2 Installing OCNWDAF
This chapter provides information about installing Oracle Communications Networks Data Analytics Function (OCNWDAF) in a cloud native environment.
OCNWDAF installation is supported over the following platforms:
- Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment (CNE): For more information about CNE, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) using OCI Adaptor: For more information about OCI, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, OCI Adaptor Deployment Guide.
2.1 Prerequisites
Caution:
User, computer and applications, and character encoding settings may cause an issue when copy-pasting commands or any content from PDF. PDF reader version also affects the copy-pasting functionality. It is recommended to verify the pasted content especially when hyphens or any special characters are part of copied content.2.1.1 Software Requirements
This section describes the software requirements for installing OCNWDAF.
Mandatory Software
The following software items must be installed before starting the OCNWDAF installation:
Table 2-1 Preinstalled Software
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes | 1.28.x, 1.27.x, 1.26.x |
| HELM | 3.1.2, 3.5.0, 3.6.3, 3.8.0, 3.9.4, 3.10.3, 3.12.0, 3.12.3 |
| Podman | 2.2.1, 3.2.3, 3.3.1, 4.4.1, 4.2.0, 4.6.1 |
Note:
- OCNWDAF 24.2.0 supports CNE 24.1.x.
- OCNWDAF 24.2.0 supports OKE managed clusters on OCI.
To verify the current Helm and Kubernetes version installed on CNE, use the following commands:
- To check Kubernetes version, run the following
command:
kubectl version - To check the Helm version, run the following
command:
helm3 version - Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
Additional Software
Depending on your requirement, you may have to install additional software while deploying OCNWDAF. The list of additional software items, along with the supported versions and usage, is given in the following table:
Table 2-2 Additional Software
| Software | App Version | Required For |
|---|---|---|
| elasticsearch | 7.9.3 | Logging |
| elastic-client | 0.3.6 | Metric Server |
| elastic-curator | 5.5.4 | Logging |
| elastic-exporter | 1.1.0 | Logging |
| elastic-master | 7.9.3 | Logging |
| logs | 3.1.0 | Logging |
| kibana | 7.9.3 | Logging |
| grafana | 9.1.7 | KPIs |
| prometheus | 2.45.0 | Metrics |
| prometheus-kube-state-metrics | 1.9.7 | Metrics |
| prometheus-node-exporter | 1.0.1 | Metrics |
| metalLb | 0.12.1 | External IP |
| metrics-server | 0.3.6 | Metrics |
| tracer | 1.21.0 | Tracing |
Note:
On OCI, the above mentioned software are not required because OCI observability and management service is used for logging, metrics, alerts, and KPIs. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, OCI Adaptor Deployment Guide.
To verify the installed software items, run the following command:
helm3 ls -AIf you need any services related to the above software items, and if the respective software is unavailable in CNE, then install that software before proceeding.
2.1.2 Environment Setup Requirements
This section provides information about environment setup requirements for installing OCNWDAF.
Client Machine Requirements
This section describes the requirements for client machine, that is, the machine used by the user to run deployment commands.
The client machine must have:
- network access to the Helm repository and docker image repository.
- Helm repository configured on the client.
- network access to the Kubernetes cluster.
- required environment settings to run the
kubectlanddockercommands. The environment must have privileges to create a namespace in the Kubernetes cluster. - Helm client installed so that the
helm installcommand deploys the software in the Kubernetes cluster.
Network Access Requirements
The Kubernetes cluster hosts must have network access to the following repositories:
- Local docker image repository: It contains the OCNWDAF docker images. To check if the Kubernetes cluster hosts can access the local docker image repository, pull any image with an image-tag, using the following command:
docker pull <docker-repo>/<image-name>:<image-tag>where:
docker-repois the IP address or host name of the docker image repository.image-nameis the docker image name.image-tagis the tag assigned to the docker image used for the OCNWDAF pod. - Local helm repository : It contains the OCNWDAF Helm charts. To check if the Kubernetes cluster hosts can access the local Helm repository, run the following command:
helm repo update
Server or Space Requirement
For information about server or space requirements, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Oracle Communications Cloud Native Environment Specification
This section is applicable only if you are installing OCNWDAF on Cloud Native Environment (CNE).
Oracle Communications Network Data Analytics Function (OCNWDAF) 24.2.0 can be installed on Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment (CNE) 24.1.x.
Verify the CNE version with the following command:
echo $OCCNE_VERSIONNote:
From CNE 1.8.x and later, the container platform is Podman instead of docker. For more information about Podman installation, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment (CNE) Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.OCI Requirements
OCNWDAF can be deployed in OCI. While deploying OCNWDAF in OCI, the user must use the Operator instance/VM instead of Bastion Host.
For more information about OCI Adaptor, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, OCI Adaptor Reference Architecture Guide.
cnDBTier Requirements
Note:
If the environment has cnDBTier 23.2.0 installation, follow the instruction below:
- If cnDBTier 23.2.0 release is installed, set the ndb_allow_copying_alter_table parameter to 'ON' in the cnDBTier custom values dbtier_23.2.0_custom_values_23.2.0.yaml file and perform cnDBTier upgrade before install, upgrade, or any fault recovery procedure is performed for OCNWDAF. Set the parameter to its default value ('OFF') once the activity is completed and perform the cnDBTier upgrade to apply the parameter changes.
- To perform cnDBTier upgrade, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, cnDBTier Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD) Requirements
Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD) serves as one of the data sources for the OCNWDAF. If OCNADD is configured as a data source, ensure the following prerequisites are met before OCNWDAF installation:
- OCNADD is setup and running.
- Access Control List (ACL) feed is enabled on OCNADD as the required data source.
- Run OCNWDAF gen_certs script under /scripts/gen_certs.sh.
Note:
Configure the ACL topic certificate from the OCNADD Kafka Cluster in the OCNWDAF Kafka Cluster to enable secure data flow between OCNADD and OCNWDAF.For more information on configuring OCNADD, see Configuring Data Director.
CNC Console Requirements
OCNWDAF supports CNC Console 24.2.0, 24.1.x, 23.3.x, and 23.2.x to configure and manage Network Functions. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Analytics Database
This database is based on MySQL cluster and stores relational and time-series data. The relational data represents all the objects within the telecommunication network, such as UEs, slices, cells, NFs, and so on and their relationships with each other. The time-series data represents all the KPIs, measurements, and event data collected over time and used in streaming analytics and training ML models.
Note:
The deployment of the Mysql Innodb cluster is based on the variable dbConfigStatus present in the values.yaml file under /helmchart. For more information, see Configure Database Flag.2.1.3 Resource Requirements
This section lists the resource requirements to install and run OCNWDAF.
OCNWDAF Services
The following table lists the resource requirement for OCNWDAF services:
Table 2-3 Core Microservices Resource Requirements
| Microservice Name | Instances | POD Replica | CPU/POD | Memory/POD (in GB) | Ephemeral Storage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min (Mi) | Max (GB) | ||
| ocn-nwdaf-analytics-info-service | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| nwdaf-ingress-gateway | 2 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 200 | 200 |
| nwdaf-egress-gateway | 2 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 200 | 200 |
| nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| ocn-nwdaf-data-collection-service | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 200 | 200 |
| ocn-nwdaf-data-collection-controller | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| ocn-nwdaf-subscription-service | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| ocn-nwdaf-mtlf-service | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| cap4c-configuration-manager-service | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| cap4c-model-controller | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| cap4c-model-executor | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| cap4c-stream-analytics | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| nwdaf-portal | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| nwdaf-portal-service | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| cap4c-scheduler-service | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| cap4c-stream-transformer | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| cap4c-api-gateway | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| cap4c-kafka-ingestor | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| ocn-nwdaf-cap4c-reporting-service | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| ocn-nwdaf-geo-redundacy-agent | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 200 | 200 |
| nwdaf-cap4c data-replicator | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 200 | 200 |
| cap4c-capex-optimization-service | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| ocn-nwdaf-analytics-decision-engine-service | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| Total | 25 | 25 | 55 | 12.5 | 45 | 30 | 55 | 4600 | 4600 |
Simulator Microservices Resource Requirements
Table 2-4 Simulator Microservices Resource Requirements
| Microservice Name | POD Replica | CPU/POD | Memory/POD (in GB) | Ephemeral Storage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min (Mi) | Max (GB) | |
| ocn-nrf-simulator-service | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| ocn-amf-simulator-service | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| ocn-smf-simulator-service | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 200 | 200 |
| ocn-oam-simulator-service | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 200 | 200 |
| mesa-simulator | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 200 |
| Total | 5 | 10 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 12 | 1000 | 1000 |
Resource Requirements for Helm Test
This section provides the details on resource requirement to install and run OCNWDAF Helm Test.
Helm Test JobThis job runs on demand when Helm test command is run. It runs the Helm test and stops after completion. These are short lived jobs, which gets terminated after the work is completed. Hence, they are not part of active deployment resource, but considered only during Helm test procedures.
Table 2-5 Helm Test Requirement
| Container Type | CPU Request and Limit Per Container | Memory Request and Limit Per Container |
|---|---|---|
| Helm Test | Request- 1 CPU, Limit- 2 CPU | Request- 1 GB, Limit- 2 GB |
Below is an example of the configurations that should be included under the global section of the oc-nwdaf-custom-values.yaml file.
global:
testJobResources:
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
ephemeral-storage: 2Gi
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 1Gi
ephemeral-storage: 200Mi2.2 Installation Sequence
This section describes preinstallation, installation, and postinstallation tasks for OCNWDAF.
You are recommended to follow the steps in the given sequence for preparing and installing OCNWDAF.
2.2.1 Preinstallation Tasks
Before installing OCNWDAF, perform the tasks described in this section.
Note:
The kubectl commands might vary based on the platform used for deploying CNC Policy. Users are recommended to replacekubectl with environment-specific command line tool to configure kubernetes resources through kube-api server. The instructions provided in this document are as per the CNE’s version of kube-api server.
2.2.1.1 Downloading the OCNWDAF package
This section provides information about how to download OCNWDAF package.
- Log in to My Oracle Support using the appropriate credentials.
- Click Patches & Updates to locate the patch.
- In the Patch Search console, select the Product or Family (Advanced) option.
- Enter Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Network Data Analytics Function in the Product field. Select the product from the Product drop-down
- From the Release drop-down, select "Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Network Data Analytics Function <release_number>" Where, <release_number> indicates the required release number of OCNWDAF.
- Click Search.
The Patch Advanced Search Results displays a list of releases.
- Select the required patch from the list. The Patch Details window appears.
- Click Download. The File Download window appears.
- Click the <p********_<release_number>_Tekelec>.zip file.
- Extract the release package zip file.
Package is named as follows:
nwdaf-pkg-<marketing-release-number>.zip
For example: nwdaf-pkg-24.2.0.0.zip
To download the package from the edelivery portal, perform the following steps:
- Login to the edelivery portal with your credentials. The following screen appears:
Figure 2-1 edelivery portal
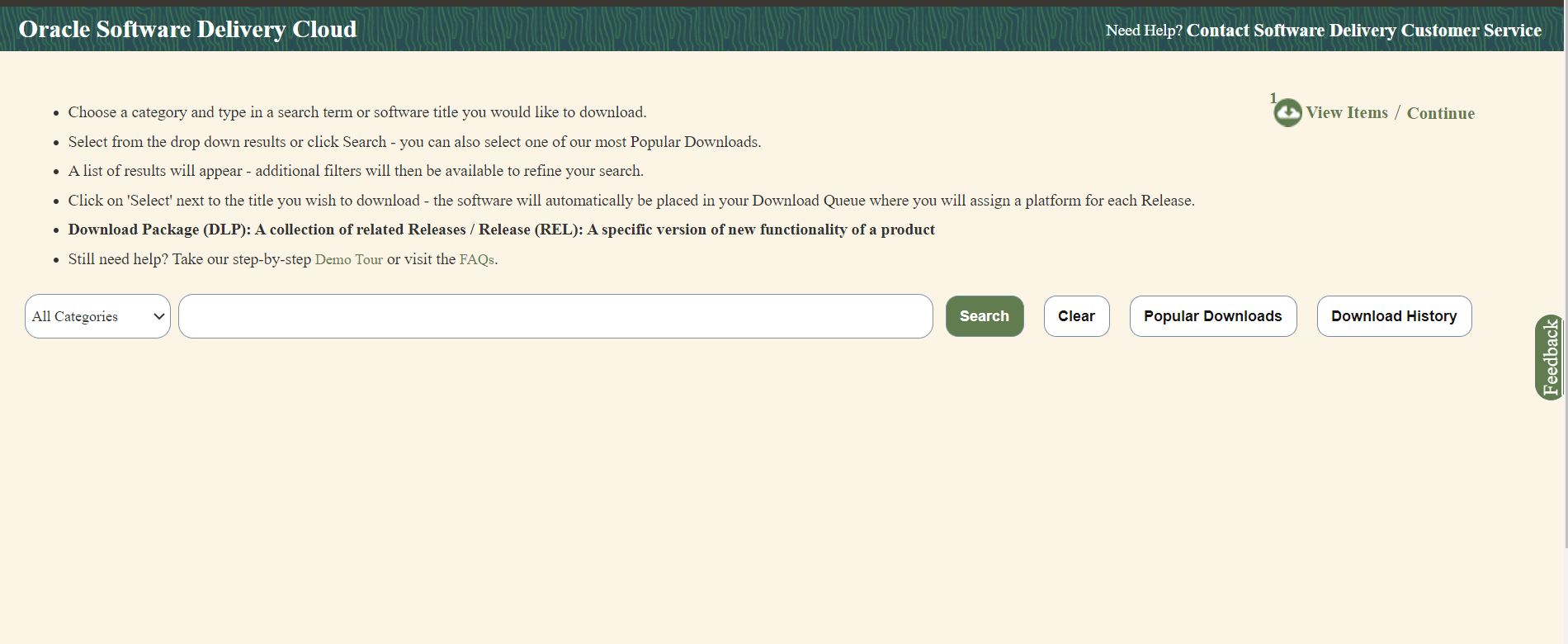
- Select the Download Package option, from All Categories drop down list.
- Enter Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Network Data Analytics Data Function in the search bar.
- List of release packages available for download are displayed on the screen. Select the release package you want to download, the package automatically gets downloaded.
Untar the Package ZIP File
Run the following command to untar or unzip the OCNWDAF package zip file to the specific repository:
tar -xvf nwdaf-pkg-<marketing-release-number>.tgzor
unzip nwdaf-pkg-<marketing-release-number>.zip# Root
- images
- tar of images
- sha 256 of images
- troubleshooting/
- nfDataCapture.sh
- installer/
- ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/
- helmChart/
- templates/
- charts/
- values.yaml
- charts.yaml
- nwdaf-pre-installer.tar.gz
- simulator-helmChart/
- templates/
- charts/
- values.yaml
- charts.yaml
- custom-templates/
- ocnwdaf_custom_values.yaml
- ocnwdaf_simulators_custom_values.yaml
- scripts/
- gen_certs.sh
- readme.txt
- nwdaf-ats/
- ocn-ats-nwdaf-tool
- ngnix
- templates
- ocnwdaf_tests
- data
- features
- scripts/
- gen_certs.sh
- readme.txtNote:
The readme.txt file under the scripts folder is for the gen_certs.sh script.2.2.1.2 Pushing the Images to Customer Docker Registry
The OCNWDAF deployment package includes ready-to-use docker images (inside the images tar file) and Helm charts to help orchestrate containers in Kubernetes. The communication between service pods of OCNWDAF are preconfigured in the Helm charts.
Table 2-6 Docker Images for OCNWDAF
| Service Name | Docker Image Name | Image Tag |
|---|---|---|
| NWDAF Analytics Info Service | ocn-nwdaf-analytics | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| NWDAF MTLF Service | ocn-nwdaf-mtlf-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| NWDAF Subscription Service | ocn-nwdaf-subscription-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| AMF NF Simulator Service | ocn-amf-simulator-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| SMF NF Simulator Service | ocn-smf-simulator-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| NRF NF Simulator Service | ocn-nrf-simulator-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| OAM Simulator Service | ocn-oam-simulator-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| Mesa Simulator Service (Data Generator) | mesa-simulator | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c ML model controller | cap4c-model-controller | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c ML model executor | cap4c-model-executor | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c stream analytics | cap4c-stream-analytics | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| kafka to mysql serializer | cap4c-kafka-ingestor | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| Reporting service | nwdaf-cap4c-reporting-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| kafka | nwdaf-cap4c-kafka | 3.4.0 |
| nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler | nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server | nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| nwdaf-portal | nwdaf-portal | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| nwdaf-portal-service | nwdaf-portal-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| redis | nwdaf-cap4c-redis | 7.2.4 |
| ocats-nwdaf | ocats-nwdaf | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| ocats-nwdaf-notify | ocats-nwdaf-notify | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| Helm Test | nf-test | 22.4.0 |
| geo redundancy agent | ocn-nwdaf-geo-redundacy-agent | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| nwdaf-egress-gateway | ocingress_gateway | 23.4.3 |
| nwdaf-ingress-gateway | ocegress_gateway | 23.4.3 |
| configurationinit (ingress and egress) | configurationinit | 23.4.3 |
| nrf client configuration server | oc-config-server | 23.4.0 |
| nrf client app info | oc-app-info | 23.4.0 |
| nrf client perf info | oc-perf-info | 23.4.0 |
| nrf client | nrf-client | 23.4.2 |
| NWDAF Data Collection Controller | ocn-nwdaf-data-collection-controller | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| NWDAF Data Collection Service | ocn-nwdaf-data-collection-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c-configuration-manager-service | cap4c-configuration-manager-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c-stream-transformer | cap4c-stream-transformer | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| nwdaf-cap4c-backuprestore | ocnwdaf-pre-install-hook-image | 1.1.5 , Job 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c-api-gateway | cap4c-api-gateway | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| Kafka init container image | nwdaf-cap4c-java | 17.0 |
| Pre-install hook Image | ocnwdaf-pre-install-hook-image | 1.1.5 |
| GRD init container image | nwdaf-cap4c-mysql | 8.0.30 |
| enterprise operator | enterprise-operator | 8.1.0 |
| enterprise router | enterprise-router | 8.1.0 |
| enterprise server | enterprise-server | 8.1.0 |
| capex-optimization service | capex-optimization service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| Executor init container image | nwdaf-cap4c-rsync | 3.1 |
To push the images to customer docker registry, perform the following steps:
- Verify the package content, checksums of tarballs in the
Readme.txtfile. - If the images of the above services are already present in the artifact, then proceed with the Preinstallation Tasks.
- (Optional) If the images of the above services are not present in the artifact, then the user has to run the following commands to manually load, tag, and push the images:
docker load --input <image_file_name.tar>Example:docker load --input images - To push the docker images to the docker repository, run the following command:
docker tag <image-name>:<image-tag> <docker-repo>/<image-name>:<image-tag>docker push <docker_repo>/<image_name>:<image-tag>Note:
It is recommended to configure the docker certificate before running the push command to access customer registry through HTTPs, otherwise, docker push command may fail. - Verify if the image is loaded correctly by running the following command:
docker images - (Optional) To push the Helm charts to the Helm repository, run the following command:
helm cm-push --force <chart name>.tgz <Helm repo>
Untar the Preinstaller
(Optional) To extract the nwdaf-pre-installer.tar.gz file outside the /helmchart directory, run the following command:
tar xzC <path to extract> -f nwdaf-pre-installer.tar.gzVerify the file structure of the extracted file:
- etc/
- nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-prod-properties/
- kafka-topics.txt
- scripts/
- util/
- kubernetes-util.sh
- helm-util.sh
- generic-util.sh
- prepare-dependencies.sh2.2.1.3 Pushing the Images to OCI Docker Registry
The OCNWDAF deployment package includes ready-to-use docker images (inside the images tar file) and Helm charts to help orchestrate containers in Kubernetes. The communication between service pods of OCNWDAF is preconfigured in the Helm charts.
Table 2-7 Docker Images for OCNWDAF
| Service Name | Docker Image Name | Image Tag |
|---|---|---|
| NWDAF Analytics Info Service | ocn-nwdaf-analytics | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| NWDAF MTLF Service | ocn-nwdaf-mtlf-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| NWDAF Subscription Service | ocn-nwdaf-subscription-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| AMF NF Simulator Service | ocn-amf-simulator-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| SMF NF Simulator Service | ocn-smf-simulator-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| NRF NF Simulator Service | ocn-nrf-simulator-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| OAM Simulator Service | ocn-oam-simulator-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| Mesa Simulator Service (Data Generator) | mesa-simulator | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c ML model controller | cap4c-model-controller | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c ML model executor | cap4c-model-executor | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c stream analytics | cap4c-stream-analytics | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| kafka to mysql serializer | cap4c-kafka-ingestor | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| Reporting service | nwdaf-cap4c-reporting-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| kafka | nwdaf-cap4c-kafka | 3.4.0 |
| nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler | nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server | nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| nwdaf-portal | nwdaf-portal | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| nwdaf-portal-service | nwdaf-portal-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| redis | nwdaf-cap4c-redis | 7.2.4 |
| ocats-nwdaf | ocats-nwdaf | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| ocats-nwdaf-notify | ocats-nwdaf-notify | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| Helm Test | nf-test | 22.4.0 |
| geo redundancy agent | ocn-nwdaf-geo-redundacy-agent | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| nwdaf-egress-gateway | ocingress_gateway | 23.4.3 |
| nwdaf-ingress-gateway | ocegress_gateway | 23.4.3 |
| configurationinit (ingress and egress) | configurationinit | 23.4.3 |
| nrf client configuration server | oc-config-server | 23.4.0 |
| nrf client app info | oc-app-info | 23.4.0 |
| nrf client perf info | oc-perf-info | 23.4.0 |
| nrf client | nrf-client | 23.4.2 |
| NWDAF Data Collection Controller | ocn-nwdaf-data-collection-controller | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| NWDAF Data Collection Service | ocn-nwdaf-data-collection-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c-configuration-manager-service | cap4c-configuration-manager-service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c-stream-transformer | cap4c-stream-transformer | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| nwdaf-cap4c-backuprestore | ocnwdaf-pre-install-hook-image | 1.1.5 , Job 24.2.0.0.0 |
| cap4c-api-gateway | cap4c-api-gateway | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| Kafka init container image | nwdaf-cap4c-java | 17.0 |
| Pre-install hook Image | ocnwdaf-pre-install-hook-image | 1.1.5 |
| GRD init container image | nwdaf-cap4c-mysql | 8.0.30 |
| enterprise operator | enterprise-operator | 8.1.0 |
| enterprise router | enterprise-router | 8.1.0 |
| enterprise server | enterprise-server | 8.1.0 |
| capex-optimization service | capex-optimization service | 24.2.0.0.0 |
| Executor init container image | nwdaf-cap4c-rsync | 3.1 |
To push the images to OCI docker registry, perform the following steps:
-
Run the following command to untar or unzip the OCNWDAF package zip file to the specific repository:
tar -xvf nwdaf-pkg-<marketing-release-number>.tgzor
unzip nwdaf-pkg-<marketing-release-number>.zipAfter the package and its content is extracted, the following directory structure is displayed:# Root - images - tar of images - sha 256 of images - troubleshooting/ - nfDataCapture.sh - installer/ - ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/ - helmChart/ - templates/ - charts/ - values.yaml - charts.yaml - nwdaf-pre-installer.tar.gz - simulator-helmChart/ - templates/ - charts/ - values.yaml - charts.yaml - custom-templates/ - ocnwdaf_custom_values.yaml - ocnwdaf_simulators_custom_values.yaml - scripts/ - gen_certs.sh - readme.txt - nwdaf-ats/ - ocn-ats-nwdaf-tool - ngnix - templates - ocnwdaf_tests - data - features - scripts/ - gen_certs.sh - readme.txtNote:
The readme.txt file under the scripts folder is for the gen_certs.sh script. - Verify the package content, checksums of tarballs in the Readme.txt file.
- Run the following commands to manually load, tag, and push the images:
docker load --input <image_file_name.tar>Example:docker load --input images - Run one of the following commands to verify that the images are loaded:
podman imagesdocker images - Verify the list of images shown in the output with the list of images shown in the Table 2-7 . If the list does not match, reload the image tar file.
- Run the following commands to log in to the OCI registry:
podman login -u <REGISTRY_USERNAME> -p <REGISTRY_PASSWORD> <REGISTRY_NAME>docker login -u <REGISTRY_USERNAME> -p <REGISTRY_PASSWORD> <REGISTRY_NAME>Where,
<REGISTRY_NAME>is <Region_Key>.ocir.io.<REGISTRY_USERNAME>is <Object Storage Namespace>/<identity_domain>/email_id.<REGISTRY_PASSWORD>is the Auth Token generated by the user.For more information about OCIR configuration and creating auth token, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, OCI Adaptor Deployment Guide.
<Object Storage Namespace>can be obtained from the OCI Console by navigating to Governance & Administration, Account Management, Tenancy Details, Object Storage Namespace.<Identity Domain>is the domain of the user.- In OCI, each region is associated with a key. For more information, see Regions and Availability Domains.
- Run one of the following commands to tag the images to the registry:
podman tag <image-name>:<image-tag> <podman-repo>/ <image-name>:<image-tag>docker tag <image-name>:<image-tag> <docker-repo>/ <image-name>:<image-tag>Where,<image-name>is the image name.<image-tag>is the image release number.<docker-repo>is the docker registry address with Port Number if registry has port attached. This is a repository to store the images.<podman-repo>is the podman registry address with Port Number if registry has port attached. This is a repository to store the images.
- Run one of the following commands to push the image:
podman push <oci-repo>/<image-name>:<image-tag>docker push <oci-repo>/<image-name>:<image-tag>Where,
<oci-repo>is the OCI registry path. - Make all the image repositories public by performing the following steps:
Note:
All the image repositories must be public.- Log in to the OCI Console using your login credentials.
- From the left navigation pane, click Developer Services.
- On the preview pane, click Container Registry.
- From the Compartment drop-down list, select networkfunctions5G (root).
- From the Repositories and images drop-down list, select the required image and click Change to Public.
The details of the images are displayed under the Repository information tab and the image changes to public. For example, the
24.2.0db/occne/cndbtier-mysqlndb-client (Private)changes to24.2.0db/occne/cndbtier-mysqlndb-client (Public). - Repeat substep 9e to make all image repositories public.
- The storage class is set to "oci-bv".
- The Load Balancer annotations are set as listed below:
oci-network-load-balancer.oraclecloud.com/internal: "true"oci-network-load-balancer.oraclecloud.com/security-list-management-mode: Alloci-network-load-balancer.oraclecloud.com/subnet: <your-lb-subnet-ocid>oci.oraclecloud.com/load-balancer-type: nlb
2.2.1.4 Configuring OCNWDAF Database
The OCNWDAF microservices store the front-end and analytics data in two MySQL databases, the cluster INNODB and Cndb. InnoDB is a self-managed cluster within the OCNWDAF namespace. InnoDB does not require any specific user configuration. The Helm pre-install hook manages the database. However, OCNWDAF requires the database administrator to create an admin user for the MySQL database and provide the necessary permissions to access the databases. Before installing OCNWDAF, create a MySQL user to manage the cluster.
Note:
- If the admin user is already created, update the credentials, such as username and password (base64 encoded) in the ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/custom-templates/ocnwdaf_custom_values.yaml file (or the copy of values.yaml used for installation or upgrade).
- If the admin user is not created, create an admin user following the procedure Creating an Admin User in the Database. Update the user's credentials in the ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/custom-templates/ocnwdaf_custom_values.yaml file (or the copy of values.yaml used for installation or upgrade).
- The admin user should be a non-root user.
- Creating this user and updating it under the secrets section is mandatory.
2.2.1.5 Creating an Admin User in the Database
Follow the steps below to create an admin user in the database:
- Run the following command to access the MySQL pod:
Note:
Use the namespace in which the Cndb is deployed. For example, if occne-cndbtier namespace is used. The default container name is ndbmysqld-0.kubectl -n occne-cndbtier exec -it ndbmysqld-0 -- bash - Run the following command to log in to MySQL server using MySQL client:
$ mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -uroot -p $ Enter password: - Run the following command to create an admin user:
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS'<nwdaf admin username>'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '<nwdaf admin user password>';For example:
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'nwdaf'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'nwdaf';Where,
nwdafis the<nwdaf admin username>andnwdafis the<nwdaf admin user password>. - Run the following command to grant the necessary permissions to the admin user and run the
FLUSHcommand to reload the grant table:GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'nwdaf'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION;FLUSH PRIVILEGES; - Run the following command to generate the base64 encoded username and password:
echo -n <string> | base64 -w 0Where,
<string>is the admin username or password created in Step 3.For example:
echo -n nwdaf| base64 -w 0 bndkYWY=
2.2.1.6 Creating Secret for the Private Image Repository
If the user image repository is private and has to be authenticated, follow the steps below:
- Run the following command to create a secret named reposecret with the credentials of the image repository:
kubectl create secret docker-registry reposecret --docker-server=reposerver --docker-username=repousername --docker-password='repopassword' --docker-email=repousermail - Update the
imagePullSecret.enableparameter totruein the ocnwdaf, simulators, and ATS values.yaml file.For example:
imagePullSecret: enable: false ## --> update this to 'true' name: reposecret
2.2.1.7 Verifying and Creating OCNWDAF Namespace
This section explains how to verify or create a new namespace in the system.
To verify if the required namespace already exists in the system, run the following command:
$ kubectl get namespacesIn the output of the above command, check if the required namespace is available. If the namespace is not available, create the namespace using the following command:
$ kubectl create namespace <required namespace>Example:
$ kubectl create namespace oc-nwdafNaming Convention for Namespaces
While choosing the name of the namespace where you wish to deploy OCNWDAF, make sure the namespace:
- starts and ends with an alphanumeric character
- contains 63 characters or less
- contains only alphanumeric characters or '-'
Note:
It is recommended to avoid using prefixkube- when creating namespace as this prefix
is reserved for Kubernetes system namespaces.
To export the installation namespace name as environment variable, run the following command:
export K8_NAMESPACE="<namespace>"2.2.2 Installation Tasks
This section explains how to install OCNWDAF.
Note:
Before installing OCNWDAF, you must complete Prerequisites and Preinstallation Tasks.
2.2.2.1 Update OCNWDAF Preinstaller Files
Note:
This is an optional procedure.To update the preinstaller file, perform the following steps:
- Make the required changes in config files present in the extracted nwdaf-pre-installer directory and create a fresh tar file by running the following command:
tar -zcvf nwdaf-pre-installer.tar.gz nwdaf-pre-installer/ -
Replace the existing tar file in the /helmChart directory with the new tar file.
2.2.2.2 Setup Encrypted Credentials
To set up encrypted credentials, perform the following steps:
- To update the secret values (username and password), replace the existing values with updated values after encoding the values using Base64 encoding method. Listed below are the secrets files:
- ocnwdaf-hooks-secret.yaml under /helmchart/templates/ directory
- simulators-hooks-secret.yaml under /simulator-helmChart/templates/ directory
- To read the secret values, decode the present values using Base64 decoding method.
2.2.2.3 Configure Database Flag
Note:
This is an optional step. Perform this step based on customer requirement.Update the dbConfigStatus flag in values.yaml file under /helmchart with any of the following values (the default value is alldb):
- alldb: This is the default value of the flag. Set this flag to create a fresh database by removing the existing database. If this flag is present, proceed with the installation of the services.
- nodb: This flag disables the dbCreation hooks for the installation of the Helm chart. Set this flag to install the services if the database is present without deleting any data.
- nwdafdb: This flag is used to create or reinstall the database only for OCNWDAF services. Set this flag to run the dbCreation hook only for OCNWDAF services (standard installation is followed for the remaining services).
- cap4cdb: This flag is used to create or reinstall the database only for CAP4C services. Set this flag to run the dbCreation hook only for CAP4C services (standard installation is followed for the remaining services).
Note:
If there is a requirement to install only OCNWDAF or only CAP4C services, set the dbConfigStatus flag to create the required DB and the charts that are not needed can be set to 'enabled: false' in the "values. yaml" under "/helm chart".
For example, if a user wants to install CAP4C services only with its database, then set the dbConfigStatus flag to 'cap4cdb', and set the value of all the OCNWDAF FE services that are not required to 'enabled: false' and proceed with the installation procedure.
2.2.2.4 Configure NRF Client Parameter
Note:
This is a mandatory procedure.Note:
By default, the NRF Client primaryNrfApiRoot is configured as ocn-nrf-simulator-service:8080.
When a single OCNRF is used, navigate to the /installer/helmChart/charts/nrf-client folder and update the values.yaml as follows:
# Microservice level control if specific microservice need to be disabled
nrf-client:
profile: |-
[appcfg]
primaryNrfApiRoot=ocn-nrf-simulator-service:8080
secondaryNrfApiRoot=2.2.2.5 Configuring Service Mesh
Note:
This configuration step is optional and only applies when a service mesh is available.- Service discovery
- Routing and traffic configuration
- Encryption and authentication/authorization
- Metrics and monitoring
Note:
To configure OCNWDAF to support a service mesh, the service mesh must be available in the cluster in which OCNWDAF is installed.Enable or Disable Service Mesh
To enable or disable service mesh support, update the Istio sidecar section in the values.yaml file.
For example:
##########################
#ISTIO SIDECAR INJECTION #
##########################
istio:
## NOTE: The label of the namespace will take precedence over the injection field that is set here. If mesh is to be disabled, make sure the namespace has no istio-injection label or set to disabled if present
injection: false
readinessCheck: &readinessCheck falseFor more information, see Global Parameters.
Update the following NRF client parameters:
istioSidecarQuitUrlistioSidecarReadyUrlserviceMeshCheck
For more information, see NRF Client Parameters.
Update the following Ingress Gateway Parameters in the values.yaml file:
serviceMeshCheck
Table 2-8 Ingress Gateway Parameter
| Parameter | Description | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| serviceMeshCheck | This is a mandatory parameter. This flag must be set to true if a Service Mesh is present in the environment where OCNWDAF is deployed. If this parameter is set to true load balancing is handled by the Service Mesh.
|
Range: True or False
Default value: False Applicable to: OCNWDAF |
Update the following Egress Gateway parameters in the values.yaml file:
serviceMeshCheck
Table 2-9 Egress Gateway Parameter
| Parameter | Description | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| serviceMeshCheck | This is a mandatory parameter. This flag must be set to true if a Service Mesh is present in the environment where OCNWDAF is deployed. If this parameter is set to true load balancing is handled by the Service Mesh.
|
Range: True or False
Default value: False Applicable to: OCNWDAF |
After Service Mesh is enabled and deployed, the proxy containers run along with the OCNWDAF application pods.
Note:
The gateways and other services inside the Service Mesh are not accessible from outside the Service Mesh. In order to use OCNWDAF with a Service Mesh, ensure that the dependencies (such as, cnDBTier or analytics consumers) are deployed within the Service Mesh.
2.2.2.6 Configuring Routing Rules in Ingress Gateway
The routing rules are configured in the Ingress Gateway values.yaml file. Once the routing rules are configured, the Ingress Gateway reroutes the incoming traffic to the microservices based on the configured routing rules.
Ingress Gateway values.yaml file:
- id: prodcon
uri: http://10.123.158.150:31457
path: /relinquishOwnerShip
order: 1
#Below field is used to provide an option to enable/disable route level xfccHeaderValidation, it will override global configuration for xfccHeaderValidation.enabled
metadata:
# requestTimeout is used to set timeout at route level. Value should be in milliseconds.
requestTimeout: 4000
requiredTime: 3000
xfccHeaderValidation:
validationEnabled: false
oauthValidator:
enabled: false
svcName: "prodcon-1"
configurableErrorCodes:
enabled: false
errorScenarios:
- exceptionType: "NOT_FOUND_EXCEPTION"
errorProfileName: "ERR_NOT_FOUND"
- exceptionType: "UNKNOWN_HOST_EXCEPTION"
errorProfileName: "ERR_UNKNOWN_HOST"
- exceptionType: "CONNECT_EXCEPTION"
errorProfileName: "ERR_400"
- exceptionType: "XFCC_HEADER_NOT_PRESENT_OR_EMPTY"
errorProfileName: "ERR_1300"
- exceptionType: "GLOBAL_RATELIMIT"
errorProfileName: "ERR_RATE_LIMIT"
# Server header configuration if defined at Route level(irrespective of being enabled/disabled) will take precedence over the Global conf. Uncomment only if needed at Route level.
#serverHeaderDetails:
# enabled: false
# errorCodeSeriesId: E2 # If not defined here, value at Global level will be used as fallback. Value need to be one among "errorCodeSeriesList" resource defined later.
filters:
controlledShutdownFilter:
applicableShutdownStates:
- "PARTIAL_SHUTDOWN"
- "COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN"
unsupportedOperations:
- "GET"
- "PUT"
#Below are Request Custom Headers
customReqHeaderEntryFilter:
headers:
- methods:
- ALL
headersList:
- headerName: x-entry-headeReq-1
defaultVal: script:shm-02,x-exit-new-req
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-entry-current-user
- headerName: x-entry-current-user
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: test
customReqHeaderExitFilter:
headers:
- methods:
- ALL
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headeReq-1
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-current-user
- headerName: x-exit-current-user
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: sbi-timer-feature
- methods:
- GET
- POST
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headeReq-3
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-new-req
override: false
- headerName: x-exit-headeReq-4
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-headeReq-1
override: false
- methods:
- DELETE
- GET
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headerReq-5
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-headerReq-new
override: false
- headerName: x-exit-headerReq-6
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-headerReq-temp
override: false
# Below are Response Custom Headers
customResHeaderEntryFilter:
headers:
- methods:
- ALL
headersList:
- headerName: x-entry-headerRes-1
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-entry-headeReq-1
override: false
- headerName: sbi-timer-feature-Res
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-new-req
customResHeaderExitFilter:
headers:
- methods:
- ALL
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headerRes-1
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-headerReq-1
override: false
- headerName: sbi-timer-feature
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingRes
sourceHeader: x-exit-headerRes-1
- methods:
- GET
- PUT
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headeRes-3
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingRes
sourceHeader: x-exit-SourceRes-a
override: true
- headerName: x-exit-headeRes-4
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-SourceRes-b
override: false
- methods:
- DELETE
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headeRes-5
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingRes
sourceHeader: ""
override: false
- headerName: x-exit-headeRes-6
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingRes
sourceHeader: ""
override: false
#Below field is used for blacklisting(removing) a request header at route level.
removeRequestHeader:
- name: myheader1
- name: myheader3
#Below field is used for blacklisting(removing) a response header at route level.
removeResponseHeader:
- name: myresponseheader1
- name: myresponseheader3id: prodconuri: http://10.123.158.150:31457path: /relinquishOwnerShip
For more information on the customizable Ingress Gateway parameters, see Ingress Gateway Parameters.
Note:
It is recommended to retain the default values of other routesConfig parameters.2.2.2.7 Enable TLS 1.3 Support
Gateway Services are integrated with OCNWDAF to support TLS 1.3 on the Ingress and Egress interfaces.
This feature enables the support for TLS 1.3 for all functions and interfaces where TLS 1.2 was supported. TLS 1.2 will continue to be supported.
This feature is enabled by default at the time of Gateway Services deployment.
You can configure this feature using Helm parameters. Configure the following parameters in the Ingress Gateway and Egress Gateway, required for TLS1.3:
clientDisabledExtension: ec_point_formats #comma-separated-values To disable extension being sent in ClientHello
serverDisabledExtension: null #comma-separated-values To disable extension being sent from server originated messages
tlsNamedGroups: null #comma-separated-values to whitelist the supported_groups extension values
clientSignatureSchemes: null #comma-separated-values to whitelist the signature_algorithms extension values
service:
ssl:
tlsVersion: TLSv1.2,TLSv1.3
allowedCipherSuites:
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
cipherSuites:
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256For detailed description of TLS 1.3 parameters, see TLS 1.3 Parameters.
Helm Configuration for Ingress Gateway HTTPS
For the Ingress Gateway set the parameters initssl and enableIncomingHttps in the values.yaml file to true.
global:
type: NodePort
staticHttpNodePort: 30788
staticHttp1NodePort: 31788
enableIncomingHttp1: true
cncc:
enablehttp1: true
minReplicas: 1
requestTimeout: 10000
fullnameOverride: ingress-gateway-service
initssl: true
enableIncomingHttp: true
enableIncomingHttps: trueWhere,
-
initssl: Generates KeyStore and TrustStore for HTTPS support. You must create TLS secret if this parameter is set to true. enableIncomingHttps: Opens https port on Egress Gateway. You must enable this parameter ifinitsslis set to true.
Helm Configuration for Egress Gateway HTTPS
For the Egress Gateway set the parameters initssl and enableOutgoingHttps in the values.yaml file to true.
fullnameOverride: egress-gateway-service
initssl: true
enableOutgoingHttps: true
http1:
enableOutgoingHTTP1: true
minReplicas: 1
requestTimeout: 30000
nettyIdleTimeout: 30000
connectionTimeout: 30000Where,
-
initssl: Generates KeyStore and TrustStore for HTTPS support. You must create TLS secret if this parameter is set to true. enableOutgoingHttps: Enables outgoing https connections at Egress Gateway. You must enable this parameter ifinitsslis set to true.enableOutgoingHTTP1: Enables http1 outgoing connections.
TLS files and Configuration for Ingress and Egress Gateways
Provide the TLS files and configuration for the Ingress and Egress gateways, update the values.yaml file:
service:
ssl:
# TLS verison used
tlsVersion: TLSv1.2
# Secret Details for certificates
privateKey:
k8SecretName: <secret name>-gateway-secret
k8NameSpace: ocnwdaf-ns
rsa:
fileName: rsa_private_key_pkcs1.pem
ecdsa:
fileName: ecdsa_private_key_pkcs8.pem
certificate:
k8SecretName: <secret name>-gateway-secret
k8NameSpace: ocnwdaf-ns
rsa:
fileName: apigatewayrsa.cer
ecdsa:
fileName: apigatewayecdsa.cer
caBundle:
k8SecretName: <secret name>-gateway-secret
k8NameSpace: ocnwdaf-ns
fileName: caroot.cer
keyStorePassword:
k8SecretName: <secret name>-gateway-secret
k8NameSpace: ocnwdaf-ns
fileName: key.txt
trustStorePassword:
k8SecretName: <secret name>-gateway-secret
k8NameSpace: ocnwdaf-ns
fileName: trust.txt
initialAlgorithm: RS256Use the same <secret name> used during Kubernetes secret creation.
Create Keys and Certificates
- Generate a root CA (Certificate Authority) and a CA Private Key. Run the following commands:
To create root certificate authority (CA) key:
openssl req -new -keyout cakey.pem -out careq.pem -config ssl.conf -passin pass:"keystorepasswd" -passout pass:"keystorepasswd"To create root certificate authority (CA) run the following commands:
openssl x509 -signkey cakey.pem -req -days 3650 -in careq.pem -out caroot.cer -extensions v3_ca -passin pass:"keystorepasswd" echo 1234 > serial.txt - Generate private keys.
Run the following commands to generate the RSA private key:
openssl req -x509 -nodes -sha256 -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout rsa_private_key -out rsa_certificate.crt -config ssl.conf -passin pass:"keystorepasswd" -passout pass:"keystorepasswd" openssl rsa -in rsa_private_key -outform PEM -out rsa_private_key_pkcs1.pem -passin pass:"keystorepasswd" -passout pass:"keystorepasswd"Run the following commands to generate the ECDSA private key:openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -noout -out ecdsa_private_key.pem openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -in ecdsa_private_key.pem -inform pem -out ecdsa_private_key_pkcs8.pem -outform pem -nocrypt - Generate the Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
Generate the RSA Certificate Signing Request using the private key, run the followig command:
openssl req -new -key rsa_private_key -out apigatewayrsa.csr -config ssl.conf -passin pass:"keystorepasswd" -passout pass:"keystorepasswd"Generate the ECDSA Certificate Signing Request using the private key, run the following commands:openssl req -new -key ecdsa_private_key_pkcs8.pem -x509 -nodes -days 365 -out ecdsa_certificate.crt -config ssl.conf openssl req -new -key ecdsa_private_key_pkcs8.pem -out apigatewayecdsa.csr -config ssl.conf -passin pass:"keystorepasswd" -passout pass:"keystorepasswd" - For each key created generate the server certificates.
Sign the RSA server certificate with root CA private key run the following command:
openssl x509 -CA caroot.cer -CAkey cakey.pem -CAserial serial.txt -req -in apigatewayrsa.csr -out apigatewayrsa.cer -days 365 -extfile ssl.conf -extensions req_ext -passin pass:"keystorepasswd"Sign the ECDSA server certificate with root CA private key run the following command:openssl x509 -CA caroot.cer -CAkey cakey.pem -CAserial serial.txt -req -in apigatewayecdsa.csr -out apigatewayecdsa.cer -days 365 -extfile ssl.conf -extensions req_ext -passin pass:"keystorepasswd" - Create key.txt by providing a password. This password is used to configure the Gateway's key store. Run the following command:
echo "keystorepasswd" > key.txt - Create trust.txt by providing a password. This password is used to configure the Gateway's trust store. Run the following command:
echo "truststorepasswd" > trust.txt
Create the Secret
Create the secret, run the following commands:
kubectl create ns <NameSpace>
kubectl create secret generic <secret name>-gateway-secret --from-file=apigatewayrsa.cer --from-file=caroot.cer --from-file=apigatewayecdsa.cer --from-file=rsa_private_key_pkcs1.pem --from-file=ecdsa_private_key_pkcs8.pem --from-file=key.txt --from-file=trust.txt -n <Namespace>The ssl.conf can be used to configure default entries along with storage area network (SAN) details for your certificate.
Sample ssl.conf:
#ssl.conf
[ req ]
default_bits = 4096
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
req_extensions = req_ext
[ req_distinguished_name ]
countryName = Country Name (2 letter code)
countryName_default = IN
stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name)
stateOrProvinceName_default = Karnataka
localityName = Locality Name (eg, city)
localityName_default = Bangalore
organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company)
organizationName_default = Oracle
commonName = Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name)
commonName_max = 64
commonName_default = localhost
[ req_ext ]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
IP = 127.0.0.1
DNS.1 = localhostValidate CA Root
Follow the steps below to validate the CA root:
- Sign all the SSL certificates with the same CA root certificate. And store the CA root in the corresponding truststore.
- Sign the SSL certificates with different CA root but exchange the certificates and store the corresponding CA roots (from A and B side) in the proper truststores.
- Disable the CA validation on both sides.
2.2.2.8 Configuring Redundancy Agent
The configuration of the Redundancy Agent microservice is through a Database (DB) query at the start of the service. The installation must enable DB scripts to prevent installation issues. To configure the Redundancy Agent, run the following command:
INSERT INTO georedagent.site_config (site, cap4c_scheduler_uri, cluster_namespace, core_component, core_component_threshold, data_collection_uri, dbtier_status_uri, geo_redundancy_enabled, mated_sites, secondary_site_id, self_address, subscription_uri, tertiary_site_id)
VALUES('SITE-NAME', 'http://nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler-service:8080/v1/job/%s/%s', 'K8-NAMESPACE', 'ocn-nwdaf-subscription,ocn-nwdaf-data-collection', 5, 'http://ocn-nwdaf-data-collection-service:8080/ra/notify', 'http://dbtier-monitor-svc:9000/status', 1, 2, 'SITE-2', 'http://ingress-gateway:80', 'http://ocn-nwdaf-subscription-service:8080/nnwdaf-eventssubscription/v1/subscriptions/updateServingOwner', 'SITE-3');
If installation is complete and you want to edit the Redundancy Agent, follow the step below to modify any value by updating the entry of your site:
- Database -> georedagent | table -> site_config |
For the complete list of Georedundancy Parameters, see Georedundancy Parameters.
2.2.2.9 Configuring Mirror Maker
Note:
This is an optional procedure.Data topics across all georedundant sites are replicated by the Kafka “Mirror Maker 2 (MM2)”. Follow the procedure below to configure the Mirror Maker for data replication:
Prerequisites
Ensure that there are two or more Zookeepers with the corresponding Kafka brokers up and running. To verify, run the following command:
kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACESample output with two clusters consisting of two Kafka brokers:
kafka-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h
kafka-sts-1 1/1 Running 0 6d22h
kafkab-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h
kafkab-sts-1 1/1 Running 0 6d22h
zookeepera-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h
zookeeperb-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22hInstall Mirror Maker
- Access the registry to download the MM2 image. Run the following search command:
podman search ocnwdaf-docker.dockerhub-phx.oci.oraclecorp.com/nwdaf-cap4cVerify if the following output is displayed:
ocnwdaf-docker.dockerhub-phx.oci.oraclecorp.com/nwdaf-cap4c/nwdaf-cap4c-data-replication - If you do not have access to Oracle's registry, the installer contains the Mirror Maker image as a tar file. Run the following command to load the Mirror Maker image to the cluster:
podman load --input ocn-nwdaf-mirror-maker-latest.tarUpload the images to the registry, run the following commands:
podman tag localhost/ocn-nwdaf-mirror-maker:<TAG> <REPOSITORY>:<TAG>podman push localhost/ocn-nwdaf-mirror-maker:<TAG> <REPOSITORY>:<TAG> - Download the Helm chart. The installer contains the Mirror Maker Helm chart. The Mirror Maker does not run by default, navigate the folder to identify the following files:
├── nwdaf-cap4c-data-replication │ ├── Chart.yaml │ ├── templates │ │ ├── config.yaml │ │ ├── sts.yaml │ │ └── svc.yaml │ └── values.yaml - Edit the fields imageRegistry, imageName, and imageVersion in the values.yaml file.
nwdafDataReplication: projectName: nwdafDataReplication imageName: <IMAGE NAME> imageVersion: <TAG> - Edit the config.yaml file to include the mm2.properties file. The mm2.properties file configures the Mirror Makers behavior. If multiple Mirror Makers are present in the deployment, create separate mm2.properties file for each Mirror Maker.
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: {{ .Values.nwdafDataReplication.projectName }}-configmap data: #################################### # MM2 Properties File # #################################### mm2.properties: |- - Install the Helm chart.
Two-site deployment
For a two-site deployment, only one Mirror Maker is required, and it can be deployed in any of the sites. Run the following command:
helm install nwdaf-data-replication nwdaf-cap4c-mirror-makerThree-site deployment
In a three-site deployment, three Mirror Makers are deployed in a circular topology in each site. Run the following commands:
helm install nwdaf-data-replication-a nwdaf-cap4c-mirror-maker-a helm install nwdaf-data-replication-b nwdaf-cap4c-mirror-maker-b helm install nwdaf-data-replication-c nwdaf-cap4c-mirror-maker-c - Verify if the Mirror Maker is running, run the following command:
kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACESample output for a two-site deployment:
kafka-a-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h kafka-a-sts-1 1/1 Running 0 6d22h kafka-b-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h kafka-b-sts-1 1/1 Running 0 6d22h nwdaf-data-replication-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h zookeeper-a-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h zookeeper-b-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22hSample output for a three-site deployment:
kafka-a-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h kafka-a-sts-1 1/1 Running 0 6d22h kafka-b-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h kafka-b-sts-1 1/1 Running 0 6d22h kafka-c-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h kafka-c-sts-1 1/1 Running 0 6d22h nwdaf-data-replication-a-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h nwdaf-data-replication-b-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h nwdaf-data-replication-c-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h zookeeper-a-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h zookeeper-b-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h zookeeper-c-sts-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h- The Mirror Maker “nwdaf-data-replication-a” handles the replication for both Sites A and B.
- The Mirror Maker “nwdaf-data-replication-b” handles the replication for both Sites B and C.
- The Mirror Maker “nwdaf-data-replication-c” handles replication for Sites C and A.
- The replicated topics appear with the cluster name as a prefix.
kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server kafka-sts-0:9092 --listFor example, if there are two clusters named clusterA and clusterB and topic1 is present in clusterB, then the replicated topic is
clusterA.topic1.
Configuring Mirror Maker
Configure the Mirror Maker's (MM2) configuration file. The file includes information on the topics to be replicated and the cluster in which replication occurs. Configure the templates/config.yaml in the Helm chart as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: {{ .Values.nwdafDataReplication.projectName }}-configmap
data:
####################################
# MM2 Properties File #
####################################
mm2.properties: |-
clusters=clusterA, clusterB
clusterA.bootstrap.servers=kafka-sts-0.{{ .Values.nwdafDataReplication.config.service1.kafkaService }}.{{ .Values.nwdafDataReplication.config.service1.namespace }}.svc.{{ .Values.nwdafDataReplication.config.service1.cluster }}:9092
clusterB.bootstrap.servers=kafka-sts-0.{{ .Values.nwdafDataReplication.config.service2.kafkaService }}.{{ .Values.nwdafDataReplication.config.service2.namespace }}.svc.{{ .Values.nwdafDataReplication.config.service2.cluster }}:9092
clusterA.config.storage.replication.factor=1
clusterB.config.storage.replication.factor=1
clusterA.offset.storage.replication.factor=1
clusterB.offset.storage.replication.factor=1
clusterA.status.storage.replication.factor=1
clusterB.status.storage.replication.factor=1
clusterA->clusterB.enabled=true
clusterB->clusterA.enabled=true
offset-syncs.topic.replication.factor=1
heartbeats.topic.replication.factor=1
checkpoints.topic.replication.factor=1
topics=nwdaf\.report\.location, nwdaf\.report\.session, nwdaf\.report\.nfload, nwdaf\.report\.oamperformance, nwdaf\.report\.oamqosflows, nwdaf\.report\.oamranthroughput, nwdaf\.report\.oamupf, nwdaf\.report\.uesinarea
groups=.*
tasks.max=10
replication.factor=1
refresh.topics.enabled=true
sync.topic.configs.enabled=true
refresh.topics.interval.seconds=10
topics.exclude=.*[\-\.]internal, .*\.replica, __consumer_offsets, .*\.checkpoints.internal, .*\.heartbeats, ^cluster.*
topics.blacklist=.*[\-\.]internal, .*\.replica, __consumer_offsets, ^cluster.*
groups.blacklist=console-consumer-.*, connect-.*, __.*
clusterA->clusterB.emit.heartbeats.enabled=true
clusterA->clusterB.emit.checkpoints.enabled=true
clusterB->clusterA.emit.heartbeats.enabled=true
clusterB->clusterA.emit.checkpoints.enabled=true
Below is the values.yaml file:
nwdafDataReplication:
projectName: nwdafDataReplication
imageName: nwdaf-cap4c/nwdaf-cap4c-mirrormaker
imageVersion: latest
deploy:
replicas: 1
securityContext:
user: 1000
group: 2000
resources:
request:
cpu: 1
memory: 2Gi
limits:
cpu: 1
memory: 4Gi
storage:
mount:
path: /app-data
size: 5Gi
configmap:
path: /var/mirrormaker
svc:
port: 9092
config:
env:
service1:
kafkaService: kafka-headless-svc
namespace: nwdaf-alpha-ns
cluster: blurr7
service2:
kafkaService: kafka-headless-svc
namespace: nwdaf-beta-ns
cluster: blurr7For more information on the customizable Mirror Maker parameters, see Mirror Maker Parameters.
Topic Configuration
This procedure describes configuring topics in the stream transformer service to accept replicated topics from the Mirror Maker. A new topic is created in the target cluster. The topic name comprises the cluster name as a prefix, followed by a period, and then the topic name.
For example:
sourceCluster.topic1Implementing this data replication method is suitable for a "Active/Active" topology, and data generated locally and externally can be distinguished. The stream processor configures topics as a list with the “topics” parameters, as displayed in the example below:
bindings:
# NWDAF - Location
nwdafLocation-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.location
nwdafLocation-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.location
# NWDAF - Nf Load
nwdafNfLoad-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.nfload
nwdafNfLoad-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.nfload
# NWDAF - Session
nwdafSession-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.session
nwdafSession-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.session
# NWDAF - OAM Performance
nwdafOamPerformance-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.oamperformance
nwdafOamPerformance-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.oamperformance
# NWDAF - UEs in Area
nwdafUesInArea-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.uesinarea
nwdafUesInArea-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.uesinarea
#NWDAF - OAM Upf
nwdafOamUpf-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.oamupf
nwdafOamUpf-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.oamupf
#NWDAF - OAM QosFlows
nwdafOamQosFlows-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.oamqosflows
nwdafOamQosFlows-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.oamqosflows
#NWDAF - OAM Ran Throughput
nwdafOamRanThroughput-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.oamranthroughput
nwdafOamRanThroughput-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.oamranthroughputThe configuration is modified to accept replicated messages from Mirror Maker 2 to cluster A.
For example:
bindings:
# NWDAF - Location
nwdafLocation-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.location,clusterB.nwdaf.report.location,clusterC.nwdaf.report.location
nwdafLocation-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.location
# NWDAF - Nf Load
nwdafNfLoad-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.nfload,clusterB.nwdaf.report.nfload,clusterC.nwdaf.report.nfload
nwdafNfLoad-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.nfload
# NWDAF - Session
nwdafSession-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.session,clusterB.nwdaf.report.session,clusterC.nwdaf.report.session
nwdafSession-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.session
# NWDAF - OAM Performance
nwdafOamPerformance-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.oamperformance,clusterB.nwdaf.report.oamperformance,clusterC.nwdaf.report.oamperformance
nwdafOamPerformance-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.oamperformance
# NWDAF - UEs in Area
nwdafUesInArea-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.uesinarea,clusterB.nwdaf.report.uesinarea,clusterC.nwdaf.report.uesinarea
nwdafUesInArea-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.uesinarea
#NWDAF - OAM Upf
nwdafOamUpf-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.oamupf,clusterB.nwdaf.report.oamupf,clusterC.nwdaf.report.oamupf
nwdafOamUpf-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.oamupf
#NWDAF - OAM QosFlows
nwdafOamQosFlows-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.oamqosflows,clusterB.nwdaf.report.oamqosflows,clusterC.nwdaf.report.oamqosflows
nwdafOamQosFlows-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.oamqosflows
#NWDAF - OAM Ran Throughput
nwdafOamRanThroughput-in-0.destination: nwdaf.report.oamranthroughput,clusterB.nwdaf.report.oamranthroughput,clusterC.nwdaf.report.oamranthroughput
nwdafOamRanThroughput-out-0.destination: cap4c.report.oamranthroughputUninstall Mirror Maker
To uninstall the Mirror Maker, run the following command:
helm uninstall nwdaf-data-replication2.2.2.10 Enable Model C Communication Support
To enable or disable Model C support, update the values.yaml file in the Egress gateway Helm chart. This feature is disabled by default.
Set the value of the parameter sbiRoutingEnabled to true. By default, it is “false”.
For example:
routesConfig:
- id: scp_via_proxy
uri: http://request.uri
path: /nsmf-event-exposure/**
order: 1
metadata:
httpsTargetOnly: false
httpRuriOnly: false
sbiRoutingEnabled: true #false for direct routing
.
.
.
- id: scp_direct1
uri: https://dummy.dontchange1
path: /namf-evts/v1/subscriptions/**
order: 2
metadata:
httpsTargetOnly: false
httpRuriOnly: false
sbiRoutingEnabled: true
To configure the SCP end point for Model C support, set the host and sbiRoutingEnabled parameters in the Egress gateway values.yaml file as follows:
#SBIRouting Configuration
sbiRouting:
# Default scheme applicable when 3gpp-sbi-target-apiroot header is missing
sbiRoutingDefaultScheme: http
sbiRoutingEnabled: true
peerConfiguration:
- id: peer1
host: ocscp-scp-worker
port: 8080
apiPrefix: "/"
healthApiPath: "/health/v3"
To enable SCP to route the requests, configure the following:
- Set the host parameter to
ocscp-scp-worker. - Set the port number to 8080.
- If the SCP is in a different namespace, add the namespace with the worker service. For example:
ocscp-scp-worker.ocnwdaf-ns. If the SCP is another tenant, use the IP address. - HTTPs is used for communication with the SCP. The SCP's configuration must be a FQDN and not an IP address.
2.2.2.11 Configure OCI Metrics
Follow the steps below to configure OCI metrics for OCNWDAF:
- Configure the
isOciClusterflag in the values.yaml file totrue. - In the oci folder, add the config and pem files.
- In the config file, update the path of the key_file container to ssh/privateKey.pem.
- Update the values of
<replace here>tag with the correct values (configured OCI metrics namespace and OCI compartment id) in values.yaml file present in the ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/helmChart/ folder.... isOciCLuster: true ociMetricsNamespace: '<replace here>' #Namespace when isOciCLuster is enabled ociCompartmentId: &ociCompartmentId '<replace here>' ...
2.2.2.12 Configure Machine Learning (ML) Model Replication
Follow the procedure below to configure ML model replication across all georedundant sites:
- On cluster A, locate the load balancer assigned to the container and obtain the external IP address:
Run the following command:
kubectl get svcSample Output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE cap4c-model-executor ClusterIP None <none> 9092/TCP 15d cap4c-model-executor-lb LoadBalancer 10.233.57.59 10.75.245.189 30000:30910/TCP 15d - On cluster B, access the Synchronization tool (rsync) container, run the
ssh-keycanand populate known_hosts file:Run the following command:kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACESample output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE cap4c-model-executor-sts-0 2/2 Running 0 15dRun the following commands:
$ kubectl exec -it cap4c-model-executor-sts-0 -c nwdaf-cap4c-rsync bashSample commands:
# $ ssh-keyscan -p 30000 {external_ip_lb} >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts $ ssh-keyscan -p 30000 10.75.245.189 >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts - On cluster B, copy the public key and paste it under the file authorized_keys in cluster A :
## Cluster B. $ kubectl exec -it cap4c-model-executor-sts-0 -c nwdaf-cap4c-rsync bash ## Copy public key. $ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub## Cluster A. $ kubectl exec -it cap4c-model-executor-sts-0 -c nwdaf-cap4c-rsync bash ## Paste key cluster B $ vi ~/.ssh/authorized_keys - On cluster B, change the destination IP of rsync:
For example:
$ vi /app/config/config_file DEST_USER=root DEST_IP=10.75.245.189 DESTINATION_PATH=/mnt/nfs DESTINATION_PORT=30000 SOURCE_PATH=/mnt/nfs
The logs of rsync jobs are located at:/var/log/rsync.log.
The following Helm charts are modified:
ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/helmChart/charts/cap4c-model-executor/templates/sts.yaml
containers:
- name: {{ .Values.rsync.projectName }}
image: {{ .Values.global.image.registry }}/{{ .Values.rsync.imageName }}:{{ .Values.rsync.imageVersion }}
imagePullPolicy: {{ .Values.global.image.imagePullPolicy }}
env:
{{- range $key, $val := .Values.modelExecutor.modelExecutor.config.env }}
- name: {{ $key }}
value: {{ $val | quote }}
{{- end }}
volumeMounts:
- name: {{ .Values.modelExecutor.modelExecutor.projectName }}-pvc
mountPath: {{ .Values.rsync.deploy.storage.mountPath }}
- name: {{ .Values.modelExecutor.modelExecutor.projectName }}
image: {{ .Values.global.image.registry }}/cap4c/{{ .Values.modelExecutor.modelExecutor.imageName }}
imagePullPolicy: {{ .Values.global.image.imagePullPolicy }}ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/helmChart/charts/cap4c-model-executor/templates/svc.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: {{ .Values.modelExecutor.modelExecutor.projectName }}-lb
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/address-pool: oam
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
allocateLoadBalancerNodePorts: true
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
selector:
app: {{ .Values.modelExecutor.modelExecutor.projectName }}
ports:
- port: {{ .Values.rsync.svc.port }}
targetPort: {{ .Values.rsync.svc.targetPort }}
protocol: {{ .Values.rsync.svc.protocol }}ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/helmChart/charts/cap4c-model-executor/values.yaml
rsync:
projectName: nwdaf-cap4c-rsync
imageName: nwdaf-cap4c/nwdaf-cap4c-rsync
imageVersion: 3.1
deploy:
storage:
size: "10Gi"
mountPath: "/mnt/nfs"
svc:
port: 30000
targetPort: 22
protocol: TCP
For more information on the customizable parameters, see ML Model Replication Parameters.
2.2.2.13 Configuring Data Director
The OCNWDAF supports the Data Director (OCNADD) as a data source. Follow the procedure below to configure the OCNADD as a data source:
- Ensure the OCNADD is set up and running.
- Configure the OCNADD to have a xDR topic:
- Ensure that the OCNADD has an appropriate ACL feed, filter, and correlation services created (and enabled).
- During OCNADD deployment, configure the parameter Include Message with xDR as METADATA_HEADERS_DATA. Select this option to include xDRs with complete messages. For more information, see "Select xDR Type Related Info" in the "Creating Correlation Configurations" procedure in the "Correlation Configurations" section of the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide.
- The OCNADD setup must have a filter configuration and correlation configuration. For
sessionBasicandcellLocationparameters, appropriate filter and correlation must be created and enabled.
- Run the gen_scripts.sh script to generate the Truststore and Keystore required for Kafka communication. The gen_scripts.sh has to be run with the same cakey.pem and cacert.pem files used during OCNADD installation.
The gen_scripts.sh requires the namespace for execution. It uses the namespace to ensure where the Truststore and Keystore are generated.
For example:
bash gen_scripts.sh <namespace>Once the script is run, a password prompt appears, provide the same password used for the CA generation in OCNADD. Additionally, provide the same OCNADD configuration. The common name, state, organization, city, and country must be the same as in the configuration.
- Update the following properties in the OCNWDAF Helm charts values.yaml file.
global: dataSource: 'data-director' kafkaMirrorMaker: env: OCNADD_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: <The OCNADD BOOTSTRAP SERVER> TOPIC_NAME: <XDR Topic Name> TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD: <TrustStore Password> KEYSTORE_PASSWORD: <Keystore Password> KEY_PASSWORD: <Key Password> JAAS_CONFIG: <Jaas config used> - Update the
sessionBasicparameter the main values.yaml file as follows:global: datatype: sessionBasic: DATA_DIRECTOR - Update the
cellLocationparameter the main values.yaml file as follows:global: datatype: cellLocation: DATA_DIRECTOR
2.2.2.14 Installing OCNWDAF Package
To install the OCNWDAF package, perform the following steps:
- Update the values in the
<replace here>tag in the values.yaml file under the <release directory>/ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/helmChart/ directory according to the setup.... image: registry: &imageRegistry '<replace here>' #Add image registry here. gateway: registry: '<replace here>' #Add gateway image registry here. imagePullPolicy: &imagePullPolicy IfNotPresent initContainer: imagePullPolicy: *imagePullPolicy #Set new value if required by removing *imagePullPolicy and adding desired value nrfClient: registry: &nrfRegistry '<replace here>' #Add gateway image registry here. ... ... cluster: name: &clusterName '<replace here>' namespace: &nameSpace '<replace here>' storageClass: '<replace here>' dbConfig: MYSQL_HOST: &mySQLHost '<replace here>' MYSQL_PORT: &mySQLPort '<replace here>' MYSQL_ENGINE: &mySQLEngine '<replace here>' CNDBTIER_NAMESPACE: &cndbNameSpace '<replace here>' CNDBTIER_SQL_POD_NAME: &cndbSQLPodName '<replace here>' - Update the
<replace here>tag under the "KAFKA_BROKERS" variable under "NWDAF CONFIGURATION VARIABLES" section with the proper Kafka broker. Note: Replace respective OCNWDAF namespaces and cluster names if example values are to be used.... ### NWDAF CONFIGURATION VARIABLES ### KAFKA_BROKERS: &nwdafkafkabroker '<replace here>' # Example value "kafka-sts-0.kafka-headless-svc.{nwdafNameSpace}.svc.{nwdafClusterName}:9092,kafka-sts-1.kafka-headless-svc.{nwdafNameSpace}.svc.{nwdafClusterName}:9092" DRUID_HOST: "" DRUID_PORT: "" ... - Update the secrets with Base64 Encoded values where the
<replace here>tag present in the ocnwdaf_custom_values.yaml file located at ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/custom-templates/ .Note:
To read the secret values, decode the present values using Base64 decoding method. When Cndb is the database update the newly created admin user.For example:
... ######################### # SECRETS CONFIGURATION # ######################### secret: #Encode the values in base64 format mysqlCndbUsername: cm9vdA== #root for example mysqlCndbPassword: cGFzc3dvcmQ= #password for example mysqlInnoDbUsername: cm9vdA== #root for example mysqlInnoDbPassword: cGFzc3dvcmQ= #password for example ... - (Optional) Follow this step to set up Data Director as a data source.
- Ensure the OCNADD is setup and running.
- Configure the OCNADD to have a xDR topic:
- Ensure the OCNADD has an appropriate ACL feed, filter, and correlation services created (and enabled).
- The OCNADD setup must have a filter configuration and correlation configuration. For
sessionBasicandcellLocationparameters appropriate filter and correlation must be created and enabled.
- Run the gen_scripts.sh script to generate the Truststore and Keystore required for Kafka communication. The gen_scripts.sh has to be run with the same cakey.pem and cacert.pem files used during OCNADD installation.
The gen_scripts.sh requires the namespace for execution. It uses the namespace to ensure where the Truststore and Keystore are generated.
For example:
bash gen_scripts.sh <namespace>When the script is executed, it prompts for the password and the same password used for the CA generation in OCNADD is supposed to be used in the script. Additionally, the same configuration (Common Name,State,Organization, City, Country) must be used which was used for OCNADD.
- Update the following properties in the OCNWDAF Helm charts values.yaml file.
global: dataSource: 'data-director' kafkaMirrorMaker: env: OCNADD_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: <The OCNADD BOOTSTRAP SERVER> TOPIC_NAME: <XDR Topic Name> TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD: <TrustStore Password> KEYSTORE_PASSWORD: <Keystore Password> KEY_PASSWORD: <Key Password> JAAS_CONFIG: <Jaas config used> - Update the
sessionBasicparameter the main values.yaml file as follows:global: datatype: sessionBasic: DATA_DIRECTOR - Update the
cellLocationparameter the main values.yaml file as follows:global: datatype: cellLocation: DATA_DIRECTOR
- Set the Subcharts flag in the centralized values.yaml file under the <release directory>/ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/helmChart/ directory. The allowed values are true or false. The services with the flag set to "false" are not deployed.
- Optionally, update any other parameter in centralized or subchart values.yaml files.
For example, Prometheus monitoring details or hooks environment variables in the centralized values.yaml under the ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/helmChart directory. Any microservice specific values like image name or tag, environment variables in microservices subchart values.yaml file.
The following list is the default variables used to configure OCNWDAF, these variables are present in the centralized values.yaml files and in the secrets:
- MYSQL_HOST
- MYSQL_PORT
- KAFKA_BROKERS
- REDIS_HOST
- REDIS_PORT
- CAP4C_KAFKA_INGESTOR_DB
- CAP4C_KAFKA_INGESTOR_DB_USER
- CAP4C_KAFKA_INGESTOR_DB_PASSWORD
- CAP4C_MODEL_CONTROLLER_DB
- CAP4C_MODEL_CONTROLLER_DB_USER
- CAP4C_MODEL_CONTROLLER_DB_PASSWORD
- CAP4C_MODEL_EXECUTOR_DB_USER
- CAP4C_MODEL_EXECUTOR_DB_PASSWORD
- CAP4C_STREAM_ANALYTICS_DB
- NWDAF_CAP4C_REPORTING_SERVICE_USER
- NWDAF_CAP4C_REPORTING_SERVICE_PASSWORD
- NWDAF_CAP4C_SCHEDULER_SERVICE_DB
- NWDAF_CAP4C_SCHEDULER_SERVICE_DB_USER
- NWDAF_CAP4C_SCHEDULER_SERVICE_DB_PASSWORD
- NWDAF_CONFIGURATION_HOST
- NWDAF_USER
- NWDAF_DB_PASSWORD
- Install OCNWDAF, run the following Helm installation command:
helm install <installation name> <path to the chart directory> -n $K8_NAMESPACE --timeout <timeout>mFor example:
helm install nwdaf helmChart/ -n ocnwdaf-ns --timeout 30mNote:
The parameter--timeoutis optional. It is recommended to use this parameter to avoid any installation failure due to slow internet or CPU speeds. Use appropriate value for this parameter depending on the speed of image pull from the nodes of the setup. The recommended timeout value is 30 minutes.Mandatory Installation Instruction
Note:
Some services are release name dependent, use "nwdaf" for <installation name> in the Helm install command.For example:
[cloud-user@occne224-cluster-bastion-1 ]$ helm install nwdaf helmChart/ -n nwdaf-test --timeout 30mSample output when the installation starts:
[cloud-user@occne224-cluster-bastion-1 ]$ helm install nwdaf helmChart/ -n nwdaf-test --timeout 30m W0404 04:44:48.456730 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler W0404 04:44:48.459573 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler W0404 04:51:41.957767 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscalerRun the following command to view all the resources present in the namespace:
kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACEFor example:
[cloud-user@occne224-cluster-bastion-1 ~]$ kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACE[cloud-user@occne224-cluster-bastion-1 ~]$ kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/ocn-nwdaf-db-creation-hook-jj9mx 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 15s NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE job.batch/ocn-nwdaf-db-creation-hook 0/1 15s 15sSample output when the installation completes:
[cloud-user@occne224-cluster-bastion-1 ]$ helm install nwdaf helmChart/ -n $K8_NAMESPACE --timeout 30m W0404 04:44:48.456730 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler W0404 04:44:48.459573 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler W0404 04:51:41.957767 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler W0404 04:51:41.963127 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler NAME: nwdaf LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Apr 4 04:44:47 2023 NAMESPACE: nwdaf-test STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: NoneVerify if all the dependencies are in Running state (if any pod is not in Running state wait for a maximum of five restarts).
Run the following command to view all the resources present in the namespace:
kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACESample output:
Figure 2-2 Sample Output
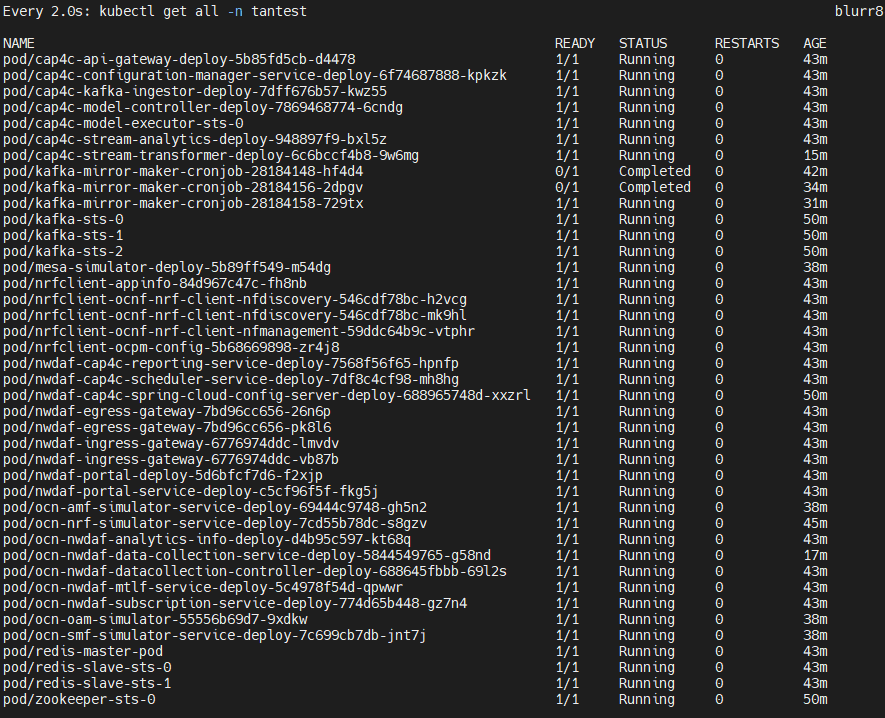
OCNWDAF Microservices Port Mapping
Table 2-10 Port Mapping
| Service | Port Type | IP Type | Network Type | Service Port | Container Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ocn-nwdaf-analytics | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-egress-gateway | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-ingress-gateway | External | NodePort | External/ K8s | 80/TCP | 8081/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-data-collection-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-datacollection-controller | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-mtlf | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-subscription-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-analytics-info | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-georedagent | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 9181/TCP | 9181/TCP |
| cap4c-kafka-ingestor | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| cap4c-model-controller | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| cap4c-model-executor | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 9092/TCP | 9092/TCP |
| cap4c-stream-transformer | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| cap4c-stream-analytics | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| cap4c-api-gateway | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-cap4c-reporting-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-portal | External | NodePort | External / K8s | 80/TCP | |
| nwdaf-portal-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| cap4c-configuration-manager-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 9000/TCP | 9000/TCP |
| cap4c-capex-optimization-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 9000/TCP | 9000/TCP |
Note:
For NodePort services, Kubernetes allocates the Service Port.Installation of Simulator Chart
Follow the procedure below to install the simulator chart:
- Update the values in the
<replace here>tag present in values.yaml under/simulator-helmchart/based on the setup:... image: registry: &imageRegistry '<replace here>' #Add image registry here Default is ocnwdaf-docker.dockerhub-phx.oci.oraclecorp.com imagePullPolicy: &imagePullPolicy IfNotPresent ... ... cluster: name: &clusterName '<replace here>' namespace: &nameSpace '<replace here>' dbConfig: MYSQL_HOST: &mySQLHost '<replace here>' MYSQL_PORT: &mySQLPort '<replace here>' MYSQL_ENGINE: &mySQLEngine '<replace here>' CNDBTIER_NAMESPACE: &cndbNameSpace '<replace here>' CNDBTIER_SQL_POD_NAME: &cndbSQLPodName '<replace here>' ... - Set the Subcharts flag in the centralized values.yaml file under the /simulator-helmchart directory. The allowed values are true or false. The services with the flag set to false are not deployed.
- Optionally, update any other parameter in centralized or subchart values.yaml files.
For example, Prometheus monitoring details or hooks environment variables in the centralized values.yaml under the /simulator-helmchart directory. Any microservice specific values like image name or tag, environment variables in microservices subchart values.yaml file.
- Install simulators, run the following Helm installation command:
helm install <installation name> <path to the chart directory> -n $K8_NAMESPACE --timeout <timeout>hFor example:
helm install simulators simulator-helmchart/ -n ocnwdaf-ns --timeout 30mNote:
The parameter--timeoutis optional. It is recommended to use this parameter to avoid any installation failure due to slow internet or CPU speeds. Use appropriate value for this parameter depending on the speed of image pull from the nodes of the Bastion host. The recommended timeout value is 30 minutes.Sample of the terminal screen once the installation starts:
[cloud-user@occne224-cluster-bastion-2 ocn-nwdaf-helmChart]$ helm install simulators simulator-helmChart/ -n ttest --timeout 30m W0511 10:38:19.670067 2848359 warnings.go:70] spec.template.spec.containers[0].env[61].name: duplicate name "SPRING_KAFKA_CONSUMER_PROPERTIES_MAX_POLL_INTERVAL_MS" NAME: simulators LAST DEPLOYED: Thu May 11 10:38:12 2023 NAMESPACE: ttest STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: None - Run the following command to verify if all the dependencies are in Running state (if any pod is not in Running state wait for a maximum of five restarts):
kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACESample output:
Figure 2-3 Sample Output
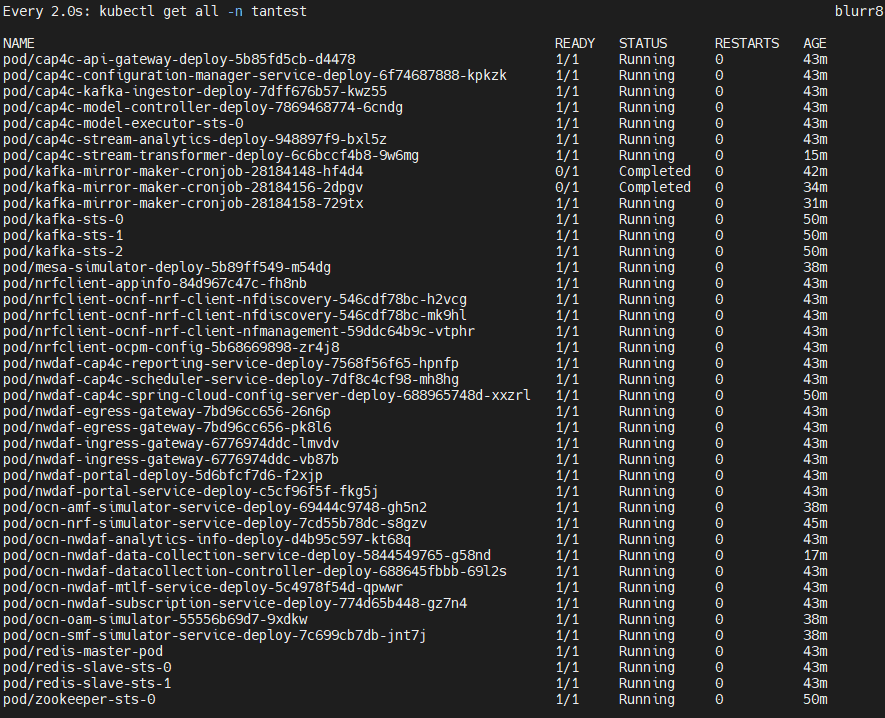
- The following services with port mapping are deployed:
Table 2-11 Port Mapping
Service Port Type IP Type Network Type Service Port Container Port ocn-nrf-simulator Internal ClusterIP Internal / K8s 8080/TCP 8080/TCP ocn-amf-simulator Internal ClusterIP Internal / K8s 8080/TCP 8080/TCP mesa-simulator Internal ClusterIP Internal / K8s 8080/TCP 8080/TCP ocn-smf-simulator Internal ClusterIP Internal / K8s 8080/TCP 8080/TCP ocn-oam-simulator Internal ClusterIP Internal / K8s 8085/TCP 8085/TCP
Configure Service Parameters
In the values.yaml under /helmchart/ select the services to deploy, the Helm chart parameters are listed below:
nrfclient.enabled: true
ocn-nrf-simulator.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-kafka.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-redis.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler-service.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-reporting-service.enabled: &isReportingServiceEnabled true
nwdaf-cap4c-stream-analytics.enabled: true
cap4c-stream-transformer.enabled: true
cap4c-api-gateway.enabled: true
cap4c-configuration-manager-service.enabled: &isCap4cConfigurationManagerEnabled true
nwdaf-cap4c-model-executor.enabled: &isCap4cModelExecutorEnabled true
nwdaf-cap4c-model-controller.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-kafka-ingestor.enabled: &isKafkaIngestorEnabled true
cap4c-capex-optimization-service.enabled: true
ocn-nwdaf-subscription.enabled: true
ocn-nwdaf-data-collection.enabled: true
ocn-nwdaf-datacollection-controller.enabled: true
ocn-nwdaf-mtlf.enabled: true
ocn-nwdaf-analytics.enabled: true
ocnNwdafGeoredagent.enabled: false
nwdaf-portal-service.enabled: true
nwdaf-portal.enabled: true
common-services-gateways.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-data-replication.enabled: false
cap4cDeployTemp.enabled: false
innodbDeploy.enabled: trueIn the values.yaml under /simulator-helmChart/ select the simulators to deploy, the simulator Helm chart parameters are listed below:
ocn-smf-simulator.enabled: true
ocn-mesa-simulator.enabled: true
ocn-amf-simulator.enabled: true
ocn-oam-simulator.enabled: true2.2.2.15 Configure Prometheus Metrics
Follow the procedure below to configure Prometheus metrics:
- Set the
enableflag totrueto activate metrics collection through Prometheus. - When the
enableflag is set totrue, you must provide theidAddressor Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) for the Prometheus monitoring service in the following format:... ################################# # PROMETHEUS MONITORING DETAILS # ################################# prometheus: enabled: true ipAddress: '<replace here>' # Format is {prometheusServiceName}.{infraNamespace}.svc.{clusterName} or keep empty ...
2.2.3 Postinstallation Tasks
This section explains the postinstallation tasks for OCNWDAF.
2.2.3.1 Verifying Installation
To verify the installation:
-
Run the following command to check the installation status:
helm status <helm-release> -n <namespace>Where,
<helm-release>is the Helm release name of OCNWDAF. <namespace><namespace>is the namespace of OCNWDAF deployment.For example:
helm status ocndaf -n ocndafIf the deployment is successful, then the
STATUSis displayed asdeployed. -
Run the following command to verify if the pods are up and active:
kubectl get pods -n <namespace>Where,
<namespace>is the namespace of OCNWDAF deployment.The
STATUScolumn of all the pods must be 'Running'.The
READYcolumn of all the pods must be n/n, where n is the number of containers in the pod. - Run the following command to verify if the services are deployed and active:
kubectl -n <namespace> get servicesWhere,
<namespace>is the namespace of OCNWDAF deployment.
If the installation is unsuccessful or the status of all the pods is not in RUNNING state, , perform the troubleshooting steps provided in Oracle Communications Networks Data Analytics Function Troubleshooting Guide.
2.2.3.2 Performing Helm Test
Helm Test is a feature that validates the successful installation of OCNWDAF and determines if the NF is ready to take traffic. The pods are tested based on the namespace and label selector configured for the helm test configurations.
Note:
Helm Test can be performed only on helm3.Prerequisite: To perform the helm test, you must have the helm test configurations completed under the "Global Parameters" section of the custom_values.yaml file. For more information on parameters, see Global Parameters.
Run the following command to perform the helm test:
helm3 test <helm-release_name> -n <namespace>where:
helm-release-name is the release name.
namespace is the deployment namespace where OCNWDAF is installed.
Example:
helm3 test ocnwdaf -n ocnwdaf
Sample output:
NAME: ocnwdaf
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Nov 14 11:01:24 2022
NAMESPACE: ocnwdaf
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: ocnwdaf-test
Last Started: Mon Nov 14 11:01:45 2022
Last Completed: Mon Nov 14 11:01:53 2022
Phase: Succeeded
NOTES:
# Copyright 2022 (C), Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved2.2.3.3 Configuring OCNWDAF GUI
This section describes how to configure Oracle Communications Networks Data Analytics Function (OCNWDAF) GUI using the following steps:
Configure OCNWDAF GUI in CNC Console
Prerequisite: To configure OCNWDAF GUI in CNC Console, you must have CNC Console installed. For information on how to install CNC Console, refer to Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Before installing CNC Console, ensure that the instances parameters are updated in the CNC Console's custom values.yaml file.
Follow the steps listed below:
-
Set the Image Repository
In the CNC Console's custom values.yaml file, set the Image Repository to the repository where the images are located. The parameter dockerRegistry is found in line number 10 of the global parameters section:For example:
dockerRegistry: ocnwdaf-docker.dockerhub-phx.oci.oraclecorp.com -
Update the Cluster Domain
Update the cluster's DNS domain based on the deployment. The parameter clusterDomain is located in line number 16 of the global parameters section:For example:
clusterDomain: &clusterDomain "sunstreaker"To identify the cluster name, run the following command:kubectl -n kube-system get configmap kubeadm-config -o yaml | grep -i dnsDomain -
Load Balancer Configuration
If a Load Balancer is used, use the following configuration:The annotation metallb.universe.tf/address-pool: signaling/oam is required in global section if MetalLB in CNE 1.8.x onwards is used # Line 25: customExtension: lbServices: labels: {} annotations: # The annotation metallb.universe.tf/address-pool: signaling/oam is required if MetalLB in CNE 1.8.x is used metallb.universe.tf/address-pool: oam service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-internal: "true" -
Set Database Details
Use the following configuration:
# DB Details by fqdn dbHost: &mySqlHostRef "mysql-connectivity-service.<namespace_name>" dbPort: &mySqlPortRef "3306" secretName: &mySqlSecretNameRef cncc-db-secret # DB Details by external ip: dbHost: &mySqlHostRef 10.233.34.56 <- External ip from mysql-connectivity-service dbPort: &mySqlPortRef 3306 secretName: &mySqlSecretNameRef cncc-db-secret -
Activate Cluster IP for Load Balancer
Set the parameter useClusterIpForLbServices to true.
Use the following configuration:
# Use ClusterIP for LoadBalancer(LB) services. # The LB services are assigned LoadBalancer service type in k8s service definition. Set this flag to true to assign ClusterIP service type. useClusterIpForLbServices: true -
Update Automatic route generation for CNC Console Manager and Agent Deployment
Update the Automatic route generation for CNC Console Manager and Agent Deployment sections either using an external IP or a Load Balancer:
Using an external IP
self: cnccId: Cluster1 mCnccIams: - id: Cluster1 # IP of one of external IP of Cluster nodes ip: <external_k8s_node_ip> # IAM app port port: <service_node_port> mCnccCores: - id: Cluster1 aCnccs: - id: Cluster1 role: Cluster1 # Path to acore ingress service "service-name.namespace.svc.clustername" fqdn: nwdaf-cncc-acore-ingress-gateway.<namespace_name>.svc.<cluster_domian> # cncc app port port: 80 instances: - id: OCCNE-NWDAF-UI-instance1 # Set type to NWDAF-UI type: NWDAF-UI owner: Cluster1 # Path to nwdaf portal UI service "service-name.namespace.svc.clustername" fqdn: nwdaf-portal.<namespace_name>.svc.<cluster_domian> # Portal UI port port: 80 # Path to NWDAF on kubernetes cluster "clustername/namespace/ocnwdaf" apiPrefix: /<cluster_domain>/<namespace_name>/ocnwdaf - id: OCCNE-NWDAF-UI-instance1 # Set type to NWDAF-API type: NWDAF-API owner: Cluster1 # Path to nwdaf API service "service-name.namespace.svc.clustername" fqdn: cap4c-api-gateway.<namespace_name>.svc.<cluster_domain> # Portal API port port: 8080 # Path to NWDAF on kubernetes cluster "clustername/namespace/ocnwdafapi" apiPrefix: /<cluster_domain>/<namespace_name>/ocnwdafapiFor example:
self: cnccId: Cluster1 mCnccIams: - id: Cluster1 ip: 10.123.158.150 port: 30085 mCnccCores: - id: Cluster1 aCnccs: - id: Cluster1 role: Cluster1 fqdn: cncc-acore-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.blurr7 port: 30076 instances: - id : Cluster1-nwdaf-instance1 # Set type to NWDAF-UI type: NWDAF-UI owner: Cluster1 fqdn: nwdaf-portal.ocnwdaf-ns.svc.blurr7 port: 80 apiPrefix: /blurr7/ocnwdaf-ns/ocnwdaf - id : Cluster1-nwdaf-instance1 type: NWDAF-API owner: Cluster1 fqdn: cap4c-api-gateway.ocnwdaf-ns.svc.blurr7 port: 8080 apiPrefix: /blurr7/ocnwdaf-ns/ocnwdafapiUsing Load Balancer
self: cnccId: Cluster1 mCnccIams: - id: Cluster1 # IP of one of Load Balancer IPs of Cluster nodes ip: 10.75.245.212 mCnccCores: - id: Cluster1 aCnccs: - id: Cluster1 role: Cluster1 # Path to acore ingress service "service-name.namespace.svc.clustername" fqdn: cncc-acore-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.sunstreaker # cncc app port port: 80 instances: - id: OCCNE-NWDAF-UI-instance1 # Set type to NWDAF-UI type: NWDAF-UI owner: Cluster1 # Path to nwdaf portal UI service "service-name.namespace.svc.clustername" fqdn: nwdaf-portal.ocnwdaf-ns.svc.sunstreaker # Portal UI port port: 80 # Path to NWDAF on kubernetes cluster "clustername/namespace/ocnwdaf" apiPrefix: /sunstreaker/ocnwdaf-ns/ocnwdaf - id: OCCNE-NWDAF-UI-instance1 # Set type to NWDAF-API type: NWDAF-API owner: Cluster1 # Path to nwdaf API service "service-name.namespace.svc.clustername" fqdn: cap4c-api-gateway.ocnwdaf-ns.svc.sunstreaker # Portal API port port: 8080 # Path to NWDAF on kubernetes cluster "clustername/namespace/ocnwdafapi" apiPrefix: /sunstreaker/ocnwdaf-ns/ocnwdafapiFor example:
self: cnccId: Cluster1 mCnccIams: - id: Cluster1 ip: 10.75.245.212 mCnccCores: - id: Cluster1 aCnccs: - id: Cluster1 role: Cluster1 fqdn: cncc-acore-ingress-gateway.cncc.svc.sunstreaker port: 80 instances: - id: OCCNE-NWDAF-UI-instance1 type: NWDAF-UI owner: Cluster1 fqdn: nwdaf-portal.ocnwdaf-ns.svc.sunstreaker port: 80 apiPrefix: /sunstreaker/ocnwdaf-ns/ocnwdaf - id: OCCNE-NWDAF-UI-instance1 type: NWDAF-API owner: Cluster1 fqdn: cap4c-api-gateway.ocnwdaf-ns.svc.sunstreaker port: 8080 apiPrefix: /sunstreaker/ocnwdaf-ns/ocnwdafapi -
Move to the CNC Console IAM Attributes Section
Move to the CNC Console IAM attributes section and update the values as follows:
Update port to the same used by IAM LOC 244: publicHttpSignalingPort: 30085 If Static node port needs to be set, then set staticNodePortEnabled flag to true and provide value for staticNodePort. Else random node port will be assigned by K8 staticNodePortEnabled: true staticHttpNodePort: 30085 staticHttpsNodePort: 30053 -
Move to the CNC Console Core Attributes Section
Move to the CNC Console Core attributes section and update the values as follows:
Update port to the same used by cncc core LOC 244: publicHttpSignalingPort: 30085 If Static node port needs to be set, then set staticNodePortEnabled flag to true and provide value for staticNodePort. Else random node port will be assigned by K8 staticNodePortEnabled: true staticHttpNodePort: 30085 staticHttpsNodePort: 30053To identify the external IPs during installation, run the following command:
kubectl get pods -n ocnwdaf-ns -owide | grep portal -
Helm Install
Run the Helm install command in the folder where the custom yaml file is located. For example:
helm install cncc occncc-xx.x.x.tgz -f occncc_custom_values_xx.x.x.yaml -n cncc -
Monitor the Installation
To monitor the installation process, run the following command:
watch kubectl get pods -n cnccYou can access the IAM and CNC Console once the pods are in up and running state.
-
Verify IAM
Verify if IAM is running. For example:IAM: http://10.123.158.150:30085/ Default user: admin Default password: password -
Login to the CNC Console.
Provide the Username and Password.
Figure 2-4 Login
Click Login.
Integrate OCNWDAF and CNC Console
If CNC Console is already installed, ensure all the parameters are updated in the occncc_custom_values.yaml file. For information refer to Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
- Login to the CNC Console
- Click Clients option, In the Settings tab update the Root URL field with the IP on which CNC Console is running and the port defined on mcore-ingress-gateway service.
Figure 2-5 Clients
Click Save
- To add new user, click Users and click Add User. Provide a Username and fill the form. Click Save.
Figure 2-6 Add User
- Click Users, select the newly added user, go to the Role Mappings tab.
For example:
Figure 2-7 Role Mapping
Add NWDAF_READ and NWDAF_WRITE to the Assigned Roles.
- Use the Reset Password screen to create a new password for the user.
Figure 2-8 Reset Password
Access OCNWDAF GUI
To access OCNWDAF GUI, follow the procedure mentioned in the "Accessing CNC Console" section of Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Uninstall CNC Console
To uninstall CNC Console, run the following commands:
helm delete cncc -n cnccDelete all jobs, run the following command:
kubectl delete jobs --all -n cncc