3 Benchmarking SCP Model C
This section describes Model C test topologies and test scenarios for benchmarking SCP.
3.1 Test Topology 1 for SCP Model C Benchmarking
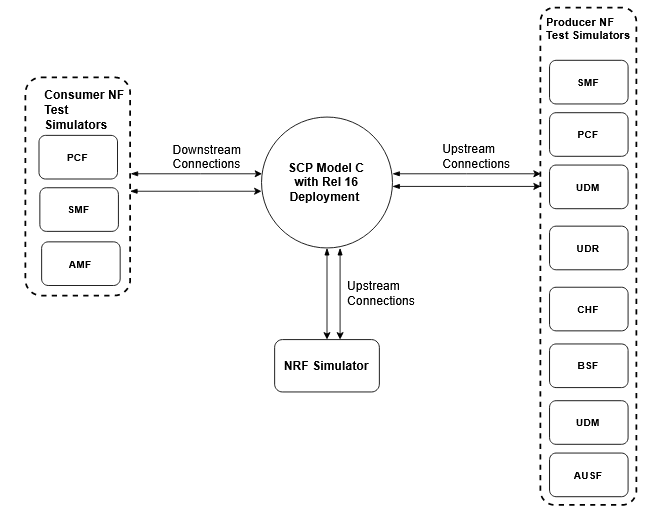
The following image represents the test topology consisting of the following components:
- SCP
- Consumer NF test simulator
- Producer NF test simulator
- NRF simulator
Figure 3-1 SCP Model C Topology 1
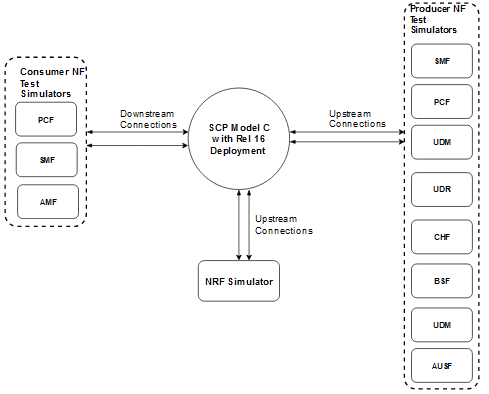
The aforementioned image represents the Model C test topology. In Release 16 Model C indirect 5G SBI communication mode, the consumer NF sends NF discovery service requests to NRF. After receiving the discovery response with NF profiles, the consumer NF performs the following tasks:
- Selects an NF Set or a specific NF instance from the NF Set
- Sends a service request to SCP with the address of the selected service producer NF in 3gpp-Sbi-Target-apiRoot header
- Creates multiple network interfaces for different subnet IPs
Then, SCP selects an NF service instance and routes the service requests to the selected producer NF. In case of failure, if reselection is required, SCP selects the producer NF instance based on the NF Set.
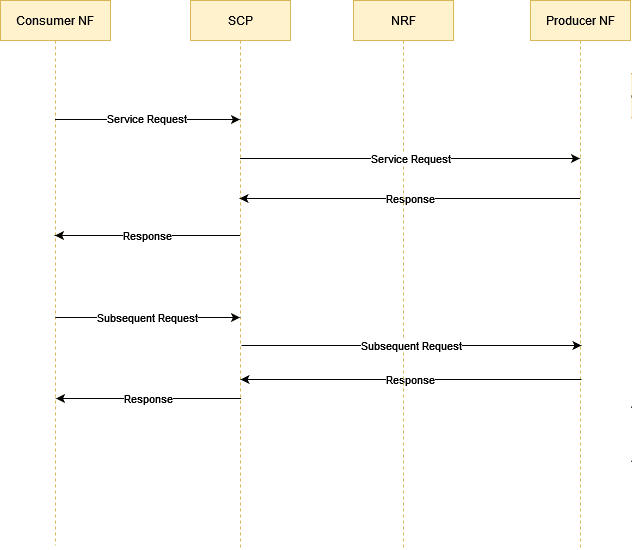
3.1.1 Topology 1 Call Flow
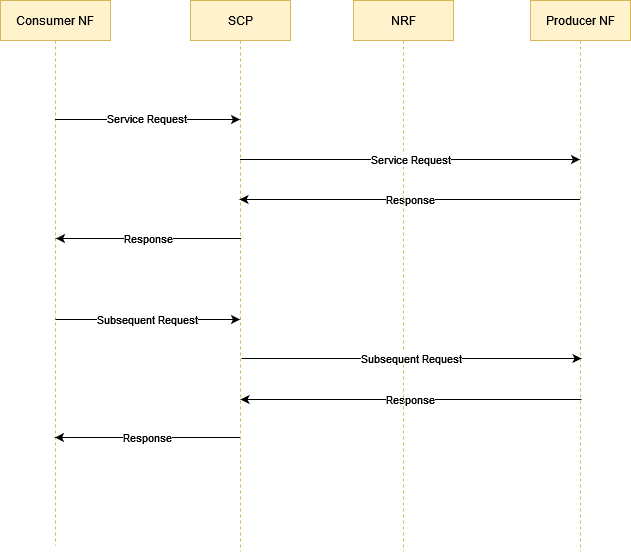
The following call flow represents how a service request is processed by SCP:
- Consumer NF sends the service request to SCP.
- SCP sends the request to the producer NF based on the NF profiles registered through NRF.
- Producer NF sends the response to SCP for the service request.
- SCP routes the response received from the producer NF to the consumer NF.
Figure 3-2 Topology 1 Call Flow
Network Topology
The following image represents communication between SCP and NRF to process service requests in different sites:
Figure 3-3 Network Topology

3.1.2 Topology 1 Traffic Distribution
The following table describes the percentage of messages processed by SCP using N11, N7, N10, N36, N28, and other interfaces:
Table 3-1 Topology 1 Traffic Distribution
| NF-C | NF-P | Interface Reference | Percentage (%) of Messages |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMF | PCF | N7 | 60 |
| SMF | UDM | N10 | 5 |
| PCF | UDR | N36 | 1 |
| PCF | CHF | N28 | 1 |
| SMF | CHF | N40 | 10 |
| NRF | SLF | - | 3 |
| PCF | BSF | Nbsf | 2 |
| AMF | UDM | N8 | 7.5 |
| AMF | AUSF | N12 | 7.5 |
| AMF | PCF | N15 | 3 |
| NRF | SCP | Notifications | 10 notifications every 15 minutes |
Note:
40% InterSCP traffic is routed towards twenty two regions.Topology 1 NF Configuration Across All Regions
The following table describes the NF configurations across multiple regions:
Table 3-2 NF Configuration Across All Regions
| Region | Total NFs | SCP | NRF | PCF | CHF | AMF | UDR | UDM | SLF | SMF | AUSF | BSF | Locality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site1 | 118 | SCP1 to SCP2 | NRF1 to NRF2 |
PCF1 to PCF8 PCF51 to PCF86 |
CHF1 to CHF2 |
AMF1 to AMF2 AMF45 to AMF52 |
UDR1 to UDR2 UDR45 to UDR52 |
UDM1 to UDM2 UDM45 to UDM52 |
SLF1 to SLF2 SLF45 to SLF52 |
SMF1 to SMF2 SMF45 to SMF52 |
AUSF1 to AUSF2 AUSF45 to SMF52 |
BSF1 to BSF2 BSF45 to BSF52 |
USEast |
| Site2 | 20 | SCP3 to SCP4 | NRF3 to NRF4 | PCF9 to PCF10 | CHF3 to CHF4 |
AMF3 to AMF4 AMF45 to AMF52 |
UDR3 to UDR4 | UDM3 to UDM4 | SLF3 to SLF4 | SMF3 to SMF4 | AUSF3 to AUSF4 | BSF3 to BSF4 | Loc1r3 |
| Site3 | 20 | SCP5 to SCP6 | NRF5 to NRF6 | PCF11 to PCF12 | CHF5 to CHF6 | AMF5 to AMF6 | UDR5 to UDR6 | UDM5 to UDM6 | SLF5 to SLF6 | SMF5 to SMF6 | AUSF5 to AUSF6 | BSF5 to BSF6 | Loc1r5 |
| Site4 | 18 | SCP7 to SCP8 | NRF7 to NRF8 | PCF13 to PCF14 | - | AMF7 to AMF8 | UDR7 to UDR8 | UDM7 to UDM8 | SLF7 to SLF8 | SMF7 to SMF8 | AUSF7 to AUSF8 | BSF7 to BSF8 | Loc1r7 |
| Site5 | 18 | SCP9 to SCP10 | NRF9 to NRF10 | PCF15 to PCF16 | - | AMF9 to AMF10 | UDR9 to UDR10 | UDM9 to UDM10 | SLF9 to SLF10 | SMF9 to SMF10 | AUSF9 to AUSF10 | BSF9 to BSF10 | Loc1r9 |
| Site6 | 18 | SCP11 to SCP12 | NRF11 to NRF12 | PCF17 to PCF18 | - | AMF11 to AMF12 | UDR11 to UDR12 | UDM11 to UDM12 | SLF11 to SLF12 | SMF11 to SMF12 | AUSF11 to AUSF12 | BSF11 to BSF12 | Loc1r11 |
| Site7 | 18 | SCP13 to SCP14 | NRF13 to NRF14 | PCF19 to PCF20 | - | AMF13 to AMF14 | UDR13 to UDR14 | UDM13 to UDM14 | SLF13 to SLF14 | SMF13 to SMF14 | AUSF13 to AUSF14 | BSF13 to BSF14 | Loc1r13 |
| Site8 | 18 | SCP15 to SCP16 | NRF15 to NRF16 | PCF21 to PCF22 | - | AMF15 to AMF16 | UDR15 to UDR16 | UDM15 to UDM16 | SLF15 to SLF16 | SMF15 to SMF16 | AUSF15 to AUSF16 | BSF15 to BSF16 | Loc1r15 |
| Site9 | 18 | SCP17 to SCP18 | NRF17 to NRF18 | PCF23 to PCF24 | - | AMF17 to AMF18 | UDR17 to UDR18 | UDM17 to UDM18 | SLF17 to SLF18 | SMF17 to SMF18 | AUSF17 to AUSF18 | BSF17 to BSF18 | Loc1r17 |
| Site10 | 18 | SCP19 to SCP20 | NRF19 to NRF20 | PCF25 to PCF26 | - | AMF19 to AMF20 | UDR19 to UDR20 | UDM19 to UDM20 | SLF19 to SLF20 | SMF19 to SMF20 | AUSF19 to AUSF20 | BSF19 to BSF20 | Loc1r19 |
| Site11 | 18 | SCP21 to SCP22 | NRF21 to NRF22 | PCF27 to PCF28 | - | AMF21 to AMF22 | UDR21 to UDR22 | UDM21 to UDM22 | SLF21 to SLF22 | SMF21 to SMF22 | AUSF21 to AUSF22 | BSF21 to BSF22 | Loc1r21 |
| Site12 | 18 | SCP23 to SCP24 | NRF23 to NRF24 | PCF29 to PCF30 | - | AMF23 to AMF24 | UDR23 to UDR24 | UDM23 to UDM24 | SLF23 to SLF24 | SMF23 to SMF24 | AUSF23 to AUSF24 | BSF23 to BSF24 | Loc1r23 |
| Site13 | 18 | SCP25 to SCP26 | NRF25 to NRF26 | PCF31 to PCF32 | - | AMF25 to AMF26 | UDR25 to UDR26 | UDM25 to UDM26 | SLF25 to SLF26 | SMF25 to SMF26 | AUSF25 to AUSF26 | BSF25 to BSF26 | Loc1r25 |
| Site14 | 18 | SCP27 to SCP28 | NRF27 to NRF28 | PCF33 to PCF34 | - | AMF27 to AMF28 | UDR27 to UDR28 | UDM27 to UDM28 | SLF27 to SLF28 | SMF27 to SMF28 | AUSF27 to AUSF28 | BSF27 to BSF28 | Loc1r27 |
| Site15 | 18 | SCP29 to SCP30 | NRF29 to NRF30 | PCF35 to PCF36 | - | AMF29 to AMF30 | UDR29 to UDR30 | UDM29 to UDM30 | SLF29 to SLF30 | SMF29 to SMF30 | AUSF29 to AUSF30 | BSF29 to BSF30 | Loc1r29 |
| Site16 | 18 | SCP31 to SCP32 | NRF31 to NRF32 | PCF37 to PCF38 | - | AMF31 to AMF32 | UDR31 to UDR32 | UDM31 to UDM32 | SLF31 to SLF32 | SMF31 to SMF32 | AUSF31 to AUSF32 | BSF31 to BSF32 | Loc1r31 |
| Site17 | 18 | SCP33 to SCP34 | NRF33 to NRF34 | PCF39 to PCF40 | - | AMF33 to AMF34 | UDR33 to UDR34 | UDM33 to UDM34 | SLF33 to SLF34 | SMF33 to SMF34 | AUSF33 to AUSF34 | BSF33 to BSF34 | Loc1r33 |
| Site18 | 18 | SCP35 to SCP36 | NRF35 to NRF36 | PCF41 to PCF42 | - | AMF35 to AMF36 | UDR35 to UDR36 | UDM35 to UDM36 | SLF35 to SLF36 | SMF35 to SMF36 | AUSF35 to AUSF36 | BSF35 to BSF36 | Loc1r35 |
| Site19 | 18 | SCP37 to SCP38 | NRF37 to NRF38 | PCF43 to PCF44 | - | AMF37 to AMF38 | UDR37 to UDR38 | UDM37 to UDM38 | SLF37 to SLF38 | SMF37 to SMF38 | AUSF37 to AUSF38 | BSF37 to BSF38 | Loc1r37 |
| Site20 | 18 | SCP39 to SCP40 | NRF39 to NRF40 | PCF45 to PCF46 | - | AMF39 to AMF40 | UDR39 to UDR40 | UDM39 to UDM40 | SLF39 to SLF40 | SMF39 to SMF40 | AUSF39 to AUSF40 | BSF39 to BSF40 | Loc1r39 |
| Site21 | 18 | SCP41 to SCP42 | NRF41 to NRF42 | PCF47 to PCF48 | - | AMF41 to AMF42 | UDR41 to UDR42 | UDM41 to UDM42 | SLF41 to SLF42 | SMF41 to SMF42 | AUSF41 to AUSF42 | BSF41 to BSF42 | Loc1r41 |
| Site22 | 18 | SCP43 to SCP44 | NRF43 to NRF44 | PCF49 to PCF50 | - | AMF43 to AMF44 | UDR43 to UDR44 | UDM43 to UDM44 | SLF43 to SLF44 | SMF43 to SMF44 | AUSF43 to AUSF44 | BSF43 to BSF44 | Loc1r43 |
| Total | 500 | 44 | 44 | 86 | 6 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 52 | - |
Topology 1 NF Profiles
The following table describes NF profile configuration, traffic, and message call flows for 280 NF profiles registered on SCP:
Table 3-3 NF Profiles
| NF-C | NF-P | Interfaces | Supported Services | Service-related Traffic | NF Range | Profiles Registered | Message Call Flows |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMF | PCF | N15 |
|
|
50 | PCF1 to PCF50 |
Npcf_AMPolicyControl
Npcf_UEPolicyControl
|
| SMF | PCF | N7 |
|
npcf-smpolicycontrol | 50 | PCF1 to PCF50 |
|
| SMF | UDM | N10 |
|
|
44 | UDM1 to UDM44 |
Nudm_sdm
Nudm_uecm
|
| AMF | UDM | N8 |
|
|
44 | UDM1 to UDM44 |
Nudm_sdm
Nudm_uecm
|
| PCF | UDR | N36 |
|
nudr-dr | 44 | UDR1 to UDR44 |
|
| PCF | CHF | N28 |
|
nchf-spendinglimitcontrol | 44 | CHF1 to CHF44 |
|
| SMF | CHF | N40 |
|
nchf-convergedcharging | 44 | CHF1 to CHF44 |
|
| AMF | AUSF | N12 |
|
nausf-auth | 44 | AUSF1 to AUSF44 | Authenticate UE |
| PCF | BSF | Nbsf | nbsf-management | nbsf-management | 44 | BSF1 to BSF44 |
|
| NRF | SLF | - | nudr-group-id-map | nudr-group-id-map | 44 | SLF1 to SLF44 | SLF Look up |
3.2 Test Topology 2 for SCP Model C Benchmarking with SBI Message Feed
The following image represents the test topology consisting of the following components:
-
SCP
- Consumer NF test simulator
- Producer NF test simulator
- NRF simulator
- Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD)
Figure 3-4 SCP Model C Topology 2
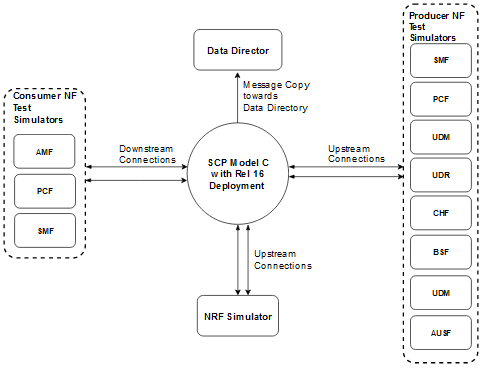
The aforementioned image represents the Model C test topology. In Release 16 Model C indirect 5G SBI communication mode, the consumer NF sends NF discovery service requests to NRF. After receiving the discovery response with NF profiles, the consumer NF performs the following tasks:
- Selects an NF Set or a specific NF instance from the NF Set
- Sends a service request to SCP with the address of the selected service producer NF
- Creates multiple network interfaces for different subnet IPs
- Service requests from consumer NF are copied to OCNADD and then forwarded to the third-party
Then, SCP selects an NF service instance and routes the service requests to the selected producer NF. In case of failure, if reselection is required, SCP selects the producer NF instance based on the NF Set.
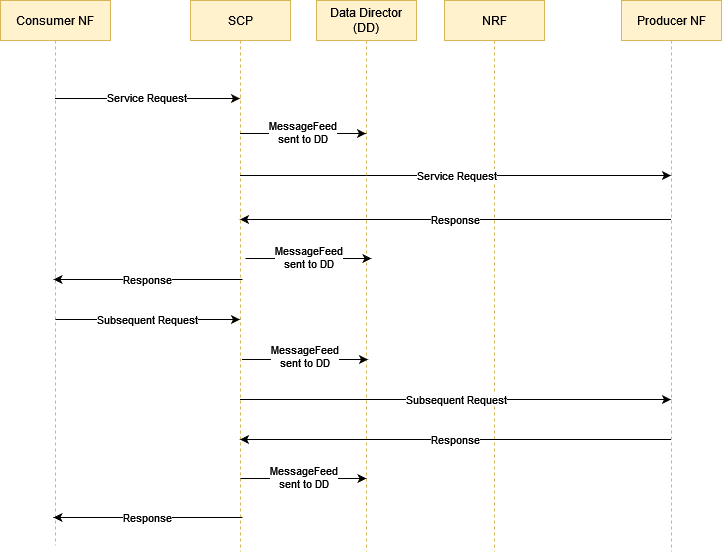
3.2.1 Topology 2 Call Flow
The following call flow represents how a service request is processed by SCP:
- Consumer NF sends the service request to SCP.
- SCP sends the request to the producer NF based on the NF profiles registered through NRF.
- Producer NF sends the response to SCP for the service request.
- SCP routes the response received from the producer NF to the consumer NF.
- SCP copies the requests and responses to DD.
Figure 3-5 Topology 2 Call Flow
3.2.2 Topology 2 Traffic Distribution
The following table describes the percentage of messages processed by SCP:
Table 3-4 Topology 2 Traffic Distribution
| NF-C | NF-P | Interface Reference | NF Service | Percentage (%) of Messages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMF | PCF | N7 |
npcf-smpolicycontrol |
79.55% |
| SMF | UDM | N10 |
|
7.58% |
| PCF | UDR | N36 |
nudr-dr |
0.76% |
| PCF | CHF | N28 | nchf-spendinglimitcontrol | 0.76% |
| SMF | CHF | N40 | nchf-convergedcharging | 11.36% |
Topology 2 Routing Configuration
The following table describes the routing configurations for the NF services:
Table 3-5 Routing Configuration
| NF | Service | Initial Message | Subsequent Message | reverseProxySupport | Deployment | ResponseTimeout | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| routePolicy | reroutePolicy | routePolicy | reroutePolicy | |||||
| PCF | npcf-smpolicycontrol | Load_Balance | RerouteDisabled | Load_Balance | RerouteDisabled | False | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| UDM | nudm-sdm | Load_Balance | RerouteDisabled | Load_Balance | RerouteDisabled | False | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| UDM | nudm-uecm | Load_Balance | RerouteDisabled | Load_Balance | RerouteDisabled | False | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| UDR | nudr-dr | Load_Balance | RerouteDisabled | Load_Balance | RerouteDisabled | False | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| PCF | nchf-spendinglimitcontrol | Load_Balance | RerouteDisabled | Load_Balance | RerouteDisabled | False | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| CHF | nchf-convergedcharging | Forward_Route | RerouteWithinSite | Forward_Route | RerouteWithinSite | True | SITE_WIDE | 1s |
Topology 2 NF Profiles
The following table describes NF profile configuration, traffic, and message call flows for 15 NF profiles registered on SCP:
Table 3-6 NF Profiles
| NF-C | NF-P | Interfaces | Supported Services | Service-related traffic | Profiles Registered | NF Range | Message Call flows |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMF | PCF | N7 |
|
npcf-smpolicycontrol | 8 | PCF1-PCF5 |
|
| SMF | UDM | N10 |
|
|
2 | UDM1 to UDM2 |
|
| PCF | UDR | N36 |
|
|
1 | UDM1 |
|
| PCF | CHF | N28 |
|
nchf-spendinglimitcontrol | 2 | CHF1-CHF2 |
|
| SMF | CHF | N40 |
|
nchf-convergedcharging | 2 | CHF1-CHF2 |
|
3.3 Test Topology 3 for SCP Model C Benchmarking
The following image represents the test topology consisting of the following components:
-
SCP
- Consumer NF test simulator
- Producer NF test simulator
- NRF simulator
Figure 3-6 SCP Model C Topology 3
The aforementioned image represents the Model C test topology. In Release 16 Model C indirect 5G SBI communication mode, the consumer NF sends NF discovery service requests to NRF. After receiving the discovery response with NF profiles, the consumer NF performs the following tasks:
- Selects an NF Set or a specific NF instance from the NF Set
- Sends a service request to SCP with the address of the selected service producer NF in 3gpp-Sbi-Target-apiRoot header
- Creates multiple network interfaces for different subnet IPs
Then, SCP selects an NF service instance and routes the service requests to the selected producer NF. In case of failure, if reselection is required, SCP selects the producer NF instance based on the NF Set.
3.3.1 Topology 3 Call Flow
The following call flow represents how a service request is processed by SCP:
- Consumer NF sends the service request to SCP.
- SCP sends the request to the producer NF based on the NF profiles registered through NRF.
- Producer NF sends the response to SCP for the service request.
- SCP routes the response received from the producer NF to the consumer NF.
Figure 3-7 Topology 3 Call Flow
3.3.2 Topology 3 Traffic Distribution
The following table describes the percentage of messages processed by SCP using N11, N7, N10, N36, N28, and other interfaces:
Table 3-7 Topology 3 Traffic Distribution
| NF-C | NF-P | Interface Reference | Percentage (%) of Messages |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMF | PCF | N7 | 60 |
| SMF | UDM | N10 | 5 |
| PCF | UDR | N36 | 1 |
| PCF | CHF | N28 | 1 |
| SMF | CHF | N40 | 10 |
| NRF | SLF | - | 3 |
| PCF | BSF | Nbsf | 2 |
| AMF | UDM | N8 | 7.5 |
| AMF | AUSF | N12 | 7.5 |
| AMF | PCF | N15 | 3 |
| NRF | SCP | Notifications | 10 notifications every 15 minutes |
Note:
Only UDM, AUSF, and UDR traffic traverses between regions through inter-SCP and is ~30% of the overall AUSF, UDM, and UDR traffic rates as represented by the rate captured for SCP.Topology 3 Routing Configuration
The following table describes the routing configurations for the NF services:
Table 3-8 Routing Configuration
| NF | Service | Initial Message | Subsequent Message | Deployment | ResponseTimeout | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| routePolicy | reroutePolicy | routePolicy | reroutePolicy | ||||
| PCF | Npcf_SMPolicyControl | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| UDR | Nudr_dm | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| CHF | Nchf_SpendingLimitControl | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| UDM | Nudm_sdm | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| UDM | Nudm_uecm | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| PCF | Npcf_AMPolicyControl | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| PCF | Npcf_UEPolicyControl | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| AUSF | Nausf_UEAuthentication | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| BSF | Nbsf_management | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
| UDR | Nudr_udrService | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 3s |
Topology 3 NF Profiles
The following table describes NF profile configuration, traffic, and message call flows for 280 NF profiles registered on SCP:
Table 3-9 NF Profiles
| NF-C | NF-P | Interfaces | Supported Services | Service-related traffic | NF Range | Profiles Registered | Message Call Flows |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMF | PCF | N15 |
|
|
30 | PCF1 to PCF30 |
Npcf_AMPolicyControl
Npcf_UEPolicyControl
|
| SMF | PCF | N7 |
|
npcf-smpolicycontrol | 30 | PCF1 to PCF30 |
|
| SMF | UDM | N10 |
|
|
6 | UDM1 to UDM6 |
Nudm_sdm
Nudm_uecm
|
| AMF | UDM | N8 |
|
|
6 | UDM6 to UDM12 |
Nudm_sdm
Nudm_uecm
|
| PCF | UDR | N36 |
|
nudr-dr | 24 | UDR1 to UDR24 |
|
| PCF | CHF | N28 |
|
nchf-spendinglimitcontrol | 6 | CHF1 to CHF6 |
|
| SMF | CHF | N40 |
|
nchf-convergedcharging | 6 | CHF1 to CHF6 |
|
| AMF | AUSF | N12 |
|
nausf-auth | 6 | AUSF1 to AUSF6 | Authenticate UE |
| PCF | BSF | Nbsf | nbsf-management | nbsf-management | 6 | BSF1 to BSF6 |
|
| NRF | SLF | - | nudr-group-id-map | nudr-group-id-map | 6 | SLF1 to SLF6 | SLF Look up |
3.4 Test Topology 4 for SCP Model C Benchmarking
-
SCP
- Consumer NF test simulator
- Producer NF test simulator
- NRF simulator
Figure 3-8 SCP Model C Topology 4

The aforementioned image represents the Model C test topology. In Release 16 Model C indirect 5G SBI communication mode, the consumer NF sends NF discovery service requests to NRF. After receiving the discovery response with NF profiles, the consumer NF performs the following tasks:
- Selects an NF Set or a specific NF instance from the NF Set
- Sends a service request to SCP with the address of the selected service producer NF in 3gpp-Sbi-Target-apiRoot header
- Creates multiple network interfaces for different subnet IPs
Then, SCP selects an NF service instance and routes the service requests to the selected producer NF. In case of failure, if reselection is required, SCP selects the producer NF instance based on the NF Set.
3.4.1 Topology 4 Call Flow
- Consumer NF sends the service request to SCP.
- SCP sends the request to the producer NF based on the NF profiles registered through NRF.
- Producer NF sends the response to SCP for the service request.
- SCP routes the response received from the producer NF to the consumer NF.
Figure 3-9 Topology 4 Call Flow

3.4.2 Topology 4 Traffic Distribution
Table 3-10 Topology 4 Traffic Distribution
| NF-C | NF-P | Interface Reference | Percentage (%) of Messages |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMF | PCF | N7 | 30 |
| AMF | PCF | N10 | 7.5 |
| AMF | AUSF | N12 | 1.5 |
| SMF | UDM | N10 | 5 |
| SMF | CHF | N40 | 5 |
| PCF | CHF | N28 | 5 |
| PCF | BSF | - | 2 |
| AMF | UDM | N8 | 7.5 |
| AMF | SMSF | - | 5 |
| PCF | BSF | - | 3 |
| PCF | UDR | N36 | 2.5 |
| PCF | AMF | - | 2.5 |
| UDM | UDR | N35 | 2.5 |
| CHF | PCF | 2.5 | |
| SMSF | AMF | 2.5 | |
| AMF | NSSF | N22 | 2.5 |
| NRF | SLF | 2 | |
| CBCF | AMF | N50 | 1.5 |
| SMSF | UDM | 1.5 | |
| GMLC | AMF | 1.5 | |
| GMLC | UDM | 1.5 | |
| LMF | AMF | 1.5 | |
| NEF | UDM | N52 | 1.5 |
| AMF | NSSAAF | N58 | 0.5 |
| AUSF | UDM | N13 | 0.5 |
| UDM | SMF | N10 | 0.5 |
| CHF | SMF | 0.5 | |
| PCF | SMF | 0.5 | |
| PCF | AMF | 0.5 | |
| AMF | PCF | 0.5 | |
| UDR | PCF | 0.5 | |
| UDM | AMF | 0.5 | |
| NRF | SCP |
|
Note:
Only UDM, AUSF, and UDR traffic traverses between regions through inter-SCP and is ~30% of the overall AUSF, UDM, and UDR traffic rates as represented by the rate captured for SCP.Topology 4 Routing Configuration
Table 3-11 Routing Configuration
| NF | Service | Initial Message | Subsequent Message | Deployment | ResponseTimeout | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| routePolicy | reroutePolicy | routePolicy | reroutePolicy | ||||
| PCF | Npcf_SMPolicyControl | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| PCF | Npcf_AMPolicyControl | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| PCF | Npcf_UEPolicyControl | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| AUSF | Nausf_UEAuthentication | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| UDM | Nudm_uecm | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| UDM | Nudm_sdm | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| CHF | Nchf_ConvergedCharging | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| CHF | Nchf_SpendingLimitControl | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| BSF | Nbsf_Management | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| UDR | Nudr_dr | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| AMF | Namf_Communication | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| PCF | SpendingLimitStatus | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| AMF | Namf_evts | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| NSSF | Nnssf_NSSAIAvailability | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| NSSF | Nnssf_NSSelection | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| UDR | Nudr_GroupIDmap | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| AMF | Namf_Communication | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| AMF | Namf_Location | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| UDM | Nudm_EventExposure | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| NSSF | Nnssaaf_nssaa | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| UDM | Nudm_UEAuthentication | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| UDM | Nudm_sucideconceal | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| UDM | Nudm_SDM_Notification | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| CHF | Nchf_ConvergedCharging_Notify | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| PCF | Npcf_SMPolicyUpdateNotification | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| PCF | Npcf_AMPolicyControl_UpdateNotify | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| PCF | N1MessageNotification | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| PCF | PolicyDataChangeNotification | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| UDM | Nudm_SDM_Notification | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
| SCP | Notifications | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | Load_Balance | RerouteWithinSite | SITE_WIDE | 2s |
Topology 4 NF Profiles
Table 3-12 NF Profiles
| NF-C | NF-P | Interface | Supported Services | Service-related traffic | NF Range | Profile Registered | Message Call Flows |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHF | PCF | SpendingLimitStatus | SpendingLimitStatus | 42 | PCF1 to PCF95 |
|
|
| NRF | SLF | Nudr_GroupIDmap | Nudr GET (SLF group id query) | 10 | UDR1 to UDR30 | Get Group ID | |
| PCF | UDR | N36 | Nudr-dr |
|
10 | UDR1 to UDR30 |
|
| UDM | UDR | N35 | Nudr-dr | Nudr_DataRepository | 10 | UDR1 to UDR30 | Get UDR SM Data |
| SMF | UDM | N10 | ul
|
|
24 |
|
Nudm_sdm
Nudm_uecm
|
| SMSF | UDM | Nudm_uecm | Nudm_UECM (Registration,Delete) | 24 | UDM1 to UDM24 |
|
|
| GMLC | UDM | Nudm_uecm | Nudm_UEContextManagement Get Request/Response | 24 | UDM1 to UDM30 | Get UE context management | |
| AUSF | UDM | N13 |
|
|
24 | UDM1 to UDM30 |
|
| NEF | UDM | N52 |
|
|
24 | UDM1 to UDM30 |
|
| AMF | UDM | N8 |
|
|
24 | UDM1 to UDM40 |
Nudm_sdm
Nudm_uecm
|
| AMF | SMSF | Nsmsf-sms |
|
6 | SMSF1 to SMSF8 |
|
|
| SMF | PCF | N7 | Npcf_SMPolicyControl |
|
30 |
|
Npcf_SMPolicyControl
|
| AMF | PCF |
|
|
12 |
|
Npcf_AMPolicyControl
Npcf_UEPolicyControl
|
|
| AMF | NSSF | N22 |
|
|
6 | NSSF1 to NSSF8 |
|
| AMF | NSSAAF | N58 | Nnssaaf-nssaa | Nnssaaf_NSSAA_Authenticate Request/Response | 6 | NSSAAF1 to NSSAAF8 | Post Slice authentication |
| PCF | CHF | N28 | Nchf_SpendingLimitControl | Nchf_SpendingLimitControl Subscribe/Unsubscribe | 6 | CHF1 to CHF10 |
|
| SMF | CHF | N40 | Nchf_ConvergedCharging |
|
6 | CHF1 to CHF10 |
|
| PCF | BSF | Nbsf_Management |
|
6 | BSF1 to BSF10 |
|
|
| AMF | AUSF | N12 | Nausf_UEAuthentication | Nausf_UEAuthentication_Authenticate | 24 | AUSF1 to AUSF40 | Authenticate UE |
| GMLC | AMF | Namf_Location | Namf_Location_ProvidePositioningInfo | 102 | AMF1 to AMF150 | Get Location Information | |
| PCF | AMF | Namf_Communication |
|
102 | AMF1 to AMF150 |
|
|
| CBCF | AMF | N50 | Namf_Communication |
|
102 | AMF1 to AMF50 |
|
| LMF | AMF | Namf_Communication | Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer | 102 | AMF1 to AMF150 | Post N1N2 message | |
| SMSF | AMF | Namf-evts |
|
102 | AMF1 to AMF150 |
|
3.5 Model C Testcases
This section provides information about SCP Model C testcases.
This test scenario describes the performance and capacity of SCP with Model C and provides the benchmarking results with latency in a network.
3.5.1 Model C Testcase Summary
The following table provides a summary of the benchmark tests.
Table 3-13 Benchmark Testcase Summary
| Benchmark Testcase Number | Description |
|---|---|
| Model C - Testcase Scenario 1 | The Model C test with message feed enabled with 2 trigger points, 270K MPS towards SCP and 270K MPS towards OCNADD. |
| Model C - Testcase Scenario 2 | The Model C test is based on the network latency of 150 milliseconds at the rate of 640K MPS with rate limit applied. |
| Model C - Testcase Scenario 3 | The Model C test is based on the network latency of 150 milliseconds at the rate of 150K MPS across 22 regions with rate limit enabled on a non ASM setup. |
| Model C - Testcase Scenario 4 | The Model C test is based on the network latency of 150 milliseconds at the rate of 620K MPS with the Mediation feature enabled. |
| Model C - Testcase Scenario 5 | The Model C test is based on the network latency of 200 milliseconds at the rate of 730K MPS, with LCI, OCI, Ingress Rate Limiting, Global Rate Limiting, and ASM enabled. |
3.5.2 Model C - Testcase Scenario 1
In Model C testcase scenario, the Message Feed feature is enabled with two trigger points, 270K MPS toward SCP, and 270K MPS toward Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD).
Objective
This testcase scenario describes the performance and capacity of SCP with Model C. It provides benchmarking results with latency in a network, and no rate limit is applied to the ingress and egress traffic.
Table 3-14 Input Parameter Details
| Input Parameter Details | Configuration Values |
|---|---|
| Duration of Test | 12 Hours |
| SCP Version Tag | 24.3.0 |
| Cluster | Test Bed 3 - CNE on Bare Metal. For more information, see Table 2-5. |
| Topology | Topology 2. For information about topology, see Test Topology 2 for SCP Model C Benchmarking with SBI Message Feed. |
Testcase Parameters
The following table describes the testcase parameters and their values:
Table 3-15 Testcase Parameters
| Input Parameter Details | Configuration Values |
|---|---|
|
Maximum SCP system wide traffic rate (in MPS) |
270K MPS for SCP and 270K MPS toward OCNADD |
| Network deployment diagram | Topology 2. For information about topology, see Test Topology 2 for SCP Model C Benchmarking with SBI Message Feed. |
| Mode of Network deployment (Model-C or Model-D) | Model C |
| Number of NFs deployed in the network which SCP is supposed to learn (number of NF Profiles) | 8 |
| NF Status Information |
|
| NF Profile - Priority, Capacity, and Load value same in all services of same kind? (Yes, No) | No |
| LAN latency in intra-SCP services and 5G NF communication (between SCP data and control plane services, SCP and other NFs ) in millisecond | 150 milliseconds |
| WAN latency in SCP services and 5G NF communication (SCP to NFs in other regions) in millisecond | 150 milliseconds |
| Number of SCP ingress IPs configured | 1 |
| How many connections per published IP/FQDN producers can handle? | 68 |
| Per Egress connection max traffic in MPS | 1000 |
| How many connections consumer can initiate toward per SCP IP? | 119 |
| Per Ingress connection max traffic in MPS | 1000 |
| Average Request and Response message size |
|
| Percentage of alternate routed requests to NF due to any reason (2% to 5%) | 2% |
| Configured audit interval and audit mode |
|
| Number of NRFs and NRF Sets deployed in the network | NA |
| Response time (latency) from NRF (NRF processing time) | 150 milliseconds |
| Delegated Discovery Traffic Information | NA |
| NF Discovery response size and Info | NA |
| Egress and Ingress Configurations | NA |
| Mediation Configurations | NA |
| Mediation Trigger point configuration | NA |
| Secured HTTPs connection - % of message on HTTPs? | NA |
| DNS SRV configuration and response time | NA |
| Roaming traffic details | NA |
| Pods deployed |
|
| SCP Worker Pod Profile | 8 vCPU and 12 Gi Memory |
| Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Configurations |
|
| LCI Configurations | NA |
| Processing latency(processing time) per producer NF | Upstream Network Latency: 150 milliseconds |
| OAuth Traffic Rate | NA |
| OCI Configurations | NA |
Result and Observation
The performance test observation data shown in the following table can be used to conduct benchmark testing to raise the traffic rate:
Table 3-16 Result and Observation
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Test Duration | 12 Hours |
| MPS Achieved | 270K MPS |
| Average MPS per scp-worker pod | 11.7K MPS |
| Success rate | ~ 99.98 % |
| Average SCP processing time (Request and Response) | Less than 25 milliseconds for both Request and Response processing |
| Response Time (from producer NF test simulator) including network latency | 150ms |
| Response time (latency) from NRF simulator | 300ms |
SCP Microservices and their Utilization
The following table describes SCP microservices and their utilization:
Table 3-17 SCP Microservices and their Utilization
| SCP Microservices | CPU | Memory | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Avg | Max | Avg | |
| scp-worker | 5.64 | 4.87 | 6.7 | 6.04 |
| scpc-notification | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.25 | 1.23 |
| scpc-audit | 0.02 | 0.005 | 0.59 | 0.58 |
| scpc-subscription | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.53 | 0.5 |
| scpc-configuration | 0.02 | 0.012 | 0.63 | 0.62 |
| scp-cache | 0.06 | 0.018 | 0.51 | 0.5 |
| scp-load-manager | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.68 | 0.67 |
Observed Values of cnDBTier Services
Table 3-18 Observed Values of cnDBTier Services
| cnDBTier Services | Value |
|---|---|
| CPU usage of data nodes | 0.125% |
| Memory usage of data nodes | 4.72% |
| Read operations per second | 4.92 seconds |
| Write operations per second | 0.001 seconds |
| Transaction rates on data nodes | 1.92 |
3.5.3 Model C - Testcase Scenario 2
The Model C test is based on the network latency of 150 milliseconds at the rate of 640K MPS with rate limit applied, Non ASM .
Objective
This testcase scenario describes the performance and capacity of SCP with Model C. It provides benchmarking results with latency in a network, and rate limit is applied to the ingress and egress traffic.
The following table describes test bed configurations:
Table 3-19 Input Parameter Details
| Input Parameter Details | Configuration Values |
|---|---|
| Duration of Test | 12 Hours |
| SCP Version Tag | 24.1.0 |
| Cluster | Test Bed 4 - CNE on Bare Metal. For more information, see Table 2-6. |
| Topology | Topology 3. For information about topology, see Test Topology 3 for SCP Model C Benchmarking. |
Testcase Parameters
The following table describes the testcase parameters and their values:
Table 3-20 Testcase Parameters
| Input Parameter Details | Configuration Values |
|---|---|
| Maximum SCP system wide traffic rate (in MPS) | 640K MPS |
| Network deployment diagram | Topology 3. For information about topology, see Test Topology 3 for SCP Model C Benchmarking. |
| Mode of Network deployment (Model-C or Model-D) | Model C |
| Number of NFs deployed in the network which SCP is supposed to learn (number of NF Profiles) | 280 |
| NF Status Information |
|
| NF Profile - Priority, Capacity, and Load value same in all services of same kind? (Yes, No) | No |
| LAN latency in intra-SCP services and 5G NF communication (between SCP data and control plane services, SCP and other NFs ) in millisecond | 150 milliseconds |
| WAN latency in SCP services and 5G NF communication (SCP to NFs in other regions) in millisecond | 150 milliseconds |
| Number of SCP ingress IPs configured | 1 |
| How many connections per published IP/FQDN producers can handle? | 260 |
| Per Egress connection max traffic in MPS | 1000 |
| How many connections consumer can initiate toward per SCP IP? | 190 |
| Per Ingress connection max traffic in MPS | 1000 |
| Average Request and Response message size |
|
| Percentage of alternate routed requests to NF due to any reason (2% to 5%) | 2% |
| Configured audit interval and audit mode |
|
| Number of NRFs and NRF Sets deployed in the network |
|
| Response time (latency) from NRF (NRF processing time) | 150 milliseconds |
| Delegated Discovery Traffic Information | NA |
| NF Discovery response size and Info | NA |
| Egress and Ingress Rate Limit Configurations |
|
| Mediation Configurations | NA |
| Mediation Trigger point configuration | NA |
| Secured HTTPs connection - % of message on HTTPs? | NA |
| DNS SRV configuration and response time |
|
| Roaming traffic details | NA |
| Pods deployed |
|
| SCP Worker Pod Profile | 12 vCPU and 16 Gi Memory |
| Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Configurations | NA |
| LCI Configurations |
|
| Processing latency(processing time) per producer NF | Upstream Network Latency: 150 milliseconds |
| OAuth Traffic Rate | NA |
| OCI Configurations |
|
Result and Observation
The performance test observation data shown in the following table can be used to conduct benchmark testing to raise the traffic rate:
Table 3-21 Result and Observation
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Test Duration | 12 Hours |
| MPS Achieved | 640K MPS |
| Average MPS per scp-worker pod | 16K MPS |
| Success rate | 100 % |
| Average SCP processing time (Request and Response) | Less than 25 milliseconds for both Request and Response processing |
SCP Microservices and their Utilization
The following table describes SCP microservices and their utilization:
Table 3-22 SCP Microservices and their Utilization
| SCP Microservices | CPU/Pod | Memory/Pod | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Avg | Max | Avg | |
| scp-worker | 9.36 | 8.59 | 9.64 GB | 9.44 GB |
| scp-nrfproxy | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| scpc-notification | 0.752 | 0.715 | 1.65 GB | 1.65 GB |
| scpc-audit | 0.0178 | 0.00677 | 604 MB | 604 MB |
| scpc-configuration | 0.0419 | 0.0344 | 769 MB | 768 MB |
| scpc-subscription | 0.0643 | 0.0499 | 821 MB | 820 MB |
| scp-cache | 0.775 | 0.695 | 921 MB | 917 MB |
| scp-load-manager | 0.402 | 0.0629 | 1.48 GB | 1.48 GB |
| scpc-alternate-resolution | 0.0175 | 0.0107 | 749 MB | 746 MB |
Observed Values of cnDBTier Services
The following table provides information about observed values of cnDBTier services:
Table 3-23 Observed Values of cnDBTier Services
| cnDBTier Services | Value |
|---|---|
| Memory usage of data nodes | 0.6% |
| CPU usage of data nodes | 0.7% |
| Write operations per second | 1 second |
| Read operations per second | 69 seconds |
| Transaction rates on data nodes | 2.8 |
3.5.4 Model C - Testcase Scenario 3
The Model C test is based on the network latency of 150 milliseconds at the rate of 150K MPS across 22 regions with rate limit enabled on a non ASM setup.
Objective
This testcase scenario describes the performance and capacity of SCP with Model C. It provides benchmarking results with latency in a network, and rate limit is applied to the ingress and egress traffic.
The following table describes test bed configurations:
Table 3-24 Input Parameter Details
| Input Parameter Details | Configuration Values |
|---|---|
| Duration of Test | 12 Hours |
| SCP Version Tag | 24.2.0 |
| Cluster | Test Bed 4 - CNE on Bare Metal. For more information, see Table 2-6. |
| Topology | Topology 1. For information about topology, see Test Topology 1 for SCP Model C Benchmarking. |
Testcase Parameters
The following table describes the testcase parameters and their values:
Table 3-25 Testcase Parameters
| Input Parameter Details | Configuration Values |
|---|---|
| Maximum SCP system wide traffic rate (in MPS) | 150K MPS |
| Network deployment diagram | Topology 1. For information about topology, see Test Topology 1 for SCP Model C Benchmarking. |
| Mode of Network deployment (Model-C or Model-D) | Model C |
| Number of NFs deployed in the network which SCP is supposed to learn (number of NF Profiles) | 500 |
| NF Status Information |
|
| NF Profile - Priority, Capacity, and Load value same in all services of same kind? (Yes, No) | No |
| LAN latency in intra-SCP services and 5G NF communication (between SCP data and control plane services, SCP and other NFs ) in millisecond | 150 milliseconds |
| WAN latency in SCP services and 5G NF communication (SCP to NFs in other regions) in millisecond | 300 milliseconds |
| Number of SCP ingress IPs configured | 1 |
| How many connections per published IP/FQDN producers can handle? | 406 |
| Per Egress connection max traffic in MPS | 1000 |
| How many connections consumer can initiate toward per SCP IP? | 190 |
| Per Ingress connection max traffic in MPS | 1000 |
| Average Request and Response message size |
|
| Percentage of alternate routed requests to NF due to any reason (2% to 5%) | 2% |
| Configured audit interval and audit mode |
|
| Number of NRFs and NRF Sets deployed in the network |
|
| Response time (latency) from NRF (NRF processing time) | 150 milliseconds |
| Delegated Discovery Traffic Information | NA |
| NF Discovery response size and Info | NA |
| Egress and Ingress Rate Limit Configurations |
|
| Mediation Configurations | NA |
| Mediation Trigger point configuration | NA |
| Secured HTTPs connection - % of message on HTTPs? | NA |
| DNS SRV configuration and response time |
|
| Roaming traffic details | NA |
| Pods deployed |
|
| SCP Worker Pod Profile | 12 vCPU and 16 Gi Memory |
| Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Configurations | NA |
| LCI Configurations |
|
| Processing latency(processing time) per producer NF | Upstream Network Latency: 150 milliseconds |
| OAuth Traffic Rate | NA |
| OCI Configurations |
|
Result and Observation
The performance test observation data shown in the following table can be used to conduct benchmark testing to raise the traffic rate:
Table 3-26 Result and Observation
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Test Duration | 12 Hours |
| MPS Achieved | 150K MPS |
| Average MPS per scp-worker pod | 11.5K MPS |
| Success rate | 100 % |
| Average SCP processing time (Request and Response) | Less than 25 milliseconds for both Request and Response processing |
SCP Microservices and their Utilization
The following table describes SCP microservices and their utilization:
Table 3-27 SCP Microservices and their Utilization
| SCP Microservices | CPU/Pod | Memory/Pod | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Avg | Max | Avg | |
| scp-worker | 7.85 | 6.86 | 5.63 GB | 5.52 GB |
| scp-nrfproxy | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| scpc-notification | 0.255 | 0.238 | 1.63 GB | 1.63 GB |
| scpc-audit | 0.0141 | 0.00778 | 855 MB | 853 MB |
| scpc-configuration | 0.0494 | 0.0117 | 623 MB | 618 MB |
| scpc-subscription | 0.0127 | 0.00828 | 909 MB | 894 MB |
| scp-cache | 0.257 | 0.209 | 1.05 GB | 1.05 GB |
| scp-load-manager | 0.0458 | 0.0363 | 668 MB | 667 MB |
Observed Values of cnDBTier Services
The following table provides information about observed values of cnDBTier services:
Table 3-28 Observed Values of cnDBTier Services
| cnDBTier Services | Value |
|---|---|
| Memory usage of data nodes | 0.48% |
| CPU usage of data nodes | 0.114% |
| Write operations per second | 0.002 seconds |
| Read operations per second | 5.95 seconds |
| Transaction rates on data nodes | 2.0 |
3.5.5 Model C - Testcase Scenario 4
The Model C test is based on the network latency of 150 milliseconds at the rate of 620K MPS with the Mediation feature enabled.
Objective
This testcase scenario describes the performance and capacity of SCP with Model C. It provides benchmarking results with latency in a network, and rate limit is applied to the ingress and egress traffic.
The following table describes test bed configurations:
Table 3-29 Input Parameter Details
| Input Parameter Details | Configuration Values |
|---|---|
| Duration of Test | 12 Hours |
| SCP Version Tag | 24.1.0 |
| Cluster | Test Bed 4 - CNE on Bare Metal. For more information, see Table 2-6. |
| Topology | Topology 3. For information about topology, see Test Topology 3 for SCP Model C Benchmarking. |
Testcase Parameters
The following table describes the testcase parameters and their values:
Table 3-30 Testcase Parameters
| Input Parameter Details | Configuration Values |
|---|---|
| Maximum SCP system wide traffic rate (in MPS) | 620K MPS |
| Network deployment diagram | Topology 3. For information about topology, see Test Topology 3 for SCP Model C Benchmarking. |
| Mode of Network deployment (Model-C or Model-D) | Model C |
| Number of NFs deployed in the network which SCP is supposed to learn (number of NF Profiles) | 280 |
| NF Status Information |
|
| NF Profile - Priority, Capacity, and Load value same in all services of same kind? (Yes, No) | No |
| LAN latency in intra-SCP services and 5G NF communication (between SCP data and control plane services, SCP and other NFs ) in millisecond | 150 milliseconds |
| WAN latency in SCP services and 5G NF communication (SCP to NFs in other regions) in millisecond | 150 milliseconds |
| Number of SCP ingress IPs configured | 1 |
| How many connections per published IP/FQDN producers can handle? | 260 |
| Per Egress connection max traffic in MPS | 1000 |
| How many connections consumer can initiate toward per SCP IP? | 185 |
| Per Ingress connection max traffic in MPS | 1000 |
| Average Request and Response message size |
|
| Percentage of alternate routed requests to NF due to any reason (2% to 5%) | 2% |
| Configured audit interval and audit mode |
|
| Number of NRFs and NRF Sets deployed in the network |
|
| Response time (latency) from NRF (NRF processing time) | 150 milliseconds |
| Delegated Discovery Traffic Information | NA |
| NF Discovery response size and Info | NA |
| Egress and Ingress Rate Limit Configurations |
|
| Mediation Configurations |
|
| Mediation Trigger point configuration | Number of Mediation Trigger Points: 367 |
| Secured HTTPs connection - % of message on HTTPs? | NA |
| DNS SRV configuration and response time |
|
| Roaming traffic details | NA |
| Pods deployed |
|
| SCP Worker Pod Profile | 12 vCPU and 16 Gi Memory |
| Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Configurations | NA |
| LCI Configurations |
|
| Processing latency(processing time) per producer NF | Upstream Network Latency: 150 milliseconds |
| OAuth Traffic Rate | NA |
| OCI Configurations |
|
Result and Observation
The performance test observation data shown in the following table can be used to conduct benchmark testing to raise the traffic rate:
Table 3-31 Result and Observation
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Test Duration | 12 Hours |
| MPS Achieved | 620K MPS |
| Average MPS per scp-worker pod | 10.5K MPS |
| Mediation pod average MPS | 3.3K MPS |
| Success rate | 100 % |
| Average SCP processing time (Request and Response) | Less than 25 milliseconds for both Request and Response processing |
SCP Microservices and their Utilization
The following table describes SCP microservices and their utilization:
Table 3-32 SCP Microservices and their Utilization
| SCP Microservices | CPU/Pod | Memory/Pod | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Avg | Max | Avg | |
| scp-worker | 9.15 | 8.89 | 9.42 GB | 9.41 GB |
| scp-nrfproxy | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| scpc-notification | 1.62 | 1.53 | 1.71 GB | 1.71 GB |
| scpc-audit | 0.00847 | 0.00748 | 758 MB | 758 MB |
| scpc-configuration | 0.0806 | 0.0777 | 804 MB | 804 MB |
| scpc-subscription | 0.0670 | 0.0664 | 829 MB | 829 MB |
| scp-cache | 1.48 | 1.39 | 1.69 GB | 1.69 GB |
| scp-load-manager | 0.234 | 0.231 | 1.84 GB | 1.84 GB |
| scpc-alternate-resolution | 0.0193 | 0.0162 | 645 MB | 645 MB |
| scp-mediation | 3.55 | 3.31 | 5.58 GB | 5.58 GB |
Observed Values of cnDBTier Services
The following table provides information about observed values of cnDBTier services:
Table 3-33 Observed Values of cnDBTier Services
| cnDBTier Services | Value |
|---|---|
| Memory usage of data nodes | 0.38% |
| CPU usage of data nodes | 0.13% |
| Write operations per second | 0.003 seconds |
| Read operations per second | 5.91 seconds |
| Transaction rates on data nodes | 2.0 |
3.5.6 Model C - Testcase Scenario 5
The Model C test is based on the network latency of 200 milliseconds at the rate of 730K MPS with the LCI, OCI, Ingress Rate Limiting, Global Rate Limiting, and ASM enabled.
Objective
This test case scenario describes the performance and capacity of SCP with Model C. It includes benchmarking results considering network latency and applies rate limits to both ingress and egress traffic.
Table 3-34 Input Parameter Details
| Input Parameter Details | Configuration Values |
|---|---|
| Duration of Test | 72 Hours |
| SCP Version Tag | 25.1.100 |
| Cluster | Test Bed 4 - CNE on Bare Metal. For more information, see Table 2-6. |
| Topology | Topology 4. For information about topology, see Test Topology 4 for SCP Model C Benchmarking. |
Testcase Parameters
Table 3-35 Testcase Parameters
| Input Parameter Details | Configuration Values |
|---|---|
|
Maximum SCP system wide traffic rate (in MPS) |
730K MPS |
| Network deployment diagram | Topology 4. For information about topology, see Test Topology 4 for SCP Model C Benchmarking. |
| Mode of Network deployment (Model-C or Model-D) | Model C |
| Number of NFs deployed in the network which SCP is supposed to learn (number of NF Profiles) | 700 |
| NF Status Information |
|
| NF Profile - Priority, Capacity, and Load value same in all services of same kind? (Yes, No) | No |
| LAN latency in intra-SCP services and 5G NF communication (between SCP data and control plane services, SCP and other NFs ) in millisecond | 200 milliseconds |
| WAN latency in SCP services and 5G NF communication (SCP to NFs in other regions) in millisecond | 300 milliseconds |
| Number of SCP ingress IPs configured | 1 |
| How many connections per published IP/FQDN producers can handle? | 1413 |
| Per Egress connection max traffic in MPS | 1000 |
| How many connections consumer can initiate toward per SCP IP? | 690 |
| Per Ingress connection max traffic in MPS | 1500 |
| Average Request and Response message size |
|
| Percentage of alternate routed requests to NF due to any reason (2% to 5%) | 3% |
| Configured audit interval and audit mode |
|
| Number of NRFs and NRF Sets deployed in the network |
|
| Response time (latency) from NRF (NRF processing time) | 150 milliseconds |
| Delegated Discovery Traffic Information | NA |
| NF Discovery response size and Info | NA |
| Egress and Ingress Rate Limit Configurations |
|
| Mediation Configurations | NA |
| Mediation Trigger point configuration | NA |
| Secured HTTPs connection - % of message on HTTPs? | NA |
| DNS SRV configuration and response time |
|
| Roaming traffic details | NA |
| Pods deployed |
|
| SCP Worker Pod Profile | 12 vCPU and 16 Gi Memory |
| Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Configurations | NA |
| LCI Configurations |
|
| Processing latency(processing time) per producer NF | Upstream Network Latency: 150 milliseconds |
| OAuth Traffic Rate | NA |
| OCI Configurations |
|
Result and Observation
Table 3-36 Result and Observation
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Test Duration | 72 Hours |
| MPS Achieved | 730K MPS |
| Average MPS per scp-worker pod | 13.9K MPS |
| Success rate | 100 % |
| Average SCP processing time (Request and Response) | Less than 25 milliseconds for both Request and Response processing |
SCP Microservices and their Utilization
The following table describes SCP microservices and their utilization:
Table 3-37 SCP Microservices and their Utilization
| SCP Microservices | CPU/Pod | Memory/Pod | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Avg | Max | Avg | |
| scp-worker | 7.701 | 7.55 | 5.24 GB | 5.13 GB |
| scp-nrfproxy | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| scp-mediation | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| scpc-notification | 1.665 | 1.472 | 2.02 GB | 2.02 GB |
| scpc-audit | 0.106 | 0.033 | 616 MB | 614 MB |
| scpc-configuration | 0.066 | 0.051 | 758 MB | 758 MB |
| scpc-subscription | 0.02 | 0.019 | 755 MB | 755 MB |
| scp-cache | 0.883 | 0.723 | 961 MB | 961 MB |
| scp-load-manager | 0.072 | 0.056 | 769 MB | 769 MB |
| scpc-alternate-resolution | 0.085 | 0.08 | 727 MB | 726 MB |
Observed Values of cnDBTier Services
Table 3-38 Observed Values of cnDBTier Services
| cnDBTier Services | Value |
|---|---|
| Memory usage of data nodes | 2.7% |
| CPU usage of data nodes | 0.3% |
| Write operations per second | 11.9 seconds |
| Read operations per second | 381 seconds |
| Transaction rates on data nodes | 24.9 |