Define Relative Repricing Patterns
The Relative Repricing Pattern is used for instruments where the repricing is determined by the elapsed time since origination. Defining a Relative Repricing Pattern involves the definition of a series of repricing events applicable to a specific Repricing Pattern Code. You need to specify the length of each Repricing Period and the number of times that event should occur before calculating the next event in the pattern.
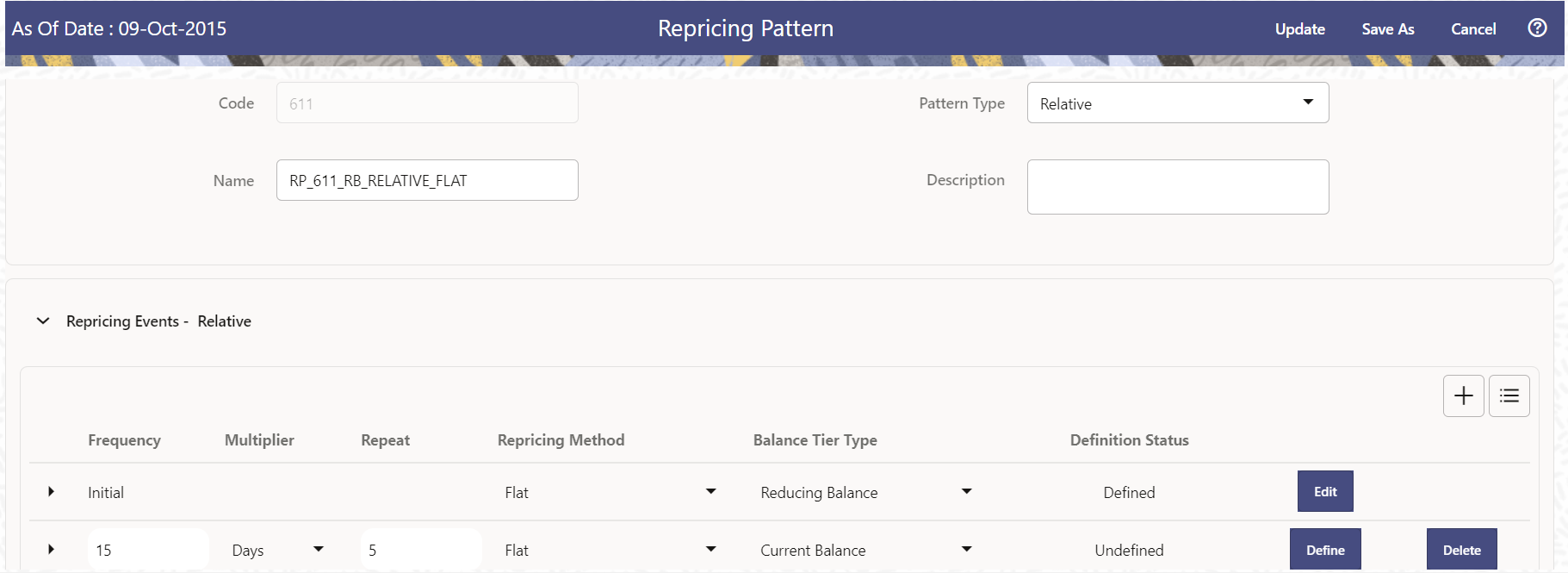
Figure 18-3 Define Relative Repricing Pattern
Prerequisites
Selecting Relative as the pattern type.
Procedure:
This table describes key terms used for this procedure.
Table: Key Terms used in Relative Repricing Pattern
| Key Terms | Description |
|---|---|
| Add Row | This allows you to Add one or more Repricing Events. |
| Add Multiple Rows | Allows you to add more Repricing Events. |
| Delete | This allows you to delete specific rows in the Repricing Events Table. You need to specify the following parameters in the Repricing Events Table for a Relative Repricing Pattern: |
| Frequency | In conjunction with the Multiplier drop-down menu, this field allows you to specify how often Repricing occurs. |
| Multiplier |
The unit of time applied to the frequency. The choices are: Days Months Years |
| Repeat | This allows you to specify the number of times a repricing event should be repeated. |
| Repricing Method | A drop-down list, it displays the Repricing Type, Flat Rate or Indexed Rate, associated with a particular event. |
The steps to create relative Repricing Patterns are similar to creating Creating Absolute Repricing Patterns.
The only difference is that the fields in the Repricing Events Table are different.
Select Pattern Type as Relative and follow the steps mentioned in Creating Absolute Repricing Patterns section.