Note:
- This tutorial requires access to Oracle Cloud. To sign up for a free account, see Get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
- It uses example values for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure credentials, tenancy, and compartments. When completing your lab, substitute these values with ones specific to your cloud environment.
Migrate your Azure Kubernetes Service Cluster or Amazon EKS Cluster to Container Engine for Kubernetes using Velero
Introduction
Velero is an open source tool to safely backup and restore, perform disaster recovery, and migrate Kubernetes cluster resources and persistent volumes. As Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object Storage is S3-Compatible, we can use Velero’s AWS plugin. In this tutorial, we will use Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) but the steps should also work seamlessly in Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS).
The following diagram is an overview of how the process works.
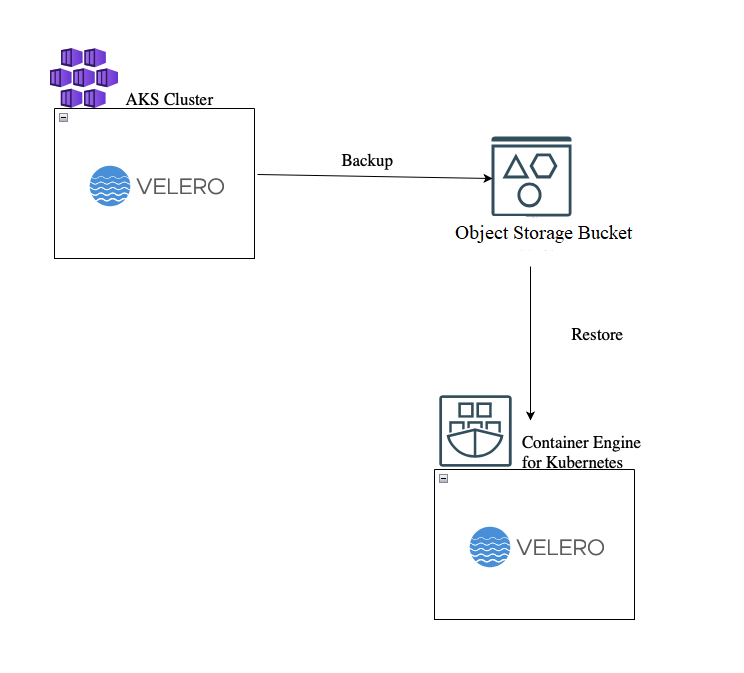
For this tutorial, we have prepared an NGINX Pod that has a persistent volume claim attached and a custom index.html file in it, and a dummy secret.
> kubectl get pods --n nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
task-pv-pod 1/1 Running 0 47h
> kubectl exec -it task-pv-pod --n nginx -- curl localhost
AKS to OKE Migration with PVC attached
>kubectl get secrets --namespace nginx
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
okemigration Opaque 1 2s
Objectives
- Create Customer Secret Keys to use with the Object Storage Bucket S3 endpoint.
- Setup Velero in AKS and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE).
- Perform a backup and restore to migrate a Kubernetes namespace to OKE.
Prerequisites
- Intermediate knowledge about Kubernetes.
- An Object Storage Bucket that will be used as the backup point.
- Read/Write user privileges in the Object Storage Bucket.
- Velero binaries on the computer you use to connect to your Kubernetes cluster, or inside the Cloud Shells of both Microsoft Azure and OCI.
Task 1: Create the velero-credentials file with the Customer Secret Key inside
-
If you don’t already have a Customer Secret Key, you can follow these steps.
-
On the machine you use to access your AKS/EKS and OKE clusters (or the Cloud Shells), create the file
velero-credentialswith the following content:[default] aws_access_key_id=<<Access Key ID>> aws_secret_access_key=<<Generated Key>>
Task 2: Download and install Velero
-
Install Velero on the machine you will use to access the clusters, following these steps, or, if you are using Cloud Shell, download it from here.
-
Proceed to install Velero in both, AKS and OKE clusters with the following command.
Note: If you downloaded the binaries, execute velero using ./ at the beginning:
velero install \ --provider aws \ --bucket <<Bucket name>> \ --prefix <<Tenancy name>> \ --use-volume-snapshots=false \ --plugins velero/velero-plugin-for-aws:v1.6.0 \ --secret-file <<Location of the file created with the customer secret key>> \ --backup-location-config region=<<Region>>,s3ForcePathStyle="true",s3Url=https://<<tenancy name>>.compat.objectstorage.<<region>>.oraclecloud.com \ --use-node-agent -
Verify that Velero was installed in AKS and OKE by running the following command.
> kubectl get deployment -n velero NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE velero 1/1 1 1 47h
Task 3: Back up the Cluster
-
In your AKS Cluster, run the following command. In this tutorial, we are using the Azure CLI with the velero binaries downloaded in it.
velero-v1.11.1-rc.1-linux-amd64> ./velero backup create nginxoke --include-namespaces nginx --default-volumes-to-fs-backup Backup request "nginxoke" submitted successfully. Run `velero backup describe nginxoke` or `velero backup logs nginxoke` for more details. -
Verify that the cluster is backed up.
velero-v1.11.1-rc.1-linux-amd64> ./velero backup describe nginxoke Name: nginxoke Namespace: velero Labels: velero.io/storage-location=default Annotations: velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-gitversion=v1.24.10 velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-major-version=1 velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-minor-version=24 Phase: Completed Namespaces: Included: nginx Excluded: <none> ................. You can also check the Object Storage Bucket: 
Task 4: Restore or Migrate to OKE
-
As AKS, EKS and OKE use different
storageClassNamesfor the persistent volume claims, we need to create a configMap that will translate the sourcestorageClassNamesto an OCI-compatible class name. To do so, we create the fileconfigMap.yamlwith the following content. Adapt it to your sourcestorageClassName.IMPORTANT: You must complete Step 1, else your Pods will remain in pending state.
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: # any name can be used; Velero uses the labels (below) # to identify it rather than the name name: change-storage-class-config # must be in the velero namespace namespace: velero # the below labels should be used verbatim in your # ConfigMap. labels: # this value-less label identifies the ConfigMap as # config for a plugin (i.e. the built-in change storage # class restore item action plugin) velero.io/plugin-config: "" # this label identifies the name and kind of plugin # that this ConfigMap is for. velero.io/change-storage-class: RestoreItemAction data: # add 1+ key-value pairs here, where the key is the old # storage class name and the value is the new storage # class name. <old-storage-class>: oci-bv -
Apply the configMap to your OKE cluster with the following command.
kubectl apply -f configMap.yaml -
Verify that your OKE cluster can access the backups from the object storage.
$ velero get backup NAME STATUS ERRORS WARNINGS CREATED EXPIRES STORAGE LOCATION SELECTOR nginxoke Completed 0 0 2023-07-22 14:40:33 +0300 EEST 29d default <none> -
Create the restore with the following command.
$ velero restore create --from-backup nginxoke Restore request "nginxoke-20230722145553" submitted successfully. Run `velero restore describe nginxoke-20230722145553` or `velero restore logs nginxoke-20230722145553` for more details. -
Verify the restore status.
$ velero restore describe nginxoke-20230722145553 Name: nginxoke-20230722145553 Namespace: velero Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Phase: Completed Total items to be restored: 7 Items restored: 7 Started: 2023-07-22 14:55:54 +0300 EEST Completed: 2023-07-22 14:56:45 +0300 EEST .......... -
Verify that the cluster has been successfully migrated.
$ kubectl get pod -n nginx NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE task-pv-pod 1/1 Running 0 2m15s $ kubectl get secrets -n nginx NAME TYPE DATA AGE okemigration Opaque 1 2m21s $ kubectl get pvc -n nginx NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE task-pv-claim Bound csi-d03267f7-32cf-4068-8809-d29aa649dcba 50Gi RWO oci-bv 2m31s $ kubectl exec task-pv-pod -n nginx -- curl http://localhost AKS to OKE Migration with PVC attached
Related Links
Acknowledgments
- Guido Alejandro Ferreyra (Principal Cloud Architect)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Migrate your Azure Kubernetes Service Cluster or Amazon EKS Cluster to Container Engine for Kubernetes using Velero
F84712-01
August 2023
Copyright © 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates.