2 Installing OCNADD
This chapter provides information about installing Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD) on the supported platforms.
- Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment (CNE)
- VMware Tanzu Application Platform (TANZU)
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
Note:
This document describes the OCNADD installation on CNE. However, the procedure for installation on OCI and TANZU is similar to the installation on CNE. Any steps unique to OCI or TANZU platform are mentioned explicitly in the document.2.1 Prerequisites
Before installing and configuring OCNADD, make sure that the following requirements are met:
2.1.1 Software Requirements
This section lists the software that must be installed before installing OCNADD:
Table 2-1 Mandatory Software
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes | 1.33.x, 1.32.x |
| Helm | 3.15.2 |
| Docker/Podman | 4.6.1 |
| OKE (on OCI) | 1.27.x |
Note:
- OCNADD 25.2.200 supports CNE 25.2.1xx and 25.1.2xx.
echo $OCCNE_VERSIONkubectl versionhelm versionNote:
- Starting with CNE 1.8.0, Podman is the preferred container platform instead of docker. For more information on installing and configuring Podman, see the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
If you are installing OCNADD on TANZU, the following software must be installed:
Table 2-2 Mandatory Software
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| Tanzu | 1.4.1 |
tanzu versionNote:
Tanzu was supported in release 22.4.0. Release 25.2.200 has not been tested on Tanzu.Depending on the requirement, you may have to install additional software while deploying OCNADD. The list of additional software items, along with the supported versions and usage, is given in the following table:
Table 2-3 Additional Software
| Software | Version | Required For |
|---|---|---|
| Prometheus-Operator | 2.52.0 | Metrics |
| Metallb | 0.14.4 | LoadBalancer |
| cnDBTier | 25.2.1xx and 25.1.2xx | MySQL Database |
| Druid | 33.0.0 | It is required for extended storage integration with the Druid database. |
Note:
- Some of the software are available by default if OCNADD is getting deployed in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment (CNE).
- Install the additional software if any of them are not available by default with CNE.
- If you are deploying OCNADD in any other environment, for instance, TANZU, then all the above mentioned software must be installed before installing OCNADD.
- On OCI, the Prometheus-Operator is not required. The metrics and alerts will be managed using OCI monitoring and Alarm services.
helm ls -A2.1.2 Environment Setup Requirements
This section provides information on environment setup requirements for installing Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD).
Network Requirements
The Data Director services, such as Kafka and Redundancy Agent, require external access. These services are created as load balancer services, and the service FQDNs should be used for communication with them. Additionally, the service FQDNs must be configured in the DNS server.
CNLB Network and NADs for Data Director
Egress NADs
- Customer must know or create Egress NADs for its third-party feed endpoint
requirements before CNLB CNE cluster installation. The Egress NADs are required
to be defined in the
cnlb.inifile of OCCNE for the CNLB support. - The Egress NADs are required to be created for the following traffic segregation
scenarios:
- Separate Egress NAD per third-party destination endpoint per third-party feed: Each destination endpoint of the consumer adapter will have its separate egress network via a separate Egress NAD managed by CNLB.
- Separate Egress NAD per third-party feed: Each consumer adapter feed will have its separate egress network via a separate Egress NAD managed by CNLB.
- Separate Egress NAD per OCNADD: All the consumer adapter feeds will have only one separate network via a separate Egress NAD managed by CNLB.
Ingress NADs
- Customer must know or create the required CNLB IPs (external IPs) and ingress OCNADDs for the Data Director Ingress Adapter service.
- Based on the ingress traffic segregation requirement for non-Oracle NFs, the
required CNLB IPs (external IPs) and ingress OCNADDs need to be configured for
the Ingress Adapter in advance. The ingress OCNADDs are required to be defined
in the
cnlb.inifile of OCCNE for CNLB support. - Each Ingress Adapter service instance must have an external IP and a corresponding ingress OCNADD created and managed by the CNLB.
- Customer must know or create the ingress OCNADD for the redundancy agent external access and IP.
- Customer must know or create the required CNLB IPs (external IPs) and ingress OCNADDs for the Data Director Kafka service. The number of ingress OCNADDs and external IPs must be the same as the number of Kafka brokers in the cluster. This must be done for every additional worker group that is present or needs to be created in the future.
- The required CNLB external IP and corresponding ingress OCNADD must be
configured in the
cnlb.inifile of OCCNE for CNLB support.
Ingress-Egress NADs
- Customer must know or create the required CNLB IPs (external IPs) and ingress-egress NADs for the Data Director Gateway service when external access is enabled for gateway services.
- Gateway service present in each NAD group must have an external IP and a corresponding ingress-egress NAD created and managed by the CNLB.
- The required CNLB external IP and corresponding ingress-egress NAD must be
configured in the
cnlb.inifile of OCCNE for CNLB support.
For more information on the CNLB and NADs, refer to the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Environment Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Environment Setup on OCCNE
Network Access
The Kubernetes cluster hosts must have network access to the following repositories:
- Local container image repository: It contains the OCNADD
container images. To check if the Kubernetes cluster hosts can access the local
container image repository, pull any image with an image-tag using the following
command:
podman pull docker-repo/image-name:image-tagwhere,
docker-repois the IP address or hostname of the container image repository.image-nameis the container image name.image-tagis the tag assigned to the container image used for the OCNADD pod.
- Local Helm repository: It contains the OCNADD Helm charts.
To check if the Kubernetes cluster hosts can access the local Helm repository,
run the following
command:
helm repo update - Service FQDN or IP Addresses of the required OCNADD services, for instance, Kafka Brokers, must be discoverable from outside of the cluster. This information should be publicly exposed so that Ingress messages to OCNADD can come from outside of Kubernetes.
Environment Setup on OCI
OCNADD can be deployed in OCI. While deploying OCNADD on OCI, the user must use the Operator instance/VM instead of Bastion Host.
For OCI infrastructure, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core OCI Adaptor, NF Deployment on OCI Guide.
After completing the OCI infrastructure setup requirements, proceed to the next section.
Client Machine Requirements
Note:
Run all thekubectl and helm commands in this guide on a
system depending on the infrastructure and deployment. This system could be a client
machine, such as a virtual machine, server, local desktop, etc.
This section describes the requirements for client machine, that is, the machine used by the user to run deployment commands.
The client machine must meet the following requirements:
- network access to the helm repository and docker image repository.
- configured Helm repository
- network access to the Kubernetes cluster.
- required environment settings to run the
kubectl,podman, anddockercommands. The environment should have privileges to create namespace in the Kubernetes cluster. - The Helm client installed with the push plugin. Configure the environment in such a manner that the
helm installcommand deploys the software in the Kubernetes cluster.
Server or Space Requirements
- Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide
- Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Benchmarking Guide
- Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, cnDBTier Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide
cnDBTier Requirement
Note:
Obtain the values of the cnDBTier parameters listed in the
section "cnDBTier Customization Parameters" from the delivered ocnadd_dbtier_custom_values.yaml
file and use these values in the new
ocnadd_dbtier_custom_values.yaml file if the parameter
values in the new file differ from those in the delivered file.
If you already have an older version of
cnDBTier, upgrade cnDBTier with
resources recommended for OCNADD by customizing the
ocnadd_dbtier_custom_values.yaml file in the
custom_templates folder of the OCNADD package with the
required deployment parameters. Use the same PVC size as in the previous
release. For more information, see the section "cnDBTier Customization Parameters."
OCNADD supports cnDBTier 25.2.1xx and 25.1.2xx in a CNE environment. cnDBTier must be up
and running before installing the Data Director. To install cnDBTier 25.2.2xx with resources recommended for OCNADD, customize the
ocnadd_dbtier_custom_values.yaml file in the custom_templates
folder in the OCNADD package with the required deployment parameters.
Note:
The ocnadd_dbtier_custom_values.yaml file in the DD
custom_templates.zip should normally correspond to the same version as the Data
Director; however, it may be possible that the cnDBTier custom values belong to
a different version than the Data Director. In this case, the
global.version parameter from the
ocnadd_dbtier_custom_values.yaml should be checked, and the
corresponding GA package of cnDBTier should be used for the installation or
upgrade of cnDBTier before installing/upgrading the Data Director package.
cnDBTier parameters for the Data Director may vary. For more information, see section cnDBTier Customization Parameters.
For more information about the cnDBTier installation procedure, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, cnDBTier Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Note:
For OCI Environment, use theStorageClass as oci-bv in cnDBTier charts. To
find the storage class name, run the below
command:kubectl get sc -n <namespace>2.1.3 Capacity Planning
2.1.3.1 OCNADD Deployment Models
- Model 1: OCNADD Management Group Services, Relay Agent Group Services and Mediation Group Services in same cluster
- Model 2: OCNADD Management Group Services, Relay Agent Group Services and Mediation Group Services in different cluster
- Model 3: OCNADD Management Group Services, Relay Agent Group Services and Mediation Group with Kafka only
Note:
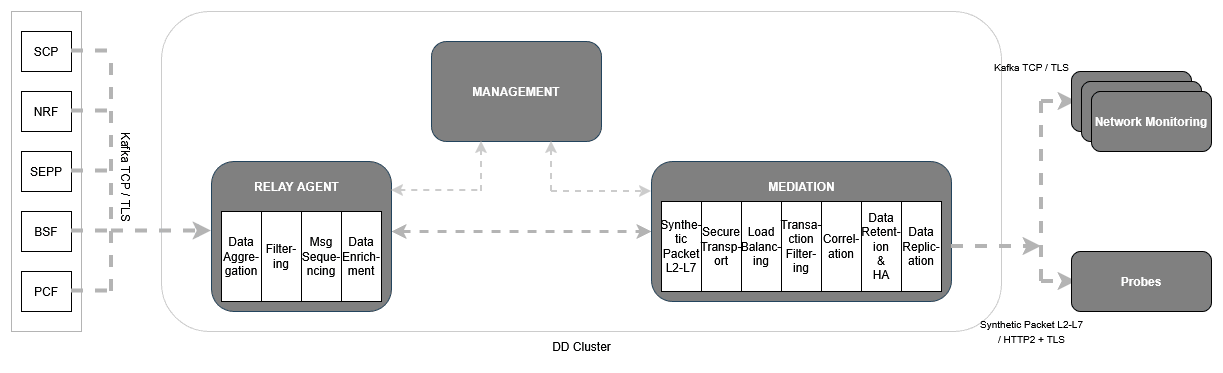
The Data Director supports egress adapters for outbound connections. The egress adapters add value to the message feed by filtering and synthesizing the packets before sending the messages out on the egress connection type 'HTTP/2' or 'Synthetic Feed'. If the customer selects a deployment model that does not include the Egress adapter, additional features such as synthetic packet generation will not be available, although the filtering and correlation features will be available using Kafka feeds only.2.1.3.1.1 Model 1: OCNADD Management Group Services, Relay Agent Group Services and Mediation Group Services in Same Cluster
This OCNADD deployment model includes all the services deployed in the same cluster. For
each OCNADD group, separate namespaces must be created during the deployment. In this
deployment option, all the features are available. This is the default model, and the
required services are enabled by default in each OCNADD group custom values file
(ocnadd-<ocnadd-group>-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml).
In this deployment model, the default Kafka storage options are as follows:
- Relay agent Kafka is enabled with the Volatile (RAM Drive) storage option.
- Mediation Kafka is deployed with the Persistence (Disk) storage option.
Use the UI to configure message feeds on OCNADD. The Oracle Producer NFs (SCP, NRF, SEPP, BSF, and PCF) copy the messages to their respective source topics.
Figure 2-1 Model 1
For this model, the user only needs to enable the required aggregation services in the
ocnadd-relayagent-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml. The default parameters are as below.
---
global:
ocnaddmanagement:
ocnaddalarm:
enabled: true
ocnaddconfiguration:
enabled: true
ocnaddhealthmonitoring:
enabled: true
ocnaddbackuprestore:
enabled: true
ocnadduirouter:
enabled: true
ocnaddgui:
enabled: true
ocnaddexport:
enabled: false
ocnaddmanagementgateway:
enabled: true
---
global:
ocnaddrelayagent:
ocnaddscpaggregation:
enabled: true
ocnaddseppaggregation:
enabled: false # Enable to 'true' if data streaming from SEPP is required
ocnaddnrfaggregation:
enabled: false # Enable to 'true' if data streaming from NRF is required
ocnaddbsfaggregation:
enabled: false # Enable to 'true' if data streaming from BSF is required
ocnaddpcfaggregation:
enabled: false # Enable to 'true' if data streaming from PCF is required
ocnaddkafka:
enabled: true
ocnaddrelayagentgateway:
enabled: true
---
global:
ocnaddmediation:
ocnaddkafka:
enabled: true
ocnaddadmin:
enabled: true
ocnaddfilter:
enabled: false
ocnaddmediationgateway:
enabled: true
2.1.3.1.2 Model 2: OCNADD Management Group Services, Relay Agent Group Services and Mediation Group Services in Different Clusters
In this OCNADD deployment model, all the OCNADD groups, for example the Management group, Relay agent group and Mediation group, are deployed in different clusters. In this deployment option, all the features are available.
For this deployment model, the default Kafka storage options are as follows:
- Relay agent Kafka is enabled with the Volatile (RAM Drive) storage option.
- Mediation Kafka is deployed with the Persistence (Disk) storage option.
Figure 2-2 Model 2
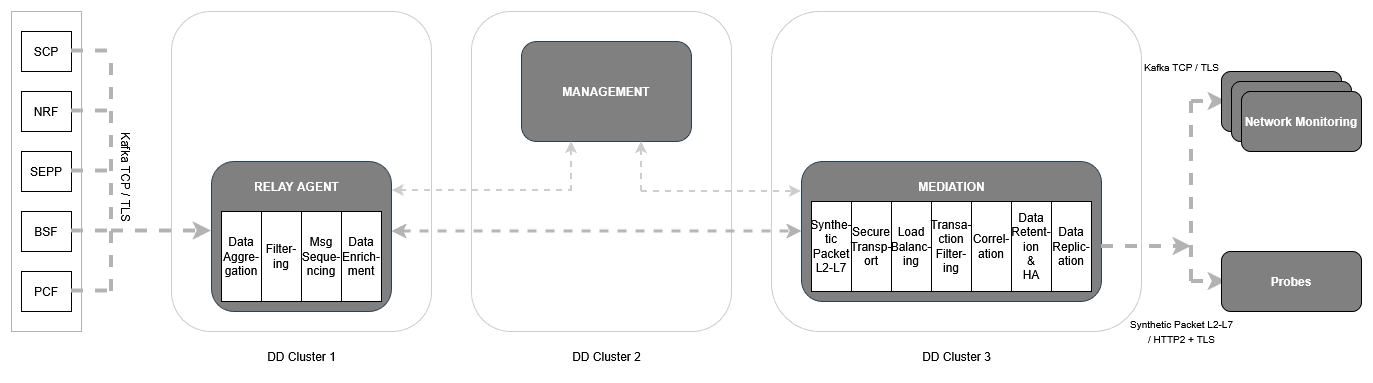
To utilise this deployment option, ensure that mTLS is enabled across OCNADD for all groups. Additionally, configure all gateways and the mediation Kafka cluster with external access enabled.
For detailed instructions on enabling External Communication Between Gateways and Enable External Access For Kafka Cluster, refer to the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide.
In this deployment mode, various combinations are supported. Some possible deployment combinations include:
- Management Group Services and Relay Agent Group Services are deployed in the same cluster, and Mediation Group Services are deployed in a different cluster (external access for Mediation Kafka must be enabled).
- Management Group Services and Mediation Group Services are deployed in the same cluster, and Relay Agent Group Services are deployed in a different cluster (external access for Mediation Kafka must be enabled).
- Relay Agent Group Services and Mediation Group Services are deployed in the same cluster, and Management Group Services are deployed in a different cluster.
Recommendation
This deployment option is recommended only when the target cluster lacks the necessary hardware resources or has suboptimal disk throughput. Note that this configuration may result in higher end-to-end latency.
2.1.3.1.3 Model 3: OCNADD Management Group Services, Relay Agent Group Services and Mediation Group with Kafka Only
Use this model when the customer does not wish to receive the message feed using HTTP/2 or TCP connection mode. The third-party monitoring application available to the customer can consume data directly from the Kafka cluster. The Egress adapter is not required in this deployment model; however, the OCNADD deployment requires common services such as UI, Configuration, Health Monitoring, Alarm, and Admin. Features like correlation-id-based load balancing, synthetic feed, and HTTP/2 feeds are unavailable in this deployment model, although the filtering and correlation features will be available using Kafka feeds only.
This model saves the Egress adapter resource; however, additional resources will be
required for Filtering and Correlation services once these features are used in the
configurations from the UI. The export feature is also possible; however, it has to be
enabled in the charts by enabling the ocnaddexport service and further
export configuration from the UI.
Figure 2-3 Model 3
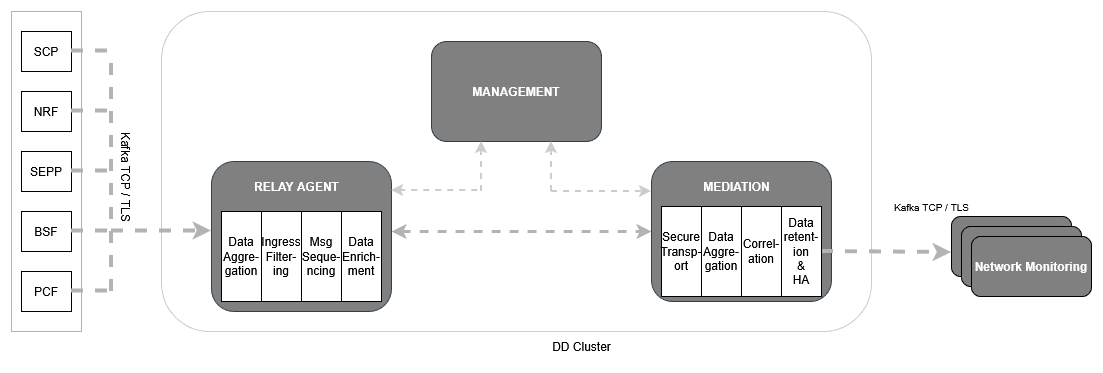
This deployment model supports a direct Kafka feed. For more information, see the External Kafka Feeds section in the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide.
In this deployment option, Mediation Group Services can co-exist with Relay Agent Group Services and Management Group Services, or they can exist independently in a separate cluster. Higher end-to-end latency may be reported if the Relay Agent Group and Mediation Group are deployed in separate clusters.
The default Kafka storage options for this model are as follows:
- Relay agent Kafka is enabled with the Volatile (RAM Drive) storage option.
- Mediation Kafka is deployed with the Persistence (Disk) storage option.
The default parameters are as below.
---
global:
ocnaddmanagement:
# services provided for management
ocnaddalarm:
enabled: true
ocnaddconfiguration:
enabled: true
ocnaddhealthmonitoring:
enabled: true
ocnaddbackuprestore:
enabled: true
ocnadduirouter:
enabled: true
ocnaddgui:
enabled: true
ocnaddexport:
enabled: false ## --> Enable to 'true' if XDR Export or Trace feature is required
ocnaddmanagementgateway:
enabled: true
---
global:
ocnaddrelayagent:
ocnaddscpaggregation:
enabled: true
ocnaddseppaggregation:
enabled: false ## --> Enable to 'true' if data streaming from SEPP is required
ocnaddnrfaggregation:
enabled: false ## --> Enable to 'true' if data streaming from NRF is required
ocnaddbsfaggregation:
enabled: false ## --> Enable to 'true' if data streaming from BSF is required
ocnaddpcfaggregation:
enabled: false ## --> Enable to 'true' if data streaming from PCF is required
ocnaddkafka:
enabled: true
ocnaddrelayagentgateway:
enabled: true
---
global:
ocnaddmediation:
ocnaddkafka:
enabled: true
ocnaddadmin:
enabled: true
ocnaddfilter:
enabled: false ## --> Enable to 'true' if FILTERED or CORRELATED_FILTERED kafka Feeds are required
ocnaddmediationgateway:
enabled: true
---- The aggregation service aggregates traffic from the source topics to the Kafka main topic. Choosing any specific combination of NFs for aggregation rules is not possible. The total traffic received is aggregated and available to the consumers.
- The third-party consumer application must create external Kafka feeds to connect with the Kafka cluster, which allows it to consume messages directly from the designated topic.
2.1.3.2 Resource Comparison
The following table depicts the resource savings in the various deployment models:
Table 2-4 Resource Comparison
| Deployment Model | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common Services | Available | Available | Available |
| Aggregation Service | Available | Available | Available |
| Adapter Service | Available | Available | Not Available |
| Kafka | Available | Available | Available |
| Resource Saving (approx. %) | 0 | 0 | 60 |
| Supported Egress Interfaces |
HTTP/2 TCP KAFKA |
HTTP/2 TCP KAFKA |
KAFKA |
The customer can customize the OCNADD deployment based on the identified resources. Plan the resources based on the deployment model and services required for the specific model.
2.1.3.3 Key Points to Consider for All Deployment Models
- The message feeds must be created from the UI, and aggregation rules determine the source NF combinations for aggregation.
- Metrics related to the feed are available on the UI.
- OCNADD alarms can be viewed on the UI.
2.1.3.4 Kafka Storage Mode Comparison
The following table outlines the benefits of different Kafka storage options. Choose the one that meets your requirements:
Table 2-5 Kafka Storage Mode Comparison
| Parameters | Relay Agent Kafka Persistence Storage (Disk) – Mediation Kafka Persistence Storage (Disk) | Relay Agent Kafka Volatile Storage (RAM Drive) – Mediation Kafka Persistence Storage (Disk) (Default) | Relay Agent Kafka Volatile Storage (RAM Drive) – Mediation Kafka Volatile Storage (RAM Drive) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Throughput | Data processing speed is largely limited by disk read/write performance | Delivers high throughput; the relay-agent Kafka runs on a RAM drive for faster I/O, while disk is used only by the Mediation Kafka, reducing overall disk usage | Delivers very high throughput as broker processing and I/O latency are minimized |
| Latency | Higher latency than RAM drives due to slower disk read/write performance | Offers low latency, but overall latency is constrained by disk I/O since Mediation Kafka uses disk storage mode | Ultra-low traffic processing latency as RAM drive read/write can be in microseconds to low milliseconds as compared to Disk |
| Data Retention and Storage | Supports high data retention; achieving longer retention requires additional disk capacity however, it is less expensive than RAM drive. Recommended for use cases where data retention is a priority. | Supports high data retention since Mediation Kafka can store data longer, but it requires additional disk capacity. Preferable for workloads where throughput and retention are of coequal priorities | Can support higher data retention, but requires substantially more RAM, which can be expensive. Best suited for scenarios with low retention needs. |
During installation, user can choose between RAM and CEPH storage modes for both the Relay Agent and Mediation Kafka clusters based on the requirements.
2.1.3.5 Source NF and OCNADD Relay Agent Kafka Access Modes
Choose the Relay Agent Kafka access mode for forwarding traffic between source Network Functions and OCNADD.
The following access modes are supported for the Relay Agent Kafka broker:
NF producers and OCNADD Relay Agent Kafka in the same cluster
In this mode, the Kafka cluster is not exposed externally. By default, the parameters to
enable external access for Kafka are set to false, hence no changes are
required.
- All three ports can be used, for example
9092forPLAIN_TEXT,9093forSSL, and9094forSASL_SSL. However, the9092port is non-secure and therefore not recommended for use. -
It is recommended to configure individual broker IPs/FQDNs in the Kafka bootstrap server list.
kafka-broker-0.kafka-broker-headless.<namespace>.svc.<domain>:9093/9092 kafka-broker-1.kafka-broker-headless.<namespace>.svc.<domain>:9093/9092 kafka-broker-2.kafka-broker-headless.<namespace>.svc.<domain>:9093/9092 kafka-broker-3.kafka-broker-headless.<namespace>.svc.<domain>:9093/9092
NF producers and OCNADD Relay Agent Kafka in different clusters
In this mode, the user must enable external access to the Kafka cluster using a
LoadBalancer service type. Certificates must also be created with
the LoadBalancer IP addresses assigned to the broker. The user can create certificates
manually, using the generate-certs script, or through OCCM. For more details, see the
Oracle Communications Network Analytics Suite User Guide, specifically the
Enable External Access For Kafka Cluster section.
2.1.3.6 Resource Requirements
This section describes the resource requirements to install and run Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD).
OCNADD deployment consists of a management group and worker group(s). Traffic processing services are managed within the worker group, while configuration and administration services are managed within the management group.
Resource planning for OCNADD should consider the following points:
- There will be only one management group consisting of the following services:
- ocnaddconfiguration
- ocnaddalarm
- ocnaddhealthmonitoring
- ocnaddui
- ocnadduirouter
- ocnaddredundancyagent
- ocnaddexport
- ocnaddmanagementgateway
- The Worker Group is administered by the Management Group. A worker group is
considered a logical entity that includes the following two OCNADD sub-groups and
their respective services:
- Relay Agent Group
- ocnaddkafka
- kraft-controller
- ocnaddnrfaggregation
- ocnaddseppaggregation
- ocnaddscpaggregation
- ocnaddpcfaggregation
- ocnaddbsfaggregation
- ocnaddrelayagentgateway
- Mediation Group
- ocnaddkafka
- kraft-controller
- ocnaddcorrelation
- ocnaddfilter
- ocnaddadmin
- ocnaddconsumeradapter
- ocnaddstorageadapter
- ocnaddmediationgateway
- Relay Agent Group
- The customer needs to plan for the resources corresponding to the management group and worker group services required.
OCNADD Resource Requirements
This following default profile can stream data from NFs up to 15K MPS and can be scaled to handle up to 100K MPS for HTTP2/Synthetic feed when "weighted_lb" feature is not enabled.
Table 2-6 OCNADD Resource Requirements (All DD features with Default profile)
| OCNADD Services | vCPU Req | vCPU Limit | Memory Req (Gi) | Memory Limit (Gi) | Min Replica | Max Replica | Partitions | Topic Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Management Services | ||||||||
| ocnaddconfiguration | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - |
| ocnaddalarm | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - |
| ocnaddhealthmonitoring | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - |
| ocnaddgui | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - |
| ocnadduirouter | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - |
| ocnaddredundancyagent | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 4 | - | - |
| ocnaddexport | 2 | 4 | 4 | 64 | 1 | 2 | - | - |
| ocnaddmanagementgateway | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - |
| Relay Agent Services | ||||||||
| ocnaddkafka | 6 | 6 | 64 | 64 | 4 | 4 | - | - |
| kraftcontroller | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | - |
| ocnaddscpaggregation | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 18 | SCP |
| ocnaddnrfaggregation | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 6 | NRF |
| ocnaddseppaggregation | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 12 | SEPP |
| ocnaddpcfaggregation | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 12 | PCF |
| ocnaddbsfaggregation | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 6 | BSF |
| ocnaddrelayagentgateway | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - |
| Mediation Services | ||||||||
| ocnaddadminservice | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - |
| <app-name>-adapter | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 14 | 126 | MAIN |
| ocnaddkafka | 6 | 6 | 64 | 64 | 4 | 4 | - | - |
| kraftcontroller | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | - |
| ocnaddcorrelation | 3 | 3 | 24 | 64 | 1 | 4 | - | - |
| ocnaddfilter | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 4 | - | - |
| ocnaddstorageadapter | 3 | 3 | 24 | 64 | 1 | 4 | - | - |
| ocnaddingressadapter | 3 | 3 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 7 | - | - |
| ocnaddmediationgateway | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - |
Note:
For detailed information on the OCNADD profiles, see the "Profile Resource Requirements" section in the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Benchmarking Guide.
Ephemeral Storage Requirements
Table 2-7 Ephemeral Storage
| Service Name | Ephemeral Storage (min) in Mi | Ephemeral Storage (max) in Mi |
|---|---|---|
| Management Services | ||
| ocnaddconfiguration | 100 | 1000 |
| ocnaddalarm | 100 | 500 |
| ocnaddhealthmonitoring | 100 | 500 |
| ocnaddredundancyagent | 100 | 500 |
| ocnaddexport | 100 | 2Gi |
| ocnaddmanagementgateway | 100 | 500 |
| ocnadduirouter | 500 | 500 |
| Relay Agent Services | ||
| ocnaddscpaggregation | 500 | 500 |
| ocnaddnrfaggregation | 500 | 500 |
| ocnaddseppaggregation | 500 | 500 |
| ocnaddpcfaggregation | 500 | 500 |
| ocnaddbsfaggregation | 500 | 500 |
| ocnaddrelayagentgateway | 100 | 500 |
| Mediation Services | ||
| ocnaddadminservice | 100 | 200 |
| <app-name>-adapter | 1000 | 1000 |
| ocnaddcorrelation | 100 | 500 |
| ocnaddfilter | 100 | 500 |
| ocnaddstorageadapter | 400 | 800 |
| ocnaddingressadapter | 400 | 800 |
| ocnaddmediationgateway | 100 | 500 |
2.2 Installation Sequence
This section provides information on how to install Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD).
Note:
- It is recommended to follow the steps in the given sequence for preparing and installing OCNADD.
- Make sure you have the required software installed before proceeding with the installation.
- This is the installation procedure for a standard OCNADD deployment. To install a more secure deployment (such as, adding users, changing password, enabling mTLS, and so on) see, Oracle Communications Network Analytics Suite Security Guide.
2.2.1 Pre-Installation Tasks
To install OCNADD, perform the preinstallation steps described in this section.
Note:
The kubectl commands may vary based on the platform used for
deploying OCNADD. Users are recommended to replace kubectl with the
environment-specific command-line tool used to configure Kubernetes resources
through the kube-api server. The instructions provided in this document are as per
the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment (CNE) version
of the kube-api server.
2.2.1.1 Downloading OCNADD Package
To download the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD) package from MOS, perform the following steps:
- Log in to My Oracle Support with your credentials.
- Select the Patches and Updates tab to locate the patch.
- In the Patch Search window, click Product or Family (Advanced).
- Enter "Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director" in the Product field, select "Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director 25.2.200.0.0 from Release drop-down list.
- Click Search. The Patch Advanced Search Results displays a list of releases.
- Select the required patch from the search results. The Patch Details window opens.
- Click Download. File Download window appears.
- Click the <p********_<release_number>_Tekelec>.zip file to download the OCNADD package file.
- Extract the zip file to download the network function patch to the system where the network function must be installed.
To download the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director package from the edelivery portal, perform the following steps:
- Login to the edelivery portal with your credentials. The following screen appears:
Figure 2-4 edelivery portal
- Select the Download Package option, from All Categories drop down list.
- Enter Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director in the search bar.
Figure 2-5 Search
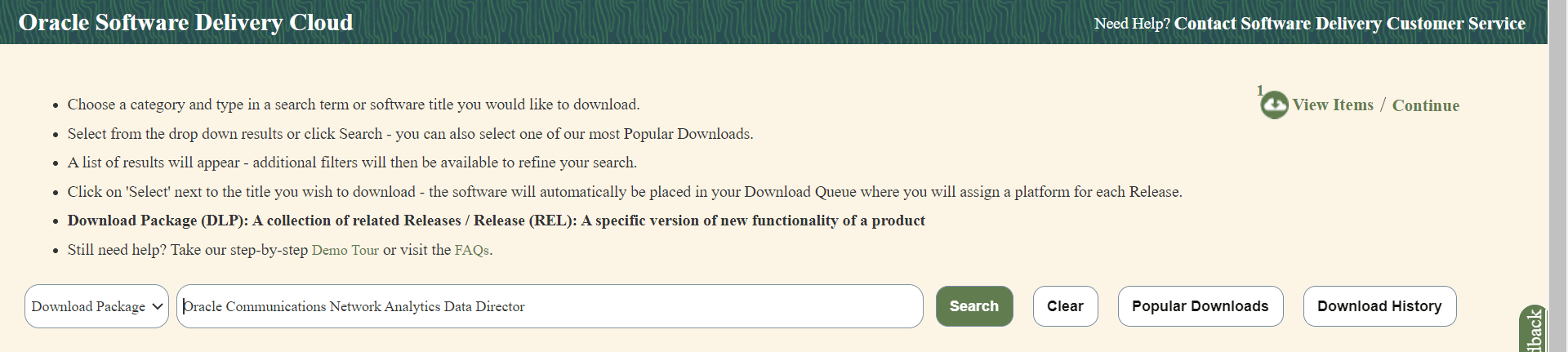
- List of release packages available for download are displayed on the screen. Select the release package you want to download, the package automatically gets downloaded.
2.2.1.2 Pushing the Images to Customer and OCI Registry
Container Images
Note:
The kubectl commands may vary based on the platform used for deploying
OCNADD. Users are recommended to replace kubectl with the
environment-specific command-line tool used to configure Kubernetes resources through the
kube-api server. The instructions provided in this document are as per the Oracle
Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment (CNE) version of the kube-api
server.
Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD) deployment package includes ready-to-use container images and helm charts to help orchestrate containers in Kubernetes. The communication between Pods of services of OCNADD are preconfigured in the helm charts.
The following table lists the container images of OCNADD. The table depicts the default OCNADD microservices and their respective images. However, a few more necessary images are delivered as part of the OCNADD package; you must push these images along with the default images. The image names are suffixed with the OCNADD release name.
Table 2-8 Container Images for OCNADD
| Service Name | Container Image Name | Image Tag |
|---|---|---|
| Management Services | ||
| OCNADD-Configuration | ocnaddconfiguration | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-Alarm | ocnaddalarm | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-HealthMonitoring | ocnaddhealthmonitoring | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-UIRouter | ocnadduirouter | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-GUI | ocnaddgui | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-Redundancyagent | ocnaddredundancyagent | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-Export | ocnaddexport | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-ManagementGateway | ocnaddmanagementgateway | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-Backup-Restore | ocnaddbackuprestore | 25.2.200 |
| Relay Agent Services | ||
| OCNADD-Kafka | kafka-broker-x | 4.1.0:25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-Aggregation |
ocnaddnrfaggregation ocnaddscpaggregation ocnaddseppaggregation ocnaddnonoracleaggregation ocnaddpcfaggregation ocnaddbsfaggregation |
25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-RelayAgentGateway | ocnaddrelayagentgateway | 25.2.200 |
| Mediation Services | ||
| OCNADD-Kafka | kafka-broker-x | 4.1.0:25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-Admin | ocnaddadminservice | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-ConsumerAdapter | ocnaddconsumeradapter | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-Filter | ocnaddfilter | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-Correlation | ocnaddcorrelation | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-StorageAdapter | ocnaddstorageadapter | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-IngressAdapter | ocnaddingressadapter | 25.2.200 |
| OCNADD-MediationGateway | ocnaddmediationgateway | 25.2.200 |
Note:
- The service image names are prefixed with the OCNADD release name.
- The above table depicts the default OCNADD microservices and their respective images. However, a few more necessary images are delivered as a part of the OCNADD package, make sure to push all the images delivered with the package.
Pushing OCNADD Images to Customer Registry
To push the images to the registry:
- Untar the OCNADD package zip file to retrieve the OCNADD docker image tar
file:
The directory consists of the following:tar -xvzf ocnadd_pkg_25_2_200.tar.gz cd ocnadd_pkg_25_2_200 tar -xvzf ocnadd-25.2.200.tar.gz- OCNADD Docker Images
File:
ocnadd-images-25.2.200.tar - Helm
File:
ocnadd-25.2.200.tgz - Readme txt
File:
Readme.txt - Custom
Templates:
custom_templates.zip - ssl_certs
folder:
ssl_certs
- OCNADD Docker Images
File:
- Run one of the following commands to first change the directory and then
load the
ocnadd-images-25.2.200.tarfile:cd ocnadd-package-25.2.200 - Run one of the following command to load the OCNADD images. Use the
appropriate group name (management, relayagent, or mediation) in place of
"<ocnadd-group>" for the images user is intended to
load.
docker load --input /IMAGE_PATH/ocnadd-images-25.2.200.tarpodman load --input /IMAGE_PATH/ocnadd-images-25.2.200.tarExample: Considering podman for this example to load imagespodman load --input /IMAGE_PATH/ocnadd-management-images-25.2.200.tar podman load --input /IMAGE_PATH/ocnadd-relayagent-images-25.2.200.tar podman load --input /IMAGE_PATH/ocnadd-mediation-images-25.2.200.tar - Run one of the following commands to verify if the images are
loaded:
docker imagespodman imagesVerify the list of images shown in the output with the list of images shown in the table Table 2-8. If the list does not match, reload the image tar file.
- Run one of the following commands to tag each imported image to the
registry:
docker tag <image-name>:<image-tag> <docker-repo>/<image-name>:<image-tag>podman tag <image-name>:<image-tag> <docker-repo>/<image-name>:<image-tag> - Run one of the following commands to push the image to the
registry:
docker push <docker-repo>/<image-name>:<image-tag>podman push <podman-repo>/<image-name>:<image-tag>Note:
It is recommended to configure the docker certificate before running the push command to access customer registry through HTTPS, otherwise, docker push command may fail. - Run the following command to push the helm charts to the helm
repository:
helm push <image_name>.tgz <helm_repo> - Run the following command to extract the helm
charts:
tar -xvzf ocnadd-25.2.200.tgz - Run the following command to unzip the custom_templates.zip file.
unzip custom_templates.zip
Pushing OCNADD Images to OCI Registry
To push the images to the registry:
- Untar the OCNADD package zip file to retrieve the OCNADD docker image tar
file:
The directory consists of the following:tar -xvzf ocnadd_pkg_25_2_200.tar.gz cd ocnadd_pkg_25_2_200 tar -xvzf ocnadd-25.2.200.tar.gz- OCNADD Docker Images
File:
ocnadd-images-25.2.200.tar - Helm
File:
ocnadd-25.2.200.tgz - Readme txt
File:
Readme.txt - Custom
Templates:
custom_templates.zip - ssl_certs
folder:
ssl_certs
- OCNADD Docker Images
File:
- Run one of the following commands to first change the directory and then
load the
ocnadd-images-25.2.200.tarfile:cd ocnadd-package-25.2.200 - Run one of the following command to load the OCNADD images. Use the
appropriate group name (management, relayagent, or mediation) in place of
"<ocnadd-group>" for the images user is intended to
load.
docker load --input /IMAGE_PATH/ocnadd-images-25.2.200.tarpodman load --input /IMAGE_PATH/ocnadd-images-25.2.200.tarExample: Considering podman for this example to load imagespodman load --input /IMAGE_PATH/ocnadd-management-images-25.2.200.tar podman load --input /IMAGE_PATH/ocnadd-relayagent-images-25.2.200.tar podman load --input /IMAGE_PATH/ocnadd-mediation-images-25.2.200.tar - Run one of the following commands to verify if the images are
loaded:
docker imagespodman imagesVerify the list of images shown in the output with the list of images shown in the table Table 2-8. If the list does not match, reload the image tar file.
- Run the following commands to log in to the OCI
registry:
docker login -u <REGISTRY_USERNAME> -p <REGISTRY_PASSWORD> <REGISTRY_NAME>podman login -u <REGISTRY_USERNAME> -p <REGISTRY_PASSWORD> <REGISTRY_NAME># It will ask for password# Enter the password generated while creating the auth token.Where,
REGISTRY_NAMEis<Region_Key>.ocir.ioREGISTRY_USERNAMEis<Object Storage Namespace>/<identity_domain>/email_idREGISTRY_PASSWORDis the Authtocken generated by the user.
For the details about the Region Key, refer to Regions and Availability Domains.
Identity Domain will the domain,to which the user is present.
Object Storage Namespace is available at OCI Console> Governanace & Administration> Account Management> Tenenancy Details> Object Storage Namespace.
- Run one of the following commands to tag each imported image to the
registry:
docker tag <image-name>:<image-tag> <docker-repo>/<image-name>:<image-tag>podman tag <image-name>:<image-tag> <docker-repo>/<image-name>:<image-tag> - Run one of the following commands to push the image to the
registry:
docker push <region>/<tenancy_namespace>/<repo-name>/<image-name>:<image-tag>podman push <region>/<tenancy_namespace>/<repo-name>/<image-name>:<image-tag>Note:
It is recommended to configure the docker certificate before running the push command to access OCI registry through HTTPS, otherwise, docker push command may fail. - Run the following command to push the helm charts to the helm
repository:
helm push <image_name>.tgz <helm_repo> - Run the following command to extract the helm
charts:
tar -xvzf ocnadd-25.2.200.tgz - Run the following command to unzip the custom_templates.zip file.
unzip custom_templates.zip
Note:
All the image repositories must be public. Run the following steps to make all image repositories public:- Go to OCI Console> Developer Services > Containers & Artifacts> Container Registry.
- Select the root Compartment.
- In the Repositories and Images Search option, the images will be listed. Select each image and click Change to Public. This step must be performed for all the images sequentially.
2.2.1.3 Creating OCNADD Namespace
This section explains how to verify or create new namespaces in the system. In this section, the namespaces for the management group and worker group should be created.
Naming Convention for Namespaces
While choosing the name of the namespace where you wish to deploy OCNADD, make sure the following requirements are met:
- starts and ends with an alphanumeric character
- contains 63 characters or less
- contains only alphanumeric characters or '-'
Note:
It is recommended to avoid using prefixkube- when creating namespace. This is
required as the prefix is reserved for Kubernetes system namespaces.
Verifying Namespaces
To verify if the required namespace already exists in the system, run the following command:
kubectl get namespacesIf the namespace exists, you may continue with the next steps of installation.
If the required namespace is not available, create a namespace using the following command:
Note:
The user must create the required namespaces for a centralized deployment with multiple worker groups. If the deployment mode is centralized with the default worker group, a single namespace is sufficient, and all Data Director services can be deployed within itCreating Namespaces
kubectl create namespace <ocnadd-group-namespace># To create Management group namespace
kubectl create namespace ocnadd-mgmt
# To create Relay Agent group namespace
kubectl create namespace ocnadd-relay
# To create Mediation group namespace
kubectl create namespace ocnadd-medkubectl get namespaces# kubectl get namepsaces
ocnadd-mgmt
ocnadd-rea
ocnadd-med 2.2.1.4 Creating Service Account, Role, and Role Binding
This section is optional and it describes how to manually create a service account, role, and rolebinding. It is required only when customer needs to create a role, rolebinding, and service account manually before installing OCNADD. Skip this if choose to create by default from helm charts.
In the case of centralized deployment, this procedure needs to be repeated for each of the management group and worker group(s).
Note:
The secret(s) should exist in the same namespace where OCNADD is getting deployed. This helps to bind the Kubernetes role with the given service account.Creating Service Account, Role, and RoleBinding
To create the service account, role, and rolebinding:
- Prepare the Resource File: Run the following command to create an OCNADD resource
file:
vi ocnadd-<ocnadd-group>-resource-file.yamlReplace
<ocnadd-group>with the required group name.For example:
vi ocnadd-management-resource-template.yaml - Update the OCNADD Resource Template: Update the created YAML file with
release-specific information. A sample template to update the YAML file is given
below:
## Sample template start # apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: <namespace>-sa-ocnadd namespace: <namespace> automountServiceAccountToken: false --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: name: <namespace>-cr rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods", "configmaps", "services", "secrets", "resourcequotas", "events", "persistentvolumes", "persistentvolumeclaims"] verbs: ["*"] - apiGroups: ["extensions"] resources: ["ingresses"] verbs: ["create", "get", "delete"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["nodes"] verbs: ["get"] - apiGroups: ["scheduling.volcano.sh"] resources: ["podgroups", "queues", "queues/status"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete", "update"] --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: name: <namespace>-crb roleRef: apiGroup: "" kind: Role name: <namespace>-cr subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: <namespace>-sa-ocnadd namespace: <namespace> --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: name: <namespace>-crb-policy roleRef: apiGroup: "" kind: ClusterRole name: psp:privileged subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: <namespace>-sa-ocnadd namespace: <namespace> --- ## Sample template end #Replace
<namespace>with the respective OCNADD group namespace. - Create Service Account, Role, and RoleBinding: Run the following command to
create the service account, role, and rolebinding for the OCNADD
group:
kubectl -n <ocnadd-group-namespace> create -f ocnadd-<ocnadd-group>-resource-file.yamlReplace
<ocnadd-group-namespace>with the namespace where the OCNADD group will be deployed.For example:
$ kubectl -n ocnadd-mgmt create -f ocnadd-management-resource-template.yaml
2.2.1.5 Configuring OCNADD Database
OCNADD microservices use MySQL database to store the configuration and run time data.
The database is managed by the helm pre-install hook. However, OCNADD requires the database administrator to create an admin user in MySQL database and provide the necessary permissions to access the databases. Before installing OCNADD it is required to create the MySQL user and databases.
Note:
- If the admin user is already available, then update the credentials,
such as username and password (base64 encoded) in
<charts_directory>/templates/ocnadd-secret-hook.yaml.. - If the admin user is not available, then create it using the
following procedure. Once the user is created, update the credentials for the
user in
<charts_directory>/templates/ocnadd-secret-hook.yaml..
Creating an Admin User in the Database
To create an admin user in the database:
- Run the following command to access the MySQL pod. Use the namespace in which
the
cnDBTieris deployed.kubectl -n <cndbtier-namespace> exec -it <mysql-pod-name> -- bashExample: The
occne-cndbtiernamespace is used. The default MySQL pod name isndbmysqld-0.kubectl -n occne-cndbtier exec -it ndbmysqld-0 -- bash - Run the following command to log in to the MySQL server using the MySQL
client:
$ mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -uroot -p Enter password: - To create an admin user, run the following
command:
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS '<ocnadd admin username>'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '<ocnadd admin user password>';Example:
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'ocdd'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'ocdd';Where:
<ocdd>is the admin username and<ocdd>is the password for the MySQL admin user. - Run the following command to grant the necessary permissions to the admin user
and run the FLUSH command to reload the grant
table:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'ocdd'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; - Access the
ocnadd-secret-hook.yamlfrom the OCNADD Helm files using the following path:ocnadd/templates/ocnadd-secret-hook.yaml - Update the following parameters in the
ocnadd-secret-hook.yamlwith the admin user credentials:data: MYSQL_USER: b2NkZA== MYSQL_ACCESS_KEY: b2NkZA== - To generate the base64-encoded user and password from the terminal, run the
following
command:
echo -n <string> | base64 -w 0Where
<string>is the admin username or password created in step 3.Example:
echo -n ocdd | base64 -w 0 b2NkZA==
Update Database Name
- Default Database Names:
configuration_schemaalarm_schemahealthdb_schemastorageadapter_schema
These correspond to the Configuration Service, Alarm Service, and Health Monitoring Service respectively.
- When to Update:
- If you plan to use the default database names, skip this step.
- If you want to use custom database names, you must modify them before installation.
- During Reinstallation:
Before reinstalling OCNADD, the four application databases must be removed manually.
Run the following command for each database:
drop database <dbname>; - Where to Update Database Names in Helm Charts:
To apply custom database names, update all occurrences of the required database names in the following file:
<charts_directory>/charts/ocnaddmanagement/ocdd-db-resource.sql
2.2.1.6 Configuring Secrets for Accessing OCNADD Database
The secret configuration for OCNADD database is automatically managed during the database creation the helm preinstall procedure.
2.2.1.7 Configuring IP Network
This section defines OCNADD IP configuration for a single stack (either only IPv4 or IPv6) or a dual stack supported infrastructure.
Note:
- The IP family remains fixed once OCNADD is deployed. To change the IP family, OCNADD must be redeployed.
- IPv6 support on OCI is not available in the current release.
- For CNE with support for IPv4 or IPv6 networks:
- IPv4 only Configurations: For the IPv4 network, update the
following parameters in
ocnadd-common-custom-values.yaml:global: ipConfigurations: ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack ipFamilies: ["IPv4"] - IPv6 only Configurations: For the IPv6 network, update the
following parameters in
ocnadd-common-custom-values.yaml:global: ipConfigurations: ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack ipFamilies: ["IPv6"]
- IPv4 only Configurations: For the IPv4 network, update the
following parameters in
2.2.1.8 Configuring SSL or TLS Certificates
In OCNADD, you can create SSL or TLS certificates using one of the following methods:
- Certificate generation using OCNADD script
- Certificate generation through Oracle Communication Certificate Manager (OCCM)
For step-by-step instructions on generating certificates, please refer to the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Suite Security Guide in the "Certificate and Secret Generation" section.
2.2.1.9 Configuring ServiceMonitor in OCCNE-INFRA
This section defines OCCNE-INFRA OCNADD ServiceMonitor configuration to scrape Kafka Prometheus metrics.
ocnadd-servicemonitorfile
cd ocnadd-package-25.2.200
sudo cp custom_templates/occne_ocnadd_servicemonitor.yaml <path>/occne_ocnadd_servicemonitor.yaml
Log in as root or any user with admin privileges and execute the following command to apply:
kubectl -n occne-infra apply -f <path>/occne_ocnadd_servicemonitor.yaml
2.2.2 Installation Tasks
Note:
Before starting the installation tasks, ensure that the Prerequisites and Pre-Installation Tasks are completed.2.2.2.1 Installing OCNADD Package
This section describes how to install the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD) package. OCNADD deployment now has three groups, that is, management, relayagent, and mediation.
Refer to the following steps to install different OCNADD groups:
Installing OCNADD Management Group
- Create OCNADD Namespace: Create the OCNADD namespace for the Management Group, if not already created. For more information, see Creating OCNADD Namespace.
- Creating Service Account, Role, and Role Binding: If the user has opted to manually create a service account, role, and role binding, follow the steps outlined in the Creating Service Account, Role, and Role Binding section.
- Generate Certificates: Follow the steps outlined in the Configuring SSL or TLS Certificates section to complete the certificate generation process for the Management Group if it is not performed.
- Update Database Parameters: To update the database parameters, see Configuring OCNADD Database.
- Update Custom Values file: Create a copy of the custom values for the
Management Group from the
ocnadd-package-25.2.200folder as shown below:# cd ocnadd-package-25.2.200 # cp custom_templates/ocnadd-management-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml ocnadd-management-custom-values-25.2.200-mgmt-group.yamlUpdate the
ocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlandocnadd-management-custom-values-25.2.200-mgmt-group.yaml(depending on the type of deployment model) with the required parameters. For more information on how to access and update the custom values files, see Customizing OCNADD.If OCCM is used to create the certificates, update the mandatory parameters specified in Helm Parameter Configuration for OCCM.
- Installing Management Group:
- Modify the
ocnadd-management-custom-values-25.2.200-mgmt-group.yamlfile created above and update it as shown below:`global.ocnaddmanagement.cluster.namespace.name`: ocnadd-mgmt ## ---> update it with namespace created for management group `global.ocnaddmanagement.cluster.serviceAccount.create`: true ## ---> update this to false only if service account is created manually `global.ocnaddmanagement.cluster.clusterRole.create`: true ## ---> update this to false only if cluster role is created manually `global.ocnaddmanagement.cluster.clusterRoleBinding.create`: true ## ---> update this to false only if cluster role binding is created manually `global.ocnaddmanagement.cluster.serviceAccount.name`: ocnadd ## ---> update ocnadd with namespace created for management group `global.ocnaddmanagement.cluster.clusterRole.name`: ocnadd ## ---> update ocnadd with namespace created for management group `global.ocnaddmanagement.cluster.clusterRoleBinding.name`: ocnadd ## ---> update ocnadd with namespace created for management group - Install the Management Group using the OCNADD Helm charts
folder:
helm install <management-release-name> -f ocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml -f <management-custom-values> --namespace <management-namespace> <helm_chart>where:
<management-release-name>release name of Management Group deployment<management-custom-values>Management custom values file<management-namespace>namespace where Management Group is deployed<helm-chart>Helm chart folder of OCNADDExample:helm install OCNADD-mgmt -f ocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml -f ocnadd-management-custom-values-25.2.200-mgmt-group.yaml --namespace ocnadd-mgmt ocnadd
- Modify the
Installing OCNADD RelayAgent Group
- Create OCNADD Namespace: Create the OCNADD namespace for the Relay Agent Group, if not already created. For more information, see Creating OCNADD Namespace.
- Creating Service Account, Role, and Role Binding: If the user has opted to manually create a service account, role, and role binding, follow the steps outlined in the Creating Service Account, Role, and Role Binding section.
- Generate Certificates: Follow the steps outlined in the Configuring SSL or TLS Certificates section to complete the certificate generation process for the Relay Agent Group if it is not performed.
- Update Custom Values file: Create a copy of the custom values for the
Relay Agent Group from the
ocnadd-package-25.2.200folder as shown below:# cd ocnadd-package-25.2.200 # cp custom_templates/ocnadd-relayagent-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml ocnadd-relayagent-custom-values-25.2.200-ra-group.yamlUpdate the
ocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlandocnadd-relayagent-custom-values-25.2.200-ra-group.yaml(depending on the type of deployment model) with the required parameters. For more information on how to access and update the custom values files, see Customizing OCNADD.If OCCM is used to create the certificates, update the mandatory parameters specified in Helm Parameter Configuration for OCCM.
- Install Relay Agent Group:
- Modify
ocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yamland update it as shown below:`global.management_info.management_namespace`: ocnadd-management ## ---> update it with namespace created for management group - Modify the
ocnadd-relayagent-custom-values-25.2.200-ra-group.yamlfile created above and update it as shown below:`global.ocnaddrelayagent.cluster.namespace.name`: ocnadd-relay ## ---> update it with namespace created for relayagent group `global.ocnaddrelayagent.cluster.serviceAccount.create`: true ## ---> update this to false only if service account is created manually `global.ocnaddrelayagent.cluster.clusterRole.create`: true ## ---> update this to false only if cluster role is created manually `global.ocnaddrelayagent.cluster.clusterRoleBinding.create`: true ## ---> update this to false only if cluster role binding is created manually `global.ocnaddrelayagent.cluster.serviceAccount.name`: ocnadd ## ---> update ocnadd with namespace created for relayagent group `global.ocnaddrelayagent.cluster.clusterRole.name`: ocnadd ## ---> update ocnadd with namespace created for relayagent group `global.ocnaddrelayagent.cluster.clusterRoleBinding.name`: ocnadd ## ---> update ocnadd with namespace created for relayagent group - Install the Relay Agent Group using the OCNADD Helm charts
folder:
helm install <relayagent-release-name> -f ocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml -f <relayagent-custom-values> --namespace <relayagent-namespace> <helm_chart>where:
<relayagent-release-name>release name of Relay Agent Group deployment<relayagent-custom-values>Relay Agent custom values file<relayagent-namespace>namespace where Relay Agent Group is deployed<helm-chart>Helm chart folder of OCNADDExample:helm install OCNADD-ra -f ocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml -f ocnadd-relayagent-custom-values-25.2.200-ra-group.yaml --namespace ocnadd-relay ocnadd
- Modify
Installing OCNADD Mediation Group
- Create OCNADD Namespace: Create the OCNADD namespace for the Mediation Group, if not already created. For more information, see Creating OCNADD Namespace.
- Creating Service Account, Role, and Role Binding: If the user has opted to manually create a service account, role, and role binding, follow the steps outlined in the Creating Service Account, Role, and Role Binding section.
- Generate Certificates: Follow the steps outlined in the Configuring SSL or TLS Certificates section to complete the certificate generation process for the Mediation Group if it is not performed.
- Update Custom Values file: Create a copy of the custom values for the
Mediation Group from the
ocnadd-package-25.2.200folder as shown below:# cd ocnadd-package-25.2.200 # cp custom_templates/ocnadd-mediation-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml ocnadd-mediation-custom-values-25.2.200-med-group.yamlUpdate the
ocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlandocnadd-mediation-custom-values-25.2.200-med-group.yaml(depending on the type of deployment model) with the required parameters. For more information on how to access and update the custom values files, see Customizing OCNADD.If OCCM is used to create the certificates, update the mandatory parameters specified in Helm Parameter Configuration for OCCM.
- Installing Mediation Group:
- Modify the
ocnadd-mediation-custom-values-25.2.200-med-group.yamlfile created above and update it as shown below:`global.ocnaddmediation.cluster.namespace.name`: ocnadd-deploy ## ---> update it with namespace created for mediation group `global.ocnaddmediation.cluster.serviceAccount.create`: true ## ---> update this to false only if service account is created manually `global.ocnaddmediation.cluster.clusterRole.create`: true ## ---> update this to false only if cluster role is created manually `global.ocnaddmediation.cluster.clusterRoleBinding.create`: true ## ---> update this to false only if cluster role binding is created manually `global.ocnaddmediation.cluster.serviceAccount.name`: ocnadd ## ---> update ocnadd with namespace created for mediation group `global.ocnaddmediation.cluster.clusterRole.name`: ocnadd ## ---> update ocnadd with namespace created for mediation group `global.ocnaddmediation.cluster.clusterRoleBinding.name`: ocnadd ## ---> update ocnadd with namespace created for mediation group - Install the Mediation Group using the OCNADD Helm charts
folder:
helm install <mediation-release-name> -f ocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml -f <mediation-custom-values> --namespace <mediation-namespace> <helm_chart>where:
<mediation-release-name>release name of Mediation Group deployment<mediation-custom-values>Mediation custom values file<mediation-namespace>namespace where Mediation Group is deployed<helm-chart>Helm chart folder of OCNADDExample:helm install OCNADD-med -f ocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml -f ocnadd-mediation-custom-values-25.2.200-med-group.yaml --namespace ocnadd-med ocnadd
- Modify the
2.2.2.2 Verifying OCNADD Installation
This section describes how to verify if Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Disaster Recovery Guide (OCNADD) is installed successfully.
To check the status of the OCNADD deployment, perform the following task:
- Run the following commands to check Helm release
status:
helm status <helm-release> -n <ocnadd-group-namespace>Example:
To check release status for the management group:
# helm status dd-mgmt -n ocnadd-mgmtTo check release status for the relay agent group:
# helm status dd-ra -n ocnadd-relayTo check release status for the mediation group:
# helm status dd-med -n ocnadd-medThe system displays the status as deployed if the deployment is successful.
- Run the following command to check whether all the services are deployed and
active:
watch kubectl get pod,svc -n <ocnadd-group-namespace>Example:
To check the status of pods for the management group:
# watch kubectl get pod,svc -n ocnadd-mgmtTo check the status of pods for the relay agent group:
# watch kubectl get pod,svc -n ocnadd-relayTo check the status of pods for the mediation group:
# watch kubectl get pod,svc -n ocnadd-med
Note:
- All microservices status must be Running and Ready.
- Take a backup of the following files that are required during fault recovery:
- Updated Helm charts for Management, Relay Agent, and Mediation Group(s)
- Updated custom values for Management, Relay Agent, and Mediation Group(s)
- Secrets, certificates, and keys that are used during the installation for Management, Relay Agent, and Mediation Group(s)
- If the installation is not successful or you do not see the status as Running for all pods, perform the troubleshooting steps. For more information, refer to the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Troubleshooting Guide..
2.2.2.3 Creating OCNADD Kafka Topics
To create OCNADD Kakfa topics, see the "Creating Kafka Topic for OCNADD" section of Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide
2.2.2.4 Installing OCNADD GUI
Install OCNADD GUI
The OCNADD GUI gets installed along with the OCNADD services.
Configure OCNADD GUI in CNCC
Prerequisite: To configure OCNADD GUI in CNC Console, you must have the CNC Console installed. For information on how to install CNC Console and configure the OCNADD instance, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Before installing CNC Console, ensure to update the instances parameters with the following details in the occncc_custom_values.yaml file:
instances:
- id: Cluster1-dd-instance1
type: DD-UI
owner: Cluster1
ip: 10.xx.xx.xx #--> give the cluster/node IP
port: 31456 #--> give the node port of ocnaddgui
apiPrefix: /<clustername>/<namespace>/ocnadd
- id: Cluster1-dd-instance1
type: DD-API
owner: Cluster1
ip: 10.xx.xx.xx #--> give the cluster/node IP
port: 32406 #--> give the node port of ocnaddbackendrouter
apiPrefix: /<clustername>/<namespace>/ocnaddapi
# Applicable only for Manager and Agent core. Used for Multi-Instance-Multi-Cluster Configuration Validation
validationHook:
enabled: false #--> add this enabled: false to validationHook
#--> do these changes under section :
cncc iam attributes
# If https is disabled, this Port would be HTTPS/1.0 Port (secured SSL)
publicHttpSignalingPort: 30085 #--> CNC console nodeport
#--> add these lines under cncc-iam attributes
# If Static node port needs to be set, then set staticNodePortEnabled flag to true and provide value for staticNodePort
# Else random node port will be assigned by K8
staticNodePortEnabled: true
staticHttpNodePort: 30085 #--> CNC console nodeport
staticHttpsNodePort: 30053
#--> do these changes under section : manager cncc core attributes
#--> add these lines under mcncc-core attributes
# If Static node port needs to be set, then set staticNodePortEnabled flag to true and provide value for staticNodePort
# Else random node port will be assigned by K8
staticNodePortEnabled: true
staticHttpNodePort: 30075 staticHttpsNodePort: 30043
#--> do these changes under section : agent cncc core attributes
#--> add these lines under acncc-core attributes
# If Static node port needs to be set, then set staticNodePortEnabled flag to true and provide value for staticNodePort
# Else random node port will be assigned by K8
staticNodePortEnabled: true
staticHttpNodePort: 30076
staticHttpsNodePort: 30044occncc_custom_values.yaml
file:instances:
- id: Cluster1-dd-instance1
type: DD-UI owner: Cluster1
ip: 10.xx.xx.xx #--> update the cluster/node IP
port: 31456 #--> ocnaddgui port
apiPrefix: /<clustername>/<management_group_namespace>/ocnadd
- id: Cluster1-dd-instance1
type: DD-API owner: Cluster1
ip: 10.xx.xx.xx #--> update the cluster/node IP
port: 32406 #--> ocnadduirouter port
apiPrefix: /<clustername>/<management_group_namespace>/ocnaddapiExample:
occncc_custom_values.yaml will be as
follows:DD-UI apiPrefix:
/occne-ocdd/ocnadd-mgmt/ocnadd
DD-API apiPrefix:
/occne-ocdd/ocnadd-mgmt/ocnaddapiAccess OCNADD GUI
To access OCNADD GUI, follow the procedure mentioned in the "Accessing CNC Console" section of Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
2.2.2.5 Adding a Mediation Group
Note:
Adding a Mediation Group is possible using the steps listed below; however, the user must note that all possible scenarios for this feature have not been verified, and you may encounter a few challenges while installing an additional Mediation Group.
Assumptions:
- OCNADD is already deployed with a worker group consisting of a Relay Agent and at least one Mediation Group.
- Management Group deployment is up and running (for example, in namespace ocnadd-mgmt).
- To utilize the extended storage feature with MySQL in the Mediation Group being deployed to a new cluster, ensure that network connectivity is established between the new cluster and the MySQL cluster hosting the management group.
Procedure for Adding a New Mediation Group:
- Follow the section Installing OCNADD Mediation Group to customize and install another Mediation Group in the same worker group.
- To verify the installation of the new Mediation Group, run the following
command:
# watch kubectl get pod,svc -n ocnadd-med2 - Follow the section Creating OCNADD Kafka Topics to create topics on the newly added Mediation Group.
- Once a Mediation Group is registered with the Management Group, all existing feed
configurations are automatically migrated to the newly added Mediation Group. If any
issues arise during this feed replication process, you can reinitiate the
replication using the steps outlined below:
- Access the configuration service pod in the Management Group
namespace
kubectl exec -ti -n <management-group-namespace> <configuration-service-pod-name> -- bash - Run the following
curlcommand to re-trigger the feed replicationcurl -k -X GET --location "http://ocnaddmanagementgateway:12889/ocnadd-configuration/v1/deploy-resources/<mediation-group-name>" - If secure communication (mTLS: true) is enabled,
use:
curl -k -X GET --location --cert-type P12 --cert /var/securityfiles/keystore/serverKeyStore.p12:$OCNADD_SERVER_KS_PASSWORD "https://ocnaddmanagementgateway:12889/ocnadd-configuration/v1/deploy-resources/<mediation-group-name>"Where:
<mediation-group-name>=<SiteName>:<WorkerName>:<Namespace>:<ClusterName>Example
If the following values are configured:
siteName: BLR ## common custom values workergroupName: wg1 ## mediation custom values clusterName: cluster-1 ## mediation custom valuesAnd the Mediation Group is deployed in the
ocnadd-med2namespace, then the Mediation Group name will be:BLR:wg1:ocnadd-med2:cluster-1Example command:
curl -k -X GET --location --cert-type P12 --cert /var/securityfiles/keystore/serverKeyStore.p12:$OCNADD_SERVER_KS_PASSWORD "https://ocnaddmanagementgateway:12889/ocnadd-configuration/v1/deploy-resources/BLR:wg1:ocnadd-med2:cluster-1" - Verify completion: Verify that the feed replication has been successfully completed. Note that this process may take some time.
- Access the configuration service pod in the Management Group
namespace
2.2.2.6 Deleting a Mediation Group
Assumptions:
- OCNADD is already deployed with at least one Mediation Group.
- Management Group deployment is up and running, for example, namespace "ocnadd-mgmt".
- Mediation groups "mediation-group-1" and "mediation-group-2" deployment is up and running, for example, namespace "ocnadd-med1" and "ocnadd-med2".
- The Mediation group "mediation-group-2" needs to be deleted.
- Clean up the configurations corresponding to the mediation group being
deleted.
(Skip this step when changing the Kafka storage mode.)
- Delete all the adapter feeds corresponding to mediation-group-2 using the curl command.
- Delete all the filters applied to mediation-group-2 using the curl command.
- Delete all the correlations applied to mediation-group-2 using the curl command.
- Delete all the Kafka feeds corresponding to mediation-group-2 using the curl
command.
curl -k -X DELETE --location "http://ocnaddmanagementgateway:12889/ocnadd-configuration/v1/delete-resources/<mediation-group-name>"If secure communication for DD is enabled (mTLS: true):
curl -k -X DELETE --location --cert-type P12 \ --cert /var/securityfiles/keystore/serverKeyStore.p12:$OCNADD_SERVER_KS_PASSWORD \ "https://ocnaddmanagementgateway:12889/ocnadd-configuration/v1/delete-resources/<mediation-group-name>"where
<mediation-group-name>=<SiteName>:<WorkerName>:<Namespace>:<ClusterName>Example:
Given the following parameter values and the mediation group deployed in ocnadd-med2 namespace:
siteName: BLR workergroupName: wg1 clusterName: cluster-1Then the mediation group name will be:
BLR:wg1:ocnadd-med2:cluster-1The command will be:
curl -k -X DELETE --location --cert-type P12 \ --cert /var/securityfiles/keystore/serverKeyStore.p12:$OCNADD_SERVER_KS_PASSWORD \ "https://ocnaddmanagementgateway:12889/ocnadd-configuration/v1/delete-resources/BLR:wg1:ocnadd-med2:cluster-1"If some feeds from the mediation group are not deleted due to a network failure, re-execute the deletion step to ensure all feeds are removed.
Note:
For the scenario where only one Mediation Group is deployed, clean up the configurations corresponding to the Mediation Group being deleted using the OCNADD UI:- Delete all the adapter feeds corresponding to the worker group.
- Delete all the filters applied to the worker group.
- Delete all the correlations applied to the worker group.
- Delete all the Kafka feeds corresponding to the worker group.
- Uninstall the Mediation
Group:
helm uninstall <mediation-group2-release-name> -n <mediation-group2-namespace>Example:
helm uninstall dd-med2 -n ocnadd-med2 - Delete the Mediation Group namespace.
(Skip this step when changing the Kafka storage mode.)
kubectl delete namespace <mediation-group2-namespace>Example:
kubectl delete namespace ocnadd-med2
2.2.2.7 Deleting a Relay Agent Group
Assumptions:
- OCNADD is already deployed with at least one Mediation Group.
- Management Group deployment is up and running, for example, namespace "ocnadd-mgmt".
- Relay Agent group "relayagent-group-1" deployment is up and running, for example, namespace "ocnadd-rea1".
- The Relay Agent group "relayagent-group-1" needs to be deleted.
- Clean up the configurations corresponding to the Relay Agent group being
deleted.
(Skip this step when changing the Kafka storage mode.)
- Delete the Global OCNADD Metadata configuration from the UI.
- Delete all the Ingress filters applied to this Relay Agent group from the UI.
- Uninstall the Relay Agent
group:
helm uninstall <relayagent-group1-release-name> -n <relayagent-group1-namespace>Example:
helm uninstall dd-rea1 -n ocnadd-rea - Delete the Relay Agent group namespace.
(Skip this step when changing the Kafka storage mode.)
kubectl delete namespace <relayagent-group1-namespace>Example:
kubectl delete namespace ocnadd-rea
2.2.2.8 Deleting a Worker Group
Deletion of a worker group involves the removal of all sub-groups, including relay agent groups and mediation groups, that are associated with it.
Assumptions
- The OCNADD is already deployed with at least one worker group.
- Management Group deployment is up and running, for example, namespace "ocnadd-mgmt".
- Worker group "worker-group1" has Relay Agent "relayagent-group1" and "mediation-group1" and their deployment is up and running, for example, namespace "ocnadd-rea" and "ocnadd-med".
- The worker group "worker-group1" needs to be removed. Therefore, the associated Relay Agent "relayagent-group1" and Mediation "mediation-group1" group must be removed.
- Clean up the configurations corresponding to the worker group being
deleted.
For example, if it is "worker-group1":
- Delete all the adapter feeds corresponding to worker-group1 from the UI.
- Delete all the filters applied to worker-group1 from the UI.
- Delete all the correlations applied to worker-group1 from the UI.
- Delete all the Kafka feeds corresponding to worker-group1 from the UI.
- Uninstall the Mediation
group:
helm uninstall <mediation-group1-release-name> -n <mediation-group1-namespace>Example:
helm uninstall dd-med1 -n ocnadd-med - Delete the Mediation group
namespace:
kubectl delete namespace <mediation-group1-namespace>Example:
kubectl delete namespace ocnadd-med - Uninstall the Relay Agent
group:
helm uninstall <relayagent-group1-release-name> -n <relayagent-group1-namespace>Example:
helm uninstall dd-rea1 -n ocnadd-rea - Delete the Relay Agent group
namespace:
kubectl delete namespace <relayagent-group1-namespace>Example:
kubectl delete namespace ocnadd-rea
2.2.2.9 Creating Alarms and Dashboard in OCI
This step is necessary only for the Data Director deployment on the OCI platform. Follow the steps explained in the section 'Creating Alarms and Dashboards in OCI' from the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide.
2.2.2.10 Adding or Updating Load Balancer IPs in SAN When OCCM is Used
The certificates created by OCCM will not contain any IP values in the SAN field except the
values provided in the global.<groupname>.certificate.occm.san.*.ips field
in the custom values file for Kafka broker, ingress adapter, redundancy agent, and gateway
certificates.
To add or update the LoadBalancer IPs of these services in the SAN, follow the steps mentioned below. Refer to Helm Parameter Configuration for OCCM for a detailed description of the different Helm parameters.
2.2.2.10.1 Adding Loadbalancer IPs for Management Gateway Services
Adding LoadBalancer IPs for Management Gateway Services
- Update the
global.ocnaddmanagement.certificates.occm.san.management_gateway.ipsfield inocnadd-management-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlof the required management group.Update Management Gateway LoadBalancer IPs
global: ocnaddmanagement: certificates: occm: san: management_gateway: ips: ["10.10.10.10"] # Add the LoadBalancer IP of the management gateway service -
- If single certificate is not enabled, update the
global.ocnaddmanagement.certificates.occm.san.management_gateway.update_requiredandglobal.ocnaddmanagement.certificates.occm.san.management_gateway.uuid.serverfields inocnadd-management-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlof the required management group.Management Gateway SAN upgrade
global: ocnaddmanagement: certificates: occm: san: management_gateway: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # Provide the UUID value of the certificate MANAGEMENTGATEWAY-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM, where <namespace> is the management group namespace - If single certificate is enabled for OCNADD, update the
global.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.update_requiredandglobal.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.uuid.serverfields inocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml.OCNADD SAN upgrade
global: certificates: occm: san: ocnadd: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # Provide the UUID value of the certificate OCNADD-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM, where <namespace> is the mediation group namespace
- If single certificate is not enabled, update the
- Run Helm upgrade for the Management Group namespace.
Helm upgrade
helm upgrade <management-group-release-name> -f <common-custom-values> -f <management-group-custom-values> -n <management-group-ns> <ocnadd-helm-chart-location> - New certificates will be created. Verify them through the OCCM UI. Management Gateway will also restart after the Helm upgrade is completed and will start using the newly created certificates.
2.2.2.10.2 Adding LoadBalancer IP for Redundancy Agent
- Update the
global.ocnaddmanagement.certificates.occm.san.redundancy_agent.ipsfield inocnadd-management-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlof the required management group.Update Agent LoadBalancer IPs
global: ocnaddmanagement: certificates: occm: san: redundancy_agent: ips: ["10.10.10.10"] # Add the LoadBalancer IP of the redundancy agent service -
- If single certificate is not enabled, update the
global.ocnaddmanagement.certificates.occm.san.redundancy_agent.update_requiredandglobal.ocnaddmanagement.certificates.occm.san.redundancy_agent.uuid.serverfields inocnadd-management-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlof the required management group.Redundancy Agent SAN upgrade
global: ocnaddmanagement: certificates: occm: san: redundancy_agent: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # Provide the UUID value of the certificate REDUNDANCYAGENT-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM, where <namespace> is the management group namespace - If single certificate is enabled for OCNADD, update the
global.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.update_requiredandglobal.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.uuid.serverfields inocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml.OCNADD SAN upgrade
global: certificates: occm: san: ocnadd: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # Provide the UUID value of the certificate OCNADD-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM, where <namespace> is the mediation group namespace
- If single certificate is not enabled, update the
- Run Helm upgrade for the Management Group namespace.
Helm upgrade
helm upgrade <management-group-release-name> -f <common-custom-values> -f <management-group-custom-values> -n <management-group-ns> <ocnadd-helm-chart-location> - New certificates will be created. Verify them through the OCCM UI. The Redundancy Agent will restart after the Helm upgrade and begin using the newly created certificates.
2.2.2.10.3 Adding Loadbalancer IPs for Relay Agent Kafka
- Update the
global.ocnaddrelayagent.certificates.occm.san.kafka.ipsfield inocnadd-relayagent-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlof the required Relay Agent group.Update Relay Agent Kafka LoadBalancer IPs
global: ocnaddrelayagent: certificates: occm: san: kafka: ips: ["10.10.10.10", "10.10.10.11", "10.10.10.12", "10.10.10.13"] # Add the LoadBalancer IP of each Kafka broker service -
- If single certificate is not enabled, update
global.ocnaddrelayagent.certificates.occm.san.kafka.update_requiredandglobal.ocnaddrelayagent.certificates.occm.san.kafka.uuid.serverin the same custom values file.Relay Agent Kafka SAN upgrade
global: ocnaddrelayagent: certificates: occm: san: kafka: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # UUID of KAFKABROKER-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM - If single certificate is enabled for OCNADD, update
global.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.update_requiredandglobal.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.uuid.serverinocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml.OCNADD SAN upgrade
global: certificates: occm: san: ocnadd: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # UUID of OCNADD-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM
- If single certificate is not enabled, update
- Run Helm upgrade for the Relay Agent group namespace.
Helm upgrade
helm upgrade <relayagent-release-name> -f <common-custom-values> -f <relayagent-group-custom-values> -n <relayagent-group-ns> <ocnadd-helm-chart-location> - New certificates will be created. Verify them through the OCCM UI. Kafka brokers will restart after the Helm upgrade and will start using the newly created certificates.
2.2.2.10.4 Adding LoadBalancer IPs for Relay Agent Gateway Services
- Update the
global.ocnaddrelayagent.certificates.occm.san.management_gateway.ipsfield inocnadd-relayagent-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlof the required Relay Agent group.Update Relay Agent Gateway LoadBalancer IPs
global: ocnaddrelayagent: certificates: occm: san: relay_gateway: ips: ["10.10.10.10"] # Add the LoadBalancer IP of the Relay Agent Gateway service -
- If single certificate is not enabled, update
global.ocnaddrelayagent.certificates.occm.san.relay_gateway.update_requiredandglobal.ocnaddrelayagent.certificates.occm.san.relay_gateway.uuid.serverin the same custom values file.Relay Agent Gateway SAN upgrade
global: ocnaddrelayagent: certificates: occm: san: relay_gateway: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # UUID of RELAYGATEWAY-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM - If single certificate is enabled for OCNADD, update
global.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.update_requiredandglobal.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.uuid.serverinocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml.OCNADD SAN upgrade
global: certificates: occm: san: ocnadd: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # UUID of OCNADD-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM
- If single certificate is not enabled, update
- Run Helm upgrade for the Relay Agent group namespace.
Helm upgrade
helm upgrade <relayagent-group-release-name> -f <common-custom-values> -f <relayagent-group-custom-values> -n <relayagent-group-ns> <ocnadd-helm-chart-location> - New certificates will be created; verify them in the OCCM UI. The Relay Gateway will restart after the Helm upgrade is completed and will start using the newly created certificates.
2.2.2.10.5 Adding LoadBalancer IPs for Mediation Kafka
- Update the
global.ocnaddmediation.certificates.occm.san.kafka.ipsfield inocnadd-mediation-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlof the required Mediation group.Update Mediation Kafka LoadBalancer IPs
global: ocnaddmediation: certificates: occm: san: kafka: ips: ["10.10.10.10", "10.10.10.11", "10.10.10.12", "10.10.10.13"] # Add the LoadBalancer IPs of each Kafka broker service -
- If single certificate is not enabled, update
global.ocnaddmediation.certificates.occm.san.kafka.update_requiredandglobal.ocnaddmediation.certificates.occm.san.kafka.uuid.serverin the same custom values file.Mediation Kafka SAN upgrade
global: ocnaddmediation: certificates: occm: san: kafka: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # UUID of KAFKABROKER-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM - If single certificate is enabled for OCNADD, update
global.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.update_requiredandglobal.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.uuid.serverinocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml.OCNADD SAN upgrade
global: certificates: occm: san: ocnadd: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # UUID of OCNADD-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM
- If single certificate is not enabled, update
- Run Helm upgrade for the Mediation group namespace.
Helm upgrade
helm upgrade <mediation-release-name> -f <common-custom-values> -f <mediation-group-custom-values> -n <mediation-group-ns> <ocnadd-helm-chart-location> - New certificates will be created; verify them through the OCCM UI. Kafka Brokers will restart after the Helm upgrade is completed and will begin using the newly generated certificates.
2.2.2.10.6 Adding LoadBalancer IPs for Ingress Adapter
- Update the
global.ocnaddmediation.certificates.occm.san.ingress_adapter.ipsfield inocnadd-mediation-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlof the required Mediation group.Update Ingress Adapter LoadBalancer IPs
global: ocnaddmediation: certificates: occm: san: ingress_adapter: ips: ["10.10.10.10", "10.10.10.11", "10.10.10.12", "10.10.10.13"] # Add the LoadBalancer IPs of each Ingress Adapter service -
- If single certificate is not enabled, update
global.ocnaddmediation.certificates.occm.san.ingress_adapter.update_requiredandglobal.ocnaddmediation.certificates.occm.san.ingress_adapter.uuid.serverin the same custom values file.Ingress Adapter SAN upgrade
global: ocnaddmediation: certificates: occm: san: ingress_adapter: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # UUID of INGRESSADAPTER-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM - If single certificate is enabled,
update
global.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.update_requiredandglobal.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.uuid.serverinocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml.OCNADD SAN upgrade
global: certificates: occm: san: ocnadd: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # UUID of OCNADD-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM
- If single certificate is not enabled, update
- Run the Helm upgrade for the Mediation group namespace.
Helm upgrade
helm upgrade <mediation-group-release-name> -f <common-custom-values> -f <mediation-group-custom-values> -n <mediation-group-ns> <ocnadd-helm-chart-location> - New certificates will be created with the updated SAN entries. Verify them through the OCCM UI.
- Run a second Helm upgrade to apply the updated certificates after
restart.
helm upgrade <mediation-group-release-name> -f <common-custom-values> -f <mediation-group-custom-values> -n <mediation-group-ns> <ocnadd-helm-chart-location> --set global.ocnaddmediation.env.admin.OCNADD_INGRESS_ADAPTER_UPGRADE_ENABLE=true
2.2.2.10.7 Adding Loadbalancer IPs for Mediation Gateway Services
- Update the
global.ocnaddmediation.certificates.occm.san.management_gateway.ipsinocnadd-mediation-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlof the required Mediation group.Update Mediation Gateway Load balancer IPs
global: ocnaddmediation: certificates: occm: san: mediation_gateway: ips: ["10.10.10.10"] # Add the loadbalancer IP of the mediation gateway service -
- If single certificate is not enabled, then update the
global.ocnaddmediation.certificates.occm.san.mediation_gateway.update_requiredandglobal.ocnaddmediation.certificates.occm.san.mediation_gateway.uuid.serverinocnadd-mediation-custom-values-25.2.200.yamlof the required Mediation group.Mediation Gateway SAN upgrade
global: ocnaddmediation: certificates: occm: san: mediation_gateway: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # Provide the UUID value of the certificate MEDIATIONGATEWAY-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM, where <namespace> is the Mediation group namespace - If single certificate is enabled for OCNADD, then update the
global.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.update_requiredandglobal.certificates.occm.san.ocnadd.uuid.serverinocnadd-common-custom-values-25.2.200.yaml.OCNADD SAN upgrade
global: certificates: occm: san: ocnadd: update_required: true # Set to true, default is false uuid: server: 5e765aeb-ae1b-426b-8481-f8f3dcdd645e # Provide the UUID value of the certificate OCNADD-SECRET-SERVER-<namespace> from OCCM, where <namespace> is the Mediation group namespace
- If single certificate is not enabled, then update the
- Run Helm upgrade for the Mediation group
namespace.
$ helm upgrade <mediation-group-release-name> -f <common-custom-values> -f <mediation-group-custom-values> -n <mediation-group-ns> <ocnadd-helm-chart-location> - New certificates will be created; verify the same through the OCCM UI. Mediation Gateway will also restart after the Helm upgrade is completed and will start using the newly created certificates.
2.2.3 Post-Installation Tasks
2.2.3.1 Enabling Traffic Segregation Using CNLB
This feature is introduced as part of traffic segregation support in OCNADD. To enable it, see 'Enabling or Disabling Traffic Segregation Using CNLB in OCNADD ' section in the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide. It is recommended to enable this feature after completing the deployment of the target release.
2.2.3.2 Enabling Two Site Redundancy
This feature is introduced as part of Georedundancy in OCNADD. To enable it, see 'Two Site Redundancy Enable' section in the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide. It is recommended to enable this feature after completing the deployment of the target release.
2.2.3.3 Enabling Druid as Extended Storage Feature
This feature is introduced as part of extended storage in Data Director. To enable it, see the “Druid Integration with OCNADD” section in the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director User Guide. The feature is recommended to be enabled after the release installation is completed. Extended storage using the cnDBTier database is available by default.
2.2.3.4 vCollector Integration for Diameter Feed
In this release, integration with vCollector has been provided. The vCollector acquires the Diameter traffic from vDSR using port mirroring. The vCollector is deployed as a virtual machine outside the OCNADD cluster and provides the acquired Diameter traffic to Data Director over the Kafka interface. The vCollector is configured and managed by the Data Director OAM services. This feature is introduced as part of the Diameter feed capabilities in Data Director. To enable integration with vCollector, refer to the vCollector Integration with Data Director section in the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Diameter User Guide. The feature is recommended to be enabled after the release installation is completed.