Example of an Alert Assignment
Alert Assignment rules are created in the editor as a series of operation sets that are chained together to form a decision tree. The assignment algorithm will move through the decision tree in ascending order of the defined operation sets until all rules have been processed and alerts assigned.
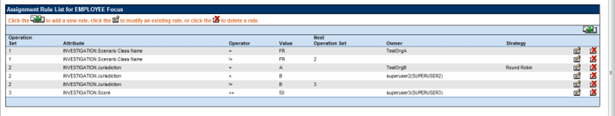
Example 1
This example demonstrates how rules can be created using multiple operation sets to
combine together to form a series of specific conditions to be met to control alert
assignment.
The rules set up in this figure reflect the following logic and use of operations sets.
- Per Operation Set 1 all alerts that are created on Scenario Class FR will be routed to Pool TestOrgA
- If the Scenario Class is not FR the algorithm will look to Next Operation Set 2.
- Per Operation Set 2 if the Jurisdiction of the alert is A then it should be routed to Pool TestOrgB with a Strategy of Round Robin.
- If the Jurisdiction of the alert is not A the algorithm will continue with the next rule that is part of Operation Set 2.
- If the Jurisdiction of the alert is B then it should be routed to Superuser2.
- If, at this point, the algorithm has determined that the alert is not of Scenario Class FR and is not in Jurisdiction A or B, then the algorithm will move to Next Operation Set 3.
- Per Operation Set 3 if the score of the alert is >= 50 then it should be routed to Superuser3.
- If none of the above rules are met the alert will be routed to the default owner defined for alert assignment.
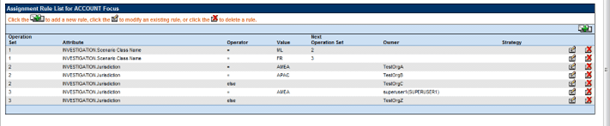
Example 2
This example demonstrates how rules can be created using the Else operator. The goal
of this set of rules is to have specific assignment for some alerts within a
scenario class based on selected criteria while all other alerts within that class
go to the same owner when that criteria is not met.
The rules set up in this figure reflect the following logic and use of operations sets.
- Per Operation Set 1 check to see if the Scenario Class is ML. If so proceed to Next Operation Set 2.
- If Scenario Class is not ML but is FR then the algorithm will proceed to Next Operation Set 3.
- Per Operation Set 2, for ML class alerts the algorithm will check if the Jurisdiction matches AMEA. If it does alerts will be assigned to TestOrgA.
- If an ML class alert and the Jurisdiction is not AMEA the algorithm will check to see if the Jurisdiction is APAC. If it is alerts will be assigned to TestOrgB.
- Otherwise, if an ML class alert and the Jurisdiction is other than AMEA or APAC the alert will be assigned to TestOrgC.
- Per Operation Set 3, for FR class alerts the algorithm will check if the Jurisdiction matches AMEA. If it does alerts will be assigned to Superuser1.
- If a FR class alert and the Jurisdiction is other than AMEA the alert will be assigned to TestOrgZ.
- If none of the above rules are met the alert will be routed to the default owner defined for alert assignment.