13.17.2 The Formula for a Coupon Rate
Suppose that the security is issued at time t and pays T year(s) after it has been issued. A typical example would be a 6-month T-bill, that is, T=0.5. The owner of the security will receive at time t+T:
Figure 13-16 Cash Flow Formula
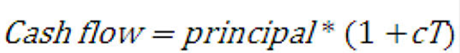
Description of formula to calculate the Cash Flow follows:
Where c is the unknown (annual) coupon rate. In a no-arbitrage economy this Cash Flow should be equal to:
Figure 13-17 Future Value Principal Calculation Formula
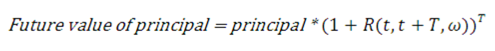
Description of formula to calculate the future value of principle follows:
Solving for the coupon rate gives the equation:
Figure 13-18 Coupon Rate Calculation Formula
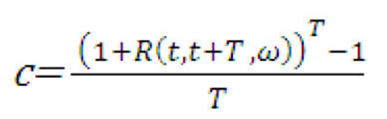
Description of formula to calculate the coupon rate follows:
Because yields are usually much smaller than 100%, we can expand the numerator of the right-hand side in a Taylor series:
Figure 13-19 Formula to calculate the Coupon Rate
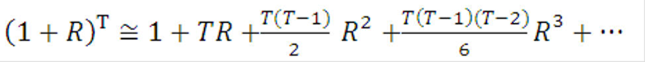
Description of formula to calculate the coupon rate follows:
Therefore:
Figure 13-20 Formula to calculate the Coupon Rate
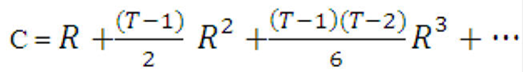
Description of formula to calculate the coupon rate follows:
The user would then input the following formula coefficients:
Table 13-14 Formula Coefficients
| i | ai | bi | i |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
T τ |
|
2 |
(T-1)/2 |
2 |
T |
|
3 |
(T-1)(T-2)/6 |
3 |
T |
All other coefficients are equal to zero. The following example shows that we do not need to go very far in the Taylor series to converge to the true value of the coupon rate. This is important to remember because a long formula necessitates more computing time than a slow one.
Term: T=0.5
Yield: R =0.05
Table 13-15 Example of the Taylor Series to Converge to the true value of the Coupon Rate
| Order of approximation | Formula | Coupon |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
R |
0.05 |
|
2 |
R+((T-1)/2)R2 |
0.049375 |
|
3 |
R+((T-1)/2)R2+((T-1)(T-2)/6)R3 |
0.049390625 |
|
True value |
((1+R)T-1)/T |
0.049390153 |