4 Credentials
Database credentials are needed to access Retail AI Foundation Cloud Service through your private endpoint. Obtain these credentials by using the Credential Exchange Service, a REST endpoint.
The endpoint provides a means of fetching the database credentials required to connect. Credentials are periodically refreshed when passwords are rotated. Notification of password rotation is received by registering one or more callback services or email addresses with the Credential Exchange Service.
It is recommended that at least an email address be registered through the rotation-notification endpoint as a fallback means of notification, otherwise the credentials may be rotated without your knowledge.
Any callback service should be accessible through the Private Endpoint. Repeatedly unavailable endpoints may be removed. Finally, credentials are not conveyed through the callback; you are only notified that they have changed.
The Credential Exchange Service uses OAuth 2.0for authentication. That token is generated using a well-known OCI IAM service, which authenticates using basic authentication. The client credentials for this (that is,, client id and client secret) are obtained from Retail Home.
Bear in mind, the OCI IAM service is rate limited (see API Rate Limits). Best practice is to reuse tokens until they expire (one hour). If you encounter an HTTP- 429 error when requesting a token or authenticating, you have hit the rate limit. When you encounter a rate limit, pause any further requests for one minute to reset the rate limiter.
Obtaining Credential Exchange Server Credentials
Base URL
The base URL mentioned below has the following form:
<host-name>/<sub-name-space-name>
The host-name can be further decomposed into:
https://home.retail.<region>.ocs.oracle.com
Likewise, the sub-namespace-name can be further decomposed into:
rgbu-common<customerid>-<env>
You can extract region, customerid, and env from your Retail Home URL. The host port of the base URL is 443.
If you are still uncertain as to how to construct the base URL or the base URL you have constructed is not working as expected, submit a Support Request for further assistance.
-
In Retail Home, navigate to Manage OAUTH Clients page by tapping settings (1), then tapping the Application Administration menu item (2), and lastly tapping the Manage OAUTH Clients menu item to arrive at the Manage OAUTH Clients page (4).
Figure 4-1 Mange OAUTH Client
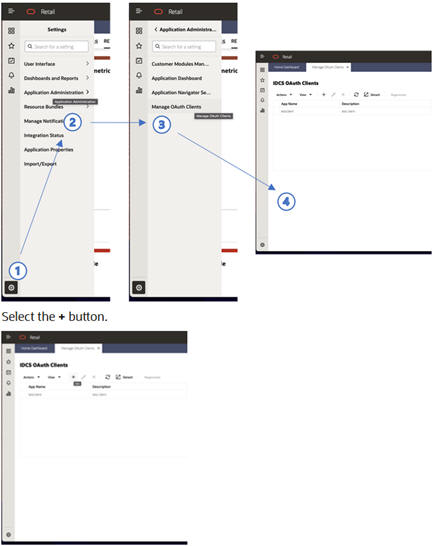
- Select the +
button.
Figure 4-2 Selecting + Button
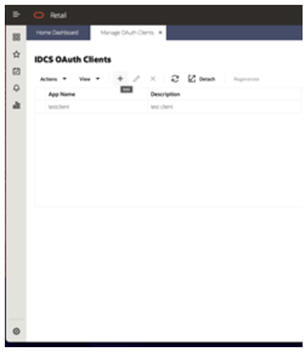
- A popup dialog appears. Provide an App Name and Description.
Leave Scope blank. Select OK.
Figure 4-3 Provide App name and Description
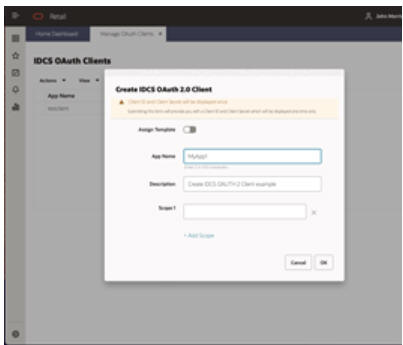
- A new dialog appears with a Display Name, Client ID and Client
Secret. You must retain this information. It will not be displayed
again. Select Done when the information has been copied. Note: New
credentials can be created at any time and that production, stage,
and development will have different credentials.
Figure 4-4 Descriptive Information

Consult the Retail Home Application Administration Guide for additional details on managing OAUTH clients.
Remember that the OCI IAM service is rate-limited (see API Rate Limits). Best practice is to reuse tokens until they expire (one hour). If you encounter a 429 error when requesting a token or authenticating, you have hit the rate limit. When you encounter a rate limit, back off for one minute to reset the rate limiter.
-
Verify that a client ID and secret can be created in Retail Home.
-
Retain the client ID and secret for future use.
There is no need to create multiple OAuth clients for each OCI IAM service. A single OAuth client can be used across all environments secured by a given IDCS.
Generating a Credential Exchange Server Access Token
You will need an IDCS Authorization Server endpoint URL and ORDS service credentials to perform the steps described below.
You will use an IDCS Authorization Server to generate an ORDS access token. There are multiple techniques for generating an access token. The example below employs cURL.
-
The IDCS Authorization Server endpoint URL
-
The IDCS Authorization Server endpoint URL
-
An Authorization
-
A grant type
-
A scope
Only the IDSC Authorization Server endpoint url and authorization are customer-specific. content type, grant type, and scope are the same for all customers.
IDSC Service Host
The IDCS endpoint URL has the following form: https://<idcs authorization server host>/oauth2/v1/token
To obtain your IDCS service host, navigate to Retail Home. When you navigate to Retail Home you will be redirected to an IDCS authorization server URL. The host of that URL is the IDCS authorization server that you will use to obtain your access token.
Basic Auth Encoding
To fetch a token, you need to use Basic Auth and Base 64 encode the credentials. For example, you could use the following script to obtain an access token on Oracle Linux 8:
CLIENT_ID=”your_client_id”
CLIENT_SECRET=”your_client_secret”
# Combine the client ID and secret, then encode in Base64
ENCODED_CREDENTIALS=$(echo -n “${CLIENT_ID}:${CLIENT_SECRET}” | base64 –w 0)
# Output the result
echo “Encoded Base64 credentials: $ENCODED_CREDENTIALS”
Replace your_client_id and your_client_secret with the credentials obtained when creating your OAUTH client.
Use the cURL command to generate a token is the following:
RESPONSE=$(curl --location --request \
POST "https://<idcs authorization server host>/oauth2/v1/token" \
--header "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
--header "Authorization: Basic ${ENCODED_CREDENTIALS}" \
--data-urlencode "grant_type=client_credentials" \
--data-urlencode "scope=urn:opc:idm:__myscopes__")
ACCESS_TOKEN=$(echo ${RESPONSE} | jq -r .access_token)
echo ${ACCESS_TOKEN}
- Verify that you can generate an access token.
- Retain the access token if you plan to use it within the next hour.
Credential Exchange Endpoints
Fetching Credentials
| Method | Endpoint |
|---|---|
|
GET |
/api/data-pe/v1/fetch-credentials |
Returns the wallet and credentials for the schemas exposed by the Database Private Endpoint.
Fetching Wallet
| Method | Endpoint |
|---|---|
| GET | /api/data-pe/v1/fetch-wallet |
This REST call returns the wallet as a compiled zip file for use with the Database Private Endpoint. The wallet does not contain credentials, these need to be fetched from the fetch-credentials endpoint.
Registering Notification Endpoints
| Method | Endpoint |
|---|---|
|
PUT |
/api/data-pe/v1/rotation-notification |
JSON payload: {"usecase": "credentialRotationNotification",
"endpoint": "http://example.org:80/foo/bar/baz/notification1" }
This method inserts unique endpoints into the notification endpoint list. Duplicates are silently ignored (intended for repeat registrations from restarted callback services). The notification endpoint can be a URL in the form of http, https, or mailto (e.g., mailto:foo@bar.baz).
{usecase:"credentialRotation", change:"<all|credentials|wallet>"
}
Note:
If an http or https endpoint is registered, you may need to add an ingress rule for <base_url> to ensure that the endpoint is reachable.Registered mailto endpoints are sent a notification email. SMTP notifications are sent from the regional OCI Email Delivery Service to the email address that the customer specifies.
After receiving this notification, the consuming applications should refresh their credentials.
| Method | Endpoint |
|---|---|
|
DELETE |
/api/data-pe/v1/rotation-notification |
JSON payload: {"usecase": "credentialRotationNotification",
"endpoint": "http://example.org:80/foo/bar/baz/notification1" }
Removes endpoints from a list. Non-existent endpoints are silently ignored.
| Method | Endpoint |
|---|---|
|
GET |
/api/data-pe/v1/rotation-notification?tenantId=abc123 |
Returns endpoints[...] containing a list of registered endpoints, or empty endpoints [] if none exist.
Example
{"endpoints": [ "http://example.org:80/foo/bar/baz/notification",
"mailto: nobody@example.org" ] }
Serialized Wallet and Credential Format
Credentials are serialized into JSON and, within that payload, Oracle Wallet file contents are base64 encoded.
| Content | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
wallets |
Array of wallets |
|
walletName |
Name of database wallet and instance, derived from tnsnames.ora within wallet |
|
walletPassword |
(Currently unused) |
|
comment |
(Currently unused) |
|
certificateEndDate |
Expiration date of wallet, derived from truststore certificate within wallet |
|
certificateStartDate |
Start date of wallet, derived from truststore certificate within wallet |
|
lastRotationDate |
Date of last rotation |
|
schemas |
Map of database credentials (username):(password) |
|
wallet |
Map of wallet file contents, (filename):(base64 encoded file) |
Example
{
"wallets": [
{
"certificateEndDate": 1746276157000,
"certificateStartDate": 1588596157000,
"comment": null,
"lastRotationDate": 1624305815466,
"schemas": {
"username1": "password1",
"username2": "password2",
"username3": "password3",
"username4": "password4",
},
"wallet": {
"README": "...base64-encoded-file...",
"cwallet.sso": "...base64-encoded-file...",
"ewallet.p12": "...base64-encoded-file...",
"keystore.jks": "...base64-encoded-file...",
"ojdbc.properties": "...base64-encoded-file...",
"sqlnet.ora": "...base64-encoded-file...",
"tnsnames.ora": "...base64-encoded-file...",
"truststore.jks": "...base64-encoded-file..."
},
"walletName": "Wallet_RDSADWABC123",
"walletPassword": null
}
]
}
Table 4-1 Troubleshooting
| HTTP Status Code | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| 404 | Incorrect API URL | Verify API URL |
| 401 | Invalid, expired, or missing token | Verify that you are using the a client ID and secret from the correct IAM service, that the token has not expired, that the token is valid (e.g., echo cURL script), and the token is not missing. |
| 403 | Internal error | Submit a support ticket with the details of the API invocation (e.g., a cURL script) |
| 200 | Response is: {"msg":"Internal error, cannot connect to upstream service", "detail":"java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused (Connection refused)"} | Submit a support ticket with the details of the API invocation (e.g., a cURL script) |