19 Special Features
This chapter describes special RPASCE features that you can use.
What-If Scenarios
What-if scenarios provide functionality for a user to create strategic planning options while keeping the original scenario intact. These are additional plan versions that are created to simulate outcomes with different inputs. You use What-if scenarios to maintain and re-forecast the primary plan while preparing a stretch plan to quickly react to upward trends or more aggressive business growth targets.
You can perform What-if analysis with different KPIs and strategies from relatively simple, tactical decisions to the complex strategic planning. You can then promote the What-if scenario to be the primary plan.
You can also see all the scenarios of the plan from the Recent Plans section of Dashboard.
Working with What-If Scenarios
As a planner, you make a number of decisions that affect your plans. These decisions can be complex and you may spend a significant amount of time developing a potential plan before you know if it is optimal or not. Since the workspace contains a single version of the plan, you cannot compare different potential approaches in the workspace to decide which is best.
In order to address these difficulties, RPASCE provides What-if functionality. You can work within the segment workspace to create a plan. You can select between alternative approaches and create scenarios to evaluate a potential approach. These scenarios provide a copy of your main plan-in-progress. While you are working on a scenario, the changes you make only affect the data in the scenario and do not impact the main plan.
In order to prevent the mixing of data from multiple scenarios, the master scenario is provided. When a segment is built into a workspace, the initial data set is the only one present and so is the master data set. As you create more scenarios, the master scenario remains privileged as the only version that sends commits back to the domain. After you develop a scenario, you select that scenario as your plan.You use a promotion process to replace the master scenario with the selected scenario. That scenario becomes the new master scenario for all future operations performed within the workspace.
Figure 19-1 illustrates the main scenario and the green icon that identifies it.
Figure 19-1 Master Scenario
You cannot delete the master scenario. As both the Open and Open in New Tab options are enabled, click either to access the opened plan. You can either duplicate the scenario to create another scenario or rename the scenario.
Figure 19-2 Duplicate Scenario
Click Duplicate Scenario and enter the appropriate label, and click OK to create a new scenario. You cannot use an existing label from the current workspace.
The new scenario is created and you can clearly differentiate the master scenario as follows.
Unlike the master scenario, the What-if scenarios cannot commit the data to the domain, as these scenarios are working copies. Calculate (F9) and Promote Scenario action items are visible in newly created scenario.
Figure 19-3 Master Scenario Identification
Figure 19-4 What-If Scenario
The actions Duplicate (to duplicate the scenario and create new one), Rename (to change the label of the scenario), Delete (to delete the scenario), Open (to open the scenario in the current browser window), and Open in new tab (to open the scenario in new browser tab window) are shown in Figure 19-5.
Figure 19-5 Actions Performed on a Scenario
You can also create the scenario by using the + icon in the Scenarios section.
Figure 19-6 Create Scenario
By default only three scenarios are allowed (including master scenario), but this is configurable from System Configuration. Once you have created three scenarios and the master scenario, the + icon and the duplicate action are not available and you cannot create more scenarios.
Figure 19-7 Maximum Number of Scenarios
You can delete the scenario in order to create a new scenario. You can promote the scenario to master scenario. In Figure 19-8, the 2% Sales Up scenario is promoted to the master scenario by clicking Promote Scenario.
Figure 19-8 Promote Scenario
After you click Promote Scenario, a toast notification is displayed, as shown Figure 19-9. Here you can either dismiss the notification or undo the promote scenario. If you dismiss the notification, the 2% Sales Up scenario is promoted to the master scenario. If you click Undo, the 2% Sales Up scenario is not promoted to the master scenario, and the earlier master scenario continues as master.
Figure 19-9 Toast Notification During Promote Scenario
The 2% Sales Up scenario is now the master scenario and you can commit the data.
Figure 19-10 What-If Scenario Promoted to Master Scenario
Viewing All Scenarios from the Dashboard
You can view all the scenarios from the recent plans section of the dashboard.
Figure 19-11 View Scenarios using the Dashboard
You can view the last opened date and time for the workspace.
Figure 19-12 View All Scenarios
You can either launch the workspace scenarios in the same browser or in a new browser tab for quick comparison.
Images
The ability to view images associated with positions on a dimension is useful in many aspects of the retail world such as assortment planning, item planning, and story boarding.
For example, you can associate an item with an image being displayed on the shelf. You can associate stores with images of the store front or interior. You can use images to storyboard themes by creating a collection of looks and colors for a particular buying period, floor set, or flow. Some retailers associate multiple types of images with multiple levels of the Product dimension. For example, you can associate images for product levels such as Department, Class, Subclass, Style and Style/Color.
With RPASCE, you can associate an image for any dimension with a configured media attribute, including calendar levels. These images can be stored on a website that must be declared under the safe hosts for the application to display the images.
Image Actions
Images can be included in a domain by configuring media dimension attributes, loading them with media bundle values referring to images, and making them visible in worksheets. A number of images may be included in each bundle value; one of those is designated as the primary image that can be seen in the pivot table. All the images, not just the primary, can be seen using View/Manage Images.
Pivot table headers display images for visible media dimension attributes. If there is more than one visible image attribute, all of their primary images (thumbnail-sized version) will be shown in a carousel control. Only one of the images can be seen at any given time. The user can scroll through all the images by clicking the left and right arrow controls that appear on either side of the image.
Figure 19-13 Image Display
You can right-click the images and perform the following actions:
-
View/Manage Images: Launches the View/Manage Images window
-
Hide Images: Hides the images.
Figure 19-14 Image Cell Actions
Viewing and Managing Images
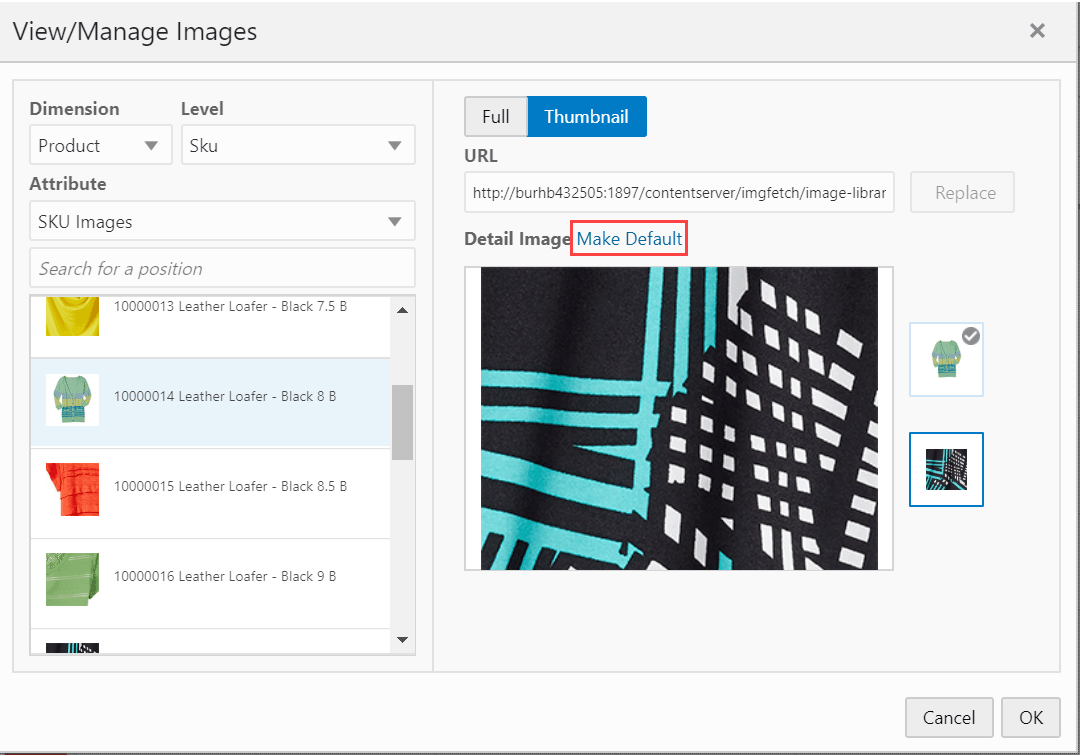
Right click on the images to launch the Figure 19-15. You can view the dimension and level of the image displayed. You can search for a particular position by using the search box or scroll bar. You can view the image as full or thumbnail and the main image (default) along with any other existing images for that level.
Figure 19-15 View and Manage Images Window

Using the URL Field
The URL text box in the Figure 19-15 allows you to:
-
Add new thumb and full sized images for dimension positions that do not have any images.
-
Replace existing thumb and full sized images associated with dimension positions.
-
Designate an existing image as the default image for a position by clicking Make Default as shown in Figure 19-16.
Figure 19-16 Make Default Link for an Image
-
Validate your inputs by only allowing:
-
URLs that are validated by the hosts
-
Images of valid file types
-
To save any updates or changes made, click OK.
To clear any updates or changes made, click Cancel.
Resizing Images
You can resize the image rows and columns in pivot table and see them persisted so that you do not have to resize them. Images should auto-scale to fit the header cell, but never increase beyond their native size.
Figure 19-17 Resize Image
Showing or Hiding Images
Right click on the Images and click Hide Images to hide the images.
Figure 19-18 Hide Images
In order to view images, you can click on the dimension position where images are enabled and click Show Images.
Figure 19-19 Show Images
You can change the axis of the dimension and the images are rearranged
Figure 19-20 Image Display with Axis Pivot
The default No Image icon is displayed when no image is associated with the dimension position. If an image URL is associated but RPASCE cannot show the image, then the Broken Image is displayed.
Figure 19-21 No Image Icon
Figure 19-22 Broken Image Icon
Enlarge Image
Double-click the image to expand it and get a better look. The enlarged image gives a better understanding of the image. After double-clicking the image, the enlarged image opens in a window that opens in the middle of the screen. On the expanded image window, you can see all facets of image shown on the left side, the position name on top of the dialog box. You can hover over the expanded image to see the zoom-in image.
Figure 19-23 Enlarge Image Window
Managing Attributes
Click Manage Attributes to open the Edit View Details tab with the Attributes tab. You can choose to view and sort attributes in the view. You can also select the attribute images for selection.
Figure 19-24 Manage Attributes
To sort or view attributes, complete the following steps:
-
Select or clear the boxes to the left of the attribute name positions to viewing and sort availability of particular attributes.
Figure 19-25 Select Attributes for Viewing and Sorting Positions

-
You can change the attribute display order by dragging and dropping the attributes or delete them from display order by clicking on the delete icon. You can also use the level selection to view the attributes at particular hierarchy level.
-
You can change the selected level sort order by changing the ascending and descending order arrows or delete them from sort order by clicking on the delete icon.
Extended Measures
You can use an extended measure to define, view, and edit a measure as a proportion or percentage of another measure for a parent that is up one or more levels. These measure relationships are also referred to as participation measures. These measures are defined in the pre-configured RPASCE in a view using the configuration.
This functionality is commonly used to define measures that are percentage participations of sales measures. Typically, these measures are defined as:
-
Absolute Percent of Parent: A percentage of a fixed level (such as class) so that the participation of each item to the class can be viewed and manipulated.
-
Relative Percent of Parent: A percentage to the next level shown in any dimension (such as Product).
-
Ranking: A value that indicates the relative order of positions in either ascending or descending order.
-
Cumulative Sum: A sequence of partial sums of a given sequence, based on an ascending or descending rank.
-
Cumulative Percent: A sequence of partial sums of a given sequence, based on an ascending or descending rank expressed as a percentage to the total.
Figure 19-26 Extended Measure
Note the following:
-
Extended measures can be defined only on measures that have Total as their default aggregate method.
-
When the percentage of the extended measure is changed, values of the underlying measure change to reflect the newly set percentage.
-
Multiple extended measures can be defined for the same underlying measure; however, only one extended measure or the underlying measure can be edited before calculation. All other versions are protected.
-
Smart editing is not allowed in the extended measure.
-
The value of an extended measure is a fraction between zero and one. If desired, you must format the measure to be displayed as a percentage.
-
For extended measures contributions in instances with very small values (such as 0.000001) in the cell, those values are considered to be 0.0 when the extended measures contribution is determined.
-
For Ranking, Cumulative Sum, and Cumulative Percent, the extended measures are read only.
-
The extended measure (for example, WP Net Sls Rtl cnt Prod %) represents the relative percentage of the parent (POP) on the PROD hierarchy. When the % contrib Prod parent measure is revised to 0 at the end of the year, then weeks for where no sales plan for the department exist, the product totals are changing during the recalc. To keep the weekly data unchanged, then modify the cnt Prod % cells in the lower intersection instead. Then the parent cells in aggregate intersection are automatically locked.
-
When a cell is modified for the cnt Prod % (for example, YEAR_DEPT_STOR) intersection and calculated, the Calc Engine first locks the parent at the (for example, YEAR_DVSN_STOR) intersection. Next it adjusts the corresponding cell for the base measure in the YEAR_DEPT_STOR intersection to match the specified percentage. The difference between the old and new values of that cell is then distributed among the other sibling cells in the YEAR_DEPT_STOR intersection proportionally. Consequently, these changes propagate down to the WEEK_DEPT_STOR intersection proportionally, affecting all the weekly cells.
-
When the parent aggregation is not visible, the system displays an error. This is because the relative POP measure has dynamic parent level which is the next visible higher level. Make sure the measure is visible to avoid this error.
User Preference Module
The User Preference module allows you to control different aspect of the system as needed. For example, you can use the User Preference module to manage what kinds of notifications you want to receive. This provides you a central location to set the preferences. This provides you a central location to set the preferences.
To access the User Preference module, click the user name and select Preferences.
Figure 19-27 User Preference Module Access
The User Preference module displays these sections:
Notifications Section
Manage your notifications with the toggle to switch On or Off the messages you are interested in. A full toggle indicates that the notification is On. An empty toggle indicates that the notification is Off.
This enables you to manage and see the notifications that are meaningful to you.
The Notifications section displays two categories:
-
Global Messages
-
Contextual Messages
Use the Message Duration list to select the time duration that messages display. For example, 3 Seconds, 5 Seconds, and so on.
Figure 19-28 Notifications Section Displays that All Notifications are On
Global Messages
Global messages appear on the top right corner of your application. Manage your Global Message notifications with the toggle to switch On or Off the messages you are interested in.
You can enable or disable the success or warning messages for following notifications:
Table 19-1 Global Messages
| Global Messages | Success or Warning |
|---|---|
|
Workspace Actions |
|
|
Build Plan Initiated |
Success |
|
Build Plan Complete |
Success and Warning |
|
Commit |
Success and Warning |
|
Segment Edits |
|
|
Rename Segment |
Success |
|
Copy Segment |
Success |
|
Delete Segment |
Success |
Contextual Messages
Contextual messages appear at the bottom of your application. For Contextual Messages, select notifications for Success and Warnings.
The following table shows how the Contextual Message notifications are grouped under heading based on the features.
You can enable or disable the success or warning messages for following notifications:
Table 19-2 Contextual Messages
| Contextual Messages | Success or Warning Notifications |
|---|---|
|
Copy |
|
|
Copy Cells |
Success |
|
Copy Row/column |
Success and Warning |
|
Paste and Fill |
|
|
Paste Cells |
Success and Warning |
|
Paste Row / Column |
Success and Warning |
|
Cut / Fill |
Success |
|
Workspace Actions |
|
|
Calculate |
Success |
|
Commit |
Success and Warning |
|
Commit Confirmation |
Success |
|
Delete Format |
Success |
|
Undo / Redo |
Success |
|
Workbook Refresh |
Success |
|
Planning Actions |
Success |
|
Filters |
|
|
Special Filters |
Success |
|
Position Filters |
Success |
|
Remove Saved Filters |
Success |
|
Import / Export |
|
|
Import |
Success |
|
Export |
Success |
Message Time Duration
Use the Message Duration list to select the time duration that messages display. For example, 3 Seconds, 5 Seconds, and so on.
Figure 19-29 Time Duration for Notification Display
Copy / Paste Section
Manage your Copy and Paste preferences for when you use the copy and paste functionality for columns or rows.
From the User Preference module, the Copy / Paste Preferences section allows you to set the Copy Levels and the Paste Levels for either:
-
Selected Level (currently visible level)
-
Base Intersection (lowest level available for the selection)
Set the preference to paste NA values or not every time you use the paste function.
Set the preference for the Confirmation Message setting when you paste data to columns or rows. The copy and paste functionality for columns or rows is a permanent change which cannot be undone.
You have two options:
-
Always automatically accept a column or row paste without confirmation.
-
Receive a confirmation message that asks you to confirm the paste every time you use the paste functionality.
Figure 19-30 Copy/Paste Preferences Options
Keyboard Shortcuts
Enable or disable keyboard shortcuts for the Commit and Refresh actions from the User Preference module. The keyboard shortcut for Commit is F8 and Refresh is ALT+F5.
Use the toggle to switch On or Off the keyboard shortcuts. A full toggle indicates that the shortcut is enabled. An empty toggle indicates that the shortcut is disabled.
Once you make changes to the User Preference module, click Save to save or click Save and Close save and close the module. If you click Cancel, then the changes made on the User Preference module are not saved.
Figure 19-31 Keyboard Shortcut Preference
Import Data Using Microsoft Excel
Importing data is a flexible feature which allows you to transfer large data to pivot table using an Excel spreadsheet. You can upload writable measures using a template without an administrator or technical support help. You can bring data into the RPASCE system using an Excel spreadsheet directly from application UI.
Importing data is a two-step process:
-
Download the Excel template of the view that you wish to upload the data to.
-
After making edits to the Excel template, upload the data back into the system using the import feature.
Importing Data for a View
Follow these pre-requisites for importing:
-
Importing data can only use a downloaded Excel template file.
-
The position count across the x-axis (number of rows) and y-axis (number of columns) should be same between the view and the Excel template.
-
The page edge position or z-axis position should be same between the view and the Excel template.
-
The Block View Export should not be used for importing the data back into the view.
Perform the following steps to import data,
-
Download the Excel template of the view that you wish to upload the data to. To download the template, use the existing export to Excel feature. For details about exporting to Excel, refer to the Export chapter.
Figure 19-32 Download the Excel Template Using the Export Feature

-
Make edits in the downloaded Excel template for writable measures and save the file in your system.
-
To import the saved Excel template, use the Import button available from the toolbar.
Figure 19-33 Toolbar Import Button

-
Click the Import button and the Import Data window opens. Follow these steps to import the file using this window.
Figure 19-34 Import Data Window

-
In the Select Import Details field, use the drop-down menu to select your view. Select the same view as your downloaded Excel template. When only one view is visible on the screen, then the view is pre-selected and the drop-down menu is unavailable. From the bottom of the window, click Next.
Figure 19-35 Select View from the Drop-down Menu

-
In the Select File field, select your edited Excel template. You can either drag and drop the file or browse to locate it in your system. Once you have made the file selection, click Next to move to next step. if you have selected wrong file, click Delete to delete the file.
Figure 19-36 Select File to Import

-
In the Review and Import phase, the system checks the Excel file format and data errors before uploading the file. If the file has no errors, then the import proceeds and the data from the Excel file is pasted on the pivot table of the selected view in edited mode. Edited mode data displays in italics. You can review the data and then click Calculate to accept the data. To cancel the imported data, click the Undo button on the toolbar to reverse the import.
Figure 19-37 Import Data in Edited Mode

-
In the Review and Import phase, if there is an error with file format, the system displays an error and requests to upload the correct file. This phase locates errors for file formatting such as the:
-
Number of columns or rows do not match between the view and Excel templates
-
Z-axis positions do not match between the view and Excel templates
-
Row or column position names do not match
Figure 19-38 Example of Error Displayed for the Wrong File Format

-
-
In the Review and Import phase, when the file format is correct but there are data errors such as data type mismatch or the upload is for read only data, protected or locked cells; then the system displays the Review and Import Mode window. In the Review and Import Mode window, the cells with errors are highlighted and the list of errors is displayed in the navigation bar. The navigation bar is available from top of the view with a count of each error type. Using the navigation bar, you can jump to cells with errors and make changes.
Hover over the information i icon to review wrong or invalid values that were imported into a highlighted cell. The information i icon indicates the error made and helps you to make correction.
After making corrections to the errors, click OK to accept the imported data. The imported data is pasted to pivot table in edited mode and displays the data in italics. If you choose to click OK without correcting all the errors, then the cells with errors are ignored and rest of the data is imported to pivot table. If you want to cancel the import, click Cancel and start over with a correct file.
Note:
The data import is ignored for read-only, protected, and locked cells.
Figure 19-39 Review and Import Mode

Points to remember:
-
Measure data types should match between the imported Excel template and pivot table.
-
Data with uppercase and lower case are accepted.
-
If the data is uploaded for an aggregated position, then the values are spread to the child position using spread method.
-
Users with read-only access to the workspace cannot import data.
-
Imports can be done for a single slice or z-axis position at a time.
-
Add Comments in Cells, Rows, or Columns
You can use the comments features to keep quick notes for yourself or you team members. This will help you to add notes for quick reference during meetings or discussions. These comments can also be used as reminders for yourself or others.
Add Comments
You can add comments in cells or column or row headers.
To add comments, perform follow the steps.
-
Select a cell or column or row header and then select Add Comment from the right-click context menu.
Note:
You can add comments to read-only, locked, protected, or undefined cells; or column or row headers.
Figure 19-40 Add Comment

-
Enter the required notes or text in the Add Comment dialog box and click OK. This dialog box is pre-populated with the user name and date-time stamp.
Figure 19-41 Add Comment Dialog Box

-
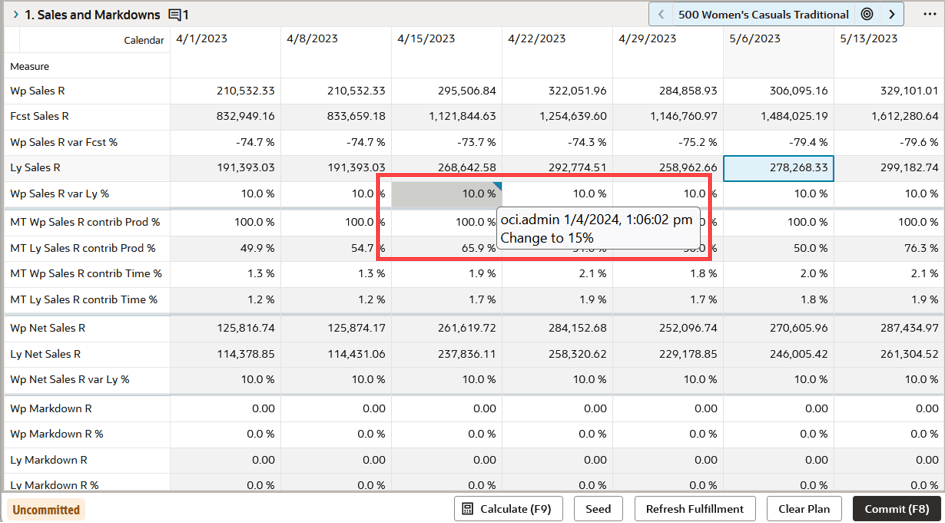
The added comment is displayed using a small triangle icon on the cell or column or row header as shown in Figure 19-42. When you hover over the icon, you can read the comment content as shown in Figure 19-43.
Figure 19-42 Comments Icon on the Cell

Figure 19-43 Hover Over the Icon to See the Comments
Edit or Delete Comments
You can also edit or delete an existing comment from the view. The edit or delete option is only available when a comment exists in a cell or for a column or row header.
To edit comments, perform follow the steps.
-
Select the cell or a column or row header with comments, and then select Edit Comment from the right-click context menu.
Figure 19-44 Edit Comment

-
When you click Edit Comment from the right-click context menu, the Edit Comment dialog box opens populated with the user name and date-time stamp. You can either add a separate note or edit the existing note in the comment dialog box. Click OK.
Figure 19-45 Edit Comment Dialog Box

Delete Comment
To delete a comment, select the cell or column or row header with an existing comment and then select Delete Comment from the right-click context menu.
Figure 19-46 Delete Comment

Points to Remember
When using the comments features, remember these conditions:
-
When a position or measure with comments is hidden using the Edit view or context menu, then the comments are hidden with the respective position or measure.
-
When a position or measure with comments is displayed using the Edit view, then the comments are visible with the respective position or measure.
-
When you select multiple cells to add comments, then comments are added to the active cell out of the selection.
-
The comments are shared when the workspace is shared with another user. The recipient user can add, edit, or delete comments on the shared workspace.
-
The comments are deleted when a segment or workspace is deleted. When a workspace is created using an existing segment, the comments are not inherited from segment.
-
You can add total 4000 characters for all comments which are made on a single intersection. This includes multiple comment lines added by different users.
Count of the Comments
The count of the comments in the view is visible on the view header and view tile on the View Management drawer. The count is visible with an icon along with the total number of comments. When you hover over the icon, it displays this message: This view has [n] comments.
Figure 19-47 Count of the Comments

Load Comments in the Workspace
When a workspace with existing comments is opened, the comments are not visible as they are not loaded automatically. When workspace is opened, you receive a notification with the Load Comments button. Click Load Comments to view the comments in workspace.
Figure 19-48 Load Comments Notification

Export Comments
You can export comments from workspace view using the Export to Excel functionality. You can select Include Comments from the export dialog box to export the comments into Excel for the current view.
Figure 19-49 Export – Include Comments

Drag and Drop Measure Columns or Rows
You can shuffle the measure columns or rows in real time by a simple hold and then drag and drop action on the pivot table. This feature allows you to change the sequence of measure on pivot table without navigating to the Edit view every time you need to rearrange the placement of measures. You can also move the measure column or row using the context menu options:
-
Cut Measures
-
Insert Measures After
-
Insert Measures Before
Move the Measure Columns or Rows by Using Drag And Drop
Perform the following steps to move the measure columns or rows by using the drag and drop action.
-
Select single or multiple measure columns or rows by using your mouse or the Ctrl key. The cursor changes to a hand icon as you hover over the selected column or row header.
As shown in the following image, the two measure columns LY Sales R and WP Sales R vs LY% are selected.
Figure 19-50 Select the Measure Columns or Rows

-
With your mouse, hold the selected columns or rows header, then drag it to the left or right and then drop it before or after any measure on the pivot table. While moving the selected measure column or row, a blue guideline is visible to assist in placing the measure column or row.
Figure 19-51 Drag the Measure Column across the Pivot Table

Figure 19-52 Drop the Measure at the New Location

Move the Measure Columns or Rows by Using the Context Menu
Perform the following steps to move the measure columns or rows by using the context menu.
-
Select single or multiple measure columns or rows by using your mouse or the Ctrl key.
Figure 19-53 Select the Measure Column or Row

-
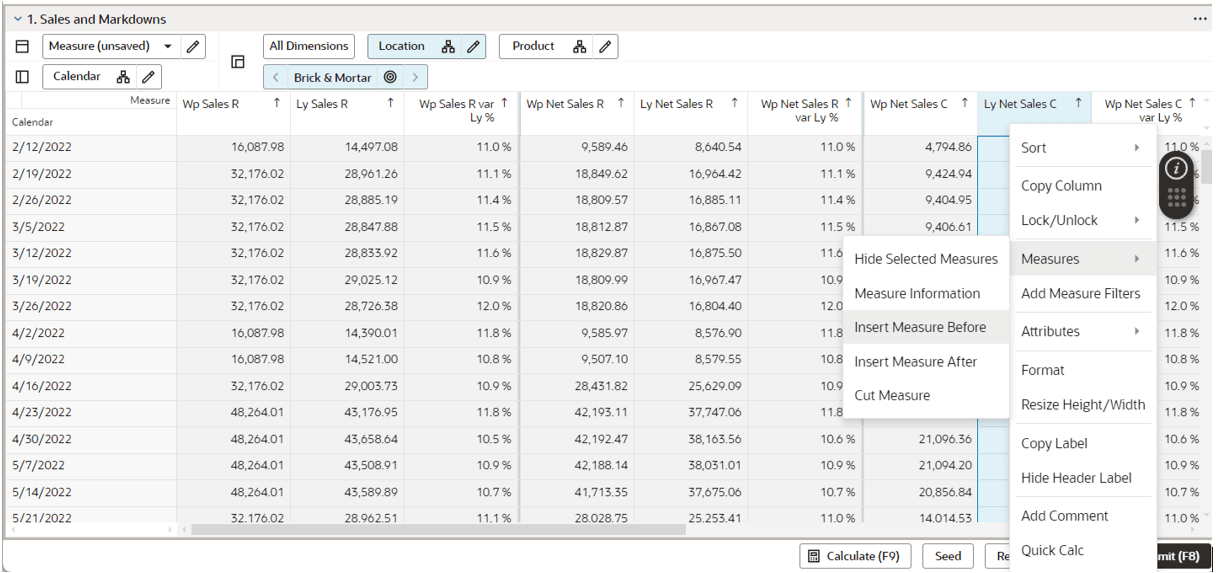
Right-click on the selected measure columns and from the context menu, select Measures and then Cut Measure.
Figure 19-54 Select the Cut Measure Context Menu Option

-
Select the measure that is located next to destination where you want to place the selected measures columns. Then right-click and from the context menu, select the option, Insert Measure Before.
Figure 19-55 Select the Option, Insert Measure Before
Points to Remember
-
You can select multiple contiguous or non-contiguous measure columns or rows to change the sequence on pivot table. For more details about selecting measure column or row refer to the section, Selecting Rows and Columns.
-
When you select non-contiguous measure columns or rows and then move them together, the result after placing them on the destination position is arranged in contiguous order.
-
When you drag the selected measures, you can scroll to far right or far left of pivot table by hovering over the pivot table cells.
-
To place the selected measure in destination position, you should place the cursor on the measure header and not at the pivot table cells. If you place the cursor on the pivot table cells, they are highlighted with an error icon and you will not be able to place the measure. as shown in the following image, the cursor is on the pivot table cells and the error icon displays.
Figure 19-56 Error Icon When Hovering Over the Pivot Table Cells

-
When you change the placement of the measure on pivot table, then the Edit view reflects the same changed arrangement of selected measures. To save the updated measure placement, you can save the measure profile.
-
When there are multiple dimensions on one axis along with the measure dimension, then you can drag and drop measures only when the measure is at its inner most dimension.
Quick Calculations on the Pivot Table
The Quick Calculation (Quick Calc) feature allows you to select a number of cells or columns or rows and then view the calculated results of simple math operations like sum, average, and so on . This feature assists you in making quick decisions since you can view quick sub-totals for the selected cells. You also check the calculations for filtered positions. For example, if you have stores filters with a 10% markdown and you want to check the average volume across the filtered stores, then you can use Quick Calc feature and view the results.
Using Quick Calc
Perform the following steps to use Quick Calc.
-
Using your mouse or keyboard controls, select the number of cells or rows header or columns header for which you need to check calculations.
You can select contiguous or non-contiguous cells or row or column header.
Figure 19-57 Select Cells

-
With the selected cells, rows, or columns, right-click and select Quick Calc from the context menu. You can also use keyboard shortcut Alt+Q for the Quick Calc action.
Figure 19-58 Context Menu Quick Calc Option

-
The Quick Calc results appear on the right-hand side panel
Figure 19-59 Quick Calc Results Panel

Note:
The panel displays results of the last two calculations with the latest calculation result present at the top of the panel. If you click X and close the panel, the results are lost.
Figure 19-60 Quick Calc – Last Two Results

About Quick Calc Results
Note:
The Quick Calc results are not consistent when workbook is closed and re-opened again. It is only consistent within the workbook session until the Quick Calc panel is closed.
-
The results are displayed with two decimal points by default, when only one measure type is selected. With multiple measure type, the results are presented with no decimal points.
-
When a single measure data type is selected, the results are presented with same prefix or suffix symbols as the selected measure. Examples of prefix or suffix symbols include $ or %. With multiple measure types, the results will not have any prefix or suffix.
-
The results panel has the heading of the date and time when the calculation performed and the View name where the data is located.
-
The results panel provides the calculations using following operators:
Table 19-3 Quic Calc Operators
| Operator | Description | Remarks | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
|
SUM |
Numeric addition of all the selected cells. |
Including displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric |
|
SUM populated |
Numeric addition of all the selected cells |
Excluding displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric |
|
AVERAGE |
Numeric average of the selected cells |
Including displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric |
|
AVERAGE populated |
Numeric average of the selected cells |
Excluding displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric |
|
MIN |
Minimum of the values of selected cells |
Including displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric |
|
MIN populated |
Minimum of the values of selected cells |
Excluding displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric |
|
MAX |
Maximum of values of selected cells |
Including displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric |
|
MAX populated |
Maximum of values of selected cells |
Excluding displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric |
|
MEDIAN |
Median value of selected cells |
Including displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric |
|
MEDIAN populated |
Median value of selected cells |
Excluding displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric |
|
COUNT |
Counting number of cells |
Including displayed NA/SP values |
Date, String, Boolean, Numeric, Picklist |
|
COUNT populated |
Counting number of cells |
Excluding displayed NA/SP values |
Numeric data type only |
|
BOOLEAN COUNT |
Count of number of selected Boolean cell with TRUE value Sum |
Including displayed NA/SP values |
Boolean |
|
BOOLEAN COUNT populated |
Count of number of selected Boolean cell with TRUE value Sum |
Excluding displayed NA/SP values |
Boolean |
Copy and Paste Quick Calc Results
You can copy the results of Quick Calc and paste them to external applications like Microsoft Excel or Notepad. This assists you in keeping notes for reference or any further analysis.
To copy the Quick Calc results, hover over the results using your mouse. The cursor changes to a hand. Click the result to copy the results to the clipboard. When you copy the result, the selection has a blue colored background and when successful, you receive a Copy notification as shown in the following image. To paste the copied values to an external application, use Ctrl+V.
Figure 19-61 Copy Quick Calc Results
