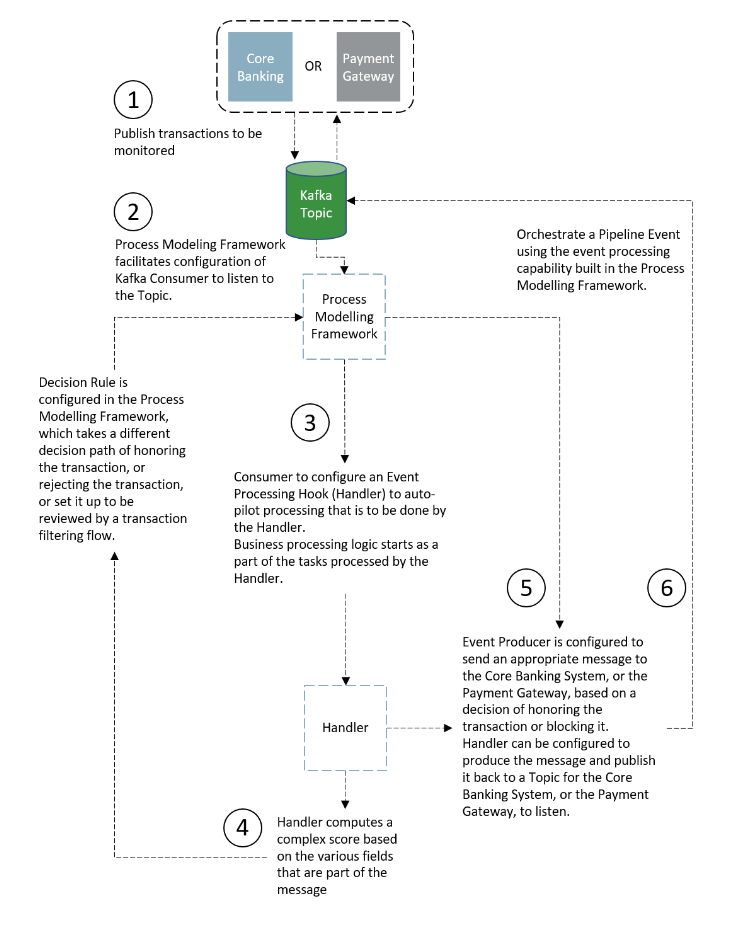
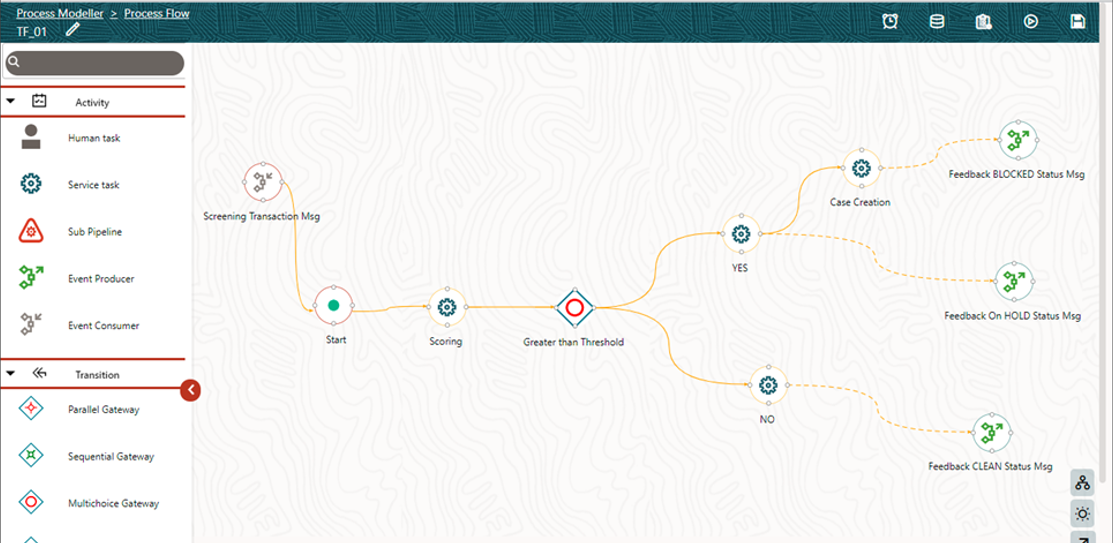
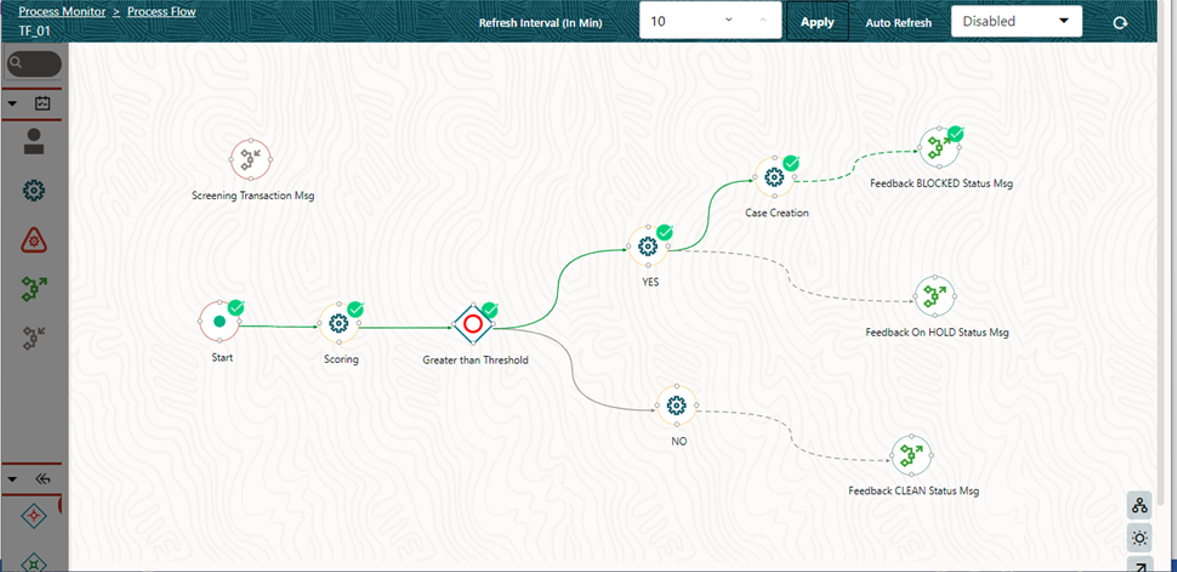
Use Case: Event-Based Framework Execution in Real-time Transaction Monitoring
The operational mechanism of the Event Processing Pipeline is better
understood with a Use Case that describes the execution of real-time Transaction
Monitoring.
The following steps describe the Use Case Configuration: