Note:
- This tutorial requires access to Oracle Cloud. To sign up for a free account, see Get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
- It uses example values for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure credentials, tenancy, and compartments. When completing your lab, substitute these values with ones specific to your cloud environment.
Deploy NVIDIA RTX Virtual Workstation on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Introduction
NVIDIA RTX Virtual Workstation software enables users to run high-performance simulations, graphic rendering, and design workloads on cloud, with a native workstation-like performance. It unlocks powerful rendering capabilities provided by graphic APIs such as OpenGL or DirectX, bringing breakthrough graphics performance to the cloud.
Objective
- Leverage RTX and NVIDIA Virtual GPU technology using NVIDIA A10 GPU-enabled compute shapes on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
Task 1: Provision a Compute Instance on OCI for NVIDIA RTX Virtual Workstation
-
Create a Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) and launch a compute instance on OCI. For more information, see Create a VCN and Launch Compute Instance.
-
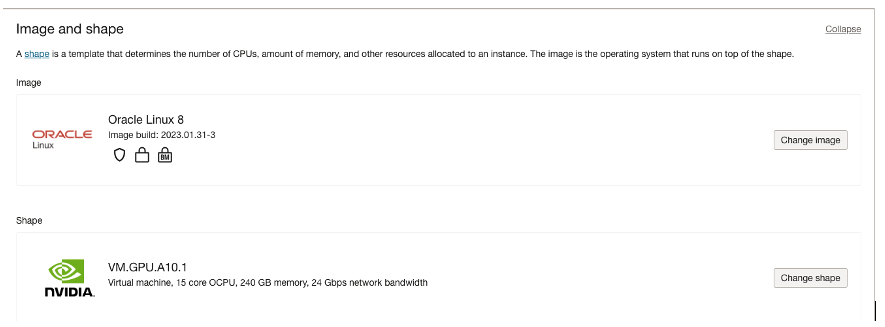
Select one from these available GPU.A10 shapes.
VM.GPU.A10.1 VM.GPU.A10.2 BM.GPU.A10.4 -
When launching a compute instance change shape to one of the above shapes. To launch GPU.A10 VM, click Specialty and Previous Generation, and select one of VM.GPU.A10 shapes. For bare metal servers, click Bare metal machines and select BM.GPU.A10.4 shape.
-
If your tenancy does not have a service limit set for GPU.A10, these shapes will not be in the shape list.
-
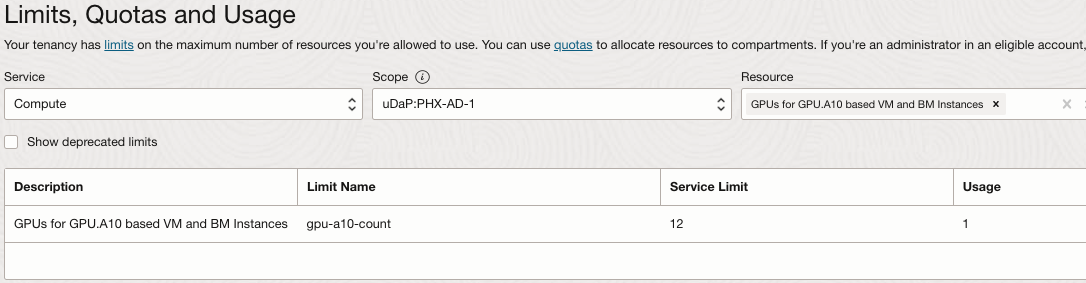
To check your tenancy limits in the OCI Console, set the region where you are going to provision a GPU.A10 compute instance, open the navigation menu and click Governance & Administration.
-
Under Tenancy Management, select Limits, Quotas and Usage.
-
Set the service to Compute, select one of availability domains in the Scope, and enter GPU.A10 in the Resource.
-
Select GPUs for A10 based VM and BM instances.
-
-
Compute limits are per availability domain. Check if the limit is set in any of availability domains of the region. If the service limit is set to 0 for all availability domains, click request a service limit increase and submit a limit increase request for this resource. For more information about service limits, see Service Limits.
Note: In order to access Limits, Quotas and Usage you must be a member of the tenancy administrators group or your group must have a policy assigned to read LimitsAndUsageViewers.
-
Currently OCI GPU.A10 compute shapes support Oracle Linux, Ubuntu and Rocky Linux. Windows is supported by VM shapes only.
Note: Rocky Linux is not officially supported by NVIDIA.
-
When provisioning a compute instance on OCI, use a standard OS image. Do not use GPU enabled images because the installed NVIDIA GPU driver does not support RTX virtual workstation (vWS) that requires NVIDIA vGPU driver to be installed.
Task 2: Download and Install NVIDIA vGPU Driver
-
Download NVIDIA vGPU driver as described in Downloading NVIDIA vGPU software. If you do not have an enterprise account with NVIDIA, you can register for trial at Virtual GPU (vGPU) Software Free 90Days Trial - NVIDIA.
-
Log in to the NVIDIA Enterprise Application HUB using your NVIDIA Enterprise account.
-
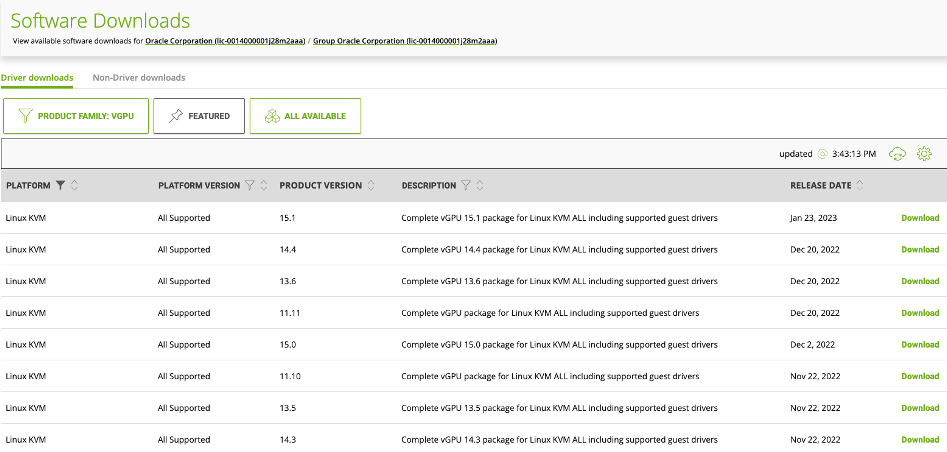
Open the NVIDIA Licensing Portal and select Software Downloads. Apply the following filters:
-
Product Family: Enter VGPU.
-
Platform: Enter Linux KVM.
-
-
Sort by Release Date and download the package with the latest vGPU driver version for Linux KVM platform. For example, currently the latest vGPU version is 17.4.
-
Unzip the file and go to the
Guest_Driversfolder. There you will find vGPU driver installation files for Windows and Linux.
Note: If you are using Linux, follow Task 3, 4, 5 and if you are using Windows, go to Task 6.
Task 3: Install NVIDIA vGPU Driver on Linux
-
Oracle Linux 8
-
Copy NVIDIA Linux driver
NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-xxx.xx.xx-grid.runto the provisioned compute instance. -
Prior to installing NVIDIA driver install and enable
gcc-12toolset by running the following command.sudo dnf install gcc-toolset-12 scl enable gcc-toolset-12 bash -
You will also need to disable
nouveaudriver that has a conflict with NVIDIA driver. Run the following command to check ifnouveaudriver is loaded.lsmod | grep nouveau -
If it shows
nouveaudriver in the output of the command, you will need to disable it first. To disablenouveaudriver on Oracle Linux create the/etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conffile and add the following content.blacklist nouveau options nouveau modeset=0 -
Save the file and regenerate initramfs.
sudo dracut --force -
After disabling the driver reboot the server.
sudo reboot -
Run the following command to install NVIDIA vGPU driver.
sudo bash ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-xxx.xxx.xx-grid.run -
Ignore warnings and click OK to continue with the installation. Reboot the server.
sudo reboot
-
-
Oracle Linux 9
-
Copy NVIDIA Linux driver
NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-xxx.xx.xx-grid.runto the provisioned compute instance. -
You will also need to disable
nouveaudriver that has a conflict with NVIDIA driver. Run the following to check ifnouveaudriver is loaded.lsmod | grep nouveau -
If it shows
nouveaudriver in the output of the command, you will need to disable it first. To disablenouveaudriver on Oracle Linux create the/etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conffile and add the following content.blacklist nouveau options nouveau modeset=0 -
Save the file and regenerate initramfs.
sudo dracut --force -
After disabling the driver reboot the server.
sudo reboot -
Run the following to install NVIDIA vGPU driver.
sudo bash ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-xxx.xxx.xx-grid.run -
Ignore warnings and click OK to continue with the installation. Reboot the server.
sudo reboot
-
-
Rocky Linux 9
-
Copy NVIDIA Linux driver
NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-xxx.xx.xx-grid.runto the provisioned compute instance. -
Install Linux headers matching the version of Linux kernel.
sudo dnf install kernel-devel-$(uname -r) -
If it fails to find Linux headers matching the kernel version, upgrade Linux kernel and reboot the server.
sudo dnf install kernel sudo rebootAfter reboot, re-install Linux headers to match Linux kernel version.
sudo dnf install kernel-devel-$(uname -r) -
Run the following command to check if
nouveaudriver is loaded.lsmod | grep nouveau -
If it shows
nouveaudriver in the output of the command, you will need to disable it first. To disablenouveaudriver on Oracle Linux create the/etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conffile and add the following content.blacklist nouveau options nouveau modeset=0 -
Save the file and regenerate initramfs.
sudo dracut --force -
After disabling the driver reboot the server.
sudo reboot -
Run the following command to install NVIDIA vGPU driver.
sudo bash ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-xxx.xxx.xx-grid.run -
Ignore warnings and click OK to continue with the installation. Reboot the server.
sudo reboot
-
-
Ubuntu 22
-
Copy NVIDIA Linux driver
NVIDIA-Linux-grid-xxx.xx.xx_amd64.debto the provisioned compute instance. -
Run the following command to check if
nouveaudriver is loaded.lsmod | grep nouveau -
If it shows
nouveaudriver in the output of the command, you will need to disable it first. To disablenouveaudriver on Oracle Linux create the/etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conffile and add the following content.blacklist nouveau options nouveau modeset=0 -
Save the file and regenerate initramfs.
sudo dracut --force -
After disabling the driver, reboot the server.
sudo reboot -
Run the following command to install NVIDIA vGPU driver.
sudo apt install ./NVIDIA-Linux-grid-xxx.xxx.xx_amd64.deb -
Reboot the server.
sudo reboot
-
Task 4: Verify NVIDIA vGPU Driver Installation
-
Run the
nvidia-smicommand to verify the NVIDIA vGPU driver installation.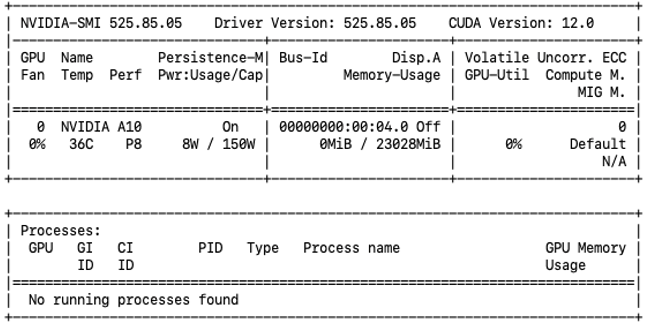
Task 5: Enable NVIDIA RTX Virtual Workstation
-
To enable the NVIDIA RTX Virtual Workstation feature, update
edit /etc/nvidia/gridd.conf.sudo vi /etc/nvidia/gridd.conf -
Add a line.
FeatureType=2 -
Save the changes and close the file.
-
Check if GSP firmware is enabled.
nvidia-smi -q | grep GSP -
If GSP firmware is enabled, the command displays GSP firmware version.
GSP Firmware Version : 525.85.05 -
If GSP firmware is enabled, disable it by setting the NVIDIA module parameter
NVreg_EnableGpuFirmwareto 0. Set this parameter by editing the/etc/modprobe.d/nvidia.conffile. If the/etc/modprobe.d/nvidia.conffile does not already exist, create it.sudo vi /etc/modprobe.d/nvidia.confAdd the following line to it (if you do not have it already).
options nvidia NVreg_EnableGpuFirmware=0 -
After disabling GSP, you must reboot the server.
sudo reboot -
Download the client configuration token from NVIDIA Licensing Portal or DLS appliance. For information about how to register the NVIDIA vGPU license, see Task 7: Register with NVIDIA vGPU Software License Server.
-
Copy the client configuration token to the default location in
/etc/nvidia/ClientConfigTokenand set the file permissions to 744.sudo chmod 744 /etc/nvidia/ClientConfigToken/client_configuration_token_*.tokNote: If you want to store the client configuration token in a custom location, copy the token to the directory that you created and set the
ClientConfigTokenPathconfiguration parameter in/etc/nvidia/gridd.confto point to this directory. -
Restart
nvidia-griddservice.sudo systemctl restart nvidia-gridd -
Run the
nvidia-smi -qcommand and check that the Product Brand is set to NVIDIA RTX and License Status shows Licensed.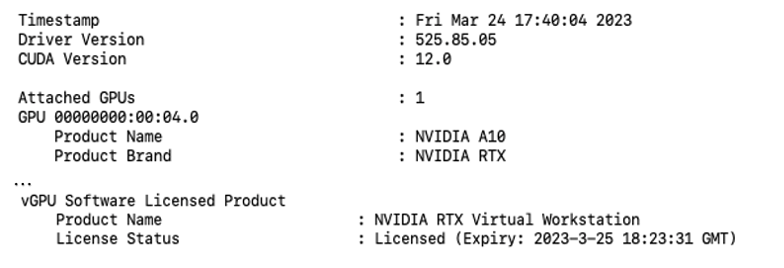
-
If it fails to obtain the license and shows License Status as Unlicensed, check the nvidia-gridd service log.
sudo grep gridd /var/log/messages
Task 6: Install NVIDIA vGPU Driver on Windows
-
Copy the NVIDIA Windows driver package to the guest VM or physical host where you are installing the driver. Run the package to unpack and run the driver installer. Accept the license agreement and select Express installation.
-
OCI A10 GPU VM is configured with GPU passthrough, and therefore you must set the vGPU driver behaviour through regedit. For more information, see Virtual GPU Client Licensing User Guide.
-
Add the
FeatureType DWord (REG_DWORD)registry value to the Windows registry key.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\nvlddmkm\Global\GridLicensing -
Set this value to 2 to enable NVIDIA RTX Virtual Workstation license.
-
Restart the NVIDIA Display Container LS service.
-
Download the client configuration token from NVIDIA Licensing Portal or DLS appliance. For information about how to register the NVIDIA vGPU license, see Task 7: Register with NVIDIA vGPU Software License Server.
-
Copy the client configuration token to the folder.
%SystemDrive%:\Program Files\NVIDIA Corporation\GRID Licensing\ClientConfigToken -
From a command line or PowerShell, run the
nvidia-smi -qcommand and check that the Product Brand is set to NVIDIA RTX and License Status shows Licensed.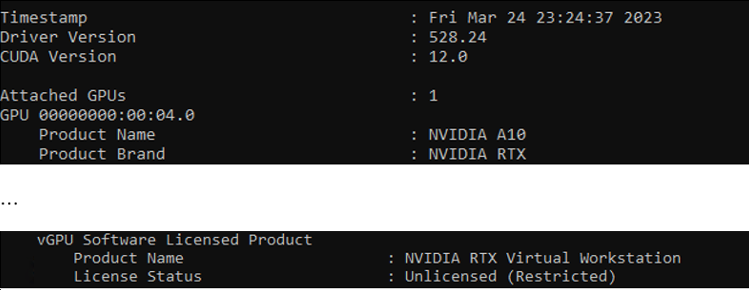
Note: On Windows,
nvidia-smi.exeis installed by default in theC:\Program Files\NVIDIA Corporation\NVSMIfolder. -
If it fails to obtain the license and shows License Status as Unlicensed, check licensing messages in the log.
%SystemDrive%\Users\Public\Documents\NvidiaLogging\Log.NVDisplay.Container.exe.log
Task 7: Register vGPUS with NVIDIA vGPU Software License Server
vGPU licensing is enforced through NVIDIA software and the performance of the virtual GPU is degraded over time if the VM fails to obtain a license. Starting from vGPU version 13.0, NVIDIA license system supports the following types of service instances:
-
Cloud License Service (CLS) instance: A CLS instance is hosted on the NVIDIA Licensing Portal.
-
Delegated License Service (DLS) instance: A DLS instance is hosted on-premises at a location that is accessible from your private network.
You can download DLS virtual appliance from NVIDIA Licensing Portal.
-
Go to Software Downloads, select Non-Driver downloads and download, set Platform to Linux KVM and download the latest version of NLS License Server (DLS) … for Linux KVM.
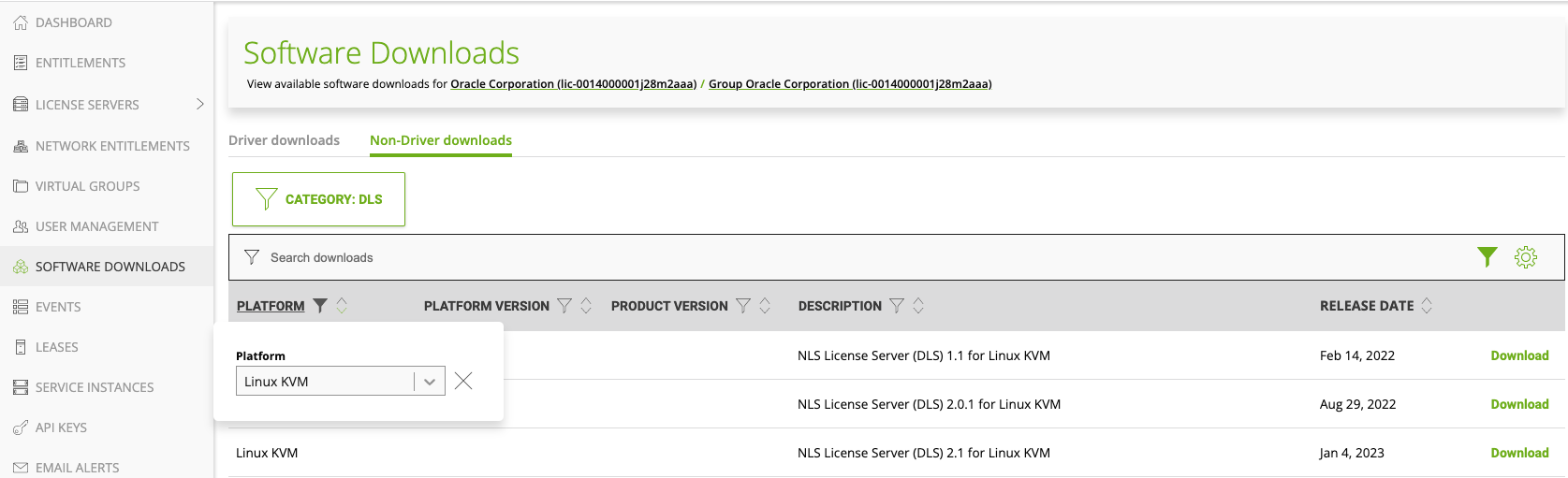
-
Unzip the file and upload DLS virtual appliance QCOW2 file to OCI Object Storage. After that you can import it to OCI as a paravirtualized custom image and create a VM from it. Alternatively, you can run DLS virtual appliance as one of VMs in the KVM environment.
- For details about how to obtain and register NVIDIA vGPU license and how to configure DLS license server, see NVIDIA License System User Guide and NVIDIA License System Quick Start Guide.
-
Once vGPU license is registered with NVIDIA vGPU software license server, you can confirm by checking License Status in the output of
nvidia-smi -qcommand.
Related Links
Acknowledgments
- Author - Michael Prestin (Master Principal Cloud Architect)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Deploy NVIDIA RTX Virtual Workstation on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
F80534-04
November 2024