Organizational Objects
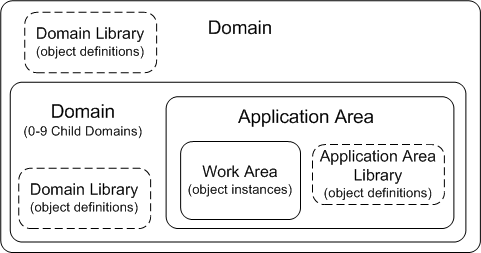
Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub has three types of container objects that hold object definitions and instances. These containers are nested, or contained within one another, as shown in Figure 1-1 and described as follows:
- Domains. Domains contain Application Areas and object definitions that have been explicitly moved into the Domain.
In addition, Domains can contain child Domains that themselves contain child Domains, up to nine (9) levels, depending on the value of the Domain Nest Value profile setting for your Oracle LSH implementation. A Domain can contain any number of Domains at a single level. For example, if the Domain Nest Value profile is set to one (1), a top-level Domain can contain any number of child Domains, but those child Domains cannot contain any child Domains of their own.
You can use child and grandchild Domains to more finely organize object definitions and applications.
In general, Domain security should be set up so that only a few people can create, modify, or move object definitions in Domains. Only object definitions that have been thoroughly tested and approved for reuse should be moved into Domains.
- Application Areas. An Application Area contains a library of definitions developed specifically for a particular application and the Work Areas necessary to develop, test, and put the application into production.
- Work Areas. A Work Area contains instances of all the object definitions required for a particular application.
Figure 1-1 Oracle LSH Organizational Structure
Description of "Figure 1-1 Oracle LSH Organizational Structure"
For information on planning an organizational structure of Domains, Libraries, Application Areas and Work Areas for your company, see "Designing an Organizational Structure" in the Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub Implementation Guide.
Parent topic: Object Definitions and Instances, and their Containers