Build Cohorts
To build cohorts of patients, the Cohort Builder screen provides features to define cohort query which specifies the selection criteria for building cohorts of patients. Cohort query can be based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, each of which can be defined using a combination of demographic and clinical attributes.
To create inclusion or exclusion criteria for a cohort query:
- Select the data category under the section Patient Info & Demographics or
Clinical Events.
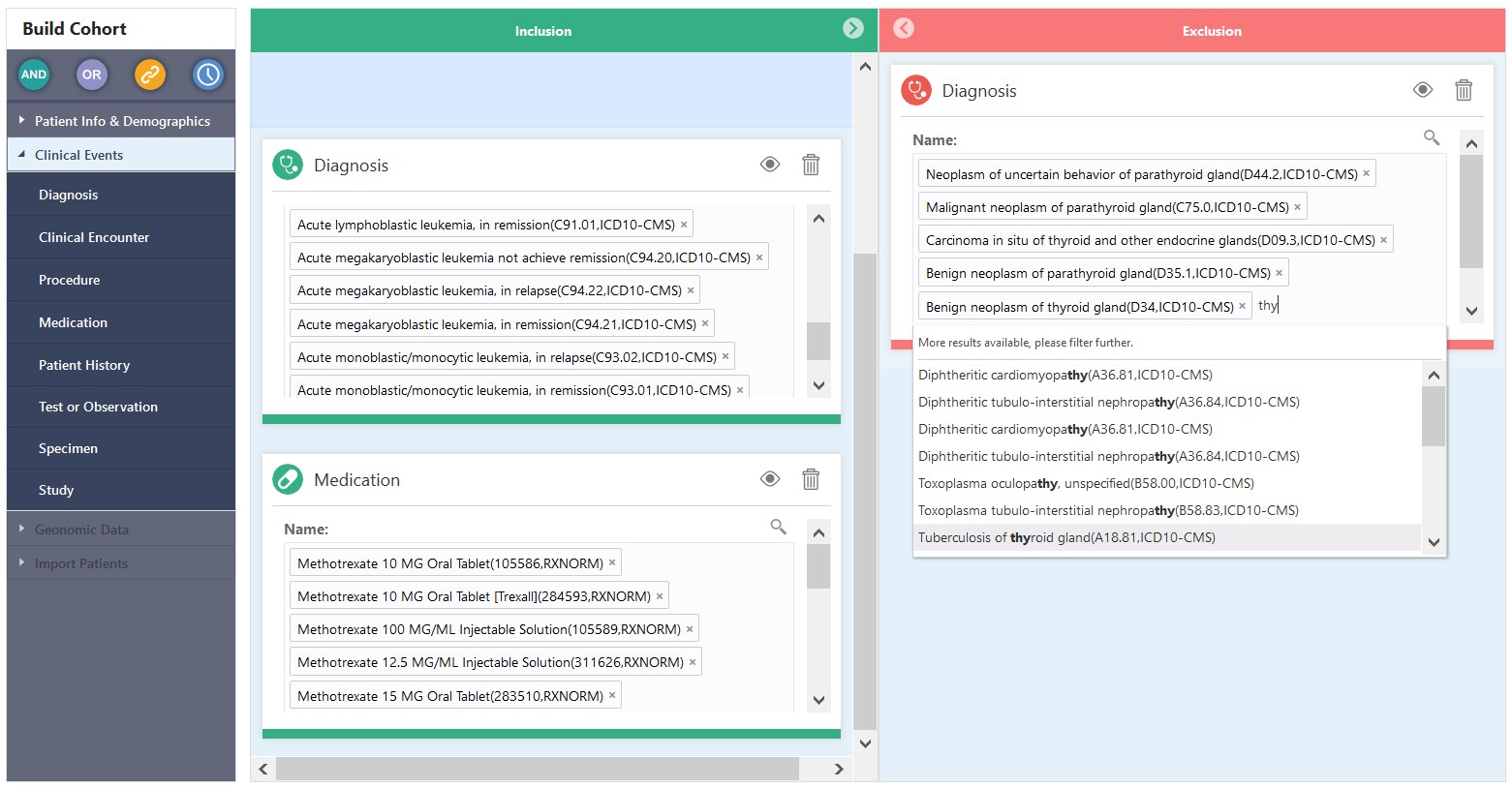
- Click on the menu item for the data category (such as Demographics, Consent, Diagnosis, Procedure etc.) and drag it to the label 'drag items here' under the Inclusion or Exclusion section.
- The above action results in placement of the criteria tile in the
Inclusion/Exclusion section.
- In the criteria tile, the primary attribute of the data
category (such as Patient ID, Diagnosis Code, Procedure Code, Medication
Code, and so forth) can be searched by typing a text string which is likely
match with the starting characters of Code Name of the primary attribute. As
the text string is typed, the input box displays a list of items in which
the typed text string matches with the initial characters of Code Name of
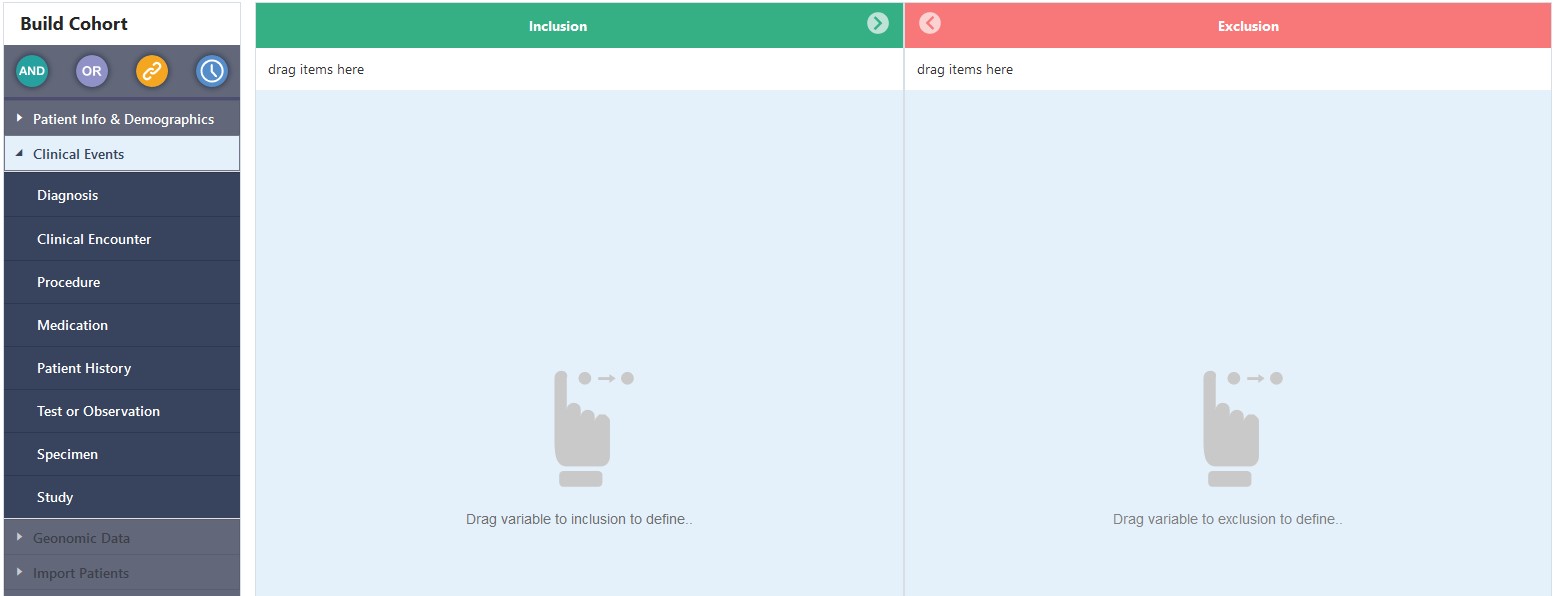
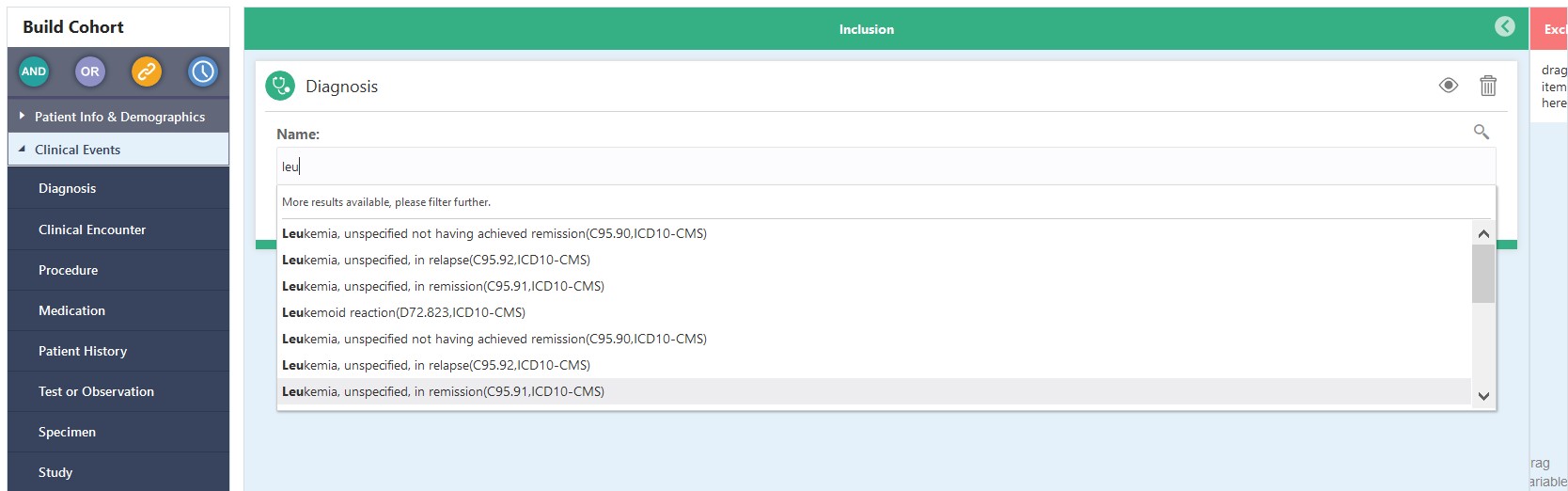
the data attribute. For example, in the Diagnosis criteria tile, the text
string 'acute l' lists all of the diagnoses in which the Code Name starts
with the letters 'acute l'.
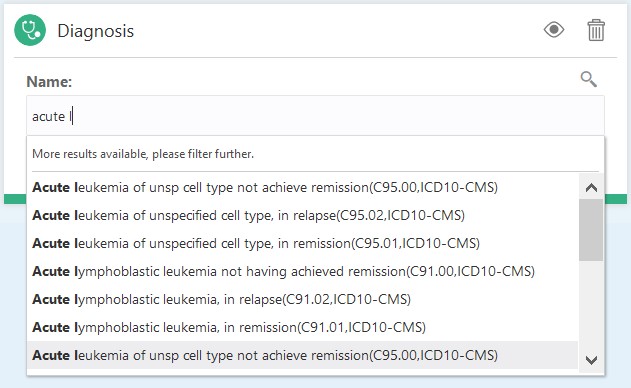
- From the displayed list, select the desired items, one at a
time, to add them to the selection criteria. The selected items are added in
the input box one by one. Depending on the number of selected items scroll
bar automatically appears in the input box. Note that an item from the drop
down has to be selected. Keying in an item that is not selected (adding an
item not in the list) would not work.
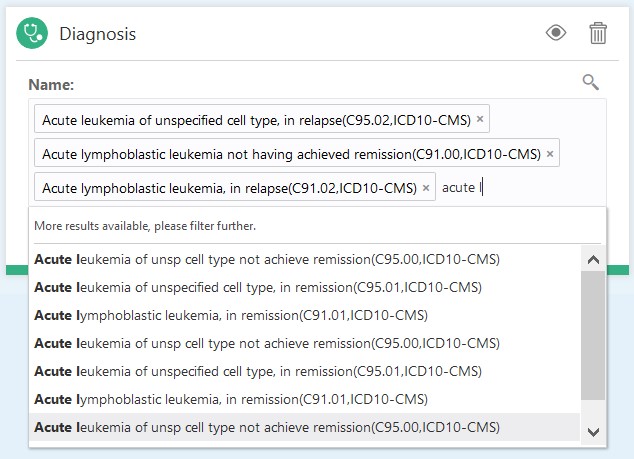
- To remove the selected items click the 'x' icon (such as
 )in the respective item.
)in the respective item.
- To perform advanced search on the primary attribute or to list
all of the matching Codes click on the magnifying glass icon (
 ) in the criteria tile, which invokes the advanced search
screen.
) in the criteria tile, which invokes the advanced search
screen.
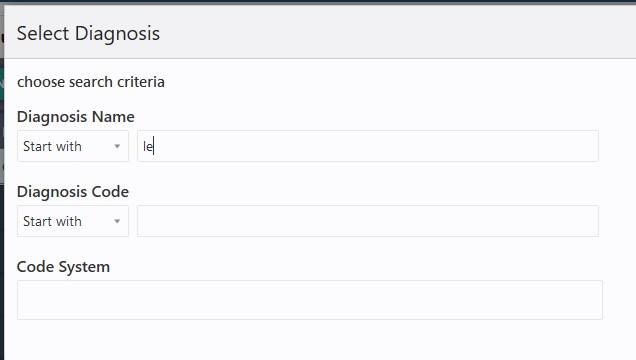
- In the above illustrated advanced search screen (for example,
the Select Diagnosis screen) the attribute values can be searched using a
combination of Code Name, Code and Code System. For all these three
attributes the search string can be provided in the respective input boxes
and a matching operator (such as, Starts With, Contains, Equals, or Not
Equals) can be selected from the corresponding drop down list.
After specifying the search criteria, click the Next button, which displays a list of matching results.
- In the selection list screen, use the checkboxes corresponding
to the list items to select one or more items from the list. In this
screen:
The label 'Search:' at the top provides information about the current search criteria.
To change the criteria use the hyperlink 'Change' to navigate back to advanced search screen.
The 'Back' button navigates back to the advanced search screen.
The 'Next' button navigates back to the criteria tile, which includes all of the items selected on this screen.
The 'x' icon at the top right section of the screen can be used to close this screen without applying the selected items in the selection criteria tile.
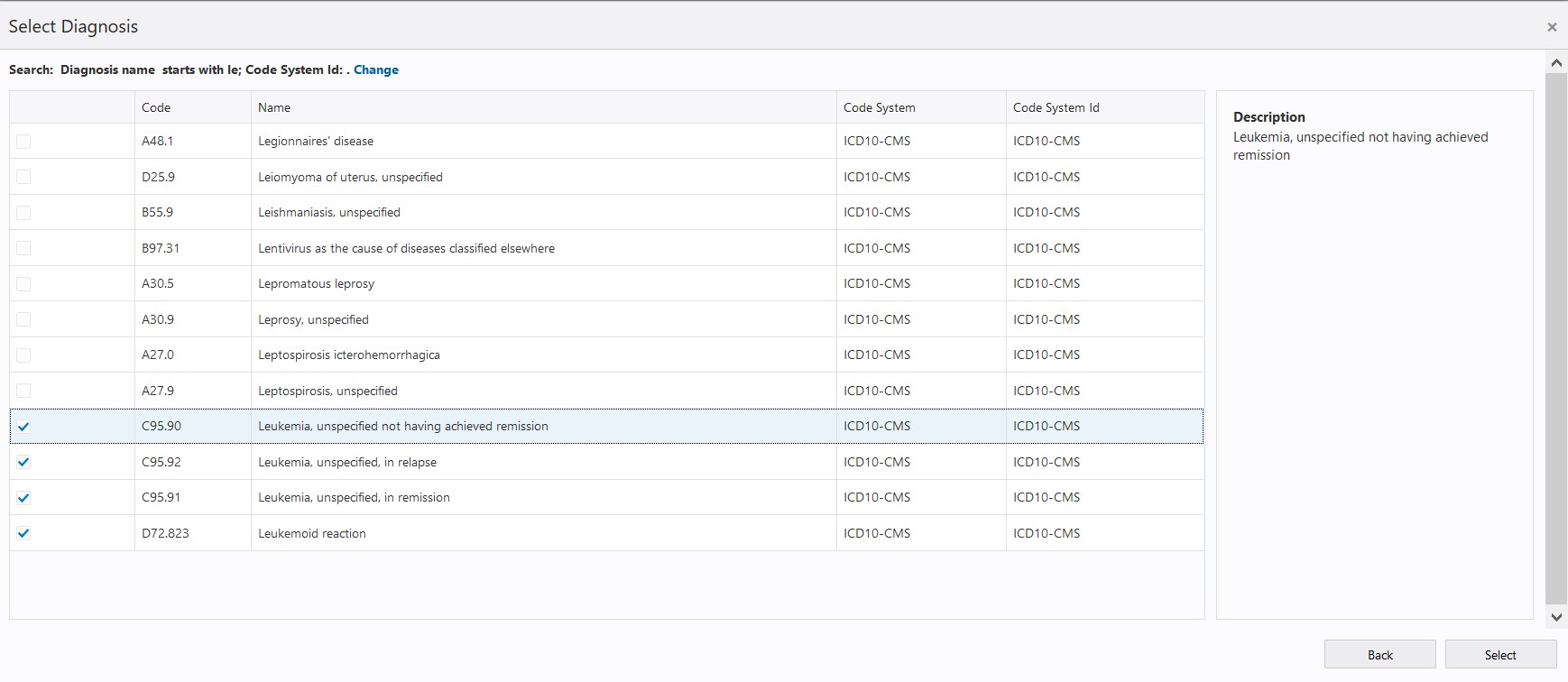
- All of the codes selected in a criteria tile are used in Patient search based on the OR condition. For example, in the Diagnosis criteria tile, if a Patient has any one of the selected Diagnosis Codes then the patient is considered a match for the selection criteria.
- More Details search screen: In the criteria tile, the More
Details (
 ) link invokes the criteria definition screen where additional
attributes of the selected data category are available for definition of
criteria. For example, for Diagnosis criteria definition, the dates
associated with diagnosis, anatomical sites, and the Grade and Stage
attributes are available. The input fields in this screen allow search by
either Code Name or Code, wherever applicable. The search is done using the
operator Starts With. Thus, for example, for the Diagnosis Grade and Stage
field, the input value is searched against both (either) Code Name and Code
of the diagnosis grade and stage.
) link invokes the criteria definition screen where additional
attributes of the selected data category are available for definition of
criteria. For example, for Diagnosis criteria definition, the dates
associated with diagnosis, anatomical sites, and the Grade and Stage
attributes are available. The input fields in this screen allow search by
either Code Name or Code, wherever applicable. The search is done using the
operator Starts With. Thus, for example, for the Diagnosis Grade and Stage
field, the input value is searched against both (either) Code Name and Code
of the diagnosis grade and stage.
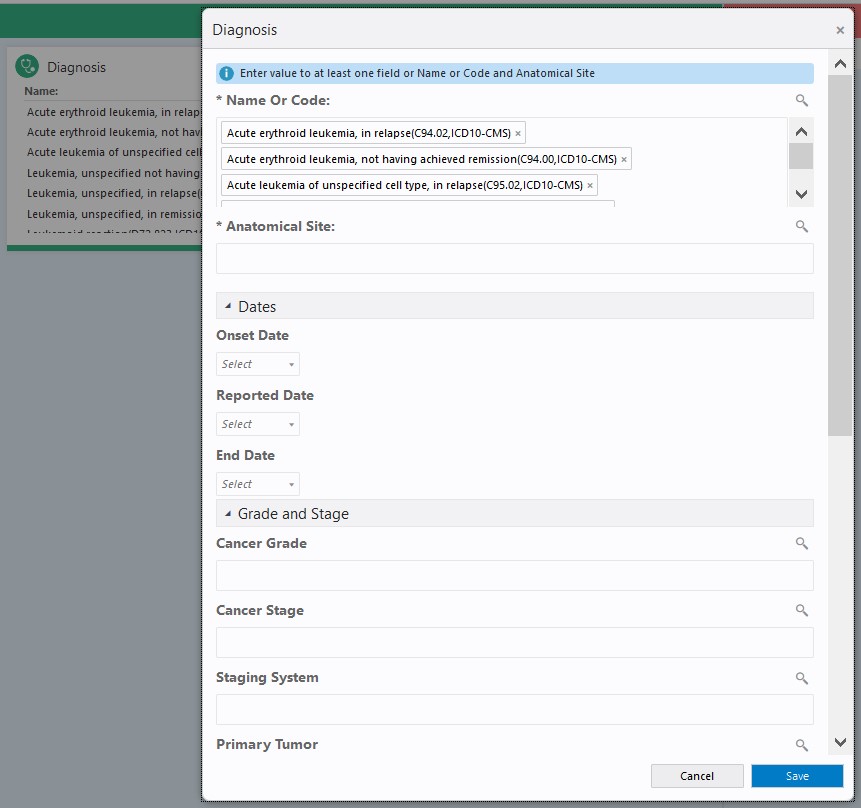
The More Details screen includes all of the attributes that can be used to define search criteria. The attributes are organized into different sections that can be expanded and collapsed by clicking on the respective section headers.
Note:
In any date fields, all dates before 1950 should be manually entered in the mm/dd/yyyy format to ensure correct retrieval of patient count.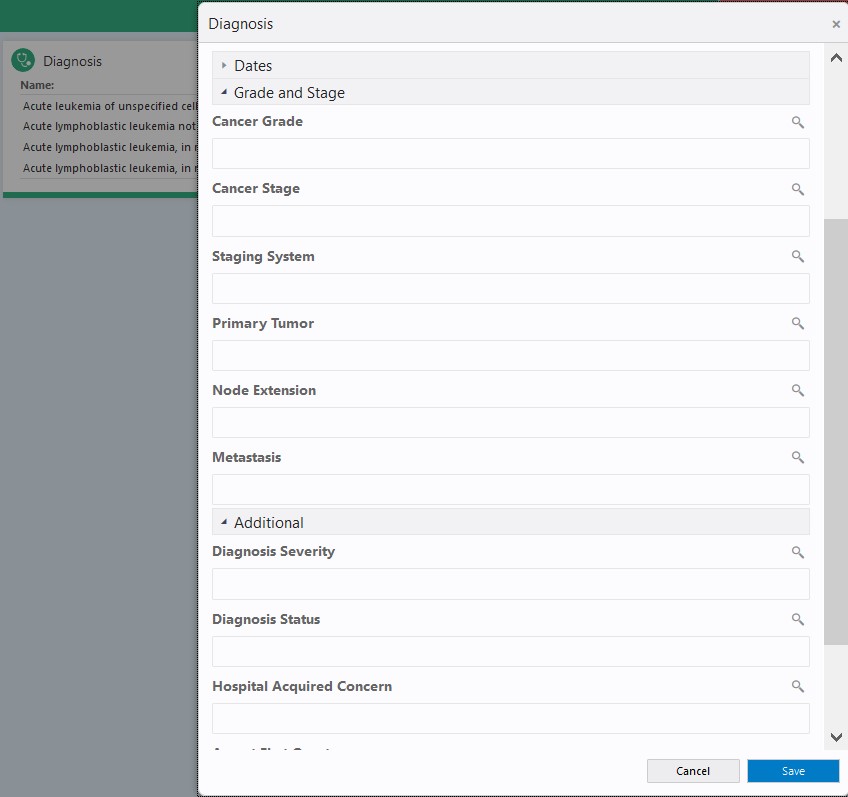
- All of the criteria a criteria tile can be enabled or disabled
using the 'Eye?' (
 ) icon. This action does not remove the criteria tile from Inclusion
or Exclusion section but the criteria defined in the tile is not used in the
cohort query while searching for the matching patients.
) icon. This action does not remove the criteria tile from Inclusion
or Exclusion section but the criteria defined in the tile is not used in the
cohort query while searching for the matching patients.
- A criteria tile can be deleted using the 'Delete'
(
 ) icon. This results in removal of the criteria tile from the
Inclusion or Exclusion pan so use this icon with caution.
) icon. This results in removal of the criteria tile from the
Inclusion or Exclusion pan so use this icon with caution.
- In the criteria tile, the primary attribute of the data
category (such as Patient ID, Diagnosis Code, Procedure Code, Medication
Code, and so forth) can be searched by typing a text string which is likely
match with the starting characters of Code Name of the primary attribute. As
the text string is typed, the input box displays a list of items in which
the typed text string matches with the initial characters of Code Name of
the data attribute. For example, in the Diagnosis criteria tile, the text
string 'acute l' lists all of the diagnoses in which the Code Name starts
with the letters 'acute l'.
- Similarly, criteria tiles for other data categories (such as Medication, Procedure, Test, or Observation and so forth) can be placed in the Inclusion or Exclusion sections to create complex criteria consisting of different categories of data.
- The Inclusion and Exclusion pans can be expanded and collapsed using the
'>' (
 ) and '<' (
) and '<' ( ) icons to view details of the criteria on the screen.
) icons to view details of the criteria on the screen.
-
The criteria across multiple criteria tiles is linked using AND operator to select Patients who match with all of the criteria. For example, if Inclusion criteria is defined using Diagnosis (D1, D2, D3…) and Medication (M1, M2, M3…) tiles then it will select all patients who have (Diagnosis D1 or D2 or D3… ) AND (Medication M1 or M2 or M3…).
-
After a criteria tile is created or updated, clicking anywhere outside the criteria tile invokes the cohort query mechanism of the application to search for the matching patients and the count of matching patients in the cohort thus created is displayed in Number of Patients.

- A cohort of patients thus created can be saved by providing a unique Cohort Name, Privacy (Public/Private) and optionally Description. After a cohort is saved, the user who owns the Cohort (that is the logged in user who created the cohort) can update and save it with the same name. Users who have access to shared Cohorts created by other users cannot modify the cohort, but can save the Cohort with a different name. Cohorts created in Oracle Healthcare Translational Research Next Gen can be accessed and updated in Oracle Healthcare Translational Research and vice versa. In this release, Cohort Queries built and saved in Oracle Healthcare Translational Research cannot be imported into Oracle Healthcare Translational Research NG and vice versa.
- List of all of the available Cohorts is available in the Cohort List screen.
Note:
If the Code/Name column in the underlying terminology data in Cohort Data Mart (CDM) contains braces, that is ( , ) , or both, then the search may result incorrect number of matching Patients.For example, if the value of Diagnosis Name column in the terminology data contains the phrase "Injury (trauma)" then search criteria based on such Diagnosis values may result in incorrect number of matching Patients.Note:
Upon modifying the criteria of an existing cohort and while saving the cohort may sometimes result in an error. If the error logs show an error occurring due to ‘timeout or end-of-fetch during message dequeue’, the possible cause could be an issue in the version of the Oracle database. This issue has been reported on the Oracle database.