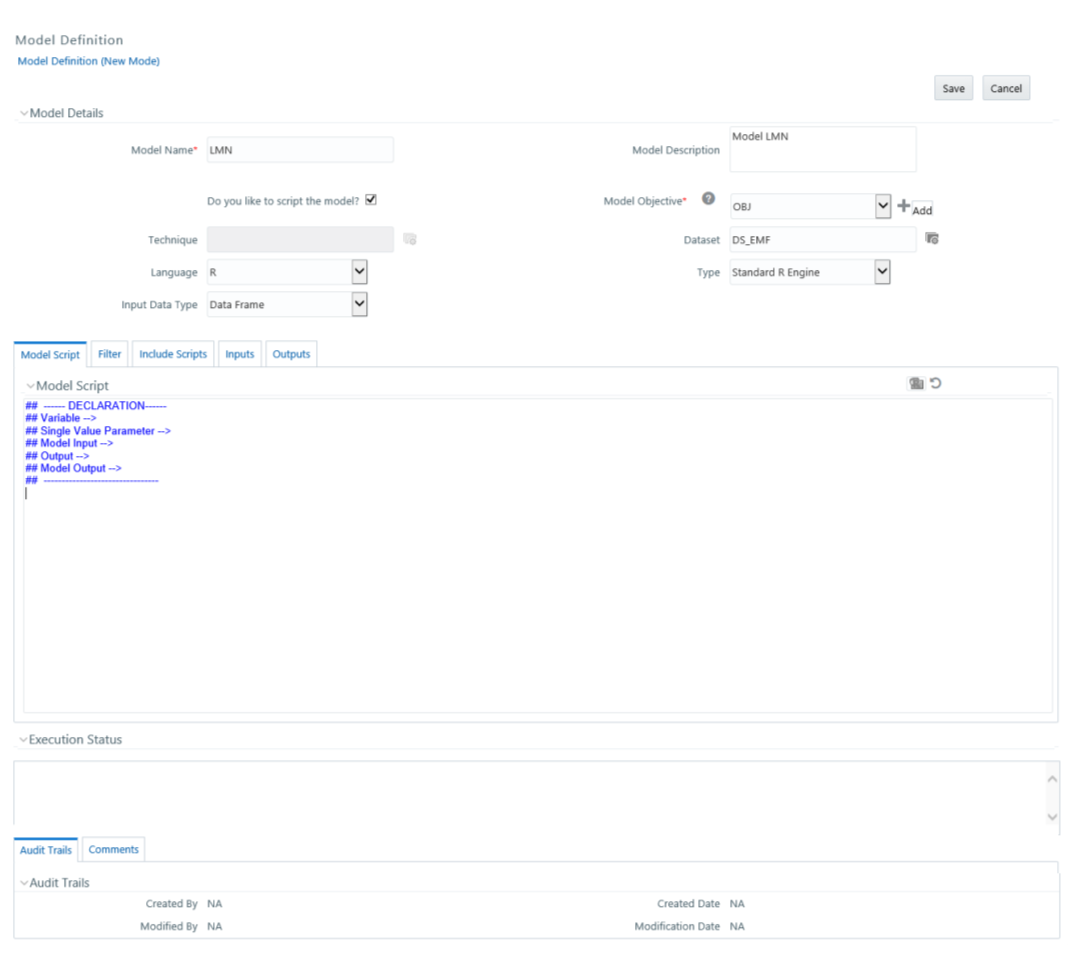
Creating a Model using Script
This feature allows you to create models based on user-written scripts. The
supported scripting languages are Standard R and ORE. The script should be valid.
In the case of the R script, all the object names used in the R-script
should be syntactically valid. You should select Language as ORE if you are using ORE
functions in the script. ORE enables transparent access to data stored in the Database
for scalability and high performance. For more information, see Enterprise Modeling
support for R Scripts and Oracle R Enterprise (ORE) Statistical Functions.
The models defined based on R scripting can be directly deployed to
the Production Infodom without an execution in the sandbox.
To create a model using a script, follow these steps: