4.5.1 Persisting the Data When F_PERSIST_GUID and F_MANUAL_APPROVAL Flags are Set to False Condition
Note:
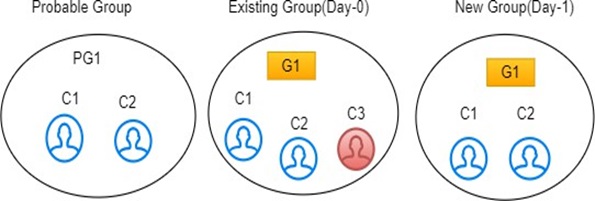
This section is applicable only if F_PERSIST_GUID and F_MANUAL_APPROVAL flags are set to False in the FCC_ER_GUID_PERSIST_CONFIG table in the ER schema.Existing group elements are a subset of probable group elements, and the number of elements is the same in both groups. All elements in the existing Group have the same global id. The existing global id is assigned to probable group elements.
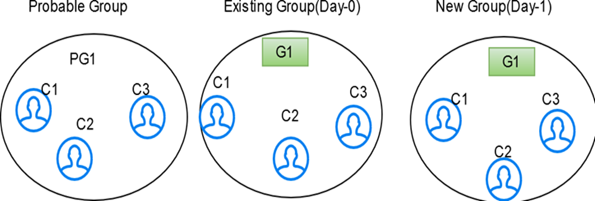
Existing group elements are a subset of probable group elements, and the number of elements in the probable Group is more than the existing Group. Extra elements in the probable Group don't have any global id assigned yet. New elements are added to the existing Group, and the same global id is assigned.
Existing group elements are a subset of probable group elements, and the number of elements is the same in both groups. Elements in the existing Group have different global ids assigned.
Elements are merged into a single group, and a new global id is assigned.
Existing group elements are a subset of probable group elements, and the number of elements in the probable Group is more than the existing Group. Extra elements in the probable Group don't have any global id assigned yet, and standard elements have different global IDs assigned already. Common elements are merged into a single group, and new elements are added to the Group with a new global id.
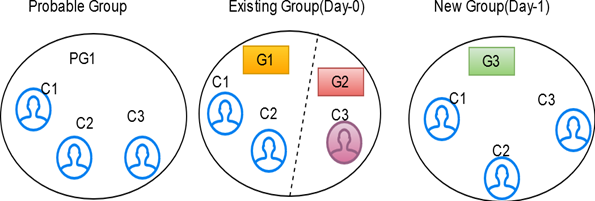
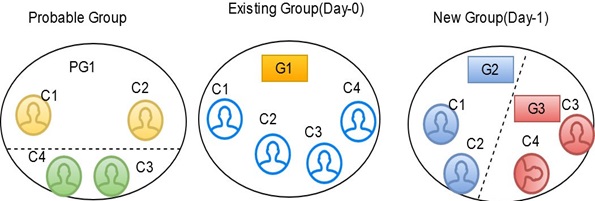
After applying merging rules criteria, if multiple groups are created for elements of a probable group, these elements are also a subset of existing group elements. The number of elements in both probable and existing groups is the same. A single global id is assigned to all elements in the existing Group, and then probable group elements are split into different groups with new global ids assigned to each.
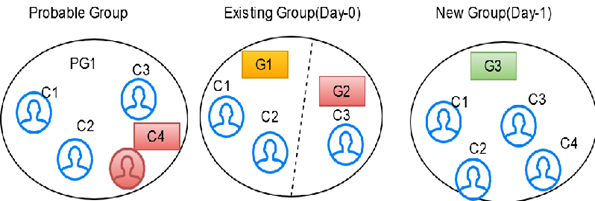
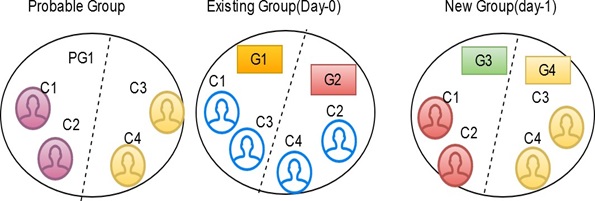
For example, G1 has C1, C2, C3 and C4 entities. After the Day 1 batch execution, if C3 and C4 entities are not matched with the existing entities of the group then C3 and C4 will be split into a new group. G2 has C1 and C2 entities and G3 has C3 and C4 entities with new global id is assigned to each group.
After applying merging rules criteria, if multiple groups are created for elements of a probable group, these elements are also a subset of existing group elements. The number of elements in both probable and existing groups is the same, and different global ids are assigned to elements in the existing Group, then probable group elements are split into different groups and merged, satisfying the same ruleset criteria with new global ids assigned to each.
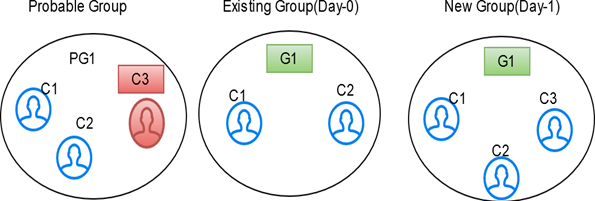
If an element exists in the existing Group, but the same element doesn't belong to any probable group and doesn't exist in the customer/entity dataset, it is deleted from the existing group with same global id assigned.If the deleted record is part of STG_DELETED_PARTIES_PRE table then underlying customers will also be deleted.