Quick Start
You can make many types of HTTP requests using Industries Framework REST APIs. You can easily make requests to view, create, update, or delete records. As an example, let's look at how to send a simple REST HTTP request to find out the structure of an organization object. You can find both cURL and Postman steps for this task in this topic.
Step 1: Consider Before You Start
Review the basics. If you're new to REST APIs, make sure you understand the basics of REST and JSON, and review our list of important terms.
Review roles and privileges. You must have the necessary security roles and privileges to use the GET, POST, PATCH, and DELETE methods on your parent and child resources.
Review opt-in requirements. Some REST resources or their attributes may be associated with features that require opt-in before you can use them. You must make sure that you enable opt-in features before you start.
Choose a REST client. REST APIs connect software programs over the HTTP protocol. You need a software client to send the HTTP requests. In our examples, we use cURL and Postman. But, these aren't the only tools you can use. To help you choose one, see Work with your REST Client.
Step 2: Get Your Oracle CX for Industries Account Info
-
REST Server URL. Typically, the URL of your Oracle Cloud service. For example,
https://servername.fa.us2.oraclecloud.com. -
User name and password. An Oracle Cloud service user with permissions to access the resources you're using.
You can find the REST Server URL, user name, and password in the welcome email sent to your Oracle Cloud service administrator.
Step 3: Configure Your Client
With the information gathered so far, you're ready to configure your client to send a REST HTTP request.
-
Construct the request URL. The URL consists of the server name and the resource path:
https://<server>/<resource-path>
The <server> is the REST Server URL from Step 2, as in:
https://servername.fa.us2.oraclecloud.com
The <resource-path> is the relative path or endpoint to the resource you're working with. You can pick any endpoint in All REST Endpoints.
/api/party/v4/organizationCombine the REST Server URL and the organization resource path, in this example, to get your complete request URL. For more information, see REST API Versions and URL Paths.
https://servername.fa.us2.oraclecloud.com/api/party/v4/organization/For Admin REST API, the complete REST Server URL, in this example, for routing rules resource would be
https://servername.fa.us2.oraclecloud.com/admin/routingRulesIn a client, such as Postman, you enter this combined URL in the Request URL field.
Note:
If you're using Visual Builder Studio to access REST APIs, see Create a Service Connection from a Service Specification. To access REST APIs using Oracle Integration Cloud, see Configure the REST Adapter to Consume an External REST API with No Metadata Described in a Document. You can also build your own client to access REST resources. To build a client using the Java programming language, see Accessing REST Resources with the JAX-RS Client API.
In cURL, you can specify the URL using -X command as follows:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer <Token> -X GET https://servername.fa.us2.oraclecloud.com/api/party/v4/organizationThis screenshot shows how to specify this information in Postman:
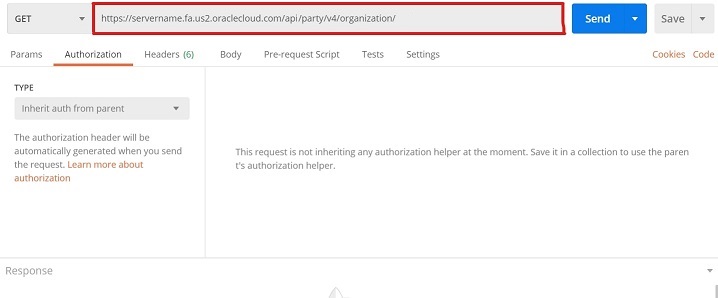
-
Set the media type. Media type defines the structure of the HTTP payloads exchanged between the server and the client. For example, if you're using cURL, you can specify a resource item media type using the header -H command as follows:
-H 'Content-Type: application/vnd.oracle.adf.resourceitem+json'For any request that has a request body (like POST or PATCH), you must include the Content-Type request header. For more on media types, see Supported Media Types.
When you're done, the complete cURL command should look as follows:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer <Token>" -X GET https://servername.fa.us2.oraclecloud.com/api/party/v4/organization/describe / -H 'Content-Type: application/vnd.oracle.adf.resourceitem+json' | json_ppapplication/vnd.oracle.adf.resourceitem+jsonYou can have multiple media types in your header.
If you're not familiar with any of the syntax used in the example, check out Work with your REST Client.
Depending on your business requirements, you might want to set the REST Framework or configure Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) now to fine-tune the REST API behavior. Otherwise, you're ready to move on to Step 4.
Step 4: Authenticate and Authorize
Now that you've configured the client with a complete request URL, it's time to authenticate and authorize yourself. Authentication proves that your credentials are genuine, and authorization allows you to apply your access privileges. In the Industries Framework, Oracle Identity Cloud Services (IDCS) provides the authentication details for the various applications that are installed and configured by the provisioning team.
Authentication
- Get the client configuration information from Oracle Identity Cloud Service (IDCS)
- Use the client configuration information in a REST API client, such as Postman, to generate new access token
Get the Client Configuration Information from IDCS
You can use your existing IDCS registered custom client (confidential application) for accessing IDCS or add and activate a new client (confidential application) in IDCS for working with REST APIs through the Industries Framework.
IDCS supports addition and activation of a confidential application (an application accessed by multiple users and hosted in a secure and protected server. The application uses OAuth 2.0. Applications that can protect their OAuth client id and client secret are called confidential applications).
For detailed information on adding a confidential application, configuring your client, authentication, and authorization, see Add a Confidential Application chapter of the Administering Oracle Cloud Identity Service guide.
Generate New Access Token
Now that your client application is registered with IDCS as a confidential application, you can request an access token to work with the resources.
- Request an authorization code from the authentication server.
- Use the authorization code to obtain the access token.
You can also use a third-party client, such as Postman, to request the access token from Oracle IDCS.
In a third-party REST API client such as Postman, complete the following steps:
- Create a new request.
- In the Authorization tab, select OAuth 2.0 as
Authorization Type and in the Configure New Token section, enter the client
configuration already captured from IDCS.
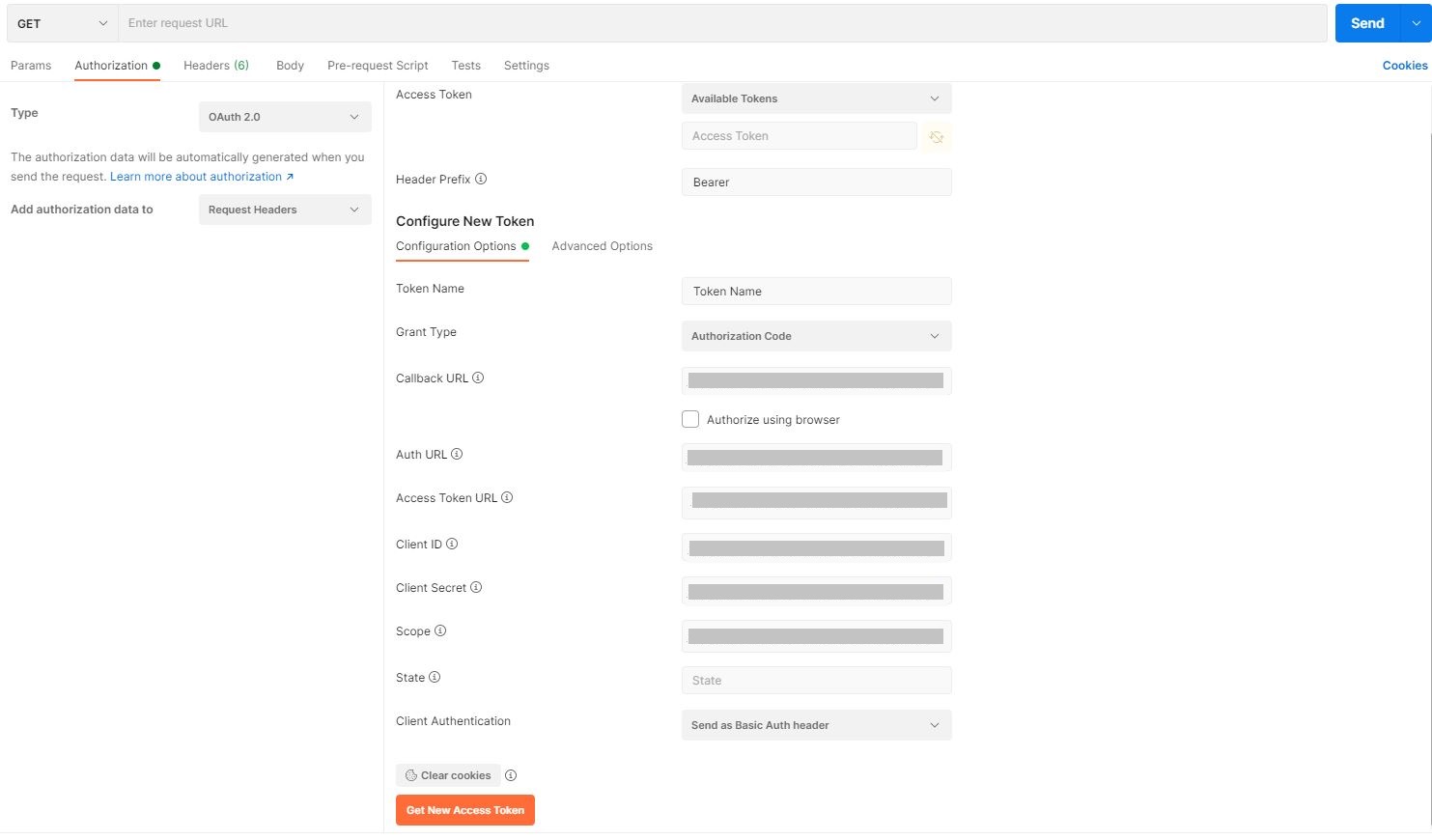
Configure New Token Fields Fields Values Callback URL Enter the Redirect URL value collected from IDCS. Auth URL The IDCS URL appended with /oauth2/v1/authorize is used as the AUTH URL. Access Token URL The IDCS URL appended with /oauth2/v1/token is used as the Access Token URL. Client ID Enter the Client ID value collected from IDCS. Client Secret Enter the Client Secret value collected from IDCS. Scope Enter the Scope value defined in IDCS. State Can be left blank. Token Name Generic name, can be anything. Grant Type Authentication Code. Client Authentication Send as Basic Auth Header. - Click Get New Access Token.
Postman passes on the information to Oracle Identity Cloud Service (IDCS).
- Login to IDCS by providing your user credentials. The login credentials are validated by IDCS and control is passed back to Postman.
-
- After the successful authentication, the GET NEW
ACCESS TOKEN screen is displayed for 5 seconds. You can wait until the time
lapses or click Proceed to navigate to the MANAGE ACCESS TOKENS screen.
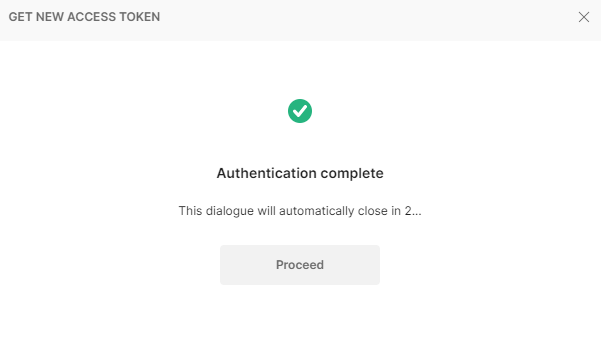
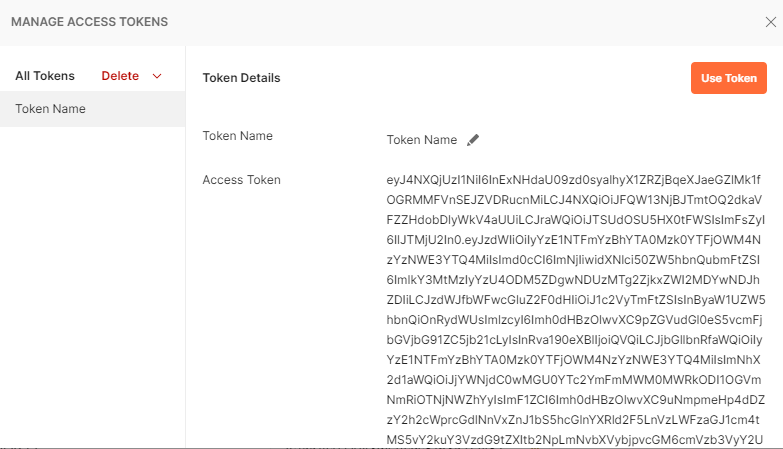
- Once the token is generated, make sure that you click
on Use Token button in the MANAGE ACCESS TOKENS window. The Access Token gets
added to the request.
Note:
The Access Token is valid only until the time period specified in the Application Configuration Setting in IDCS. At the end of the specified time period, the token expires. Click the Get New Access Token button in the Authorization tab of the request to regenerate the Access Token.
Alternatively, you can use the cURL option to pass the token for your Oracle
Cloud account, as in this example:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer Token>" \
-X GET https://servername.fa.us2.oraclecloud.com/api/productCatalogManagement/v4/productOffering
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'Authorization
Authorization enforces access privileges by service role. Access to an object determines access to a resource. So, make sure that your user has the proper role.
Step 5: Send an HTTP Request
You're almost done. Now that your authentication and
authorization are set, you're ready to send a test HTTP request. Continuing with our
example, you want to get all the information about the structure of the Organization
object in REST. You can do this using the describe action in cURL:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer <Token>" \
-X GET https://servername.fa.us2.oraclecloud.com/crmRestApi/api/party/v4/organization/describe \
-H 'Content-Type: application/vnd.oracle.adf.resourceitem+json'This is how the request looks in Postman:
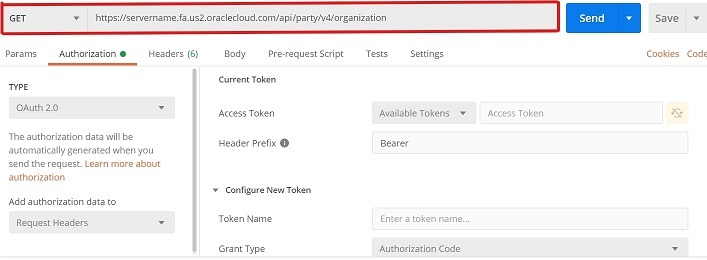
If your request for information about the Organization object is successful, you receive a response with a body similar to the following abbreviated example. If your request fails, and you're using cURL, review the response comments, adjust your request, and then try again. If you're using other clients, review the failure Status Codes, and then try again.
{
"id": "CDRM_888893",
"href": "/cx/industry/party/v4/organization/CDRM_888893",
"tradingName": "Oracle123",
"@type": "organization"
},
{
"id": "CDRM_887781",
"href": "/cx/industry/party/v4/organization/CDRM_887781",
"tradingName": "party organization",
"@type": "organization"
},
{
"id": "CDRM_887650",
"href": "/cx/industry/party/v4/organization/CDRM_887650",
"tradingName": "Oracle123",
"contactMedium": [
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732526",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732527",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732578",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732572",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732680",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732576",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732570",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732575",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732573",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732536",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732537",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732538",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732533",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732535",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732532",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732534",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732838",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732830",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732831",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732845",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732846",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732982",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_732980",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_733109",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
},
{
"mediumType": "postalAddress",
"id": "CDRM_733110",
"preferred": false,
"characteristic": {
"country": "US",
"formattedAddress": "UNITED STATES"
}
}
],
"@type": "organization"
},
...
}
In a client such as Postman, the results are formatted and displayed in the Response section. For example, Postman lets you view the output in multiple formats. This screenshot shows the response in JSON.
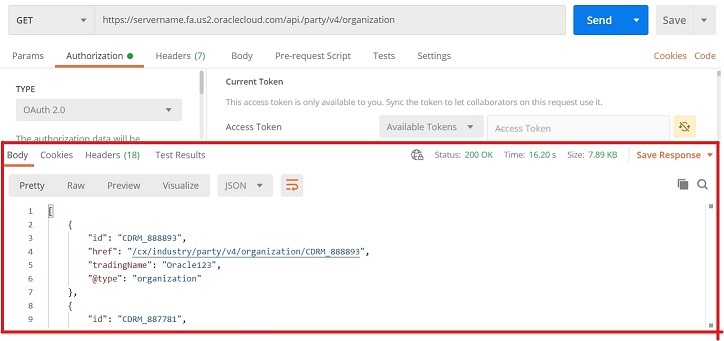
Note:
While working with a resource that exposes both the auto-generated unique ID and a user-defined key, you must use only one of the parameters in the request payload for any of the CRUD actions. For example, the organization resource has a unique identifierId.
Congratulations! Now you're ready to do more with your REST APIs.
- Explore the Learn More section to better manage collections, and create and run batch actions.
- Join the Oracle Developer Community, where you can share tips and advice with others.