10 Charts
You can use the charting feature to generate a visual representation of the data in the form of charts. This chapter describes the available chart types and provides instructions on the various tasks you can perform with charts.
Viewing Charts
If a chart view exists in the View Management Drawer, you can drag the view to the content area to view it. This action is similar to dragging the views from the View management drawer to the content area for viewing.
You can view the existing chart views in the Full View, 2-Horizontal View, 2-Vertical View, or 4-View layout. You can also create a new view with View type as chart.
You can view the chart in the Full view mode.
Figure 10-1 Chart in Full View Mode
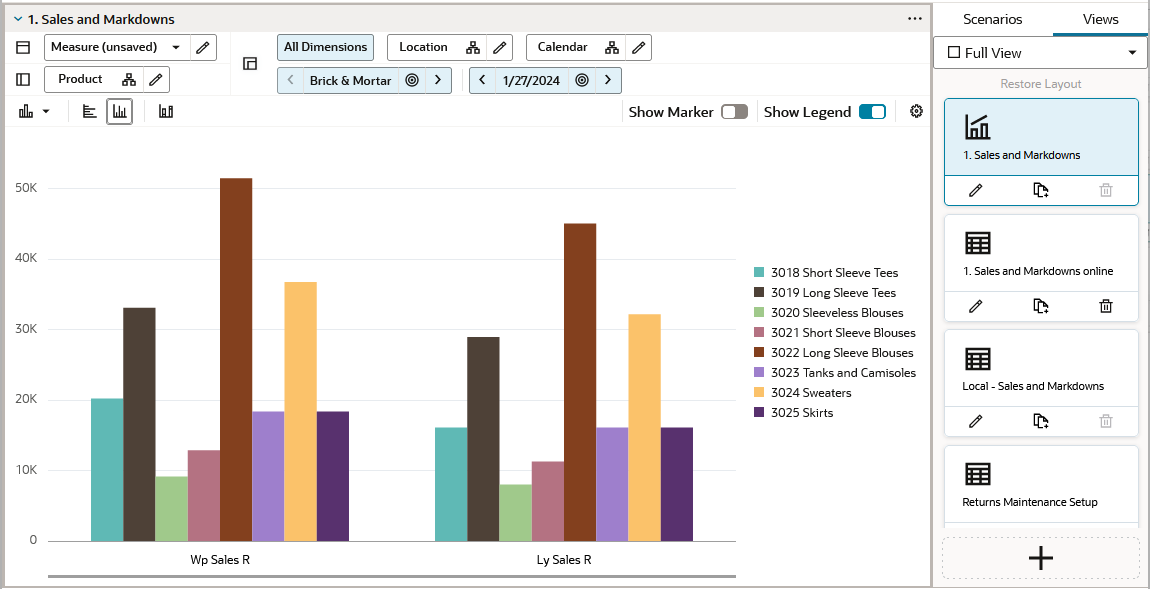
Figure 10-2 Chart in 2-Horizontal View Mode
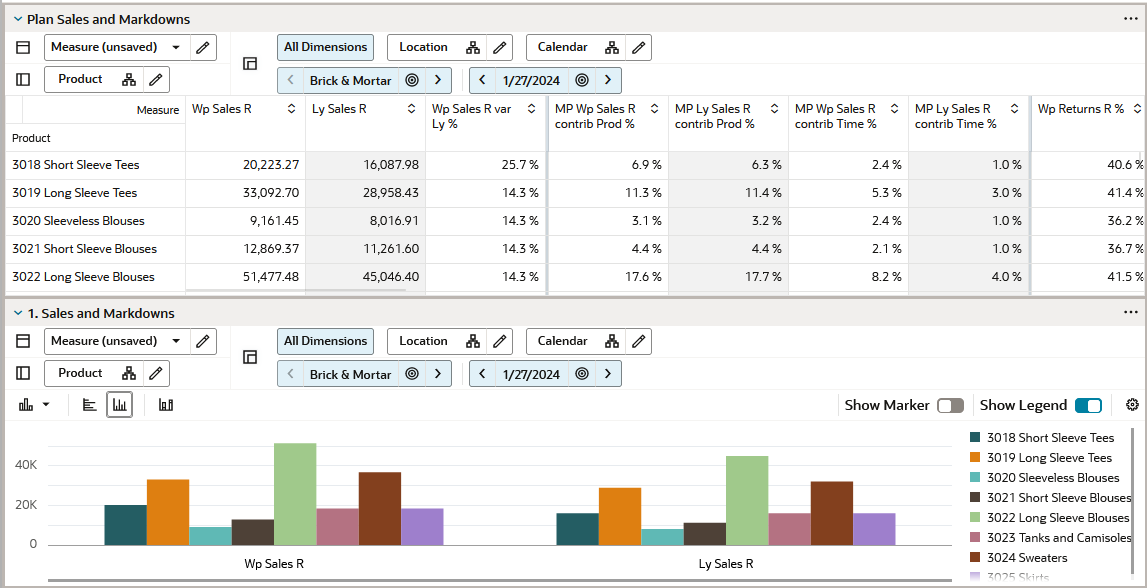
Figure 10-3 Chart in 2-Vertical View Mode
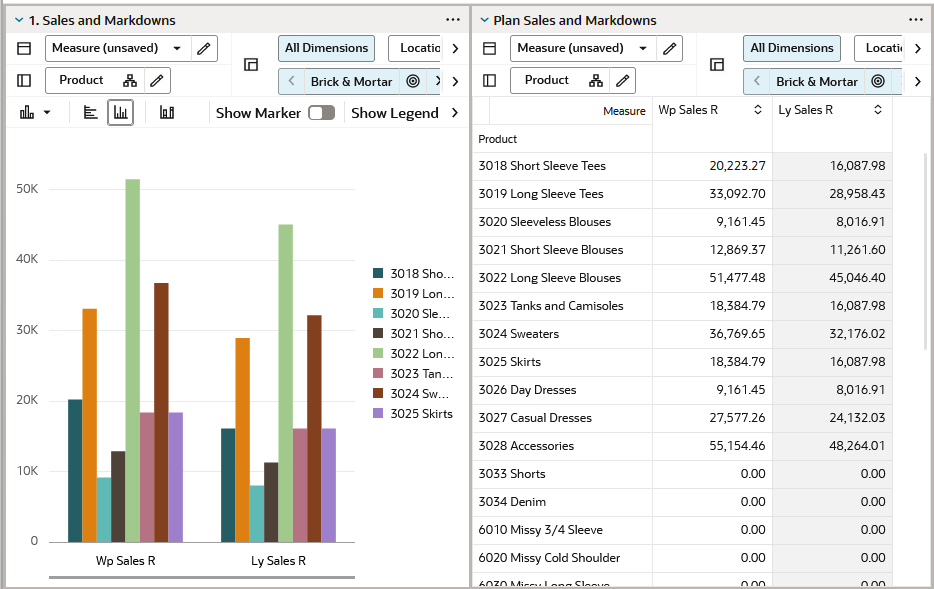
Creating a Chart
You can create a chart for any of the existing views containing the same or different data. It can be helpful to have a pivot table view and a chart view open at the same time to make changes to the pivot table values and see the results in the chart value.
-
Click Plus in the View Management Drawer.
Figure 10-4 Creating a Chart
-
In Edit View, Select a Source and select from the existing views. This example uses 1.Sales and Markdowns as the source. All data that exists in the 1.Sales and Markdowns view is available in the new chart view being created.
Figure 10-5 Select a Source
-
In the Edit View window, enter a name for the new view. Here, it is a name similar to the source.
Figure 10-6 New View Name
-
Select the type of chart from the list.
Figure 10-7 Chart Type
-
Click the Details tab to add, remove, or rearrange any levels or positions on the chart and click OK.
Figure 10-8 Chart Details
-
Drag the new Chart view tile into the content area to view the chart.
Figure 10-9 Chart View
-
Another way to create charts in the existing tile view is to click the Charts icon (Figure 10-10 on the content area. This option helps you to switch between pivot table and charts with just one click. It allows you to view data in a graph format for analyzing data. You can revert back to the pivot table when you click the Pivot Table icon (Figure 10-11).
Figure 10-10 Switch to Charts Icon
Figure 10-11 Switch to Pivot Table Icon
Data in Charts
In chart view, the positions on row are represented as series. The data values in a column are plotted together as a group.
Figure 10-12 Data Mapping in Charts
Key for Figure 10-12:
A:X-axis Data Mapped as a Group (red)
B: Y-axis Data Mapped as a Series (blue)
C: Data for all the Series belonging to a Group (green)
Customizing a Chart
You can customize a chart using Edit View, just like any other view. You can change the data representing dimension levels, change axes, measures, and so on. For more information, see Editing Views..
Figure 10-13 Customize a Chart
To change the orientation of the x-axis labels, an administrator can set the orientation in self-service configuration feature. The orientation of the chart can be set either as horizontal or auto-orientation to manage the space of the chart view. For more information, see the Oracle Retail Predictive Application Server Cloud Edition Administration Guide.
Deleting a Chart
To delete a chart, you delete the chart view from the View Management Drawer. Default views cannot be deleted.
Click Delete on the chart view in the View Management Drawer:
Figure 10-14 Deleting a Chart
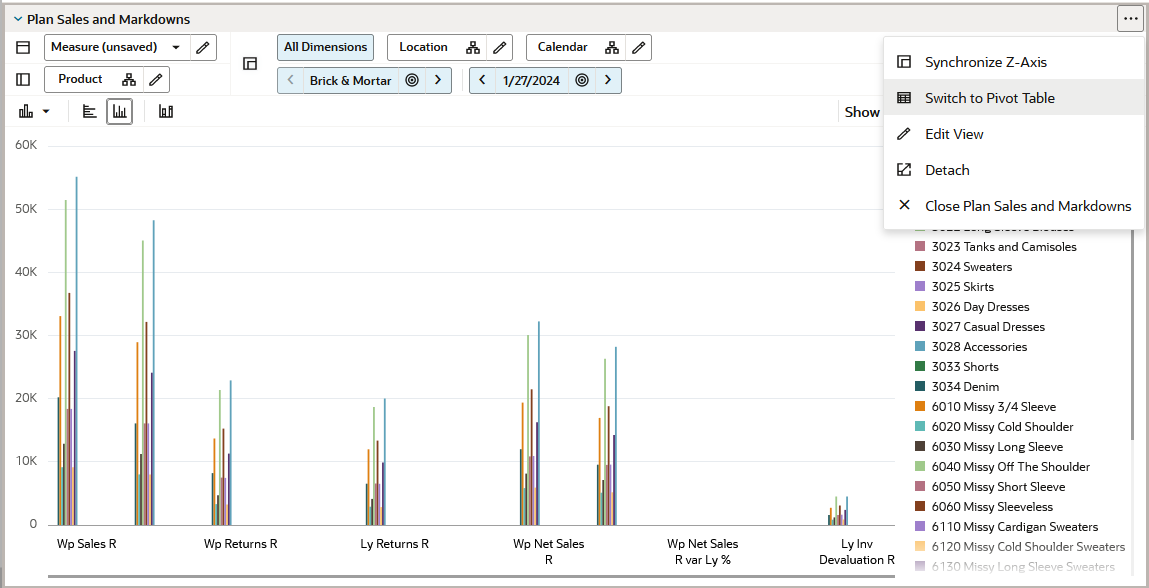
Synchronize the Z-axis with Charts
It can be helpful to have a pivot table view and a chart view open at the same time to make changes to the pivot table values and see the results in the chart value. By enabling the Synchronize Z-axis button with both views displayed, you can scroll through positions on the z-axis, and both views will stay in synch.
-
In the View Layout list, select any option except for Full View. In this example, 2 Horizontal has been selected.
Figure 10-15 Select View Layout
-
Add at least two views to a layout by dragging the View Tiles from the View Management Drawer. In this example, the 1. Sales and Markdowns tile and the Plan Sales and Markdowns Bar Chart View tile have been dragged into the layout.
Figure 10-16 Add Chart View to Layout
-
Click Synchronize Z-axis to activate it.
Figure 10-17 Activate Synchronize Z-axis
-
The activated Synchronize Z-axis button displays in blue on both tiles. Both views have scrolled to the same Product position.
Figure 10-18 Synchronize Z-axis
Edit Data Values in the Chart Views
The data in the pivot table can be edited from charts views. It can be helpful in making changes to data without navigating to pivot table. Changing data value in the chart view gives a quick look at the graph trend and planner can make faster decisions. You can edit charts by two ways:
Dragging the Chart Line
Perform the following steps to edit a chart by Dragging the chart line:
-
Change the view to the chart view. When you bring the cursor to the point of intersection, the marker is highlighted and the cursor changes to pointer finger.
Figure 10-19 Chart View - Marker Point Highlight
-
Double-click and then hold and drag the marker point where the data change is required. To increase the value of data, drag upwards and to decrease drag the point of intersection downwards on the chart layout.
When you move the point of intersection, you can see the value of the current selection changing on the chart tool bar.
Figure 10-20 Drag the Chart Line Upward to Increase the Data Value
Figure 10-21 Edit Result after Dragging a Chart Line
Note:
When you edit the numeric value in the chart view, the value may display in decimal points but in pivot table the value is rounded off.
Using the Edit Window to Edit Charts
Perform the following steps to edit charts using the Edit Window:
-
Change your view to the chart view. Bring the cursor to the point of intersection, the marker ID is highlighted and the cursor changes to pointer finger.
-
Click the point of intersection where the data change is required and an Edit Chart dialog box opens. The edit chart dialog box shows the description of Series, Group and text input box for Value.
Figure 10-22 Chart View - Edit Chart Dialog Box
-
Enter the data value in the Value input box and click Done to accept. To cancel, click X and the value is not updated.
Figure 10-23 Edit Value in the Dialog Box
Figure 10-24 Edit Result in the Chart View
Note:
When you enter a decimal value in the Edit dialog box, the value is rounded off in the pivot table.
Points to Remember
Consider the following points when you edit data values in the Chart Views:
-
The data edited in chart is reflected in the pivot table.
-
You can edit only the bar graph, line, area, line and area, combination charts, bubble, and scatter charts.
-
Edit in Scatter chart—Drag and drop functionality enables to edit both the measure which are plotted at the x-axis and y-axis by dragging the point of intersection vertically and horizontally. The edit of value can also be made by using Edit Window functionality.
-
Edit in Bubble chart—Drag and drop functionality enables to edit two measure which are plotted at x-axis and y-axis of chart. The third measure representing the size of bubble can be edited using Edit window functionality. You can edit the value of all three measures by within the Edit Window.
-
You can use Undo, Redo function in chart view as well.
-
You can edit chart in Horizontal orientation.
-
You can right- click on the point of intersection to access the Edit chart option from chart context menu.
-
You can edit only numeric values in graph. SHS, pick list, date, date time, Boolean measures will not be edited from chart.
-
You cannot edit the read-only, protected and or locked data values from chart view. When you click the locked, protected or read only data point in chart view, and alert message is shown. The value cannot be edited as it is read-only, protected, or locked.
Chart Types
The following chart types are available:
Multi Group Charts
A multi-group chart shows data for multiple columns or groups. For example, the chart in Figure 10-25 plots WP Sales R values for Missy Short Sleeve Sweaters across 10 different locations over time (three months).
Figure 10-25 Multi-group Chart
Bar Chart
In a Bar Chart, the data is represented as a series of vertical or horizontal bars. It can be used to examine trends over time or compare items at the same time (for example, sales for different products in different quarters).
Figure 10-26 Bar Chart
Area Chart
In an Area chart, the data is represented as a filled-in area. An area chart can be used to show trends over time, such as sales for the past 12 months. Area charts require at least two groups of data along an axis.
Figure 10-27 Area Chart
Line Chart
In a Line Chart, the data is represented as a line, a series of data points, or data points connected by a line. Line Charts require data for at least two points for each member in a group.
Figure 10-28 Line Chart
Line with Area Chart
Line with Area Chart is a combination of Line Chart and Area Chart. In a Line with Area Chart, the data is represented as a line, series of data points, or data points connected by a line, with a filled-in area. Line with Area Charts require data for at least two points for each member in a group.
Figure 10-29 Line with Area Chart
Polar Chart
A Polar Chart is a diagram in which a point of origin is surrounded by a curve whose radius at any given point is proportional to the magnitude of some property measured in the direction of that point.
Figure 10-30 Polar Chart
Stacked Area Chart
Area markers are stacked, and the values of each set of data are added to the values of previous sets. The size of the stack represents a cumulative total. This type of chart has the following variations.
Figure 10-31 Stacked Area Chart
Scatter Chart
A Scatter chart displays two variable for a set of data which helps in comparison of data and understand the relationship between two variables. Usually the independent variable is plotted along the horizontal axis (x-axis) and the dependent variable is plotted on the vertical axis (y-axis). The scatter chart has a different view as scatter chart needs two measure values to display the chart.
Figure 10-32 Scatter Chart
Perform the following steps to plot scatter chart:
-
Select the chart type Scatter Chart from the chart drop-down list in Edit view.
Figure 10-33 Edit View Scatter Chart Type
-
To plot a scatter chart, bring the Measure dimension to X-axis in the workspace view. In case the measure dimension is in different axis then a message appears on the chart area to move the measure dimension to X-axis.
Figure 10-34 Measure on the X-axis
-
Select two measures for which you need to plot the scatter chart using the drop-down list 1 and the drop-down list 2. Measure 1 is the plot at y-axis on the chart and Measure 2 is plot at x-axis on the chart.
Figure 10-35 Scatter Chart Measure Drop-down List
Figure 10-36 Scatter Chart
Bubble Chart
A Bubble chart is a multi-variable graph where three variables of the data display as bubbles in the chart. Two variables are plotted through the x-axis and y-axis. The third variable is represented by the size of the bubble. You can use a Bubble chart to compare and show the relationship between categorized bubbles by the use of positioning and proportions or size of bubbles.
Figure 10-37 Bubble Chart
Perform the following steps to plot a bubble chart:
-
Select the chart type Bubble Chart from the chart drop-down list in Edit view.
Figure 10-38 Edit View Bubble Chart Type
-
To plot a bubble chart, bring the Measure dimension to the X-axis in the workspace view. In case the measure dimension is in a different axis then a message appears on the chart area to move the measure dimension to X-axis. The Bubble size will plot size of the bubble.
Figure 10-39 Measure on the X-axis
-
Select three measures for which you need to plot the bubble chart using the drop-down list 1, the drop-down list 2 and the Bubble Size drop-down list. Measure 1 is the plot at y-axis on the chart and Measure 2 is plot at x-axis on the chart. The Bubble Size plots size of the bubble.
Figure 10-40 Bubble Chart Measure Drop-down List
Figure 10-41 Bubble Chart
Custom Charts
Custom charts enable you to create dual y-axis charts, combination charts and Boolean charts. You can select the custom chart option from chart menu drop down. The custom chart option displays the setting option. From chart setting option you can select the marker symbol, color, chart type/style, axis. To enable custom menu chart, place the measure tile on y-axis.
Dual Y-axis Chart
The Dual Y-axis chart allows you to set summaries or plot two y-axis variables. Example you can plot number of units on one axis and gross margin on another axis. Dual y-axis chart helps in presenting plenty of information in the limited space present on the screen and allows you to understand the trend. Using dual y-axis chart, you can easily validate / invalidate relations between two variable with different scale of measurement. To create dual y-axis chart, Place the measure tile on y-axis, select the custom chart option from chart drop down. Click Setting to see a dialog box with list of measures plotted on charts. To display the measure on second axis, change the Axis selection from drop-down to Top Axis and click OK. Your measure is plotted on top with a second y-axis for you to compare the data.
Figure 10-42 Dual Y-axis Chart
Combination Chart
The Combination Chart uses three different types of data markers to display different kinds of data items. The Combination Chart can be plotted by using custom chart option and changing the Chart Style as per requirement. You can compare bars and lines, bars and areas, lines and areas, or all three combinations. Combination charts require at least two groups of data for the chart to render an area marker or a line marker.
Figure 10-43 Combination Chart
Boolean Charts
Boolean data can also be represented in chart along with other measures. Boolean measure data is represented in chart if the value of Boolean is True. Visual representation of Boolean in a chart helps the user to understand the data better and enables the ability to review the data visually. Examples of Boolean data include calendar events such as promotion weeks, selling weeks, stock-outs, and so on. To plot a Boolean measure, select the custom chart option, Click Setting and change the Boolean measures to Top Axis from Axis drop-down and click OK. The Boolean measure is plotted on the top area of the chart to display separately. This provides a clear indication of the Boolean measure and make it easier for you to read the Boolean measures along with other measures. The Boolean data is presented by colored symbols in the charts. Multiple Boolean measures in a single chart represented by different color symbols.
For example, the Figure 10-44 shows Assorted options - Boolean measure against Sales Reg+Promo R, Sales Reg+Promo U.
In the chart the Purple Star symbol represents the assorted options Boolean Value = True.
The Boolean measure assorted option is represented separately on the chart area along with Sales Reg+Promo R and Sales Reg+Promo U.
Figure 10-44 Boolean Data in Chart
The Boolean data can be represented in following charts:
Single Group Charts
A single-group chart shows data for only one column or group. For example, the chart in Figure 10-45 compares WP Sales R values for Missy Short Sleeve Sweaters across 10 different locations for one month.
Figure 10-45 Single Group Chart
Pie Chart
In a Pie Chart, the data is represented as sections of a circle. Pie charts can be used to show the relationship of parts to a whole.
In Figure 10-46, because this is a single-group chart, only one measure is shown at a time.
Figure 10-46 Pie Chart
Funnel Chart
Funnel charts are useful for viewing data for stages of a process, such as the stages of a sales process. The area of a funnel slice is proportional to its value for the corresponding stage.
Figure 10-47 Funnel Chart
Pyramid Chart
A pyramid chart has the form of a triangle with lines dividing it into sections. Each section contains a related topic or idea. Because of the triangular shape, each section is a different width from the others; this width indicates a level of hierarchy among the topics. For example, the widest section may contain a general topic and the narrowest section may contain a much more specific topic from within that general topic. However, the width is not visually representative of the quantity beyond larger or smaller.
Figure 10-48 Pyramid Chart
Formatting Charts
Each of the chart types has different types of formatting options. To change the chart format, click one of the buttons beneath the Dimension Tiles area. Note that not all formatting options work with all chart types:
-
Stacked charts help in displaying the cumulative magnitude of two or more data series. They are useful in representing a data value as a sum of two or more values. Each data series can be distinguished by the color of its section in the stack.
Figure 10-49 Stacked Chart
-
The 3-D charts icon shown in Figure 10-50 rotates the chart into a 3-D display.
Figure 10-50 3-D Chart
-
The Horizontal icon shown in Figure 10-51 rotates the chart from vertical to horizontal.
Figure 10-51 Horizontal Chart
-
The Vertical icon shown in Figure 10-52 rotates the chart from vertical to horizontal.
Figure 10-52 Vertical Chart
-
The Change Chart Type icon shown in Figure 10-53 allows you to quickly change the chart type to any of the other types not currently displayed.
Figure 10-53 Change Chart Type
-
The Show Legends toggle button shown in Figure 10-54 allows you to show or hide the legends of charts. Hiding the legend gives more space to view the graph on the layout.
Figure 10-54 Show or Hide Legends Toggle
-
The Show Marker toggle button shown in Figure 10-55 allows you to show or hide the markers on the chart. This option is enabled only for line, area, combination and line with area chart. This marker points makes it easy to read data on the chart.
Figure 10-55 Show or Hide Marker Toggle
-
Chart setting allows you to edit the marker symbol and color for the series mapped on the chart. Ability to assign the different symbols helps you to identify the markers clearly for measures plotted on the charts. You can also assign colors to the series mapped on the charts.
The Edit Marker window shown in Figure 10-56 has the list of the series mapped on the chart. You can edit the marker symbol and color from the available list shown in Figure 10-57 and Figure 10-58 next to each series. To access the Edit Marker window, click the gear icon next to the Show Marker and Show Legend toggle buttons.
Figure 10-56 Chart Setting Window
Figure 10-57 Edit the Marker
Figure 10-58 Edit the Color