5 Configuring OCNADD Using CNC Console
OCNADD provides a console interface using the highly secure GUI service, which allows you to use an interactive interface for interacting with the other OCNADD services.
This chapter describes how to configure different services in Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD) or access OCNADD dashboards using Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console (CNC Console).
It also describes how to configure different global and service parameters in OCNADD, create and manage data feeds, data filters, and monitor alarms using the CNC Console.
OCNADD Console Interface
This section provides an overview of the CNC Console, which includes an interface to help in creating data feeds, data filters, and access dashboards in OCNADD.
You can use OCNADD integration with CNC Console, only after logging successfully into the CNC Console application. To log in successfully into CNC Console, ensure that the CNC Console installation steps are complete. For more information about GUI installation, see "Installing OCNADD GUI" section of Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide
Note:
Before logging in to the OCNADD Console, create a user and password. Using these login details, you can log in to the OCNADD Console application. For more information about creating a user and password, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation Guide.- Open a web browser and enter the URL:
http://cncc-core-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.cluster.local:port number/and press Enter.Note:
port number is thecncc-iam-ingress-portnumber.The login page opens.
- Enter the Username and Password.
- Click Sign In.
- On the Welcome page, select the required instance from the
Please Select Instance drop-down field.
This opens the Console home page for the selected instance.
- To use OCNADD services integrated with the Console, click Data Director in the left navigation pane.
5.1 Home Page Display and Operations
After you log in, the GUI displays the OCNADD home page as the default landing page.
The following screen capture shows an illustration of the OCNADD home page:

The home page consists the following element:
Create Data Feed button
Use this button to create new feeds. For more information about creating data feeds, see Data Feeds List.
Note:
OCNADD shows the above home page as the default landing page when no data feeds have been created previously. However, once you create at least one data feed, the home page switches to the Data Feeds page as default landing page, which lists all the available data feeds.
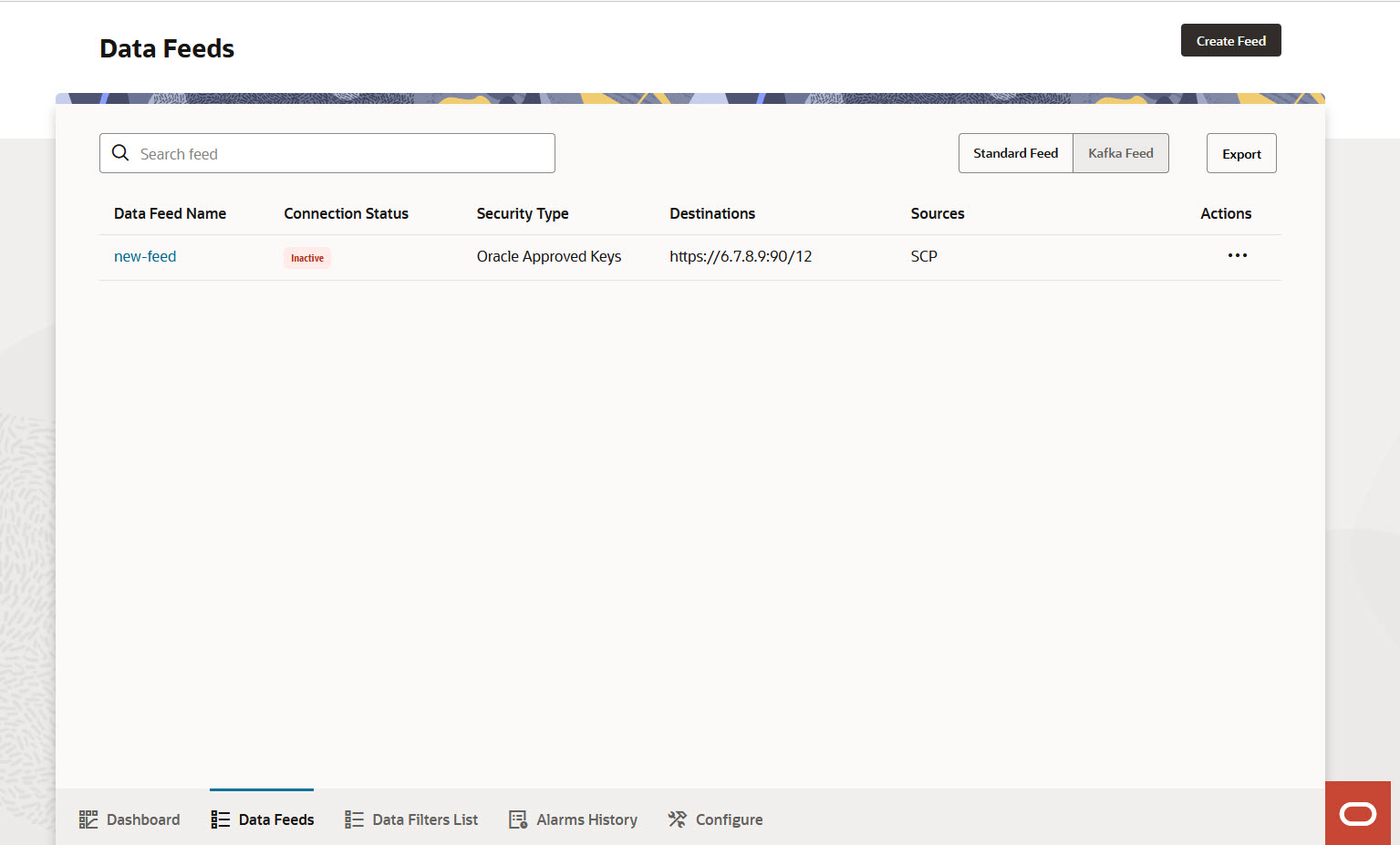
- Create Feed button
Use this button at the top right-hand side of the page to create new feeds. For more information about creating data feeds, see Data Feeds List.
- Standard Feed button
This button opens the list of existing standard feeds.
- Kafka Feed button
This button opens the list of existing Kafka feeds.
Note:
Kafka Feed is enabled only when OCNADD services are on Transport Layer Security (TLS). For more information, see Kafka Feed. - Export button
Based on the list of feeds, when you click the Export button, the particular feeds (standard or Kafka) get downloaded as CSV file.
- Dashboard icon
This icon at the bottom of the page opens the Dashboard view where you can view and manage various OCNADD metrics, KPIs, alarms, Ingress and Egress Gateway traffic, and so on.
- Data Feeds icon
This icon at the bottom of the page opens the existing Data Feeds page.
- Data Filters List icon
This icon at the bottom of the page opens the Data Filters page.
- Alarm History icon
This icon at the bottom of the page navigates you to the OCNADD alarms page to view the alarms. For more details about the page, see Alarms History.
- Configure icon
This icon at the bottom of the page navigates you to the Synthetic Data Feeds page where you can see the list and details of existing synthetic data feeds. For more information, see Configure.
- Global L3L4 button
This button is located at the top-right corner of the Synthetic Data Feeds page. It takes you to the Global L3L4 Configuration page.
- Global L3L4 button
- Ask Oracle
Use the
 icon to navigate to Dashboard, 5G
Data Feeds, 5G Data Filters,
Create New Filter, Create New
Feed, or Alarms History pages from
any page of the GUI.
The Ask Oracle option also allows you to view the following details:
icon to navigate to Dashboard, 5G
Data Feeds, 5G Data Filters,
Create New Filter, Create New
Feed, or Alarms History pages from
any page of the GUI.
The Ask Oracle option also allows you to view the following details:- Information about the OCNADD release including version, release number, and product name
- OCNADD GUI Help
5.2 OCNADD Dashboard
This chapter describes how to use the OCNADD dashboard to view metrics, KPIs, critical and major alarms, as well as Ingress and Egress Gateway traffic.
To view the dashboard, click the Dashboard icon at the bottom of the page or click Dashboard on the Ask Oracle page.
Active Issues
In case of an active issue, the Dashboard page displays the respective metric or alert at the top of the page with the page title as Active issue needs your attention.
Click View Details to see the detailed description of the issue and the affected data feeds. The page also provides the recommended action to fix the issue. For more details about OCNADD alerts and respective actions, see Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide.
To view the details of any active issues, click View Details. Viewing details allows you to understand the impact of any issues immediately, and therefore, prioritize the relevant troubleshooting tasks.
Metrics
- Switch on to view all the metrics
- Switch off to view only Ingress and Egress metrics
- Ingress & Egress
- MPS based on NF
- Avg Msg Size
- Disk IO
Monitoring Alarms, Metrics, and KPIs
The dashboard allows monitoring of major and critical alarms that must be resolved. It provides the details of the severity of a specific alarm and its impact on the data feed.
The dashboard also allows monitoring Ingress & Egress Data Traffic, MPS based on NF type & Aggregate, Average Message Size per NF, Disk IO, and All Microservices Details. Using the dashboard, you can check the details of all the metrics and alarms related to a specific microservice.
- Ingress & Egress Data Traffic
- Use the Select Interval drop-down to specify monitoring interval for Ingress and Egress data traffic.
- Use the Select Traffic drop-down to
apply traffic filters for monitoring. This drop-down provides the
following options:
- All traffic
- Ingress traffic
- Egress traffic
- MPS based on NF type & Aggregate
- Use Select NF drop-down to choose
the Network Function (NF) for monitoring the Message Per Second (MPS).
This drop-down provides the following options:
- All
- NRF
- SCP
- SEPP
- Use Select NF drop-down to choose
the Network Function (NF) for monitoring the Message Per Second (MPS).
This drop-down provides the following options:
- Average Message Size per NF
- Use Select NF drop-down to choose the
NF for monitoring the average message size. This drop-down provides the
following options:
- All
- NRF
- SCP
- SEPP
- Use Select NF drop-down to choose the
NF for monitoring the average message size. This drop-down provides the
following options:
- Disk IO
- Use Select Interval drop-down to choose the monitoring interval for Read or Write speed.
- Use Select IO drop-down to select
the type of Disk IO. This drop-down provides the following options:
- All
- Read
- Write
- All Microservices Details
- Use this table to monitor the following details of each
microservice:
- Connection Status: Defined using different color notations.
- CPU Utilization: Defined using a horizontal progress bar. Hover over the progress bar to view the CPU utilization numbers.
- Memory Utilization: Defined using a horizontal progress bar. Hover over the progress bar to view the CPU utilization numbers.
- Click on a microservice name to open more details page with
the following options:
- View details of CPU Utilization and Memory Utilization by the microservice in numbers.
- Click Export Metrics to download the microservice-specific metrics.
- Use All instances drop-down to filter the graphical view of Overall CPU utilization
- Use < and > on top-left corner to navigate to the details page of the next or previous microservice.
- Click X on top-right corner to close the details page and go back to the dashboard.
- Use this table to monitor the following details of each
microservice:
5.3 Data Feeds List
This chapter describes how to use the OCNADD to view, create, edit, clone, and delete data feeds.
The Data Feeds page allows you to perform the message data feed related configurations. To open the page, click Data Feeds List at the bottom of the page or click 5G Data Feeds on Ask Oracle page. This opens the Data Feeds page showing a table with details of existing data feeds, if any.
This page provides the following options:
Table 5-1 Data Feed Page Options
| Option Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Search Box | Search data feeds using data feed name. |
| Standard Feed | View the list of existing standard data feeds. |
| Kafka Feed | View the list of existing Kafka consumer feeds. |
| Export | To export standard feed or Kafka consumer feed in a CSV file. |
5.3.1 Standard Feed
To view the list of standard data feeds, click Standard Feed.
5.3.1.1 Creating Standard Feed
This section describes how to create a standard data feed using the OCNADD console. The configurations include proving application details, adding destinations, selecting Transport Layer Security (TLS), creating synthetic packet, L3L4 mapping, selecting data source, and handling failure.
The Data Feeds page displays the Create Feed button to create a data feed.
- Navigate to Data Feeds page.
- Click Create
Feed.
This opens a dialog box with the option to select the type of feed you want to create.
- Select the Standard Feed option.
- Click Proceed to open Create Data
Feed wizard.
Follow the steps below in the Create Data Feed wizard:
- Step 1: Provide Application Details
- Step 2: Add Destination & Distribution Plan
- Step 3: Create Synthetic Packet (Available only for Synthetic Feeds)
Note:
This step is conditional. It is available only for synthetic feeds. For more information, see Step 3. - Step 4: L3L4 Mapping (Available only for Synthetic Feeds)
Note:
This step is conditional. It is available only for synthetic feeds. For more information, see Step 4. - Step 5: Choose Data Source(s)
- Step 6: Handle Failure
5.3.1.1.1 Step 1: Provide Application Details
This section describes how to provide application details in Create Data Feed wizard to create standard feed using the OCNADD console.
- Enter application information and select connection type using the
following options:
Table 5-2 Application info and connection type
Option Name Detail Application Name Enter the name of the destination application. The name should not start with a capital letter and should not contain special characters other than -. Connection Type Select one of the following drop-down items: - HTTP2
- H2C
- TCP
- TCP_SECURED
Note:- Top create a Synthetic Feed, select Connection Type as TCP or TCP_SECURED.
- TCP and TCP_SECURED are not applicable to a IPv6 deployment. Hence, Synthetic Feed is not supported in a IPv6 deployment.
Does your application require synthetic data? This switch is updated based on the selected Connection Type. Note: It is only enabled for TCP and TCP_SECURED connection types.
Do you want to include meta data? Toggle this switch to include or skip metadata. The switch indicates if the outbound packet from the OCNADD should contain the optional metadata. By default, the switch remains enabled. - Select security level using the following options:
Note:
Only one Select security level type can be selected at a time. Also, the options available to select from is automatically updated as per the selected Connection Type.Table 5-3 Select security level
Connection Type Available Security Level Options HTTP2 - Oracle Approved TLS: TLS cipher is selected automatically from an Oracle approved Cipher Suite during the handshake with the peer.
- Static Key TLS: The data is
transferred to HTTP/2 peer using a Static Key
Cipher. Data Director security is weakened as
forward secrecy is not supported. Proceed at your
own risk.
If Static Key TLS is selected, the following options are available to select from the Select Static Cipher drop-down:
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
H2C No TLS: The data is transferred to HTTP/2 peer over cleartext TCP. Security is weakened as there is no secrecy of data. Proceed at your own risk. TCP No TLS: The data is transferred to HTTP/2 peer over cleartext TCP. Security is weakened as there is no secrecy of data. Proceed at your own risk. TCP_SECURED - Oracle Approved TLS: TLS Cipher is selected automatically from an Oracle approved Cipher Suite during the handshake with the peer.
- Static Key TLS: The data is
transferred to HTTP/2 peer using a Static Key
Cipher. Data Director security is weakened as
forward secrecy is not supported. Proceed at your
own risk.
If Static Key TLS is selected, the following options are available to select from the Select Static Cipher drop-down:
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- Click Continue to save application details and move to Step 2: Add Destination & Distribution Plan. To leave the wizard and discard the changes, click Cancel.
5.3.1.1.2 Step 2: Add Destination & Distribution Plan
This section describes how to add destinations and distribution plan in Create Data Feed wizard to create standard feed using the OCNADD console.
- Add destination and distribution plan
using the following options:
Table 5-4 Add Destination & Distribution Plan
Field Name Description Add destinations Provide the destination URL in the Enter URL Address or IP Address field. The URL can start with the http,https,tcp, ortcpsprotocols.Note:- The URL protocol automatically populates on the configuration of the Create Synthetic Packet switch and the TLS option.
- In a IPv6 deployment, provide a valid IPv6
address, where Application
IP should be enclosed in a square
bracket. For example,
https://[2606:b400:c10:5018::a]:9090/v1for ahttpsprotocol.
Use the Plus or Delete button to add or remove destinations.
If multiple destinations are configured, the option to select the Select distribution type is enabled.
If the Select distribution type selected is Weighted Load Balancing. The user can assign load factors to each destination individually. The load factor is a percentage value between 0 to 100. The sum total of the load factors assigned to each destination must be 100%.
Select distribution type When multiple destinations are configured, the user can select the distribution type by using Load Balancing Type drop-down menu. The options available are: - Round Robin: This option is selected by default.
- Weighted Load
Balancing: When multiple destinations
are configured, the user can assign load factors to
each destination. The sum total of the load factors
assigned to each destination must be 100%.
Note: The maximum number of destination endpoints allowed is “2”.
- Click Continue to save destination and distribution plan and move to Step 3: Create Synthetic Packet (Available only for Synthetic Feeds). To leave the wizard and discard the changes, click Cancel.
5.3.1.1.3 Step 3: Create Synthetic Packet (Available only for Synthetic Feeds)
This section describes how to create synthetic packet in Create Data Feed wizard to create standard feed using the OCNADD console.
Note:
This step is available only for synthetic feeds if all the following conditions met:- When Does your application require synthetic data? switch is enabled in the Provide Application Details page, which is updated based on the selected Connection Type on the same page.
- The Does your application require synthetic data? switch is enabled only when the Connection Type is either TCP or TCP_SECURED.
- Enter the following information on the Create Synthetic
Packet page:
Table 5-5 Create Synthetic Packet
Option Name Description Device Details Enter the following device-related details: - Mac Source
- Mac Destination
Network Details Source Details- Source IP
- Source Port
Destination Details- Destination IP
- Destination Port
Do you want to allow L3L4 Mapping Rule? Toggle the switch to allow or deny L3L4 Mapping Rule. If allowed, a new page, L3L4 Mapping, is added to the right sidebar links.
Note: This option is available for synthetic feeds only.
- Click Continue to create synthetic packet information and move to Step 4: L3L4 Mapping (Available only for Synthetic Feeds). To leave the wizard and discard the changes, click Cancel.
5.3.1.1.4 Step 4: L3L4 Mapping (Available only for Synthetic Feeds)
This section describes how to perform L3L4 mapping at the feed level in Create Data Feed wizard to create standard feed using the OCNADD console.
Note:
This step is available only for synthetic feeds if all the following conditions met:- When the Does your application require synthetic data? switch is enabled on the Provide Application Details page, which is updated based on the selected Connection Type on the same page.
- The Do you want to allow L3L4 Mapping Rule? switch is enabled on the Create Synthetic Packet page.
- Enter the information on the L3L4 Mapping
page for RxRequest, TxRequest,
RxResponse, and TxResponse
tables:
Table 5-6 L3L4 Mapping
Option Name Description Address The following rows are available for this column. - Source IP
- Destination IP
- Source Port
- Destination Port
Preference The following value is available to select from a drop-down list: - Data Director
Priority Select one of the following options from the drop-down list: - Data Director
- Metadata
Rule 1 Select one of the following options from the drop-down list: - consumer-fqdn
- producer-fqdn
- api-name
- feed-source-nf-fqdn
- message-direction
- consumer-id
- producer-id
Rule 2 Select one of the following options from the drop-down list: - consumer-fqdn
- producer-fqdn
- api-name
- feed-source-nf-fqdn
- message-direction
- consumer-id
- producer-id
- none
Least Priority Address There are two types of fields. - Enter IP
- Enter Port
- Click Continue to create L3L4 mapping and move to Step 5: Choose Data Source(s). To leave the wizard and discard the changes, click Cancel.
5.3.1.1.5 Step 5: Choose Data Source(s)
This section describes how to choose data source(s) in Create Data Feed wizard to create standard feed using the OCNADD console.
- Select one or multiple data sources from the following options in
the Choose Data Source(s) page:
Table 5-7 Choose Data Source(s)
Option Name Description Service Communication Proxy (SCP) Select this option if the data must come from SCP, which allows securing and managing 5G networks by providing routing control, resiliency, and observability to the core network. Network Repository Function (NRF) Select this option if the data must come from NRF, which allows 5G NFs to register and discover one another through a standard API. NRF is also a critical component required to implement the new Service Based Architecture (SBA) in the 5G core. Security Edge Protection Proxy (SEPP) Select this option if the data must come from SEPP, which acts as a security gateway by enabling secure Interconnect between 5G networks. It ensure end-to-end confidentiality and integrity between the source and the destination networks. - Click Continue to save data source(s) information and move to Step 6: Handle Failure. To leave the wizard and discard the changes, click Cancel.
5.3.1.1.6 Step 6: Handle Failure
This section describes how to handle failures in OCNADD standard data feed connections. You can configure the failure management scenarios in the Create Data Feed wizard using the OCNADD console.
- Select any of the following options to determine the behavior of
OCNADD if the data cannot reach your application:
Note:
This option is not available for synthetic data feeds.Table 5-8 Handle Failure - OCNADD Behavior
Option Name Description Do not try again Specifies that Data Director reaches out just one time if the data cannot reach the external application Keep trying Specifies that Data Director continually reaches out to the external application until it successfully connects to it. - Select any of the following options to determine how OCNADD resumes the sending of data after reconnection if a failure occurs.
Table 5-9 Handle Failure - Resuming services
Option Name Description Resume from point of failure Specifies that Data Director resumes from point of failure if a failure occurs. This reduces the chance of losing data. Proceed with latest data Specifies that Data Director proceeds with latest data transfer once the connection is established. This might result in data loss. - Click Submit to create data feed with the selected configurations. To leave the wizard and discard the changes, click Cancel.
5.3.1.2 Editing Standard Data Feed
This section describes how to edit a standard data feed using the OCNADD console.
- Navigate to Data Feeds page.
- Click Standard Feed.
The Data Feeds page opens listing all the existing standard feeds.
- To edit a standard data feed, click the Ellipsis Points under the Actions column.
- Select Edit to update the fields or options
for the selected data feed. This opens the Edit Data Feed
page.
The edit page can also be accessed by clicking on the data feed name.
- Click on Edit icon to open a drawer where you can edit the selected data feed configurations.
- After performing the modifications, click Save
Changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
5.3.1.3 Cloning Standard Data Feed
This section describes how to clone a standard data feed using the OCNADD console.
- Navigate to Data Feeds page.
- Click Standard Feed.
The Data Feeds page opens listing all the existing standard feeds.
- To clone a data feed, click Ellipsis Points under the Actions column.
- Click Clone to create a clone of the
selected data feed. This creates a clone of the selected data feed.
The clone has all the configurations similar to the data feed from which it is created.
5.3.1.4 Deleting Standard Data Feed
This section describes how to delete data feeds using the OCNADD console.
- Navigate to Data Feeds page.
- Click Standard Feed.
The Data Feeds page opens listing all the existing Standard feeds.
- Click Ellipsis Points under the Actions column to delete a data feed.
- Click Delete to delete the data feed. This opens a dialog box to confirm the deletion.
- On the dialog box, click Delete. This deletes the data feed permanently.
5.3.2 Kafka Feed
To view the list of Kafka feeds, click Kafka Feed on list data feeds.
Prerequisite:
- Kafka Feed is enabled only when OCNADD services are on TLS.
- Create ACL user prior to creating Kafka feeds.
- OCNADD supports creation of up to two Kafka feeds only.
Note:
Kafka Feed is not supported in a IPv6 deployment.For more information, see "Support for External Kafka Consumer Feed" in "OCNADD Features" section of Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide.
5.3.2.1 Creating Kafka Feed
This section describes how to create a Kafka feed using the OCNADD console.
The Data Feeds page displays the Create Feed button to create a data feed.
- Navigate to Data Feeds page.
- Click Create
Feed.
This opens a dialog box with the option to select the type of feed you want to create.
- Select the Kafka Feed option.
- Click Proceed to open
Create Kafka Feed wizard.
Follow the steps below in the Create Kafka Feed wizard:
5.3.2.1.1 Step 1: Provide Application Details
This section describes how to provide application details in Create Kafka Feed wizard to create Kafka feed using the OCNADD console.
- Enter application information using the following options on the
Provide Application Details page:
- Feed Name
- Acl User
- Host Name
- Click Submit to create Kafka feed with the selected configurations. To leave the wizard, click Cancel.
5.3.2.2 Editing Kafka Feed
This section describes how to edit a Kafka feed using the OCNADD console.
To edit Kafka feeds:
- Navigate to Data Feeds page.
- Click Kafka Feed.
The Data Feeds page opens listing all the existing Kafka feeds.
- To edit a Kafka feed, click Ellipsis Points under the Actions column.
- Click Edit icon to update the fields or options
for the selected Kafka feed. This opens the Edit Data Feed
page.
The edit page can also be accessed by clicking on the data feed name.
- Click on Edit icon to open a drawer where you can
edit the selected data feed configurations.
Note:
Currently, you can edit only Acl User and Host Name fields. - After performing the modifications, click Save
Changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
5.3.2.3 Cloning Kakfa Feed
This section describes how to clone a Kafka feed using the OCNADD console.
- Navigate to Data Feeds page.
- Click Kafka Feed.
The Data Feeds page opens listing all the existing Kafka feeds.
- To clone a Kafka feed, click Ellipsis Points under the Actions column.
- Click Clone to create a clone of the selected Kafka feed. This creates a clone of the selected feed.
The clone has all the configurations similar to the Kafka feed from which it is created.
5.3.2.4 Deleting Kafka Feed
This section describes how to delete Kafka feeds using the OCNADD console.
- Navigate to Data Feeds page.
- Click Kafka Feed button.
The Data Feeds page opens listing all the existing Kafka feeds.
- Click Ellipsis Points under the Actions column to delete a Kafka feed.
- Click Delete to delete the Kafka feed. This opens a dialog box to confirm the deletion.
- On the dialog box, click Delete. This deletes the Kafka feed permanently.
Note:
For more information about Kafka Feed, see "Support for External Kafka Consumer Feed" section in "OCNADD Features" chapter of Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide.5.4 Data Filters List
This chapter describes how to use the OCNADD to view, create, edit, and delete data filters.
The Data Filters List page allows you to view the configured data filters, modify, create, or delete data filters. To open this page, click the Data Filters List icon at the bottom of the homepage or click 5G Data Filters on the Ask Oracle page.

Use the Search option to search by Filter Name.
Use the Sort By option to sort data filters based on different parameters.
Use Export option to download the CSV file of the data filters.
Use the Ellipsis Points in the Action column to Edit or Delete a filter.
The Status of a filter can be changed by enabling the Status switch for the filter. If the status is changed, a notification appears on the screen indicating the change.
5.4.1 Create Filter
This section describes how to create a data filter using the OCNADD console.
To create a new data filter, click Create Filter on the Data Filters List page or click Create New Filter on the Ask Oracle page.
To create a data filter, enter the following information:
- Add a Filter Name. The name should not contain capital letters or special characters except for hyphen.
- Select the Filter Type from the drop-down list. The available options are Egress and Ingress. The default filter type is Egress.
- Select the Association. If the Filter Type is configured as Egress, the data feeds created by the user are the options available to select for Association and you can associate a maximum of two filters with same application in case of filter chaining. If the Filter Type is configured as Ingress, select NRF or SEPP or SCP as the Association.
- The Action is automatically populated based configured Filter Type. If the Filter Type is Ingress, the Action is DENY. If the Filter Type is Egress, you can select the Action as ALLOW or DENY.
- Use the Filter Condition drop-down list to select condition.
If the Filter Type is Egress, the available options are:
- service-name
- user-agent
- consumer-id
- producer-id
- consumer-fqdn
- producer-fqdn
- message-direction
- reroute-cause
- feed-source-nf-type
- feed-source-nf-fqdn
- feed-source-nf-instance-id
- feed-source-pod-instance-id
Note:
When message-direction is added in single or combination filter, transaction filter is not applied. Each message is evaluated separately with configured filter rule and filter condition.If the Filter Type is Ingress, the available options are:
- consumer-id
- producer-id
- consumer-fqdn
- producer-fqdn
- reroute-cause
- feed-source-nf-type
- feed-source-nf-fqdn
- feed-source-nf-instance-id
- feed-source-pod-instance-id
Note:
- A maximum of four Filter Conditions can be specified.
- Click Add Condition to add a filter condition.
- Click Remove Condition to remove a filter condition.
- With some filter conditions, you get a list of available values for selection based on the message feed. There is also an option to enter the values manually by using the More Value field. Use + and - buttons to add or remove filter condition values.
- Select the Status from the drop-down list. The options available are ACTIVATE and DEACTIVATE. The default status is ACTIVATE.
- The Filter Rule option appears only when more than one condition is specified for the filter. Use this option to specify the filter rule.
- Click Create on the top-right corner of the screen to create the filter.
On successful creation of the filter, the filter is listed on the Data Filters List page.
5.4.2 Editing Data Filter
Note:
Ensure that the filter is deactivated before updating (edit or change) the filter type.This section describes how to edit a data filter using the OCNADD console.
- Click Data Filters List icon at the bottom of the page or click 5G Data Filters on the Ask Oracle page. The Data Filters List page opens, this page lists all the existing data filters.
- To edit a data filter, click Ellipsis Points under the Actions column.
- Select Edit icon to update the fields or options for the
selected data filter. This opens the Edit Data Filter
page.
The edit page can also be accessed by clicking on the data filter name.
- Click Edit to edit the selected data filter configurations.
- After performing the modifications, click Save Changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
5.4.3 Deleting Data Filter
This section describes how to delete a data filter using the OCNADD console.
- Click the Data Filters List icon at the bottom of the page. The page lists all the existing data filters.
- Click Ellipsis Points under the Actions column to delete a data filter.
- Select Delete to delete the data filter. This opens a dialog box to confirm the deletion.
- On the dialog box, click Delete. This deletes the data filter permanently.
Note:
For more information about Data Filtering feature, see "Data Filtering" section in "OCNADD Features" chapter of Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide.5.5 Alarms History
This chapter describes how to use OCNADD to view Alarm History.
To view the alarms history, click the Alarms History icon at the bottom of the page. This open the Alarms History page with alarm details in a tabular format.
- Use Search Alarms to search and filter through all the alarms that may have occurred in the system since the beginning. The alarms are defined using different color notations in the severity column.
- You can filter alarms based on the following options below the search
box:
- Description
- Type
- Status
- Severity
- Date Time
- Use Sort By drop-down to sort the alarms based
on the following options:
- None
- Severity
- Type
- Date Time
- Affected Microservices
- Click the Download button located on the right side of the Sort By drop-down to export alarm details as a CSV file.
To access the list of OCNADD alarms, see OCNADD Alarms.
5.6 Configure
This chapter describes how to use Configure section to perform various configurations related to L3L4 mapping and synthetic data feeds.
IPv6 Deployment
Since IPv6 deployment does not support Synthetic Feeds, Kafka Feeds, or L3L4 Mapping,
Configure tab is not available in a IPv6
deployment.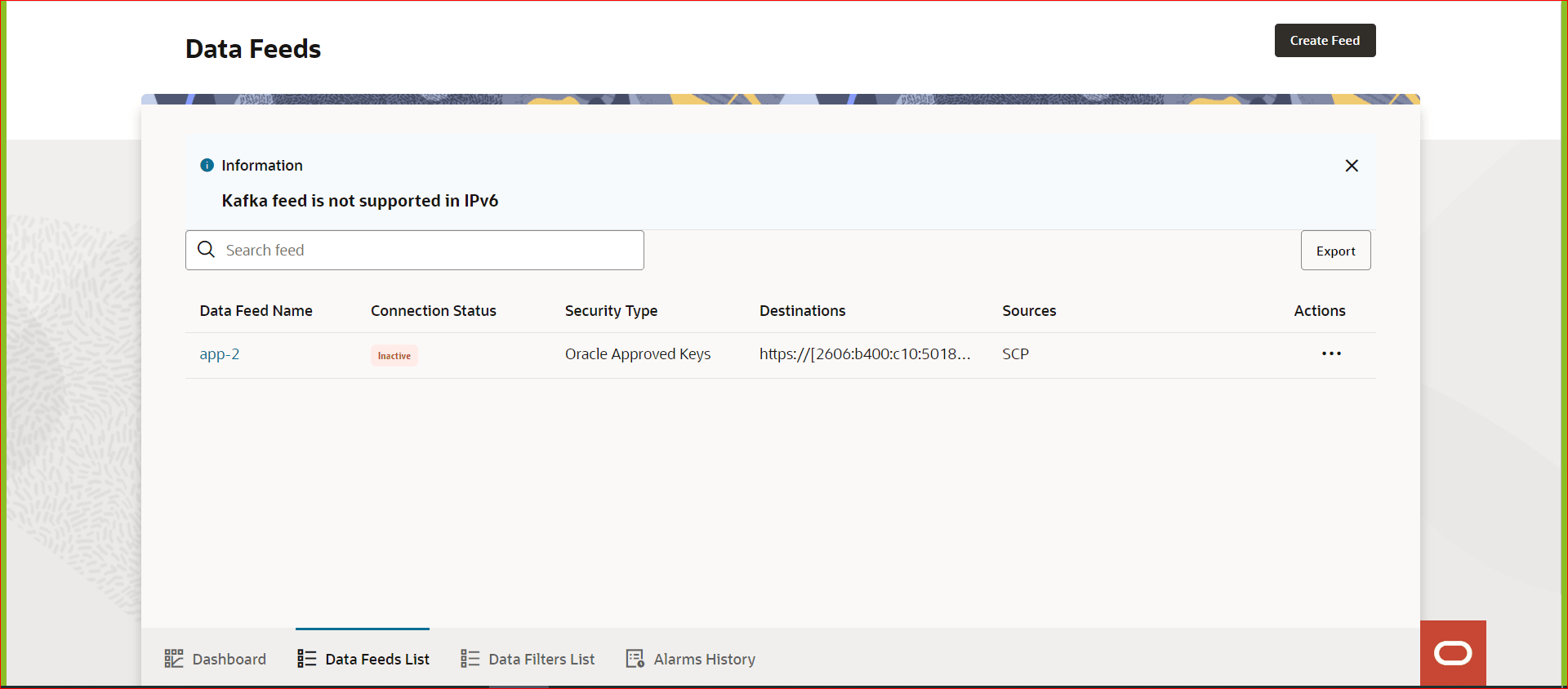
Non IPv6 Deployment (IPv4 Deployment)
To view Configure, click Configure at the bottom of the page on the Ask Oracle page or navigation list. This opens the Synthetic Data Feeds page with the listing of all the existing synthetic data feeds.
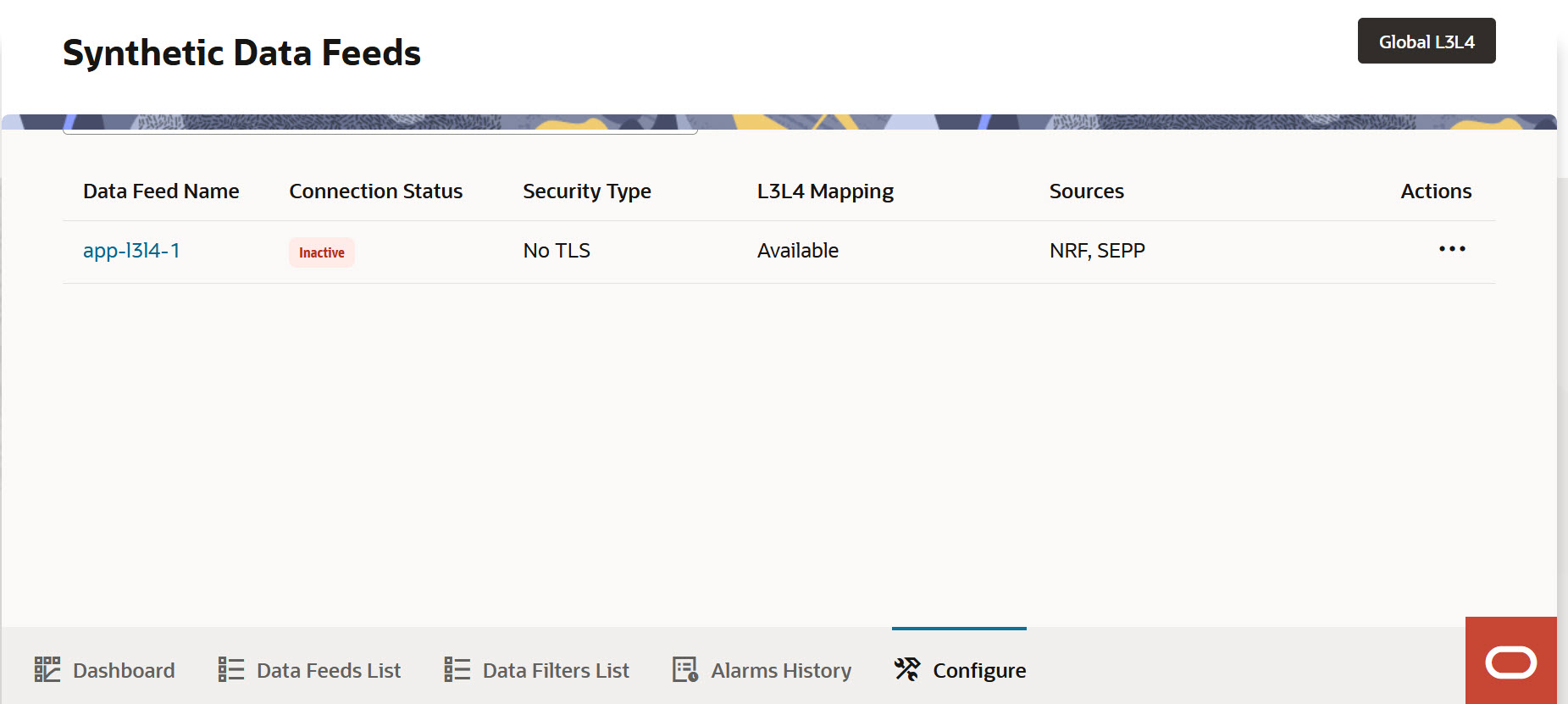
Use the Search feed option to search for a synthetic data feed using Data Feed Name.
Click Global L3L4 to configure Global L3L4 mapping.
5.6.1 Editing Feed Level L3L4 Configuration
This section describes how to edit feed level L3L4 configuration or add feed level L3L4 mapping to the existing synthetic feeds in OCNADD console.
- Click Configure icon at the bottom of the page on the Ask Oracle page or navigation list. The Synthetic Data Feeds page opens listing all the existing synthetic data feeds.
- To edit a data feed, click Ellipsis Points under the Actions column.
- Select Edit Feed L3L4 to update the fields
or options for the selected data feed. This opens the Edit
<data-feed-name> Feed for L3L4 Mapping page.
The edit page can also be accessed by clicking on the synthetic data feed name.
Note:
- Ensure that Do you want to allow L3L4 Mapping Rule? toggle is switched on to view or edit the L3L4 Mapping configurations.
- If the feed already has some existing L3L4 configurations, the toggle remains in the ON state and you can see existing L3L4 configuration parameters.
- If you don't want to map L3L4 to the existing feed, you can toggle off the switch, and L3L4 mapping will be removed from the existing feed.
- Edit the selected data feed configurations by modifying the options as shown in Step 4: L3L4 Mapping (Available only for Synthetic Feeds).
- After performing the modifications, click Save
Changes.
Note:
Click Cancel to discard the changes. - <Optional>You can use Export button to download your feed level L3L4 configuration in a CSV file.
5.6.2 Configuring Global L3L4 Mapping
The Global L3L4 configuration allows you to include the configured or desired L3 and L4 information in every message of the synthetic packet feed
To configure Global L3L4 mapping:
- Click the Configure icon at the bottom of the page on the Ask Oracle page or navigation list. The Synthetic Data Feeds page opens listing all the existing synthetic data feeds.
- Click Global L3L4 at the top-right corner of the page.
This opens Global L3L4 Configuration page. This page has two components:
- A form to create a mapping rule
- L3L4 preview pane, which shows a list of configured rules with their details.
Note:
- You can create a maximum of one Global L3L4 configuration in OCNADD.
- You can create upto 500 global mapping rules for a Global L3L4 configuration.
- Use the following options create a Global Mapping Rule:
Table 5-10 Create a Global Mapping Rule
Option Name Description Select Attribute1 Select from the following drop-down list: - consumer-fqdn
- producer-fqdn
- api-name
- feed-source-nf-fqdn
- message-direction
- consumer-id
- producer-id
- none
Note: OCNADD does not support more than two attributes in each row.
Enter or Select value Enter value of the selected Attribute1 Note: This value is case-sensitive
Select Attribute2 Select from the following drop-down list: - consumer-fqdn
- producer-fqdn
- api-name
- feed-source-nf-fqdn
- message-direction
- consumer-id
- producer-id
- none
Enter or Select value Enter value of the selected Attribute2 Note: This value is case-sensitive
Enter IP Address Enter IP Address. Note: This is a mandatory field.
Enter Port Enter Port number. Note: This is a mandatory field.
Add Click to create your Global Mapping Rule. Note: This button will be enabled once you enter all the required values in the form correctly.
Once you click Add the preview of the rule created will be added to the preview pane.
Update Click to update your existing Global Mapping Rule. Remove Click to remove your selected Global Mapping Rule. Reset Click to revert the changes done to the selected Global Mapping Rule. Drag and Drop You can use this option to upload a CSV file for creating your Global L3L4 configuration. Note: Ensure that you follow the supported format while creating your CSV file. You can download the CSV template by clicking on the download button at the top-right side of the page.
Export You can use this option to download Global L3L4 configuration as a CSV file. - After performing the configurations or modifications, click Apply to save the changes.
- Use Action drop-down list to Delete or Reset the Global L3L4 Configuration.
- Click Configure at the top-left corner to go back to Synthetic Data Feeds page.
Note:
For more information about L3L4 Mapping feature, see "L3-L4 Information for Synthetic Packet Feed" section in "OCNADD Features" chapter of Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide.