4 Entity Resolution
OFS Compliance Studio provides Entity Resolution (ER) capability. It allows firms to break through barriers in their data by gaining single views of their customers and their external entities and have the choice of monitoring them both under one consolidated Global Party.
OFS Compliance Studio Entity Resolution is a configurable process that allows data to be matched and merged to create contextual links in the global graph or resolve relational party records to a global party record as part of ingestion. OFS Compliance Studio has pre-built configurations supporting matching (or linking) in the FCGM and resolving entities in CSA for data being loaded into Financial Services Data Foundation (FSDF).
- Comparison for Delta Processing
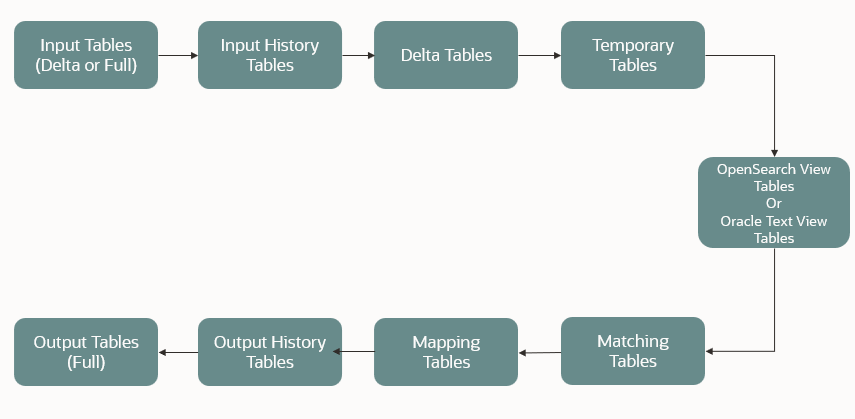
The first time Entity Resolution runs, it operates on the full data set. This means the initial run will take longer than subsequent runs after the initial processing where deltas (changed records) are calculated (regardless of whether full or delta data is populated in the input tables) so that matching happens only on new and changed records for improved performance.
- Candidate Selection
Scoring on all pairs of records is not performant, so the Entity Resolution process first finds candidates with similar attributes and only scores on those pairs of records. Candidate Selection can either be run using Oracle OpenSearch or in the database using Oracle Text (OT).
- Matching
Matching rules are used to compare entities to identify pairs that refer to the same entity. It creates a probable link between entities by comparing the attributes of the entities.
For example, deduplicating customers, resolving derived entities, or linking customers or derived entities to external data such as Panama papers or sanctions lists with different rules and thresholds.
- Grouping
It is used to Group (entity Ids or Customer Ids) based on similarity links between entities using matching rules and applying the merge rules on similarities. Once it is grouped, the system assigns the global party id to each Group.
Note:
Grouping is an automatic process. Grouping will be based on the match edges without any configuration. - Merge Rules
Merging rules are used to group multiple entities or customers into a single global party based on the merge ruleset.
- Persisting
Records identified for merging will be collapsed into a single global party record, and a mapping from this global party record to the original party records will be created. Ongoing changes to the original party records may impact the global parties.
- Data Survival
When party records are identified for merging, a single output party record is created for the main or parent Dataset. Entity Resolution provides a mechanism to select the best data view from across the multiple-party records using attribute-by-attribute selection functions like Most Common or Maximum. It also provides a mechanism for transforming the child records stored in related tables, such as an address, email, or document ids.
- Merge and Split Global Parties:Entity Resolution provides a mechanism to merge, split, create manually, and rearrange the entities for Global parties. Whenever there is a manual action (merge, split, create, rearrange) to the entities of a global party, the same data survival logic will be applied.
Note:
- When the records are not matched and not merged, they pass straight through and have a one-to-one mapping with the global party.
- Where Entity has been resolved/unresolved, data origin is set to EntRes for all the records.
- The Data Survival job cannot override the manual actions to a global party in batch mode.