7 About Runtime Order Management
This chapter provides an overview of the Oracle Communications Order and Service Management (OSM) runtime tasks. Before reading this chapter, read "Order and Service Management Overview."
For information about using the OSM web clients, see OSM Order Management Web Client User's Guide and OSM Task Web Client User's Guide.
About Managing Orders
Order management personnel use the Task web client and the Order Management web client to manage orders. Order management tasks include:
-
Completing manual tasks. Most of the tasks required to complete an order are automated. Manual tasks are completed in the Task web client. An order manager can add comments to the order, attach documents, display the history of the order, and receive notifications about at-risk orders or tasks.
-
Managing fallout. You can identify errors that occur during order fulfillment, notify the appropriate individuals or systems, and take corrective measures.
-
Managing the order life cycle. Most changes to the order life cycle occur automatically. However, an order manager can manually suspend and resume orders, cancel orders, update orders, and create orders.
-
Running reports. You can run reports to get information about the overall order processing load. You can run the following summary reports:
-
Pending Orders
-
Order Volume
-
Completed Order Statistics
-
Completed Tasks Statistics
-
Assigning Tasks to OSM Users
There are two approaches to assigning tasks to users in OSM:
-
A work offer approach, which is by role, where tasks are associated to a role and users performing that role may select tasks from their worklist to work on them. This is the standard task assignment approach in OSM.
-
A work assign approach, where a task assignment algorithm is used to specifically assign each task to a user performing the role. This approach requires additional OSM modeling.
For each manual task, you can specify how it is assigned to an OSM user for completion. You can use the following methods:
-
Round robin assignment automatically assigns tasks to users in a workgroup alphabetically by user name.
-
Load balancing assignment automatically assigns users in a workgroup to balance the workload across users, based on the number of tasks assigned to each user. The user with the least number of tasks is assigned the task.
You can also create custom automatic assignment methods. For example, you might specify that the first task received is the first one assigned or that the last task received is the first one assigned.
About Workflow and Workstream Processes
When you create processes in Design Studio, you specify if a process is a workflow process or a workstream process.
With a workflow process, the Task web client displays the worklist after it completes each task. This is because a workflow process is intended to distribute work among different users in different workgroups. The next task in the process might be handled by a different user.
With a workstream process, OSM displays the order editor page for the next task automatically without first returning you to the worklist.
A workstream process can include manual and automated tasks. If an automated task occurs, OSM processes it and displays a message indicating that processing is taking place. While automated processing is occurring in the workstream, you can return to the worklist to work on other tasks. The automated task in the workstream will continue to progress to completion. This type of process is useful when the automated task in the workstream takes some time.
After the automated task finishes, and the next task becomes available, any user in the workgroup can pick up the workstream from that point. When the final task in a workstream completes, OSM returns the user to the worklist. OSM automatically displays the order editor page for the next manual task in the workstream to the user.
About the Order Lifecycle Management UI
Using the Order Lifecycle Management UI, you can view information about an order, such as fulfillment dates, the order's progress on a timeline, and order processing errors. The Order Lifecycle Management UI is available on the Timeline tab of the Order Management web client. If your system uses the Oracle Configure, Price, and Quote Cloud (Oracle CPQ Cloud) application as the order capture software, you can view the Order Lifecycle Management UI within Oracle CPQ Cloud.
The Order Lifecycle Management UI provides online Help. Click the Help icon in the UI for more detailed information.
About Managing OSM Users
Order managers use the Task web client to manage an order in runtime. To control which users can process specific types of tasks or perform specific actions in OSM, you define users in Oracle WebLogic Server. You can assign users to two types of groups:
-
Use WebLogic Server groups to define who can access system administration tasks, such as who can use client tools, read log files, and start and stop OSM server components.
-
Use OSM workgroups to define how users can perform order management tasks, for example:
-
You can assign permissions to carry out tasks such as assigning tasks to other users, running reports, changing order priority, and so on.
-
You can specify the data that a user can see in the Task web client.
-
You can specify the orders that OSM users can manage, based on data in the order. For example, you specify that a user can see only orders from a region or for a specific type of service.
-
To create OSM workgroups, you do the following:
-
Create roles in Oracle Communications Design Studio. The term role in Design Studio means the same as the term workgroup in the Task web client and the Order Management web client.
When you create roles, you define permissions; for example, you can specify who can display reports in the Task web client or who can change the priority of a task during order processing. You can assign roles when you model OSM entities. For example, you can specify the roles that can manage an order, or process a task.
-
Assign users to workgroups by using the Order Management web client. This is typically performed as a one-time configuration task.
For example, you might create roles based on what a user can do in the Task web client. You can assign the same tasks to multiple workgroups, but users in each workgroup can work with it differently; for example, you might have a workgroup specifically for fallout management.
Roles are also used by automated tasks. For example, automated tasks use OSM roles to restrict who can receive a notification.
About Using Behaviors to Customize the Task Web Client
You can use behaviors to specify how OSM manages data. For example:
-
You can specify the maximum allowed number of characters for text string data.
-
You can add the values of multiple fields and display the sum in another field.
-
You can specify the minimum and maximum times that a data element can be used in an order. For example, an order might require that exactly two IP addresses are added.
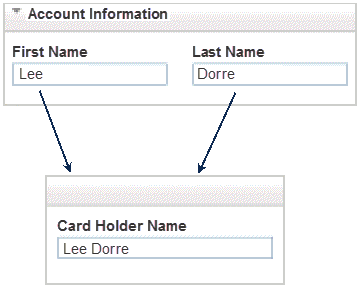
Figure 7-1 shows an example of changing the user interface by using behaviors. In this example, data from two fields is combined into one field.
For more information, see the discussion about modeling behaviors in OSM Modeling Guide.