Meter Solution Products Functional Overview
-
Defining meters, meter configurations, service points, and meter installations.
-
Loading meter readings and interval data from a head-end system or other source.
-
Automatic validation, editing, and estimating measurement data.
-
Robust editing capabilities for readings and interval data
-
Calculating and publishing bill determinants, and other data, from measurement data to be used in external, down-stream systems; such as, billing or pricing.
Oracle Utilities meter solution products store a lot of important data; including, meters, service points, customer contacts, and everything in between.
Measurement, VEE, and Usage Calculation for Billing
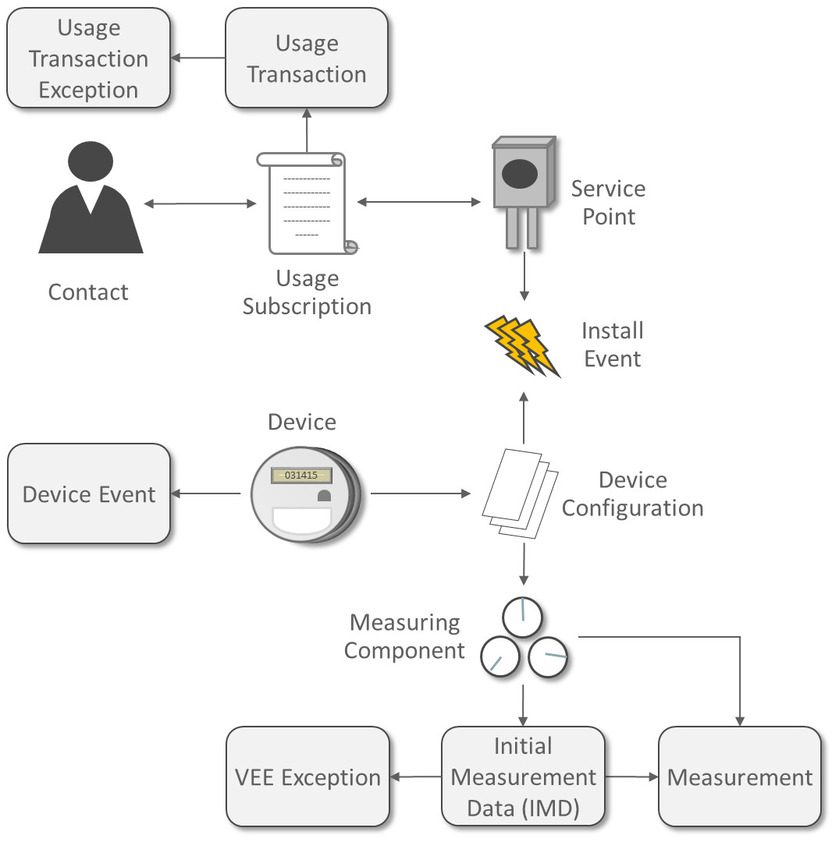
A Device represents a physical meter, communication module, or some other device in the field. A Service Point is the point where service is delivered to a customer and a device can be installed. The Install Event is a record of a specific device that is installed at a Service Point. A Contact is the customer that is associated with the Usage Subscription.
In order to properly track the way that a device is configured, the Device Configuration keeps a record of which types of data should be measured for the device. A Measuring Component represents a single channel of data for a device; for example, a device may have multiple measuring components: one that represents kWh interval data, another that represents kWh scalar readings, and a third that registers Voltage interval data.
Energy data received from meters is initially stored as Initial Measurement Data (IMD). Once the VEE process is executed, if the data passes then Measurements are created. If the data fails, however, then VEE Exceptions are created.
A Usage Subscription tracks a set of usage calculations that should be performed for a single or multiple Points. In order to perform calculation of usage (often referred to as bill determinants), a Usage Transaction is created through a request from the billing system. If any issues are encountered in the usage calculation process, or from a usage transaction validation, then Usage Transaction Exceptions are created.
Service Orders and Remote Commands
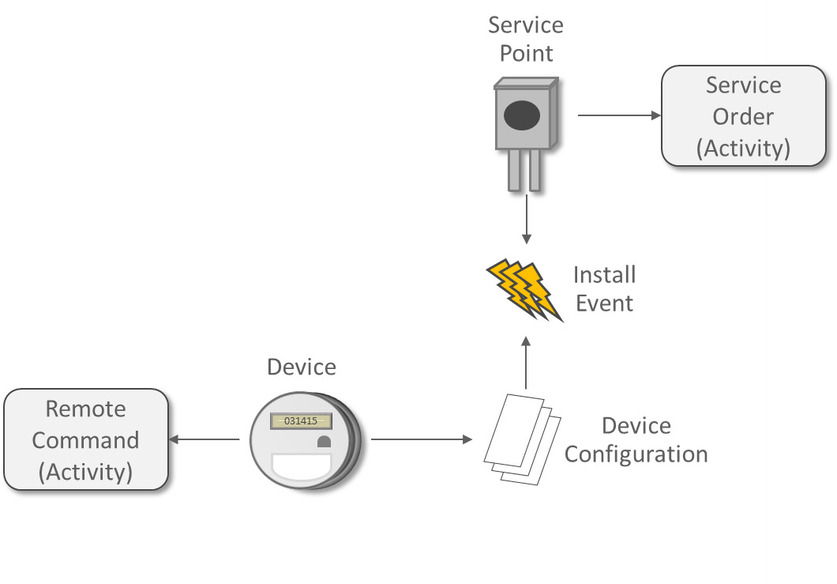
- Remote Commands involve communicating with a Head End system to perform actions or retrieve data from a meter; for example, remote connects, remote disconnects, and on-demand reading.
- Service Orders are methods where work can be performed at a Service Point; for example, enabling service, disabling service, and meter exchanges.
- Device Management is used by analysts and administrators to manage and define the devices used to record and capture meter data.
- Device Installation is used by analysts and administrators to manage device installation; including, defining markets and service providers, service points, contacts, and installation events.
- Measurement Data is a normalized way of storing data from a meter that involves some form of measurement (such as, kWh and CCF). Both interval data and scalar readings are held in this common storage location.
- Validation, Editing, and Estimation (VEE) is used by administrators to define validation, editing, and estimation rules to be applied to measurement data. VEE Exceptions may result from validation or estimation failures and should be worked by analysts through the To Do process.
- 360 Degree Search and View is used by analysts and administrators to search and view data for devices, measuring components, service points, usage subscriptions, and contacts.
- Consumption Sync provides an automatic method to keep interval data and scalar readings in sync with one another.
- Usage Calculation is used by administrators to manage the calculation of usage data and to provide the results of those calculations (commonly referred to as bill determinants) to external systems and parties. Usage calculation groups and rules define calculation rules to be applied to measurement data. Usage Transaction Exceptions may result from usage calculation and should be worked by analysts through the To Do process.
- Device Events provide a view of specific events that have occurred on a meter. These are often unexpected and can indicate an issue with the meter.
- Communication helps track the instances when communication occurs with external systems. This is heavily used to track remote commands against Head End systems.
- Aggregations are used by analysts and administrators to search, view, and maintain aggregated measurements that represent a summarization of other measurements from a set of devices and/or measuring components.
- Master Data Sync defines the methods that data is automatically synchronized to Oracle Utilities Meter Data Management from external sources; such as, a CIS and/or Asset Management system.
- Outage Storm Mode is a way for Oracle Utilities Meter Data Management to detect widespread outages and suppress estimation for those meters until normal data communication resumes.
- Dashboards provide high level metrics for Oracle Utilities Meter Data Management operators to monitor operational trends as well as overall system health.
- Service Issue Monitor can be setup by administrators to monitor various conditions within Oracle Utilities Meter Data Management and automatically create a Service Investigative Order, if those conditions are met.
- Service Order Management provides a centralized program for managing the complex interactions required for Service Order processing. This area is especially valuable for managing service order processing that involves remote communication with a Head End for connects, disconnects, and on-demand readings.
- Market Settlement provides the core functionality for calculating and settling energy changes.
- Information Lifecycle Management is an automated method that administrators can configure to prepare data for archiving or purging after a defined period of time for the record type.
