Data Access Restriction
Access to data in Oracle Health Insurance Value-Based Payments needs to be restricted based on user authorizations for several reasons. These reasons include privacy (secret addresses) and user skill level. This document describes the features that are provided by the Oracle Health Insurance Value-Based Payments data access restriction solution.
Concepts
This section describes general aspects of data access restrictions.
Data access restrictions are based on the use of access restrictions. An access restriction can be specified for a record or item of information to restrict access to it. Access restrictions behave as 'security labels' that can be attached to records. For example:
-
The person record of Bob could be labeled with the 'SECRET' access restriction.
-
The person record of Jane could be labeled with the 'TOP_SECRET' access restriction.
-
The person record of John could have no access restriction specified.
When an access restriction is specified for a record or other information item, that record or information item is said to be restricted. So if records had access restrictions as indicated above, both Bob and Jane would be restricted while John would be unrestricted.
Access labels are implemented as access restrictions of a certain type. For example, for person records, access restrictions of type 'Person details' are used.
See User Access Restriction Model in the common features guide for a complete description of access restrictions and possible types.
A user can only access a restricted item when he has been granted access to the access restriction (via a role). For example, if only the 'SECRET' access restriction has been granted to user Philip, he can access the person record of Bob and John whereas he cannot access the person record of Jane.
The following diagram provides an overview of the end-to-end chain that gives a user access to a record of an Oracle Health Insurance Value-Based Payments entity that is protected with an access restriction.
| This diagram is not a data model, but an example of the relations between types of records and objects. |
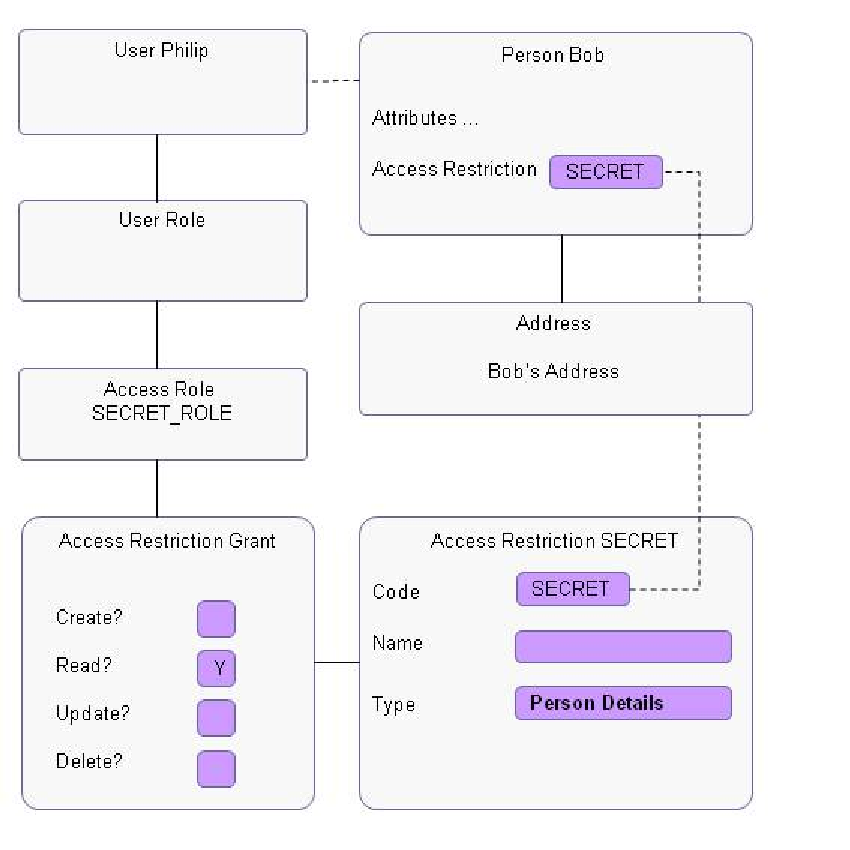
The diagram shows the following:
-
The person record of Bob has access restriction SECRET attached. This means that this record is only accessible for users that have been granted access to this access restriction.
-
Access restriction SECRET is granted to access role SECRET_ROLE.
-
Access Role SECRET_ROLE is granted to user Philip, so Philip has access to records labeled with access restriction SECRET and thus can access the person record of Bob. Because only the Read? indicator is checked, Philip cannot change or remove the person record of Bob.
Related Entities
Records in Oracle Health Insurance Value-Based Payments can be related to multiple detail records. For example: a person has attributes, but also has multiple addresses. In such a situation, the restrictions of the parent record cascade to the detail records; this also holds true for dynamic records: they behave as a child table. So when person Bob has access restriction 'SECRET', the restriction also applies to Bob’s addresses.
For each entity (record type) for which data access restriction is implemented, the restriction also applies to the related entities of that entity. Per restricted entity, the related entities are fixed. See the description of each restriction for its specific related entities.
Protected Items
Access restrictions can also be used to specify access to some groups of items (for example several specific attributes of a record). An example is Non-Address Contact Detail Restrictions.
Setup of Access restrictions
The type attribute of an access restriction defines where the access restriction can be used, that is, which type of records can be labeled with that access restriction.
The type attribute has a fixed list of values for each place in Oracle Health Insurance Value-Based Payments where data access restriction is built in. See table below:
| Type | Usage | Detailed in Section |
|---|---|---|
Address contact detail |
Restrict access to a person address. |
Address Contact Detail |
Data access group |
Restrict access to a contract and its configuration details |
Data Access Group |
Dynamic Field Usage |
Restrict access to dynamic field and record usages |
#DynamicFieldUsage[Dynamic Field Usage] |
Function |
Restrict access to a UI page. |
|
Non-address contact detail |
Restrict access to non-address contact details of a person. |
Non-Address Contact Detail |
Identifier Type |
Restrict access to Identifiers of a relation |
Identifiers Type |
For each restriction type, multiple access restrictions can be defined. It is not possible to define an access restriction that applies to multiple restriction types. So when the Address restriction type and the Person restriction type both should have an access restriction 'Secret', two different access restrictions need to be defined. See the following table for an example:
| Restriction | Access Restriction Code |
|---|---|
Address Contact Detail |
ADSECRET |
Person Details |
PERSECRET |
Person Details |
VIP |
Granting Access Restriction / CRUD Matrix
Access restrictions are assigned to roles using an access restriction grant. In an access restriction grant, Create, Retrieve, Update and Delete (CRUD) indicators can be set. The CRUD indicators in general have the following meaning:
-
©reate - Records protected by the access restriction can be created by the users with the role. In addition, existing records can have the access restriction applied to them by the users with the role.
-
®etrieve or Read - Records protected by the access restriction can be seen by users with the role.
-
(U)pdate - Records protected by the access restriction can be updated by the users with the role.
-
(D)elete - Records protected by the access restriction can be deleted by the users with the role.
Granting of create, update and / or delete rights without retrieve rights is not allowed. If none of the CRUD rights are selected, the grant on this Access Restriction is effectively disabled.
The record to which the access restriction is directly linked is not always part of the records protected by the access restriction. In particular in setup pages, users with the right to create or update records in that page will also have the right to link an access restriction, without explicit CRUD grants that access restriction. For operational data like Persons and Addresses, stricter rules apply.
The following table (the "CRUD Matrix") lists per access restriction type what the CRUD indicators mean, for several types it deviates from or extends the general meaning:
| Type \ CRUD indicator | Create grant on access restriction | Retrieve/read grant on access restriction | Update grant on access restriction | Delete grant on access restriction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Address contact detail (NOTE: only applies to Addresses of Persons, not of Organizations) |
may link an access restriction of this type to an Address |
can query Addresses with this access restriction |
may update Addresses with this access restriction, including the access restriction itself (may change it to another access restriction if create rights on that access restriction) |
may delete Addresses with this access restriction |
Data access group |
may link a Data Access Group with this access restriction to a Contract |
can query Contracts that are linked to Data Access Groups with this access restriction |
may update Contracts that are linked to a Data Access Group (old Data Access Group in case that field is being updated) with this access restriction, including insert/update/delete of (grand)child configuration entities |
may delete Contracts that are linked to Data Access Groups with this access restriction |
Dynamic Field Usage |
may create dynamic records of the specified usage |
no concealing of non time valid dynamic fields of the specified usage. time valid dynamic fields and dynamic records of the specified usage are shown |
contents of dynamic fields and records of the specified usage may be updated. |
may delete dynamic records of the specified usage |
Non-address contact detail |
may link an access restriction of this type to a Person |
can see non-address contact attributes of Persons with this access restriction |
may update non-address contact attributes of Persons with this access restriction and may remove the link of a Person to this access restriction (may change it to another access restriction if create rights on that access restriction) |
not used |
Identifiers Type |
may create identifiers of the specified usage |
may query restricted identifiers |
identifiers may be updated |
may delete identifiers |
Person details |
may link an access restriction of this type to a Person |
can query Persons with this access restriction and no concealing of Persons with this access restriction in contract alignment page |
may update Persons with this access restriction, including insert/update/delete of child entities shown in the Persons page, and including the access restriction itself (may change it to another access restriction if create rights on that access restriction) |
may delete Persons with this access restriction |
The following table gives an example setup for two Address access restrictions: SECRET and TOP_SECRET and how the CRUD indicators are set for three different roles.
| Address Access Restriction | Role 'Secret Read Only' | Role 'Secret' | Role 'Top Secret' |
|---|---|---|---|
SECRET |
R |
CRUD |
CRUD |
TOP_SECRET |
not granted |
RUD |
CRUD |
Based on this example setup, the following table shows the different actions these roles can perform using these access restrictions:
| Action | Possible for role 'Secret read only'? | Possible for role 'Secret'? | Possible for role 'Top Secret'? | Possible for other role? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Create address without access restriction |
yes |
yes |
yes |
yes |
Retrieve address without access restriction |
yes |
yes |
yes |
yes |
Update/Delete address without access restriction |
yes |
yes |
yes |
yes |
Create address with access restriction SECRET |
no |
yes |
yes |
no |
Retrieve address with access restriction SECRET |
yes |
yes |
yes |
no |
Update/Delete address with access restriction SECRET |
no |
yes |
yes |
no |
Create address with access restriction TOP_SECRET |
no |
no |
yes |
no |
Retrieve address with access restriction TOP_SECRET |
no |
yes |
yes |
no |
Update/Delete address with access restriction TOP_SECRET |
no |
yes |
yes |
no |
For restriction types that restrict access to the whole record, restriction of access is implemented in two different ways, depending on the type of access:
-
Restricted records may be completely hidden from users without read access. This implementation applies when the restricted records are accessed directly. For example, person records can not be seen at all by users without access to them from person search functions.
-
The attributes of restricted records may be concealed. This implementation applies when the restricted records are accessed indirectly as in when they are referred to from other records.
| The restriction not only applies to the entity itself, but also to the related detail entities. For example: a reference to a bank account number of a restricted person is also concealed. |
| The restrictions are implemented consistently throughout the whole {capComponent. For example, LOV’s are also restricted. |
| A restriction also applies to the dynamic fields defined for that entity. So when access to a record is restricted, access to the dynamic fields of that record is also restricted. |
An attribute is concealed by displaying '*' in the field.
For restriction types that restrict access to a subset of attributes of the restricted record (like Non-Address Contact Detail restrictions), restricted attributes also display '*' in the field. This is done whether or not the attribute actually has a value. Therefore, users will not know if a value is actually present or not.
Inference Prevention
It should not be possible to infer concealed values. For example, if Person Bob has a restricted address with postal code 1234, this address is not to be shown to users that do not have rights for the address. This also applies indirectly, for example, when searching for relations with postal code 1234. Bob must not be found as this would reveal Bobs address. The prevention of inference differs per restriction and is indicated in the 'Inference Prevention' part of the description of each restriction.
Restriction Type Specific Aspects
This paragraph describes each specific restriction type. Note that an entity can be subject to multiple restrictions. When an entity is subject to multiple restrictions, all involved access restrictions must be granted to a user to gain access to that entity.
Protecting sensitive information
Address Contact Detail Restrictions
This feature allows access to specific person addresses (of at risk individuals) to be restricted. For example, this would apply to individuals that have been granted the right to have their details to be kept secret by the government or otherwise have made such a request.
An access restriction can be applied to each individual address. An address with an access restriction applied can only be accessed by users that have been granted access to that access restriction. Addresses for which a user has no access, are not visible at all. There is no indication that there is a restricted address. It is possible that a person has multiple addresses, of which some are shown and some are not, depending on the access restrictions applied and the privileges of the user accessing them.
Example
User Bob is granted access restriction SECRET_ADDRESS. No access restrictions have been granted to user Pete. The following table shows which addresses they can access.
| Person | Postal Code | Address Access Restriction | Accessible by Bob? | Accessible by Pete? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Mary |
1234 |
SECRET_ADDRESS |
yes |
no |
Jane |
1234 |
empty |
yes |
yes |
Susan |
1234 |
TOP_SECRET_ADDRESS |
no |
no |
Inference Prevention
When searching for relations/persons based on address, only addresses a user has access to are used:
-
When user Bob searches for persons with postal code 1234, only Mary and Jane are returned.
-
When user Pete searches for persons with postal code 1234, only Jane is returned.
These restrictions do not apply when relations/persons are searched for without any address search criteria.
| Addresses of organizations are not protected. |
Non-Address Contact Detail Restrictions
This feature allows access to specific contact details (of at risk individuals) to be restricted. For example, this would apply to individuals that have been granted the right to have their details to be kept secret by the government or otherwise have made such a request.
A contact details access restriction can be applied to a person. Non-address contact details can only be accessed by users with a role that includes the restriction. Non-address contact details are: business phone number, private phone number, mobile phone number, fax number and e-mail addresses.
When a user views a person with non-address contact details that they are not allowed to see, these details will not be displayed.
Example
User Bob is granted access restriction SECRET_CONTACT_DETAIL. No access restrictions have been granted to user Pete. The following table shows which contact details they can access.
| Person | Phone Number Business |
|---|---|
Address Access Restriction |
Accessible by Bob? |
Accessible by Pete? |
Mary |
123-456-789 |
SECRET_CONTACT_DETAIL |
yes |
no |
Jane |
123-456-789 |
empty |
yes |
yes |
Susan |
123-456-789 |
TOP_SECRET_CONTACT_DETAIL |
no |
no |
Inference Prevention
When searching for relations/persons, only contact details a user has access to are used:
-
When user Bob searches for persons with phone number business 123-456-789, only Mary and Jane are returned.
-
When user Pete searches for persons with phone number business 123-456-789, only Jane is returned.
These restrictions do not apply when relations/persons are searched for, without any contact detail search criteria.
Identifiers Type
This feature allows access to identifiers of a person or an organization to be restricted. The identifiers can only be accessed by users with a role that includes the restriction. The identifier types can be of various types such as the social security number, drivers license number etc.
When a user views a person or an organization with the identifiers that they are not allowed to see, the identifiers will be concealed.
-
Identifiers
When a user searches for the protected identifiers that they are not allowed to see, the identifier will not be returned at all.
Example
User Bob is granted access restriction SECRET_IDENTIFIER. No access restrictions have been granted to user Pete. The following table shows which contact details they can access.
| Person | Identifier | Identifier Type | Identifier Access Restriction | Accessible by Bob? | Accessible by Pete? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mary |
123-456-789 |
Social Security Number |
SECRET_IDENTIFIER |
yes |
no |
Jane |
289-68c-180D |
Pan Card Number |
empty |
yes |
yes |
Susan |
-*-890E |
Driver’s License Number |
TOP_SECRET_IDENTIFIER |
no |
no |
Inference Prevention
When searching on an object with a restricted identifier as search criterion, the object is not returned when the user doesn’t have the appropriate access restrictions for that identifier type.
Related Entities
Not applicable.
Person Details Restriction
This feature allows access to details of persons who need special protection to be restricted. Examples for the use of this feature include protection of VIPs, celebrities, and at risk individuals.
It is possible to apply an access restriction to a person to indicate that the person can only be accessed by users with a role that includes the restriction.
When a user searches for relations, protected persons that they are not allowed to see will not be returned at all.
Inference Prevention
A restricted person is restricted throughout the whole Oracle Health Insurance Value-Based Payments as if that person does not exist. So if person P is restricted for a user, searching for contract alignments of person P will not return any data for that user.
Related Entities
When access to a person is restricted, the following details are also restricted:
-
Person Titles
-
Addresses
-
Bank Account Numbers
-
Assigned Providers
-
Contract Alignments
Division of work / need to know (general)
These features cover broad filtering of data from users that simply don’t need access to it. For example, this could apply where a separate group of users works on contracts of specific data access groups and they have no need to access contracts from additional data access groups.
Dynamic Field Usages
This feature provides restricting access to dynamic fields and records. If a user has an access restriction of type Dynamic Field Usage, then he is authorized to view and/or update non time valid dynamic fields of the restricted usage and, depending on the access rights, view/create/update/delete dynamic records of the restricted usage.
Example
If a user is authorized to view dynamic records defined on a contract with usage name 'Medical Data', these dynamic records are visible for the user. However, the user is not able to create new, delete or modify dynamic records with usage name 'Medical Data'.
Inference Prevention
When searching on an object (e.g. a contract) with a restricted dynamic field as search criterion, the object is not returned when the user doesn’t have the appropriate access restrictions for that dynamic field.
Related Entities
Not applicable.
Data Access Group Contract Restriction
Data access groups are used to allow a system administrator to differentiate data access over contracts. A user can be excluded access to the contracts linked to specific data access groups.
Data Access Group
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Code |
The unique code of the data access group. |
Description |
The description of the data access group. |
Access Restriction |
The access restriction restricting access to this data access group. |
Inference Prevention
When a user searches for contracts of data access groups that they are not allowed to see, they will not be returned at all.
Related Entities
When access to a contract is restricted, the following details are restricted also:
-
Contract Adjustments
-
Contract Adjustment Override
-
Contract Alignments
-
Contract Calculation Periods
-
Contract Payment Receivers
-
Contract Provider Filter Rules
-
Contract Rate Splits
-
Contract Time Periods
-
Calculation Result and related Calculation Result Lines