Retrieving the Latest Event
To get only the latest update for a fast-changing resource, set the
offsetType parameter to "highest." This approach allows
applications to efficiently access the current state without processing the entire event
history.
When to Apply The Latest Event Use Case
This use case is appropriate when:
- Monitoring Real-Time Changes: You must monitor the latest state of a resource that undergoes frequent updates, such as room availability or pricing changes, without concern for intermediate states.
- Reducing Data Processing Overhead: Your application requires only the most recent event, thereby minimizing the processing and storage of unnecessary historical data.
- Ensuring Data Freshness: Accessing the latest event ensures that your application reflects the current state of the resource, which is critical for decision-making processes.
earliest |-0-|-1-|-2-|-3-|-4-|-5-|-6-|-7-|-8-|-9-|-10-| highest
- A stream has produced 10 events over the previous 24 hours. A consumer has connected and consumed events 0 to 6 inclusive and then disconnected again.
- While the consumer is disconnected, events 7 to 10 occur.
If the consumer connects with the offsetType highest, then only event 10 is sent, followed by subsequent events.
- The
offsetType: "highest"parameter is suitable when you are only interested in the most recent state of a rapidly changing resource. It is not recommended for scenarios requiring synchronization with OPERA Cloud because it does not provide historical events, potentially leading to data inconsistencies. - Using
offsetType: "highest"means you will not receive previous events, and the sequence of events cannot be maintained. Ensure this aligns with your application's requirements.
Figure 4-5 Sequence Diagram for the Latest Event Flow
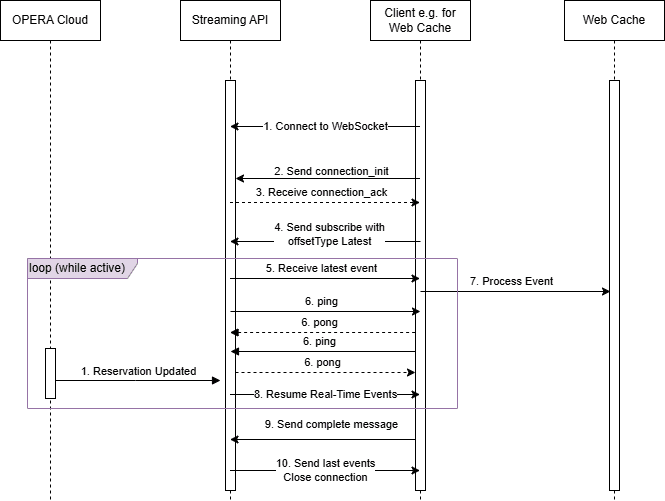
Detailed Steps for the Latest Event Flow
- Establish WebSocket Connection and send
connection_initmessage.A WebSocket is a way to keep a live channel open between your app and the server, so you can receive updates almost instantly.
Use the hashed key (in Application Key, see "Hashing the Application Key") to build your connection URL. For example:
wss://OHIP_Gateway_URL/subscriptions?key=Hashed_Application_KeyYour client should support the "graphql-transport-ws" subprotocol, so send the header:
Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: graphql-transport-wsSend the call to:
wss://OHIP_Gateway_URL/subscriptions?key=Hashed_Application_Key - Send
connection_initmessage.Within 5 seconds of connecting, send the
connection_initmessage to initiate the connection.Sample message:{ "type": "connection_init", "payload": { "Authorization": "Bearer <Access_Token>", "x-app-key": "<Application_Key>" } } - Receive the
connection_ackmessage.Upon successful initialization, the server responds with a
connection_ackmessage, indicating readiness to accept subscription requests.Sample response:{ "type": "connection_ack" } - Send the
subscribemessage with the following:
Send a subscribe message specifying theoffsetType:"highest"chainCodeand set theoffsetTypeparameter to "highest." This configuration ensures only the latest event is retrieved.Use the GraphQL schema to decide which fields to include in the request. Including the
primaryKeyis advised, since this is the internal OPERA ID of the resource to which the event occurred and can optionally be used to GET the resource via an inbound API call.Ensure the
idis a unique value that will be used throughout the life of this stream, that is, until thecompletemessage is sent.Sample Message:{ "id": "<id>", "type": "subscribe", "payload": { "variables": { "input": { "chainCode": "<Chain_Code>" } }, "extensions": {}, "operationName": null, "query": "subscription { newEvent(input: { chainCode: \"<Chain_Code>\" offsetType: \"highest\"}) { metadata { offset uniqueEventId } moduleName eventName primaryKey detail { oldValue newValue elementName } } }" } }Optionally, you can choose to receive only the changed attributes in thedetailarray of the events you receive. To achieve this, use the below sample request:{ "id": "<id>", "type": "subscribe", "payload": { "variables": { "input": { "chainCode": "<Chain_Code>" } }, "extensions": {}, "operationName": null, "query": "subscription { newEvent(input: { chainCode: \"<Chain_Code>\" offsetType: \"highest\" delta: true }) { metadata { offset uniqueEventId } moduleName eventName primaryKey detail { oldValue newValue elementName } } }" } } - Receive Latest Event.
The server will emit the latest event in the queue at the time of the subscribe request as a
nextmessage containing the event data.Treat event payloads as sensitive and mask personal data in logs.
See the sample event in Subscribing and Consuming Events.
Keep a record of the
offsetvalue; it is a string, not a number.Upon receiving an event, process the data as required by your application. This may involve updating records, triggering workflows, or other business logic.
Security and Privacy: Treat event payloads as sensitive and mask personal data in logs.
- Heartbeats and Keep alive:
Keep the connection alive and establish the line speed; it is essential to send the
pingmessage every 15 seconds.Sample message:{"type":"ping"}The server will also be sending the client
pingmessages to which the client must respond with thepongmessage.Sample message:{"type":"pong"}Note:
The server will close the connection if it does not receive apongwithin 180 seconds. In Performance Considerations, see "Maintain a Healthy Connection and Token Lifecycle."Note:
During Backpressure Mode bursts, the server may defer replying to clientpings withponguntil the burst completes. Treat continuednextmessages as proof of life. - Process Replayed Event.
Upon receiving an event, process the data as required by your application. This may involve updating records, triggering workflows, or other business logic.
Since the volume of events can be large, writing to a cache before updating a database is advised.
- Resume Real-Time Event processing.
After emitting the latest event, the system will continue to receive and process new events in real-time, ensuring ongoing data synchronization.
- Send the
completemessage.When you intend to stop receiving events, send a complete message to terminate the subscription. Ensure you use the same ID as in the
subscribemessage.Sample Message:{ "id": "<id>", "type": "complete" } - After sending the
completemessage, wait until the last events are received, then wait until OHIP closes the WebSocket connection. Do not close the connection from the client side.Ensure there is a minimum of 10000 ms (10 seconds) between sending the "Complete" message to close a WebSocket connection and sending the next "Subscribe" message to reopen a WebSocket connection.
Parent topic: Use Cases