An Illustration Of A Premise
The following picture illustrates a premise with 2 service points, 2 meters, and 2 badged items:
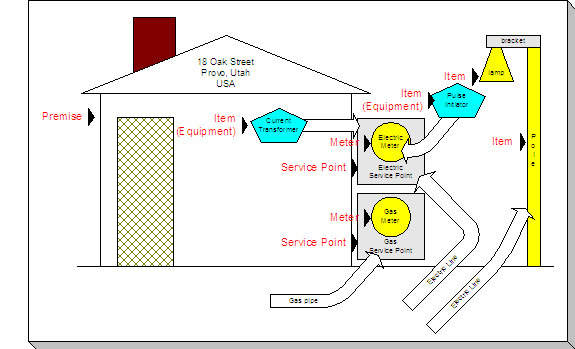
The following concepts are illustrated above:
Premise A premise describes a location at which your company supplies some type of service. In addition to the obvious address information, a premise also contains geographic coordinates, meter read instructions, and taxation jurisdiction information.
For more information about the control tables that must be set up before you can define a premise see Setting Up Premise Options.
Service Point A service point (SP) is a geographic location at which service(s) are delivered to a premise. The SP record maintains information about the type of service, the service cycle (if the service is metered), the field office responsible for maintaining the service, the distribution company that supplies the service, etc.
There are three major categories of service points:
- Those where the rate of consumption and the total amount of consumption is measured (e.g., electricity, gas, water) by a meter. You can think of this type of service point as a "socket" into which a meter can be plugged. Over time, many meters may be plugged into the socket. We refer to these types of service points as metered.
- Those that hold badged items. A badged item is a physical device with a unique identity (e.g., a specific street light, a specific hydrant). You can think of this type of service point as a "socket" into which a badged item can be plugged. Over time, many items may be plugged into the socket. We refer to these types of service points as item-based.
- Those used to hold one or more non-badged items. For example, if your organization doesn't badge street lamps, you can use a single service point to hold an infinite number of lamps. We refer to these types of service points as non-badged.
Refer to Service Points (SPs) for more information about non-badged items.
An unlimited number of SPs may exist at a premise. However in reality, the number of SP's is related to the number of services supplied by your company. For example, an electric and gas company will typically have two SPs per premise.
For more information about the control tables that must be set up before you can define service points refer to Setting Up Generic Service Point Options, Defining Meter and Item Options .
Field activities may be dispatched to all types of service points.
Meter A meter is a physical device used to measure the amount of gas, water, or electricity used by a customer. While most meters measure consumption in a single unit of measure (e.g., gallons, cubic feet, kilowatt-hours), some electric meters are extremely sophisticated and measure several different factors. For example, some electric meters measure how much was used, when it was used, the efficiency of consumption, the maximum amount used, and a few other unusual things.
For more information about the control tables that must be set up before you can define a meter, refer to Setting Up Meter Options , and Setting Up Consumption Estimation Parameters.
Item (Equipment) An item that is considered to be "equipment" is a physical device that regulates consumption; it does NOT measure consumption. You would only define equipment if it is of interest to your organization. For example, if your organization periodically tests the pulse initiators associated with your meters, you will need to set up items for each pulse initiator and link them to their respective meters. Equipment can be linked to either a service point (e.g., a current transformer, a backflow device), a meter (e.g., a pulse initiator), or an item (e.g., the components of an installation).
Equipment and billing. Be aware that the only way equipment can impact billing would be if you developed pre-processing calculation groups that analyzed the equipment associated with a service point (directly or indirectly via the meters and items) and manipulated billed consumption accordingly. Refer to Understanding Calculation Groups and Rules for more information.
Item (NOT Equipment) An item is a physical device that does NOT measure consumption, but impacts billing in some way (i.e., there are charges in your rates based on the number and type of items installed at a service point). Examples include street lights, light poles, and security cameras. Items are related to service points and a service point can have one or more items linked to it.
For more information about the control tables that must be set up before you can define an item, refer to Setting Up Items .
For more information about premises and service points, refer to Understanding The "V".
