9 Automating OSM Cloud Native Operations for Continuous Delivery
OSM cloud native provides flexible options to automate its operations for continuous delivery. You can choose to build custom pipelines by invoking OSM cloud native toolkit scripts directly, using your preferred tools and a backing store for configuration management. Alternatively, for organizations adopting GitOps practices, a streamlined integration is available by leveraging Flux-CD, enabling declarative management of deployments through Git as the source of truth.
GitOps allows you to manage and deploy applications by keeping all configuration files and settings in a Git repository. For more details on GitOps, see https://about.gitlab.com/topics/gitops/ .
Flux-CD is a tool that helps keep your Kubernetes environment in sync with the files you store in Git. It constantly compares your running environment with your Git repository, and if something does not match, it automatically makes the necessary updates to keep them aligned. For more details on Flux-CD, see https://fluxcd.io/flux/get-started/.
About Continuous Delivery Mechanism
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a process that automatically gets applications ready for release every time a change is made. With CD, new updates are automatically tested and prepared, so that new features or fixes can be delivered safely and automatically. For more details on Continuous Delivery, see https://about.gitlab.com/topics/continuous-delivery/.
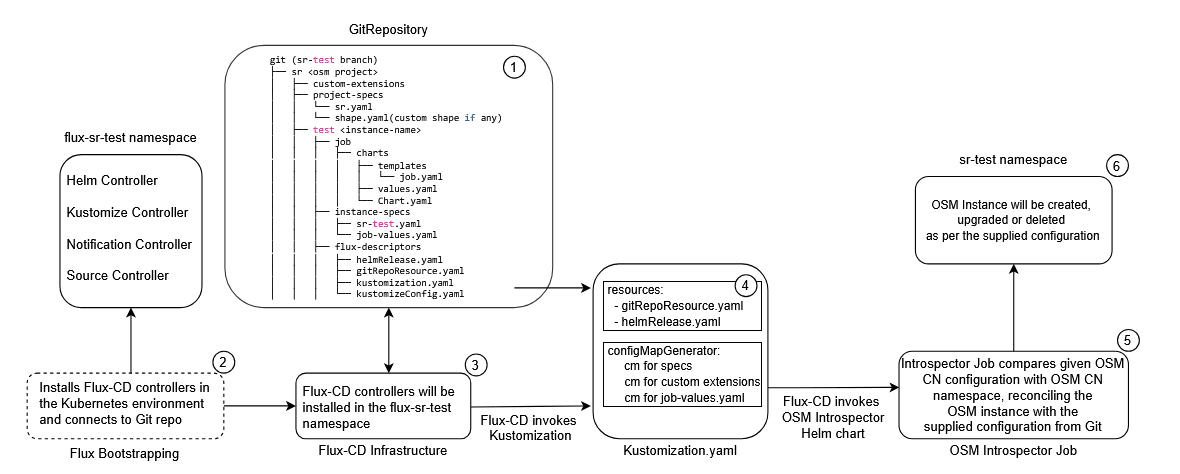
- Git Repository: All configuration for Flux-CD, Kustomize and OSM CN is stored in a git repository.
- Flux Bootstrapping: Flux-CD is instructed to monitor and process this using a bootstrap command.
- Flux-CD Infrastructure: This reads the configuration and installs Flux-CD controllers in a flux-CD namespace for this OSM instance.
- Kustomization.yaml: Using one of these controllers - the Kustomization controller, Flux-CD generates resources in the OSM CN namespace to hold configuration from git that will be required at runtime.
- OSM Introspector Job: Finally, the Flux-CD Helm controller invokes the OSM CN Introspector Helm chart. The OSM CN Introspector Job then compares the desired target state configuration (as relayed from git) with the actual state of the instance. It calculates the operations required to reconcile the two states and runs them.
- sr-test namespace: This results in the OSM cloud native instance being brought in line with the configuration.
Prerequisites for Creating an OSM Instance Using the Introspector Job
Before creating an OSM cloud native instance using the Introspector Job, ensure the following requirements are met:
-
Create Required Secrets and pdb (and pvc if you are using it):
All Kubernetes secrets, pdb, and pvc (if you are using it) required for the OSM cloud native instance need to be created before you run the Introspector Job.
-
Namespace Registration:
Register the required namespace with one or both of the following as needed:
- WebLogic Operator
- Ingress Controller
-
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
Create a Service Account for OSM Introspector with the RBAC specified in the OSM cloud native toolkit samples. If you are using an existing Service Account, ensure it has the required RBAC.
Git Strategy for OSM Instances
A structured Git strategy is recommended to ensure a robust and reliable deployment
process for OSM instances (such as prod and test).
This section describes a sample branching approach and directory structure. OSM cloud
native has been validated against this strategy. The goal is to use the main
branch as the “source of truth,” which holds only the latest,
production-ready code and shared configurations. You can manage instance specific
deployment and customizations in dedicated branches.
- It organizes the directory structure which separates common content (such as project specifications, custom model extensions, and custom shapes) from instance specific configurations (such as instance specifications and job-values.yaml).
- The
mainbranch serves as a reference and shows the complete set of content for all instances, but does not drive any changes to the Kubernetes environment. - For each OSM instance, a dedicated branch is created from
main. Changes to these branches are directly reflected in the associated Kubernetes environment for that instance. - You can develop and deliver changes on the instance branch, and merge them back
into
main, while keeping the instance branch active for ongoing updates. - To incorporate updates from common configurations, you can rebase the instance branch from the main branch.
- When an OSM instance is deleted, its related branch can also be removed. However, instance details continue to live inert in the main branch for reference, future resurrection or future cleanup.
- Create a new instance branch from the main
branch:
This ensures that the new branch includes the latest common code and configuration.# Pull the latest changes to the main branch git pull origin main # Checkout a dedicated branch for 'test' instance from main branch git checkout -b <project>-<instance> origin/main eg: git checkout -b sr-quick origin/main (where "sr" and "quick" represents OSM project and instance name respectively) - Switch to the instance branch: Set up directory structure and instance specific configurations in the instance branch.
- Push your changes and Bootstrap:
- Commit and push updates to your remote instance branch. It will trigger the OSM cloud native instance creation/upgradation for that instance environment.
- Bootstrap your instance branch (eg: sr-quick). This needs to be done only once for a given branch, because after that Flux-CD will continue to monitor for ongoing changes.
- Deliver to main: Deliver changes back into main branch, while keeping the instance branch active for ongoing updates.
The following example shows how to create a test environment, for an OSM cloud native
project sr.
-
Create a branch: sr-test
git pull origin maingit checkout -b sr-test origin/main
- Switch to the sr-test branch, setup up directory structure and instance
specific changes in the sr-test branch as
required.
git (in sr-test branch) ├── sr <project-name> │ ├── custom-extensions │ ├── project-specs │ │ └── sr.yaml │ │ └── shape.yaml(custom shape if any) │ ├── test <instance-name> │ │ ├── job │ │ │ ├── charts │ │ │ ├── templates │ │ │ │ └── job.yaml │ │ │ ├── values.yaml │ │ │ └── Chart.yaml │ │ ├── instance-specs │ │ │ ├── sr-test.yaml │ │ │ └── job-values.yaml │ │ ├── flux-descriptors │ │ ├── helmRelease.yaml │ │ ├── gitRepoResource.yaml │ │ ├── kustomization.yaml │ │ └── kustomizeConfig.yaml -
Push your changes and Bootstrap:
- Commit and push changes to the sr-test branch, this will trigger the OSM cloud native instance creation/upgradation for the test environment.
- Bootstrap the sr-test instance.
- Deliver changes back into main branch, and keep the sr-test instance branch active for ongoing updates.
Table 9-1 Directory Structure and Contents
| Directory | Contents |
|---|---|
| osm-project | Top-level directory named after your OSM project (for example,
sr)
|
| osm-project/custom-extensions | Provide all OSM custom extension files |
| osm-project/project-specs | Project specification file and custom shape file (if required) |
| osm-project/instance-name | Subdirectory for each OSM instance |
| osm-project/instance-name/job | OSM cloud native toolkit Introspector Job Helm Chart. Copy all
contents from the job directory present in OSM
cloud native toolkit.
|
| osm-project/instance-name/instance-specs | Instance specification file and
job-values.yaml, from the OSM cloud native
toolkit samples directory.
|
| osm-project/instance-name/flux-descriptors | Flux-CD resources: HelmRelease,
GitRepository,
Kustomization, kustomizeConfig.yaml
(with nameReference). Copy all files from the OSM cloud
native toolkit samples/flux-descriptors directory
|
The following example shows how to create a production instance, for an OSM cloud native
project sr.
-
Create a branch: sr-prod
git pull origin maingit checkout -b sr-prod origin/main
- Switch to the sr-prod branch, setup up the directory structure and the
instance specific changes in the sr-prod branch as
required.
git (in sr-prod branch) ├── sr │ ├── custom-extensions │ ├── project-specs │ │ └── sr.yaml │ │ └── shape.yaml (custom shape if any) │ ├── prod (newly added in this step) │ │ ├── job │ │ │ ├── charts │ │ │ ├── templates │ │ │ │ └── job.yaml │ │ │ ├── values.yaml │ │ │ └── Chart.yaml │ │ ├── instance-specs │ │ │ ├── sr-prod.yaml │ │ │ └── job-values.yaml │ │ ├── flux-descriptors │ │ ├── helmRelease.yaml │ │ ├── gitRepoResource.yaml │ │ ├── kustomization.yaml │ │ └── kustomizeConfig.yaml │ ├── test │ │ ├── job │ │ │ ├── charts │ │ │ ├── templates │ │ │ │ └── job.yaml │ │ │ ├── values.yaml │ │ │ └── Chart.yaml │ │ ├── instance-specs │ │ │ ├── sr-test.yaml │ │ │ └── job-values.yaml │ │ ├── flux-descriptors │ │ ├── helmRelease.yaml │ │ ├── gitRepoResource.yaml │ │ ├── kustomization.yaml │ │ └── kustomizeConfig.yaml -
Push changes and Bootstrap:
- Commit and push changes to the sr-prod branch, this will trigger the OSM cloud native instance creation/upgradation for the production environment.
- Bootstrap the sr-prod instance.
- Deliver changes back into main branch, and keep the sr-prod instance branch active for ongoing updates.
OSM Cloud Native Toolkit Introspector Job Helm Chart
The Introspector Job Helm chart provisions a Kubernetes Job that runs the OSM cloud native toolkit Introspector script.
The introspector script automates and manages the lifecycle of OSM instance. It performs the following tasks sequentially:
- Delete or restart the OSM Instance. This is done only if it is specifically requested.
- Determine if the operation will trigger an outage.
- Validate if the outage is allowed.
- Shutdown pods if the outage is required and permitted.
- Install or skip the RCU schema as per the requiremenets.
- Install or upgrade the OSM schema as per the requirements.
- Deploy or sync OSM cartridges.
- Create or upgrade the OSM cloud native instance. This depends on the configuration.
- Create or upgrade ingress.
Note:
All customization and operational parameters for the Introspector Job are defined externally in the job-values.yaml configuration file. The Helm chart itself must not be modified.Creating an OSM Cloud Native Instance Using Flux-CD
This section describes how to create an OSM cloud native instance, expanding on the configuration changes required in git and the setup of Flux-CD. This can only be done after you have set up the basic file system for the instance on the instance's branch.
Setup Flux-descriptors Configuration
- Kustomization
- HelmRelease
- GitRepository
Table 9-2 Placeholders in the Cloud Native Toolkit
| Placeholder | Value |
|---|---|
| <project> | Name of your OSM project, for example
sr.
|
| <instance> | Name of your OSM instance, for example
quick.
|
| <git-repository-url> | URL of the Git repository that Flux-CD will watch. |
| <branch-name> | Branch that Flux-CD will watch. |
| <git-repo-secret> | Secret to access the Git repository referenced via <git-repository-url>. For more infomation, see Git Access Secret. |
| <PATH-TO-JOB> | Location of the Job directory in the provided Git repository source. In the branching structure described previously, this would be <project>/<instance> |
Kustomization Resource
The Kustomization resource acts as the primary entry point for Flux-CD. When Flux-CD detects a Kustomization resource inside the flux-descriptors directory, it orchestrates the creation and management of related resources defined within it. The Kustomization resource creates two resources, gitRepository and helmRelease. It also creates configuration maps to hold the configuration derived from Git to make it available to the OSM Introspector Job.
If you are using custom extensions, uncomment the configMap specific to Custom Extensions. This will be disabled by default. For example, sr-quick-customs-cm and you will need to mention the files provided in the custom-extensions directory in this configMap. For more information on adding custom extensions, refer to Custom Extensions.
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
namespace: sr
resources:
- gitRepoResource.yaml
- helmRelease.yaml
configMapGenerator:
## configMap for specs
- name: sr-quick-specs-cm
## add all specs and shape files here. This will be mounted in /osm-specs folder in job container
files:
- ../../project-specs/sr.yaml
- ../instance-specs/sr-quick.yaml
- ../../project-specs/shape.yaml
## configMap for job-values.yaml
- name: sr-quick-helm-values-cm
files:
- values.yaml=../instance-specs/job-values.yaml
generatorOptions:
disableNameSuffixHash: true
configurations:
- kustomizeConfig.yamlGitRepository Resource
The GitRepository resource defines the Git project that Flux-CD continuously monitors. It specifies the repository URL, the branch, and the directory path that Flux-CD will watch to monitor configuration changes.
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta2
kind: GitRepository
metadata:
name: sr-quick-flux-cntk-gr
namespace: sr
spec:
interval: 1m
# Git-Repository URL for Flux-cd to watch
url: https://<git-repo-url>
ref:
# Specify the branch to watch
branch: sr-quick
secretRef:
# Secret to access the above mention Git Repository
name: gitlab-creds
ignore: |-
#Exclude all
/*
#Include specific directory to watch
!/sr/custom-extensions/
!/sr/project-specs/
!/sr/quick/HelmRelease Resource
The HelmRelease resource defines the deployment of Helm charts within the cluster and ensures that they remain synchronized with the desired state stored in Git. It leverages the GitRepository resource as the source for pulling Helm charts and applies updates automatically when it detects changes.
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta1
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: cntk-flux-hr
namespace: sr
spec:
interval: 1m
timeout: 60m
releaseName: sr-quick-osmcn-release
chart:
spec:
chart: sr/quick/job/charts
reconcileStrategy: Revision
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: sr-quick-flux-cntk-gr
valuesFrom:
- kind: ConfigMap
name: sr-quick-helm-values-cmSetup Job-Values Configuration
- introspectorJobVersion: This version is a suffix appended to the job name to distinguish between different iterations of the job. Every time there is a change to the specification or configuration, this version must be incremented or changed.
- project: This specifies the name of the project.
- instance: This specifies the name of the instance.
- image: This specifies the container image that needs to be used for the Introspector Job.
- imagePullPolicy: This defines how Kubernetes pulls the container image for the Introspector Job's pods.
- imagePullSecret: (Optional) This provides the credentials to pull container images from secured registries.
- customModel: This field is used to enable or disable the Custom Model Extensions. By default it is set to False (disable).
- customFiles: This field is used to enable or disable the Custom Files. By default it is set to False (disable).
- serviceAccountName:
(Optional) This specifies a custom service account. If you do not mention
a custom service account, a default service account will be used.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you do not use the default service account but that you create a custom service account. - targetState: This specifies the desired end state of the OSM instance as running or notRunning. If you set it to notRunning, the instance will not be created if it is a new instance, or it will get deleted if it is an existing instance.
- action: This applies operational actions on the OSM instance. These actions are only performed if the job version listed under the action matches the introspectorJobVersion. At present, the restart operation is controlled using action.
- tolerance: This sets the deployment tolerance for various
runtime situations. Tolerances are applied if their jobVersion matches the
introspectorJobVersion. The tolerance for OSM outage is controlled here. By
default, any change that will result in an OSM outage will not be allowed to
proceed, and will return a failure from the Introspector Job. If it is
acceptable for a change to cause an outage, the fullOutage tolerance can be set
to true. OSM production systems have minimum cluster size of 2 or more.
For development systems, which tend to have cluster size of 1, you can either
setup outage tolerance on each change that requires pod restart, or simply set
the jobVersion value to all.
WARNING:
Setting the jobVersion to all is not recommended for production systems as that bypasses the tolerance safety net.
# This version need to be changed to rerun Introspector Job
introspectorJobVersion: v1
# Provide project name in place of <project-name>
project: sr
# Provide instance name in place of <project-name>
instance: quick
# Provide the OSM CNTK image
image: osm-cntk:8.0.0
# Provide when the container image should be pulled from the container registry
# Valid values (Always, IfNotPresent, Never)
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# Provide authentication credentials for pulling container images,
# Optional field, uncomment to specify the imagePullSecret
#imagePullSecret: <image-pull-secret-name>
# Enable if there are any OSM CN model extensions, by default it will be disabled.
customModel: false
# Enable if there are customFiles provided in the project specification.
customFiles: false
# Provide service account name,
# Optional field, if not provided 'default' serviceAccount will be used,
# Uncomment to specify custom serviceAccount.
#serviceAccountName: <service-account-name>
# To manage OSM CN instance create/upgrade OR delete.
# running : OSM Introspector Job will 'create' or 'upgrade' the instance.
# notRunning : OSM Introspector Job will 'delete' the instance.
targetState: running
# Actions that can be applied based on jobVersion.
action:
# OSM Introspector Job will restart or skip the restart, based on the jobVersion value,
# if jobVersion is same as introspectorJobVersion, restart will be applied,
# otherwise if jobVersion is different from introspectorJobVersion, restart will be skipped.
# valid values for Restart.Type are: full, admin, ms
# * full : Restarts the whole instance (rolling restart)
# * admin : Restarts the WebLogic Admin Server only
# * ms : Restarts all the Managed Servers (rolling restart)
restart:
type: full
appliesTo:
jobVersion: v0
# Deployment tolerance that can be applied based on jobVersion.
tolerance:
# OSM Introspector Job will upgrade or skip the upgrade based on fullOutage allowed,
# This will applies to provided jobVersion only,
# if jobVersion is different from introspectorJobVersion, fullOutage will not be allowed.
# if jobVersion value is "all", this tolerance will be applicable for all introspectorJobVersion.
# if fullOutage is allowed : Upgrade will be done (with or without full outage).
# if fullOutage is not allowed : Upgrade will fail if full outage is required, else upgrade will be done.
fullOutage:
allowed: false
appliesTo:
jobVersion: v0Note:
A sample job-values.yaml file is provided in the OSM cloud native toolkit package under samples/job-values.yaml.Triggering CD for a New Instance
The Flux-CD bootstrap command links Flux-CD to the namespace, the branch and path in your Git repository. This allows automated deployment and lifecycle management of your OSM cloud native instances. Flux-CD also requires its bootstrap command to be run by a user who has cluster administration rights on the target Kubernetes cluster.
Oracle recommends using the main branch as the source of truth for maintaining the latest code. Do not use this branch directly to create instances. For each environment (for example, prod, dev, or test), create a separate branch cloned from the main branch. Each branch will contain the required flux-descriptor path to bootstrap and create its own OSM cloud native instance. token-auth is required for Flux-CD to interact with the Git repository, and tokens need be generated from an appropriate Git repository account.
- -n flux-<project>-<instance>: Assigns a unique namespace for the Flux-CD components.
- --url: The Git repository URL.
- --branch: The branch associated with the environment/instance.
- --path: The directory path (within the branch) containing the flux-descriptor manifests.
- --token-auth: Enables authentication using a git access token.
bash-4.4$ flux bootstrap -n flux-<project>-<instance> git \
--url=<Provide your Git repository URL> \
--branch=<Provide your branch here> \
--path=<project>/<instance>/flux-descriptors \
--token-authAfter bootstrapping, Flux-CD will process the kustomization.yaml file located in the specified flux-descriptor directory. Flux-CD will create various housekeeping resources in the flux-<project>-<instance> namespace, as well as operational pods.
Making Changes to an OSM Instance
When modifying the configuration of an instance managed by Flux-CD, it is important to ensure that Flux-CD detects and reconciles the changes correctly.
- Modify Configuration: Make the required changes in the configuration files (for example, the job-values.yaml, project, and instance specification). This can also include normal git operations like rebasing from main or cherry-picking a commit from elsewhere. If it is okay for this instance to experience an outage, then set the outage tolerance as well.
- Increment the Job Version: Update the introspectorJobVersion in the
job-values.yaml file. For example,
introspectorJobVersion: v2 # previously v1 - Commit and Push as One Transaction: All the configuration changes and the introspectorJobVersion updates must be committed and pushed in a single Git transaction. This ensures that the Flux-CD identifies the update as a new version.
Once the changes are pushed, Flux-CD will detect them. A new Job will be created with the updated version. The Job’s name will automatically include a suffix corresponding to the specified introspectorJobVersion , for example, sr-quick-osmops-v2. The versioned job name provides clear traceability of configuration changes applied over time.
Adding Custom Content
This section explains how you can configure the custom content supported by OSM cloud native.
Custom Extensions
- Add all the custom extensions files under the custom-extensions directory
present under <project>/custom-extensions. Refer to Git Strategy for OSM Instances for more information about the directory
structure.
git (dev branch) ├── project │ ├── custom-extensions # Specify all the .tpl files under this directory. │ │ └── _custom-domain-model.tpl │ │ └── _custom-jms-support.tpl ... - Update the Kustomization resource with all the custom extension files:
- Open the Kustomization resource present in the flux-descriptors directory present under <project>/<instance>/flux-descriptors. Refer to Git Strategy for OSM Instances for more information about the directory structure.
- In Kustomization resource under the configMapGenerator tag, a
configMap is available that has been configured for custom extensions.
Uncomment that
section.
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization ... configMapGenerator: ... ## configMap for custom extensions ## Please uncomment this section and add all custom extension tpl files. #- name: <project>-<instance>-customs-cm # ## add all custom extensions files here. This will be mounted in /osm-customs folder in job container # files: # - ../../custom-extensions/_custom-jms-support.tpl # - ../../custom-extensions/_custom-domain-model.tpl ... - Replace the placeholders
<project>and<instance>in the uncommented section with real values.configMapGenerator: ... # configMap for custom extensions # Please uncomment this section and add all custom extension tpl files. - name: sr-quick-customs-cm ## add all custom extensions files here. This will be mounted in /osm-customs folder in job container files: ... - After setting up the name, under the files tag, you need to specify each
custom extension tpl file path. The path will always follow the format
../../custom-extensions/<name-of-custom-extension>.tpl.
For example, if the custom extension name is _custom-domain-model.tpl
then you need to add an entry
../../custom-extensions/_custom-domain-model.tpl under the
files
tag.
configMapGenerator: # configMap for custom extensions # Please uncomment this section and add all custom extension tpl files. - name: sr-quick-customs-cm ## add all custom extensions files here. This will be mounted in /osm-customs folder in job container files: - ../../custom-extensions/_custom-domain-model.tpl - ../../custom-extensions/_custom-jms-support.tpl - The following is a sample Kustomization resource with custom model
extensions:
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization namespace: sr resources: - gitRepoResource.yaml - helmRelease.yaml configMapGenerator: ## configMap for specs - name: sr-quick-specs-cm ## add all specs and shape files here. This will be mounted in /osm-specs folder in job container files: - ../../project-specs/sr.yaml - ../instance-specs/sr-quick.yaml # configMap for custom extensions # Please uncomment this section and add all custom extension tpl files. - name: sr-quick-customs-cm ## add all custom extensions files here. This will be mounted in /osm-customs folder in job container files: - ../../custom-extensions/_custom-domain-model.tpl - ../../custom-extensions/_custom-jms-support.tpl ## configMap for job-values.yaml - name: sr-quick-helm-values-cm files: - values.yaml=../instance-specs/job-values.yaml generatorOptions: disableNameSuffixHash: true configurations: - kustomizeConfig.yaml
- Enable custom extensions in the job-values.yaml file present under
<project>/<instance>/instance-specs/job-values.yaml.
Note:
By default custom extensions are disabled and set to false. To enable custom extensions, set it to true.# Enable if there are any OSM CN model extensions, by default it will be disabled. customModel: true - Enable custom extension in the project specification. To do this, set the
enabled tag as true and specify the model extension files
names in the wdtFiles list element. Ensure this list matches the list
provided in
<project>/<instance>/flux-descriptors/kustomization.yaml.
# Sample WDT extensions can be enabled here. When enabled is true, then # _custom-domain-model.tpl needs to be un-commented. Custom template files can # also be added. custom: enabled: true application: false jdbc: false jms: true #wdtFiles: [] # This empty declaration should be removed if adding items here. wdtFiles: - _custom-jms-support.tpl - _custom-domain-model.tpl
Custom Files
If you need to include custom files as part of your OSM cloud native deployment, follow these steps in the <instance> branch:
- Add the configured custom-file-support.yaml file under the
custom-extensions directory present under
<project>/custom-extensions. A sample file for this is present in the
OSM cloud native toolkit. Refer to Git Strategy for OSM Instances for more information about the directory
structure.
git (dev branch) ├── project │ ├── custom-extensions │ │ └── custom-file-support.yaml ... - Update the Kustomization resource with the custom-file-support.yaml file.
- Open the Kustomization resource present in the flux-descriptors directory present under <project>/<instance>/flux-descriptors.
- In Kustomization resource under the configMapGenerator tag, a
configMap is available that has been configured for custom extensions.
Uncomment that section and replace the placeholders
<project>and<instance>in the uncommented section with real values.configMapGenerator: ... # configMap for custom extensions # Please uncomment this section and add all custom extension tpl files. - name: sr-quick-customs-cm ## add all custom extensions files here. This will be mounted in /osm-customs folder in job container files: ... - After setting up the name, you need to specify custom file path under the
files tag as ../../custom-extensions/custom-file-support.yaml.
configMapGenerator: # configMap for custom extensions - name: sr-quick-customs-cm ## add all custom extensions files here. This will be mounted in /osm-customs folder in job container files: - ../../custom-extensions/custom-file-support.yaml
- Enable custom files in the job-values.yaml file present under
<project>/<instance>/instance-specs/job-values.yaml.
Note:
By default custom files are disabled and set to false. To enable custom file, set it to true.# Enable if there are customFiles provided in the project specification. customFiles: true - Edit your project specification to reference the desired files in the customFiles
element:
#customFiles: # - mountPath: /some/path/1 # configMapSuffix: "path1" # - mountPath: /some/other/path/2 # configMapSuffix: "path2"
Custom Shapes
You can use custom shapes as part of your OSM cloud native deployment. For more information on creating custom shapes, refer to Creating Custom Shapes.
- Under the <project>/project-specs directory add the file of the custom shape.
- In the instance specification specify the name of the custom
shape.
shape: <custom-shape-filename-without-extension>