19 Sales Audit
The purpose of Sales Audit is to accept transaction data from point-of-sale (POS) and order management (OMS) solutions and move the data through a series of processes that culminate in "clean" data. Data that Sales Audit finds to be inaccurate is brought to the attention of the auditors who can use the features in Sales Audit to correct the exceptions.
Sales Audit uses several batch-processing modules to:
-
Import POS/OMS transaction data sent from the store to the Sales Audit database
-
Produce totals from user-defined totaling calculation rules that a user can review during the interactive audit
-
Validate transaction and total data with user-defined audit rules that generate errors whenever data does not meet the criteria
-
Create and export files in formats suitable for transfer to other applications
-
Update previously exported data with adjustments received from external systems
The term store day is used throughout this chapter. Store day describes all transactions that occur in one business day at one store or location. Because retailers need the ability to audit transactions on a store-by-store basis for a defined period of time, store day data is maintained separately, beginning with the initial import of data from the POS/OMS system.
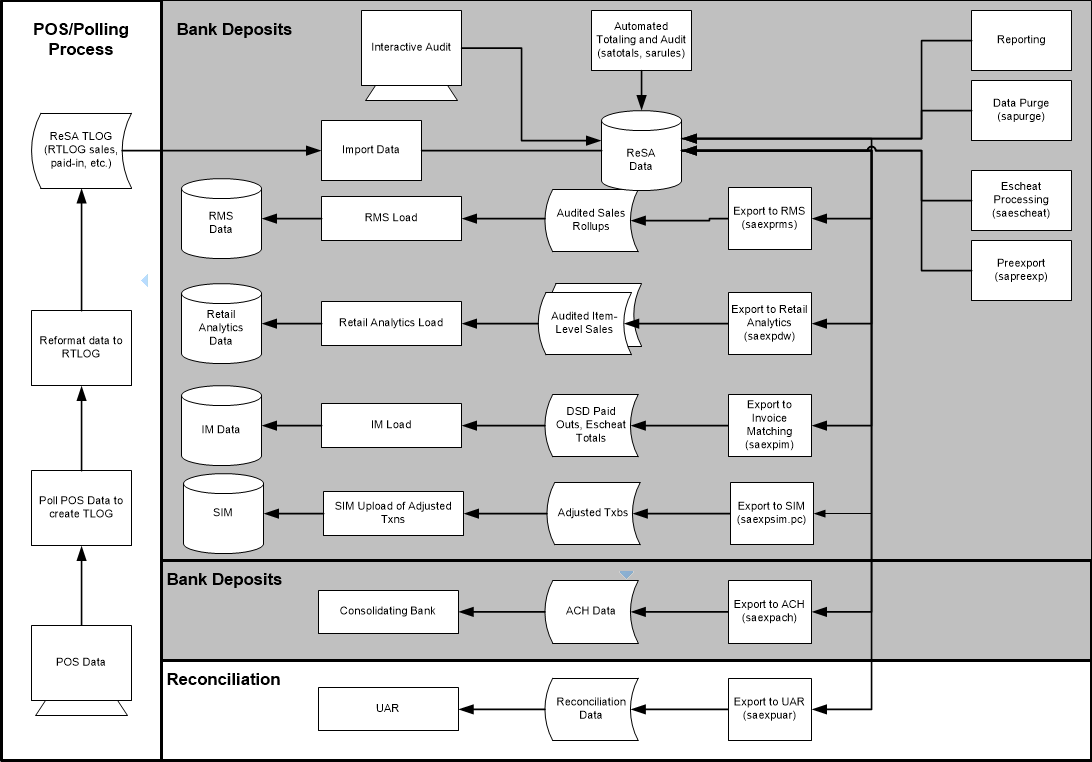
The following diagram illustrates how data flows within Sales Audit and between Sales Audit and other applications.
Note:
All integrations are not depicted in this diagram.
Figure 19-1 Oracle Retail Sales Audit Dataflow Diagram