3 Configuring Unified Data Repository using CNC Console
This section describes how to configure global and service parameters on UDR using CNC Console. The service configuration includes data repository service, notify service, NRF client service and diameter service. Through CNC Console, you can view the bulk import status and logging level details, perform provisioning operations for profile data, PCF data, SLF data, UDM data and schema management and validate the access token.
3.1 Logging into CNC Console
After logging successfully into the CNC Console application, you can use UDR integrated with CNC Console. To log in successfully into the CNC Console, edit the hosts file available at the C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc location.
In the Windows system, open the hosts file in the notepad as an Administrator and append the following set of lines at the end:
Example:
10.75.212.88
cncc-iam-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local
10.75.212.88
cncc-core-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local
Note:
The IP Address in the above lines may change when deployment cluster changes.Save and close the notepad.
Note:
Before logging to CNC Console, it is important to create a CNC user. Using this user details, you can log in to the CNC Console application. For information on creating a CNC Console user, you can refer to its user guide.- Type
http://cncc-core-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local:<PortNumber>/
in the web browser and press Enter. The login page appears:
Figure 3-1 CNC Console Login Page

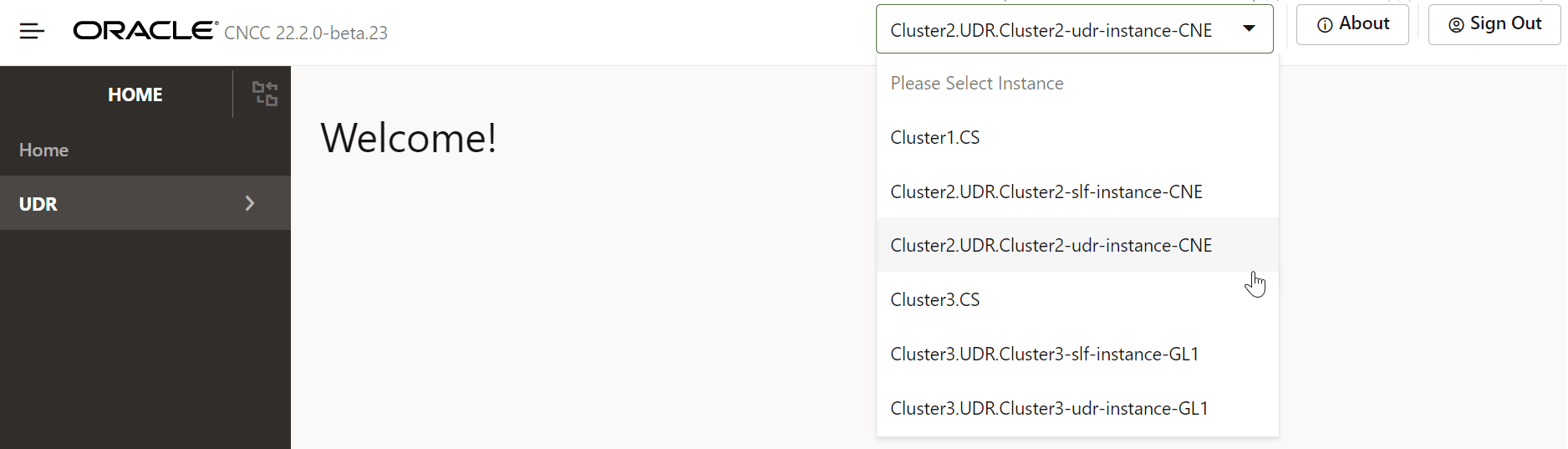
- Enter the Username and Password and click Log
In. The CNC Console Home page appears from where a user can select
different instances in the drop down, for example, the EIR, SLF, or the UDR
instance.
Figure 3-2 CNC Console Home Page
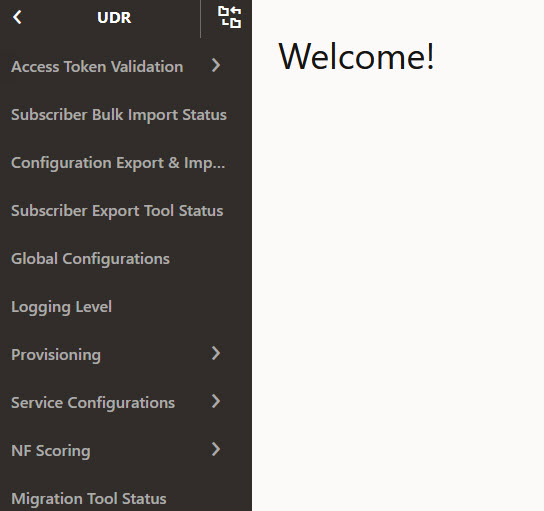
 The following NF services appear in the left navigation pane for the selected instance:
The following NF services appear in the left navigation pane for the selected instance:- Access Token Validation
- Bulk Import Status
- Configuration Export & Import
- Global Configurations
- Logging Level
- Provisioning
- Service Configurations
- NF Scoring
- Migration Tool Status
- Select the service to be used from the left navigation pane:
Figure 3-3 CNC Console Home Page with Services
Note:
The NF services appear in the left navigation pane for the EIR and SLF instance.
3.2 Egress Gateway
- In the left navigation pane, click UDR and then Egress Gateway.
- Using Egress Gateway, you can configure following services:
3.2.1 Configurable Error Codes
- In the CNC Console, click UDR and then Ingress Gateway or Egress Gateway
- For Ingress Gateway only, from the left navigation menu, navigate to the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click the Configurable Error
Codes option.
The Configurable Error Codes page is displayed with default values.
- Click Edit to update the
Configurable Error Codes
configuration.
The Edit Configurable Error Codes page is displayed.
- Click Add .
The Add Error Scenarios page is displayed.
- Update the configuration details as required and
click Save.
A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
. - Click Edit .
The Edit Error Scenarios page is displayed.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel.
- Click Delete and click OK to delete the selected configuration.
- Click Save on the Edit Configurable Error Codes page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Configurable Error Codes page.
- Click Refresh to reload the Configurable Error Codes page.
3.2.2 Error Code Profile
This configuration is used to update the errorcodeprofiles that is used in Overload Control, Controlled Shutdown feature for populating details in error responses when a request is discarded.
- In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Ingress Gateway or Egress Gateway
- For Ingress Gateway only, from the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click Error Code Profiles option.
The Error Code Profiles page is displayed with default values for few fields.
- Click Add to add the profiles.
The Create Error Code Profiles page is displayed.
. - Configure the fields in the Create Error Code Profiles page as mentioned in Table 3-1.
- Click Save on the Create Error Code Profiles page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Error Code Profiles page.
Note:
- Use the Edit icon available in the next column of the specific entry to update the route error profile information.
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the route error profile information.
Table 3-1 Error Code Profile Configuration
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Indicate the error name. | DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Error Code | This field determines the HttpStatusCode that needs to be populated in ProblemDetails (HttpStatus field) response from Ingress Gateway when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType field. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Error Cause | This field determines the error cause that needs to be populated in ProblemDetails (Cause field) response from Ingress Gateway when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: O |
| Error Title | This field determines the title that needs to be populated in ProblemDetails (Title field) response from Ingress Gateway when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: O |
| Redirect URL | This field determines the redirection URL, this value is populated in LOCATION header while sending response from Ingress Gateway. The header is populated only when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter, the errorCode configured for the particular errorScenario lies in 3xx error series and the redirectUrl field for the particular errorScenario is configured appropriately. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: O |
| Retry After | This field determines the value in seconds or particular date after which the service should be retried, this value is populated in Retry-After header while sending response from Ingress Gateway. The header is populated only when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter, the errorCode configured for the particular errorScenario lies in 3xx error series and the retry-after field for the particular errorScenario is configured appropriately in seconds. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: O |
| Error Description | This field determines the description that needs to be populated in ProblemDetails (Detail field) response from Ingress Gateway when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType field. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: O |
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.2.3 Peer Configuration
This URI is used to add or update the list of peers wherein each peer consists of ID, host, port or virtualHost, and apiPrefix. The ID of each peer is mapped to Peer Identifier in Peer Set Configuration. The default value is null.
Perform the following configurations:
- In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Egress Gateway.
- Click the Egress Gateway option to configure the Egress Gateway APIs.
- Click the Peer Configuration option under
Egress Gateway to configure peers.
The Peer Configuration page is displayed.
- Click Add to add the peer configuration.
The Create Peer Configuration page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Create Peer
Configuration page:
- ID: Enter a unique Peer identifier.
- Host: Enter the Host details of a local peer. It can be IPv4, IPv6, and FQDN details.
- Port: Enter the port details of the local host peer.
- API Prefix: Enter the API prefix details
of a peer.
Note: It is recommended to set the value as /.
- Virtual Host: Enter the Host details of a remote peer. This FQDN is sent to an alternate route service.
- healthApiPath: Parameter to support SCP health check API. It contains path of the health API
- Click Save on the Create Peer Configuration page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Peer Configuration page.
Note:
- Use Edit icon available in the next column of the specific entry to update configured the Peer Configuration information.
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the list of peers configured.
3.2.4 Peer Set Configuration
This URI is used to add or update the list of peer sets wherein each peer set consists of id and list of http/https instances. Each instance consists of priority and peer identifier that is mapped to id in peerconfiguration resource. The id of each peer set is mapped to peerSetIdentifier in routesconfiguration resource. The default value is null.
Perform the following configurations:
- In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Egress Gateway.
- Click the Egress Gateway option to configure the Egress Gateway APIs.
- Click the Peer Set Configuration option under
Egress Gateway to configure peers.
The Peer Set Configuration page is displayed.
- Click Add to add the peer set configuration.
The Create Peer Set Configuration page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Create Peer
Configuration page:
- ID: Enter a unique Peer set identifier.
- Click Add in HTTP
Configuration section to add HTTP Configuration. The
Add HTTP Configuration dialog box is displayed.
- Enter the following information on this page:
- Priority: Enter the Priority of peer to be used in a peer set.
- Peer Identifier: Enter the Peer identifier is the value of peer configured during Peer Configuration.
- Click Save to save HTTP Configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the dialog box, and go back to Create Peer Set Configuration page.
- Enter the following information on this page:
- Click Add in HTTPS
Configuration section to add HTTPs Configuration. The
Add HTTPS Configuration page is displayed.
- Enter the following information on this page:
- Priority: Enter the Priority of peer to be used in a peer set.
- Peer Identifier: Enter the Peer identifier is the value of peer configured during Peer Configuration.
- Click Save to save HTTP Configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the dialog box, and go back to Create Peer Set Configuration page.
- Enter the following information on this page:
- Click Save on the Create Peer Set Configuration page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Peer Set Configuration page.
Note:
- Use Edit icon available in the next column of the specific entry to update configured the Peer Set Configuration information.
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the list of peer sets configured.
3.2.5 Routes Configuration
The configuration of "routesconfiguration" is required for Server Header and Overload control feature to map route ID and its corresponding route-level configuration. By default, this configuration is null.
- In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Ingress Gateway or Egress Gateway
- For Ingress Gateway only, from the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click the Routes Configuration option.
The Routes Configuration page is displayed.
- Click Add to add the configuration.
The Create Routes Configuration page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Create Routes
Configuration page.
- ID: Value of "id" attribute defines a
specific service for route configuration. It specifies the route IDs for
which you need to define server header.
Note:
Ensure that route ID used in REST configuration is same as the route ID used in values.yaml file - URI: Enter URL, or leave the existing URL with existing value.
- Order: Provide the order of the execution of this route.
- FailureReqCountErrorCodeSeriesId: Indicates the ID that is used to map the service with the error code ID defined in errorcodeserieslist.
- Filters: Click
Add in the Filters
section and configure the following fields in Add
Filters window:
- args: Click
Add in the
args section and configure the
following fields in Add args window:
- Name: Enter the args name.
- Value: Enter the args value.
- Click Save on the Add args window to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Add Filters window.
- name: Enter the filter name.
- Click Save on the Add Filters page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Create Routes Configuration page.
- args: Click
Add in the
args section and configure the
following fields in Add args window:
- metadata: Click Add in the right side column to add metadata.
- predicates: Click
Add in the right side column to add
predicates.
Add predicates window is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the
Add predicates window:
- pattern: Enter pattern details.
- Name: Enter name of the predicate.
- Click Save to save predicates configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the window, and go back to Create Routes Configuration page.
- Configure the following fields in the
Add predicates window:
- rateLimiting: Click
Add in the right side column of
methods section to add methods.
Add methods window is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the
Add methods window:
- Name: Enter the method name.
- Rate: Enter the method rate.
- rateLimitPolicy: Enter the rateLimitPolicy name.
- Click Save to save methods configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the window, and go back to Create Routes Configuration page.
- Configure the following fields in the
Add methods window:
- serverHeaderDetails: Configure the
following fields in serverHeaderDetails
section:
- Enabled: Use the switch to enable or disable server header at route level.
- Error Code Series Id: :
Specify the error list ID.
Note:
Ensure that an errorCodeSeries exists corresponding to the errorCodeSeriesId.
- ID: Value of "id" attribute defines a
specific service for route configuration. It specifies the route IDs for
which you need to define server header.
- Click Save to save Routes configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the window, and go back to Create Routes Configuration page.
3.2.6 SBI Error Action Sets
This URI is used to list or update SBI error action sets configuration at Egress gateway. By default this configuration is disabled.
- In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Egress Gateway
- Click the Egress Gateway option to configure the Egress Gateway APIs.
- Click the SBI Error Action Sets option under
Egress Gateway to configure peers.
The SBI Error Action Sets page is displayed.
- Click Add to add an error action set
configuration.
The Create SBI Error Action Sets page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Create SBI Error
Action Sets page:
- ID: Enter an unique ID for SBI routing error action set.
- Action: The action that needs to be taken when specific criteria set is matched.
- Attempts: Maximum number of retries to either same or different peer in case of error or failures from backend.
- Black List: Perform the following
configuration:
- Enabled: This flag enables the peer blacklist feature using the server headers received in the response.
- Duration: The duration for which the peer is blacklisted and no traffic is routed to that peer for this period.
- Click Save on the Create SBI Error Action Sets page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to SBI Error Action Sets page.
Note:
- Use Edit icon available in the next column of the specific entry to update configured the SBI Error Action Sets information.
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the configuration.
3.2.7 SBI Error Criteria Sets
This URI is used to list or update SBI error criteria sets configuration at Egress Gateway. By default, this configuration is disabled.
- In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Egress Gateway
- Click the Egress Gateway option to configure the Egress Gateway APIs.
- Click the SBI Error Criteria Sets option
under Egress Gateway to configure peers.
The SBI Error Criteria Sets page is displayed.
- Click Add to add an error action set
configuration.
The Create SBI Error Criteria Sets page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Create SBI Error
Criteria Sets page:
- ID: Enter an unique ID for SBI routing error action set.
- Method: Indicate the action that needs to be taken when specific criteria set is matched.
- Exceptions: Enter the maximum number of retries to either same or different peer in case of error or failures from backend.
- Response: Configure the following
fields under Statuses section. Click
Add to add HTTP status details:
- Status Series: Enter the HTTP status series for which reroute or retry is triggered, when the error response is received from downstream.
- Status: Specify HTTP statuses that belongs to above mentioned status series for which reroute or retry is triggered. To enable retry or reroute for all the HTTP status belonging to a status series, configure this as -1.
- Click Save in Add Statuses window to save statuses configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Create SBI Error Criteria Sets page.
- Cause: Configure the following field
under Cause section.
- ignoreCauseIfMissing: Enable the switch to ignore cause if it is missing.
- Path: Enter path of the cause.
- Reason: Enter reason of the cause.
- Headers Matching Script: Enter headers matching script.
- Click Save on the Create SBI Error Criteria Sets page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to SBI Error Criteria Sets page.
- Click Refresh to reload the SBI Error Criteria Sets page.
3.2.8 User Agent Header Generation
This URI is used to Enable or Disable User-Agent Header.
- In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Egress Gateway
- Click the Egress Gateway option to configure the Egress Gateway APIs.
- Click the User Agent Header Generation option
under Egress Gateway to configure peers.
The User Agent Header Generation page is displayed with default configured values.
- Click Edit to update the User Agent Header
Generation.
The Edit User Agent Header Generation page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Edit User Agent
Header Generation page:
- Enabled: Use the switch to enable or disable User Agent Header feature.
- NF Type: : Attribute to configure the nfType that is used to generate the User Agent Header.
- NF Instance ID: : Indicates the UUID (Instance ID) of the UDR deployment used to generate the User Agent Header.
- NF FQDN: : Use the allow or deny User Agent from appending the UDR FQDN information while generating the User Agent Header.
- Add Fqdn To Header: : It indicates the number of successful responses after which an unhealthy SCP can be marked as healthy.
- Overwrite Header: Use this switch to
govern if you want to include the User Agent Header generated at UDR
Egress Gateway or forward the User Agent received from service
request.
Note:
- When User Agent Header is enabled but the header information is missing, then it is picked from the OAuthClient module.
- If the User Agent Header is present in the request towards AMF or NRF, then the value present in the header is overwritten or forwarded based on the Overwrite Header switch. If this switch is enabled, then the header is overwritten.
- Click Save on the Edit User Agent Header Generation page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to User Agent Header Generation page.
Note:
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the User Agent Header Generation.
3.3 Ingress Gateway
This section describes the Ingress Gateway configurations.
In the left navigation pane of the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Ingress Gateway.
You can select Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning to view their services.
- Configurable Error Codes
- Discard Policy Mapping
- Error Code Profile
- Error Code Series
- OAuth2 Configurations
- Overload Control Discard Policy
- Routes Configuration
- Route level Rate Limiting
- Server Header Details
- User Agent Header Validation
- Pod Protection
- Readiness Configuration
- Controlled Shutdown Error Mapping
- XFCC Header Validation
- Pod Protection By Rate Limiting
- Congestion Level Configuration
3.3.1 Configurable Error Codes
- In the CNC Console, click UDR and then Ingress Gateway or Egress Gateway
- For Ingress Gateway only, from the left navigation menu, navigate to the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click the Configurable Error
Codes option.
The Configurable Error Codes page is displayed with default values.
- Click Edit to update the
Configurable Error Codes
configuration.
The Edit Configurable Error Codes page is displayed.
- Click Add .
The Add Error Scenarios page is displayed.
- Update the configuration details as required and
click Save.
A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
. - Click Edit .
The Edit Error Scenarios page is displayed.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel.
- Click Delete and click OK to delete the selected configuration.
- Click Save on the Edit Configurable Error Codes page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Configurable Error Codes page.
- Click Refresh to reload the Configurable Error Codes page.
3.3.2 Discard Policy Mapping
This URI can be used to update service names and corresponding policy names for the service which is mapped to "ocDiscardPolicies" based on "policyName" and also to enable or disable the Overload Control feature and the sampling period in overload control. By default, the Overload Control feature is disabled and the sampling period is 6000.
Perform the following configurations:
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to UDR and click the Ingress Gateway option.
- For Ingress Gateway, from the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click the Discard Policy Mapping option.
The Discard Policy Mapping page is displayed with default configured values.
- Click Edit to update the Discard Policy
Mapping.
The Edit Discard Policy Mapping page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Edit Discard Policy
Mapping page:
- Enabled: Use the switch to enable or disable discard policy mapping.
- Mappings: Configure the following fields
in Mappings section. Click Add
to open Add Mappings window and add mapping details:
- Service Name: Enter the service
name. This field is used to determine a mapping between service and
discard policy name per service name. It must be added in the
following format:
<deployment-name>-<servicename>
Note: servicename is fixed and cannot be changed. - Policy Name: Enter the policy name. It determines a mapping between the service and discards policy name per service.
- Service Name: Enter the service
name. This field is used to determine a mapping between service and
discard policy name per service name. It must be added in the
following format:
- Click Save on the Add
Mappings window to save the details. Click
Cancel to discard your progress and go back to
Edit Discard Policy Mapping page.
Note:
- Use Edit icon to edit an existing configuration.
- Use Delete icon to remove an existing configuration.
- Sampling Period: Add sampling period. It is the time frame for each cycle of Overload Control per service. Its value is in milliseconds.
- Click Save on the Edit Discard Policy Mapping page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Discard Policy Mapping page.
Note:
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the peer monitoring configuration.
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.3 Error Code Profile
This configuration is used to update the errorcodeprofiles that is used in Overload Control, Controlled Shutdown feature for populating details in error responses when a request is discarded.
- In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Ingress Gateway or Egress Gateway
- For Ingress Gateway only, from the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click Error Code Profiles option.
The Error Code Profiles page is displayed with default values for few fields.
- Click Add to add the profiles.
The Create Error Code Profiles page is displayed.
. - Configure the fields in the Create Error Code Profiles page as mentioned in Table 3-1.
- Click Save on the Create Error Code Profiles page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Error Code Profiles page.
Note:
- Use the Edit icon available in the next column of the specific entry to update the route error profile information.
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the route error profile information.
Table 3-2 Error Code Profile Configuration
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Indicate the error name. | DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Error Code | This field determines the HttpStatusCode that needs to be populated in ProblemDetails (HttpStatus field) response from Ingress Gateway when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType field. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Error Cause | This field determines the error cause that needs to be populated in ProblemDetails (Cause field) response from Ingress Gateway when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: O |
| Error Title | This field determines the title that needs to be populated in ProblemDetails (Title field) response from Ingress Gateway when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: O |
| Redirect URL | This field determines the redirection URL, this value is populated in LOCATION header while sending response from Ingress Gateway. The header is populated only when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter, the errorCode configured for the particular errorScenario lies in 3xx error series and the redirectUrl field for the particular errorScenario is configured appropriately. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: O |
| Retry After | This field determines the value in seconds or particular date after which the service should be retried, this value is populated in Retry-After header while sending response from Ingress Gateway. The header is populated only when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter, the errorCode configured for the particular errorScenario lies in 3xx error series and the retry-after field for the particular errorScenario is configured appropriately in seconds. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: O |
| Error Description | This field determines the description that needs to be populated in ProblemDetails (Detail field) response from Ingress Gateway when the exception occurred at Ingress Gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType field. | DataType: integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: O |
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.4 Error Code Series
This configuration is used to map errorCodeSeries id and the corresponding errorCodeSeries configuration. By default this configuration is null.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to UDR and click the Ingress Gatewayoption.
- For Ingress Gateway, from the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click Error Code Series option.
The Error Code Series page is displayed.
- Click Add to add the error code series.
The Create Error Code Series page is displayed.
- Configure the fields in the Create Error Code Series page as mentioned in Table 3-3.
- Click Add in the Error Code Series
section.
The Add Error Code Series page is displayed.
- Configure the fields in the Add Error Code Series page as mentioned in Table 3-4.
- Click Save on the Add Error Code Series page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Create Error Code Series page.
- Click Save on the Create Error Code Seriespage to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Error Code Series page.
Note:
- Use the Edit icon or Delete available in the next column of the specific entry to update or delete the error code series information.
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the error code series information.
Table 3-3 Error Code Series
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| ID | Indicates the error code identifier. | DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Exception List |
Lists the configurable exception or error for an error scenario in Ingress Gateway. The only supported values are: ConnectionTimeout, RequestTimeout, UnknownHostException, ConnectException, RejectedExecutionException, InternalError and NotFoundException, ClosedChannelException, BlackListIpException |
DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Error Code Series |
Lists the error codes for a specific service. Note: "ErrorCodeSeries" is configured only if a set of error responses with specific error codes is expected in server header. If it is not configured then all the error responses will have server header. |
DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
Table 3-4 Error Code Series Configuration
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Error Set | Possible values for "errorSet" attribute: 5xx, 4xx, 3xx, 2xx, 1xx | DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Error Codes |
Possible values include all error codes in the respective HttpSeries value assigned for "errorSet". Note: Use single value of "-1" if all error codes in that HttpSeries are to be considered. |
DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.5 OAuth2 Configurations
This REST API configuration is required for enabling access token validation using NRF Instance ID and key-ID (K-ID).
Before this configuration, perform the prerequisite steps and helm configuration explained in Oauth2.0.
After Helm configuration, send the REST requests to use configured public key certificates. Using REST-based configuration, you can distinguish between the certificates configured on different NRFs and can use these certificates to validate the token received from a specific NRF.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to UDR and click the Ingress Gatewayoption.
- For Ingress Gateway, from the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click the OAuth2 Configurations option.
The OAuth2 Configurations page is displayed.
- Click Edit to add the OAuth2
Configurations.
The Edit OAuth Signaling page or Edit OAuth Provisioning is displayed.
for Ingress Gateway Signaling and Ingress Gateway Provisioning respectively. - Configure the following fields in the Edit OAuth
Signaling page or Edit OAuth Provisioning
page:
- Key ID List: Click
Add in the Key ID List
section and configure the following fields in Add Key ID
List window:
- Key ID: Enter the Key-ID.
- Kubernetes Secret Name: Enter Kubernetes Secret Name.
- Kubernetes Secret Key For Certificate: Enter Kubernetes Secret Key for the certificate.
- Access Token Generation Algorithm: Enter the Access Token Generation Algorithm.
- Click Save on the Add Key ID List page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the window, and go back to Edit OAuth Signaling or Provisioning page.
- Instance ID List: Click
Add in the Instance ID
List section and configure the following fields in
Add Instance ID List window:
- Instance ID: Enter the NRF Instance ID.
- Kubernetes Secret Name: Enter the Kubernetes Secret Name.
- Kubernetes Secret Key For Certificate: Enter Kubernetes Secret Key for the certificate.
- Access Token Generation Algorithm: Enter the Access Token Generation Algorithm.
- Key ID List: Click
Add in the Key ID List
section and configure the following fields in Add Key ID
List window:
- Click Save on the Add Instance ID List page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the window, and go back to Edit OAuth Signaling or Provisioning page.
- Access Token Validation Mode: Enter the mode of validation, which are INSTANCEID_ONLY, KID_ONLY, or KID_PREFERRED. It will check for keyIdList or instanceIdList for validation of token received based on mode selected.
- Click Save on the Edit OAuth Signaling or Provisioning page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Edit OAuth Signaling or Provisioning page.
Note:
- Use Edit icon available in the next column of the specific entry to update the Key ID List or Instance ID List.
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the configuration.
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.6 Overload Control Discard Policy
This configuration is used to update discard policies that are used in
overload control to select the appropriate policy from the configured list based on the
load level of a particular service. By default, ocdiscardpolicies is
null.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to UDR and click the Ingress Gateway option.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress
Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway
Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling
or Provisioning APIs.
The Overload Control Discard Policy page is displayed.
- Click Add to add the configuration.
The Create Overload Control Discard Policy page is displayed.
- Configure the fields in the Create Overload Control Discard Policy page as mentioned in Table 3-5.
- Click Add in the Policies
section.
The Add Policies page is displayed.
- Configure the fields under the Add Policies page as mentioned in Table 3-6.
- Click Save on the Add Policies page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Create Overload Control Discard Policy page
- Click Save on the Create Overload Control Discard Policy page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Overload Control Discard Policy page
Note:
- Use the Edit icon available in the next column of the specific entry to update the policy information.
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the policy information.
Table 3-5 Discard Policy Configuration
| Attribute Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Name |
Name of the discarded policy. Note: name must be the value configured in policyName under ocpolicymapping. |
DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Scheme | Discarded policy scheme based on percentage. | DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
Table 3-6 Policies
| Attribute Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Value | Value of priority above which requests are considered as potential candidates for drop. Percentage of requests to drop in the current sampling period over the calculated rate in the previous sampling period. | DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Action | Defines the action to be taken on selected requests rejection based on error code. | DataType: string
The value can be: RejectWithErrorCode Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Level | Defines the overload level. | DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
| Error Code Profile | Define the error code profiles. | DataType: string
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA Presence: M |
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.7 Routes Configuration
The configuration of "routesconfiguration" is required for Server Header and Overload control feature to map route ID and its corresponding route-level configuration. By default, this configuration is null.
- In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Ingress Gateway or Egress Gateway
- For Ingress Gateway only, from the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click the Routes Configuration option.
The Routes Configuration page is displayed.
- Click Add to add the configuration.
The Create Routes Configuration page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Create Routes
Configuration page.
- ID: Value of "id" attribute defines a
specific service for route configuration. It specifies the route IDs for
which you need to define server header.
Note:
Ensure that route ID used in REST configuration is same as the route ID used in values.yaml file - URI: Enter URL, or leave the existing URL with existing value.
- Order: Provide the order of the execution of this route.
- FailureReqCountErrorCodeSeriesId: Indicates the ID that is used to map the service with the error code ID defined in errorcodeserieslist.
- Filters: Click
Add in the Filters
section and configure the following fields in Add
Filters window:
- args: Click
Add in the
args section and configure the
following fields in Add args window:
- Name: Enter the args name.
- Value: Enter the args value.
- Click Save on the Add args window to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Add Filters window.
- name: Enter the filter name.
- Click Save on the Add Filters page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Create Routes Configuration page.
- args: Click
Add in the
args section and configure the
following fields in Add args window:
- metadata: Click Add in the right side column to add metadata.
- predicates: Click
Add in the right side column to add
predicates.
Add predicates window is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the
Add predicates window:
- pattern: Enter pattern details.
- Name: Enter name of the predicate.
- Click Save to save predicates configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the window, and go back to Create Routes Configuration page.
- Configure the following fields in the
Add predicates window:
- rateLimiting: Click
Add in the right side column of
methods section to add methods.
Add methods window is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the
Add methods window:
- Name: Enter the method name.
- Rate: Enter the method rate.
- rateLimitPolicy: Enter the rateLimitPolicy name.
- Click Save to save methods configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the window, and go back to Create Routes Configuration page.
- Configure the following fields in the
Add methods window:
- serverHeaderDetails: Configure the
following fields in serverHeaderDetails
section:
- Enabled: Use the switch to enable or disable server header at route level.
- Error Code Series Id: :
Specify the error list ID.
Note:
Ensure that an errorCodeSeries exists corresponding to the errorCodeSeriesId.
- ID: Value of "id" attribute defines a
specific service for route configuration. It specifies the route IDs for
which you need to define server header.
- Click Save to save Routes configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the window, and go back to Create Routes Configuration page.
3.3.8 Route Level Rate Limiting
This section describes how to configure Route Level Rate Limiting using the CNC Console.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to UDR and click the Ingress Gateway option.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click the Route Level Rate Limiting option.
The Route Level Rate Limiting page is displayed.
- Click Edit to update the Route Level Rate
Limiting.
The Edit Route Level Rate Limiting page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Edit Route Level
Rate Limiting page:
- Enabled: Use the switch to enable or disable Route Level Rate Limiting.
- Sampling Period: Add sampling period.
- Rate Limit Policies: Configure the
following fields in Rate Limit Policies section.
Click Add to open Add Rate Limit
Policies window and add Rate Limit Policies details:
- Name: Enter the rate limit policy name.
- Value: Value of priority above which requests are considered as potential candidates for drop. Percentage of requests to drop in the current sampling period over the calculated rate in the previous sampling period..
- Action: Defines the action to be taken on selected requests rejection based on error code.
- Scheme: Rate limit policy scheme based on percentage.
- Error Code Profile: Define the error code profiles.
- Click Save on the Add
Rate Limit Policies window to save the details. Click
Cancel to discard your progress and go back
to Edit Route Level Rate Limiting page.
Note:
- Use Edit icon to edit an existing configuration.
- Use Delete icon to remove an existing configuration.
- Click Save on the Edit Route Level Rate Limiting page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Route Level Rate Limiting page.
Note:
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the Route Level Rate Limiting.
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.9 Server Header Details
This API can be used for adding Server Header in the error responses sent from Ingress Gateway. By default, this feature is disabled. To enable the feature, invoke the following REST API and update the enable switch.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to UDR and click the Ingress Gateway option.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling .
- Click the Server Header Details option.
The Server Header Details page is displayed with default configured values.
- Click Edit to update the Server Header
Details.
The Edit Server Header Details page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Edit Server Header
Details page:
- Enabled: Use the switch to enable or disable Server Header.
- Error Code Series Id: Specify the
error list ID.
Note:
Ensure that an Error Code Series exists corresponding to the errorCodeSeriesId. - Configuration: Configure the
following fields in Configuration section:
- NF Type: Specify the type of network function. In this case, it is UDR.
- NF Instance Id:: Enter the UDR instance ID.
- Click Save on the Edit Server Header Details page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Server Header Details page.
Note:
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the Server Header Details.
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.10 User Agent Header Validation
This section describes how to configure User Agent Header Validation using the CNC Console.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to UDR and click the Ingress Gateway option.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling .
- Click the User Agent Header Validation option
under Ingress Gateway Signaling to configure peers.
The User Agent Header Validation page is displayed with default configured values.
- Click Edit to update the User Agent Header
Validation.
The Edit User Agent Header Validation page is displayed.
- Configure the following fields in the Edit User Agent
Header Validation page:
- Enabled: Use the switch to enable or disable User Agent Header feature.
- Validation Type: Add the required validation type.
- Consumer NF Types: Attribute to configure the consumer nfType.
- Click Save on the Edit User Agent Header Validation page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to User Agent Header Validation page.
Note:
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the User Agent Header Validation.
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.11 Pod Protection
This configuration is used to configure the pod protection for Ingress Gateway pod.
Note:
- Use the Edit icon available in the next column of the specific entry to update or delete the states information.
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the states information.
Table 3-7 Pod Protection Options
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | This attribute indicates if the Pod Protection feature is enabled or disabled. | DataType: Boolean
Constraints: true, false Default Value: false |
| Monitoring Interval |
This attribute indicates the periodicity at which the overload state is monitored. Unit: Milliseconds Note: The proposed value for this attribute is 100. |
DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
Table 3-8 Congestion Control Configurations
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | This attribute allows the configuration of pod
protection attributes for the Ingress Gateway pods.
Note: This must be set to
|
DataType: Boolean
Constraints: true, false Default Value: false |
| State Change Sample Count |
This attribute indicates the number of times the pod must be in the particular congestion state before transitioning to another state. Note: The proposed value for this attribute is 10. |
DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
| Action Sampling Period |
This attribute indicates the interval at which
the configured action must be considered. The actions are
configured under The interval is calculated as
( Note: The proposed value for this attribute is 3. |
DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
Table 3-9 States
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Name |
The name of the congestion state.
|
DataType: String
Constraints: Normal, Doc, Congested Default Value: NA |
| Weight | The weight of the congestion state. The weight indicates the critical of the congestion state. The lower the value, the lower the criticality. | DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
Table 3-10 Congestion Control Threshold
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | The CPU threshold is expressed in percentage. | DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
| Pending Message | The number of pending messages to be processed,
expressed in absolute count.
Note:: The recommended value for this attribute is for DoC is 1500 and for Congested is 2000. |
DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
Table 3-11 Entry Action
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Action | This attribute indicates the action for the
congestion state.
|
DataType: String
Constraints: MaxConcurrentStreamsUpdate, AcceptIncomingConnections Default Value: NA |
Table 3-12 Possible Arguments
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Accept | The attribute indicates if the incoming
connection should be accepted or not. Applicable when the action
is AcceptIncomingConnections.
true: The incoming connection is accepted. false: The incoming connection is rejected. The proposed value for Normal
state is |
DataType: Boolean
Constraints: true, false Default Value: NA |
| Increment by | The attribute indicates the factor by which the
current concurrent streams value will be incremented till it
reaches maxConcurrentStreamsPerCon.
Note: The proposed value for this attribute is 30 for Normal and DoC state. |
DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
| Increment by Action Sampling Period | The attribute indicates the time interval at
which the incrementBy is applied to reach
maxConcurrentStreamsPerCon. If not
provided, the actionSamplingPeriod is used.
Note: The proposed value for this attribute is 3 for Normal and DoC state. Unit is seconds. |
DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
| Decrement by |
The attribute indicates the factor by which the
current concurrent streams value will be decremented till it
reaches Note: The proposed value for this attribute is 30 for DoC and Congested state. |
DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
| Decrement by Action Sampling Period | The attribute indicates the time interval at
which the decrementBy is applied to reach
maxConcurrentStreamsPerCon. If not
provided, the actionSamplingPeriod is used.
Note: The proposed value for this attribute is 1 for DoC and Congested state. Unit is seconds. |
DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
| Max Concurrent Streams Per Con | The attribute indicates the maximum number of concurrent streams per connection allowed. | DataType: Integer
Constraints: NA Default Value: NA |
Note:
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the Pod Protection.
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.12 Readiness Configuration
This section describes how to configure Readiness Configuration using the CNC Console.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to UDR and click the Ingress Gateway option.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click the Readiness Configuration option.
The Readiness Configuration page is displayed.
- Click Edit to add the configuration.
The Edit Readiness Configuration page is displayed.
- Click Add to add the configuration.
The Add Service Profiles page is displayed.
- Update the configuration details as required in the Add Service Profiles page.
- Click Save to save the configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress, close the window, and go back to Edit Readiness Configuration page.
- Click Save to save Readiness Configuration. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Readiness Configuration page.
3.3.13 Controlled Shutdown Error Mapping
This configuration is used for mapping between the routes and the error code profile that is used when the Ingress Gateway rejects incoming requests.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to UDR and click the Ingress Gateway option.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling or Ingress Gateway Provisioning option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling or Provisioning APIs.
- Click Controlled Shutdown Error Mapping option.
The Controlled Shutdown Error Mapping page is displayed.
- Click Edit to edit the configuration.
The Edit Controlled Shutdown Error Mapping page is displayed.
- Click Add in the Edit Controlled Shutdown
Error Mapping section.
The Add Route Error Profile List page is displayed.
- Configure the fields in the Add Route Error Profile List page as mentioned in Table 3-13.
- Click Save on the Add Route Error Profile List page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Edit Controlled Shutdown Error Mapping page.
- Click Save to save Controlled Shutdown Error Mapping. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Controlled Shutdown Error Mapping page.
Note:
- Use Refresh icon to refresh the Route Level Rate Limiting.
Table 3-13 Controlled Shutdown Error Mapping
| Field Name | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Route ID | The route id that is configured in routes configuration. |
DataType: string Constraints: NA Possible values: <subscription_mapping, accesstoken_mapping, registration_mapping, disc_mapping> The possible values should match with the routeId of the routes configuration. Default Value: NA |
| Error Profile Name | The error profile name that is used to fetch the error from errorcodeprofiles. |
DataType: string Constraints: NA Default Value: shutdownerror503 |
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.14 XFCC Header Validation
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to UDR and click the Ingress Gateway option.
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling option to configure the Ingress Gateway Signaling APIs.
- Click the XFCC Header Validation option.
The XFCC Header Validation page is displayed with default values.
- Click Edit to update the XFCC
Header Validation configuration.
The Edit XFCC Header Validation page is displayed.
- Click Add.
The Add PeerList page is displayed.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save.
- Click Edit .
The Edit PeerList page is displayed.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel.
- Click Delete and click OK to delete the selected configuration.
- Click Save on the Edit XFCC Header Validation page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to XFCC Header Validation page.
- Click Refresh to reload the Configurable Error Codes page.
For more information about the configuration parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.3.15 Congestion Level Configuration
Perform the following procedure to configure the congestion level of the pods.
- In the CNC Console, click UDR and then Ingress Gateway
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling.
- Click the Congestion Level Configuration option
under Ingress Gateway Signaling.
The Congestion Level Configuration page is displayed.
- Click Edit to edit the configuration.
The Edit Congestion Level Configuration page is displayed.
- Configure the fields in the Edit Congestion Level Configuration
page as follows:
Table 3-14 Congestion Level Configuration
Field Name Description Details Refresh Interval (seconds) This attribute indicates the refresh interval for the scheduler to calculate congestion level in milliseconds. CPU levels are stable when tested with values more than 500 ms as a refresh interval. Any value less than this, the CPU spikes are observed for a shorter period of time, and denied requests are processed based on the action defined for that congestion level.
Data Type: Integer
Constraints: NA
Default Value: 500
Levels This attribute indicates an array of different levels of congestion. Data Type: Object
Constraints: NA
Default Value: NA
- Click Add to add the configuration levels.
- Configure the fields in the Add Levels page as follows:
Table 3-15 Congestion Levels
Attribute Name Description Details Level Name Indicates the name of the congestion level.
The possible values are Normal, Danger of Congestion, and Congested.
Data Type: String
Constraints: Normal, Danger of Congestion, Congested
Default Value: NA
Level Value Indicates numerical values for each congestion level. The value ranges from 1-10.
The values should be defined from 1 to 10 in increasing order. The default level of the system is 0. This is the state of the system when the CPU is less than the onset of L1 defined in the configuration.
Data Type: Integer
Constraints: 1 -10
Default Value: 0
Resources Indicates the list of resources. Data Type: Object
Constraints: NA
Default Value: NA
- Click Add to add the resource details.
- Configure the fields in the Add Resources page as mentioned in
the below table.
Table 3-16 Resources
Attribute Name Description Details Resource Name Indicates the resource names. The possible value is CPU. Data Type: String
Constraints: NA
Default Value: CPU
Onset Threshold Indicates the onset threshold.
Note: Onset must be more than the level of abatement. It is denoted by percentage.
Data Type: Integer
Constraints: NA
Default Value: NA
Abatement Threshold Indicates the abatement threshold. It is denoted by percentage.
Note:
- Abatement must be less than the onset of the same level.
- Abatement must be more than the onset of the previous level.
Data Type: Integer
Constraints: NA
Default Value: NA
- Click Save on the Add Resources page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to the Add Levels page.
- Click Save on the Add Levels page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Edit Congestion Level Configuration page.
- Click Save on the Congestion Level Configuration page to save the details.
3.3.16 Pod Protection By Rate Limiting
- In the CNC Console, click UDR and then Ingress Gateway
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Ingress Gateway Signaling.
- Click the Pod Protection By Rate Limiting
option under the Ingress Gateway Signaling.
The Pod Protection By Rate Limiting page is displayed.
- Click Edit to edit the configuration.
The Edit Pod Protection By Rate Limiting page is displayed.
- Configure the fields in the Edit Pod Protection By Rate
Limiting page as mentioned in the following table.
Table 3-17 Pod Protection By Rate Limiting
Field Name Description Details Enabled The attribute indicates if rate limiting feature is enabled for the Ingress Gateway pod protection. Data Type: Boolean Constraints: true or false
Default Value: false
Fill Rate This attribute indicates the number of requests to be processed by an Ingress Gateway pod in one second (1000 ms). Data Type: Integer
Constraints: more than 0
Default Value: 2800
Unit: milliseconds
Routes This attribute indicates the route levels for the rate limiting. Data Type: Array (object of Routes)
Constraints: NA
Default Value: For more information, see Table 3-18.
Error Code Profile This attribute indicates the error profile to be sent for the rejected requests. Data Type: String
Constraints: HELM, REST, ERR_RATE_LIMIT
Default Value: error429
Denied Request Actions This attribute indicates the request actions to be performed for the rejected requests. Data Type: Object
Constraints: NA
Default Value: For more information, see Table 3-19.
Priority Header Name Determines the priority of the request using the configured header. Indicates the name of the header.. Data Type: String
Constraints: NA
Default Value: 3gpp-sbi-message-priority
Default Priority This attribute determines the priority of the request. Data Type: Integer
Constraints: 0-31
Default Value: 24
- Click Add in the Routes section to configure the different routes for Pod Protection By Rate Limiting feature.
- The page is displayed.
- Configure the fields in the Add Routes page as
follows:
Table 3-18 Routes
Field Name Description Details Id Indicates the route ID that processes the request.
The number of route IDs can be more than 1.
Data Type: Integer
Constraints: 1-10
Default Value: 1
Path Indicates the path to be matched to apply fill rate on the route. Data Type: String
Constraints: NA
Default Value: /nudr-group-id-map/**
Methods Indicates the HTTP method of the route for which the rate limiting is defined.
All valid HTTP methods are allowed, for example:
- POST
- PUT
- PATCH
- DELETE
- GET
Data Type: String
Constraints:- POST
- PUT
- PATCH
- DELETE
- GET
Default Value: GET
Percentage This attribute indicates the percentage of requests for a route.
If the fill rate is 1000 and
routes.percentageis 40%, the route process 400 requests in 1000 ms.The minimum value is 0.1.
Note: The total percentage across all routes must not exceed 100.
Data Type: Integer
Constraints: 1-100
Default Value: 100
Default Priority This attribute determines the priority of the request. Data Type: Integer
Constraints: more than 1
Default Value: 24
- Click Save on the Add Routes page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Edit Pod Protection By Rate Limiting page.
- Click Add in the Denied Request Actions section to configure the actions for rejected requests.
- The Add Denied Request Actions page is displayed.
- Configure the fields in the Add Denied Request Actions page
as follows:
Table 3-19 Denied Request Actions
Field Name Description Details Id Indicates the unique ID of the rejected request. Data Type: Integer
Constraints: 1-10
Default Value: 1,2,3,4
Congestion Level Indicates the congestion level of the pods.
This value depends on the value field in the congestion level configuration or the default value 0. For more information about congestion level configuration, see Congestion Level Configuration.Data Type: Integer
Constraints: 1-10
Default Value: 0,1,2,3,4
Action Rejects or processes a denied request based on the value of
congestionLevelattribute in thedeniedRequestActionsobject.The possible values are REJECT and CONTINUE.
Data Type: String
Constraints: REJECT, CONTINUE
Default Value:
0- CONTINUE
1- CONTINUE
2- REJECT
3- REJECT
Error Code Profile Indicates a valid error code for the rejected requests based on the action. Data Type: String
Constraints: Any error code profile that is configured using
errorcodeprofilesAPIDefault Value: error429
- Click Save on the Add Denied Request Actions page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Edit Pod Protection By Rate Limiting page.
- Click Save on the Edit Pod Protection By Rate Limiting page to save the details. Click Cancel to discard your progress and go back to Pod Protection By Rate Limiting page.
3.4 cnDBTier
Note:
The following cnDBTier APIs are read only.3.4.1 cnDBTier Health
- From the left navigation pane, click the UDR tab, and then click the cnDBTier tab. The cnDBTier page is displayed.
- Click cnDBTier Health to view the health
status of the databases and their services.
The cnDBTier Health page is displayed.
-
Click the Backup Manager Health Status to view the health status of the backup manager.
The Backup Manager Health Status page is displayed.
Note:
The following APIs are read-only.Table 3-20 Backup Manager Health Status
Fields Description Service Name This attribute displays the name of the service. Service Status This attribute displays the status of the service. Possible values are UP, DOWN. DB Connection Status This attribute displays the database connection status. Possible values are UP, DOWN. Overall Backup Manager Service Health This attribute displays the overall health status of the backup manager service. Possible values are UP, DOWN. Backup Executor Health Status This attribute displays the details of the backup executor. Node Id This attribute displays the id of the node. DB Connection Status This attribute displays the database connection status with the nodes. Possible values are UP, DOWN. - Click the Monitor Health Status to
view the health status of the services.
The Monitor Health Status page is displayed.
Note:
The following APIs are read-only.Table 3-21 Monitor Health Status details
Attribute Description Service Name This attribute displays the database service name. DB Connection Status This attribute displays the database connection status. Possible values are UP, DOWN. Metric Scrape Status This attribute displays the status of the metric scrape, that is if the metrics are fetched or not. If the metrics are fetched then the service is up and vice versa. Possible values are UP, DOWN. Overall Monitor Service Health This attribute displays the overall health status of the monitor service. Possible values are UP, DOWN. - Click the NDB Health Status to view
the health status of the network database.
The NDB Health Status page is displayed.
Note:
The following APIs are read-only.Table 3-22 NDB Health Status details
Attribute Description Local Site Name This attribute displays the name of the local site. NDB Health Status Details This attribute displays the health status of the network database. Service Name This attribute displays the name of the service. Service Status This attribute displays the status of the service. Possible values are UP, DOWN. PVC Health Status This attribute displays the health status of the PVC. Possible values are UP, DOWN, and NA. Note: This attribute is set to NA when some of the database pods are not connected to the PVC.
- Click the Replication Health Status
to view the health status of the replication sites.
The Replication Health Status page is displayed.
Note:
The following APIs are read-only.Table 3-23 Replication Health Status details
Attribute Description Local Site Name This attribute displays the name of the local site. Health Status Details This attribute displays the health status details. The number of rows in this table varies depending on the type of deployment (for example, two-site, three-site deployments). Service Name This attribute displays the name of the available service. Service Status This attribute displays the status of the available service. Possible values are UP, DOWN. DB Connection Status This attribute displays the database connection status. Possible values are UP, DOWN. Overall Replication Service Health This attribute displays the overall health status of the replication service. Possible values are UP, DOWN.
-
3.4.2 Backup List
- From the left navigation pane, click the UDR tab, and then click the cnDBTier tab. The cnDBTier page is displayed.
- Click the Backup List to create and check the
status of on-demand backups in the cnDBTier.
Table 3-24 Backup List
Fields Description Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which UDR is connected. Backup Details This attribute displays the following information such as backup id, backup size, and backup creation timestamp. Backup Id This field displays the ID of the stored backup. Backup Size (bytes) This field displays the size of the stored backup. Creation TimeStamp This field displays the time recorded when the backup was stored.
3.4.3 cnDBTier Backup Status
- From the left navigation pane, click the UDR tab, and then click the cnDBTier tab. The cnDBTier page is displayed.
- Click the cnDBTier Backup Status to check the
status of backups in the cnDBTier.
Table 3-25 cnDBTier Backup Status
Fields Description Current Timestamp This field displays the current date and time. Is Backup in Progress This field displays whether the On Demand Backup is in progress or not. Next Backup Scheduled Timestamp This field displays the scheduled (date and time) of the next On Demand Backup.
3.4.4 cnDBTier Version
- From the left navigation pane, click the UDR tab, and then click the cnDBTier tab. The cnDBTier page is displayed.
- Click the cnDBTier Version to view the
version.
Table 3-26 cnDBTier Version Attributes
Fields Description cnDBTier Version This field displays the cnDBTier version. NDB Version This field displays the network database (NDB) version.
3.4.5 Database Statistics Report
- From the left navigation pane, click the UDR tab, and then click the cnDBTier tab. The cnDBTier page is displayed.
- Click the Database Statistics Report to view
the available database.
Table 3-27 Database Statistics Report
Fields Description Database Count This field displays the number of available database. Database Tables Count This field displays the available database names and their table count. Database Name This field displays the database name. Table Count This field displays the table count for each database. Database Table Rows Count This field displays the table rows present in each table. Database Name This field displays the database name. - Click on the View. The View Database Table Rows Count page is displayed.
Table 3-28 View Database Table Rows Count
Fields Description Database Name This field displays the database name. Tables This field displays the table names and the corresponding rows in each table. Database Name This field displays the database name. Table Name This field displays the table name. Row Count This field displays the table rows present in each table.
3.4.6 Georeplication Recovery
Perform the following procedure to mark cnDBTier cluster as failed, execute georeplication recovery, and monitor their status:
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to NRF and then click cnDBTier tab.
- Click Georeplication Recovery to access the Georeplication
Recovery Status of the cnDBTier cluster. This includes options such as Update
Cluster As Failed, Start Georeplication Recovery, and Georeplication Recovery
Status.
- Click Update Cluster As Failed to mark the cnDBTier
cluster as FAILED.
The Update Cluster As Failed page is displayed.
Table 3-29 Update Cluster As Failed
Fields Description Cluster Names This field displays a list of cnDBTier clusters that can be marked as failed. Failed Cluster Names This field displays the list of cnDBTier clusters that are marked as failed. Click Update Cluster. The selected cnDBTier cluster name is updated in the Failed Cluster Names field.
- Click Start Georeplication Recovery to start the
georeplication recovery process for a failed site.
The Start Georeplication Recovery page is displayed.
Table 3-30 Start Georeplication Recovery
Attribute Description Failed Cluster Name This field displays a list of all the cnDBTier clusters that have been marked as failed. Backup Cluster Name (Optional) This field displays a list of all the healthy cnDBTier clusters. If no cnDBTier cluster is selected, the system uses the first available healthy cnDBTier cluster for the backup. Click Start Georeplication Recovery to initiate georeplication recovery.
- Click Georeplication Recovery Status to view the status
of georeplication recovery for cnDBTier clusters.
The Georeplication Recovery Status page is displayed.
Table 3-31 Georeplication Recovery Status
Attribute Description Local Cluster Name This field displays the name of the local cnDBTier cluster. Georeplication Recover Status Details This field displays the details of the georeplication recovery status of cnDBTier clusters. Cluster Name This field displays the cnDBTier clusters by name. Georeplication Recovery Status This field displays the current georeplication recovery status of the corresponding cnDBTier cluster. For more information about the georeplication recovery status, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, cnDBTier User Guide.
- Click Update Cluster As Failed to mark the cnDBTier
cluster as FAILED.
3.4.7 GeoReplication Status
- From the left navigation pane, click the UDR tab, and then click the cnDBTier tab. The cnDBTier page is displayed.
- Click the GeoReplication Status to view the
local site and remote site name to which UDR is connected.
Table 3-32 GeoReplication Status
Fields Description Local Site Name This field displays the local site name to which UDR is connected. Remote Site Name This field displays the remote site name. Replication Status This field displays the replication status with corresponding sites. Seconds Behind Remote Site This field displays the number of seconds that the last record read by the local site is behind the latest record written by the remote site for all the replication groups. - Click the View icon in the
Actions menu to view the View Geo
Replication Status screen.
Table 3-33 Geo Replication Status
Fields Description Replication Group Delay This field displays the number of seconds that the last record read by the local site is behind the latest record written by the remote site for individual replication groups. Replication Channel Group Id This field displays the ID of the replication channel group. - Click the View icon to view the
Replication Group Delay attributes:
Table 3-34 View Replication Group Delay
Fields Description Channel Details This field displays the channel details such as Remote Replication IP and Role. Remote Replication IP This field displays the IP of the remote replication channel. Role This field displays the role of the replication channel IP.
3.4.8 HeartBeat Status
- From the left navigation pane, click the UDR tab, and then click the cnDBTier tab. The cnDBTier page is displayed.
- Click the HeartBeat Status to view the
connectivity between local site and remote site name to which UDR is
connected.
Table 3-35 HeartBeat Status Details
Fields Description Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which NRF is connected. HeartBeat Details This field displays the following information like remote site name, heart beat status, heart beat lag, and replication channel group id. Remote Site Name This field displays the remote site name. Heartbeat Status This field displays the connectivity status with corresponding sites. Heartbeat Lag This field displays the lag or latency in seconds it took to synchronize between sites. Replication channel Group Id This field displays the ID of the replication channel group.
3.4.9 Local Cluster Status
- From the left navigation pane, click the UDR tab, and then click the cnDBTier tab. The cnDBTier page is displayed.
- Click the Local Cluster Status to view the
local cluster status for the current site:
Table 3-36 Local Cluster Status
Fields Description Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which UDR is connected. Cluster Status This field displays the local cluster status for the current site.
3.4.10 On Demand Backup
- From the left navigation pane, click the UDR tab, and then click the cnDBTier tab. The cnDBTier page is displayed.
- Click the On Demand Backup to view the
initiated on-demand backups to store data.
Table 3-37 On Demand Backup Details
Fields Description Site Name This field displays the name of the current site to which UDR is connected. DR Status This field displays the status of DR. Backup Id This field displays the ID of the stored backup. Backup Status This field displays the status of backup. Remote Transfer Status The field displays the status of remote transfer. Initiate Backup The field displays whether the backup is initiated or not. - Click Edit. The
Edit On Demand Backup page appears.
Note:
The Edit mode is available only for Initiate Backup. - Use the toggle option to Initiate Backup and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully" appears.
- Click Cancel to navigate back to the On Demand Backup page.
- Click Refresh to reload the On Demand Backup page.
- Click Edit. The
Edit On Demand Backup page appears.
3.5 Access Token Validation
To validate an access token, go to UDR then, Access Token Validation in the left navigation pane of the CNC Console application, and then Signaling or Provisioning. Based on the selected option, the Access Token Validation page for either Signaling or Provisioning appears, respectively.
This page when loads for the first time shows empty value with labels.
To edit this configuration, you are required to set the Oauth validation flag as true at the time of NF installation. Otherwise, it sends a Bad Request Response. For more information, see Oauth2.0.
Editing the Access Token Validation Details
To edit the access token details:
- Click Edit. The Edit Access Token Validation page appears.
- To add the instance ID, click Add.
- The Add Instance ID List dialog box appears.
Figure 3-4 Add Instance ID List

- Fill in the required details and click Save to add the instance ID.
- Click Cancel to exit the Add Instance ID List dialog box.
Note:
Similarly, you can add the Key ID List details. - The Add Instance ID List dialog box appears.
- To edit any Instance ID or Key ID detail, click Edit
corresponding to that particular record under relevant section.
- The Edit Instance ID List or Edit Key ID List dialog box appears.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- Click Cancel to access the Edit Access Token Validation page.
- To delete any Instance ID or Key ID detail, click Delete
corresponding to that particular record.
- A confirmation message appears. Click OK to confirm the deletion of record.
- Click Cancel to exit the delete dialog box and access the Edit Access Token Validation page.
- Update the Access Token Validation Mode if required.
- Click Save to update the changes [OR] click Cancel to exit the Edit Access Token Validation page.
- Click Refresh to reload the Access Token Validation page.
3.6 Subscriber Bulk Import Status
The Subscriber Bulk Import Status page is a monitoring page, which is read-only. This page allows the operator to monitor the Subscriber Bulk Import status, which initiates on running the Subscriber Bulk Import tool. For more information, see bulk import tool.
To access the Subscriber Bulk Import Status page, click UDR and then, Subscriber Bulk Import Status in the left navigation pane of the CNC Console application. The following page appears:
Figure 3-5 Subscriber Bulk Import Status Page

- Import File: shows the csv file name that has bulk import data.
- Time Queued: shows the time when bulk import transaction was initiated.
- Time Started: shows the time when bulk import transaction begins.
- Time Completed: shows the time when bulk import transaction completes.
- Progress (%): shows the percentage completion of bulk import.
- Pass Count: shows the number of records that have been successfully imported.
- Fail Count: shows the number of records that failed to import.
- Total Count: shows the total number of records in the import file.
- Status: shows the overall status of the bulk import transaction.
- Failed Keys: shows information about those transactions, which are not provisioned (by bulk import tool) due to any failure. CNC Console displays failed keys only if the failed key count is less than 100.
Note:
Using Filter option, you can filter the records you are interested in and using Refresh option, you can refresh the Subscriber Bulk Import Status page.3.7 Configuration Export & Import
This section describes how to perform bulk export and bulk import of the UDR configuration data using CNC Console.
Figure 3-6 Configuration Export & Import

- Export the configuration data.
- Download the exported data.
- Import the data (zip file) that you have exported earlier.
- Generate report to view details of successful and failed configurations.
Exporting Configuration Data
- Click the Bulk Export button in the Export tab.
The Objects to be Exported dialog box
appears.
Figure 3-7 Objects to be Exported Dialog Box

- Select the objects that you want to export. Click the Selection button to either 'Select All' or 'Deselect All' the objects.
- Click Export to export the selected objects data. The data in the Configuration Export & Import page is updated.
- Click Cancel to exit the dialog box.
Downloading Exported Configuration Data
- Click the Export Configuration Download icon available under the Actions column of the Export tab.
- The "Export Data downloaded Successfully" message appears and the zip file of the exported data is saved to your system. For example: exportedFiles_1.12.41_20210807133529.zip
Downloading Exported Configuration Data Report
- Click the Export Report Download icon available under the Actions column of the Export tab.
- The "Export status report downloaded successfully" message appears and the export report in the .txt file format is saved to your system. For example: exportReport_1.12.41_20210807134056.txt
Importing Configuration Data
- Navigate to the Import tab. The
Configuration Export & Import page
appears as follows:
Figure 3-8 Importing Configuration Data

- Click the Import button. The Import Data
dialog box appears.
Figure 3-9 Import Data Dialog Box

- Select the file that has configuration data
and click Import.
Note:
You can only import the configuration data that you had exported earlier. - The data in the Configuration Export & Import page is updated.
- Click Cancel to exit the dialog box.
Downloading Imported Configuration Data Report
- Click the Import Report Download icon available under Actions column of the Import tab.
- The "Import status report downloaded successfully" message appears and the import report in the .txt file format is saved to your system. For example: importReport_1.12.41_20210807134056.txt
Using REST APIs for Export & Import
UDR provides REST APIs to bulk export and bulk import its configuration data. For more information about REST APIs, see the Configuration APIs for Import and Export section of the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
3.8 Subscriber Export Tool Status
The Subscriber Export Tool Status page is a monitoring page, which is read-only. This page allows the operator to monitor the Subscriber Export Tool Status, which initiates on running the Subscriber Export tool. For more information, see Subscriber Export Tool.
To access the Subscriber Export Tool Status page, click UDR and then, Subscriber Export Tool Status in the left navigation pane of the CNC Console application. The following page appears:
Figure 3-10 Subscriber Export Tool Status

- Job Id: Generates unique ID for export.
- Subscriber Count: Total subscriber count present in the database
- Exported Subscriber Count: Total subscriber count exported from the database.
- Job Progress: Shows the progress of dump in percentage.
- Status: Shows the overall status of the export transaction. For example, RUNNING, COMPLETED, SKIPPED, or FAILED.
- Export State: This field indicates number of completed stages. For example, export from database is successful (1/1) and transfer of data from path to remote is successful (2/2).
Note:
Using Filter option, you can filter the records you are interested in and using Refresh option, you can refresh the Subscriber Export Tool Status page.3.9 Global Configurations
Figure 3-11 Global Configurations

Table 3-38 Global Configurations Parameters
| Field Name | Default Value | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| DB Service Name | mysql-connectivity-service.occne-db | Read-only | Displays the name of the DB Service. |
| UDR Services | All | Read-only | Displays 'All' when all the UDR services are engaged. |
| UDSF Enabled | false | Read-only | Displays 'true' when UDSF is enabled and 'false' when UDSF is not enabled. |
| Ingress HTTTP Port | 80 | Read-only | Defines the Ingress Gateway signaling port for HTTP. |
| Ingress HTTPS Port | 443 | Read-only | Defines the Ingress Gateway signaling port for HTTPS. |
| SNSSAI | 2-FFFFFF | Read-only | Single – Network Slice Selection Assistance Information (SNSSAI) is used to uniquely identify a Network Slice. The S-NSSAI contains Slice/Service Type (SST) and an optional Slice Differentiators (SD) components. |
| DNN | dnn1 | Read-only | Used to identify 5G Data Networks. The DNN is typically in the form of an Access Point Name (APN). |
| Consumer NF | PCF,UDM,NEF | Read-only | Displays the Consumer network functions for UDR |
| Auto Create Subscriber | true | Editable | Indicates the flag to enable or disable the auto creation of subscriber when the PUT operation is performed on a new UEID. |
| SBI Correlation Info Header Enable | false | Editable | If the flag is enabled, the 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header is added in the dr-services responses and notifications requests in Egress GW. |
| NF InstanceId | 5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03 | Read-only | Indicates the NF Instance ID for UDR. The same is registered with NRF. |
| VSA Default Billing Day | 1 | Read-only | Indicates the billing day value. |
| Subscriber Activity Enabled | false | Editable | Enables or disables the subscriber activity |
| Add Default Billing Day | true | Editable | Indicates the flag to enable or disable the add default billing day. |
| Auto Enroll On Signalling | true | Editable |
Indicates the flag to enable or disable the auto enroll of subscriber data. Note: This flag is applicable only for sm-data. It is not applicable for am-data and UE policyset. |
| E-tag Enabled | false | Editable | Indicates the flag to enable or disable the ETag. |
| Enable Controlled Shutdown | false | Editable | Indicates the flag to enable or disable the operational state. |
| OnDemandMigration Key Type | "msisdn" | Editable | Indicates the type of the key for the keyRange for On-demand. The keyType can either be "msisdn" or "imsi". |
| OnDemandMigration Key Range | "000000-000000" | Editable | This defines the range of subscribers for On-demand. Multiple key ranges are not allowed. |
| Enable Suppress Notification | true | Editable | Indicates the flag to enable or disable the suppress notification. |
| Subscriber Identifiers | NA | NA | Configure different subscriber identifiers for each keys. |
| NAI | NA | Editable | Subscriber identifier can be configure up to 100 keys. |
| IMSI | NA | Editable | Subscriber identifier can be configure up to 100 keys. |
| EXTID | NA | Editable | Subscriber identifier can be configure up to 100 keys. |
| MSISDN | NA | Editable | Subscriber identifier can be configure up to 100 keys. |
| Access Log Enabled | true | Editable | Flag to enable or disable the Access Log feature. |
| Default EIR Response | EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN | Editable | Flag to set the default EIR response.
Accepted
values are as follows:
|
| Default EIR Response when IMEI not present | EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN | Editable | Flag to set the default EIR response when IMEI is
not found in the EIR database.
Accepted values are as follows:
|
| Imsi Lookup Fallback Enabled | true | Editable | Flag to enable or disable the IMSI lookup fallback feature. |
| s13 Interface Enabled | true | Editable | Flag to enable or disable diameter S13 interface feature. |
Note:
These values are extracted from the database and on every Helm upgrade, users need to click the Refresh icon to see the latest values.3.10 Logging Level Configuration
Perform the following procedure to configure the Logging Level:
The Logging Level Configuration page allows its operators to view and edit the log level details at the application log level and package log level for each service.
To access the Logging Level Configuration page, click UDR and then Logging Level in the left navigation pane of the CNC Console application.
- Service: This field shows UDR microservice name.
- Application Log Level: This field shows the log level of the microservice
- Additional Error Logging: This flag enables or disables the error logging feature when set to enable or disable respectively.
- Logging Subscriber Info: This flag enables or disables the
logging of UE Identifier and subscriberid. when set to enable or disable
respectively.
Note:
Additional Error Logging and Log Subscriber Info fields are applicable for UDR microservices only. - View: Click View corresponding to each microservice.
The View Log Level List page appears.
Figure 3-12 Sample: View Log Level List
Editing Log Level Details
- Click Edit on the Logging Level Configuration page. The Edit Log Level page appears.
- Select the Service Type from the drop-down list to select anyone of
the following NF Service type:
- Data Repository Service
- Alternate Route
- Bulk Import Tool
- Bulk Export Tool
- Diameter Service
- Diameter Gateway
- Data Repository Provisioning Service
- Egress Gateway
- Ingress Gateway Signaling
- Ingress Gateway Provisioning
- Notify Service
- NRF Client NF Management
- On Demand Migration
- App Info
- Perf Info
- Nudr Config Service
- Select the Application Log Level from the dropdown menu to set the
constraints of the log. Possible values are:
- DEBUG
- ERROR
- INFO
- TRACE
- WARN
- Select the Additional Error Logging status from the drop-down list.
- Select the Log Subscriber Info status from the drop-down list.
- To add the Package Log Level details:
- Click the Add button available in the Package
Log Level section. The Add Package Log Level dialog
box appears:
Figure 3-13 Add Package Log Level
- Enter the Package name and select the Log
Level from the list. The Log Level options are:
- DEBUG
- ERROR
- INFO
- TRACE
- WARN
- Click Save to add the package log level details. [OR] Click Cancel to exit the Add Package Log Level dialog box.
- Click the Add button available in the Package
Log Level section. The Add Package Log Level dialog
box appears:
- Click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any log level detail, click Cancel. The Logging Level Configuration page appears.
- Click Refresh to reload the Logging Level Configuration page.
3.11 Controlled Shutdown Configurations
This section describes how to perform Controlled Shutdown configurations.
3.11.1 Operational State
- In the CNC Console application, under UDR,
click Controlled Shutdown, and then select
Operational State.
This opens the page displaying the two groups, Switch Operational State and Operational State History:
Figure 3-14 Operational State
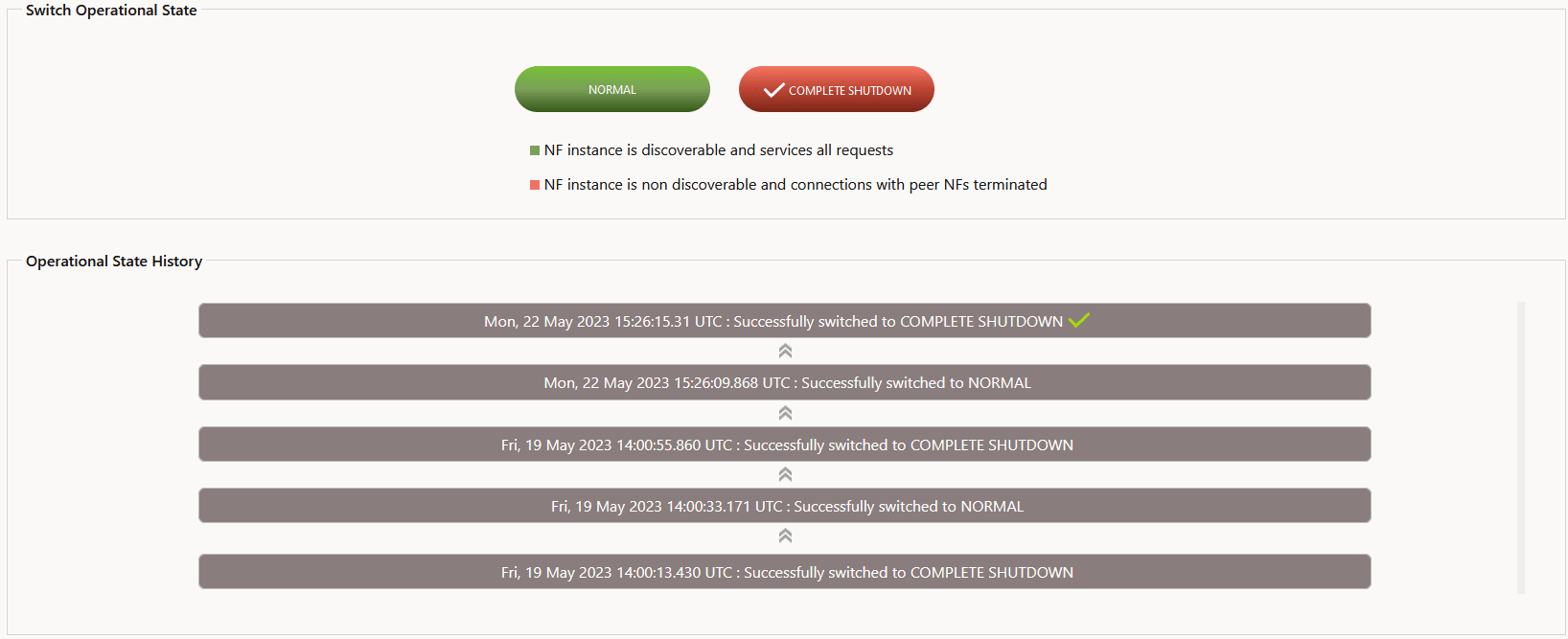
- Switch Operational State
displays the following operational states:
- NORMAL: NF instance is discoverable and services all requests.
- COMPLETE SHUTDOWN: NF instance is non discoverable and no new session creation requests accepted.
Note:
The current state of any site can be identified with a tick mark.You can switch to a different operational state by clicking the NORMAL or COMPLETE SHUTDOWN button.
- Operational State History: It displays the history of the operational states along with the timestamp.
- Switch Operational State
displays the following operational states:
3.12 Provisioning
To configure UDR services using CNC Console, you can use Provisioning. In the left navigation pane of the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Provisioning.
3.12.1 Provisioning - NEF Data
This section describes how to provision operations for NEF Data.
In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Provisioning. From the Provisioning menu, select NEF Data in the left navigation pane. The Provisioning Operations for NEF Data page appears:
Figure 3-15 Provisioning Operations for NEF Data
- Extract NEF data from UDR database based on the UE ID entered
- Add new NEF data to the UDR database
- Modify an existing NEF data on the based on a UE ID
- Delete existing NEF data that is not needed in the UDR database
Extracting Profile Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'NEF Data'
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111114
- Click Get. A confirmation message, 'Fetched
Successfully' appears for a second, and the result appears in the
Response text area as follows:
Figure 3-16 Sample Page: Get - NEF Data - Response
- An Error message summary appears in case of incorrect UE ID entered.
Adding NEF Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'NEF Data'.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111114
- Click Add. The Request text area appears.
- Enter the NEF data that you want to add to the UDR database.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message
appears.
Note:
If you enter an incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Editing Profile Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'NEF Data'.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111114
- Click Edit. The Request text area displays existing NEF data.
- Enter the updated NEF data.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message
appears.
Note:
If you enter an incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Deleting NEF Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'NEF Data'.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111114
- Click Delete.
- The 'Deleted Successfully' message appears.
Note:
If you enter an incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Clearing NEF Data
Click the Clear option to clear all the text fields and text areas of the Provisioning Operations for NEF Data.
3.12.2 Provisioning - Profile Data
This section describes how to operate provisioning operations for Profile Data.
In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Provisioning. From the Provisioning menu, select Profile Data in the left navigation pane. The Provisioning Operations for Profile Data page appears:
Figure 3-17 Provisioning Operations for Profile Data
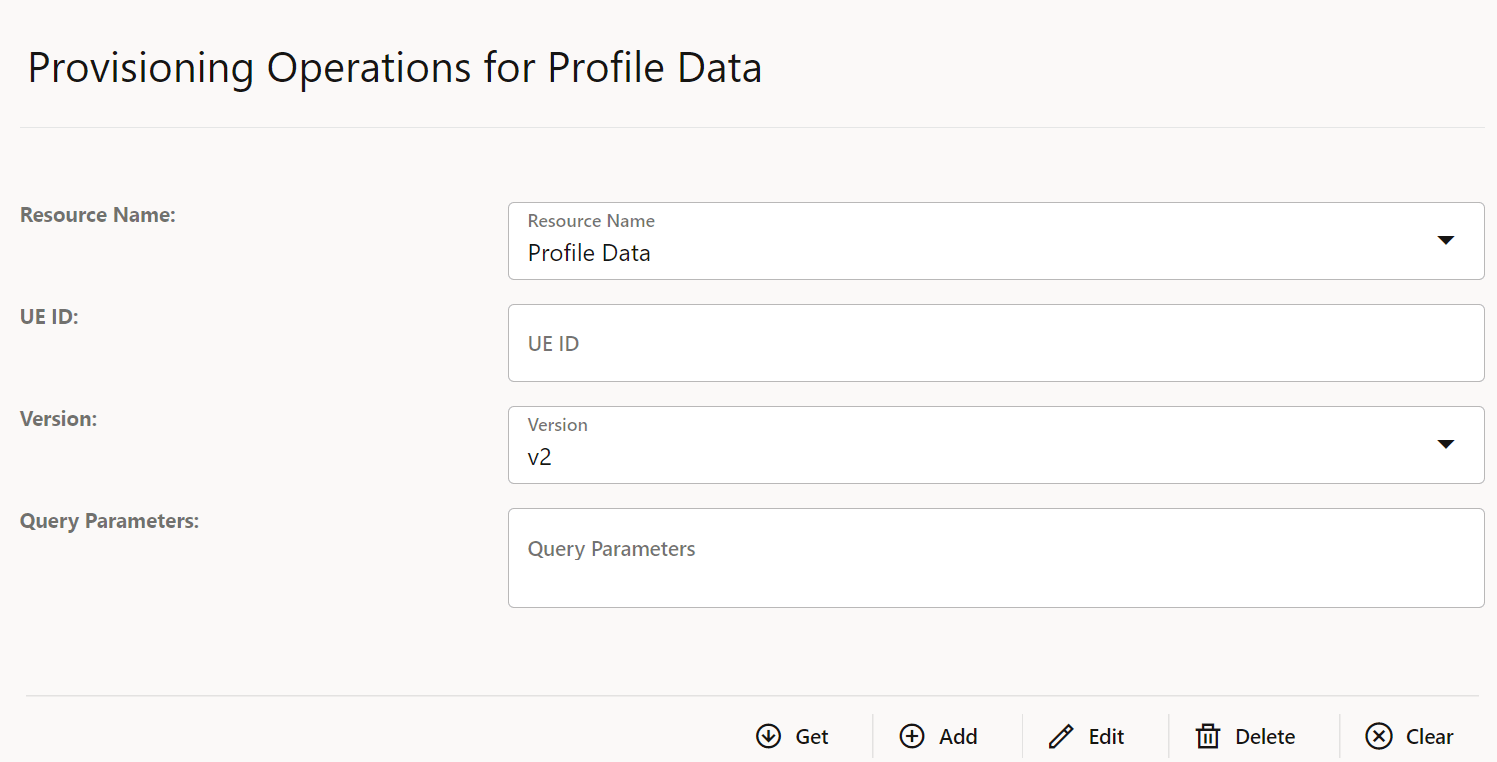
- Extract profile data from UDR database on the basis of UE ID entered
- Add new profile data to the UDR database
- Modify an existing profile data on the basis of UE ID
- Delete an existing profile data that is no more needed in the UDR database
Extracting Profile Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'Profile Data'.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111114
- Click Get. A confirmation message, 'Fetched Successfully'
appears for a second and the result appears in the Response text area
as follows:
Figure 3-18 Sample Page: Get - Profile Data - Response
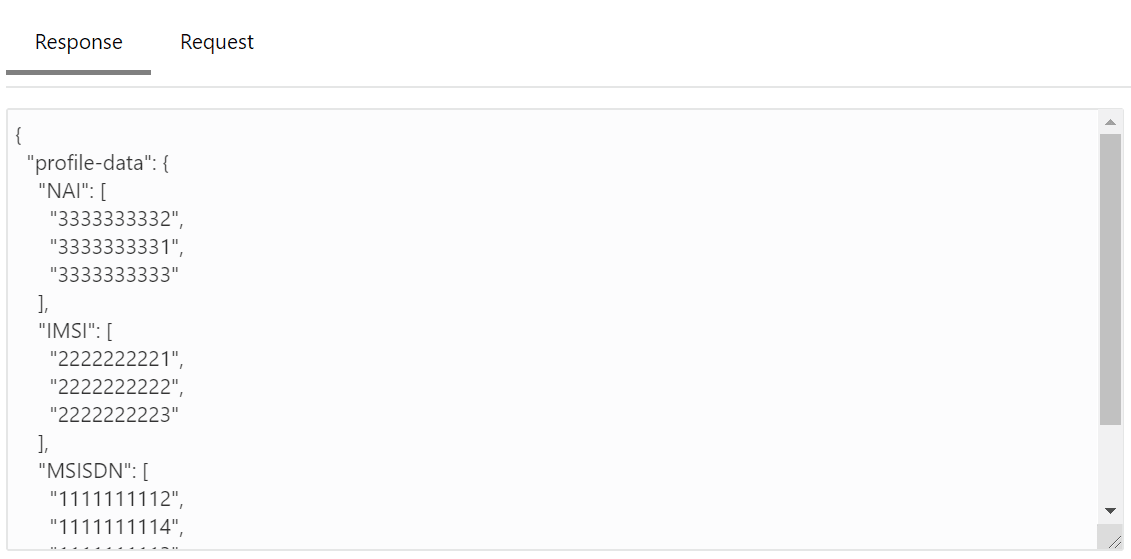
- An Error message summary appears in case of incorrect UE ID entered.
Adding a Profile Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'Profile Data'.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111114
- Click Add. The Request text area appears.
- Type-in the profile data that you want to add to the UDR database.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message
appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Editing a Profile Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'Profile Data'.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111114
- Click Edit. The Request text area displays an existing profile data.
- Type-in the updated profile data.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message
appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Deleting a Profile Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'Profile Data'.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111114
- Click Delete.
- The 'Deleted Successfully' message appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Clearing a Profile Data
Click the Clear option to clear all the text fields and text areas of the Provisioning Operations for Profile Data.
3.12.3 Provisioning - EIR Data
This section describes provisioning operations for EIR Data.
In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Provisioning. From the Provisioning menu, select EIR Data in the left navigation pane. The Provisioning Operations for EIR Data page appears:
Figure 3-19 Provisioning GUI for EIR Data
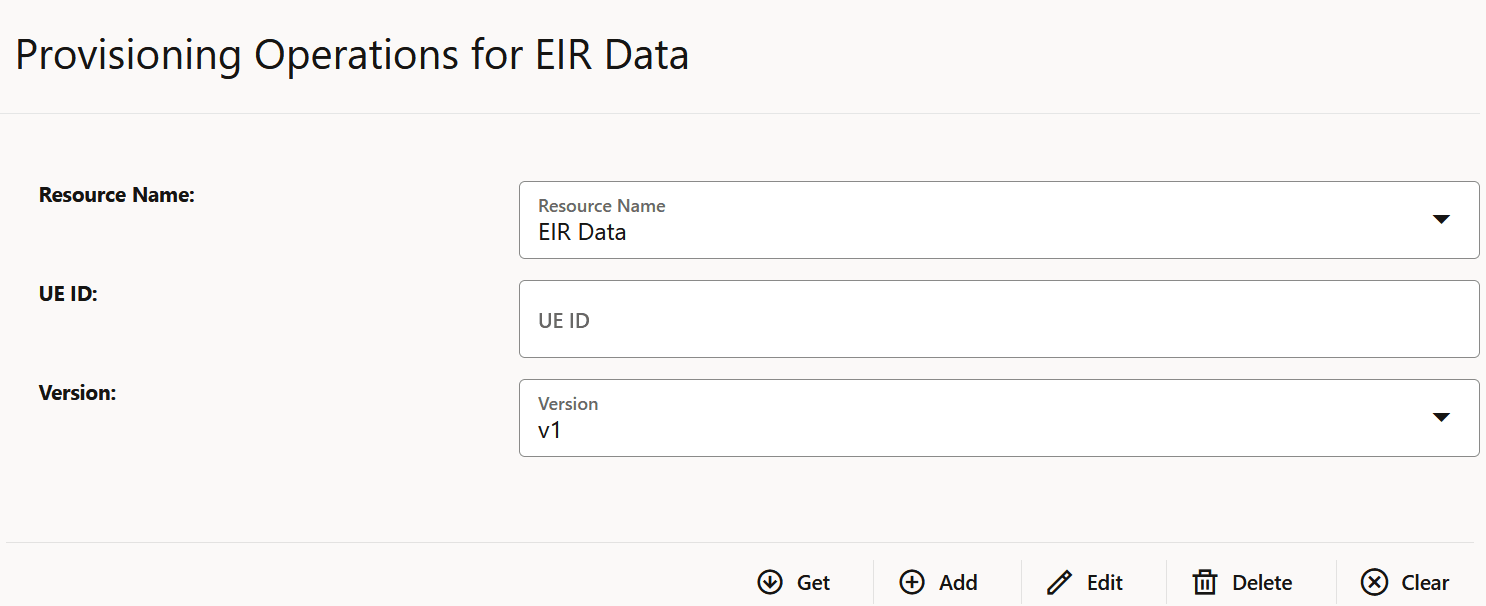
- Extract EIR data from UDR database based on the UE ID entered
- Add new EIR data to the UDR database
- Modify an existing EIR data on the based on a UE ID
- Delete existing EIR data that is not needed in the UDR database
Extracting Profile Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'EIR Data'
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: UE ID - imei-1111111111
- Click Get. A confirmation message, 'Fetched
Successfully' appears for a second, and the result appears in the
Response text area as follows:
Figure 3-20 Sample Page: Get - EIR Data - Response
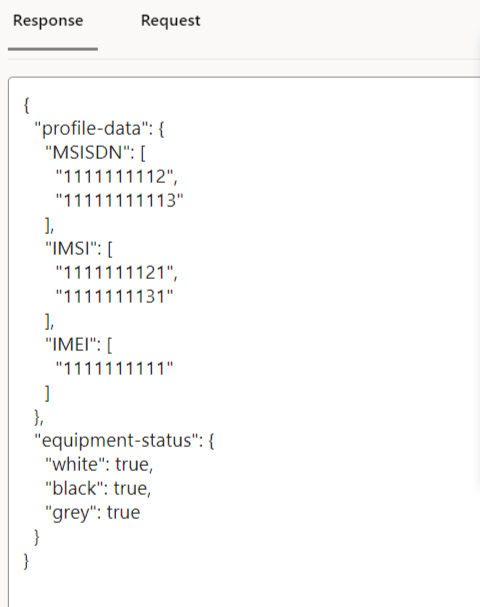
- An Error message summary appears in case of incorrect UE ID entered.
Adding EIR Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'EIR Data'.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111112
- Click Add. The Request text area appears.
- Enter the EIR data that you want to add to the UDR database.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message
appears.
Note:
If you enter an incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Editing Profile Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'EIR Data'.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111112
- Click Edit. The Request text area displays existing NEF data.
- Enter the updated EIR data.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message
appears.
Note:
If you enter an incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Deleting EIR Data
- Ensure Resource Name is set to 'EIR Data'.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111112
- Click Delete.
- The 'Deleted Successfully' message appears.
Note:
If you enter an incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Clearing EIR Data
Click the Clear option to clear all the text fields and text areas of the Provisioning Operations for EIR Data.
3.12.4 Provisioning - PCF Data
This section describes how to operate provisioning operations for PCF (Policy Control Function) Data.
In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Provisioning. From the Provisioning menu, select PCF Data in the left navigation pane. The Provisioning Operations for PCF Data page appears:
Figure 3-21 Provisioning Operations for PCF Data
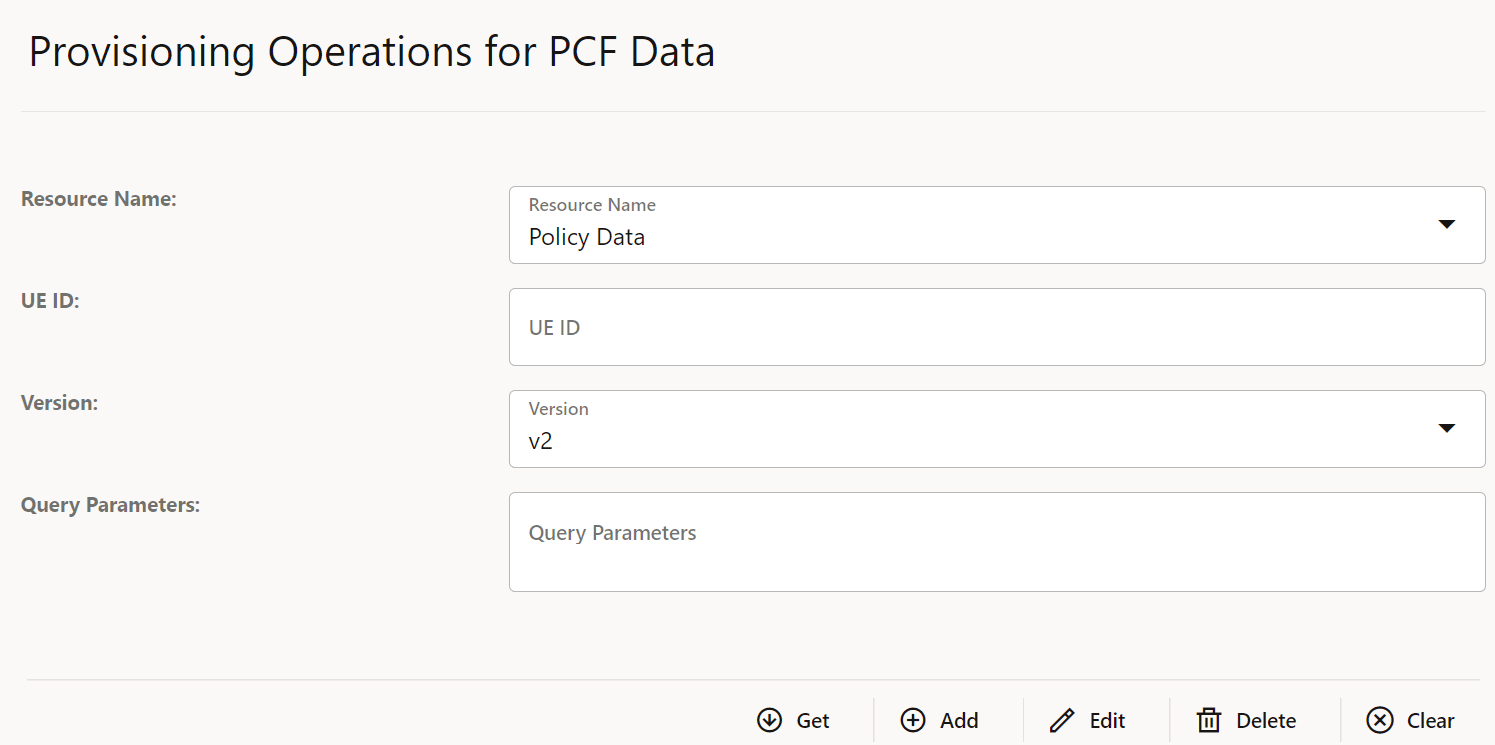
- Select the Resource Name from the drop-down list.
- Extract PCF data from UDR database on the basis of UE ID entered.
- Add PCF Data on the basis of payload.
- Modify the existing PCF data on the basis of UE ID.
- Delete the existing PCF data that is no more needed in the UDR database.
Extracting PCF Data
- Select the Resource Name from the drop-down list.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-9111111112.
- Click Get. A confirmation message, 'Fetched Successfully.'
appears and the result appears in the Response text area as
follows:
Figure 3-22 Provisioning PCF Get Response
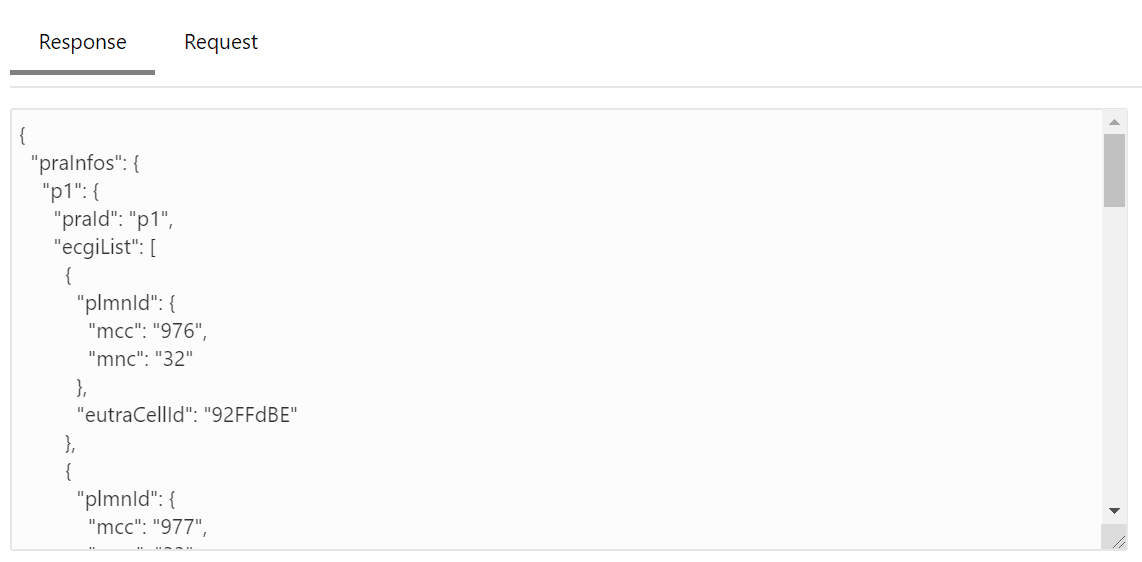
- An Error message summary appears in case of incorrect UE ID entered.
Adding a PCF Data
- Select the Resource Name from the drop-down list.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-9111111112.
- Click Add. The Request text area displays an existing PCF data.
- Type-in the updated profile data.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message
appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Editing a PCF Data
- Select the Resource Name from the drop-down list.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-9111111112.
- Click Edit. The Request text area displays an existing PCF data.
- Type-in the updated profile data.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message
appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Deleting a PCF Data
- Select the Resource Name.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-9111111112.
- Click Delete.
- The 'Deleted Successfully.' message appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Clearing a PCF Data
Click the Clear option to clear the text fields and text areas of the Provisioning Operations for PCF Data page.
3.12.5 Provisioning - SLF Data
In this section, you will learn to operate provisioning operations for SLF (Subscriber Location Function) Data.
In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Provisioning. From the Provisioning menu, select SLF Data in the left navigation pane. The Provisioning Operations for SLF Data page appears:
Figure 3-23 Provisioning Operations for SLF Data
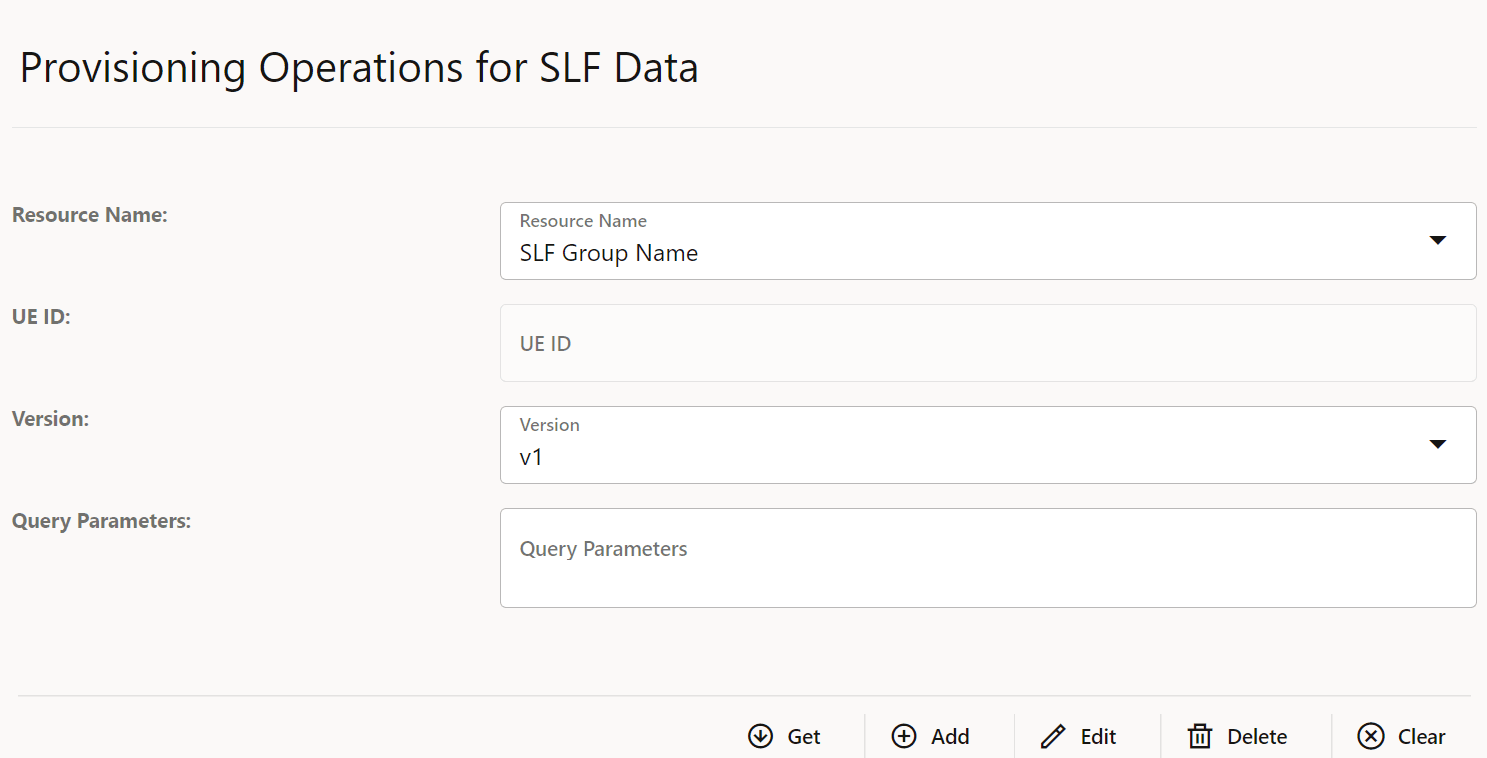
Note:
SLF Group Name must be provisioned before SLF Subscriber is provisioned.- Extract SLF data from UDR database on the basis SLF Group Name (Query Parameter) or SLF Subscriber (UEID).
- Add or edit an existing SLF data on basis of SLF Group Name (Query Parameter) or SLF Subscriber (UEID).
- Delete an existing SLF data that is no more needed in the UDR database.
Extracting SLF Data on the basis of SLF Group Name
- Select the Resource Name as SLF Group Name.
- Enter the Query Parameters.
- Click Get. A confirmation message, 'Fetched
Successfully.' appears and the result appears in the Response
text area as follows:
Figure 3-24 Provisioning SLF Get Response
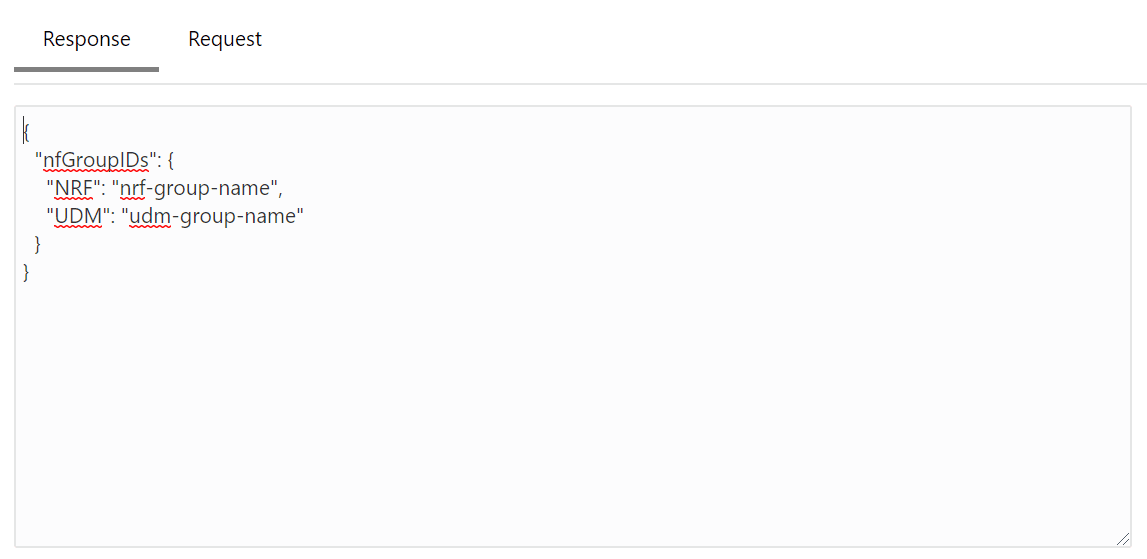
Extracting SLF Data on the basis of SLF Subscriber
- Select the Resource Name as SLF Subscriber.
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111112
- Click Get. A confirmation message, 'Fetched
Successfully.' appears and the result appears in the Response
text area as follows:
Figure 3-25 Provisioning SLF Get Response

- An Error message summary appears in case you enter an incorrect UE ID.
Adding SLF Data on the basis of SLF Group Name or SLF Subscriber
- Select the Resource Name as either SLF Group Name or SLF Subscriber.
- If you have selected the Resource Name as SLF Group Name
then,
- Enter the Query Parameters.
- Click Add. The Request text area appears.
- Type the SLF data.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message appears.
- If you have selected the Resource Name as SLF Subscriber
then,
- Type an appropriate UE ID. For example: msisdn-1111111112.
- Click Add. The Request text area appears.
- Type-in the SLF data.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.Editing SLF Data
- Select the Resource Name as either SLF Group Name or SLF Subscriber.
- If you have selected the Resource Name as SLF Group Name
then,
- Type in the Query Parameters and click Get. The result appears in the Response text area.
- Click Edit. The Request text area displays an existing SLF data. Modify the relevant details.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message appears.
- If you have selected the Resource Name as SLF Subscriber
then,
- Type in the UE ID and click Get. The result appears in the Response text area.
- Click Edit and modify the required details. The Request text area displays an existing SLF data. Modify the relevant details.
- Click Submit. The 'Saved Successfully.' message appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.Deleting a SLF Data
- Select the Resource Name as either SLF Group Name or SLF Subscriber.
- If you have selected the Resource Name as SLF Group Name then enter the 'Query Parameters' and if you have selected the Resource Name as SLF Subscriber then enter the 'UE ID'. For example: msisdn-1111111112
- Click Delete.
- The 'Deleted Successfully.' message appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Clearing a SLF Data
Click the Clear option to clear the text fields and text areas of the Provisioning Operations for SLF Data page.
3.12.6 Provisioning - UDM Data
This section describes how to operate provisioning operations for UDM (Unified Data Management) Data.
In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Provisioning. From the Provisioning menu, select UDM Data in the left navigation pane. The Provisioning Operations for UDM Data page appears:
Figure 3-26 Provisioning Operations for UDM Data
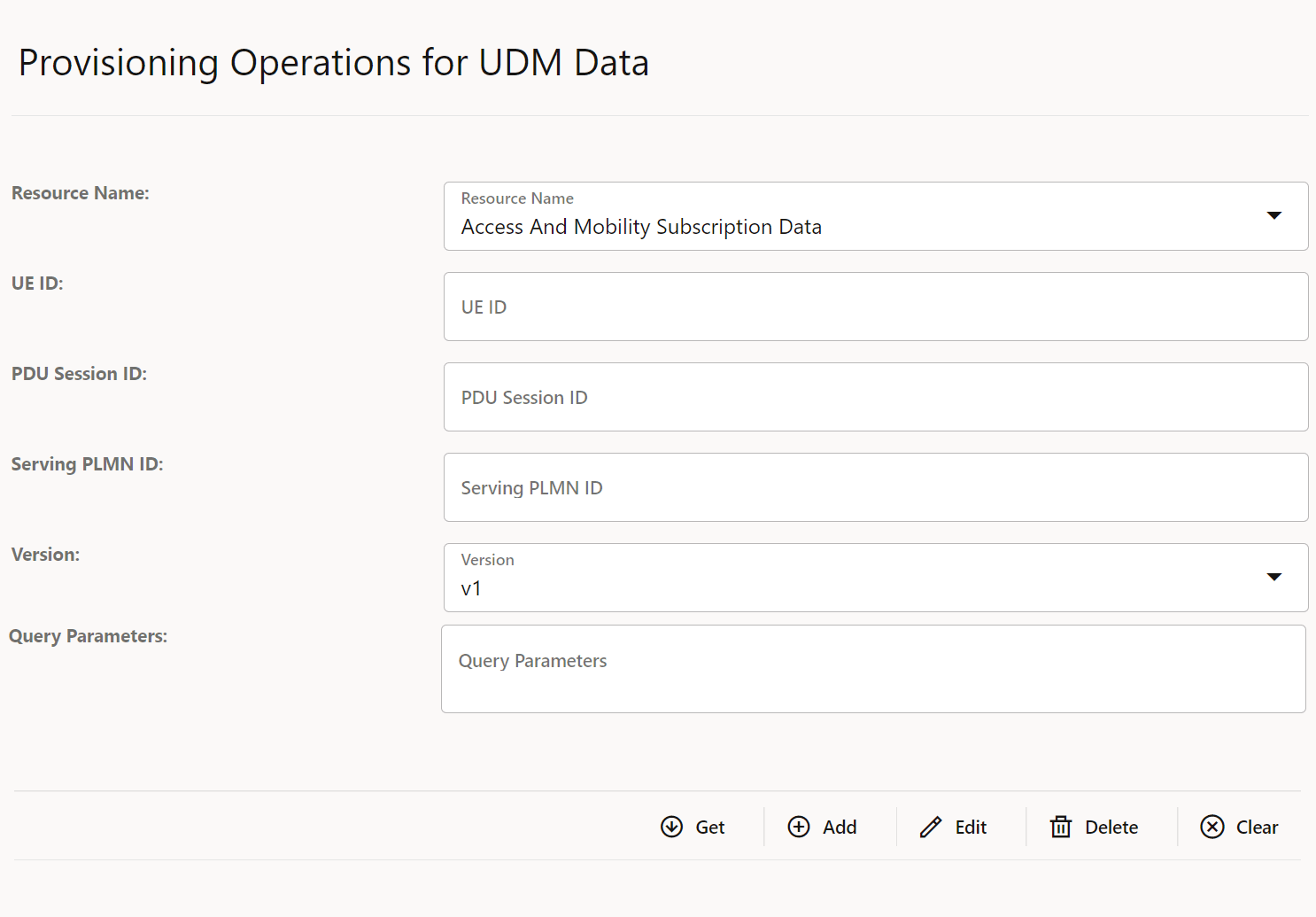
In the Provisioning Operations for UDM Data page, user can extract, modify and delete UDM data on the basis of Resource Name, UE ID, PDU Session ID, Serving PLMN ID, Version, and Query Parameters entered.
Extracting UDM Data
- Select the Resource Name from the drop-down list.
- Type an appropriate UE ID, PDU Session ID and Serving PLMN ID in their respective fields.
- Select an appropriate Version and enter Query Parameters.
- Click Get. A confirmation message, 'Fetched Successfully.' appears and the result appears in the Response text area.
- An Error message summary appears in case of incorrect UE ID entered.
Adding a UDM Data
- Select the Resource Name.
- Type an appropriate UE ID, PDU Session ID and Serving PLMN ID in their respective fields.
- Select an appropriate Version and enter Query Parameters.
- Click Edit. The Request text area appears.
- Enter details and click Submit. The 'Saved
Successfully.' message appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Editing a UDM Data
- Select the Resource Name.
- Type an appropriate UE ID, PDU Session ID, and Serving PLMN ID in their respective fields.
- Select an appropriate Version and enter Query Parameters.
- Click Edit. The Request text area displays an existing UDM data.
- Edit as required and click Submit. The 'Saved
Successfully.' message appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Deleting a UDM Data
- Enter the Resource Name.
- Type an appropriate UE ID, PDU Session ID, and Serving PLMN ID in their respective fields.
- Select an appropriate Version and enter Query Parameters.
- Click Delete.
- The 'Deleted Successfully.' message appears.
Note:
If a user enters any incorrect input, an Error message summary appears.
Clearing a UDM Data
Click the Clear option to clear the text fields and text areas of the Provisioning Operations for UDM Data page.
3.12.7 Provisioning - Schema Management Data
This section describes how to operate provisioning operations for schema.
In the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Provisioning. From the Provisioning menu, select Schema Management Data in the left navigation pane. The Schema Management page appears:
Figure 3-27 Schema Management
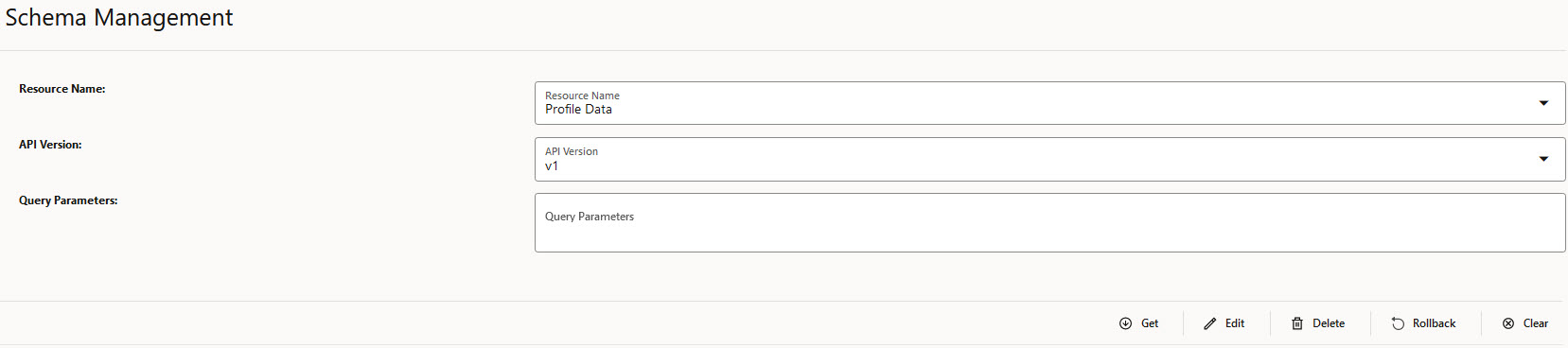
In the Schema Management page, user can extract, modify, and delete a schema on the basis of Resource Name and Query Parameters.
Extracting a Schema
- Select the Resource Name.
- Enter the Query Parameters.
- Click Get. A confirmation message, 'Fetched Successfully.'
appears and the result appears in the Response text area as
follows:
Figure 3-28 Schema - Get - PCF AM Data
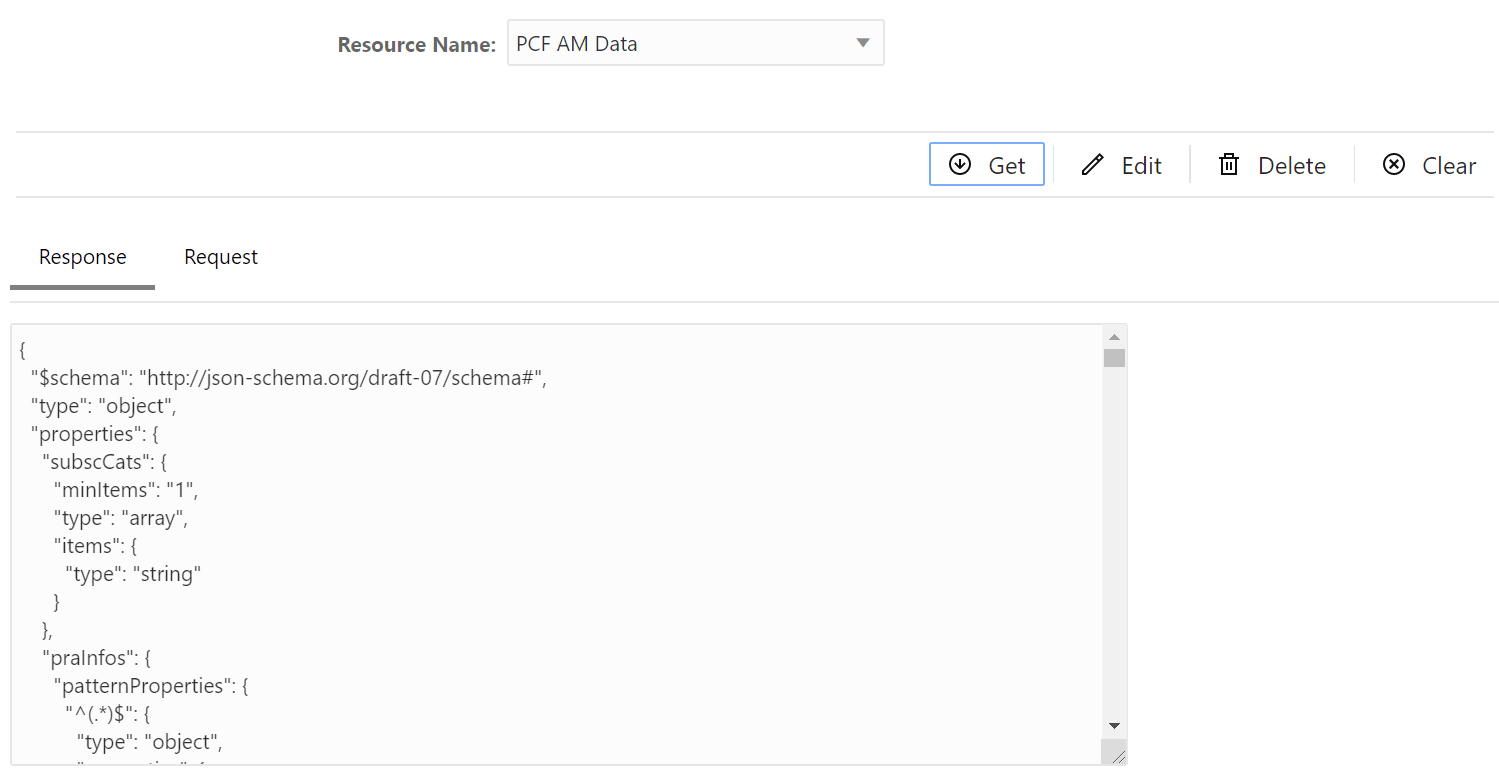
- An Error message summary appears in case of incorrect UE ID entered.
Adding or Editing a Schema
- Select the Resource Name.
- Enter the Query Parameters.
- Click Edit. The Request text area displays the selected schema.
- Edit as required and click Submit. The 'Saved
Successfully.' message appears.
Note:
If a user edits the schema inappropriately, an Error message summary appears.
Deleting a Schema
- Select the Resource Name.
- Enter the Query Parameters.
- Click Delete.
- The 'Deleted Successfully.' message appears.
Note:
If a user selects a schema that does not exists, an Error message summary appears.
Clearing a Schema Management Data
Click the Clear option to clear the text fields and text areas of the Schema Management page.
3.13 Service Configurations
To configure UDR services using CNC Console, you can use Service Configurations. In the left navigation pane of the CNC Console application, click UDR and then Service Configurations.
3.13.1 Subscriber Bulk Import Configurations
Click UDR and then Service Configurations. From the Service Configurations menu, select Subscriber Bulk Import Configurations. The Subscriber Bulk Import Configurations page appears:
Figure 3-29 Subscriber Bulk Import Configurations
Table 3-39 Subscriber Bulk Import Configurations Parameters
| Field Name | Default Value | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Import File Expiry Time | 7d | Editable | Expiry time for all the PDBI files including the result log files. |
| Remote Directory Path | /home/cloud-user/ocudr/ | Editable | Remote host path |
| Remote Directory Transfer Out | /home/cloud-user/transferOut/ | Editable | The log files are transferred to this remote host server path when the bulk-import processing is completed. |
| File Extension | .pdbi | Editable | Shows the file type |
| Delete File From PVC | false | Editable | Flag to enable or disable the delete file from PVC feature |
Editing Subscriber Bulk Import Configurations
- Click Edit. The Edit Subscriber Bulk Import Configurations page appears.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel. You can navigate back to the Bulk Import Configurations page.
- Click Refresh to reload the Subscriber Bulk Import Configurations page.
3.13.2 Data Repository Service
Click UDR and then Service Configurations. From the Service Configurations menu, select Data Repository Service. The Data Repository Service Configurations page appears:
Figure 3-30 Data Repository Service Configurations
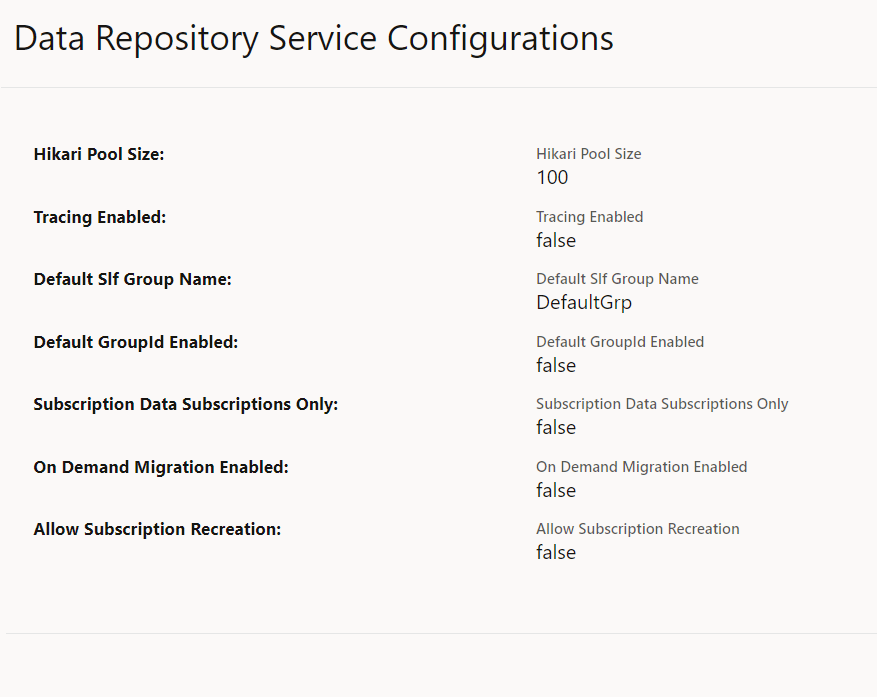
Table 3-40 Data Repository Service Configuration Parameters
| Field Name | Default Value | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hikari Pool Size | 25 | Read-only | Hikari pool connection size to be created at start up. |
| Tracing Enabled | false | Read-only | Flag to enable tracing. |
| Default SLF Group Name | DefaultGrp | Editable | The default group name is provisioned. If there are any changes done to this through CNC console, then the default group must be reprovisioned with the modified group name. But if the change is done through helm values and helm upgrade is performed, then the default group will be created with the updated name. |
| Default GroupId Enabled | false | Editable | Flag to enable or disable the Default Group ID feature. |
| Subscription Data Subscriptions Only | false | Read-only | Flag to enable subscription data. |
| On Demand Migration Enabled | false | Editable | Flag to enable or disable on-demand migration. |
| Allow Subscription Recreation | false | Editable | Flag to enable or disable overwriting of existing subscription for the POST request. |
Editing Data Repository Service Configurations
- Click Edit. The Edit Data Repository Service Configurations page appears.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel. You can navigate back to the Data Repository Service Configurations page.
- Click Refresh to reload the Data Repository Service Configurations page.
3.13.3 Diameter Gateway Service
Click UDR and then Service Configurations. From the Service Configurations menu, select Diameter Gateway. The Diameter Gateway Configurations page appears:
Figure 3-31 Diameter Gateway Configurations

The following table explains the parameters in the Diameter Gateway Configurations page in detail:
Table 3-41 Diameter Gateway Configurable Parameters
| Field Name | Default Value | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Realm | oracle.com | Read-only | UDR Diameter Gateway server realm. |
| Identity | nudr.oracle.com | Read-only | UDR Diameter Gateway identity or FQDN. |
| Reconnect Delay | 4 | Editable | Waiting time for reconnecting server peer in seconds. |
| Response Timeout | 4 | Editable | Time period to get the response from server peer in seconds. |
| Connection Timeout | 7 | Editable | Time period in which both client and server should establish the connection. |
| Watchdog Interval | 7 | Editable | Interval of time to send Diameter watchdog message periodically. |
| Reconnect Limit | 70 | Editable | Number of attempts allowed to reconnect with diameter server peer if server is unreachable or down. |
| On Demand Migration Enabled | False | Editable | Flag to indicate whether on demand migration is enabled or disabled. |
| Allowed Client Nodes For Diameter SH Ingress |
|
Editable | If responseOnly parameter is present and the value is
"true", then mandatory fields are:
If responseOnly parameter is not present or the value is false, then mandatory fields are:
|
| Type | NA | Editable | Type of peer node |
| Response only | NA | Editable | Flag to initiate connection to the peer node. |
| Host | NA | Editable | Peer node IP address or FQDN |
| Identity | seagull1a.seagull1.com | Editable | Identity of Peer node |
| Realm | seagull1.com | Editable | Realm of peer node |
| Port | NA | Editable | Peer node port used by diameter gateway when initiating connection. |
Editing Diameter Gateway Configurations
- Click Edit. The Edit Diameter Gateway Configurations page appears:
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel. The Diameter Gateway Configurations page appears.
- Click Refresh to reload the Diameter Gateway Configurations page.
3.13.4 Diameter Gateway Congestion
Click UDR and then Service Configurations. From the Service Configurations menu, select Diameter Gateway Congestion. The Diameter Gateway Congestion Configurations page appears:
Figure 3-32 Diameter Gateway Congestion
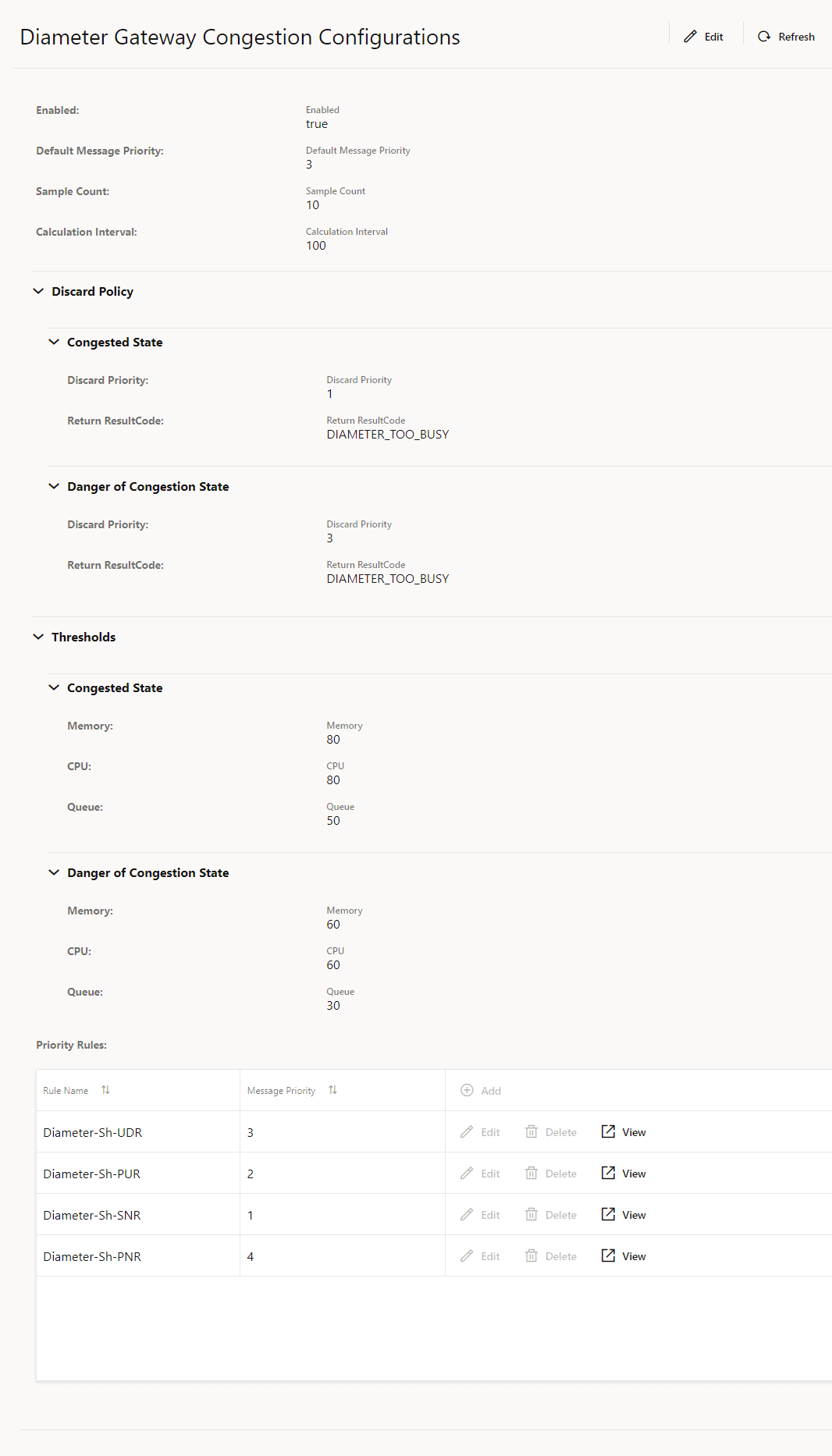
The following table explains the parameters in the Diameter Gateway Congestion Configurations page in detail:
Table 3-42 Diameter Gateway Congestion Configurable Parameters
| Field Name | Default Value | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| enabled | true | Editable | Flag to enable or disable the Diameter Gateway Pod Congestion feature |
| defaultMessagePriority | 2 | Editable | Default diameter message priority which is not specifically assigned any priority |
| sampleCount | 10 | Editable | Sample request count for deciding pod state |
| calculationInterval | 100 | Editable | Congestion state calculation every configured time (in ms) |
| loadSheddingRulesMap | NA
|
Editable |
Indicates the decision for the pod in a particular state |
| loadSheddingRulesMap.<CONGESTED/DOC> | NA | Editable | Indicates the pod congestion state. |
| loadSheddingRulesMap.<CONGESTED/DOC>.state | NA | Editable | Indicates the name of the state. |
| loadSheddingRulesMap.<CONGESTED/DOC>.discardPriority | NA | Editable | Indicates the diameter message discard priority. |
| loadSheddingRulesMap.<CONGESTED/DOC>.ansWithResultCode | NA | Editable | Indicates the diameter return string result code when the message get discarded. |
| priorityRules | NA |
Editable | NA |
| Priority Rules.Rule Name | NA | Editable | Specifies the unique name of the message priority rule. |
| Priority Rules.Message Priority | NA | Editable | Specifies the priority assigned to the message. It can be a number from 0 to 15. |
| PriorityRules.Conditions.Request Type | NA | enum | Specifies the type of message for the selected
application. The supported request values for the application type are
as follow:
|
| Priority Rules.Conditions.Application | NA | enum |
Specifies the type of application. Users can select any
of the following values from the drop-down list:
|
| Thresholds | NA |
Editable | NA |
| Thresholds.Congested State.Memory | NA | Editable | Memory percentage of pod state |
| Thresholds.Congested State.CPU | NA | Editable | CPU percentage of pod state |
| Thresholds.Congested State.Queue | NA | Editable | Queue percentage of pod state |
| Thresholds.Danger of Congested State.Memory | NA | Editable | Memory percentage of pod state |
| Thresholds.Danger of Congested State.CPU | NA | Editable | CPU percentage of pod state |
| Thresholds.Danger of Congested State.Queue | NA | Editable | Queue percentage of pod state |
| Discard Policy.Congested State.Discard Priority | NA | Editable | Specifies the discard priority for the load shedding rule. The discard priority value can be a number from 0 to 15. Any request message with equal or lower priority is rejected. |
| Discard Policy.Congested State.Return ResultCode | NA | enum | Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of congestion control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down list: DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY, DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY |
| Discard Policy.Danger of Congested State.Discard Priority | NA | Editable | Specifies the discard priority for the load shedding rule. The discard priority value can be a number from 0 to 15. Any request message with equal or lower priority is rejected. |
| Discard Policy.Danger of Congested State.Return ResultCode | NA | enum | Specifies the result code, returned in the answer response, when request message is rejected as part of congestion control. Users can select any of the following values from the drop-down list: DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY, DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY |
Editing Diameter Gateway Congestion Configurations
- Click Edit. The Edit Diameter Gateway Congestion Configurations page appears:
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel. The Diameter Gateway Congestion Configurations page appears.
- Click Refresh to reload the Diameter Gateway Congestion Configurations page.
3.13.5 Provisioning Data Repository Service
Click UDR and then Service Configurations. From the Service Configurations menu, select Provisioning Data Repository Service. The Provisioning Data Repository Service Configurations page appears:
Figure 3-33 Provisioning Data Repository Service Configurations

Table 3-43 Provisioning Data Repository Service Configurations Parameters
| Field Name | Default Value | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hikari Pool Size | 25 | Read-only | The Hikari pool connection size to be created at start up. |
| Tracing Enabled | False | Read-only | By default, tracing is not enabled. |
| On Demand Migration Enabled | False | Editable | By default, on demand migration is not enabled. |
| Prov Logs Enabled | False | Editable | Flag to enable or disable the provisioning logs. |
| Prov Logs API Names Supported | nudr-dr-prov | Editable | Supported API for provisioning logs. The supported
provisioning APIs are as follows:
|
Editing Provisioning Data Repository Service Configurations
- Click Edit. The Edit Provisioning Data Repository Service Configurations page appears.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel. The Provisioning Data Repository Service Configurations page appears.
- Click Refresh to reload the Provisioning Data Repository Service Configurations page.
3.13.6 Notify Service
Click UDR and then Service Configurations. From the Service Configurations menu, select Notify Service. The Notify Service Configurations page appears:
Figure 3-34 Notify Service Configurations

Table 3-44 Notify Service Configurations Parameters
| Field Name | Default Value | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Notify Retry Count | 3 | Editable | Number of notification attempts to be done in case
of notification failures.
Retries are based on notification.retryerrorcodes configuration. |
| Notif Retry Interval | 5 | Editable | The retry interval for notifications in case of
failure. It is measured in seconds.
Retries are based on notification.retryerrorcodes configuration. |
| Retry Error Codes | 400,429,500,503 | Editable | This field displays comma separated error codes. These error codes are eligible for retry notifications in case of failures. |
| Hikari Pool Size | 25 | Read-only | The Hikari pool connection size to be created at start up. |
| Tracing Enabled | false | Read-only | This enables tracing on jaeger. By default, tracing is not enabled. |
| Resource Removal Notification Enabled | true | Editable | It is the PCF notifications for delete subscriber and deletion of policy data. When enabled, the "delResources" attribute/key is included in the notification payload. |
Editing Notify Service Configurations
- Click Edit. The Edit Notify Service Configurations page appears.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel. The Notify Service Configurations page appears.
- Click Refresh to reload the Notify Service Configurations page.
3.13.7 On Demand Migration
Click UDR and then Service Configurations. From the Service Configurations menu, select On Demand Migration. The On Demand Migration page appears:
Figure 3-35 On Demand Migration Configurations
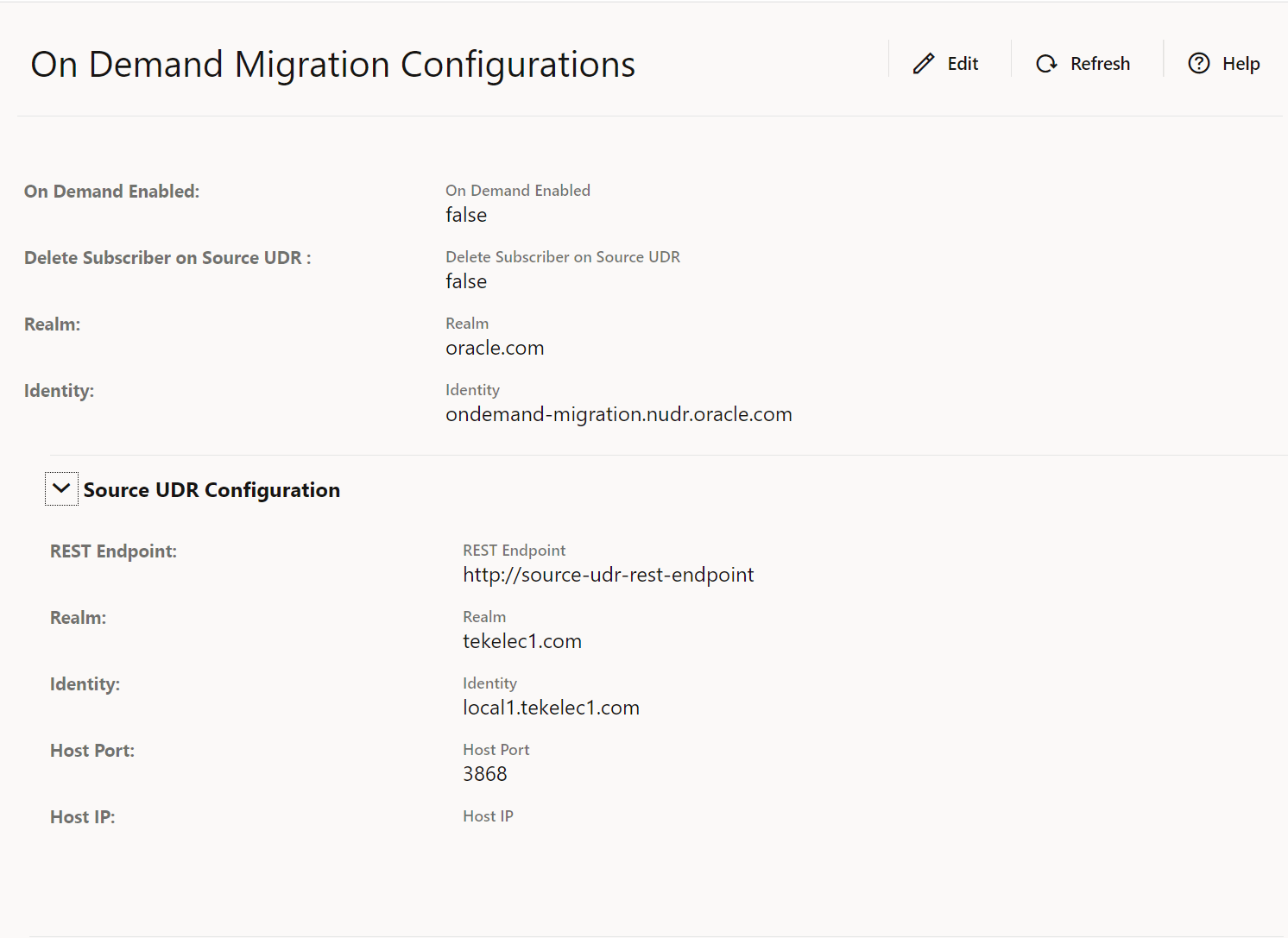
Table 3-45 On Demand Migration Configuration Parameters
| Field Name | Default Value | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| On Demand Enabled | false | Read-only | Flag to enable on-demand migration for migrating subscriber from 4G UDR |
| Delete Subscriber on Source UDR | False | Editable | Flag to delete subscriber data when it is successfully migrated from target UDR to 5G UDR |
| Realm | NA | Editable | Diameter realm of the target UDR |
| Identity | ondemand-migration.udr.oracle.com | Read-only | Diameter client identity in ondemand-migration tool |
| Source UDR Configuration: REST Endpoint |
NA | Editable | Target UDR rest endpoint for deleting subscriber when the deleteSubcriber flag is enabled |
| Realm | udr.oracle.com | Read-only | Diameter client realm in ondemand-migration tool |
| Identity | ondemand-migration.udr.oracle.com | Read-only | Diameter client identity in ondemand-migration tool |
| Host Port | NA | Editable | Port number of target UDR where diameter service is running |
| Host IP | NA | Editable | IP address of target UDR |
Editing On Demand Migration Configurations
- Click Edit. The On Demand Migration Configurations page appears.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel. You navigate back to the On Demand Migration Configurations page.
- Click Refresh to reload the On Demand Migration Configurations page.
3.13.8 Subscriber Export Tool Configurations
Click UDR and then Service Configurations. From the Service Configurations menu, select Subscriber Export Tool Configurations. The Subscriber Export Tool Configurations page appears:
Figure 3-36 Subscriber Export Tool Configurations

Table 3-46 Subscriber Export Tool Configurations Parameters
| Field Name | Default Value | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency Of Periodic Export | DAILY | Editable | It is the frequency of periodic export of subscriber data. This is configurable as ONE_TIME/DAILY/WEEKLY/MONTHLY |
| Export Start Time | 14/09/2022 17:32:10 | Editable | Time at which periodic export starts. 24 hours format is used. |
| Maximum Number of Export Dumps | 5 | Editable | Maximum number of export |
| Export File Name Suffix | SLFTestSegment | Editable | The prefix name of the exported file |
| Multi Valued Field Delimiter | | | Editable | This separator is used to differentiate multiple values for a single key type. |
| Field Delimiter | , | Editable | Delimiter for fields |
| File Extension | .csv | Editable | Extension for file. This can be .csv/.txt |
| IMSI Count | 5 | Editable | Number of IMSI for EIR export.
If 5 IMSIs are not provisioned for a given IMEI, then 0 value is supplied for remaining IMSI . |
| MSISDN Count | 5 | Editable | Number of MSISDN for EIR export.
If 5 MSISDNs are not provisioned for a given IMEI, then 0 value is supplied for remaining MSISDN. |
| Remote Path | /home/cloud-user/ | Editable | Path in remote server where the exported files is stored. |
| Delete Local Copy | true | Editable | Flag to enable or disable deletion of files from SFTP. |
| Subscriber Range Enabled | false | Editable | Flag to enable or disable the range based subscriber export. Default is set to false for full range of 4G policy subscriber data export. |
| New File Per Subscriber Range Enabled | False | Editable | When enabled creates a separate EXML file for each range. Default is set to false. |
| Exported Files Expiry Time | 7d | Editable | The exported file expiry time, after which the file is deleted. |
| Key Type | IMSI | Editable | To export the range based subscriber data with keys. The two key type are IMSI and MSISDN. |
| Subscriber Ranges | NA | Editable | Configures the start and end ranges that is given to
export the data. This works only if
subscriberRangeEnabled parameter is
enabled.
|
| Policy Data Resource for CSV Export | It is the type of data that needs to be exported for the policy data. By default, profile data is included. | Editable | sm-data,am-data,ue-policy-set |
Editing Subscriber Export Tool Configurations
- Click Edit. The Edit Subscriber Export Tool Configurations page appears.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully" appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel. You can navigate back to the Subscriber Export Tool Configurations page.
- Click Refresh to reload the Subscriber Export Tool Configurations page.
3.13.9 Migration Tool Configurations
Figure 3-37 Migration Tool Configurations
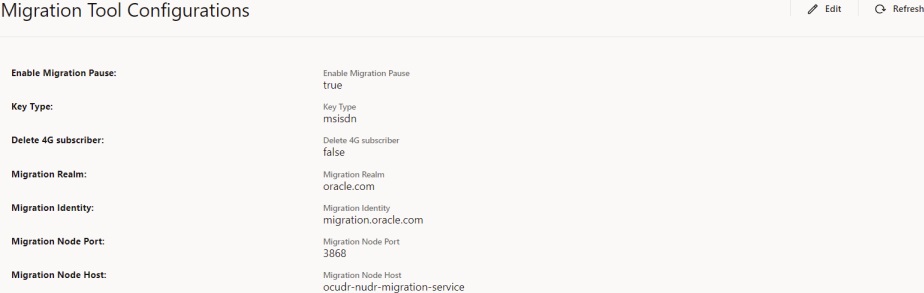
Table 3-47 Migration Tool Configurations Parameters
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Migration Pause | If it is set to true the migration process is
temporarily paused.
Default Value: false Attribute: Editable |
| Key Type | Specifies the type of key used in the migration
process. The two key types are IMSI and MSISDN.
Default Value: MSISDN Attribute: Read-only |
| Delete 4G subscriber | Boolean field that determines whether 4G data should
be deleted.
Default Value: false Attribute: Read-only |
| Migration Realm | Represents the migration tool realm.
Default Value: oracle.com Attribute: Read-only |
| Migration Identity | Represents the migration tool identity.
Default Value: migration.oracle.com Attribute: Read-only |
| Migration Node Port | Represents the port number used for the migration
node.
Default Value: 3868 Attribute: Read-only |
| Migration Node Host | Specifies the host name or network address of the
migration node.
Default Value: ocudr-nudr-migration-service Attribute: Read-only |
Editing Migration Tool Configurations
- Click Edit. The Edit Migration Tool Configurations page appears.
- Update the configuration details as required and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel. You can navigate back to the Migration Tool Configurations page.
- Click Refresh to reload the Migration Tool Configurations page.
3.14 NF Scoring Configurations
- Settings
- Calculated Score
Settings:

Table 3-48 NF Scoring Settings for SLF
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable NF Scoring | Specifies whether to enable or disable the NF
Scoring. This is a mandatory parameter.
Data Type: Boolean Default Value: false Range: true or false |
| TPS | Specifies the Transaction Per Second. |
| Enable | Enables the TPS.
Data Type: Boolean Default Value: false Range: true or false |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the TPS. If
enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter.
Data Type: Integer Default Value: 20 Range: 1 to 100. |
| Max TPS | Specifies the maximum TPS. If enable is set to
true then this is a mandatory parameter.
Data Type: Integer Range: 1 to 1000000 |
| Service Health | Specifies the Service Health of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Service Health. This is a mandatory
parameter.
Data Type: Boolean Default Value: false Range: true or false |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the Service
Health. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory
parameter.
Data Type: Integer Default Value: 30 Range: 1 to 100 |
| Signaling Connections | Specifies the Signaling Connections of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Signaling Connections. This is a
mandatory parameter.
Data Type: Boolean Default Value: false Range: true or false |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the Signaling
Connections. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory
parameter.
Data Type: Integer Default Value: 20 Range: 1 to 100 |
| Max Connections | Specifies the maximum connections. If enable is
set to true then this is a mandatory parameter.
Data Type: Integer Range: 1 to 10000 |
| Replication Health | Specifies the Replication Health of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Replication Health.
Data Type: Boolean Default Value: false Range: true or false |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score of the Replication
Health. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory
parameter.
Data Type: Integer Default Value: 30 Range: 1 to 100 |
| Locality or Site preference | Specifies the Locality or Site Preference. |
| Enable | Enables the Locality or Site Preference.
Data Type: Boolean Default Value: false Range: true or false |
| Score | Specifies the score of the Locality or Site
Preference. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory
parameter.
Data Type: Integer Default Value: 5 Range: 1 to 100 |
| Active Alert | Specifies the Active Alerts of a site. |
| Enable | Enables the Active Alert.
Data Type: Boolean Default Value: false Range: true or false |
| Critical Alert Weightage | The site with more critical alerts is unhealthy.
If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter.
Data Type: Integer Default Value: 2 Range: 0 to 100 |
| Major Alert Weightage | The site with more major alerts is unhealthy. If
enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter.
Data Type: Integer Default Value: 1 Range: 0 to 100 |
| Minor Alert Weightage | The site with more minor alerts is unhealthy. If
enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter.
Data Type: Integer Default Value: 0 Range: 0 to 100 |
| Custom Criteria | Specifies the Custom Criteria of a site. |
| Enable | Specifies whether to enable or disable the
Custom Criteria.
Data Type: Boolean Default Value: false Range: true or false |
| Name | Name of the Custom Criteria. The two applicable
criteria are Subscriber Bulk Import tool and Subscriber Export
tool.
Data Type: String |
| Metric Name | Specifies the name of the Metric.
Data Type: String |
| Scoring Type | Specifies the scoring type. The two scoring
types are ratio and weightage.
Data Type: String |
| Max Score | Specifies the maximum score.
Data Type: Integer Default Value: 30 Range: 1 to 100 |
| Max Value | Specifies the maximum value.
Data Type: Integer Range: 0 to 10000 |
| Weightage | Specifies the weightage of the alert.
Data Type: Integer Default Value: 1 Range: 1 to 100 |
- Click Edit. The Edit Settings page appears.
- To add the Custom Criteria, click Add.
- The Add Custom Criteria dialog box appears.
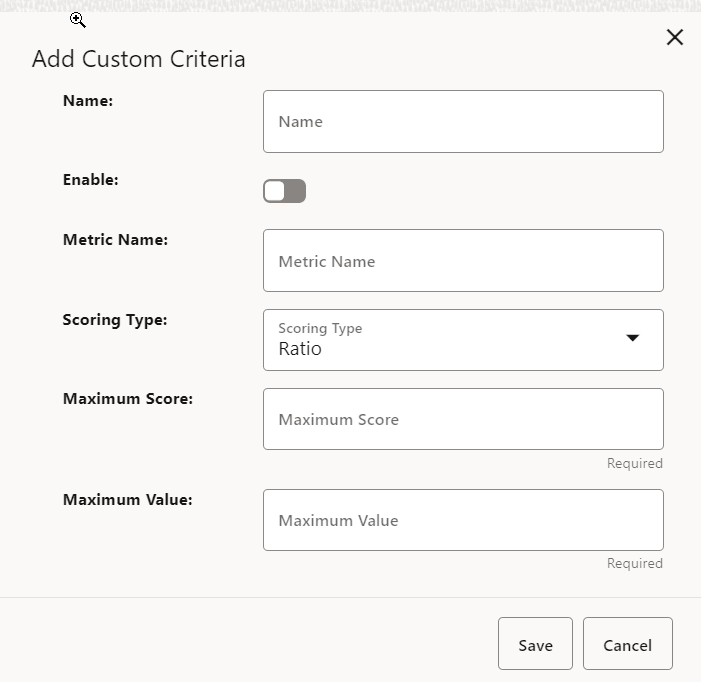
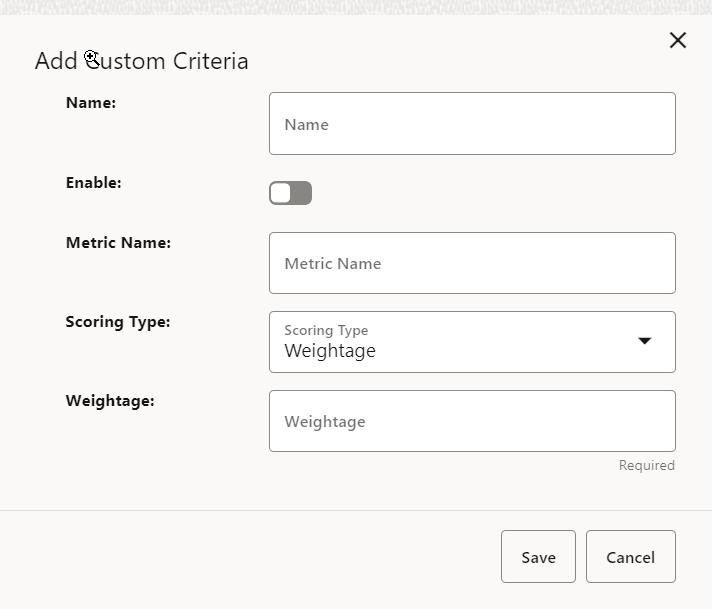
-
Fill in the required details and click Save to add the custom criteria.
Note:
If the scoring type is selected as weightage then maximum score and minimum score fields are disabled. - Click Cancel to exit the Add Custom Criteria dialog box.
- The Add Custom Criteria dialog box appears.
- Update the configuration details as required in the settings page and click Save. A confirmation message, "Save successfully." appears.
- If you do not want to modify any configuration, click Cancel.
- Click Refresh to reload the Settings page.
Calculated Score:
From the NF Scoring menu, select Calculated Score. If the NF Scoring feature is enabled. The Calculated Score page appears as below:
Figure 3-38 Calculated Score
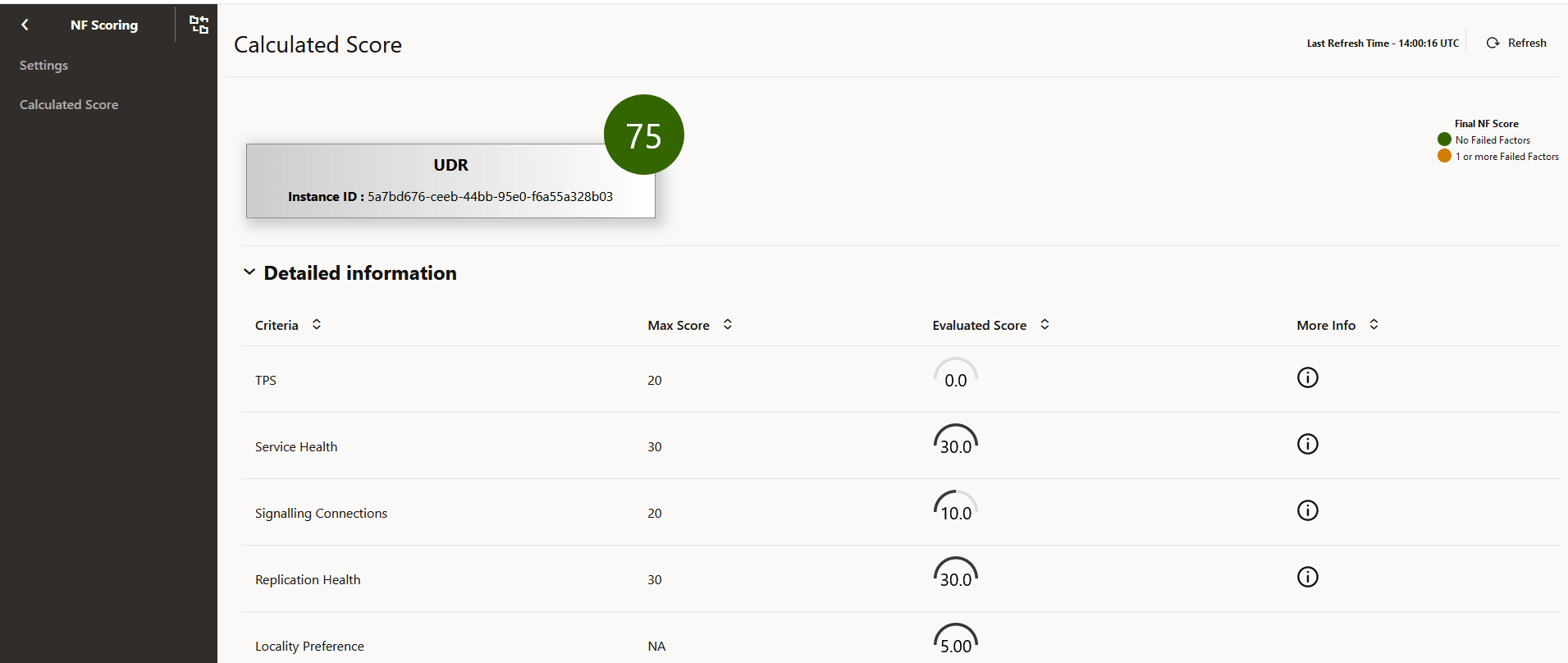
Note:
If app-info pod is down, you will not be getting the NF Score. You will get an error message that "Data can't be fetched due to internal server error".Calculated Score shows the total score along with the Instance ID. The total score is shown in either Green or Orange color. If the NF Score is shown in green color then there are no failed factors. And, if the NF Score is shown in Orange color there are one or more failed factors.
You can click on Detailed information to view different criteria and their Max Score, Evaluated Score, and More Info. The criteria in the detailed information tab show the evaluated score. The failed factors are shown with a warning symbol under the evaluated score. On the top-right of the screen, the Last Refresh Time information is available and a Refresh button is given to refresh the NF Score of a site.
3.15 Migration Tool Status
The Migration Tool Status page is a monitoring page, which is read-only. This page allows the operator to monitor the Migration Tool Status, which initiates on running the Migration Tool. For more information, see Migration Tool.
Figure 3-39 Migration Tool Status Page
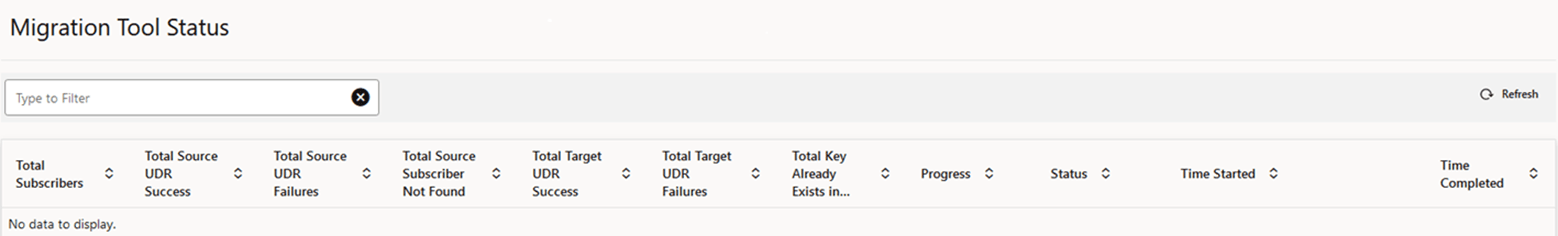
- Total Subscribers: The total number of subscribers included in the migration process.
- Total Source UDR Success: The total number of records successfully migrated from 4G UDR.
- Total Source UDR Failure: The total number of records failed during the migration from 4G UDR.
- Total Source Subscriber Not Found: The total number of subscribers not found for migration from 4G UDR.
- Total Target UDR Success: The total number of records successfully migrated to 5G UDR.
- Total Target UDR Failure: The total number of record failed during the migration in 5G UDR
- Total Key Already Exists in the Target UDR: The total number of keys that already exist in 5G UDR.
- Progress: Shows migration progress completion in percentage.
- Status: The overall status of the migration process. For example, STARTED, IN PROGRESS, PAUSED, or COMPLETED.
- Time Started: Shows the migration process start time.
- Time Completed: Shows the migration process completion time.
Note:
Using Filter option, you can filter the records you are interested in and using Refresh option, you can refresh the Subscriber Bulk Import Status page.