What is a data mining run?
A data mining run is a three-step process: 1) extraction of data from source data; 2) application of statistical algorithms to the extracted data; and 3) generation of statistical values.
When these statistical values, or scores, exceed a predetermined threshold, they alert reviewers to a potential safety signal. The two primary types of data mining runs are MGPS runs and logistic regression runs. Within a two-dimensional MGPS run, you can include:
- Information Component (IC) computations
- Regression-Adjusted GPS Algorithm (RGPS) computations
- Proportional Reporting Ratio (PRR) computations
- Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) computations
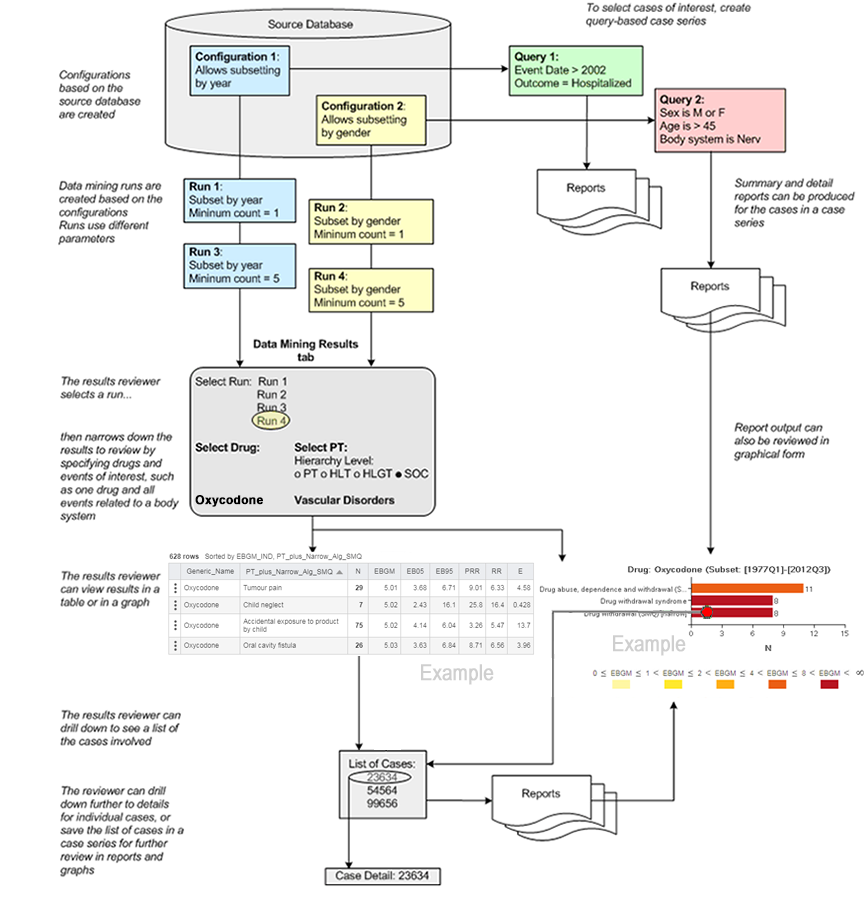
Data mining runs are batch jobs that Oracle Empirica Signal submits to a queue for processing. Depending on the number of processors on the Oracle Empirica Signal server, it is possible for several data mining runs to run at the same time. However, Oracle Empirica Signal queues RGPS jobs so that two do not run simultaneously. The run submitter can request that the run be performed immediately, when a processor is available, or at a scheduled date and time. When a user submits a data mining run, the run appears on the Data Mining Runs home page and can be published to other users, even if it has not started running. A user can also cancel, delete, or re-run a data mining run. The data mining runs that appear on the Data Mining Runs home page and the tasks that you can perform for specific runs depend on your user permissions and the publication level of runs.
To create a data mining run, you must select a data configuration that determines the source data on which the run is based. You can base multiple runs on the same configuration. You then specify the type of run and other run parameters. When the run is complete, Oracle Empirica Signal can display the results in tabular or graphical format. When reviewing the results, users with appropriate permissions can drill down on counts to view case details.
Parent topic: Initiate and monitor data mining runs