4.2.5 Entity Resolution Mapping Information
FCC_ER_MAPPING: It stores the mapping between Customer IDs in the input table STG_PARTY_MASTER_PRE and Global Party IDs in the output table STG_PARTY_MASTER.
The following table describes column details in the FCC_ER_MAPPING.
Table 4-1 FCC_ER_MAPPING Details
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| V_GLOBAL_ID | It represents the global party id generated after Entity Resolution. |
| V_ENTITY_ID | It represents the original entity ids.
For example, STG_PARTY_MASTER_PRE.V_PARTY_ID |
| F_LRI_FLAG | It indicates the state of a global id. The expected
values are ‘Y’ or ‘N’.
‘Y’ indicates active and ‘N’ indicates inactive. |
| D_CREATED_DATE | It stores the date and timestamp of a newly created
Global Id from both ER batches and manual actions.
Note: In case of add scenario, the D_CREATED_DATE column will be updated for the added entity in a global party. Existing entities will remain unchanged. |
| D_UPDATED_DATE | It stores the date and timestamp of an
updated/deactivated Global Id from ER batches and manual
actions.
Note: In case of split and merge, the D_UPDATED_DATE column will be updated only for the deactivated global ids, and D_CREATED_DATE will be updated for the newly generated global ids. |
| V_ACTION | Information about V_ACTION column, see the following section. |
| V_PIPELINE_ID | It represents the implementation of Entity Resolution flow. For example, you have two pipeline ids for two versions of FSDF (i.e., 811 and 812). |
| V_COMMENT_ID | It stores the ID reference of the comments that are entered by a user while performing manual actions on a global party from Manual Decision UI and Merge and Split UI. This column will only store the Id and the respective comment will be stored in the fcc_er_gp_comments table. |
| F_OVERRIDE_FLAG | This flag controls whether to override the manual
decision or not irrespective of the V_MD_FLAG value.
By default it should be null. |
| V_MD_FLAG | It stores the state of the records upon which manual
actions are taken from Manual Decision UI and Merge and Split
UI.
The expected values are:
Note: The value in this column will be NULL for the records generated from Entity Resolution batches. The values will be populated for the entities upon which any manual action has been taken from Merge and Split UI. |
| N_RUN_SKEY | It signifies the execution identifier of an Entity
Resolution batch. This identifier will be updated for all the impacted
entities in an ER batch.
For example: When a new global party is created, a new entity is added to an existing global party, an existing global party is split, existing global parties are merged or an existing global party is deactivated. |
| N_CREATED_RUN_SKEY | It contains runskey on which the global party was created. This column would be null if the global party was created as a result of manual action taken from the Merge and Split Global Entities UI. |
The following section describes V_ACTION column in the FCC_ER_MAPPING.
V_ACTION Details for Batch Execution
- New Global Party: On the first run of ER batches, the value of the
V_action column will be a new global party for all the records. In
subsequent batches, if there is no change in the existing entities, it will
remain the same as new global party.
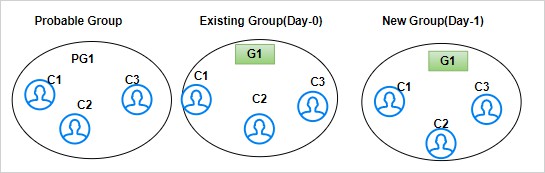
For example, G1 has C1, C2 and C3 entities. After the Day 1 batch execution, if there is no change in the existing group. Still, G1 has C1, C2 and C3 entities with the same global id.
- add: If a new entity is available and matches the existing group, then it
is defined as add in the V_ACTION column for a newly added entity. If a
new entity matches the existing group, it will be added to the existing group
and assigned the same global id.
For example, G1 has C1 and C2 entities. After the Day 1 batch execution, if C3 entity matches with C1 or C2 then C3 will be added to the existing group G1 with the same global id.
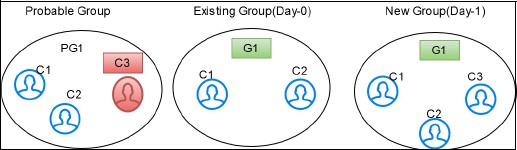
- merge: If there is a data change in the entity of a
different group and it merges with another group, then it is defined as
merge in the V_ACTION column for the merged entities. The changed
entities can be merged with an existing group with new global id is assigned and
the previous global id will be de-activated.
For example, G1 has C1 and C2 entities and G2 has a C3 entity. After the Day 1 batch execution, if C3 entity matches with an existing group then C3 will be merged into the existing group with a new global id. The V_ACTION column for G3 will merge and G1 and G2 will be deactivated.
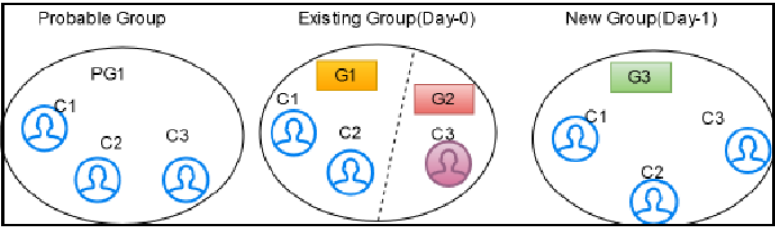
- split: If there is a data change in the existing group entity
which does not matches with other entities of an existing group; then it is
defined as split in the V_ACTION column for the split entities. The
changed entities can be split into a new group and a new global id is assigned
to each.
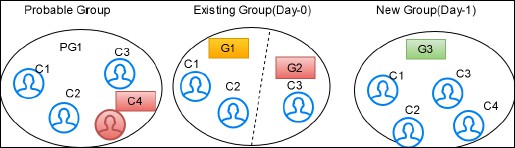
For example, G1 has C1, C2, C3 and C4 entities. After the Day 1 batch execution, if C3 and C4 entities are not matched with the existing entities of the group then C3 and C4 will be split into a new group. G2 has C1 and C2 entities and G3 has C3 and C4 entities with a new global id assigned to each group. The V_ACTION column for G2 and G3 will split and G1 will be deactivated.
- merge and add: If there is a data change in the existing group and a new
entity is available, which also matches with the existing group; then it is
defined as merge and add in the V_ACTION column for the updated and new
entities. All the entities are grouped into a single group with a new global
id.
For example, G1 has C1 and C2 entities, G2 has C3 entity. After the Day 1 batch execution, if C4 entity is added newly and C3 entity got changed then common entities are merged into a single group and a new entity is added to the group with a new global id (G3 has C1, C2, C3, and C4 entities). The V_ACTION column for G3 will merge and add, G1 and G2 will be deactivated.
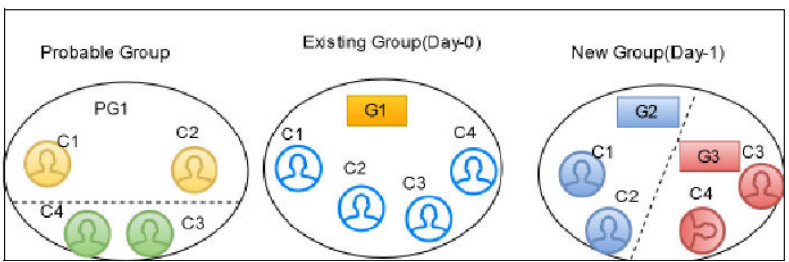
- split and merge: If there is a data change in the entity of the first group that
matches with another entity of the second group and also an entity from the
second group matches with any entity of first group; then it is defined as
split and merge in the V_ACTION column for affected entities. The
changed entities can be split and merged into a new group with a new global id
is assigned to each group.
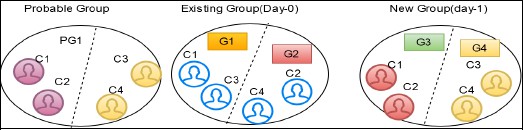
For example, G1 has C1 and C3 entities and G2 has C2 and C4 entities. After the Day 1 batch execution, if C1 matches with C2 and C3 matches with C4 then C2 and C4 will be split separately and merged with C1 and C3 respectively. G3 has C1 and C2 entities and G4 has C3 and C4 entities with a new global id assigned to each group. The V_ACTION column for G3 and G4 will split and merge and G1 and G2 will be deactivated.
V_ACTION Details for Manual Action
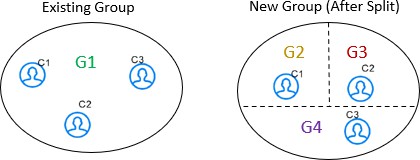
- split: You can split the entities into different groups with new global
ids assigned to each.
For example, G1 has C1, C2, and C3 entities. After split, G2 has C1, G3 has C2 and G4 has C3 with new global ids assigned to each group. The V_ACTION column for G2, G3 and G4 will split and G1 will be deactivated.
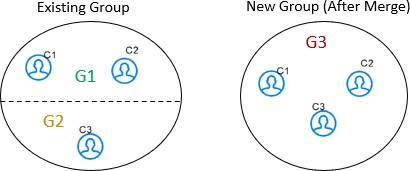
- merge: You can merge the different entities into a single group with a
new global id is assigned.
For example, G1 has C1 and C2 entities, G2 has C3 entities. After merge, G3 has C1, C2, and C3 entities with a new global id. The V_ACTION column for G3 will merge and G1 will be deactivated.
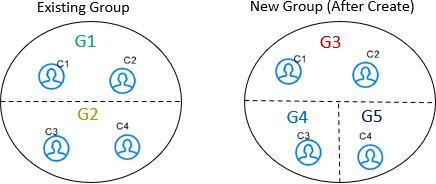
- create: You can create a new entity from the existing group with a new
global id is assigned.
For example, G1 has C1 and C2 entities, G2 has C3 and C4 entities. After create, G3 has C1 and C2 entities, G4 has C3 entity and G5 has C4 entity with new global ids assigned to each group. The V_ACTION column for G3, G4 and G5 will create and G1 will be deactivated.
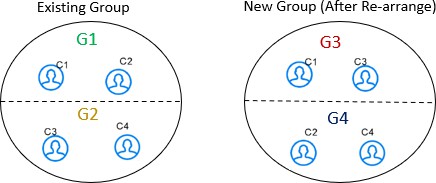
- rearrange: You can rearrange the entities from another group with a new
global id is assigned.
For example, G1 has C1 and C2 entities, G2 has C3 and C4 entities. After rearrange, G3 has C1 and C3 entities and G4 has C2 and C4 entities with new global ids assigned to each group. The V_ACTION column for G3 and G4 will rearrange and G1 and G2 will be deactivated.