10.1.2 Definitions
Neither the static spread nor the OAS can be defined directly as they are solutions of two different equations. We give hereafter a simplified version of the equations that the system solves, using the assumptions described earlier. The static spread is the value ss that solves the following equation:
Equation 1
Figure 10-1 Equation 1
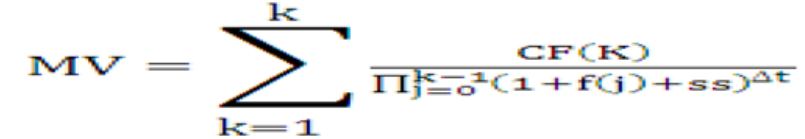
Description of the Transfer Pricing Option Cost Equation 1 follows:
Where:
Table 10-1 Transfer Pricing Option Cost Equation 1
| :MV | market, or book, or par value of the instrument (as selected in the Transfer Pricing rule) |
|---|---|
|
CF(k) |
cash flow occurring at the end of month k along with the forward rate scenario |
|
:f(j) |
forward rate for month j |
|
∆t |
length (in years) of the compounding period; hard-coded to a month, such as 1/12 |
In the Monte Carlo Methodology, the option adjusted-spread is the value OAS that solves the following equation:
Equation 2:
Figure 10-2 Equation 2
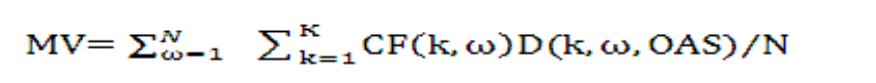
Description of the Transfer Pricing Option Cost Equation 2 follows:
Where:
Table 10-2 Transfer Pricing Option Cost Equation
| : N | total number of Monte Carlo scenarios |
|---|---|
|
CF(K,ω) |
cash flow occurring at the end of month k along scenario ω |
|
D(k, ω,OAS) |
fstochastic discount factor at the end of month k along scenario ω for a particular OAS |
- Cash Flows are calculated up till maturity even if the instrument is
adjustable.
Note:
Otherwise, the calculations would not catch the cost of caps or floors. - In the real calculations, the formula for the stochastic discount factor is simplified.