20.21 Event Expiry
This section describes the Event Expiry.
ECM Engine accepts the events generated from various transaction monitoring applications (CS, KYC, and so on) and processes these for correlation. After scoring each event, the engine will promote these correlations which have a score more than a threshold score. But, some events in the back end are not used because the associated attributes of these events didn't yield enough score. So these events/correlations are not promoted to a case. A few events scores may also drop to '0' or below by increase in age. ECM engine identifies such events and removes them from the correlation process.
The engine will not only remove these events but also remove the evented data related to events. Following are the conditions by which events are identified for expiry:
- Events with age greater than the specified time period. For more information, see the Identifying Events by Age section.
- Events score <= 0. For more information, see the Identifying Events by Scoresection.
Identifying Events by Age
The ageing rules are defined in IPE to identify the events by age for expiry. This IPE rule is configurable by
- Age
- EventType
- Jurisdiction
- Domain
This rule runs post correlation batch and identifies the events that need to be archived, which is move to the expiry events table.
Identifying Events by Score
Events that need to be expired can be identified through event score.
Examples
The following is the list of examples:
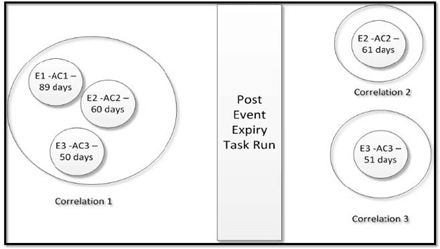
- In the below example, Event E1, E2, and E3 are correlated in Correlation 1. When the
task for Event expiry is executed, Event E1 will be out of the case correlation
based on the defined IPE rule. Event E2 and Event E3 will be correlated to
Correlation 2 and Correlation 3 respectively.
Figure 20-27 Event E1, E2, and E3 are correlated in Correlation 1
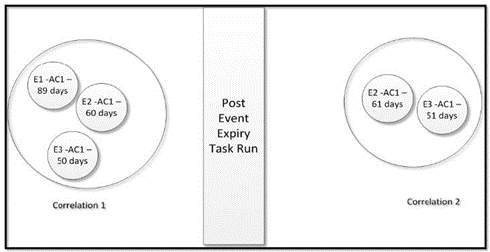
- In the below example, Event E1, E2, and E3 are correlated in Correlation 1. When the
task for Event expiry is executed, Event E2 will not be promoted to the case based
on the defined IPE rule. Event E1 and Event E3 will be correlated together in
Correlation 2.
Figure 20-28 2nd example of Event E1, E2, and E3 are correlated in Correlation 1
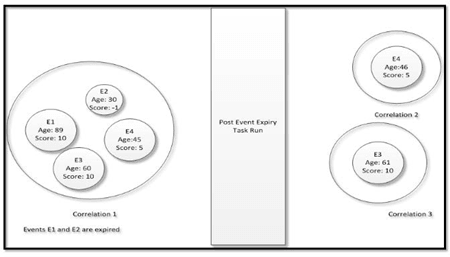
- In the below example, Event E1, E2, E3, and E4 are correlated in Correlation 1. When
the task for Event expiry is executed, Event E1 and Event E2 will not be promoted to
case based on defined scoring.Event E3 and Event E4 will be correlated to
Correlation 2 and Correlation 3 respectively.
Figure 20-29 3rd example of Event E1, E2, and E3 are correlated in Correlation 1
Configuring Event Expiry
To configure the event expiry, follow these steps:
- Create an IPE rule for event expiry. For more information, see the IPE User Guide on OHC.
- Navigate to Enterprise Case Management Application.
- Go to the Common task section. Select the Run Rule Framework.
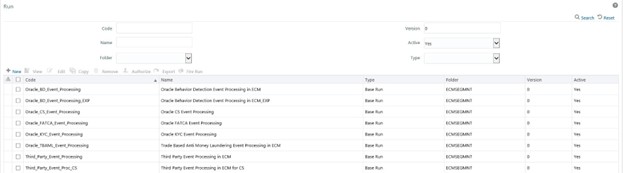
- Click Run. The Run Summary window is displayed with the available
Processes.
Figure 20-30 Run Summary screen
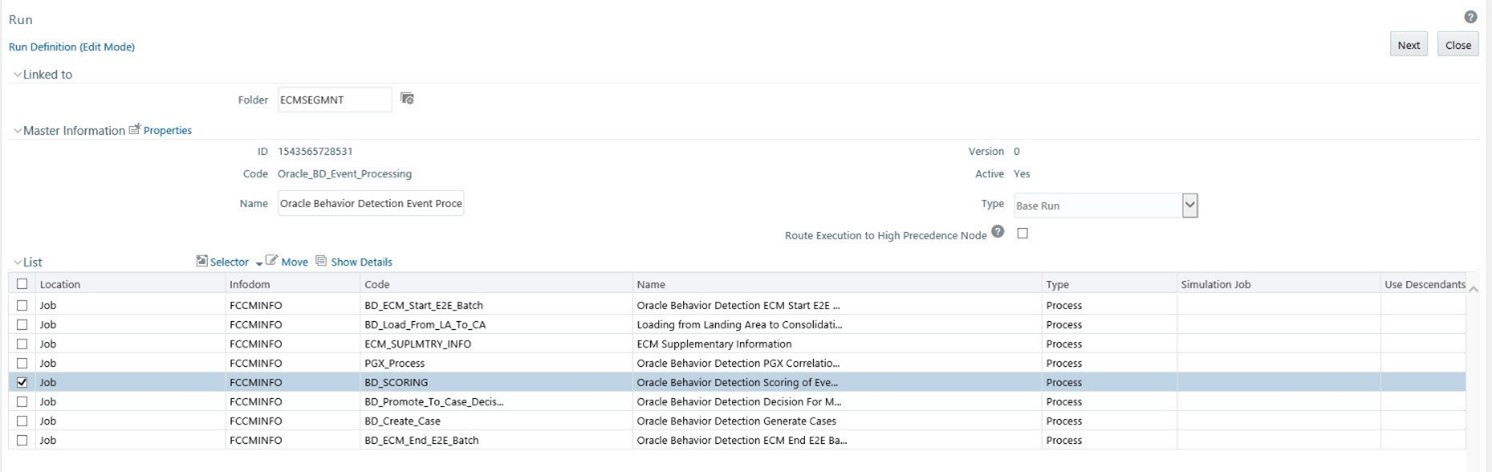
- Go to the List section. Select Oracle_BD_Event_Processing. The list of
processes for OBD is displayed. Select the BD_Scoring code and Job
option from Selector.
Figure 20-31 Run Summary Details screen
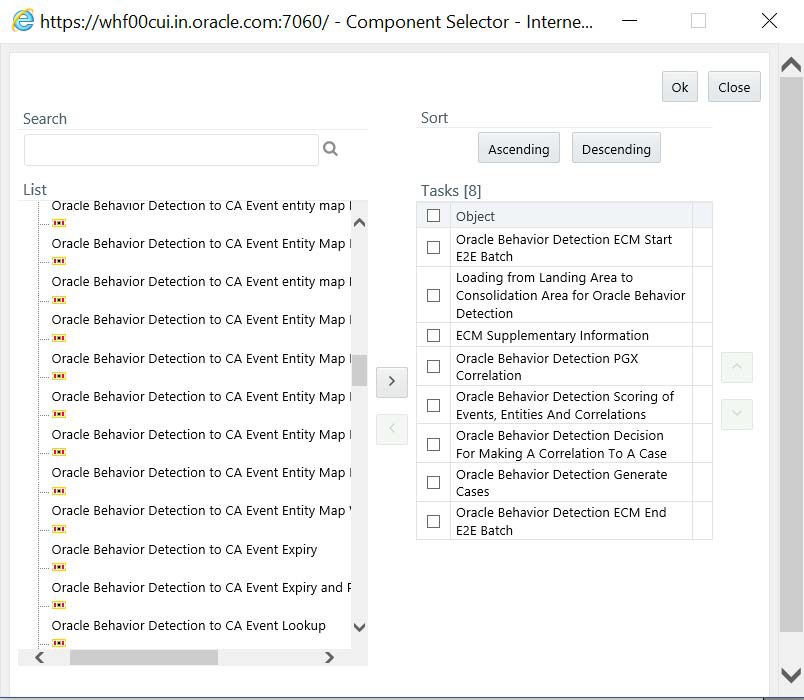
- The Component Selector window is displayed. Select Oracle Behavior
Detection to CA Event Expiry and Prege process from the list and move it to
Task list.
This process has the following two sub-processes:
- Oracle Behavior Detection to CA Event Expiry
- Oracle Behavior Detection to CA Orphaned Event Purge
Figure 20-32 Component Selector
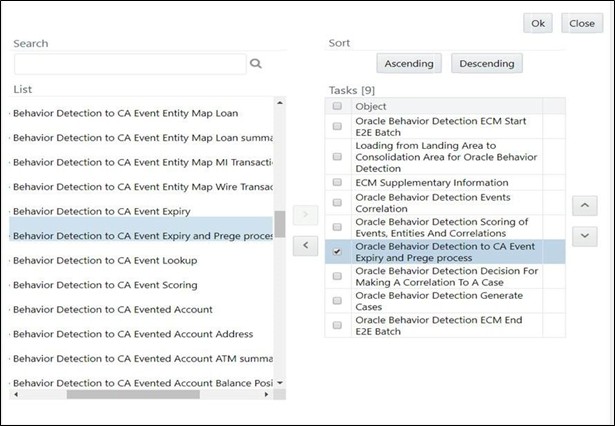
- Select the precedence of Oracle Behavior Detection to CA Event Expiry and Prege
process after the Oracle Behavior Detection Scoring of Events, Entities And
Correlations. Click Ok.
Figure 20-33 OBD to CA Event Expiry and Prege Process Components
- Modify the configuration table FCC_EVENT_EXPIRY_CONF.
Table 20-17 FCC_EVENT_EXPIRY_CONF Table
Column Name Primary Key Column Type Nullable N_CONF_ID Y NUMBER N_GROUP_ID NUMBER F_IS_ASSMNT_ENABLED VARCHAR2 N_ASSESSMENT_ID NUMBER F_IS_EVENT_SCORE_ENABLED VARCHAR2 N_SCORE_THRESHOLD NUMBER - N_CONF_ID: This is the sequence ID of the event. This should be a numeric value. For example, 1 and so on.
- N_GROUP_ID: Provide the ECM Processing Group Id
- F_IS_ASSMNT_ENABLED: Set this flag to Y if you want to enable the event assessment. If this value is set to Y, then provide the assessment ID in the N_ASSESSMENT_IDfield.
- N_ASSESSMENT_ID: Provide the assessment ID if the F_IS_ASSMNT_ENABLED field is set to Y. This assessment ID should be a valid IPE rule number.
- F_IS_EVENT_SCORE_ENABLED:Set this flag to Y if you want to enable the event score. Enable this flag before defining the threshold score in the N_SCORE_THRESHOLDfield.
- N_SCORE_THRESHOLD: Define the threshold score value.