The Calculation Definition
The Calculation Definition section contains the calculation definition and real time information.
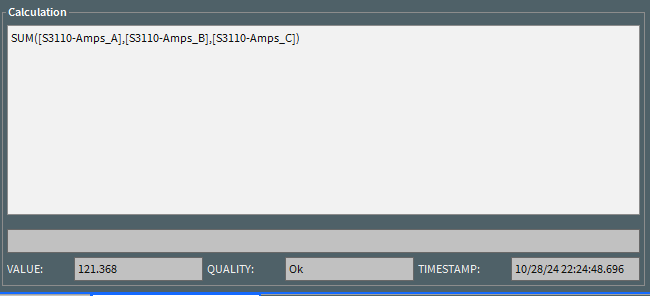
The Calculation Definition consists of:
• The Definition is a text area that allows you to modify the calculations definition.
• The Error field displays any error information associated with the definition.
• The Value field holds the real-time value of the calculation.
• The Quality field contains the quality of the calculation. If this field is empty then calculation has good quality, otherwise it is one of the following values:
• Parse Error: There is a syntax error in the definition of the calculation.
• Circular Reference: There exists a circular reference within this calculation. See Understanding Circular References for more details.
• Missing Dependency: There is a missing dependency within the calculation. See Understanding Missing Dependencies for more details.
• Suspect: One of the calculations dependencies is not good quality. See Understanding Quality Propagation for more details.
• Inhibit: The calculation has been inhibited by an operator.
• Manual: The value of the calculation has been manually entered by an operator.
• Override: The value of the calculation has been manually overridden by an operator.
• The Timestamp field contains the last time the calculation was evaluated.
The Calculation Functions
The Calculation Functions section consists of five tabs:
• The Reference tab allows you to add a calculation, variable, attribute, or SCADA measurement as a dependency to the calculation definition.
• The Operations tab allows you to add a mathematical operator to the calculation definition.
• The Logical tab allows you to add a logical function.
• The Mathematics tab allows you to add a mathematical function.
• The Trigonometry tab allows you to add a trigonometry function.
Selecting a Function
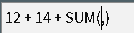
Selecting any function in the Operations, Logical, Mathematics, or Trigonometry tabs will add that function to the calculations definition at the cursor location. The function is added taking into account whether any parameters are required and will move the cursor location to the location of the first parameter required by the function. For example adding the SUM function from the Mathematics tab to the following definition:
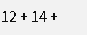
Results in:
Adding a Single Dependency
A single dependency can be added to a calculation definition at the current cursor location by double clicking the item in the Measurements, Attributes, Calculations, or Variables tab. For example, to the variable SQRT3 to the following definition at the current cursor position:

Double click the SQRT3 variable in the variables tab:

In this case a Hard reference to the SQRT3 variable is added as the first parameter of the SUM function.
Adding Multiple Dependencies
Multiple dependencies can be added to the calculation definition at once. First select all the measurements, attributes, calculations, and variables to be added. In this example, the Amps_A, Amps_B, Amps_C measurements and the AMP_LIMIT attribute are selected for device S3111. At this point any function in the Operations, Logical, Mathematics, or Trigonometry tabs can be selected. For instance, selecting the + function in the Operations tab would result in the following being added to the definition at the current cursor position:

Likewise, if the SUM function is selected from the Mathematics tab:

Once the function has been added to the definition all selected measurements, attributes, calculations and variables are unselected.
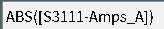
If too many rows are selected for the chosen function then the selected rows will be truncated to the number that makes sense for the function. For instance selecting the Amps_A, Amps_B, Amps_C measurements for device S3111 and then selecting the ABS function in the Maths tab (which only accepts one parameter) will result in the following:
The Reference Tab
The Reference tab allows you to reference other calculations, variables, attributes or SCADA measurements in a definition. The Reference tab consists of the following sections:
• The Reference Device Selection
• The Reference Type
• The Measurements table
• The Attributes table
• The Calculations table
• The Variables table
The Reference Device Selection
The Reference Device Selection allows you to select any device in the NMS model and see its SCADA Measurements, Attributes, and Calculations. The reference device will default to the device associated with the calculation by default but can be changed in order to add entities from another device to the currently edited calculation so a calculation can be dependent on entities from another device. Once the device is selected the Measurements, Attributes and Calculations tables are automatically populated for that device. See Understanding Device Selection for details.
The Reference Type
The Reference Type allows you to define what type of dependency is created when adding a measurement, attribute, calculation or variable to a calculations definition.
• A Hard Reference is denoted by square brackets [] surrounding the id of the measurement, attribute, calculation or variable. A hard reference indicates that if the encased dependency changes value or quality then this calculation will be re-evaluated.
• A Soft Reference is denoted by curly brackets {} surrounding the id of the measurement, attribute, calculation or variable. A soft reference indicates that if the encased dependency changes value or quality then this calculation will not be re-evaluated.
Measurements
The Measurements table contains all the measurements for the Reference Device. The table consists of:
• The Measurement name
• The Value of the measurement
• The Quality of the measurement
Attributes
The Attributes table contains all the attributes for the Reference Device. The table consists of:
• The Attribute name
• The Value of the attribute
Calculations
The Calculations table contains all the calculations for the Reference Device. The table consists of:
• The Inheritance of the calculation
• The Calculation name
• The Value of the calculation
• The Quality of the calculation
• The inhibit Comment of the calculation
• Who inhibited the calculation
• The Comment Time indicating when the inhibit operation was applied.
The calculations have the following popup menu items available:
Menu Option | Description | Toolbar Icon |
|---|---|---|
Details… | Opens the Calculation Editor to allow you to view or edit the calculation details. See Understanding the Calculation Editor for details. | |
Delete… | Opens the Delete dialog box for the selected calculations. See Understanding the Delete Dialog Box for details. | |
Inhibit… | Opens the Inhibit dialog box for the selected calculation. See Understanding the Inhibit Dialog Box for details. | |
Manual Entry… | Opens the Manual Entry dialog box for the selected calculation. See Understanding the Manual Entry Dialog Box for details. | |
Manual Override… | Opens the Manual Override dialog box for the selected calculation. See Understanding the Manual Override Dialog Box for details. | |
Cancel Inhibit… | Cancels inhibit for the selected calculation. See Understanding Cancel Inhibit for details. | |
Cancel Manual Entry… | Cancels manual entry for the selected calculation. See Understanding Cancel Manual Entry for details. | |
Cancel Override… | Cancels manual override for the selected calculation. See Understanding Cancel Manual Entry for details. |
Variables
The Variables table contains all the variables in the system. The table consists of:
• The Variable name
• The Value of the variable
• The Quality of the variable
• The inhibit Comment of the variable
• Who inhibited the variable
• The Comment Time indicating when the inhibit operation was applied.
The variables have the following popup menu items available:
:
Menu Option | Description | Toolbar Icon |
|---|---|---|
Details… | Opens the Calculation Editor to allow you to view or edit the calculation details. See Understanding the Calculation Editor for details. | |
Delete… | Opens the Delete dialog box for the selected calculations. See Understanding the Delete Dialog Box for details. | |
Inhibit… | Opens the Inhibit dialog box for the selected calculation. See Understanding the Inhibit Dialog Box for details. | |
Manual Entry… | Opens the Manual Entry dialog box for the selected calculation. See Understanding the Manual Entry Dialog Box for details. | |
Manual Override… | Opens the Manual Override dialog box for the selected calculation. See Understanding the Manual Override Dialog Box for details. | |
Cancel Inhibit… | Cancels inhibit for the selected calculation. See Understanding Cancel Inhibit for details. | |
Cancel Manual Entry… | Cancels manual entry for the selected calculation. See Understanding Cancel Manual Entryfor details. | |
Cancel Override… | Cancels manual override for the selected calculation. See Understanding Cancel Manual Override for details. |
The Operations Tab
The Operations tab contains the following set of operators that can be added to the calculations definition:
Function | Description |
|---|---|
+ | Addition |
- | Subtraction |
* | Multiplication |
/ | Division |
= | Equality |
<> | Not equals |
> | Greater than |
< | Less than |
>= | Greater than equals |
<= | Less than equals |
\ | Integer division |
^ | Power |
( | Open bracket |
) | Close bracket |
The Logical Tab
The Logical tab contains the following set of operators that can be added to the calculations definition:
Function | Description |
|---|---|
AND | Logical AND |
OR | Logical OR |
NOT | Logical NOT |
IF | IF statement in the form: IF(condition, true path, false path) |
TRUE | True constant |
FALSE | False constant |
The Mathematics Tab
The Mathematics tab contains the following set of functions that can be added to the calculations definition:
Function | Min Params | Max Params | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ABS | 1 | 1 | Returns the absolute value of a value |
CBRT | 1 | 1 | Returns the cube root of a double value. |
CEILING | 1 | 2 | Returns the smallest (closest to negative infinity) double value that is greater than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. for example, CEILING(value) or CEILING(value,significance) |
COPYSIGN | 2 | 2 | Returns the first floating-point argument with the sign of the second floating-point argument. for example, COPYSIGN(magnitude,sign) |
DECEXACT | 1 | 1 | Returns the argument decremented by one. |
EXP | 1 | 1 | Returns Euler's number e raised to the power of a double value. |
EXPM1 | 1 | 1 | Returns e^x -1. Note that for values of x near 0, the exact sum of expm1(x) + 1 is much closer to the true result of ex than exp(x). |
FLOOR | 1 | 2 | Returns the largest (closest to positive infinity) double value that is less than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. for example, Floor(a) or Floor(a, significance) |
FLOORDIV | 2 | 2 | Returns the largest (closest to positive infinity) integer value that is less than or equal to the algebraic quotient. |
FLOORMOD | 2 | 2 | Returns the floor modulus of the arguments |
GETEXP | 1 | 1 | Returns the unbiased exponent used in the representation of a double. |
HYPOT | 2 | 2 | Returns SQRT(x^2 +y^2) without intermediate overflow or underflow |
INCEXACT | 1 | 1 | Returns the argument incremented by one |
INT | 1 | 1 | Round down to integer |
LOG | 1 | 1 | Returns the natural logarithm (base e) of a value |
LOG10 | 1 | 1 | Returns the base 10 logarithm of a value |
LOG1P | 1 | 1 | Returns the natural logarithm of the sum of the argument and 1 |
MAX | 2 | M | Returns the greater of two or more values |
MIN | 2 | M | Returns the lesser of two or more values |
MOD | 2 | 2 | Returns the mod of two values |
MULTIPLYEXACT | 2 | 2 | Returns the product of the arguments as an integer |
NEGATEEXACT | 1 | 1 | Returns the negation of the argument as an integer |
PI | 0 | 0 | The double value that is closer than any other to pi, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter. |
POWER | 2 | 2 | Returns the value of the first argument raised to the power of the second argument. |
RAND | 0 | 2 | Returns a random number. RAND() returns a random integer. RAND(a) returns a random number between 0(inclusive) and a(exclusive). RAND(a,b) returns a random number between a(inclusive) and b(exclusive) |
RANDBOOLEAN | 0 | 0 | Returns a random Boolean value |
RANDDOUBLE | 0 | 0 | Returns a random double value |
RANDLONG | 0 | 0 | Returns a random long value |
RINT | 1 | 1 | Returns the double value that is closest in value to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. |
ROUND | 1 | 1 | Returns the closest value to the argument, with ties rounding to positive infinity. |
SCALB | 2 | 2 | Returns d × 2^scaleFactor rounded as if performed by a single correctly rounded floating-point multiply to a member of the double value set. for example, SCALB(a, scalefactor) |
SIGN | 1 | 1 | Returns the sign of a value for example, SIGN(-a) returns -1, SIGN(0) returns 0, SIGN(+a) returns 1 |
SQRT | 1 | 1 | Returns the correctly rounded positive square root of a value. |
SUBTRACTEXACT | 2 | 2 | Returns the difference of the arguments as an integer. |
SUM | 1 | M | Returns the sum of all arguments. |
TODEGREES | 1 | 1 | Converts an angle measured in radians to an approximately equivalent angle measured in degrees. |
TORADIANS | 1 | 1 | Converts an angle measured in degrees to an approximately equivalent angle measured in radians. |
The Trigonometry Tab
The Trigonometry tab contains the following set of functions that can be added to the calculations definition:
:
Function | Min Params | Max Params | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ACOS | 1 | 1 | Returns the arc cosine of a value; the returned angle is in the range 0.0 through pi. |
ASIN | 1 | 1 | Returns the arc sine of a value; the returned angle is in the range -pi/2 through pi/2. |
ATAN | 1 | 1 | Returns the arc tangent of a value; the returned angle is in the range -pi/2 through pi/2. |
ATAN2 | 2 | 2 | Returns the angle theta from the conversion of rectangular coordinates (x, y) to polar coordinates (r, theta). This method computes the phase theta by computing an arc tangent of y/x in the range of -pi to pi. |
COS | 1 | 1 | Returns the trigonometric cosine of an angle. |
COSH | 1 | 1 | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a double value. |
SIN | 1 | 1 | Returns the trigonometric sine of an angle. |
SINH | 1 | 1 | Returns the hyperbolic sine of a double value. |
TAN | 1 | 1 | Returns the trigonometric tangent of an angle. |
TANH | 1 | 1 | Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a value. |