2 Using the FTRA
This chapter contains information regarding the various ways to use the FTRA.
FTRA Initialization
To start the FTRA, double-click the FTRA icon on the desktop. When the application starts, the FTRA window is displayed.
STP Connection Configuration Menu
Before database tables can be retrieved from an STP or command files can be sent to an STP, the STP must be defined in the STP Connection Configuration database.
Select Edit > STP Connection Configuration.
The below figure shows the description of the fields, buttons, and boxes in the STP Connection Configuration Menu window.
Figure 2-1 STP Configuration
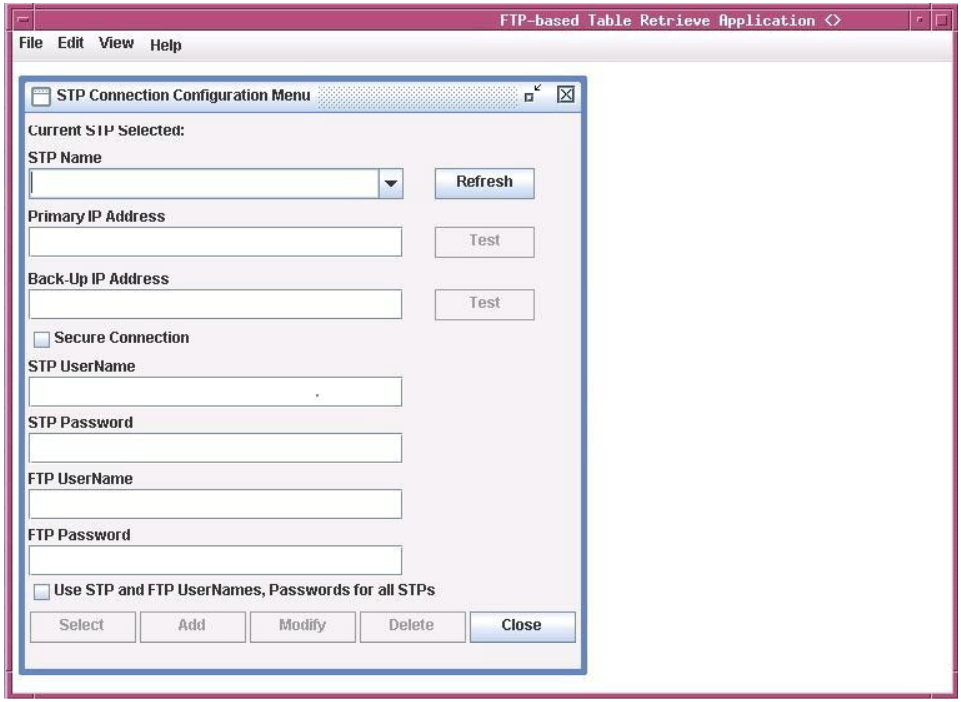
Table 2-1 STP Connection Configuration Menu Description
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
|
Fields |
|
|
STP Name |
The STP name must contain at least one alphanumeric character and a maximum of 64 upper-case alphanumeric characters. The STP Name must always be entered in uppercase regardless of the Caps Lock key setting on your keyboard. This field also provides a drop down list for selecting stored STP configuration records. |
|
Primary IP Address |
It is the primary IP Terminal card address of the associated STP (used for telnet sessions). The FTRA uses this IP Terminal card address first when connecting to the STP. The primary IP Terminal card address is the IP address of a service module in the associated EAGLE. |
|
Backup IP Address |
It is the backup IP Terminal card address of the associated STP (used for telnet sessions). The FTRA uses this IP address when the connection using the primary IP address fails. The backup IP address is the IP address of anotherservice module in the same EAGLE. The FTRA does not attempt to make a Telnet connection with the backup IP address (if the backup IP address is configured) of the alternate service module on the EAGLE if the connection with the primary IP address is established but no IP terminal is available. |
|
STP UserName |
It is the user name assigned to the user by the STP system administrator (used for telnet sessions). |
|
STP Password |
It is the password assigned to the user by the STP system administrator (used for telnet sessions). |
|
FTP UserName |
It is the username assigned to the user by the
administrator (used for FTP). Any FTP user name with symbols must be
enclosed within double quotation marks. (For example, to specify the
FTP user name |
|
FTP Password |
It is the FTP password assigned to the user by the administrator (used for FTP) |
|
Buttons |
|
|
Refresh |
It displays the data of the STP configuration record typed in the STP Name field. If an STP name is selected from the STP Name drop down list, the data fields are automatically displayed. |
|
Test |
It verifies that the FTRA can successfully connect and login to the EAGLE through an available telnet terminal at the specified IP Terminal card address. The STP Connection Configuration Menu window has two Test buttons, one for the Primary IP address, and one for the Backup IP address. |
|
Select |
It selects the displayed STP name to be connected to the FTRA. |
|
Add |
It adds a newly entered STP configuration record and associated data to the STP Connection Configuration database. |
|
Modify |
It modifies the fields of the displayed STP configuration record. |
|
Delete |
It deletes the displayed STP configuration record and associated data from the STP Connection Configuration database. |
|
Close |
It closes the STP Connection Configuration Menu window. |
|
Boxes |
|
|
Secure Connection |
It enables the FTRA to use a secure IP connection to the STP. To use a secure connection for the FTRA to EAGLE communication, make
sure the EAGLE OA&M IP Security Enhancements feature is enabled
and activated, and SSH and SECURITY parameters are ON. The OA&M
IP security feature can be verified by entering the
If the EAGLE OA&M IP Security Enhancements feature is not enabled or activated, perform the “Activating the EAGLE OA&M IP Security Enhancements Controlled Feature” procedure in Database Administration - System Management User's Guide and enable and activate the EAGLE OA&M IP Security Enhancements feature. The SSH and SECURITY parameters
can be verified by following the below mentioned procedures:
Note: This box should be unchecked if the EAGLE OA&M IP Security Enhancements feature is not enabled or activated, and will not be enabled or activated, or either of SSH and SECURITY parameter is not ON.If this box is checked, the public key fingerprint for the EAGLE specified in this window must be installed onto the FTRA for the FTRA and the specified EAGLE to use a secure connection. After the STP is added to the STP Connection Configuration database, add the public key fingerprint to the FTRA. For this, see the "Secure EAGLE Host Key Provisioning' section. |
|
Use STP and FTP UserNames, Passwords for all STPs Box |
All the STP and FTP user names and passwords of all the provisioned STPs are changed to the user name and password of the displayed STP name. This change occurs only when the Add or Modify buttons are used. |
Displaying an Existing STP Configuration Record
An existing STP configuration record can be displayed by either selecting the STP Name from the STP Name drop down list, or by re-entering the STP name in the STP Name field in the STP Connection Configuration Menu window and clicking the Refresh button.
To Use the STP Name Drop Down List
Testing an STP Configuration Record
Selecting the Current STP
Before retrieving database tables from an EAGLE, or sending commands to an EAGLE, that STP name must be shown in the STP Connection Configuration Menu window as the current STP. The Current STP Selected: indicator in the STP Connection Configuration Menu window shows which STP is the current STP.
Secure EAGLE Host Key Provisioning
An EAGLE using secure connections has a unique host key for each service module in the EAGLE. This key is used by the FTRA to positively identify or authenticate each service module’s telnet server on the EAGLE. The FTRA will not connect to an unauthenticated server. The FTRA authenticates the server by matching its pre-installed host key with the key received from the EAGLE when the connection between the EAGLE and the FTRA is made.
This procedure adds the IP addresses of the EAGLE to
the FTRA in the hosts.xml
file placed in the cfg directory under the
FTRA installation directory.
This procedure must be performed for each IP Terminal card on each EAGLE that the FTRA will connect to, but only for EAGLE using secure connections to connect to the FTRA. This procedure must be performed before any secure connection between the EAGLE and the FTRA is initiated.
If an IP address has not been added to the FTRA’s hosts.xml file and you try to initiate a secure connection to the EAGLE, you will receive the STP Primary IP address is missing from host.xml file. To use this IP address with security. check the secure connection checkbox and add IP address in hosts.xml file. warning message.
If the warning message is received, either clear the Secure Connection check box in the STP Configuration Record for the STP or add the IP address to the FTRA’s hosts.xml file.
Note:
Once the IP Terminal card is installed into the EAGLE, the public host key fingerprint for the service module will change only when power to the service module is disrupted by removing the service module from the shelf, then reinserting the service module into the shelf, or as the result of any event that interrupts power to the service module. Re-initializing the service module will not change the public host key fingerprint for the service module. This procedure will have to be performed for each public host key fingerprint on the EAGLE that has changed.The public host key fingerprint is added to the FTRA’s hosts.xml file. If the public host key fingerprint has not been added to the FTRA’s hosts.xml file, and you try to initiate a secure connection to the EAGLE, you will receive the STP Primary IP address is missing from host.xml file. To use this IP address with security either clear the secure connection checkbox or add it's host key to this hosts.xml file. warning message.
If the above warning message is received, then either clear the Secure Connection check box in the STP Configuration Record for the STP, or add the public host key fingerprint to the FTRA’s hosts.xml file.
The verification that the keys are installed on the FTRA is called strict host key checking. By default, strict host key checking is on. This enforces server (EAGLE) strong authentication, designed to provide security between the FTRA and the EAGLE. This also prevents a hostile server from tricking the FTRA into exposing any EAGLE login and password combinations.
Caution:
Do not set strict host key checking to off, unless your network is in a controlled and secure environment. If you set strict host key checking to off, the Connectivity Test Log will warn you each time you try to connect that the EAGLE public host key fingerprint has not been added to the hosts.xml file on the FTRA.
To set the strict host key flag:
FTP Server Configuration
An FTP server must be configured on the EAGLE using the FTP Server Configuration menu before database tables can be retrieved from the EAGLE, or command files can be sent to the EAGLE.
Note:
- If the Secure Connection box in the STP Connection Configuration Menu window is checked, the IP address specified in the FTP Server Configuration menu must be the IP address of a secure FTP server. If the Secure Connection box in the STP Connection Configuration Menu window is not checked, the IP address specified in the FTP Server Configuration menu must be the IP address of a FTP server.
- Any firewall between the FTRA and the FTP server configured in the FTP Server Configuration Menu window, must allow FTPs to the IP address specified in the FTP Server Configuration Menu window.
Retrieving Database Tables from an STP
Retrieve Tables Window
The Figure 2-10 is used to select the database tables to be retrieved from the selected STP. The Retrieve Tables window contains a list of predefined retrieve commands.
The Retrieve from STP and Retrieve from Local Database buttons determine whether new database tables are retrieved from the selected STP or if existing tables already retrieved from that STP will be used. If no tables exist for the selected STP, the Retrieve from Local Database button will be grayed out.
The output from the retrieve commands is converted to CSV files. When the retrieve operation is completed, the Command Complete window opens notifying the user if the retrieval was executed with or without errors. The Retrieve Tables Log opens allowing the user to view the events.
Note:
- If you attempt to retrieve and convert the database tables
for the GTT commands (
rtrv-tt,rtrv-gtt) and the EGTT commands (rtrv-gttsel,rtrv-gttset,rtrv-gta) in the same retrieve tables request, you will receive a warning that errors can be caused by attempting to retrieve and convert the GTT and EGTT database tables from the same EAGLE. Click Yes to continue. - You may only retrieve and convert the tables corresponding
to which feature is on, GTT or EGTT. If the EGTT feature is on, shown in the
rtrv-featoutput, the database tables for thertrv-gttsel,rtrv-gttset, andrtrv-gtacommands can be retrieved and converted. If the EGTT feature is off, the database tables for thertrv-ttandrtrv-gttcommands can be retrieved and converted. - The errors will be caused when the retrieved GTT and EGTT database tables are converted to CSV files. Because only one set of the database tables, GTT or EGTT, can be retrieved and converted. The error will occur when the attempt is made to convert the database tables that could not be retrieved.
Figure 2-10 Retrieve Tables Window

The following Table shows the description of the fields and buttons in the Retrieve Tables window.
Table 2-4 Retrieve Tables Window Description
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
|
Fields |
|
|
Command List |
Contains a predefined list of retrieve commands. |
|
Selected Commands |
These commands are used to determine which database tables are retrieved from the selected STP. Any number of retrieve commands can be selected for retrieval. |
|
Buttons |
|
|
Add |
Moves the highlighted commands from the Command List box to the Selected Commands box. |
|
Remove |
Moves any highlighted commands in the Selected Commands box back to the Command List box and places them in the Command List box in alphabetical order. |
|
Reset |
Moves all commands in the Command List box to the Selected Commands box. All highlights in the Selected Commands box are removed. |
|
Retrieve |
Initiates the retrieval of all the selected database tables represented by the selected retrieve commands. The database tables are transferred using an FTP connection and converted to CSV files. |
|
Store |
Stores the commands in the Selected Commands box which will be used by the Command Line Interface. This list is maintained even when the FTRA is shut down and restarted. |
|
Load |
Loads the commands into the Selected
Commands box which are currently stored for Command Line
Interface usage. This allows the user to verify the |
|
Retrieve from STP |
Retrieves the database tables, based on the selected retrieve commands, from the selected STP instead of using the tables previously retrieved. |
|
Retrieve from Local Database |
When selected, the FTRA uses the database table previously retrieved from the selected STP. |
|
Close |
Closes the Commands Menu window. |
When a Retrieve Tables command is performed, the FTRA verifies that the EAGLE is running one of the supported releases. If the EAGLE is not supported, an error message is displayed and the Retrieve Tables command is terminated.
Figure 2-11 Retrieve Table Log - Release Not Supported Error

If the EAGLE release is supported, the Retrieve Tables command is performed and operations on the FTRA can continue.
Retrieve Tables Log
Figure 2-13 Retrieve Tables Log Window without Errors

rtrv-stp
CSV file. Since the rtrv-stp
command CSV is not generated by the CSVGEN(X) utility, the CSV filename for the
rtrv-stp command is not displayed in the sorted
order with other CSV filenames, but it is displayed as the
last entry in the filenames list. Since the Retrieve Tables Log is generated by the
CSVGEN(X) utility, no record of processing the rtrv-stp command is displayed in this log. See the following
figure as an example of the Retrieve Tables Log when the rtrv-stp
command is processed
Figure 2-14 Retrieve Table Log with the RTRV-STP Command CSV Example

Figure 2-15 Retrieve Table Log with Errors

Clearing the Retrieve Tables Log Display
The display can be cleared, enabling new entries to be captured to the log. Once the log is cleared, the existing entries are lost unless the log is saved to a file or printed before the display is cleared.
- From the Retrieve Tables Log window, select File > Clear Display.
- From the FTRA window, select View > Retrieve Tables Log. Select File > Clear Display in the Retrieve Tables Log window.
Command Line Interface
The FTRA Command Line Interface allows the user to retrieve the same database tables, using the EAGLE retrieve commands, from all configured STPs in the STP configuration database. The Store and Load buttons in the Retrieve Tables window are used to select these retrieve commands.
The Command Line Interface allows the user to change the STP Username and Password for an STP already configured in the system.
Before the Command Line Interface can be started, you must exit the FTRA
application. To start the Command Line Interface retrieve process, enter the
(ftra -c) at the DOS
command prompt (in Windows) or at a shell command prompt (in Linux).
For modifying the Username and Password for an STP, three command line arguments have to be specified with the “-c”
option (ftra –c stpname username password).
The user can automate this retrieve process through the use of external
scheduling software such as Task Scheduled (on the Windows platform) and “cron” (on
the Linux platform). Please see the platform's scheduling program for specifics on
how to use the external scheduling software. For example, on the Linux platform,
enter the man crontab command.
-
Exit the FTRA application.
-
On the Windows platform, at a DOS prompt, go to the
\bindirectory of the FTRA <install_directory> location. -
On the Linux platform, at a shell prompt, go to the
/bindirectory of the FTRA <install_directory> location. -
Enter the
ftra -c stpname username passwordcommand. The storedrtrvcommands are then sent to the provisioned STP. The data tables are retrieved and converted to the CSV file format.Result: The username and password shall be modified in the STP configuration for the specified stpname.
Figure 2-16 FTRA Windows Scheduled Task

Note:
The parameters specified in the command line are case sensitive. For example, anstpnamespecified as EAGLE, Eagle, or eagle are treated separately.
Figure 2-17 LINUX cron job scheduled via crontab

Figure 2-18 FTRA wrapper script example for LINUX

Figure 2-19 FTRA wrapper script example on LINUX for modifying STP configuration
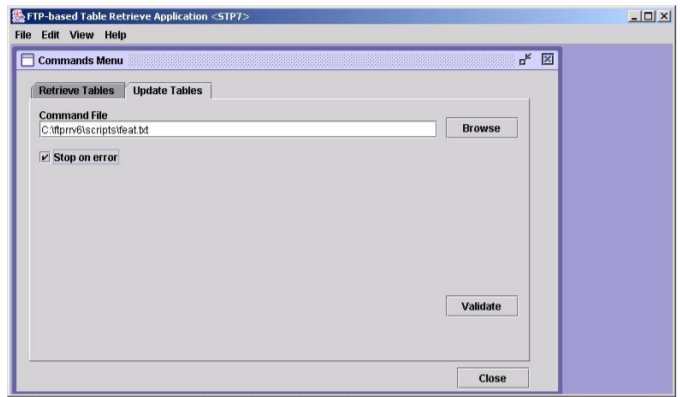
Updating Database Tables in the Selected STP
The Update Tables window is used to send EAGLE commands to the selected STP. The commands, in the form of a command file, are validated before being sent.
To send the command file to the selected STP, the command file is selected by entering the path and file name of the command file, or by selecting the file name of the command file from the Select window. The command file is then validated by clicking the Validate button in the Update Tables window. When the validation is completed, the Update Validation Complete window appears. From the Update Validation Complete window, the command file can be edited, sent to the selected STP or the Update Validation Complete window can be closed without sending the command file to the selected STP. The Update Tables Log contains the events of the command validation and any error messages that may have occurred.
The following table shows the description of the fields and buttons in the Update Tables window.
Figure 2-20 Update Table Window

Table 2-5 Update Tables Window Description
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
|
Fields |
|
|
Command File |
The path and file name of the command file are entered here. A command file contains the EAGLE commands used to modify database tables of the STP. |
|
Stop on error box |
If the box is checked, and an error is found during the validation of the commands, the validation stops and no further commands are validated. If the box is not checked, all commands are processed regardless of errors. The error results are displayed in the Update Tables Log. |
|
Buttons |
|
|
Browse |
Opens the Select window to select the command file to send to the selected STP. |
|
Validate |
Validates the EAGLE commands using the offline database. |
|
Close |
Closes the Commands Menu window. |
Update Validation Complete Window
When the command validation has completed, the Update Validation Complete window opens notifying the user if the commands validated with or without errors. From the Update Validation Complete window, the command file can be edited, sent to the selected STP, or the window can be closed without sending the command file to the selected STP.
The following table shows the description of the buttons in the Update Validation Complete window.
Table 2-7 Update Validation Complete Window Description
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
|
Edit |
Opens the Command File Editor window and allows the user to make changes to the command file. To edit a command file, go to the section. |
|
Commit |
Sends the commands in the command file to the STP. A Command Complete window is opened and the Update Tables Log is updated. If the Update Tables validation is completed with errors the Commit button is not displayed. |
|
Stop |
Closes the Update Validation Complete window without sending the commands in the command file to the STP. |
Update Validation Complete Window with Errors
If the Update Validation Complete window shows that errors have occurred, the command file can be edited or the window can be closed without sending the command file to the selected STP. There is no Commit button in the Update Validation Completewindow and hence it prevents the sending of invalid commands.
To fix the errors in the command file, click the Edit button and go to the "Editing a Command File" section.
Sending a Command File to the Selected STP
To send the command file, click the Commit button in the Update Validation Complete window. The Commit button is shown only on the Update Validation Complete without Errors window. The validated command file is sent to the selected STP.
The Command Complete window opens and displays: “Update Tables processing completed without errors” and “Please check Update Tables Log for results.” Click OK to continue. The Update Tables Log contains the commit processing events.
Stopping Without Sending or Editing a Command File
To stop the process without sending or editing a command file, click the Stop button in the Update Validation Complete window. The Update Validation Complete window is closed. No changes are made to the command file and the command file is not sent to the selected STP.
Update Tables Log Window
The Update Tables Log contains the processing events and any error messages that may have occurred during the validation and sending of a command file. The Update Tables Log window opens at the beginning of the validation process and displays “Processing Validate Request, Please Wait” until the command file validation is completed. The Update Tables Log window is automatically cleared when the next command file validation is started. Selecting View > Update Tables Log from the menu can also open the Update Tables Log window.
The System Log
Figure 2-23 System Log Window

RTRV-STP Command
The rtrv-stp command provides a consolidated report of STP configuration on a system-wide basis.
Figure 2-24 Retrieve Tables window with rtrv-stp command selected for retrieval

RTRV-STP Command Retrieval Session
Below represented is the FTRA retrieval session when rtrv-stp command is supported on EAGLE. If the command is not supported
on EAGLE, an error will be displayed and the retrieval session will be terminated.
Figure 2-25 Successful Retrieval Session for rtrv-stp command
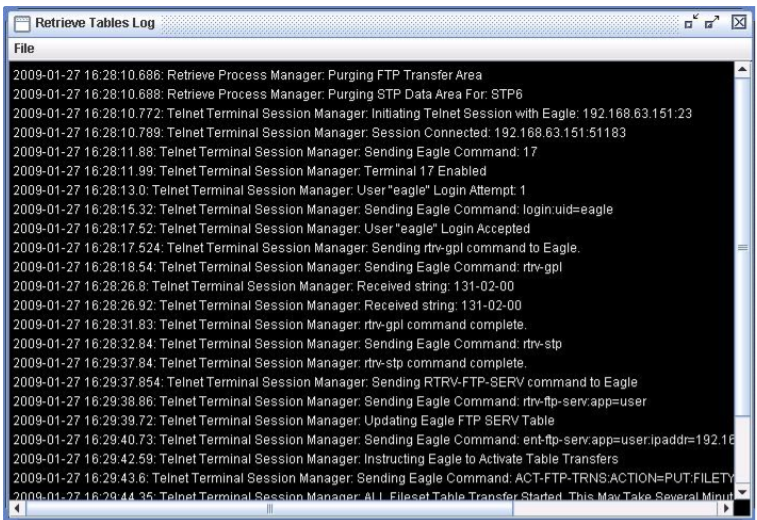
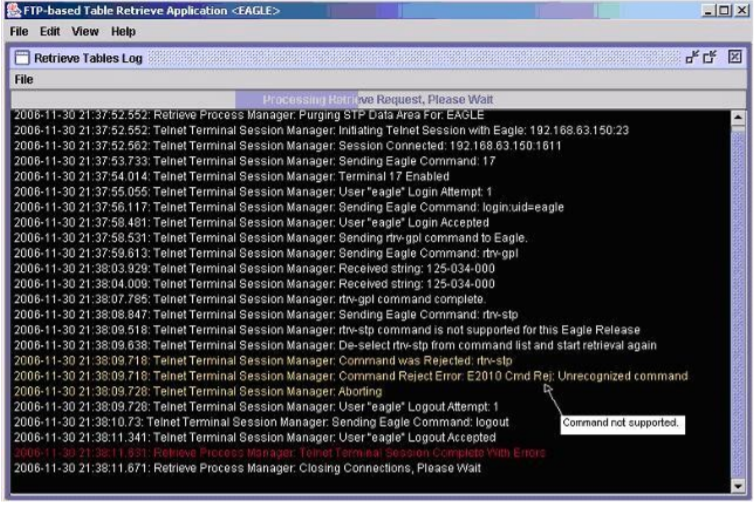
Figure 2-26 Rtrv-stp Command unsupported on EAGLE release
About FTRA Window
The About FTRA window displays the version level of the FTRA and copyright information. To display the About FTRA window, select Help>About in the FTRA window.
SSH/SFTP Error Codes
Table 2-8 and Table 2-9 contain a list of the error codes that can be generated when making a secure connection between the FTRA, version 4.0 or greater, and the EAGLE. Each error code contains a brief description of the error and the suggested recovery action.
This section also contains procedures, following Table 2-8 and Table 2-9, for testing connectivity and network problems, and to verify that the setup for making secure connections is correct.
If secure connections to the EAGLE cannot be made, verify
that the EAGLE OA&M IP Security Enhancements feature is enabled and activated by
entering the rtrv-ctrl-feat command and verify the SSH and SECURITY parameters are ON by entering the rtrv-secu-dflt and rtrv-ftp-serv commands, respectively, at the EAGLE before
performing any of the actions in Table 2-8 and Table 2-9.
If the EAGLE OA&M IP Security Enhancements feature is not enabled or activated, perform the “Activating the EAGLE O&AM IP Security Enhancements Controlled Feature” procedure in Database Administration - System Management User's Guide and enable and activate the EAGLE OA&M IP Security Enhancements feature.
If the SSH or SECURITY parameters are not ON, these parameters can be turned ON by entering chg-secu-dflt:ssh=on and chg-ftp-serv, respectively.
If any of the errors shown in Table 2-8 or Table 2-9 are encountered after the recovery procedure is verified, contact Customer Care center.
Table 2-8 FTP/SFTP/SSH Error Codes
| SFTP SSH Generic Network Client Error Code | Description | Action/Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
User Errors |
||
|
592 |
File open failed. |
Invalid file name in the download list, or out of resources. Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
593 |
The file name is already specified. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. (Internal SFTP implementation error). |
|
594 |
Invalid Path |
Verify that the path is valid in the FTP Server Configuration Menu window. |
|
598 |
The SSHD daemon is not running on the destination system or the server IP address unavailable. |
Verify that the IP address exists on network with a ping
(See Connectivity Test – I and Connectivity Test – II). If the IP
address exists on network, then verify that SSHD
daemon is running on the
destination machine using the |
|
629 |
The SFTP daemon is not running |
Verify that the subsystem entry in the |
|
633 |
Verify that the Username and Password in the STP Connection Configuration Menu window is valid and an account exists for the username and password on the SSHD server host. |
|
|
SFTP Errors |
||
|
SFTP Client Errors |
||
|
597 |
SFTP client packet send failure |
Perform these tests: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
598 |
The SFTP connection is closed. |
|
|
599 |
SFTP packet read failure |
|
|
600 |
SFTP protocol error. The received message is larger than the expected packet size. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing the tests in Network Outage Trouble Shooting. If the error persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
601 |
SFTP client invalid ID failure |
Notify Customer Care Center. |
|
608 |
SFTP received an invalid ID in the response received during a read operation on remote directory. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing the tests in Network Outage Trouble Shooting. If the error persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
609 |
SFTP handle mismatch error. This error is displayed when there is a failure to receive an expected handle upon successful READ/WRITE/ CREAT/TRUNC/EXCL of a file using SSH_FXP_OPEN on remote server. |
|
|
610 |
Unexpected SSH2_FXP_ATTRS. |
|
|
611 |
Unexpected SSH_FXP_NAME. SFTP using the SSH_FXP_OPENDIR opens a directory for reading. The server responds to this request with either aSSH_FXP_NAME or a SSH_FXP_STATUS message. This error code implies that an unexpected SSH_FXP_NAME is received. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing the tests in Network Outage Trouble Shooting. |
|
612 |
The SFTP client uses the SSH_FXP_REALPATH request to have the server localize any given path name to an absolute path. This is useful for converting path names containing “..” components or relative pathnames without a leading slash into absolute paths. This error implies that there is a failure during this operation. |
Check if the access to the path specified in the FTP Server Configuration Menu window is accessible and re-try the connection. |
|
613 |
The SSH_FXP_READLINK request is used by the SFTP client to read the target of a symbolic link. The server will respond with aSSH_FXP_NAME packet containing only one name and a dummy attributes value. The name in the returned packet contains the target of the link. This failure implies that there is a failure during the READLINK operation. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing the tests in Network Outage Trouble Shooting. |
|
614 |
The SFTP client receives SSH_FXP_DATA as a response to any file operations from the server. This error implies that the client received an unexpected SSH_FXP_NAME from the server. |
|
|
615 |
The SFTP client received more data than expected. |
|
|
616 |
The SFTP client failed to read the data from the file descriptor of the file specified for transfer. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
SSH Client Errors |
||
|
617 |
Excessive identity files. OpenSSH implementation contains the maximum of 100 identity files or the client configuration file is corrupted. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
624 |
The debug levels allowed for SSH protocol in openSSH is 0-9. The client configuration file contains an error or is corrupted. |
|
|
625 |
Failure to read the client configuration file. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
626 |
Invalid compression level is specified in the client configuration file. |
|
|
627 |
SSH failure to setup the IO with the server. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing these tests: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
628 |
SSH failure to open the channel for theSSH connection with the server. |
|
|
629 |
SSH failure to setup the channel for theSSH connection with the server. |
|
|
630 |
SSH failure to verify the SSH client host key. |
|
|
631 |
SSH user authentication failure. Please verify that only the password authentication is set to “yes” in the SSH server configuration file. See SSHD server configuration provided by vendor of the product. The FTRA and the EAGLE is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. |
Report the issue to Customer Care Center if the problem persists after the SSHD configuration file is verified. |
|
632 |
The authentication method is NULL in the client software. This error is a failure to set the null authentication method. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
633 |
Permission is denied by the server due to authentication failure. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing these tests: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
640 |
A bad message was received during the SSH authentication. |
|
|
641 |
Missing authentication context, encountered during the SSH user authorization. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
642 |
Failure during the public key read/verification operation. |
|
|
643 |
Undefined SFTP SSH error. |
|
|
644 |
UnexpectedSSH_FXP_STATUS error. An invalid status was received by the SFTP server. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing these tests: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
645 |
A bad option was specified in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
|
|
646 |
An unsupported escape character was used in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
|
|
647 |
An unsupported cipher type was used in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
648 |
An unsupported MAC type was used in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing these tests: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
649 |
A bad port was used in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
656 |
Bad forwarding was used in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
|
|
657 |
Bad forwarding ports were specified in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
|
|
658 |
A bad dynamic port was specified in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
|
|
659 |
The host was not specified in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing these tests: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
660 |
An invalid option or argument was specified in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
661 |
The hostname was not specified in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
|
|
663 |
The SSH client was unable to load the cipher type on the EAGLE. |
|
|
664 |
SFTP SSH SET NON BLOCKING CALL FAILURE |
|
|
665 |
Compression is already enabled in the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
|
|
666 |
Unknown cipher number on the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
|
|
667 |
The SSH client key length is invalid. |
|
|
668 |
No key is available on the SSH client on the EAGLE. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
669 |
The secure connection was closed by the remote server, see the error on the SFTP/SSHD server side. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing these tests: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
670 |
Connection failure due to network outage or the connection was lost due to a faulty SSHD/SFTP server or network. |
|
|
671 |
An unexpected packet type was received from the SFTP/SSHD server. |
|
|
672 |
A bad packet length was received from the SSHD/SFTP server. |
|
|
673 |
A cryptographic attack was detected by the SSH client. Please notify the local system administrator. |
Report the issue to Customer Care Center. This is not a software problem but there is a security threat. The keys/authentication may have to be updated immediately. |
|
674 |
The SSH/SFTP client on the EAGLE failed to read from the remote side. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing these tests: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
675 |
Corrupted check bytes were detected on the SSH/SFTP client on the EAGLE. |
|
|
676 |
Corrupted MAC on input was detected by the SSH/SFTP client on the EAGLE. |
Verify that the <!-- The Message Authentication Code configuration, add or override default mac implementations --> <MacConfiguration> <DefaultAlgorithm>hmac-md5</DefaultAlgorithm> </MacConfiguration> |
|
677 |
Corrupted pad on input was detected by the SSH/SFTP client on the EAGLE. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
678 |
SSH/SFTP tried to close a connection that is already closed. |
|
|
679 |
The SSH/SFTP client on the EAGLE failed to write to the remote side. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing these tests: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
680 |
SSH/SFTP tried to set the packet size twice. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center immediately. |
|
681 |
A bad packet size was detected by the SSH/SFTP client on the EAGLE. |
|
|
SSH/SFTP Connection/Setup Errors |
||
|
682 |
The connection timed out when SSH tried to connect to SSHD. |
Verify that the SFTP/SSHD version is compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1. Verify there is no network outage by performing these tests: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
683 |
The SSH connection was refused by the remote server. |
|
|
684 |
The SSHD server is unreachable. |
|
|
685 |
The network has reset. |
|
|
686 |
The SSH/SFTP connection has been aborted. |
|
|
687 |
The SFTP/SSH connection has been reset by the peer. |
|
|
688 |
Failed to allocate network buffers. |
|
|
689 |
The SSH/SFTP socket is already connected. |
|
|
690 |
The SSH/SFTP socket is not connected. |
|
|
691 |
||
|
692 |
The SSHD/SFTP server connection host is down. |
|
|
694 |
SFTP client channel read failure. |
|
|
695 |
SFTP client channel write failure. |
|
|
696 |
SFTP client channel open failure. |
|
Table 2-9 Generic Network Error Codes
| SFTP/SSH Generic Network Client Error Code | Description | Action/Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
40 |
A destination address is required. |
Verify that there is an FTP server entry on the EAGLE
using the |
|
41 |
Protocol wrong type for socket |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
42 |
The protocol is not available. |
|
|
43 |
The protocol is not supported. |
|
|
44 |
The socket type is not supported. |
|
|
45 |
The operation is not supported on the socket. |
|
|
46 |
The protocol family is not supported. |
|
|
47 |
The address family is not supported. |
|
|
48 |
The address is already in use. |
|
|
49 |
The requested address cannot be assigned. |
|
|
50 |
Socket operation on non-socket |
|
|
51 |
The network is unreachable. |
Verify that the connection tests and network outage numbers match as shown in these sections: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
52 |
The network dropped the connection on reset. |
|
|
53 |
Software caused the connection to abort. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
54 |
The connection was reset by the peer. |
Verify that the connection tests pass and network outage numbers are within the allowed limits as shown in these sections: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
55 |
No buffer space available. |
Report this issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
56 |
The socket is already connected. |
|
|
57 |
The socket is not connected. |
|
|
58 |
Can't send after socket shutdown |
|
|
59 |
Too many references: can't splice |
|
|
60 |
The connection timed out. |
Perform these tests and verify that the FTP server address responds to the ping command from the ISPM. |
|
61 |
The connection was refused. |
Verify that there is a FTP server is running on the remote station by performing the FTP Server Verification test. |
|
62 |
The network is down. |
Verify that the connection tests pass and network outage numbers are within the allowed limits as shown in these sections: Make any fixes necessary and retry the connection. If the problem persists, report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
65 |
There is no route to the host. |
|
|
67 |
The host is down. |
|
|
30 |
Read-only file system |
|
|
32 |
Broken pipe |
Report the issue to Customer Care Center. |
|
35 |
Unsupported value |
Troubleshooting Procedures
FTP Server Verification
Component: The FTP server IP address shown in the FTP Server Configuration Menu window.
Supported Version/Specification: Any FTP server compliant with IETF RFC 959.
Test: On the Linux platform,
execute the netstat -a|grep 21 command to verify
that the FTP server is running on the machine with the
IP address shown in the FTP
Server Configuration Menu window.
On the Windows platform, check the Task Manager to verify that the FTP daemon is running.
SFTP /SSHD Server Verification
Component: The SSHD /SFTP server IP address shown in the FTP Server Configuration Menu window.
Supported Version/Specification: Version compatible with openSSH 3.0.2p1.
Test: On the Linux
platform, execute the ps -ef|grep sshd command. See
Linux MAN pages for help with ps command.
On the Windows platform, use the Task Manager to verify that the SSHD daemon process is running.
On the Windows platform, use the Task Manager to verify that the FTP daemon is running.
Connectivity Test – I
Component: Connectivity Test - I.
Supported Version/Specification: N/A
Test: To verify that there is a network connection available between the EAGLE and the FTP/SFTP server shown in the FTP Server Configuration Menu window.
On an EAGLE terminal, enter the pass:loc=xxxx:cmd="ping
yy.yy.yy.yy" command, where xxxx is
location of the service module associated with the IP address entered in the STP Connection Configuration
Menu window, and yy.yy.yy.yy is the IP address of the FTP/SFTP server
shown in the FTP Server
Configuration Menu window.
Expected Result:
Note:
The RTT time and data sizes may vary.
> pass:loc=xxxx:cmd="ping yy.yy.yy.yy"
Command Accepted - Processing
rlghncxa03w 05-09-31 13:57:59 GMT EAGLE5 34.0.0
pass:loc=xxxx:cmd="ping yy.yy.yy.yy"
Command entered at terminal #5.
;
rlghncxa03w 05-09-31 13:57:59 GMT EAGLE5 34.0.0
PASS: Command sent to card
;
rlghncxa03w 05-09-31 13:57:59 GMT EAGLE5 34.0.0
PING command in progress
;
rlghncxa03w 05-09-31 13:57:59 GMT EAGLE5 34.0.0
;
rlghncxa03w 05-09-31 13:58:01 GMT EAGLE5 34.0.0
PING yy.yy.yy.yy: 56 data bytes
64 bytes from yy.yy.yy.yy: icmp_seq=0. time=10. ms
64 bytes from yy.yy.yy.yy: icmp_seq=1. time=5. ms
64 bytes from yy.yy.yy.yy: icmp_seq=2. time=5. ms
----yy.yy.yy.yy PING Statistics----
3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 5/6/10
PING command complete
Connectivity Test – II
Component: Connectivity Test - II.
Supported Version/Specification: N/A.
Test: To verify that there is a network connection available between the EAGLE and FTP/SFTP server shown in the FTP Server Configuration Menu window.
Execute the ping -s zz.zz.zz.zz command on the
FTP server machine where zz.zz.zz.zz is the IP address of the EAGLE shown in the STP Connection Configuration
Menu window.
Expected Result:
ping -s zz.zz.zz.zz
PING zz.zz.zz.zz: 56 data bytes
64 bytes from e1011501-3-a (zz.zz.zz.zz): icmp_seq=0. time=5. ms
64 bytes from e1011501-3-a (zz.zz.zz.zz): icmp_seq=1. time=4. ms
64 bytes from e1011501-3-a (zz.zz.zz.zz): icmp_seq=2. time=5. ms
64 bytes from e1011501-3-a (zz.zz.zz.zz): icmp_seq=3. time=4. ms
----zz.zz.zz.zz PING Statistics----
4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 4/4/5
Network Outage Trouble Shooting
Component: Network Outage Troubleshooting
Supported Version/Specification: N/A.
Test: To verify the TCP/IP traffic/network statistics are within the supported network statistics.
At the EAGLE, enter the pass:loc=xxxx:cmd="netstat -p
tcp" command at the EAGLE terminal, where xxxx is location of the service module associated with the IP address entered in the STP Connection Configuration
Menu window, and analyze the data from output which is
similar to the following example output.
Note:
The specific information for the command may vary depending upon the system used.
> pass:loc=3102:cmd="netstat -p tcp"
Command Accepted - Processing
rlghncxa03w 05-09-31 19:32:52 GMT EAGLE5 34.0.0
pass:loc=3102:cmd="netstat -p tcp"
Command entered at terminal #5.
;
rlghncxa03w 05-09-31 19:32:52 GMT EAGLE5 34.0.0
PASS: Command sent to card
;
rlghncxa03w 05-09-31 19:32:52 GMT EAGLE5 34.0.0
TCP:
161 packets sent
156 data packets (28411 bytes)
0 data packet (0 byte) retransmitted
5 ack-only packets (1 delayed)
0 URG only packet
0 window probe packet
0 window update packet
0 control packet
161 packets received
156 acks (for 28255 bytes)
0 duplicate ack+C2
0 ack for unsent data
5 packets (9 bytes) received in-sequence
0 completely duplicate packet (0 byte)
0 packet with some dup. data (0 byte duped)
0 out-of-order packet (0 byte)
0 packet (0 byte) of data after window
0 window probe
0 window update packet
0 packet received after close
0 discarded for bad checksum
0 discarded for bad header offset field
0 discarded because packet too short
0 connection request
1 connection accept
1 connection established (including accepts)
0 connection closed (including 0 drop)
0 embryonic connection dropped
156 segments updated rtt (of 157 attempts)
0 retransmit timeout
0 connection dropped by rexmit timeout
0 persist timeout
0 keepalive timeout
0 keepalive probe sent
0 connection dropped by keepalive
0 pcb cache lookup failed
;
rlghncxa03w 05-09-31 19:32:52 GMT EAGLE5 34.0.0
NETSTAT command complete
Expected Result:
The network outage causes the TCP/IP problems such as:
-
Network latency
-
Packet drop
-
Duplicate packets.
If the TCP Packet Delay, TCP Packet Loss, TCP Packet Error, or TCP Out of Order values are greater than the values shown in Table 2-10, fix the network problems and retry the connection.
Table 2-10 TCP Fault Tolerance Table for FTP/SFTP
| Protocol | Fault | Threshold Value |
|---|---|---|
|
SFTP/FTP |
TCP Packet Delay |
175 milliseconds |
|
SFTP/FTP |
TCP Packet Loss |
40% packet loss |
|
SFTP/ FTP |
TCP Packet Errors |
10% |
|
SFTP/FTP |
TCP Out of Order |
30% of packets with offset of 30 packets |