2 Roles
Figure 2-1 Sales Audit Roles
Roles Provided at Initial Setup
A default security configuration is provided with each application during installation and is intended to be used as a starting point as you define the roles that align for your business and users. The provided roles can be modified by adding or removing duties and/or individual privileges to adjust the access granted to the role, or the roles can be deleted completely. Additional roles can be created as well and can be mapped to the desired duties or privileges. Administrator users can change the mappings of roles, duties and privileges in Sales Audit's User Interface.
Details about how to manage these application security policies are available in Chapter 2, Manage Security Policies in the Oracle Retail Merchandising Administration Guide.
There are four roles provided in the default security configuration:
Sales Audit Application Administrator
The Application Administrator is a part of a retailer's IT department responsible for maintaining and configuring the Sales Audit application. Primary responsibilities include:
-
Maintain daily operations, such as daily batch processes of the application.
-
Supporting end-users and providing the first level of support for the application.
-
Applying patches and upgrades to the application on a regular basis.
-
Troubleshooting and resolving product issues.
-
Setting up users and security privileges for the application.
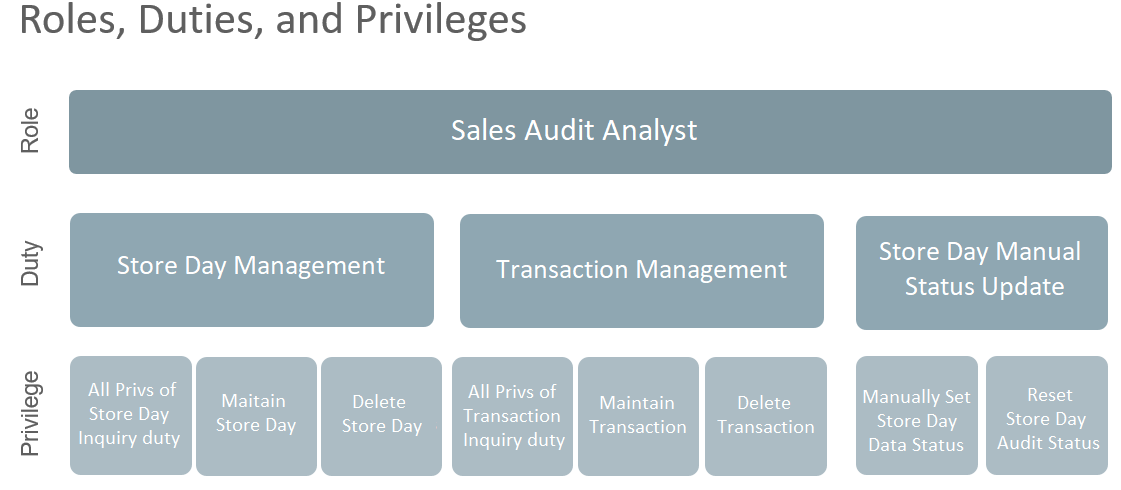
Sales Audit Analyst
The Sales Auditor is responsible for reviewing the sales data from the stores that assigned to them, reviewing any errors or exceptions and investigating and making corrections as necessary to ensure that stores sales logs are clean and closed on a timely basis so that this data can be passed on to other systems such as Merchandising, Inventory, and Financials. Primary responsibilities include; - Review, investigate and correct audit errors - Close each store day in as timely a manner as possible - Identify reasons for Over Shorts and correct if possible - identify any recurring patterns of errors or Over Shorts and raise concerns to manager.
Sales Audit Manager
The Sales Audit Manager manages a team of Sales Auditors who review transactions and any exceptions or errors raised by the sales audit process and systems, investigates the exceptions and makes any corrections that are required so that clean sales data can be passed on to other systems such as Merchandising, Inventory Management, and Financials, among others. The sales audit manager is typically responsible for the same processes and responsibilities at the sales auditors, plus others such as - Managing workload of the auditors - Developing rules for use in the sales audit process - Ensuring all sales auditors are meeting goals and timelines for auditing and closing stores - Helping auditors to identify patterns of irregularities and possible loss prevention issues - Identifying consistent areas of concern across locations.
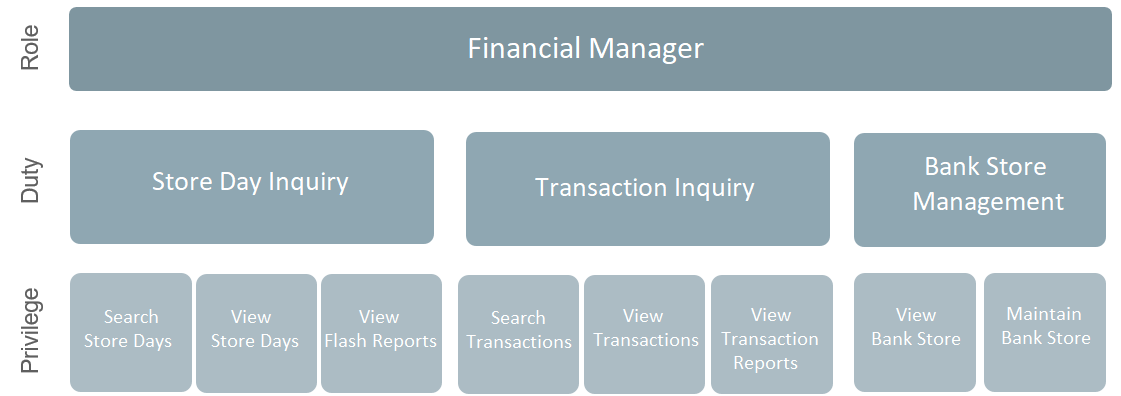
Financial Manager
Responsible for the financial accounting of a retailer's business, which includes making sure that all financial operations are running smoothly, bills are paid on time, figures are reported timely and accurately, period end books are closed properly. This includes:
-
Ensuring period end reporting is completed in a timely manner.
-
Ensuring the timely resolution of auditing issues.
-
Ensuring in the timely resolution of vendor payment issues, including the resolving cost and other invoicing discrepancies- Identifying risks and opportunity areas to the operations.
-
Providing performance reporting highlighting trends and opportunities to assist in improving profits, margins and reducing costs.