4 Troubleshooting Unified Data Repository
This chapter provides information to troubleshoot the common errors, which can be encountered during the preinstallation, installation, upgrade, and rollback procedures of Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository (UDR).
4.1 Generic Checklist
The following sections provide generic checklist for troubleshooting UDR:
Deployment Related Checklist
- Run the following command to check the installation of kubectl.
If kubectl is not installed, you can visit https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl/
$ kubectl - Run the following command to check the installation of UDR.
$ kubectl get pods -n <ocudr-namespace>Figure 4-1 Sample Output: UDR Pods Status

Note:
The STATUS of all the pods is 'Running'. - Run the following command to view all the events related to a
particular namespace.
kubectl get events -n <ocudr-namespace> - Ensure the preinstall job is in the completed state and all the UDR microservices are in the running state.
- To verify the database and user creation, the following guidelines
must be followed:
- If the preinstall pod is in the 'ERROR' state, run the
following command to check the logs to debug the
issue.
kubectl logs -n <namespace> <pre install pod name> - If you see the following message in logs, it is possibly
because the MySQL server does not allow remote connections to the
privileged
users.
{"thrown":{"commonElementCount":0,"localizedMessage":"Access denied for user 'root'@'10.233.118.132' to database 'saqdb'","message":"Access denied for user 'root'@'%' to database 'saqdb'","name":"java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException","extendedStackTrace":"java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: Access denied for user 'root'@'%' to database 'saqdb'\n\tatTo fix the user access error, run the following steps on all the SQL nodes to modify the user table in MySQL DB.1. mysql> update mysql.user set host='%' where User='<privileged username>'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 0 Warnings: 0 2. mysql> flush privileges; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec) - If the preinstall job is complete but the dr-service and
notify-service pods are crashing with a similar error message in logs as
above, then the user may not be created. To fix this, you need to set
the value of createUser field in the
custom-values.yaml file to 'true' before installing UDR.
Note:
For more information on creating a database user, see the Creating Database User or Group section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.preInstall: image: name: nudr_pre_install_hook tag: 25.2.100 config: logLevel: WARN # Flag to enable user creation. Keep this flag true. # Change to false when installed with vDBTier. For vDBTier instllation user creation on DB # should be manually done createUser: true - If the preinstall pod is in the ERROR state with the
following error message in
logs:
"message":"Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'createUser': Invocation of init method failed; nested exception is java.sql.SQLException: NDB_STORED_USER privilege is not supported. Please use MySQL version 8.0.22 or higher",Then, it could be because the data tier you are trying to connect has a MySQL package installed that does not support the NDB_STORED_USER privilege. To fix this, set the createUser flag to 'false' and create the user manually on all SQL nodes.
- If there is "The database secret is empty" or "Invalid data present in the secret" error message in the preinstall hook logs, then create the secret as mentioned in the Installing Unified Data Repository chapter in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide . Check for the case sensitivity of the keys in the secret. For example, encryptionKey, dsusername, and so on.
- If the preinstall pod is in the 'ERROR' state, run the
following command to check the logs to debug the
issue.
- Run the following command to verify whether UDR specific pods are
working as expected:
$ kubectl get pods -n <ocudr-namespace>Figure 4-2 Sample Output: UDR Pods Status
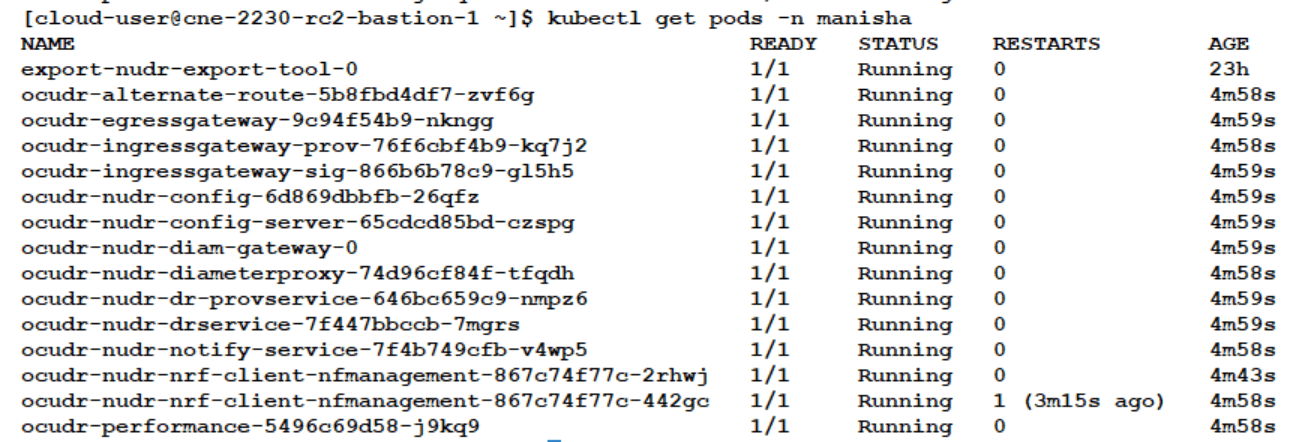
Result: In the figure given above, you can see that the status of all the pods is 'Running'.
Note:
The number of pods for each service depends on Helm configuration. In addition, all pods must be in a ready state and you need to ensure that there are no continuous restarts.
Helm Installation Checklist
Run the following command to check the installation of helm.
$ helm lsIf helm is not installed, run the following set of commands one after another to install helm:
Replace with the latest Helm download link.curl -o /tmp/helm.tgz https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-helm/helm-v2.9.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz.-
tar -xzvf /tmp/helm.tgz -C /usr/local/bin --strip-components=1 linux-amd64/helmrm -f /tmp/helm.tgz -
kubectl create serviceaccount --namespace kube-system tiller -
kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller-cluster-rule --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller -
helm init --service-account tiller
# Wait for the tiller pod to be upkubectl get po -n kube-system
# Does not return any error. Try again if an error is returned as the tiller pod may be coming up.helm ls
. If this command fails immediately with a syntax error, check for the required data for the helm install command to run.helm install
Database Related Checklist
To verify database connectivity:
- Log in to the NDB cluster and verify the creation of UDR database
with all the tables. To check the entries in the database tables, run the
following command:
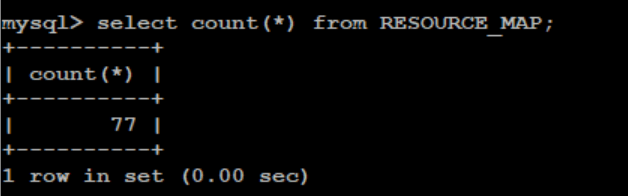
It ensures that the connection is fine and the database is created successfully. This count differs based on the udrServices option selected under the global section of the custom-values.yaml file. But this table cannot be empty.
select count(*) from RESOURCE_MAPFigure 4-3 Sample Output: Verifying Table Entries in Database
- To verify UDR subscribers, check the provisioning flow on UDR. Use
the following provisioning URL supported on UDR to verify the provisioning
flow:
- If you use external tools like postman and http2 curl, then
follow this URL:
In case of curl, the client must support an http2 curl utility.http://<ocudr-ingress-gateway-ip>:<http-external-port>/nudr-dr-prov/v1/profile-data/msisdn-1111111113 - If HTTPS is enabled in UDR Ingress Gateway, then follow
this URL:
https://<ocudr-ingress-gateway-ip>:<https-external-port>/nudr-dr-prov/v1/profile-data/msisdn-1111111113
Verifying provisioning flow on UDR also confirms the udrdb status on the NDB cluster.
- If you use external tools like postman and http2 curl, then
follow this URL:
- Check the nudr-nrf-client-nfmanagement logs for no 503 errors. This helps to find out if all the FQDN configured, as part of helm configurations, in values are resolvable.
- Verify NRF registration by checking the nrfclient_current_nf_status and nrfclient_nf_status_with_nrf metrics on Prometheus.
4.2 Database Related Issues
This section describes the database related issues.
Verifying SQL Exception Failures with nudr-pre-install-hook pod
The nudr-pre-install-hook pod creates UDR database along with the tables required. If it does not create the database, then perform the following steps to debug the pod failure.
- Verify whether the helm install command hangs for longer time or fails with the BackOffLimit Exceeded error.
- Watch the kubectl get pods command based on the release namespace.
- Check whether nudr-preinstall pod is going to error state. This means the DB creation has failed or connection to DB is not successful.
- Run the following command on logs:
kubectl logs <udr-pre-install-hook pod id> --n <ocudr-namespace> - Check the log output of the pods for any warning or SQL exceptions using above command continuously. If any warning or SQL exception is found, it means there is an issue with the SQL connection or the SQL Node. Examine each exception thoroughly to find the root cause.
- Verify the following information in the values.yaml
file.
global: ... ... ... # MYSQL Connectivity Configurations mysql: dbServiceName: &dbHostName "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-ndb" #This is a read only parameter. Use the default value. port: &dbPortNumber "3306" configdbname: &configdbname udrconfigdb dbname: &dbname udrdb # Do not change the below values dbUNameLiteral: &dbUserName dsusername dbPwdLiteral: &dbUserPass dspassword dbEngine: &dbEngine NDBCLUSTER nrfClientDbName: *configdbname dbCredSecretName: &dbSecretName 'ocudr-secrets - Ensure that the following service is available in the Cloud Native
Environment (CNE).
Figure 4-4 Service Availability in CNE

- Check whether Kubernetes secrets are present. If secrets exist, then check their encrypted details like username, password, and DB name. If these details do not exist, then update the secrets.
- After making any changes, run the following command to upgrade
Helm.
helm upgrade <helm chart> [--version <OCUDR version>] --name <release> --namespace <ocudr-namespace> -f <ocudr_values.yaml>For more information, see the Creating Kubernetes Secret - DBName, Username, Password, and Encryption Key section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide .
Verifying SQL Exception Failures with Common Services pre-install-hook pod
- Run the following command on logs:
kubectl logs <failed-pre-install-hook-pod> -n <ocudr-namespace> - Check the log output of the pods for any warning or SQL exceptions using above command continuously. If any warning or SQL exception is found, it means there is an issue with the SQL connection or the SQL Node. Examine each exception thoroughly to find the root cause.
- Verify the following information in the values.yaml
file.
global: ... ... ... # MYSQL Connectivity Configurations mysql: dbServiceName: &dbHostName "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-ndb" #This is a read only parameter. Use the default value. port: &dbPortNumber "3306" configdbname: &configdbname udrconfigdb dbname: &dbname udrdb # Do not change the below values dbUNameLiteral: &dbUserName dsusername dbPwdLiteral: &dbUserPass dspassword dbEngine: &dbEngine NDBCLUSTER nrfClientDbName: *configdbname dbCredSecretName: &dbSecretName 'ocudr-secrets' - Ensure that the following service is available in the Cloud Native
Environment (CNE).
Figure 4-5 Service Availability in CNE

- Check whether Kubernetes secrets are present. If secrets exist, then check their encrypted details like username, password, and DB name. If these details do not exist, then update the secrets.
- After making any changes, run the following command to upgrade
Helm.
helm install <helm chart> [--version <OCUDR version>] --name <release> --namespace <ocudr-namespace> -f <ocudr_values.yaml>For more information, see the Creating Kubernetes Secret - DBName, Username, Password, and Encryption Key section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide .
Verifying SQL Exception Failure with nudr-pre-upgrade-hook pod
- Checks whether the helm upgrade command hangs for long time or fails with BackOffLimit exceeded error.
- Ensure that the pre_upgrade_hook.yaml file is present in
the templates directory of the target charts, with the required annotation.
This is for the nudr-pre-upgrade-hook pod to come up.
"helm.sh/hook": "pre-upgrade" - Watch the kubectl get pods command based on the release namespace.
- Run the following command on the pods to check if the
nudr-pre-upgrade pod is going to error state. It means that the
DB schema upgrade has failed or connection to DB is not successful.
kubectl logs <nudr-pre-upgrade-hook pod id> --n <ocudr-namespace> - Check the log output of the pod for any warning or SQL Exception. If there is any, it means there is an issue with the SQL connection or the SQL Node. Check the Exception details to get the root cause.
- After the upgrade completes, run the following command to
verify whether all the pods are running containers with the updated
images.
kubectl describe pod <pod id> --n <ocudr-namespace> - If the nudr-pre-upgrade pod throws an error, check the logs. If the logs has "Change in UDR Mode not allowed" error, then check if the configuration of udrServices in the values.yaml file is different from previous version. If the logs has "Change in VSA Level not allowed" error, then check if the configuration of vsaLevel in the values.yaml file is different from previous version.