4.3 Deployment Related Issues
This section describes the most common deployment related issues and their resolution steps. Users are recommended to attempt the resolution provided in this section before contacting Oracle Support.
4.3.1 Debugging Pre-Installation Related Issues
As of now, there are no known preinstallation related issues that you may encounter before installing UDR. However, it is recommended to see the Prerequisites and PreInstallation Tasks section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide to prepare for UDR installation.
4.3.2 Debugging Installation Related Issues
This section describes how to troubleshoot the installation related issues. It is recommended to see the Generic Checklist section also in addition to the information shared in this section.
4.3.2.1 Debugging Pod Creation Failure
A pod creation can fail due to various reasons. Some of the possible scenarios are as follows:
Verifying Pod Image Correctness
To verify pod image:
- Check whether any of the pods is in the ImagePullBackOff state.
- Check whether the image name used for any pod is incorrect. Verify the
following values in the custom-values.yaml
file.
global: dockerRegistry: ocudr-registry.us.oracle.com:5000/ocudr nudr-drservice: image: name: nudr_datarepository_service tag: 25.2.100 nudr-dr-provservice: image: name: nudr_datarepository_service tag: 25.2.100 nudr-notify-service: image: name: nudr_notify_service tag: 25.2.100 nudr-config: image: name: nudr_config tag: 25.2.100 config-server: # Image details image: ocpm_config_server imageTag: 25.2.102 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent ingressgateway-sig: image: name: ocingress_gateway tag: 25.2.104 initContainersImage: name: configurationinit tag: 25.2.104 updateContainersImage: name: configurationupdate tag: 25.2.104 dbHookImage: name: common_config_hook tag: 25.2.104 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent ingressgateway-prov: image: name: ocingress_gateway tag: 25.2.104 initContainersImage: name: configurationinit tag: 25.2.104 updateContainersImage: name: configurationupdate tag: 25.2.104 dbHookImage: name: common_config_hook tag: 25.2.104 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent egressgateway: image: name: ocegress_gateway tag: 25.2.104 initContainersImage: name: configurationinit tag: 25.2.104 updateContainersImage: name: configurationupdate tag: 25.2.104 dbHookImage: name: common_config_hook tag: 25.2.104 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent nudr-diameterproxy image: name: nudr_diameterproxy tag: 25.2.100 nudr-ondemandmigration: image: name: nudr_ondemandmigration tag: 25.2.100 alternate-route: deploymentDnsSrv: image: alternate_route tag: 25.2.104 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent dbHookImage: name: common_config_hook tag: 25.2.104 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent perf-info: image: perf-info imageTag: 25.2.102 imagepullPolicy: Always dbHookImage: name: common_config_hook tag: 25.2.104 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent app-info: image: app-info imageTag: 25.2.102 imagepullPolicy: Always dbHookImage: name: common_config_hook tag: 25.2.104 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent nrf-client: image: nrf-client imageTag: 25.2.102 imagepullPolicy: Always dbHookImage: name: common_config_hook tag: 25.2.104 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent nudr-dbcr-auditor-service: image: name: nudr_dbcr_auditor_service tag: 25.2.100 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent - After updating the values.yaml file, run the following command for helm
upgrade:
helm upgrade <helm chart> [--version <OCUDR version>] --name <release> --namespace <ocudr-namespace> -f <ocudr_values.yaml> - If the helm install command is stuck for a long time or fails with timeout
error, verify whether the pre install hooks have come up. Verify whether there exists any
ImagePullBackOff status check as follows.
hookImageDetails
global: dockerRegistry: ocudr-registry.us.oracle.com:5000/ocudr preInstall: image: name: nudr_common_hooks tag: 25.2.100 preUpgrade: image: name: nudr_common_hooks tag: 25.2.100 postUpgrade: image: name: nudr_common_hooks tag: 25.2.100 postInstall: image: name: nudr_common_hooks tag: 25.2.100 preRollback: image: name: nudr_common_hooks tag: 25.2.100 postRollback: image: name: nudr_common_hooks tag: 25.2.100 test: image: name: nf_test tag: 25.2.102After updating these values, you can purge the deployment and install helm again.
Verifying Resource Allocation Failure
To verify any resource allocation failure:
- Run the following command to verify whether any pod is in the Pending
state.
kubectl describe <nudr-drservice pod id> --n <ocudr-namespace> - Verify whether any warning on insufficient CPU exists in the describe output of the respective pod. If it exists, it means there are insufficient CPUs for the pods to start. Address this hardware issue.
- If any preinstall hooks are in pending state, then check the resources
allocated for hooks. Do not allocate higher values for hooks. If hooks with lower CPU or
memory are going to pending state, then there is an issue with available resources on
cluster. Check the resources and reduce the number of CPUs alloted to the pod in the
values.yaml file.
hookresources
global: hookJobResources: limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi requests: cpu: 1 memory: 1Giresources
nudr-drservice: resources: limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi requests: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi nudr-dr-provservice: resources: limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi requests: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi nudr-notify-service: resources: limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi requests: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi nudr-config: resources: limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi requests: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi config-server: resources: limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi requests: cpu: 2 memory: 512Mi nudr-client: resources: limits: cpu: 1 memory: 2Gi requests: cpu: 1 memory: 512Mi nudr-diameterproxy: resources: limits: cpu: 3 memory: 4Gi requests: cpu: 3 memory: 4Gi nudr-ondemand-migration: resources: limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi requests: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi ingressgateway: resources: limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi initServiceCpu: 1 initServiceMemory: 1Gi updateServiceCpu: 1 updateServiceMemory: 1Gi commonHooksCpu: 1 commonHooksMemory: 1Gi requests: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi initServiceCpu: 1 initServiceMemory: 1Gi updateServiceCpu: 1 updateServiceMemory: 1Gi commonHooksCpu: 1 commonHooksMemory: 1Gi egressgateway: resources: limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi initServiceCpu: 1 initServiceMemory: 1Gi updateServiceCpu: 1 updateServiceMemory: 1Gi commonHooksCpu: 1 commonHooksMemory: 1Gi requests: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi initServiceCpu: 1 initServiceMemory: 1Gi updateServiceCpu: 1 updateServiceMemory: 1Gi commonHooksCpu: 1 commonHooksMemory: 1Gi alternate-route: resources: limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi commonHooksCpu: 1 commonHooksMemory: 1Gi requests: cpu: 2 memory: 2Gi commonHooksCpu: 1 commonHooksMemory: 1Gi perf-info: resources: limits: cpu: 1 memory: 1Gi requests: cpu: 1 memory: 1Gi app-info: resources: limits: cpu: 1 memory: 1Gi requests: cpu: 1 memory: 1Gi - Run the following helm upgrade command after updating the values.yaml
file.
helm upgrade <helm chart> [--version <OCUDR version>] --name <release> --namespace <ocudr-namespace> -f <ocudr_values.yaml>
Verifying Resource Allocation Issues on Webscale Environment
Webscale environment has openshift container installed. There can be cases where,
- Pods does not scale after you run the installation command and the helm install command fails with timeout error. In this case, check for preinstall hooks failure. Run the oc get job command to create the jobs. Describe the job for which the pods are not getting scaled and check if there are quota limit exceeded errors with CPU or memory.
- Any of the actual microservice pods do not scale post the hooks completion. In this case, run the oc get rs command to get the list of replicaset created for the NF deployment. Then, describe the replicaset for which the pods are not getting scaled and check for resource quota limit exceeded errors with CPU or memory.
- Helm install command times-out after all the microservice pods are scaled as expected with the expected number of replicas. In this case, check for post install hooks failure. Run the oc get job command to get the post install jobs and do a describe on the job for which the pods are not getting scaled and check if there are quota limit exceeded errors with CPU or memory.
- Resource quota exceed beyond limits.
4.3.2.2 Debugging Pod Startup Failure
- If dr-service, diameter-proxy, and diam-gateway services are stuck
in the CrashLoopBackOff state, then the reason could be that config-server is
not yet up. A sample log on these services is as
follows:
"Config Server is Not yet Up, Wait For config server to be up."To resolve this, make sure the dependent services nudr-config and nudr-config-server is up or the startup probe will attempt to restart pod for every configured amount of time.
- If the notify-service and on-demand migration service is stuck in
the Init state, then the reason could be the dr-service is not yet up. A sample
log on these services is as
follows:
"DR Service is Not yet Up, Wait For dr service to be up."To resolve this, check for failures on dr-service or the startup probe will attempt to restart pod for every configured amount of time.
- If the microservices connecting to mySQL database is stuck in Crashloopbackoff
state, check for mySQL exceptions in the logs and fix accordingly or If you
receive error messages
The database secret is emptyorInvalid data present in the secretin the main service container logs make sure that the secret is created as mentioned in document and check for the case sensitivity of the keys in the secret. For example, encryptionKey, dsusername, and so on.
4.3.2.3 Debugging UDR with Service Mesh Failure
- Istio-Proxy side car container not attached to Pod: This
particular failure arises when istio injection is not enabled on the NF
installed namespace. Run the following command to verify the same:
kubectl get namespace -L istio-injectionFigure 4-6 Verifying Istio-Proxy
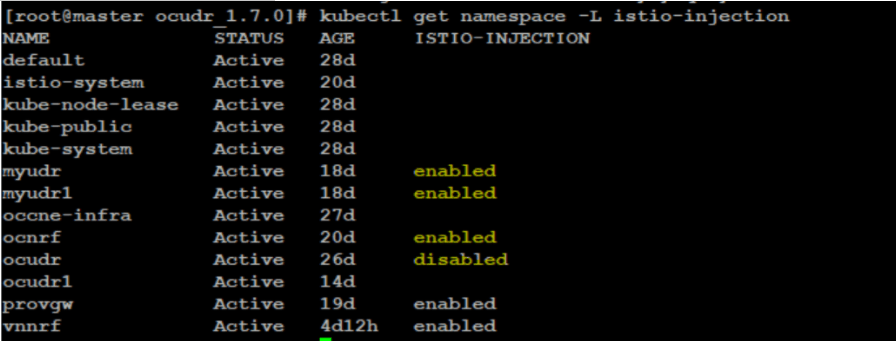
To enable the istio injection, run the following command:
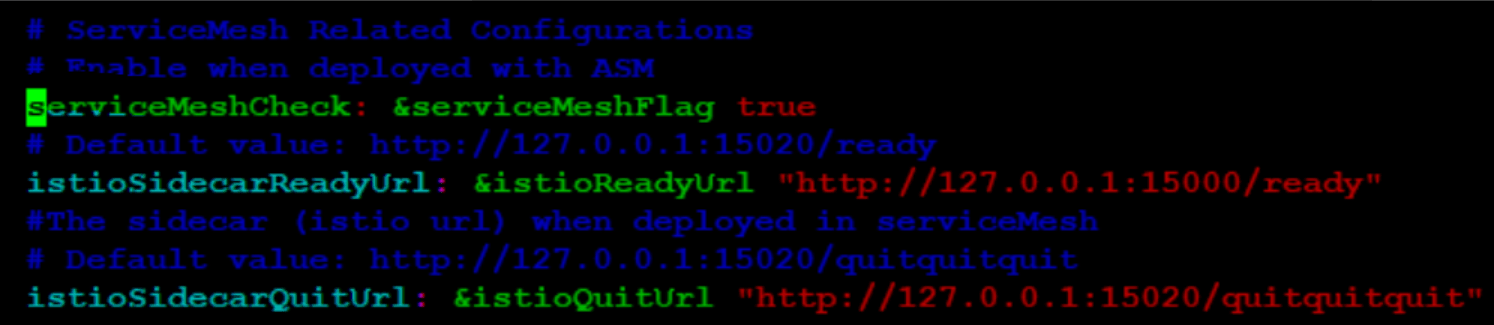
kubectl label --overwrite namespace <nf-namespace> istio-injection=enabled - If any of the hook pods is not responding in the 'NotReady' state
and is not cleared after completion, check if the following configuration is set
to 'true' under global section. Also, ensure that the URL configured for
istioSidecarQuitUrl is correct.
Figure 4-7 When Hook Pod is NotReady
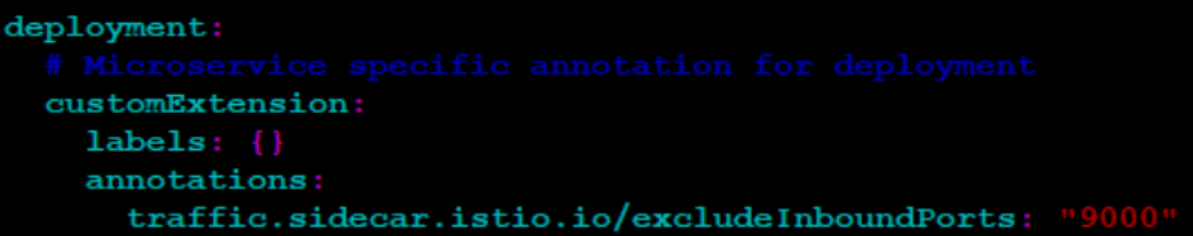
- When Prometheus does not scrape metrics from
nudr-nrf-client-service, see if the following annotation is present under
nudr-nrf-client-service:
Figure 4-8 nrf-client service
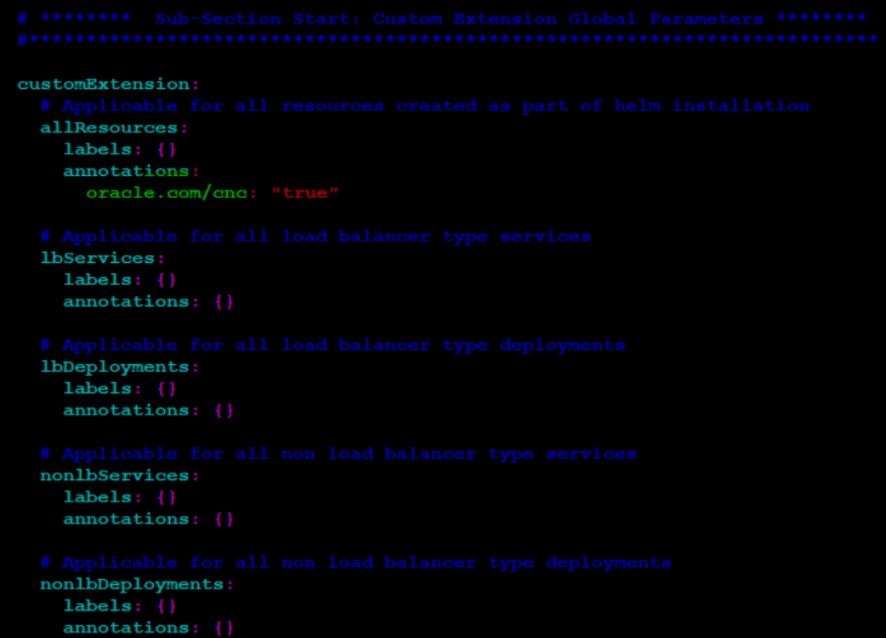
- If there are issues in viewing UDR metrics on OSO Prometheus, you
need to ensure that the following highlighted annotation is added to all
deployments for the NF.
Figure 4-9 Issues in Viewing UDR Metrics - Add Annotation
- When vDBTier is used as backend and there are connectivity issues, and when nudr-preinstall communicates with DB, which can be seen from error logs on preinstall hook pod, then make the destination rule and service entry for mysql-connectivity-service on occne-infra namespace.
- When installed on ASM, if ingressgateway, egressgateway, or alternate-route services go into CrashLoopBackOff, you must check if the coherence ports is excluded for inbound and outbound on the istio-proxy.
- On the latest F5 versions, if the default istio-proxy resources assigned is
less, make sure that you assign minimum one CPU and one GB RAM for all UDR
services. The traffic handling services must be same as mentioned in the
resource profile. If the pods crash due to less memory, you must check the
configuration. You can refer the following annotations in the custom values
file.
deployment: # Replica count for deployment replicaCount: 2 # Microservice specific notation for deployment customExtension: labels: {} annotations: sidecar.istio.io/proxyCPU: "1000m" sidecar.istio.io/proxyCPULimit: "lOOOm" sidecar.istio.io/proxyMemory: "lGi" sidecar.istio.io/proxyMemoryLimit : "lGi" proxy.istio.io/config: | terminationDrainDuration: 60s
4.3.2.4 Debugging SLF Default Group ID related Issues
http://localhost:8080/slf-group-prov/v1/slf-group{
"slfGroupName": "DefaultGrp",
"slfGroupType": "LteHss",
"nfGroupIDs": {
"NEF": "nef-group-default",
"UDM": "udm-group-default",
"PCF": "pcf-group-default",
"AUSF": "ausf-group-default",
"CHF": "chf-group-default"
}
}The default group name is dynamically editable through CNCC. If user changes default group name on CNCC and does not add the same to SLF_GROUP_NAME, then the default group name can be added through API as mentioned above.
4.3.2.5 Debugging Subscriber Activity Logging
- If subscriber activity logging is not enabled, check the subscriberAcitivtiyEnabled flag and subscriberIdentifiers keys in the Global Configurations Parameters. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository User Guide.
- If you are not getting the subscriber logs after enabling the flag, then make sure that the subscriber identifiers mentioned in the configuration API contains the same key value as the testing subscriber identifiers.
- Each subscriber identifiers can be configured up to 100 keys using CNC Console or REST API .
- You can remove a subscriber from this feature by removing the subscriber
identifiers key from the Global Configurations Parameters as shown
below:
"subscriberActivityEnabled": true, "subscriberldentifers": { "nai": [], "imsi": [ "1111111127,1111111128" ], "extid": [], "msisdn": [ "1111111129,1111111130" ]
4.3.2.6 Debugging Subscriber Bulk Import Tool Related Issues
- Resources is not available. In this case, allocate more resources for the namespace. The "kubectl describe pod" will give you more details on this issue.
- PVC allocation failed for subscriber bulk import tool. During re-installation, there can be a case where the existing PVC is not linked to subscriber bulk import tool. You can debug the issue based on the details from the describe pod output.
- The storage class is not configured correctly. In this case, check the
correctness of the configuration as below.
Figure 4-10 Bulk Import Persistent Claim

- When subscriber bulk tool installation is complete, there can be a case where
REST APIs configurations is not working. In this case, make sure that the below
configuration is updated in the custom-values.yaml file.
Figure 4-11 OCUDR Release name

- If the transfer-in and transfer-out functionality are not working after the
remote host transfer is enabled. Make sure that the below steps are performed to
resolve the issue:
- The kubernetes secrets created are correct for the private and public keys.
- The remote host configured and secrets created are of the same remote host.
- The remote path is correct.
- The space remaining in the remote host is within the limits of the file size that you are transferring.
4.3.2.7 Debugging NF Scoring for a Site
- Perform a GET request using
http://<nudr-config-host>:<nudr-config-port>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/app-info/nfScoringto check if the NF Scoring feature is enabled. If the feature is disabled, the request will show an "ERROR feature not enabled". To enable the feature, use the above GET API to set the feature flag to true and then fetch the NF score. - To get the detailed information on provisioning and signaling, multiple ingress gateways must be set to true for UDR and SLF.
- If the
Custom Criteriais enabled and the calculation of NF score for custom criteria fails, you must check the name of the metric and other configured details in custom criteria.
4.3.2.8 Debugging Subscriber Export Tool Related Issues
- Resources is not available. In this case, allocate more resources for the namespace. The "kubectl describe pod" will give you more details on this issue.
- PVC allocation failed for subscriber bulk import tool. During re-installation, there can be a case where the existing PVC is not linked to subscriber export tool. You can debug the issue based on the details from the describe pod output.
- The storage class is not configured correctly. In this case, check the
correctness of the configuration as below.
Figure 4-12 Export tool Presistent Claim
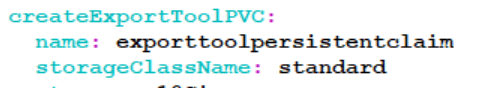
- When subscriber export tool installation is complete, there can be a case where
the REST APIs configuration is not working. In this case, make sure that the
below configuration is updated in the custom-values.yaml file.
Figure 4-13 OCUDR Release name

- If the export dump is not generated, you can check the logs for more details.
Check the configuration is updated correctly as below.
Figure 4-14 Export Tool Persistent Claim Standard

- If the transfer-in and transfer-out functionality are not working after the
remote host transfer is enabled. Make sure that the below steps are performed to
resolve the issue:
- The kubernetes secrets created are correct for the private and public keys.
- The remote host configured and secrets created are of the same remote host.
- The remote path is correct.
- The space remaining in the remote host is within the limits of the file size that you are transferring.
4.3.2.9 Debugging Controlled Shutdown Related Issues
- Check the REST API GLOBAL configuration section if the control shutdown is not
enabled. Make sure the flag
enableControlledShutdownparameter is set to true to enable the feature. - Once the flag is enabled to true, you can do a PUT request to
udr/nf-common-component/v1/operationalState. The PUT request throws an error if the flag is disabled. - When the operational state is set to COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN, all the
ingress gateway requests are rejected with the configured error codes. If the
request is not rejected, check if the feature flag is enabled and do a GET
request on
udr/nf-common-component/v1/operationalState. - The subscriber export tool and subscriber import tool rejects all the new request that is queued for processing.
- When the operational state is COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN the NF status is updated as SUSPENDED at NRF. Check the app-info logs if the status is not updated to SUSPENDED. The logs contain the operational state of COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN.
4.3.2.10 Debug Readiness Failure
- Make sure that the dependent services is up. Check the logs for the
below content:
Dependent services down, Set readiness state to REFUSING_TRAFFIC - Make sure that the database is available and the app-info is ready
to monitor the database. Check the logs for the below content:
DB connection down, Set readiness state to REFUSING_TRAFFIC - The readiness failure can occur, if resource map or key map table in
the database are not having proper content. Check the logs for the below
content:
ReourceMap/KeyMap Entries missing, Set readiness state to REFUSING_TRAFFIC
4.3.2.11 Enable cnDBTier Metrics with OSO Prometheus
kubectl create -f <.yaml> -n <nsdbtier>apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: cndb-to-mysql-external-se
spec:
exportTo:
- "."
hosts:
- mysql-connectivity-service
location: MESH_EXTERNAL
ports:
- number: 3306
name: mysql2
protocol: MySQL
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: nf-to-nf
spec:
exportTo:
- "."
hosts:
- "*.$DOMAIN_NAME" # DOMAIN_NAME must be replaced with the deployed CNE Domain name
location: MESH_EXTERNAL
ports:
- number: 80
name: HTTP2-80
protocol: TCP
- number: 8080
name: HTTP2-8080
protocol: TCP
- number: 3306
name: TCP-3306
protocol: TCP
- number: 1186
name: TCP-1186
protocol: TCP
- number: 2202
name: TCP-2202
protocol: TCP
resolution: NONE
---
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: PeerAuthentication
metadata:
name: default
spec:
mtls:
mode: PERMISSIVE
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: nf-to-kube-api-server
spec:
hosts:
- kubernetes.default.svc.$DOMAIN_NAME # DOMAIN_NAME must be replaced with the deployed CNE Domain name
exportTo:
- "."
addresses:
- 172.16.13.4
location: MESH_INTERNAL
ports:
- number: 443
name: https
protocol: HTTPS
- number: 6443
name: https-1
protocol: HTTPS
resolution: NONE
---##################################################################################
# #
# Copyright (c) 2022 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. #
# #
##################################################################################
nameOverride: prom
## Helm-Test (Optional)
# Values needed for helm-test, Comment the entire Section if Helm-test not needed.
helmtestimage: occne-repo-host:5000/k8s.gcr.io/ingress-nginx/controller:v1.3.1
useasm: false
namespace: ocudr-ns
clustername: cne-23-1-rc2
resources:
limits:
cpu: 10m
memory: 32Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 32Mi
promsvcname: oso-prom-svr
almsvcname: oso-prom-alm
prometheushealthyurl: /prometheus/-/healthy
prometheusreadyurl: /prometheus/-/ready
# Note: There are 3 types of label definitons provided in this custom values file
# TYPE1: Global(allResources)
# TYPE2: lb & nonlb TYPE label only
# TYPE3: service specific label
## NOTE: POD level labels can be inserted using the specific pod label sections, every pod/container has this label defined below in all components sections.
# ******** Custom Extension Global Parameters ********
#**************************************************************************
global_oso:
# Prefix & Suffix that will be added to containers
k8Resource:
container:
prefix:
suffix:
# Service account for Prometheus, Alertmanagers
serviceAccountNamePromSvr: ""
serviceAccountNameAlertMgr: ""
customExtension:
# TYPE1 Label
allResources:
labels: {}
# TYPE2 Labels
lbServices:
labels: {}
nonlbServices:
labels: {}
lbDeployments:
labels: {}
nonlbDeployments:
labels: {}
lbStatefulSets:
labels: {}
# Add annotations for disabling sidecar injections into oso pods here
# eg: annotations:
# - sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
annotations:
- sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
## Setting this parameter to false will disable creation of all default clusterrole, clusterolebing, role, rolebindings for the componenets that are packaged in this csar.
rbac:
create: true
podSecurityPolicy:
enabled: false
## Define serviceAccount names for components. Defaults to component's fully qualified name.
##
serviceAccounts:
alertmanager:
create: true
name:
annotations: {}
nodeExporter:
create: false
name:
annotations: {}
pushgateway:
create: false
name:
annotations: {}
server:
create: true
name:
annotations: {}
alertmanager:
enabled: true
## Use a ClusterRole (and ClusterRoleBinding)
## - If set to false - Define a Role and RoleBinding in the defined namespaces ONLY
## This makes alertmanager work - for users who do not have ClusterAdmin privs, but wants alertmanager to operate on their own namespaces, instead of clusterwide.
useClusterRole: false
## Set to a rolename to use existing role - skipping role creating - but still doing serviceaccount and rolebinding to the rolename set here.
useExistingRole: false
## alertmanager resources name
name: alm
image:
repository: occne-repo-host:5000/quay.io/prometheus/alertmanager
tag: v0.24.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
extraArgs:
data.retention: 120h
prefixURL: /cne-23-1-rc2/alertmanager
baseURL: "http://localhost/cne-23-1-rc2/alertmanager"
configFileName: alertmanager.yml
nodeSelector: {}
affinity: {}
podDisruptionBudget:
enabled: true
minAvailable: 1
persistentVolume:
enabled: true
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
annotations: {}
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume existing claim name
## Requires alertmanager.persistentVolume.enabled: true
## If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
existingClaim: ""
mountPath: /data
size: 2Gi
storageClass: "standard"
## Annotations to be added to alertmanager pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
## Labels to be added to Prometheus AlertManager pods
##
podLabels: {}
replicaCount: 2
## Annotations to be added to deployment
##
deploymentAnnotations: {}
statefulSet:
## If true, use a statefulset instead of a deployment for pod management.
## This allows to scale replicas to more than 1 pod
##
enabled: true
annotations: {}
labels: {}
podManagementPolicy: OrderedReady
## Alertmanager headless service to use for the statefulset
##
headless:
annotations: {}
labels: {}
## Enabling peer mesh service end points for enabling the HA alert manager
## Ref: https://github.com/prometheus/alertmanager/blob/master/README.md
enableMeshPeer: true
servicePort: 80
## alertmanager resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources:
limits:
cpu: 20m
memory: 64Mi
requests:
cpu: 20m
memory: 64Mi
service:
annotations: {}
labels: {}
clusterIP: ""
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 80
# nodePort: 30000
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
## Monitors ConfigMap changes and POSTs to a URL
## Ref: https://github.com/jimmidyson/configmap-reload
##
configmapReload:
prometheus:
enabled: true
## configmap-reload container name
##
name: configmap-reload
image:
repository: occne-repo-host:5000/docker.io/jimmidyson/configmap-reload
tag: v0.8.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# containerPort: 9533
## Additional configmap-reload mounts
##
extraConfigmapMounts: []
## Security context to be added to configmap-reload container
containerSecurityContext: {}
## configmap-reload resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources:
limits:
cpu: 10m
memory: 32Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 32Mi
alertmanager:
enabled: true
name: configmap-reload
image:
repository: occne-repo-host:5000/docker.io/jimmidyson/configmap-reload
tag: v0.8.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# containerPort: 9533
## Additional configmap-reload mounts
##
extraConfigmapMounts: []
# - name: prometheus-alerts
# mountPath: /etc/alerts.d
# subPath: ""
# configMap: prometheus-alerts
# readOnly: true
resources:
limits:
cpu: 10m
memory: 32Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 32Mi
kubeStateMetrics:
enabled: false
nodeExporter:
enabled: false
server:
enabled: true
## namespaces to monitor (instead of monitoring all - clusterwide). Needed if you want to run without Cluster-admin privileges.
namespaces: []
# - ocudr-ns
name: svr
image:
repository: occne-repo-host:5000/quay.io/prometheus/prometheus
tag: v2.39.1
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
prefixURL: /cne-23-1-rc2/prometheus
baseURL: "http://localhost/cne-23-1-rc2/prometheus"
## Additional server container environment variables
env: []
# List of flags to override default parameters, e.g:
# - --enable-feature=agent
# - --storage.agent.retention.max-time=30m
defaultFlagsOverride: []
extraFlags:
- web.enable-lifecycle
## web.enable-admin-api flag controls access to the administrative HTTP API which includes functionality such as
## deleting time series. This is disabled by default.
# - web.enable-admin-api
##
## storage.tsdb.no-lockfile flag controls BD locking
# - storage.tsdb.no-lockfile
##
## storage.tsdb.wal-compression flag enables compression of the write-ahead log (WAL)
# - storage.tsdb.wal-compression
## Path to a configuration file on prometheus server container FS
configPath: /etc/config/prometheus.yml
global:
scrape_interval: 1m
scrape_timeout: 30s
evaluation_interval: 1m
#remoteWrite:
#- url OSO_CORTEX_URL
# remote_timout (default = 30s)
#remote_timeout: OSO_REMOTE_WRITE_TIMEOUT
# bearer_token for cortex server to be configured
# bearer_token: BEARER_TOKEN
extraArgs:
storage.tsdb.retention.size: 1GB
## Additional Prometheus server Volume mounts
##
extraVolumeMounts: []
## Additional Prometheus server Volumes
##
extraVolumes: []
## Additional Prometheus server hostPath mounts
##
extraHostPathMounts: []
# - name: certs-dir
# mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/certs
# subPath: ""
# hostPath: /etc/kubernetes/certs
# readOnly: true
extraConfigmapMounts: []
nodeSelector: {}
affinity: {}
podDisruptionBudget:
enabled: false
maxUnavailable: 1
persistentVolume:
enabled: true
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
annotations: {}
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume existing claim name
## Requires server.persistentVolume.enabled: true
## If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
existingClaim: ""
size: 2Gi
storageClass: "standard"
## Annotations to be added to Prometheus server pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
## Labels to be added to Prometheus server pods
##
podLabels: {}
## Prometheus AlertManager configuration
##
alertmanagers:
- kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
# Namespace to be configured
namespaces:
names:
- ocudr-ns
- dbtier-ns
path_prefix: cne-23-1-rc2/alertmanager
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
# namespace to be configured
regex: ocudr-ns
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app]
regex: prom
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_component]
regex: alm
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_probe]
regex: .*
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number]
regex:
action: drop
## Use a StatefulSet if replicaCount needs to be greater than 1 (see below)
##
replicaCount: 1
## Annotations to be added to deployment
##
deploymentAnnotations: {}
statefulSet:
## If true, use a statefulset instead of a deployment for pod management.
## This allows to scale replicas to more than 1 pod
##
enabled: false
annotations: {}
labels: {}
podManagementPolicy: OrderedReady
resources:
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 4Gi
requests:
cpu: 2
memory: 4Gi
service:
enabled: true
annotations: {}
labels: {}
clusterIP: ""
externalIPs: []
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 80
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
## If using a statefulSet (statefulSet.enabled=true), configure the
## service to connect to a specific replica to have a consistent view
## of the data.
statefulsetReplica:
enabled: false
replica: 0
retention: "7d"
pushgateway:
## If false, pushgateway will not be installed
##
enabled: false
## alertmanager ConfigMap entries
##
alertmanagerFiles:
alertmanager.yml:
global: {}
# slack_api_url: ''
receivers:
- name: default-receiver
# slack_configs:
# - channel: '@you'
# send_resolved: true
route:
group_wait: 10s
group_interval: 5m
receiver: default-receiver
repeat_interval: 3h
## Prometheus server ConfigMap entries for rule files (allow prometheus labels interpolation)
ruleFiles: {}
## Prometheus server ConfigMap entries
##
serverFiles:
## Alerts configuration
## Ref: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/alerting_rules/
alerting_rules.yml: {}
## DEPRECATED DEFAULT VALUE, unless explicitly naming your files, please use alerting_rules.yml
alerts: {}
## Records configuration
## Ref: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/recording_rules/
recording_rules.yml: {}
## DEPRECATED DEFAULT VALUE, unless explicitly naming your files, please use recording_rules.yml
rules: {}
prometheus.yml:
rule_files:
- /etc/config/recording_rules.yml
- /etc/config/alerting_rules.yml
## Below two files are DEPRECATED will be removed from this default values file
- /etc/config/rules
- /etc/config/alerts
scrape_configs:
- job_name: prometheus
metrics_path: cne-23-1-rc2/prometheus/metrics
static_configs:
- targets:
- localhost:9090
extraScrapeConfigs: |
- job_name: 'oracle-cnc-service'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
namespaces:
names:
- ocudr-ns
- dbtier-ns
# - ns2
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_oracle_com_cnc]
regex: true
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_service_name
- job_name: 'oracle-cnc-pod'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
namespaces:
names:
- ocudr-ns
- dbtier-ns
# - ns2
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_oracle_com_cnc]
regex: true
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_pod_name
- job_name: 'oracle-cnc-endpoints'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
#namespaces:
# names:
# - ns1
# - ns2
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_oracle_com_cnc]
regex: true
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme]
action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- job_name: 'oracle-cnc-ingress'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: ingress
#namespaces:
# names:
# - ns1
# - ns2
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_annotation_oracle_com_cnc]
regex: true
action: keep4.3.2.12 Debugging ndbmysqld Pods Restart During cnDBTier Installation or Upgrade
During cnDBTier Installation or Upgrade the readiness probe fails as the ndbmysqld pods
wait for the data nodes to be up and running. This causes the ndbmysqld pods to restart
with Reason: Error and Exit Code: 1 error. If the data nodes takes time
to come up for any reason, such as slowness of cluster, the ndbmysqld pods will restart.
The ndbmysqld pods stabilize when the data nodes comes up.
4.3.2.13 Debugging Error Logging Related Issues
- You must set the
additionalErrorLoggingparameter to ENABLED per microservice for the Error Logging feature to work. This feature is "DISABLED" by default and it can be ENABLED or DISABLED using REST APIs, CNC console, or by changing the values in custom values yaml file during installation. - For logging subscriber information in the logs, you must set the
logSubscriberInfoparameter to "ENABLED" per microservice. The parameter can be ENABLED or DISABLED using REST APIs, CNC console, or by changing the values in custom values yaml file during installation.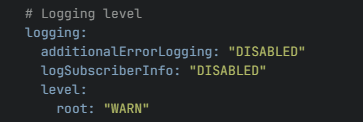
4.3.2.14 Debugging Suppress Notification Related Issues
- You must set the
suppressNotificationEnabledparameter to true in the global section of the custom values yaml file for the Suppress Notification feature to work. This feature is enabled by default and it can be enabled or disabled using REST APIs, CNC console, or by changing the values in custom values yaml file during installation. - If you observe unexpected notification then check if the feature is enabled from the global configuration using configuration REST APIs.
- If the feature is enabled and you observe unexpected notifications for update requests then compare the User-Agent received in the request header with the User-Agent received in the subscription request.
- This feature is applicable only for signaling requests. For provisioning request the notification generation behavior remains same as earlier.
- This feature does not work with the subscription created in the
previous release versions. You must create new subscriptions with the feature
enabled for Suppress Notification feature to work.
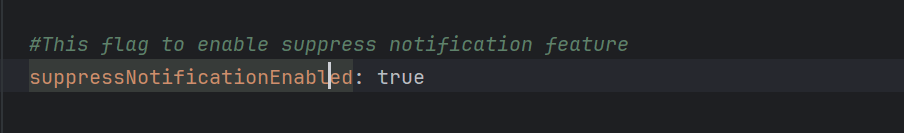
4.3.2.15 Debugging Diameter S13 Interface Related Issues
- If
global.s13InterfaceEnableflag is set to true and if the helm installation is throwing errors, you must enable the following parameters inocudr-custom-values.yamlfile:global.diamGatewayEnablenudr-diameterproxy.enabled
- If the NRF client heartbeats do not consider the diameter services
when diameter S13 interface is enabled, you must check the following
configuration in the
ocudr-custom-values.yamlfile.Note:
The NRF client does not register the EIR with NRF if diameter services is down.#eir mode eir: &eir - '{{ .Release.Name }}-nudr-drservice' - '{{ .Release.Name }}-egressgateway' - '{{ .Release.Name }}-ingressgateway-sig' - '{{ .Release.Name }}-ingressgateway-prov' - '{{ .Release.Name }}-nudr-config' #uncomment only if config service enabled - '{{ .Release.Name }}-nudr-config-server' #uncomment only if config service enabled - '{{ .Release.Name }}-alternate-route' #uncomment if alternate route enabled - '{{ .Release.Name }}-nudr-dr-provservice' # uncomment only if drProvisioningEnabled is enabled - '{{ .Release.Name }}-nudr-diameterproxy' # uncomment only if s13InterfaceEnable is enabled - '{{ .Release.Name }}-nudr-diam-gateway' # uncomment only if s13InterfaceEnable is enabled - If the diameter gateway is answering CEA message with
DIAMETER_UNKNOWN_PEER, then client peer configuration is incorrect. You must perform the configuration inallowedClientNodessection of diameter gateway service configuration using REST API for the client to connect to EIR and send an ECR request. - If the diameter gateway is answering CEA message as success and
other diameter message responds with
DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY/DIAMETER_MISSING_AVP, then the issue could be in the diameter message request. - If there are error logs in diameter gateway microservice stating that the connection is refused with IP and port numbers, then the specified configured peer node was not able to accept CER request from diameter gateway. The diameter gateway retries multiple times to connect that peer.
- If you are getting
DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVERYerror message, then diameterproxy microservice is down. - If the diam-gateway goes to crashloop back off state, then it could be due to incorrect peer node configuration.
- Active connections to the existing peer nodes can be verified using
ocudr_diam_conn_networkmetric.
4.3.2.16 Debugging TLS Related Issues
This section describes the TLS related issues and their resolution steps. It is recommended to attempt the resolution steps provided in this guide before contacting Oracle Support.
Problem: Handshake is not established between UDRs.
Scenario: When the client version is TLSv1.2 and the server version is TLSv1.3.
Server Error Message
The client supported protocol versions[TLSv1.2] are not accepted by server preferences [TLSv1.3]Client Error Message
Received fatal alert: protocol_versionScenario: When the client version is TLSv1.3 and the server version is TLSv1.2.
Server Error Message
The client supported protocol versions[TLSv1.3]are not accepted by server preferences [TLSv1.2]Client Error Message
Received fatal alert: protocol_versionSolution:
If the error logs have the SSL exception, do the following:
Check the TLS version of both UDRs, if both support different and single TLS versions, (that is, UDR 1 supports TLS 1.2 only and UDR 2 supports TLS 1.3 only or vice versa), handshake fails. Ensure that the TLS version is same for both UDRs or revert to default configuration for both UDRs. The TLS version communication supported are:
Table 4-1 TLS Version Used
| Client TLS Version | Server TLS Version | TLS Version Used |
|---|---|---|
| TLSv1.2, TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.2, TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.3 |
| TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.3 |
| TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.2, TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.3 |
| TLSv1.2, TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.3 |
| TLSv1.2 | TLSv1.2, TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.2 |
| TLSv1.2, TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.2 | TLSv1.2 |
Check the cipher suites being supported by both UDRs, it should be either the same or should have common cipher suites present. If not, revert to default configuration.
Problem: Pods are not coming up after populating the
clientDisabledExtension or serverDisabledExtension
Helm parameter.
Solution:
- Check the value of the
clientDisabledExtensionorserverDisabledExtensionparameters. The following extensions should not be present for these parameters:- supported_versions
- key_share
- supported_groups
- signature_algorithms
- pre_shared_key
If any of the above values is present, remove them or revert to default configuration for the pod to come up.
Problem: Pods are not coming up after populating the
clientSignatureSchemes Helm parameter.
Solution:
- Check the value of the
clientSignatureSchemesparameter. - The following values should be present for this parameter:
- rsa_pkcs1_sha512
- rsa_pkcs1_sha384
- rsa_pkcs1_sha256
4.3.2.17 Debugging Dual Stack Related Issues
global.deploymentMode parameter to indicate the
deployment mode of the cnUDR in the global section of the ocudr-custom
values.yaml file. The default value is set as
ClusterPreferred and the values can be changed in
ocudr-custom values.yaml file during installation. The Helm
configuration is as follows:
- To use this feature, cnUDR must be deployed on a dual stack Kubernetes infrastructure either in IPv4 preferred CNE or IPv6 preferred CNE.
- If the
global.deploymentModeparameter is set to 'IPv6_IPv4' then, when all the pods are running, the services, such as ingressgateway-prov and ingressgateway-sig must have both IPv6 and IPv4 addresses assigned. The default address must be IPv6 . The IP family policy must be set toRequireDualStack. The load balancer assigned must have both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. - All internal services must be single stack and must have only IPv6 and IP family policy. All the pods must have both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
- This feature does not work after upgrade since the upgrade path is not identified for this feature. The operators must perform a fresh installation of the NF to enable the Dual Stack functionality.
#Possible values : IPv4, IPv6, IPv4_IPv6,IPv6_IPv4,ClusterPreferred
global:
deploymentMode: ClusterPreferred4.3.2.18 Debugging Lifecycle Management (LCM) Based Automation Issues
- Make sure that the
autoCreateResources.enabledandautoCreateResources.serviceaccounts.enabledflags are enabled. - During upgrade, if a new service
account name is provided in the
serviceAccountNameparameter withautoCreateResources.enabledandautoCreateResources.serviceaccounts.enabledflags enabled, then a new service account name is created. If the service account name is not created, then you must check the configuration and the flags again. - During upgrade, you must use a different service account name when you upgrading from manual to automation. If you use same service account name when upgrading from manual to automation, then Helm does not allow upgrade due to ownership issues.
- To use the OSO alerts automation feature, you must follow the
installation steps of the
oso-alr-configHelm chart by providing the alert file that needs to be applied to the namespace. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Operations Services Overlay Installation and Upgrade Guide. If the alert file is not provided during Helm installation, you can provide the alert file during upgrade procedure. Alert file can be applied to the namespace during Helm installation or upgrade procedure. - If an incorrect data is added to the alert file, you can clear the entire data
in the alert file by providing the empty alert file
(
ocslf_alertrules_empty_<version>.yaml). For more information, see "OSO Alerts Automation" section in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository User Guide. - If you provide the service account name during the upgrade but the feature is disabled, the nudr-pre-upgrade hook fails because it cannot find the service account. If the upgrade fails, the rollback to the previous version will be unsuccessful due to the missing alternate route service account, resulting in an error message indicating that the service account for the alternate route service is not found. To address this issue, it is necessary to manually create the service account after the initial upgrade failure, then continue with the upgrade, this will also ensures a successful rollback.
4.3.2.19 Troubleshooting TLS 1.3 Support for Kubernetes API Server
If you enable the TLS 1.3 Support for Kubernetes API Server feature by setting
tlsEnableForKubeApiServer to true and if there is a configuration
mismatch, the Helm installation and upgrade fails. For example, if you configure
global.tlsVersionForKubeApiServer and
global.cipherSuitesForKubeApiServer incorrectly, as shown in the
following example:
tlsEnableForKubeApiServer: &tlsEnableForKubeApiServer true
tlsVersionForKubeApiServer: &tlsVersionForKubeApiServer TLSv1.1
cipherSuitesForKubeApiServer: &cipherSuitesForKubeApiServer
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
featureSecretsForKubeApiServer: &featureSecretsForKubeApiServer
- ocudr-gateway-secretError: INSTALLATION FAILED: execution error at (ocudr/charts/ingressgateway-sig/templates/gateway.yml:181:28): Invalid ciphers configured for the configured kube-api-server tls version4.3.3 Debugging Post Installation Related Issues
This section describes how to troubleshoot the post installation related issues.
4.3.3.1 Debugging Helm Test Issues
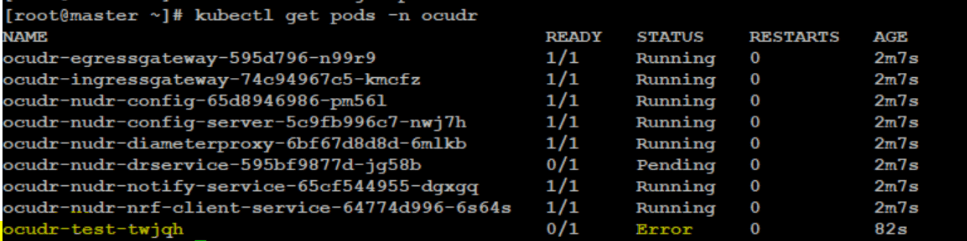
- Run the following command to get the Helm Test pod name.
kubectl get pods -n <deployment-namespace> - Check for the Helm Test pod that is in error state.
Figure 4-15 Helm Test Pod
- Run the following command to check the Helm Test pod:
kubectl logs <helm_test_pod_name> -n <deployment_namespace>In the logs, concentrate on ERROR and WARN level logs. There can be multiple reasons for failure. Some of them are shown below:-
Figure 4-16 Helm Test in Pending State
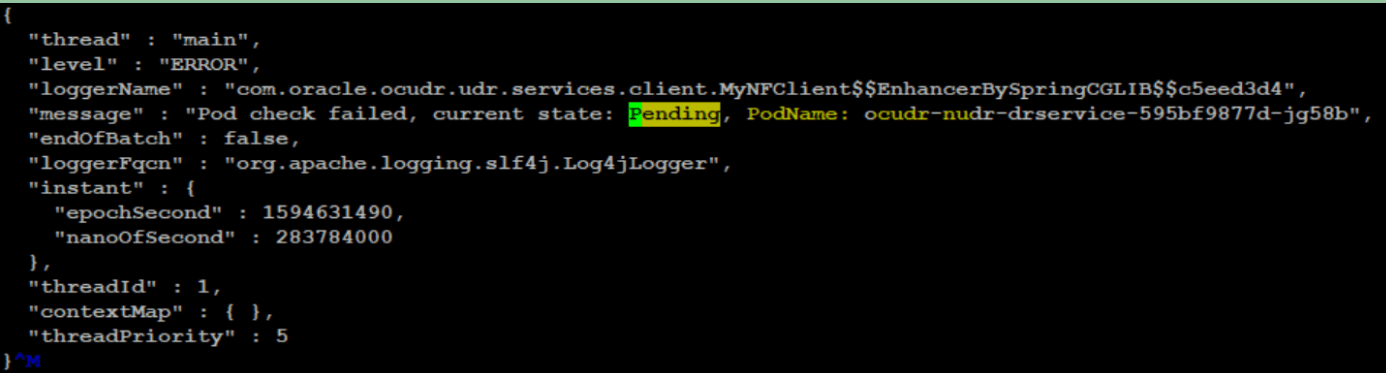
In this case, check for CPU and Memory availability in the Kubernetes cluster.
-
Figure 4-17 Pod Readiness Failed
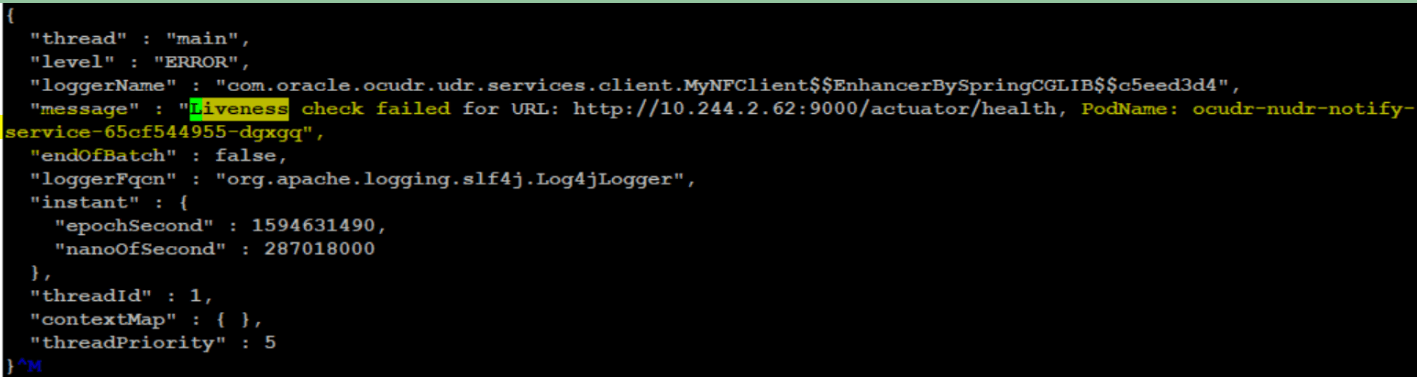
In this case, check for the correctness of the readiness probe URL in the particular microservice Helm charts under charts folder. In the above case, check for charts of notify service or check if the pod is crashing for some reason when the URL configured for readiness probe is correct.
- There are a few other cases where the httpGet parameter is not configured for the readiness probe. In this case, Helm Test is considered a success for that pod. If the Pod or PVC list is fetched based on namespace and the labelSelector is empty, then the helm test is considered a success.
-
The Helm test logs generate the following error:
Figure 4-18 Helm Test Log Error
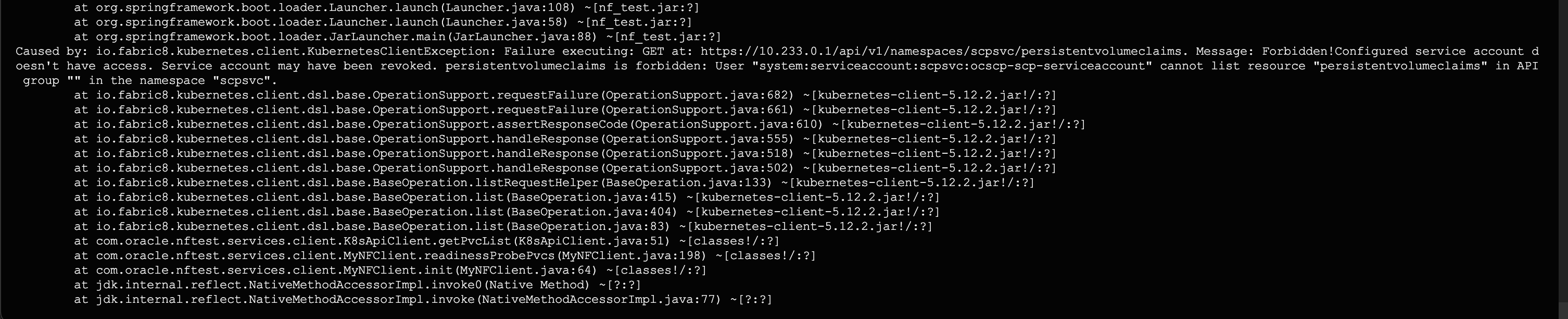
- Check whether the required permission for te resource of the group is missing in the
deployment-rbac.yamlfile. The above sample shows that the permissions are missing for the persistent volume claims. - Give the appropriate permissions and redeploy.
Check if the following error appears while running the helm test:
14:35:57.732 [main] WARN org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext - Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'k8SFabricClient': Invocation of init method failed; nested exception is java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 1 out of bounds for length 1 { {} } - Check the custom values file that is used to create the deployment. The resources
should be mentioned in the form of an array under the resources section in the
following format:
<k8ResourceName>/<maxNFVersion>.
4.3.3.2 Debugging Horizontal Pod Autoscaler Issues
There can be scenarios where Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) running on
nudr-drservice deployment and nudr_notify_service
might not get the CPU metrics successfully from the pods. Run the following command to
view the HPA details:
kubectl get hpa
- Check whether the metrics server is running on the Kubernetes
cluster. If the server is running and the CPU usage pod is still not accessible,
check the metrics-server values.yaml file for the arguments passed shown as
follows:
Figure 4-19 metrics-server yaml file

- If any changes are required, make them, restart the metrics server
pod, and check for correctness. Wait a couple of minutes after the metrics
server starts to see the CPU usage update on running
kubectl get hpacommand.Figure 4-20 Debugging HPA Issues

4.3.3.3 Debugging HTTPS Support Related Issues
- HTTPS port is not exposed: Run the following command to
verify if the HTTPS port is exposed:
kubectl get svc --n <ocudr-namespace>Figure 4-21 HTTPS Port Exposed
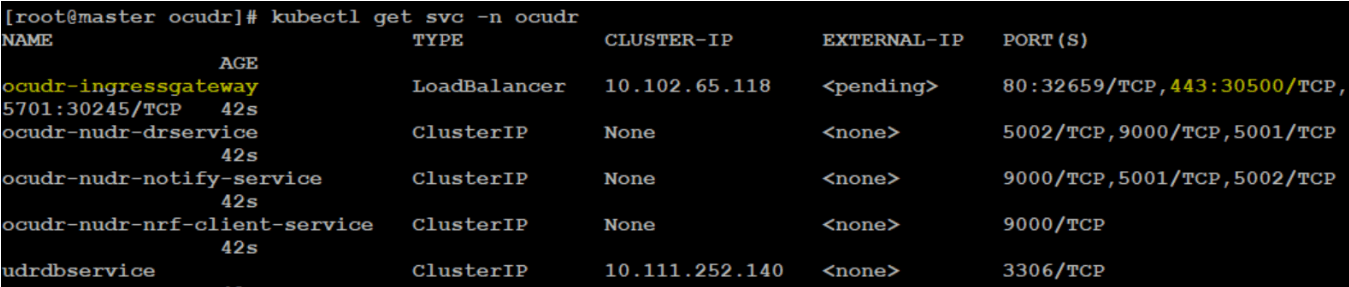
Note:
In the above figure, the secure port is 443.If the HTTPS port is not exposed, then enable the configuration information highlighted in the following figure under the ingressgateway section of the values.yaml file.Figure 4-22 Configuration Info under Ingressgateway
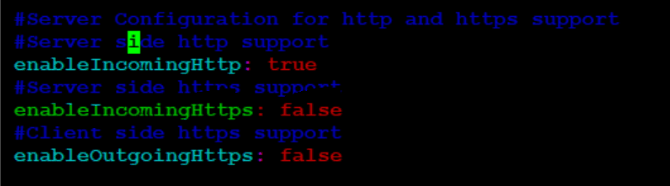
- Ingress Gateway Container is stuck in Init State/Failed: The
Ingress Gateway container may stop responding due to any one of the following
reasons:
- When config initssl is enabled under ingressgateway section
of the values.yaml file.
Figure 4-23 config initssl

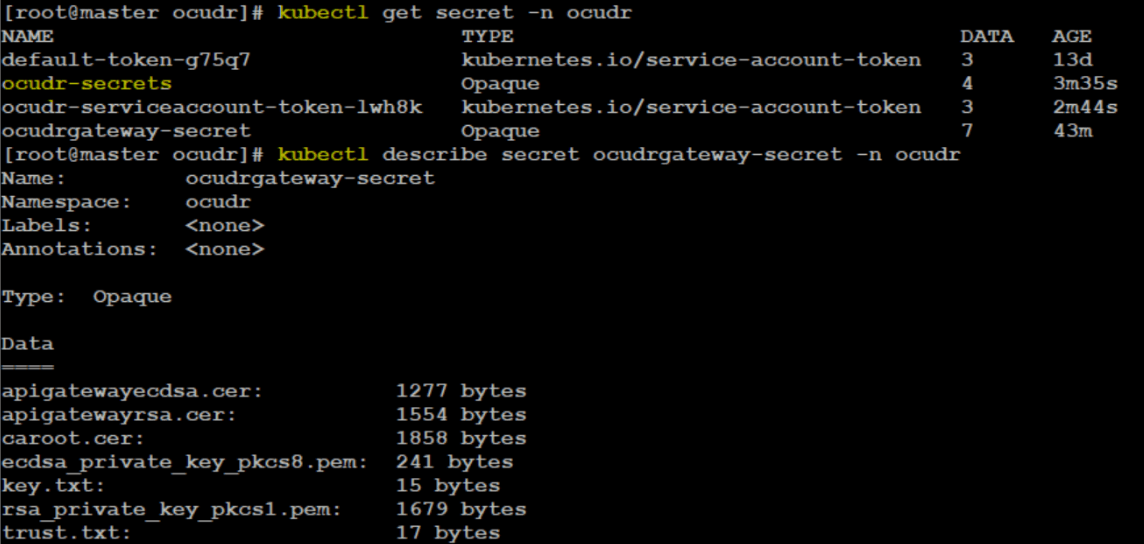
- If config initssl is enabled, then check whether secrets
are created with all required certificates. The following figure shows
the commands that you need to run to check whether secrets are present
and have all the required data.
Figure 4-24 Commands to Check Secrets
- When config initssl is enabled under ingressgateway section
of the values.yaml file.
- Config-Server Container not responding in Hooks Init State:
UDR does not respond in the Hooks Init state when there is a database connection
failure.
Figure 4-25 Config Server Container Status

In this case, run the describe pod command (on the above pod). In most cases, it is due to secrets not being found.
Also, verify the configuration given below to ensure config-server deployment refers to the correct secret values.global: dbCredSecretName: 'ocudr-secrets' - Config-Server Post Upgrade Hooks with below error.:
When more than one UDR is installed with the same nfInstanceId and in the same udrDB, installation does not cause any issue or error. However, for the second UDR, there are no config-server related tables in the udrConfigDB. So when upgrade is performed on the second UDR setup, then the following error occurs.
Figure 4-26 Config-Server Post Upgrade Hooks Error
- OAuth2 Related Issues:If you do not mention the OAuth secret name and namespace properly or if the public key certificate in secret is not in correct format, then the Ingress Gateway crashes.
Figure 4-27 Ingress Gateway Crashed
 Other scenarios are:
Other scenarios are:- The secret name in which public key certificate is stored is incorrect: In this scenario, it is advisable to check the logs of a pod that states "cannot retrieve secret from api server".
- The public key certificate stored in secret is not
in proper format: The public key format is
{nrfInstanceId}_RS256.crt (6faf1bbc-6e4a-4454-a507-a14ef8e1bc5c_RS256.crt).If the public key is not stored in this format, then check the logs of pod that states "Malformed entry in NRF PublicKey Secret with key ecdsa.crt". Here, ecdsa.crt is the public key certificate in oauthsecret.
By using public key certificate in required format, you can resolve these issues. You need to correct the fields with the proper secret name and namespace.
4.3.3.4 Debugging PodDisruptionBudget Related Issues
- Disappearance of a node from the cluster due to cluster network partition
- Accidentally deleting a virtual machine instance
- Eviction of a pod when a node runs out of resources
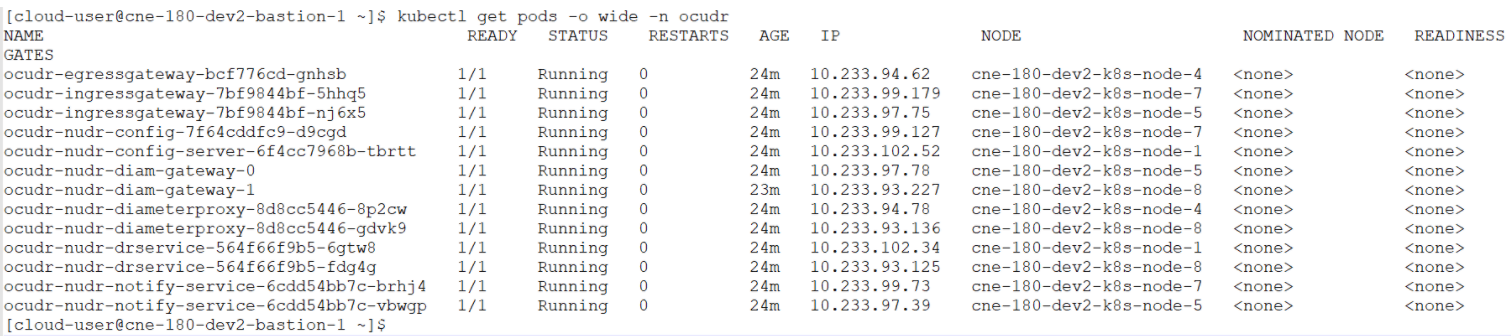
- Run the following command to check the pods running on different
nodes:
kubectl get pods -o wide -n ocudrFigure 4-28 Pods Running on Different Nodes
- Run the following set of commands to unschedule the
node:
kubectl cordon cne-180-dev2-k8s-node-4 kubectl cordon cne-180-dev2-k8s-node-7 kubectl cordon cne-180-dev2-k8s-node-5 kubectl cordon cne-180-dev2-k8s-node-8 kubectl cordon cne-180-dev2-k8s-node-1After unscheduling the nodes, the state of the nodes changes to 'Ready,SchedulingDisabled' as follows:Figure 4-29 After Nodes are Unscheduled
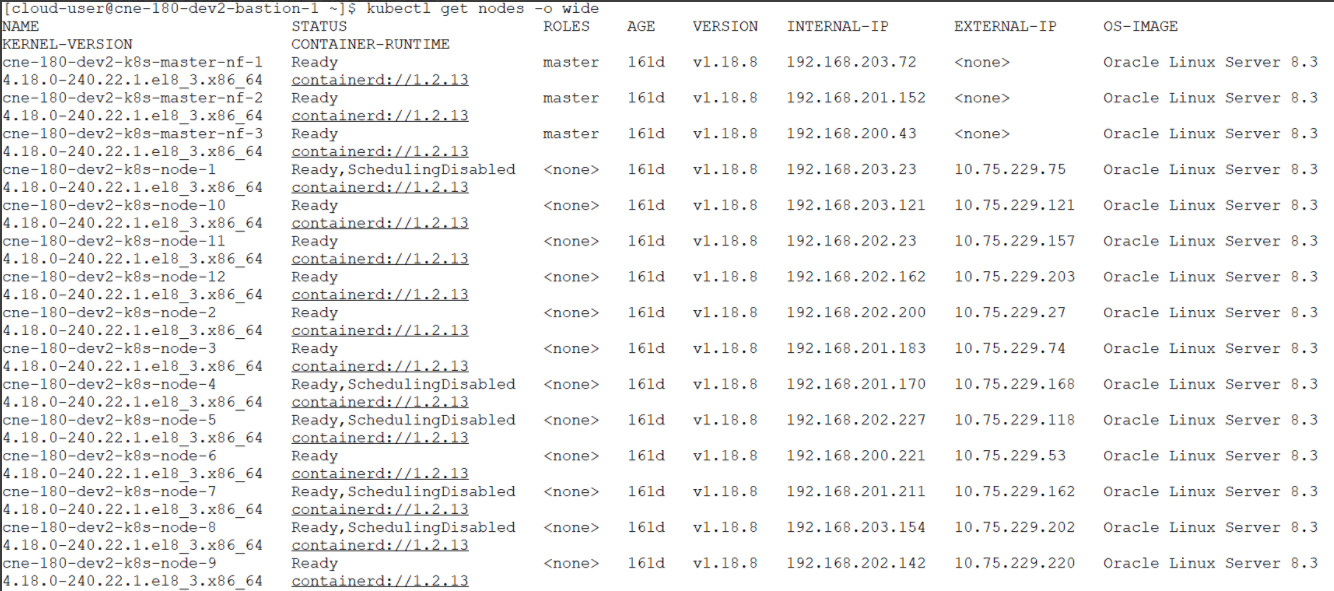
- Run the following set of commands to drain the
nodes:
kubectl drain cne-180-dev2-k8s-node-1 --ignore-daemonsets --delete-local-data kubectl drain cne-180-dev2-k8s-node-8 --ignore-daemonsets --delete-local-data kubectl drain cne-180-dev2-k8s-node-5 --ignore-daemonsets --delete-local-data kubectl drain cne-180-dev2-k8s-node-4 --ignore-daemonsets --delete-local-data kubectl drain cne-180-dev2-k8s-node-7 --ignore-daemonsets --delete-local-data - If you are required to drain the nodes or evict the pods, then
ensure the minimum number of pods are in ready state to serve the application
request. To configure the minimum number of pods value, set the
minAvailable parameter in the Helm charts for
individual microservices. This ensures the availability of a minimum number of
pods and they are not evicted. You can check logs while draining the nodes as
follows:
Figure 4-30 Logs When Trying to Evict Pod

4.3.3.5 Debugging Pod Eviction Issues
Figure 4-31 Configuring Container Log Storage
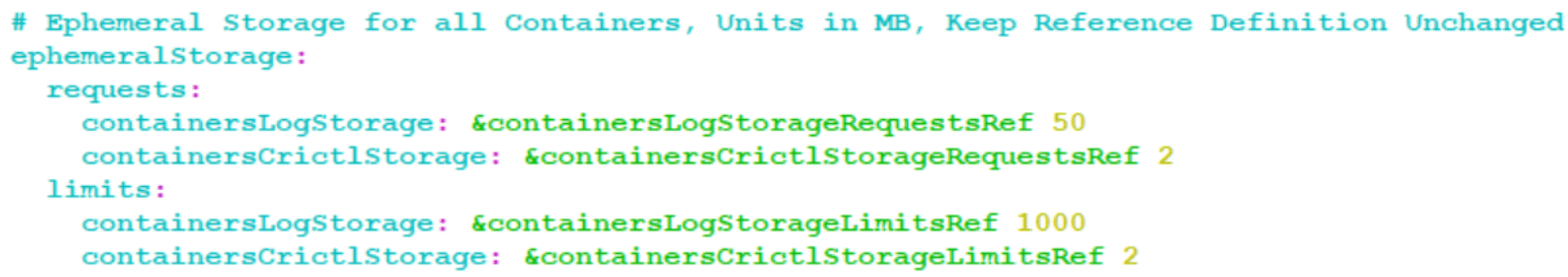
Figure 4-32 Ingress Gateway or Egress Gateway - Evicted State

4.3.3.6 Debugging Taints or Tolerations Misconfigurations
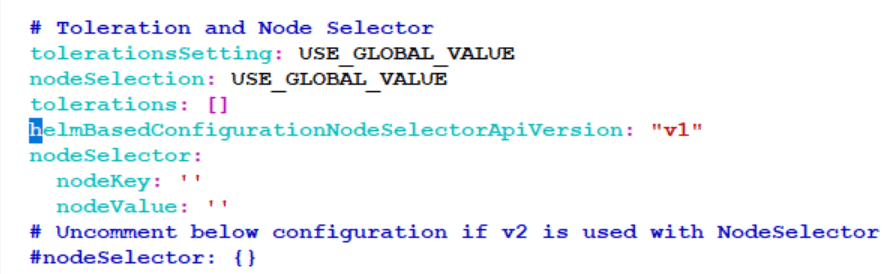
The following points should be considered when the Node Selector and Taints or Toleration feature is used on UDR or Provisioning Gateway:
- If any of the pods are going to the Pending state, ensure that the node selector
used is pointing to the correct slave node name, and it has enough space to place
the pod.
Figure 4-33 Global Configuration
- Use the following configuration to configure toleration settings for the tainted
nodes.Update the Global section configurations for the settings to be applicable for
all the services.
Figure 4-34 Global Configuration
- For Node Selector and Tolerations, configuration at the microservice level takes
priority over configuration at the global level.
Figure 4-35 Toleration and Node Selector
4.3.3.7 Debugging UDR Registration with NRF Failure
- Confirm whether registration was successful from the nrf-client-service pod.
- Check the ocudr-nudr-nrf-client-nfmanagement logs. If the log has
"UDR is Deregistration" then:
- Check if all the services mentioned under allorudr/slf (depending on UDR mode) in the values.yaml file has same spelling as that of service name and are enabled.
- Once all services are up, UDR must register with NRF.
- If you see a log for SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE(503), check if the primary and secondary NRF configurations (primaryNrfApiRoot/secondaryNrfApiRoot) are correct and they are UP and Running.
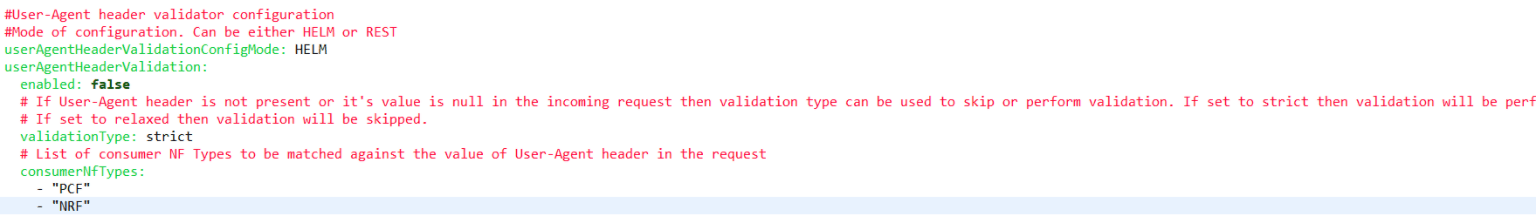
4.3.3.8 Debugging User Agent Header Related Issues
- Under Ingressgateway section, enable the user-agent flag to true.
- If there are issues in the consumer NFTypes validations for NF's, then check the
NF types in the configurations present under ingressgateway section.
Figure 4-36 Enabling User Agent Header
- If the userAgentHeaderValidationConfgMode set to REST, the custom-values.yaml configurations are ignored. The configuration is loaded based on userAgentHeaderValidationConfgMode is set.
Note:
From UDR 24.1.0 release onwards this feature is supported using REST API mode. If the feature does not work, make sure the feature is enabled and configured post UDR is upgraded, see Postupgrade Tasks section in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide
4.3.3.9 Debugging LCI and OCI Header Related Issues
If there are issues related to the LCI and OCI Header feature, perform the following:
Note:
- Configured the names of the headers the same as in the default configuration.
- Ensure to wait upto the validity period to report LCI and OCI Header in the next response.
- For OCI, check the overloadconfigrange and reduction metrics. Based on which, OCI is reported.
4.3.3.10 Debugging Conflict Resolution Feature
- If the exception tables or UPDATE_TIME column are missing from the UDR
subscriber database, perform the following steps:
- Ensure to run the SQL command from the SQL files on the
database ndbappsql node.
Note:
Following SQL files are available in Custom_Templates file:- ALL_mode_ndb_replication_insert.sql
- SLF_mode_ndb_replication_insert.sql
- EIR_mode_ndb_replication_insert.sql
- ALL_mode_ndb_replication_insert_UPGRADE.sql.file
- SLF_mode_ndb_replication_insert_UPGRADE.sql
- EIR_mode_ndb_replication_insert_UPGRADE.sql
- after setting the
global.dbConflictResolutionEnabledparameter to true in ocudr_custom_values.yaml file, if the UPDATE_TIME column is updated as 0, then run the REST APIs to fetch the global configurations and check theglobal.dbConflictResolutionEnabledis set to true. If the parameter is not set to true, perform a PUT operation for global configuration update to set the parameter to true. - If nudr_dbcr_auditor service is not enabled, then make sure
to enable the
global.dbConflictResolutionEnabledparameter and perform an Helm upgrade. - If nudr_dbcr_auditor service is not clearing exception tables or fixing data conflict, then make sure that the database replication is running.
- If nudr_dbcr_auditor service is not clearing exceptions on IDXTODATA$EX
exception tables then you must check if have the error log
"Communication failed to Mate site during audit". If you get this error
make sure to check if the following configuration on the custom values
file is configured
correctly.
# Provide MateSite IGW IP List, Comma separated values. Provide fqdn or IP with port mateSitesIgwIPList: 'http://ocudr-ingressgateway-prov.myudr2:80,http://ocudr-ingressgateway-prov.myudr3:80'
- Ensure to run the SQL command from the SQL files on the
database ndbappsql node.
4.3.3.11 Debugging UDR Error Responses Using App Error Code
ProblemDetails.detail parameter as part of the error responses
feature. This is applicable for all UDR mode deployments which includes signaling and
provisioning error responses from UDR.
Note:
The responses from nudr-config service for the REST APIs configuration remains same.Sample ProblemDetails.detail as follows:
<nfFqdn>: <service-name>: <Readable Error details>:
<App-Error-Code>, example,
slf01.abc.com: Nudr_GroupIDmap: Request header Issue, Unsupported Media Type:
OSLF-DRS-HDRVLD-E001
Table 4-2 Parameters of the Details Field of the Payload
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| nfFqdn |
Indicates the NF FQDN. It is obtained from the nfFqdn Helm Chart parameter. Sample Value: |
| service-name |
Indicates the microservice name. It is the originator of the error response. This value is static and cannot be configured. Sample Value: |
| Readable Error details |
Provides a short description of the error. Sample Value: |
| App-Error ID |
Indicates the microservice ID and the error
ID Sample Value:
OSLF-DRS-SIG-E302,
where,
|
| nftype |
Indicates the vendor or NF type. This parameter is prefixed with “O”, which indicates Oracle. For example, if the NF type is SLF, the vendor name becomes OSLF. It is obtained from the nfType Helm Chart parameter. Sample Value: |
| serviceId | It is either DRS (nudr-drservice) or DRP (nudr-dr-provservice). This value is set based on container name. |
| Category | Category to be used is fetched from error catalog.
Errors are classified into categories based on serviceid. Following are
the list of categories:
|
4.3.3.12 Debugging Provisioning Logs Related Issues
- You can enable or disable the provisioning log feature by setting the
provLogsEnabledparameter flag to true using REST APIs, CNC Console, or by changing the values in custom.yaml file. By default provision logging feature is disabled. - You can set the provisioning API names that are supported for provision logging
by changing the
provLogsApiNamesconfiguration field to the required value. The default value is nudr-dr-prov. The accepted values are as follows:- nudr-dr-prov
- nudr-group-id-map-prov
- slf-group-prov
- n5g-eir-prov
- If
provLogsEnabledflag is set to true, then it is recommended to change the values of logStorage to 4000 MB (apporx. equal to 4GB) for nudr-dr-prov pods to store provision logging files. If the values are not updated, then nudr-dr-prov pods will crash when ephemeral storage is full.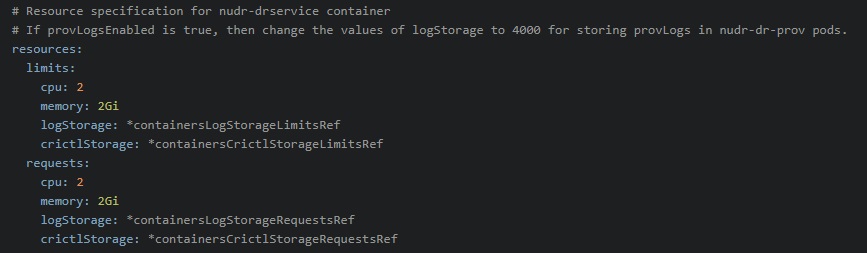
4.3.4 Debugging Upgrade or Rollback Failure
When Unified Data Repository (UDR) upgrade or rollback fails, perform the following steps:
- Run the following command to check the pre or post upgrade or rollback hook
logs:
kubectl logs <pod name> -n <namespace> - After detecting the cause of failure, do the following:
- For upgrade failure:
- If the cause of upgrade failure is database or network connectivity issue, then resolve the issue and rerun the upgrade command.
- If the cause of failure is not related to database or network connectivity issue and is observed during the preupgrade phase, then do not perform rollback because UDR deployment remains in the source or previous release.
- If the upgrade failure occurs during the post upgrade phase. For example, post upgrade hook failure due to target release pod not moving to ready state, then perform a rollback.
- For rollback failure: If the cause of rollback failure is database or network connectivity issue, then resolve the issue and rerun the rollback command.
- For upgrade failure:
- If the issue persists, contact My Oracle Support.