Migration Behavior
The migration function creates, updates and deletes configuration. To do this, the function needs to recognize the same configuration item across environments. Finding the existing counterpart of an configuration item in the migration payload is called matching.
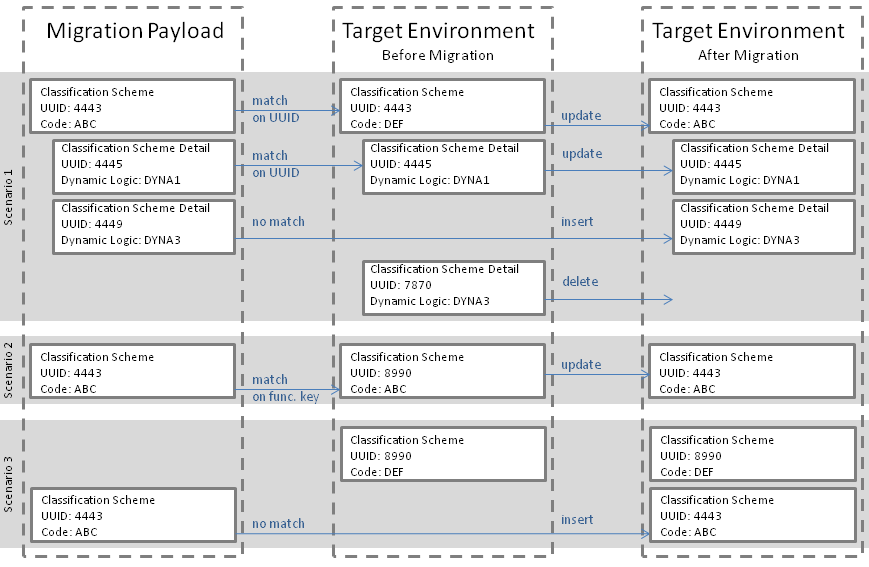
Matching top level items is a two-pass process. The first pass attempts to match the universally unique identifier (UUID) of the item in the migration set to an existing item on the target environment. The UUID is a system generated key, that is assigned to each configuration item upon creation, unless created through a migration. If the item is created through a migration the UUID of the item in the migration payload is adopted. This ensures that the UUID for the same configuration item is the same across all environments, as long as the migration function is the only means of creating new configuration items on target environments. If the function succeeds in finding an existing configuration item with the same UUID, then that item is updated.
If the UUID match fails, the second pass attempts to match on a functional key, that is, a user defined key. For most configuration items the "Code" field is the functional key. This means that if the item in the migration payload has the same code as an item in the target environment then it is considered a match. Some configuration items have a more elaborate functional key, because they do not have a code, for example, a provider pricing clause. For these items the secondary match is based on a combination of functional attributes.
The reason for the two-pass approach is that neither UUID matching, nor functional key matching is foolproof; matching exclusively on UUID fails if the same configuration already exists on the target environment (inserted by means other than migration), matching exclusively on the functional key fails when (part of) the key is updated on either environment. The two-pass approach counters these drawbacks - it gives robustness against updates of key fields and the ability to identify the same configuration items across environments.
Some of the functional keys comprise language dependent fields. The functional keys in the migration set are the keys in context of the default language on the source environment. Upon import, language dependent functional keys are interpreted in context of the default language of the target environment.
If neither the UUID nor the functional key matches, the migration import function inserts the configuration item on the target environment. If matched successfully, then all functional attributes of the existing item are updated with the value provided in the migration payload. Any existing detail matched with a detail in the migration set is updated. Details in the migration payload that do not exist on the target environment are inserted.
If the migration set does not specify an inclusion date, then any existing detail that is not matched, is deleted.
Because most details are matched on UUID alone, updates to those details that have not been created by a prior migration follow a replacement pattern (that is as opposed to an 'update' pattern). This is illustrated in scenario 1; the classification scheme detail referring to DYNA3 has been keyed in on both the source and target environment.
If an item (top level or detail) is matched on functional key then the existing item adopts the UUID in the migration payload.
Configuration Linked to Operational Data
Some dependent configuration items can be linked to operational data for auditing purposes. For example, if a fee schedule line has been applied to a claim line, then the claim line refers to the fee schedule line. This means the fee schedule line can no longer be deleted.
Instead of physically deleting these configuration records, the migration function 'disables' them. This exception applies to fee schedule lines and product benefit specifications.
Items Matched on UUID and Functional Key
The following items are matched on both UUID and functional key.
Access restriction |
Currency |
Post benefits regime |
Most top level items have a single attribute that is the designated functional key, that is the "Code" of the item.
The following items are matched on both their UUID and functional key as well, but are exceptional in that they use a set of attributes serving as a composite functional key, rather than a single field.
| Item | Functional Key |
|---|---|
Activity type |
Code, level |
Authorization regime period |
Authorization regime, sequence |
Authorization regime period tranche |
Authorization regime period, sequence |
Coverage regime period |
Coverage regime, sequence |
Coverage regime period tranche |
Coverage regime period, sequence |
Cover withhold rule |
Coverage regime period tranche, sequence |
Diagnosis |
Code, flex code definition |
Diagnosis group detail |
Diagnosis group, diagnosis, start range, flex code definition (range), start date |
Diminishing rate block |
Diminishing rate, sequence |
Dynamic field usage |
Usage name, table |
Exchange rate |
Currency from, currency to, context, start date |
Fee schedule line [1] |
fee schedule |
Flex code |
Key value, start date, flex code definition |
Flex code field usage |
Usage name, flex code definition |
Flex code set detail |
Flex code set, flex code definition |
Floorplan tag detail |
Tag, Floorplan |
HTTP link |
Page, display name |
Location type |
Code, claim form type |
Parameter set |
Activity type, code |
Payer code |
Code, start date, payer |
Post cover withhold rule |
Post benefits regime, sequence |
Pricing rule |
Code, subtype |
Procedure |
Code, flex code definition |
Procedure group detail |
Procedure group, procedure, start range, flex code definition (range), start date |
Product benefit specification |
Product, benefit specification, start date |
Provider |
Code, flex code definition |
Provider Identifier |
Identifier |
Provider group affiliation |
Provider group, provider, start date |
Provider pricing clause [2] |
individual provider |
Reference sheet line [3] |
Reference sheet, key, start date |
Reimbursement method |
Code, subtype |
Reimbursement method type |
Code, subtype |
Transaction source usage |
Transaction source, table |
Items Matched on UUID Alone
The following objects are always integral to another object and cannot exist standalone. These are typically intersection objects without a functional key - they are matched only on UUID.
Adjustment rule percentage |
Supported insurable entity type |
Items Matched on Functional Key Alone
The following items cannot be added to a migration set but may be referenced by items that can be. These items never match on UUID because they are seeded or because they are not considered configuration.
Language |
The following items are matched on functional key alone as well, but are exceptional in that they use a set of attributes serving as a composite functional key, rather than a single field.
| Item | Functional Key |
|---|---|
Bank account number |
Relation, account number, bank, start date |
Delete by Omission
The following configuration items depend on top level items - they cannot exist by themselves. The configuration import function treats these just like other attributes on the top level item; if not present in the payload, that means these items have been removed on the source environment and therefore can be deleted in the target environment as well.
Note that the 'High Volume' configuration items (see Building a Migration Set) are not deleted on the target environment if the configuration set specifies an inclusion date. The reason is that the target environment is not able to distinguish between records that are omitted from the set because they are deleted or because they have not been updated since the inclusion date.
Fee schedule lines are details of fee schedules and they are top level items themselves (to make selection of fee schedule lines across fee schedules possible). If a fee schedule is included as a dependent item of selected fee schedule lines, the deletion by omission is not executed for that specific fee schedule.
Adjustment rule percentage |
Geographic condition |
Switching Off Delete by Omission
The ‘delete by omission’ behavior is enabled by default. The user can override this behavior either when creating a new migration set in the source environment or when importing a migration set in the target environment. This behavior applies across all entities in the migration set; either all dependent items are deleted by omission or none of them are.
If the user overrides the behavior upon generation of the migration set, then the payload is marked so that the target system knows not to delete by omission. If the user specifies the desired delete behavior upon importing a migration set, then the import ignores the whatever instructions are included in the payload.
To clarify this feature, consider the image above. The default system behavior removes item 7870 but if the user disables the ‘delete by omission’ feature then item 7870 remains unaffected.
Exclude Options
Exclude options are the check boxes on the 'Exclude Options' section of page CL0101 Configuration Migration Sets. They allow the user to carve out a specific group of dependent items within the context of the top level item. This carve out applies to the top level item itself as well as all dependent items, dependents of those dependent items and so on.
For example, if the user chooses to exclude dynamic logic (check box checked) within the context of the top level item 'provider pricing clauses' then the payload will not contain the dynamic logic records referenced by the provider pricing clause conditions, nor records referenced by the underlying pricing rules (such as an adjustment rule formula) or reimbursement methods (such as a fee schedule line condition).
Exclude options apply only within the top level object that they belong to. To clarify, consider a scenario where the payload contains two fee schedules. The first fee schedule (F1) has not been excluded as a dependent of a provider pricing clause and is therefore subject to all other exclude options specified for provider pricing clauses. So if dynamic logic is excluded within the context of provider pricing clauses, none of the dynamic logic records used by F1 are in the payload. The second fee schedule (F2) was selected as a top level item with none of the exclude options checked. Therefore the payload includes all messages, dynamic logic records etc. that are used by F2.
Multiple Languages
It is possible to install an Oracle Health Insurance application with multiple languages. A configuration item will have a representation for each of the installed languages. When creating a migration set, each of those representations is automatically included; there are no options to exclude a particular language.
In the scenario where the source and target environment do not have the same languages installed, the following happens upon importing the migration set: the configuration item representations of any language that is not installed on the target environment are ignored; the existing configuration items representations of a language that is not in the migration set is left untouched.
For example, suppose the target environment supports both Spanish and English and the source environment supports only English. In this scenario, only the English language specific fields will be updated on the target environment.
Business Rules
Business rules protect the configuration consistency and remain active during migration. When a piece of configuration is updated, it will automatically be re-validated against its business rules. Because some business rules are controlled by set-up, it is possible for configuration to be out of sync with its governing business rules. In other words, changing a business rule does not automatically re-validate existing data. If a source environment has such inconsistencies, a migration may lead to unexpected business rule violations.
For example, consider the scenario where - on the source environment - a new mandatory dynamic text field is added to the messages table (OHI_MESSAGES). When this new field is set up, none of the existing messages will have a value; the existing messages are in conflict with the new set-up. It is only when updating an existing message or add a new message that the system requires the user to enter a value for the mandatory dynamic field. When the existing messages are migrated, they will run into that same violation on the target environment.
Oracle Health Insurance Specific Configuration
Oracle Health Insurance specific configuration is seeded configuration that cannot be removed or inserted by the users of the application. It is possible to update specific fields on Oracle Health Insurance specific configuration, so for that reason Oracle Health Insurance specific configuration can be included in the migration payload. The migration import function never inserts or deletes Oracle Health Insurance specific configuration. Messages are the primary example of Oracle Health Insurance specific configuration.
Default Indicators
Some configuration item have a default indicator, meaning that within its context - the configuration item is applicable unless specifically specified otherwise. Examples are the default country (when creating a new address), and the default bank account validation (when creating a new bank account. The default indicator is always complemented by a system rule that make sure that there is only a single default item of its kind, e.g., there can be only one default country. Such a system rule applies across the set of configuration items, rather than on a single item. For this reason, configuration settings like the default indicator cannot be updated through the configuration migration function.