Report
Fields Description Database Count This field displays the number of available database. Database Tables Count This field displays the available database names and their table count. Database Name This field displays the database name. Table Count This field displays the table count for each database. Database Table Rows Count This field displays the table rows present in each table. -
Click the View icon available next to the database name to view the View Database Table Rows Count screen.
Table 4-73 View Database Table Rows Count
Fields Description Database Name This field displays the database name. Tables This field displays the table names and the corresponding rows in each table. Table Name This field displays the table name. Row Count This field displays the table rows present in each table.
-
4.11.3 Georeplication Status
- From the left navigation pane, click the BSF tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the Georeplication Status to view the
local site and remote site name to which BSF is connected.
Table 4-74 GeoReplication Status
Fields Description Local Site Name This field displays the local site name to which BSF is connected. Remote Site Name This field displays the remote site name. Replication Status This field displays the replication status with corresponding sites. Seconds Behind Remote Site This field displays the number of seconds that the last record read by the local site is behind the latest record written by the remote site for all the replication groups. - Click the View icon in the
Actions menu to view the View
Georeplication Status screen.
Table 4-75 Georeplication Status
Fields Description Replication Group Delay This field displays the number of seconds that the last record read by the local site is behind the latest record written by the remote site for individual replication groups. Replication Channel Group Id This field displays the ID of the replication channel group. - Click the View icon to view the
Replication Group Delay attributes.
Table 4-76 View Replication Group Delay
Fields Description Channel Details This field displays the channel details such as Remote Replication IP and Role. Remote Replication IP This field displays the IP of the remote replication channel. Role This field displays the role of the replication channel IP.
- Click the View icon in the
Actions menu to view the View
Georeplication Status screen.
4.11.4 Heartbeat Status
- From the left navigation pane, click the BSF tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the HeartBeat Status to view the
connectivity between local site and remote site to which BSF is connected.
Table 4-77 HeartBeat Status Details
Fields Description Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which BSF is connected. HeartBeat Details This field displays information such as the remote site name, heartbeat status, heartbeat lag, and replication channel group id. Remote Site Name This field displays the remote site name. Heartbeat Status This field displays the connectivity status with corresponding sites. Heartbeat Lag This field displays the lag or latency in seconds it took to syncronize between sites. Replication Channel Group Id This field displays the ID of the replication channel group.
4.11.5 Georeplication Recovery
- From the left navigation pane, click the BSF tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click Georeplication Recovery to access the
Georeplication Recovery Status of the cnDBTier cluster. This includes options
such as Update Cluster As Failed, Start Georeplication Recovery, and
Georeplication Recovery Status.
- Click the Update Cluster As Failed to mark the
cluster as FAILED.
The Update Cluster As Failed page is displayed.
Table 4-78 Update Cluster As Failed
Fields Description Cluster Names This attribute lists the names of cnDBTier clusters. It allows you to select a cluster from the available list to mark as failed. Failed Cluster Names This attribute displays the list of names of cnDBTier clusters that are marked as failed. Update Cluster Click the Update Cluster to mark the cluster as FAILED. Cancel Click the Cancel to cancel the process. - Click the Start Georeplication
Recovery to start the georeplication recovery process
for a failed site.
The Start Georeplication Recovery page is displayed.
Table 4-79 Start Georeplication Recovery
Attribute Description Failed Cluster Name This attribute displays a list of cnDBTier clusters that have been marked as failed. Backup Cluster Name (Optional) This attribute displays the list of active cnDBTier clusters designated for georeplication recovery. Start Georeplication Recovery Click the Start Georeplication Recovery to start the georeplication recovery process for a failed site. Cancel Click the Cancel to cancel the process. - Click the Georeplication Recovery
Status to view the status of georeplication recovery for
cnDBTier clusters.
The Georeplication Recovery Status page is displayed.
Table 4-80 Georeplication Recovery Status
Attribute Description Local Cluster Name This attribute displays the name of the local cluster. Georeplication Recover Status Details This attribute displays the details of the georeplication recovery status for cnDBTier clusters. Cluster Name This attribute displays the names of all the clusters. Georeplication Recovery Status This attribute displays the current status of georeplication recovery for a cluster. Refresh Click Refresh to view the most current data.
The following are the states of Georeplication Recovery:Table 4-81 Georeplication Recovery States
Georeplication Recovery State Description ACTIVE The cluster is in a healthy state, and replication is up and running with its respective mate cluster. REINSTALLED The cluster enters this state during fatal error recovery when the end user reinstalls the cluster. STARTDRRESTORE When Georeplication recovery is started, the cluster will transition into this state. INITIATEBACKUP Once Georeplication recovery is started, the cluster will identify a healthy cluster for backup initiation and transition into this state. CHECKBACKUP Once the backup is initiated, the georeplication recovery cluster will monitor the progress of the backup until its completion. If the backup fails, the cluster will restart the backup. COPY_BACKUP Upon completion of the backup, the georeplication recovery cluster will request the transfer of the backup from the healthy cluster to the georeplication recovery cluster. CHECK_BACKUP_COPY Once backup copy is started georeplication recovery cluster will monitor for the backup transfer progress till it's completion and if it's fails the cluster will re-initiates the backup transfer. BACKUPCOPIED Once the backup copy is started, the georeplication recovery cluster will monitor the progress of the backup transfer until its completion. If the transfer fails, the cluster will restart the backup transfer. BACKUPEXTRACTED This state indicates that the backup has been successfully extracted at the georeplication recovery cluster, allowing the restoration of the backup to start. FAILED This state is used by end user to mark specific cluster as failed and hence georeplication recovery is essential to recover the cluster.This state can also indicates that georeplication recovery started and the database is restored using the healthy cluster backup. UNKNOWN This state is used by the end user to mark a specific cluster as failed, necessitating georeplication recovery for cluster recovery. Additionally, this state can indicate that georeplication recovery has started and the database has been restored using the backup from the healthy cluster. RECONNECTSQLNODES This state is used to instruct SQL nodes to be offline during backup restoration to prevent any records from entering the binlog of the georeplication recovery cluster. BACKUPRESTORE This state indicates that the backup, successfully copied from the healthy cluster, is currently being used to restore the georeplication recovery cluster. RESTORED Once the backup is successfully restored in the georeplication recovery cluster, the cluster will enter this state to start the reestablishment of replication channels. BINLOGINITIALIZED This state indicates the start of binlogs for the restoration of replication channels, necessary to start the restore process RECONFIGURE Once the binlog is restarted, the georeplication recovery cluster will reestablish the replication channels with respect to all its mate clusters. - Click the Update Cluster As Failed to mark the
cluster as FAILED.
4.11.6 Local Cluster Status
- From the left navigation pane, click the BSF tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the Local Cluster Status to view the
local cluster status for the current site:
Table 4-82 Local Cluster Status
Fields Description Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which BSF is connected. Cluster Status This field displays the local cluster status for the current site.
4.11.7 On Demand Backup
- From the left navigation pane, click the BSF tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the On Demand Backup to create a new
backup and view the status of initiated on-demand backups.
Note:
On Demand Backup can be initiated on both single site and multi-site cnDBTier cluster and can be used to restore the first standalone site. DB Backup will not be initiated if sites are not properly configured.Table 4-83 On Demand Backup Details
Fields Description Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which BSF is connected. DR Status This field displays the status of DR. Backup Id This field displays the ID of the stored backup. Backup Status This field displays the status of backup. Remote Transfer Status The field displays the status of remote transfer. Initiate Backup The field displays whether the backup is initiated or not. - Click the Edit icon.
The Edit On Demand Backup screen appears.
Note:
The Edit mode is available only for Initiate Backup. - To enable the Initiate Backup option, click
Save.
A confirmation message "Save successfully" appears.
- Click Cancel to navigate back to the On Demand Backup screen.
- Click Refresh to reload the On Demand Backup screen.
- Click the Edit icon.
4.11.8 Version
- From the left navigation pane, click the BSF tab, and then click the DB Tier tab.
- Click the cnDBTier Version to view the
version.
Table 4-84 cnDBTier Version Attributes
Fields Description cnDBTier Version This field displays the cnDBTier version. NDB Version This field displays the network database (NDB) version.


