Note:
- This tutorial requires access to Oracle Cloud. To sign up for a free account, see Get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
- It uses example values for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure credentials, tenancy, and compartments. When completing your lab, substitute these values with ones specific to your cloud environment.
Use NAT Gateway to allow Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Instances to Access the Internet
Introduction
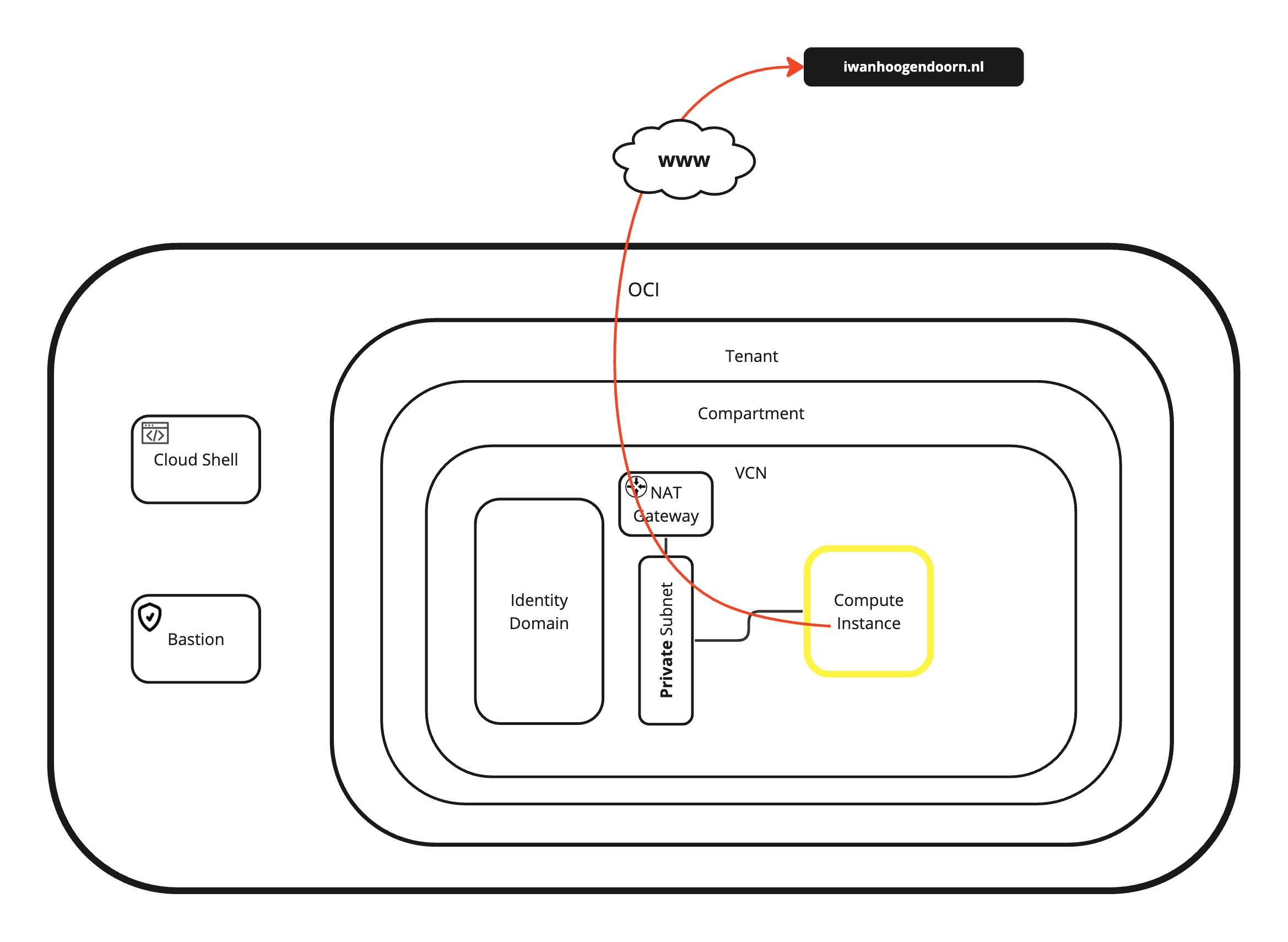
By default RFC1918 IPv4 addresses cannot be routed to the internet and to reach the internet the private RFC1918 address needs to be translated to a public IP address. Within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) we can do this using a Network Address Translation (NAT) gateway inside the corresponding virtual cloud networks (VCNs). This tutorial will explain how internet access is provided from an instance connected to a subnet using a private RFC1918 IPv4 address.
We will create a new compute instance connected to a private subnet. By default an instance connected to a private subnet is not able to reach the internet, so we will create a NAT gateway and route all traffic to that NAT gateway so that compute instance will be able to reach the internet.
Objectives
-
Use NAT Gateway to allow Oracle Cloud Infrastructure instances to access the internet.
- Task 1: Create a new VCN.
- Task 2: Create a private subnet inside the VCN.
- Task 3: Create a new instance.
- Task 4: Create a private network definition.
- Task 5: Verify internet connectivity on the instance.
- Task 6: Create a NAT gateway and route the internet traffic to the NAT gateway.
Task 1: Create a New VCN
Note: If there is an already existing VCN, you can skip this task and continue with Task 2.
-
Click the hamburger menu.
-
Click Virtual Cloud Networking.
- Select the compartment that you want to work in. If you have not set up the compartment, use the root compartment.
- Click Create VCN.
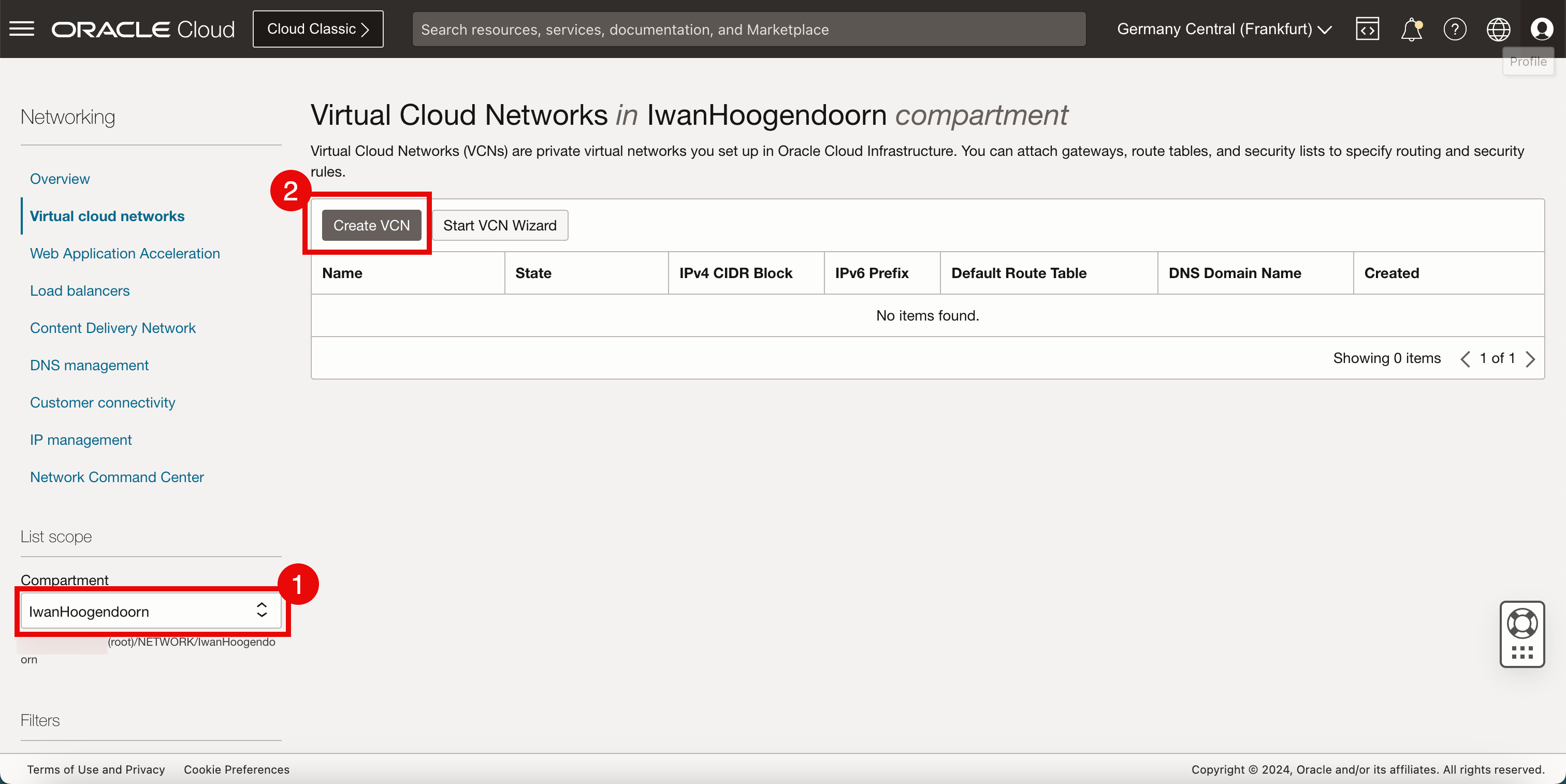
-
In Create a Virtual Cloud Network, enter the following information.
- Enter a VCN Name.
- Select the IPv4 CIDR that you want to use inside this VCN. For this tutorial, we have used a /16 CIDR because IPv4 subnets (typically, /24’s) will be carved out of this CIDR block.
- Scroll down.
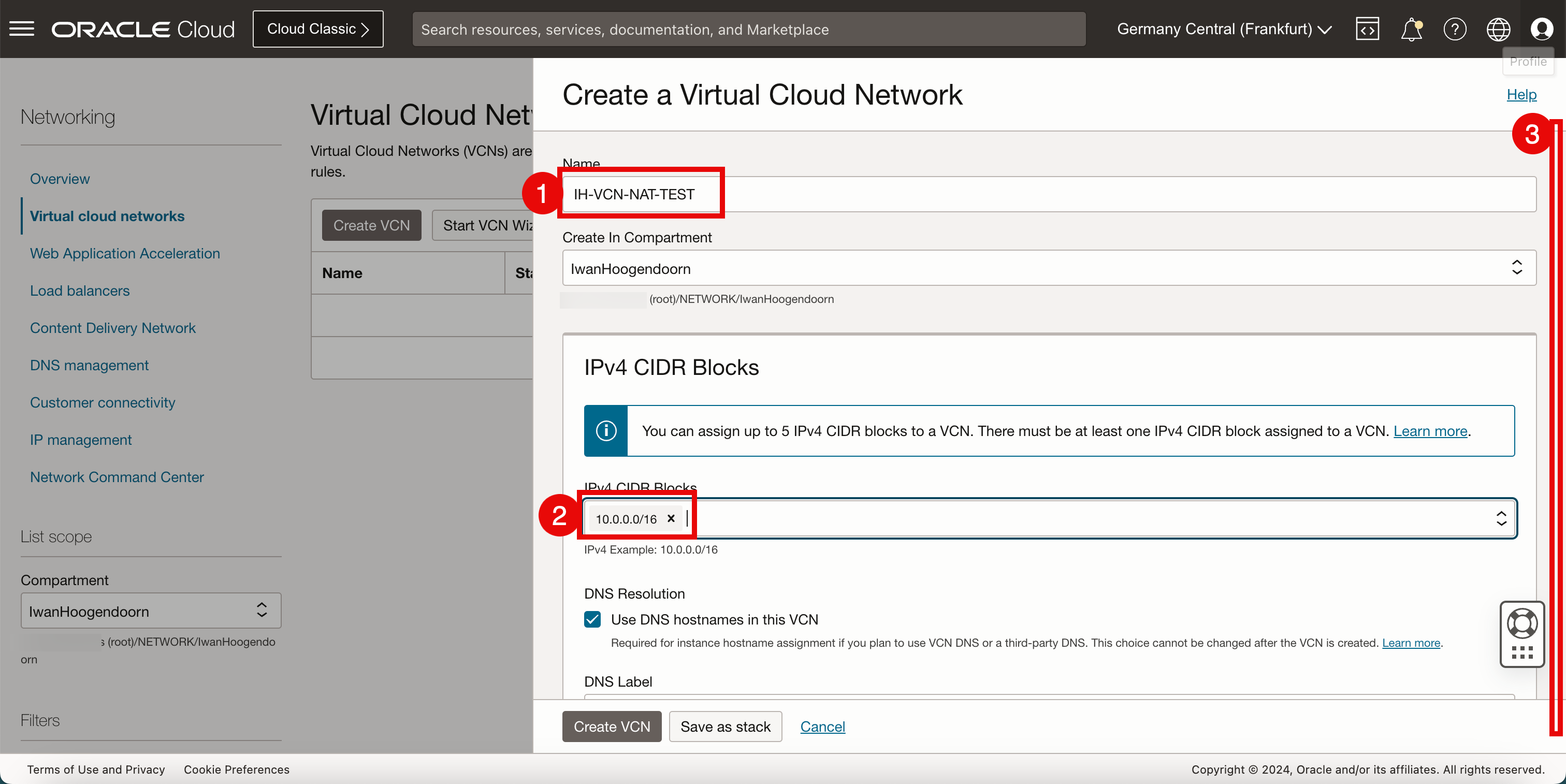
Keep everything default and scroll down.
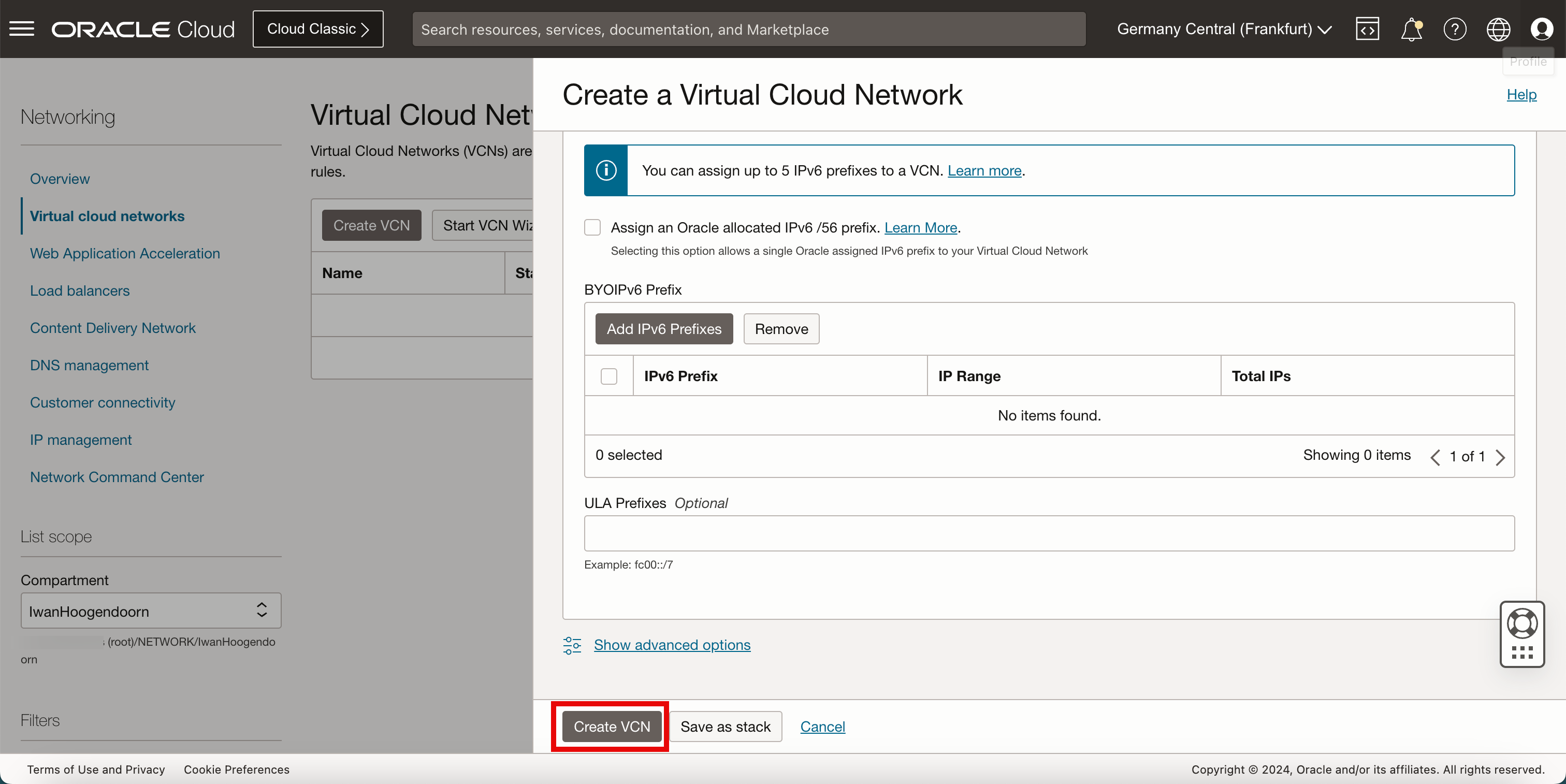
-
Click Create VCN.
Task 2: Create a Private Subnet inside the VCN
-
To create a private subnet, follow the steps.
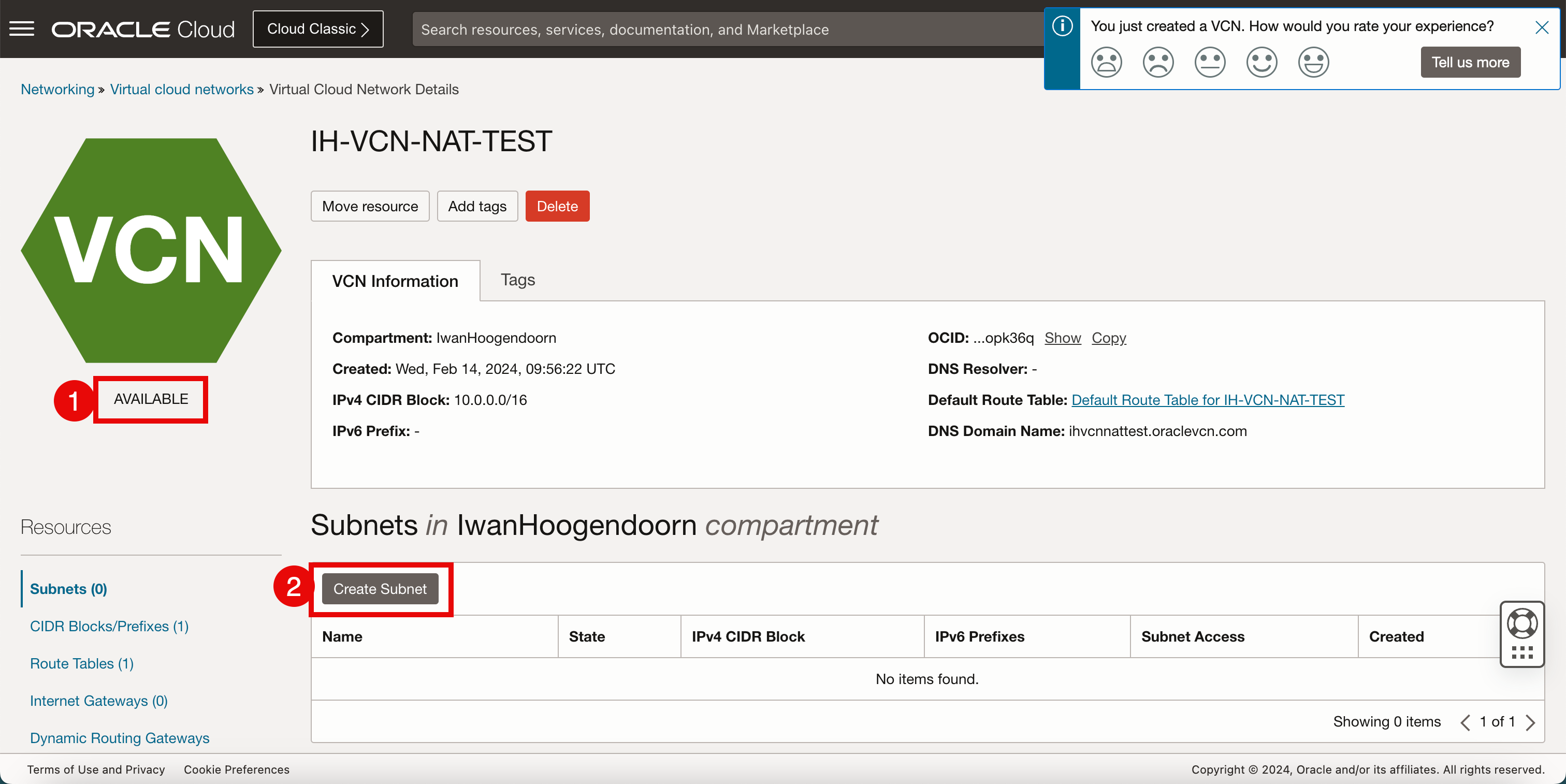
- Verify the VCN is Available.
- Click Create Subnet.
-
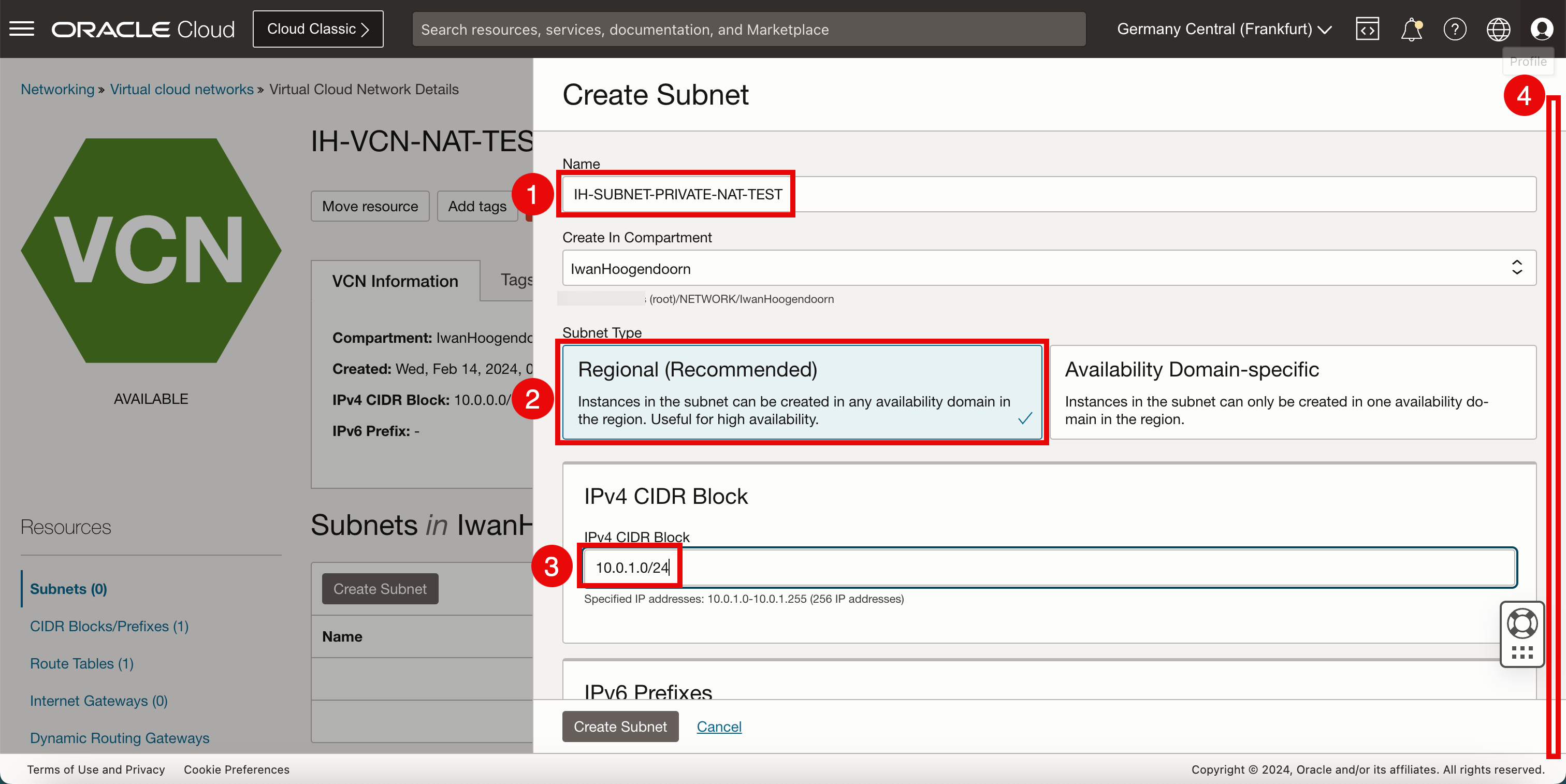
In Create Subnet, enter the following information.
- Enter a Name for the subnet.
- For the Subnet Type, we will select Regional.
- Enter the IPv4 subnet that we will carve out of the CIDR block we have assigned in the VCN. Make sure the new /24 CIDR block falls within the /16 that was determined in the VCN.
- Scroll down.
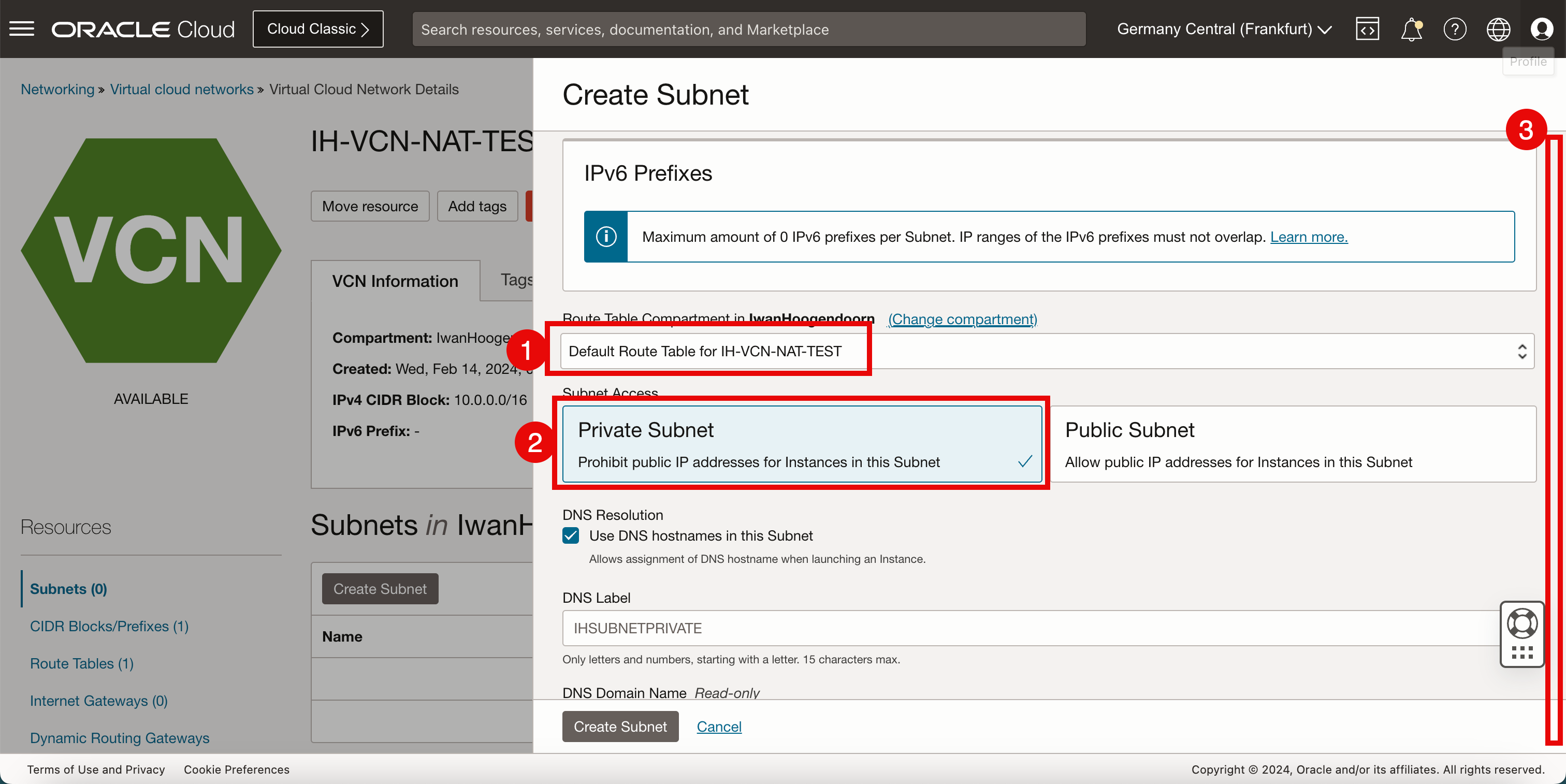
- Select the default route table for the VCN.
- Make the subnet private, so that we get private (RFC1918) IP addresses.
- Scroll down.
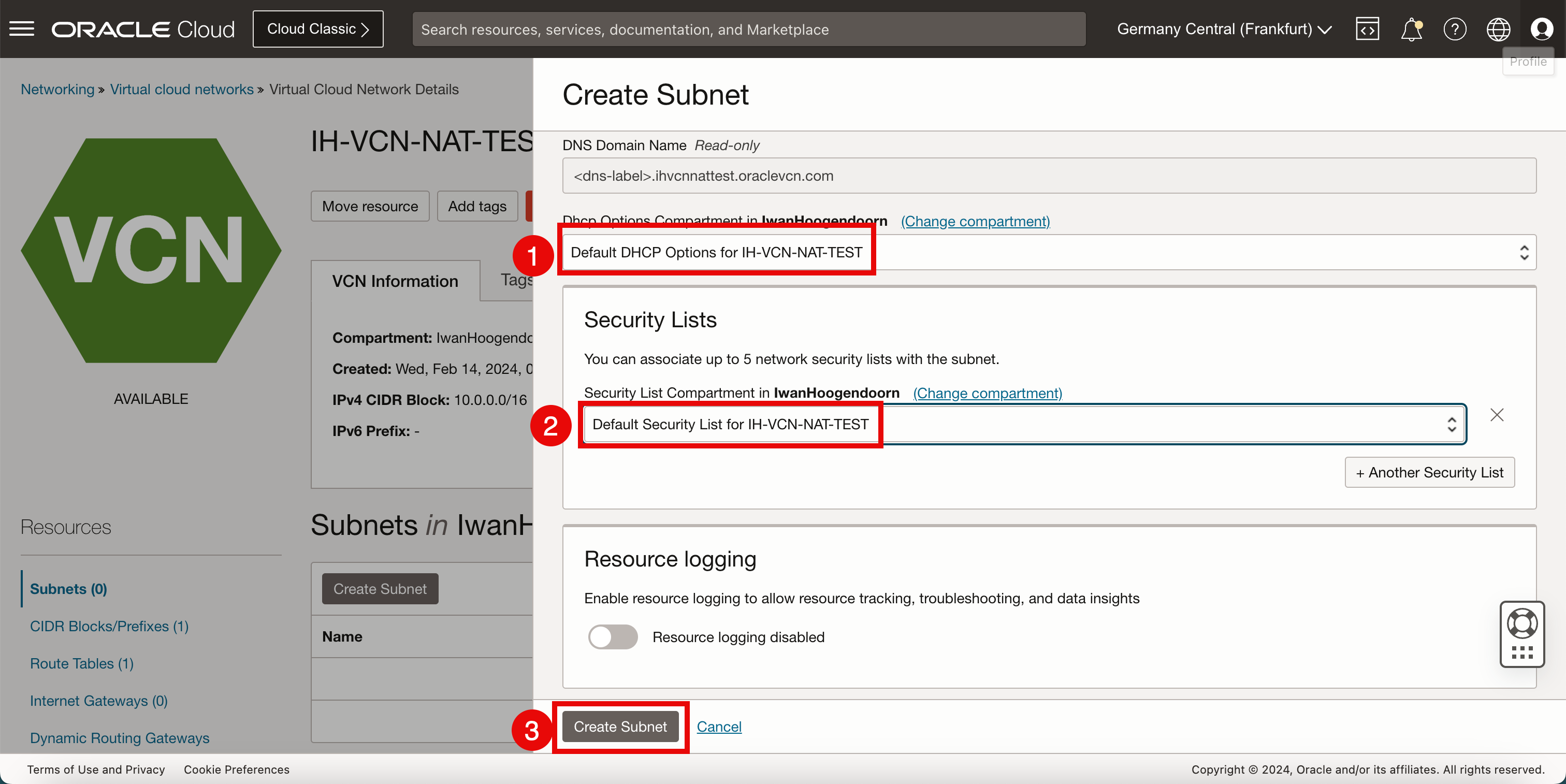
- Select Default DHCP Options for the VCN.
- Select Default Security List for the VCN.
- Click Create Subnet.
-
Notice that the state of the newly created subnet is Provisioning.
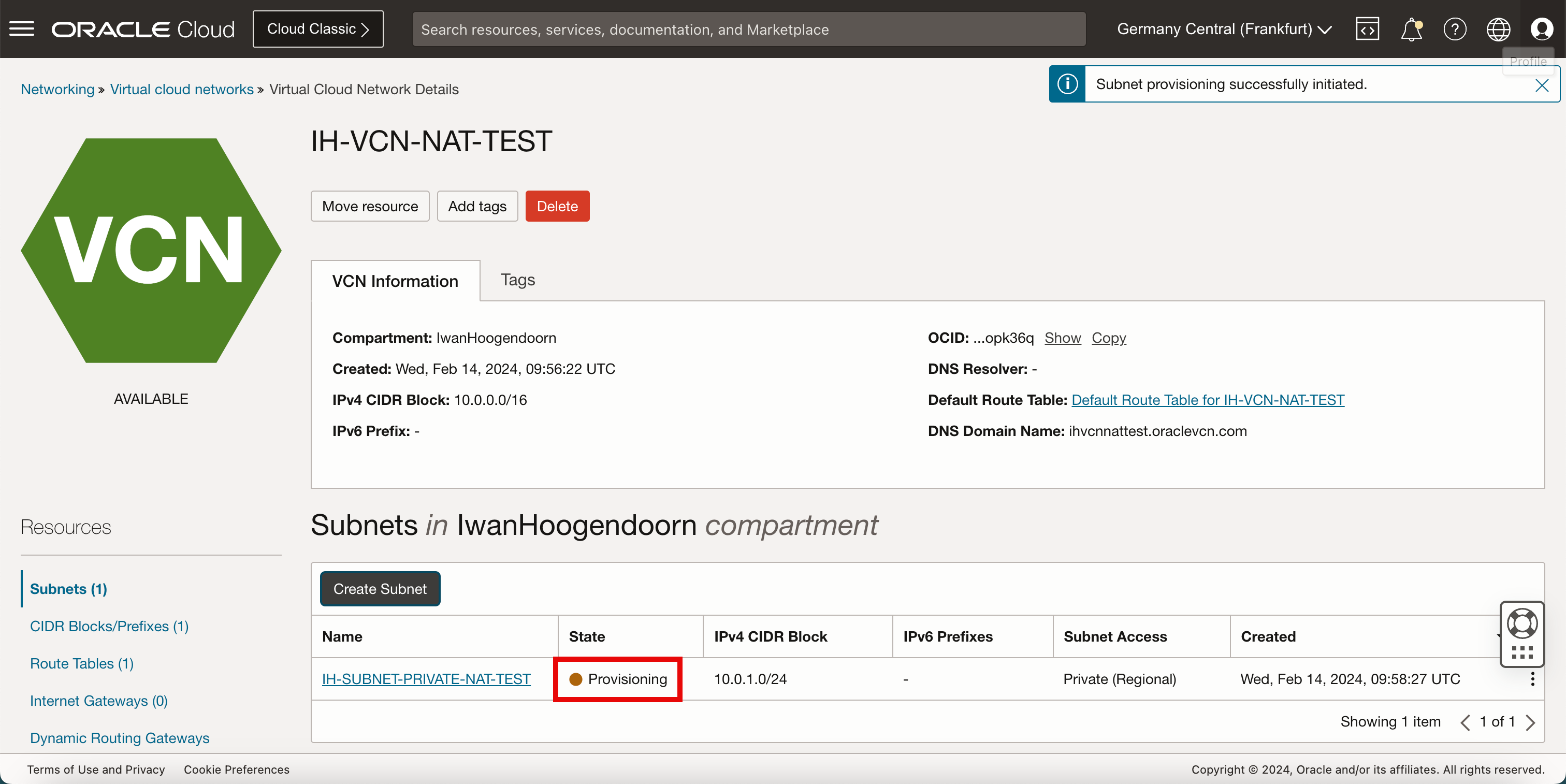
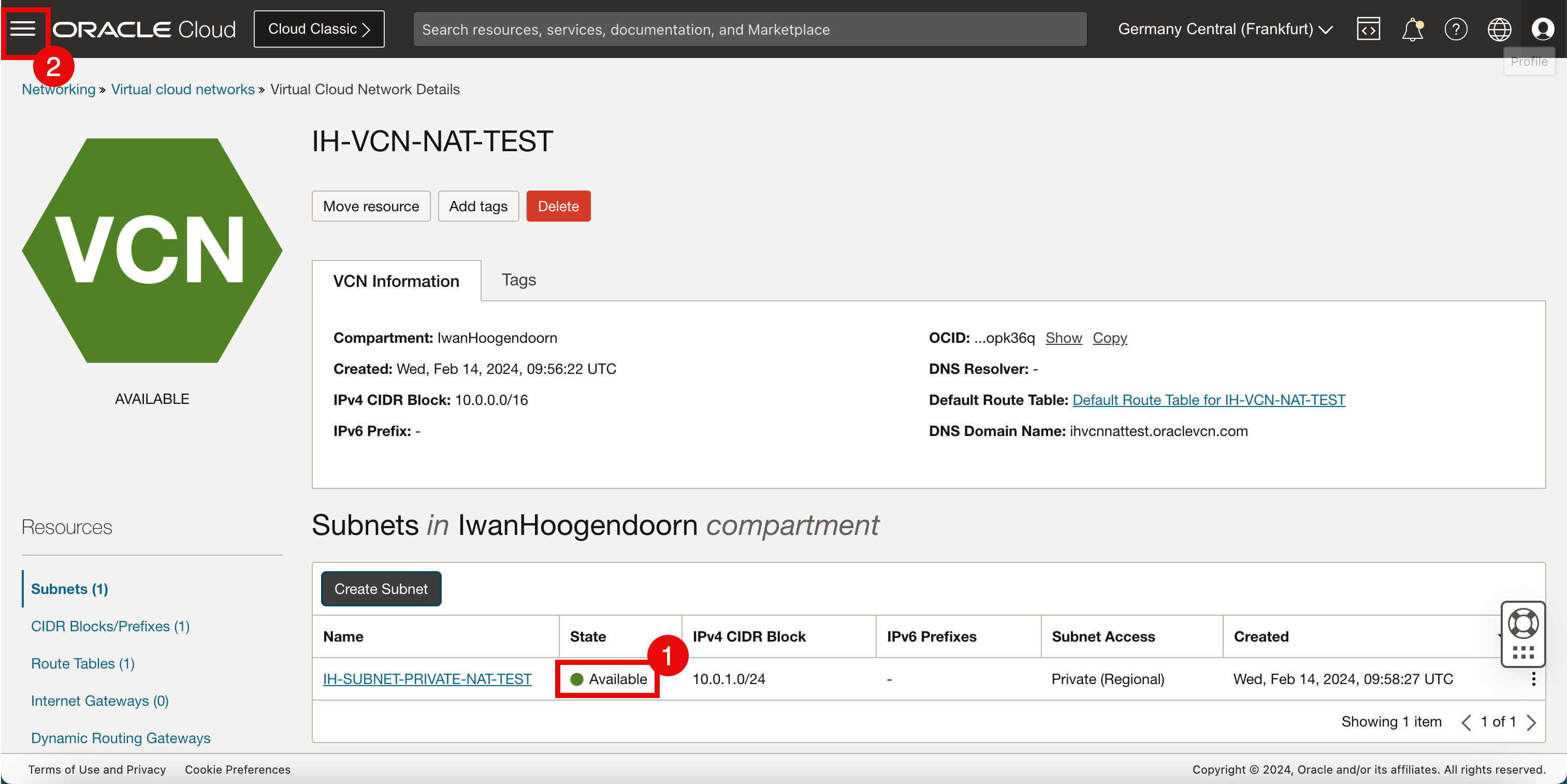
- After a few minutes, the state of the new subnet will be Available.
- Click the hamburger menu in the top left corner.
Task 3: Create a New Instance
-
Click Instances from the Pinned section.
-
Click Create Instance.
-
In Create compute instance, enter the following information.
- Enter the Name of the instance.
- Scroll down.
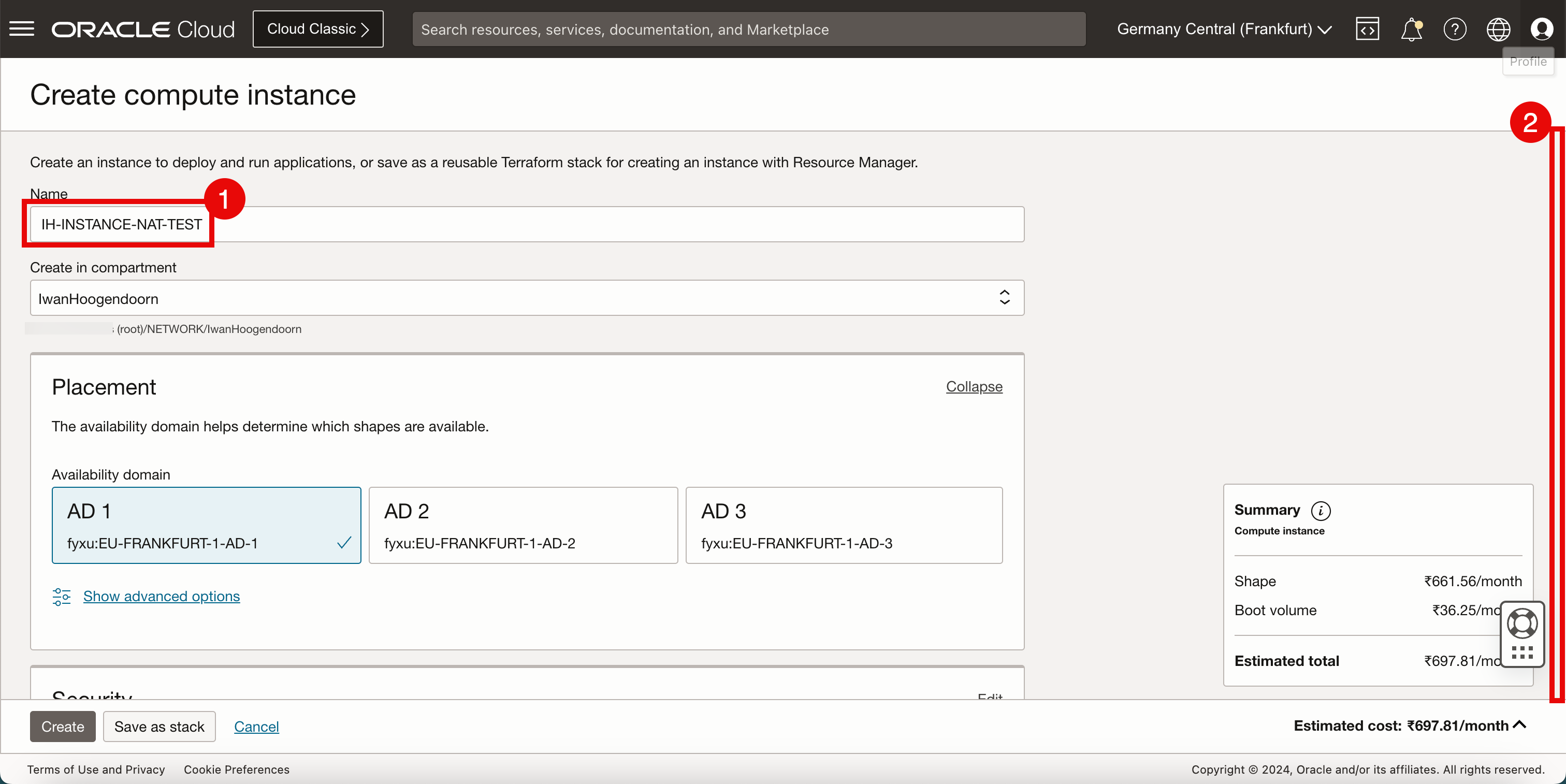
Keep everything default and scroll down.
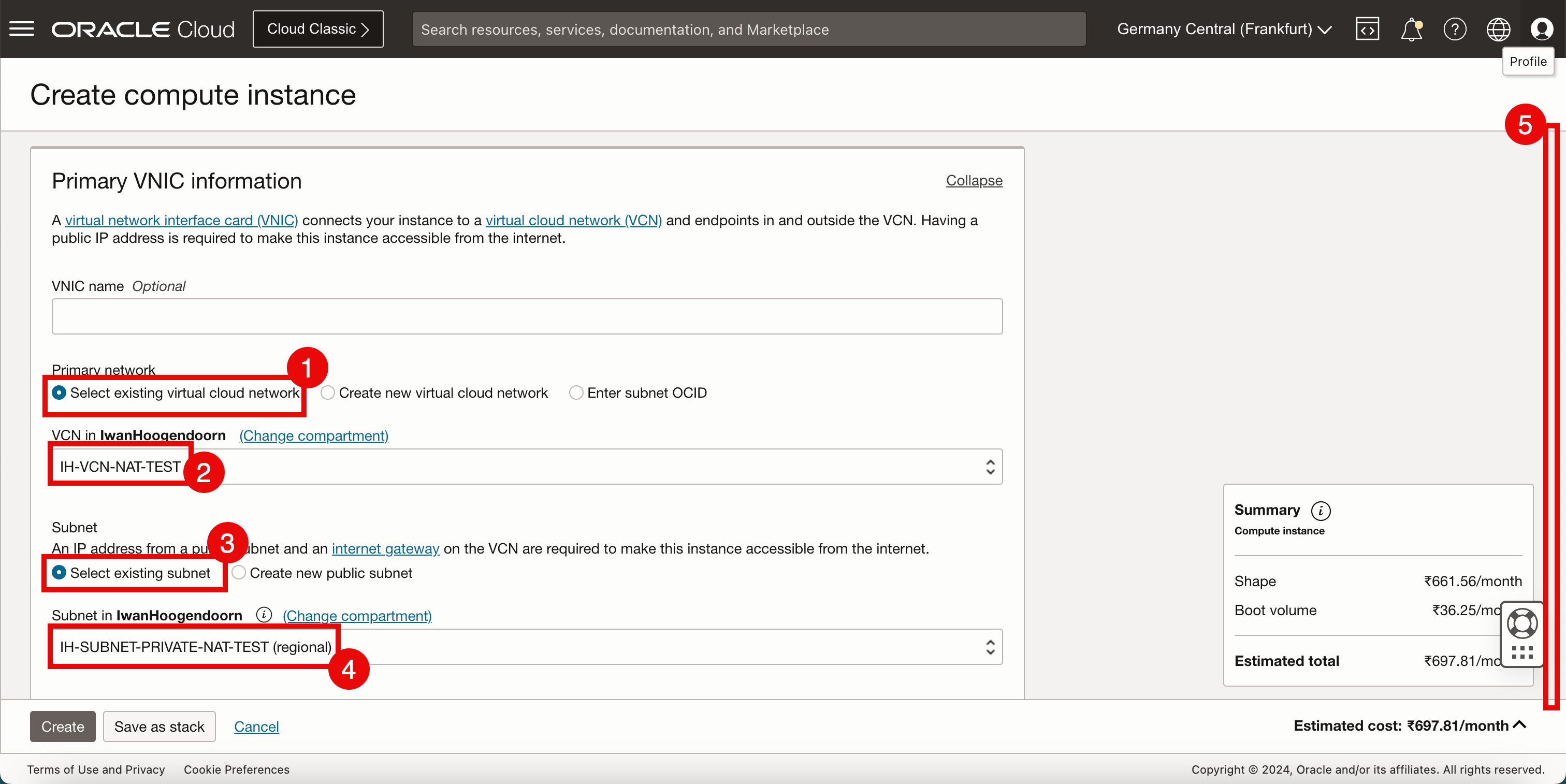
- In Primary network, select Select existing virtual cloud network.
- Select the VCN created in Task 1.
- For the subnet, select Select existing subnet.
- Select the subnet created in Task 2.
- Scroll down.
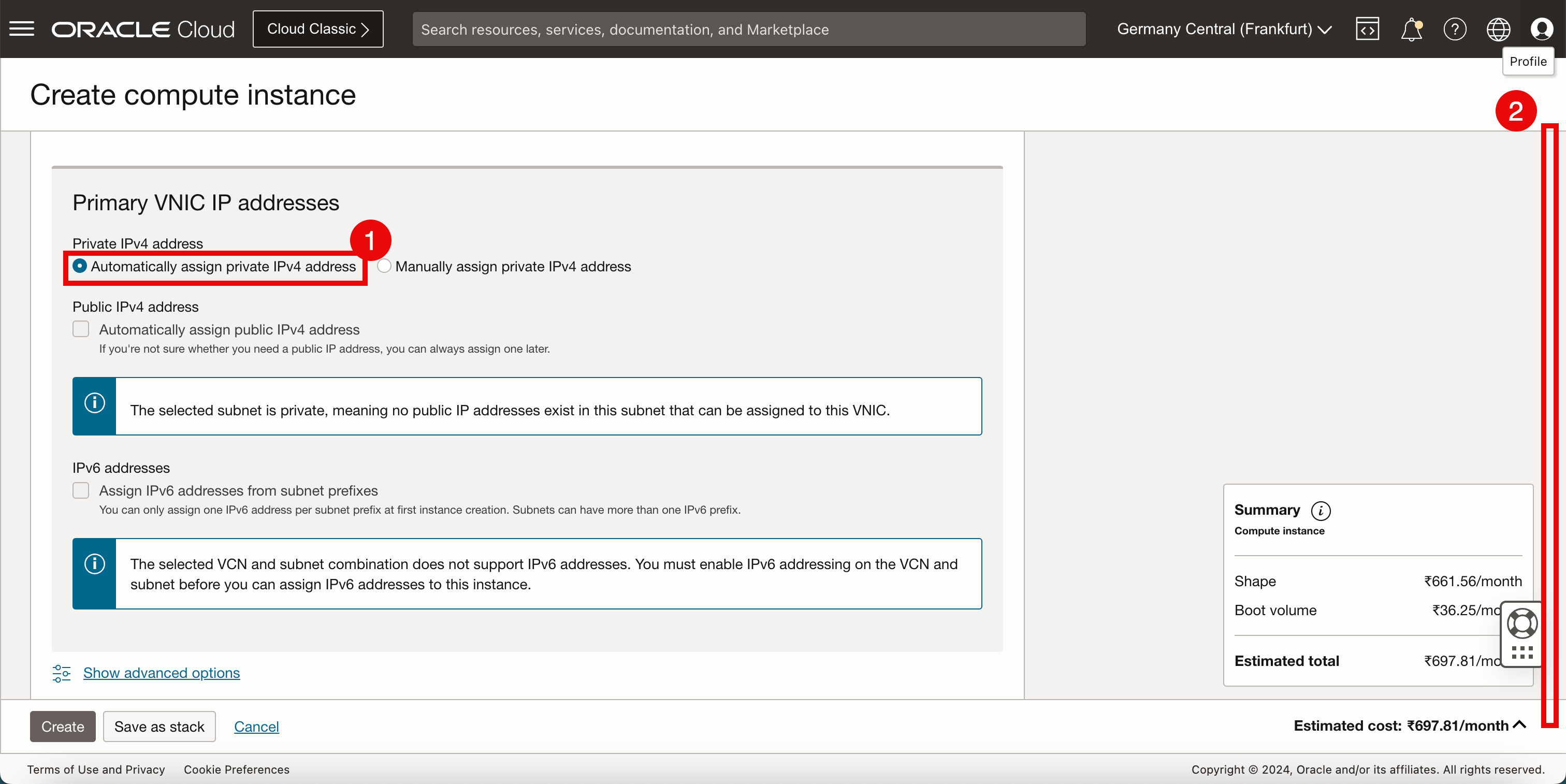
- In Private IPv4 address, select Automatically assign private IPv4 address.
- Scroll down.
- In order to access and manage the Linux instance, we need to work with SSH keys. For this tutorial, we will let OCI generate a new SSH key pair.
- Download the private and public keys on the local computer so we can use these to access and manage this Linux instance after creation.
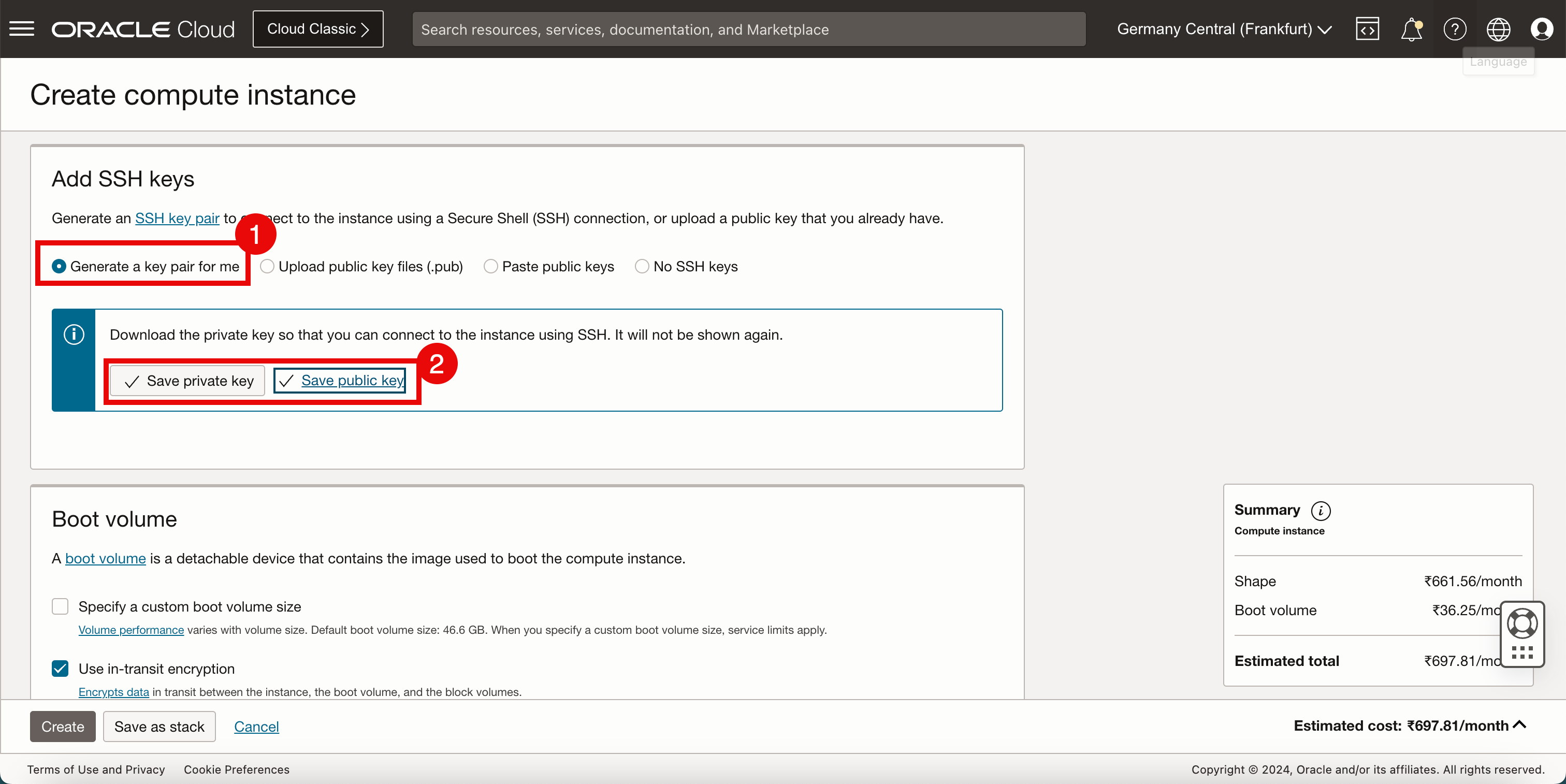
-
Make sure you download the private and public keys on the local computer so that we can use these to access and manage this Linux instance after creation.
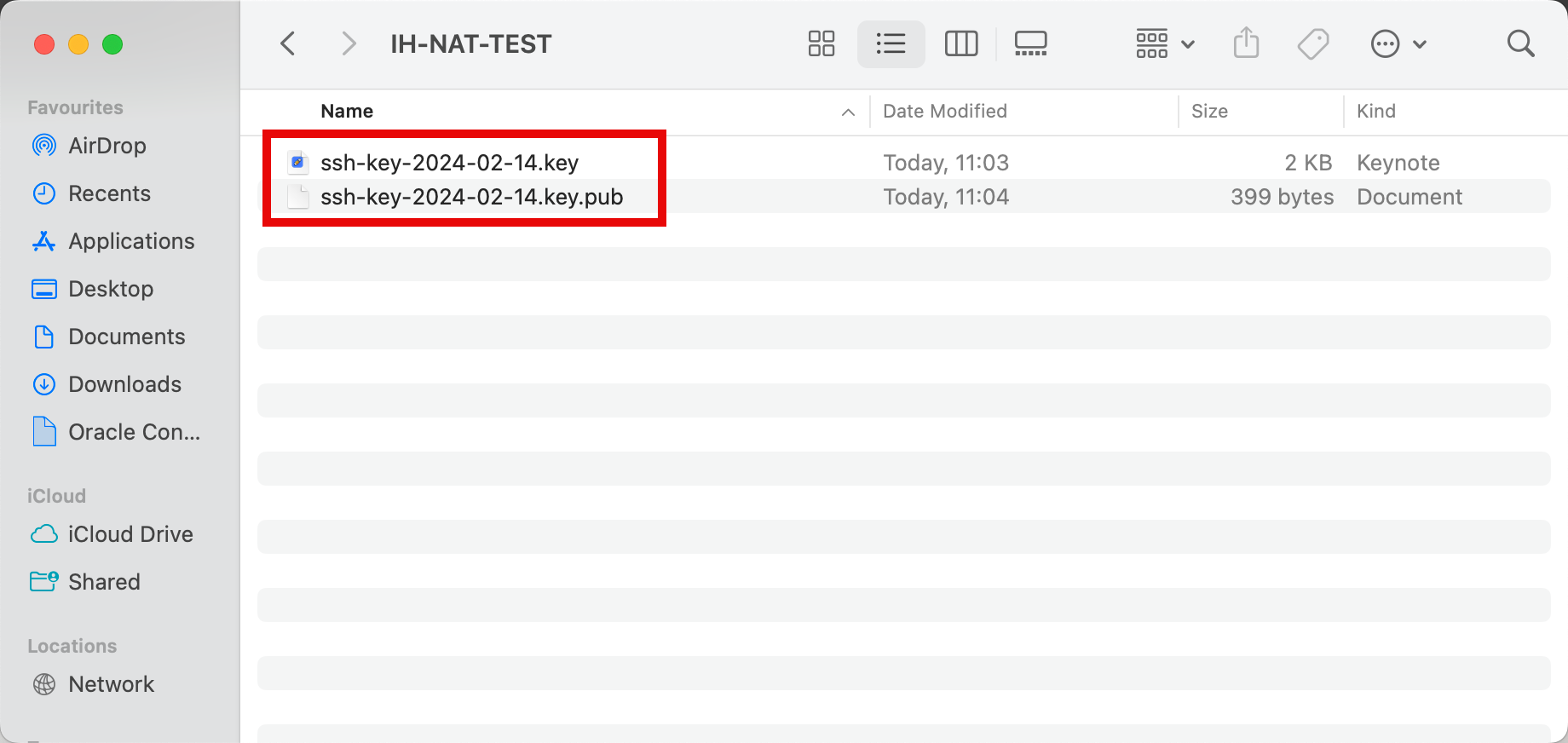
- Scroll down.
- Click Create to create the Linux instance.
-
After a few seconds, we will see that some information is populated that we will need to access the instance like the IP addresses and the username.
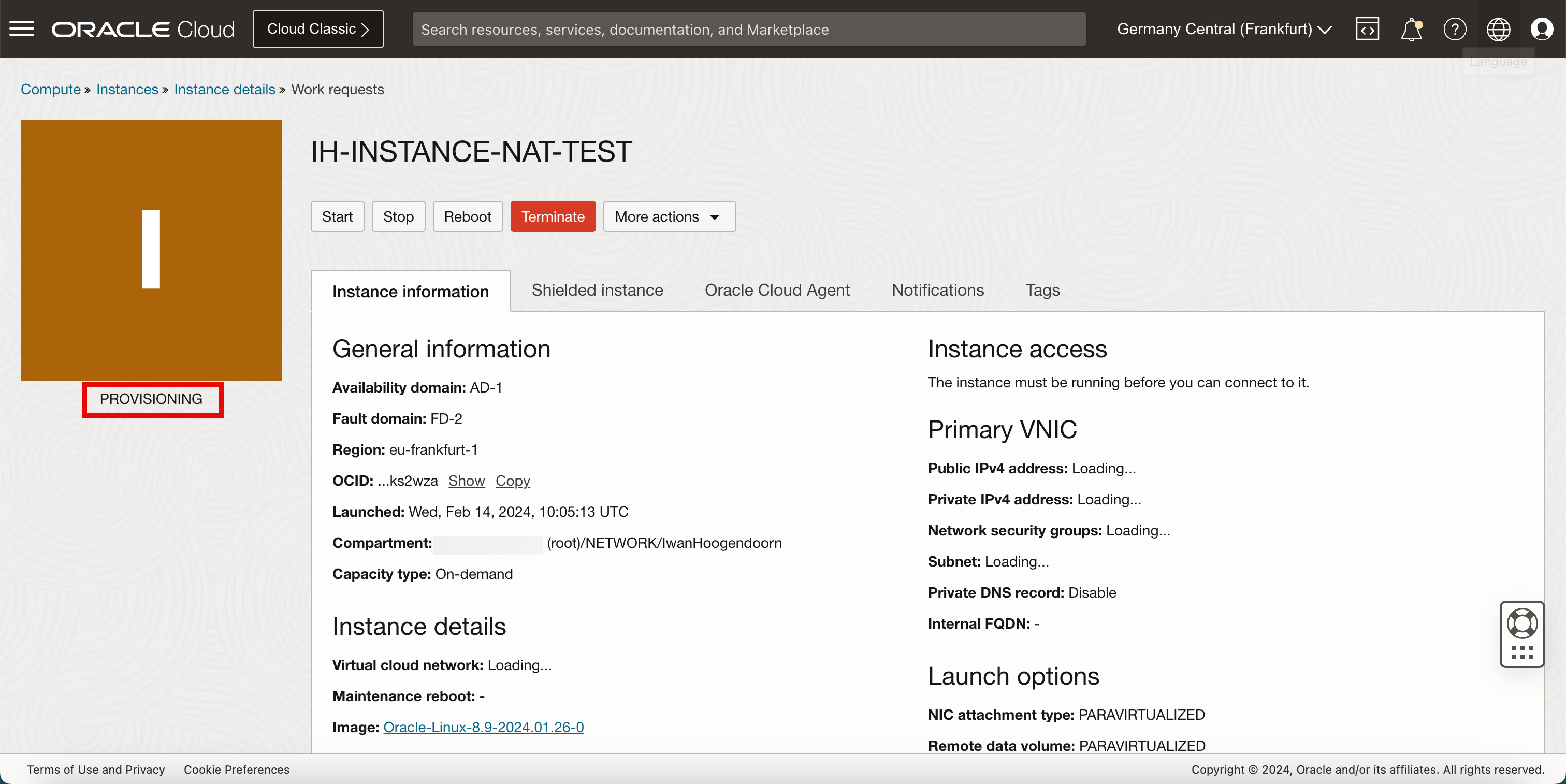
- Eventually the instance status will be RUNNING and we can start logging into the instance to perform some management tasks and start installing applications.
- From the upper right corner of the OCI Console, open OCI Cloud Shell.
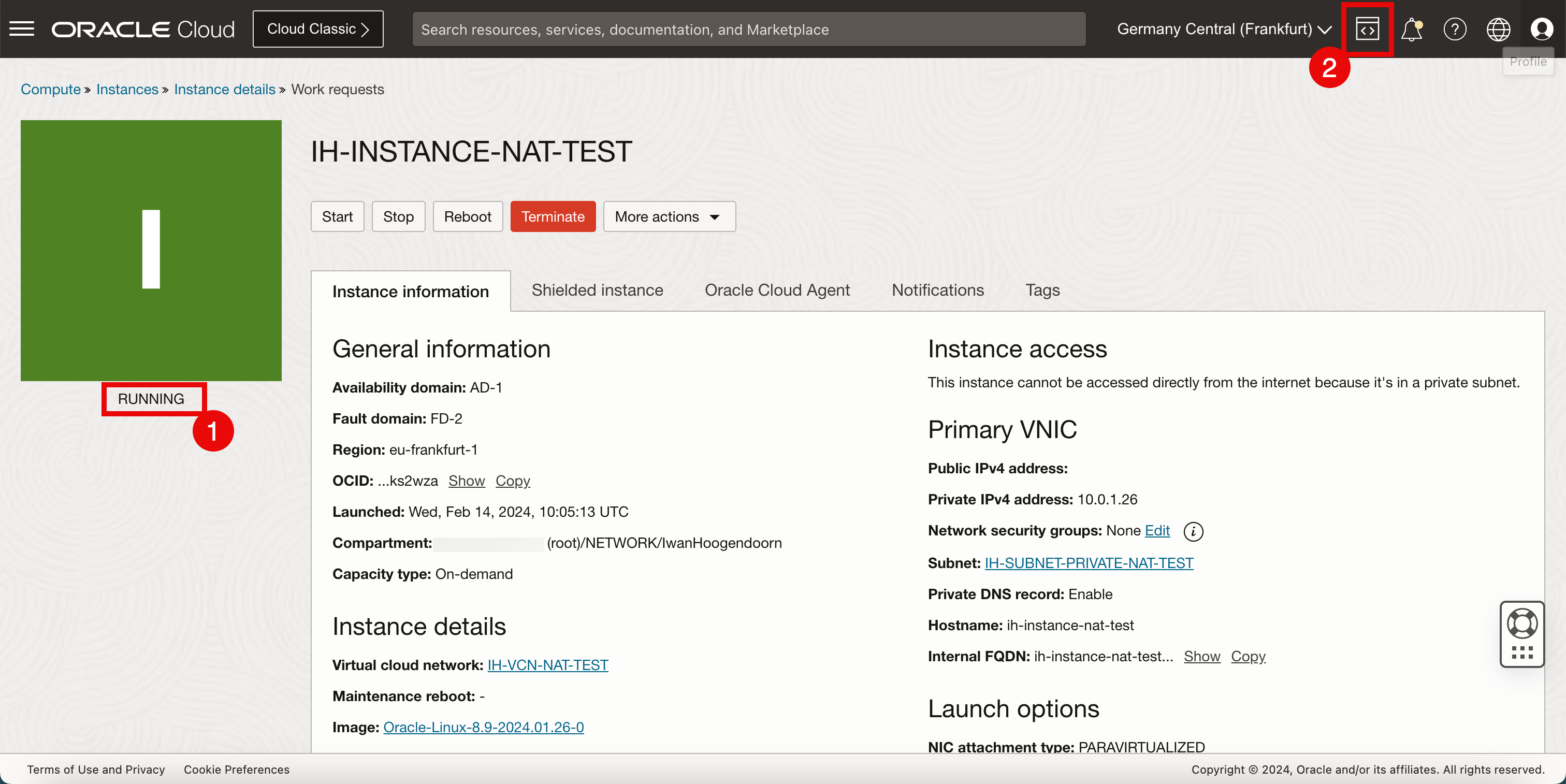
Task 4: Create a Private Network Definition
Create a private network definition so that we can log in to the instance using OCI Cloud Shell.
-
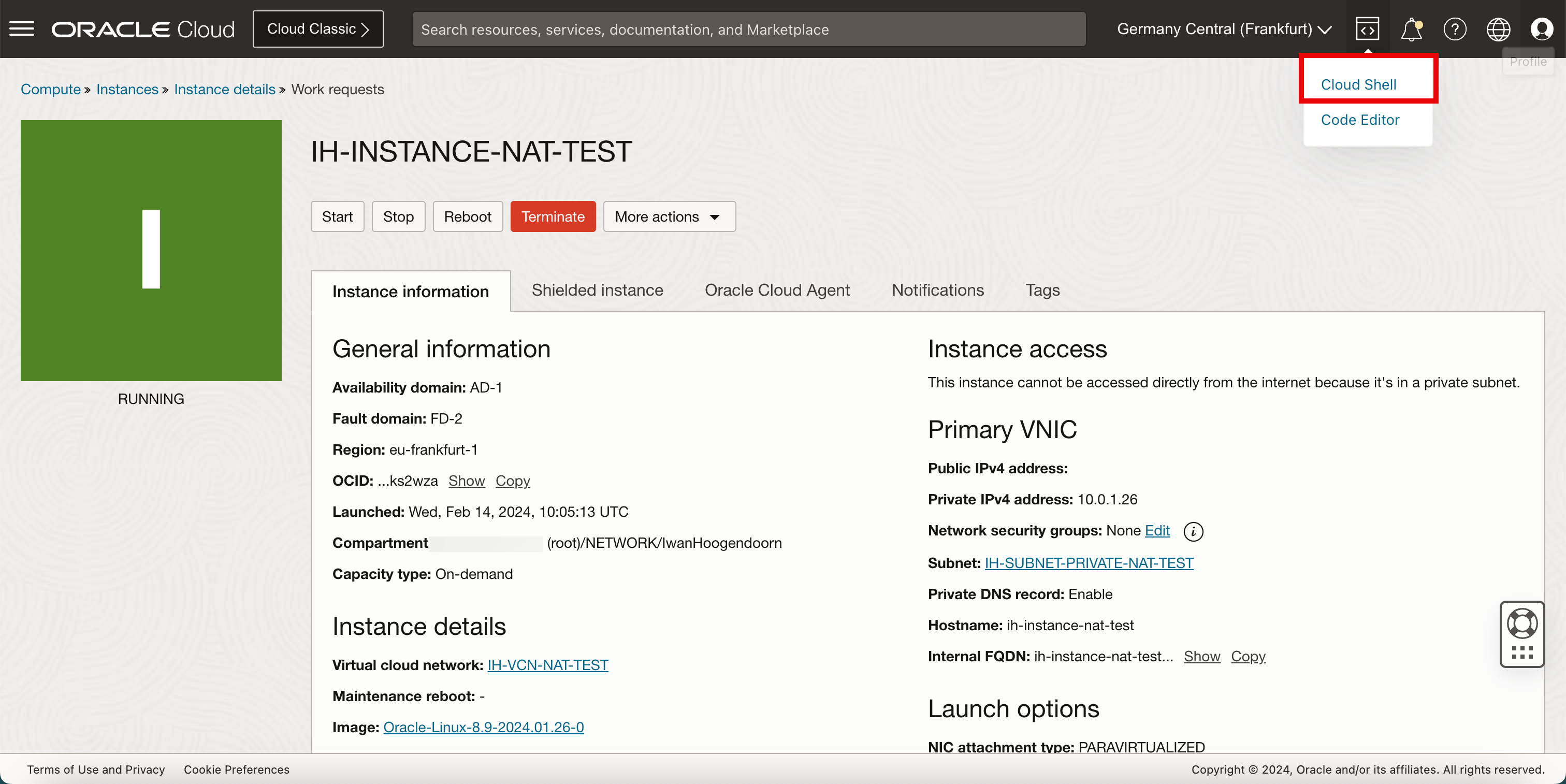
Click Cloud Shell.
-
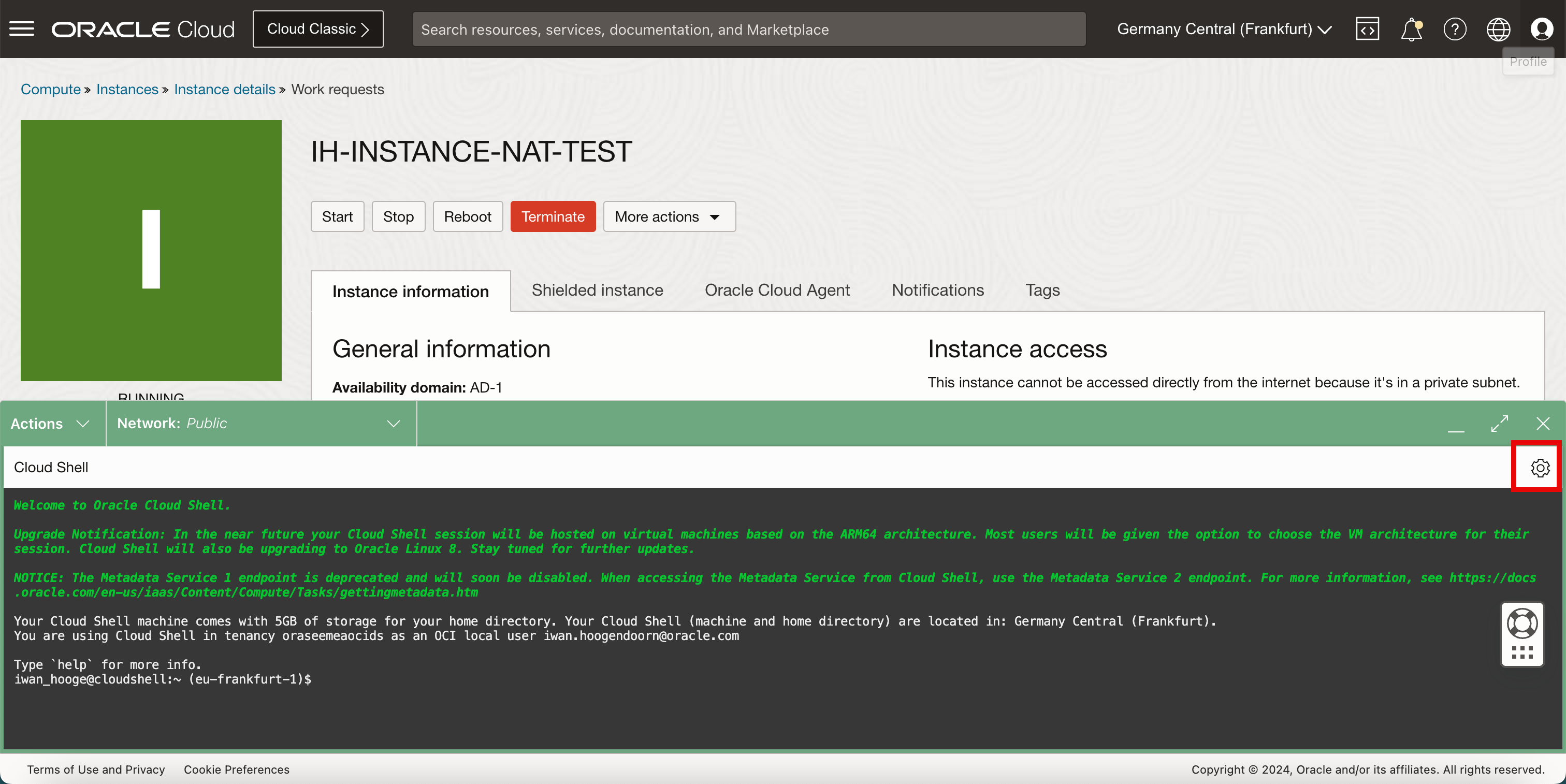
The Cloud Shell does not contain the private key. To upload the private key, click the wheel in the right upper corner.
-
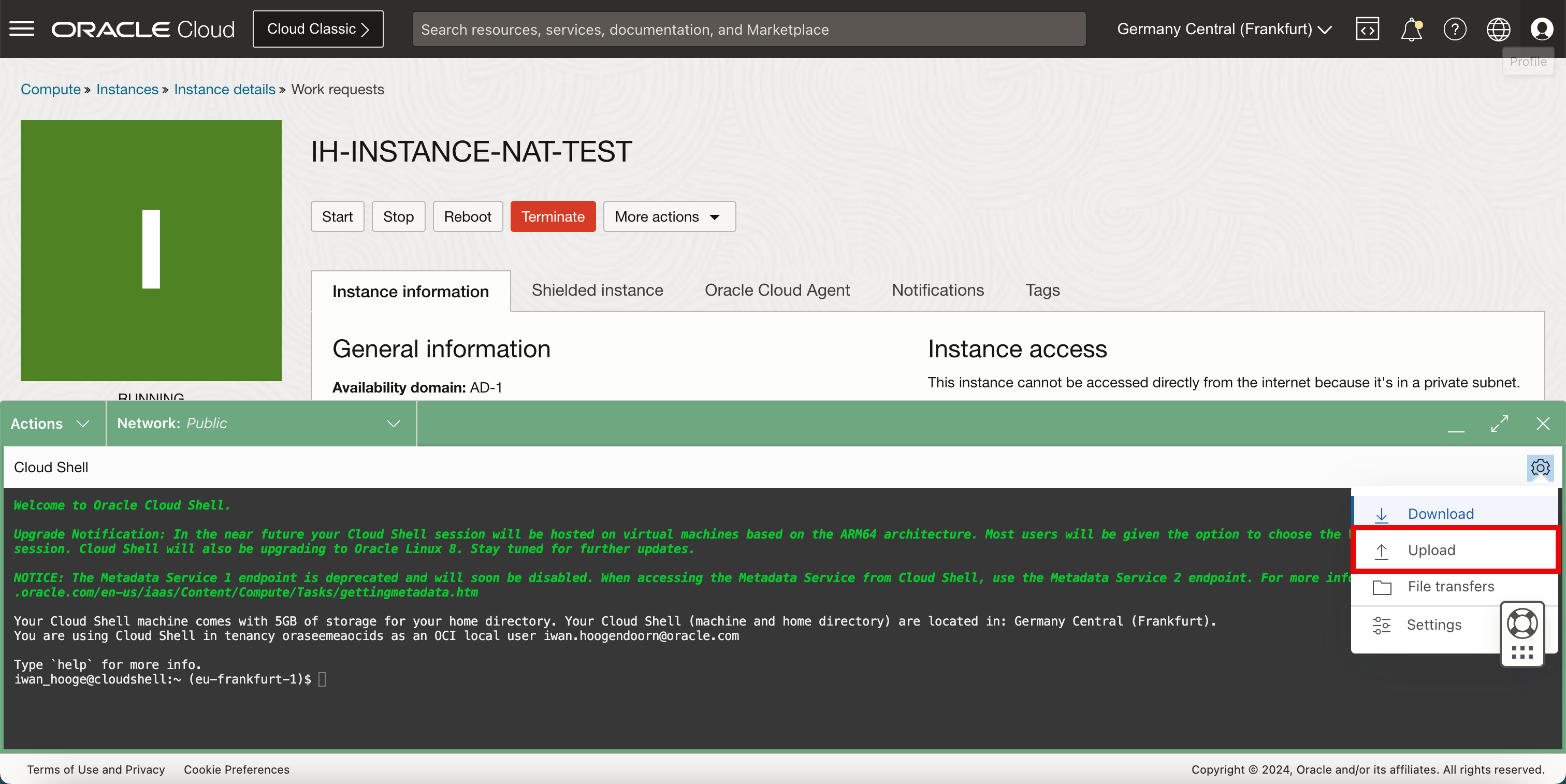
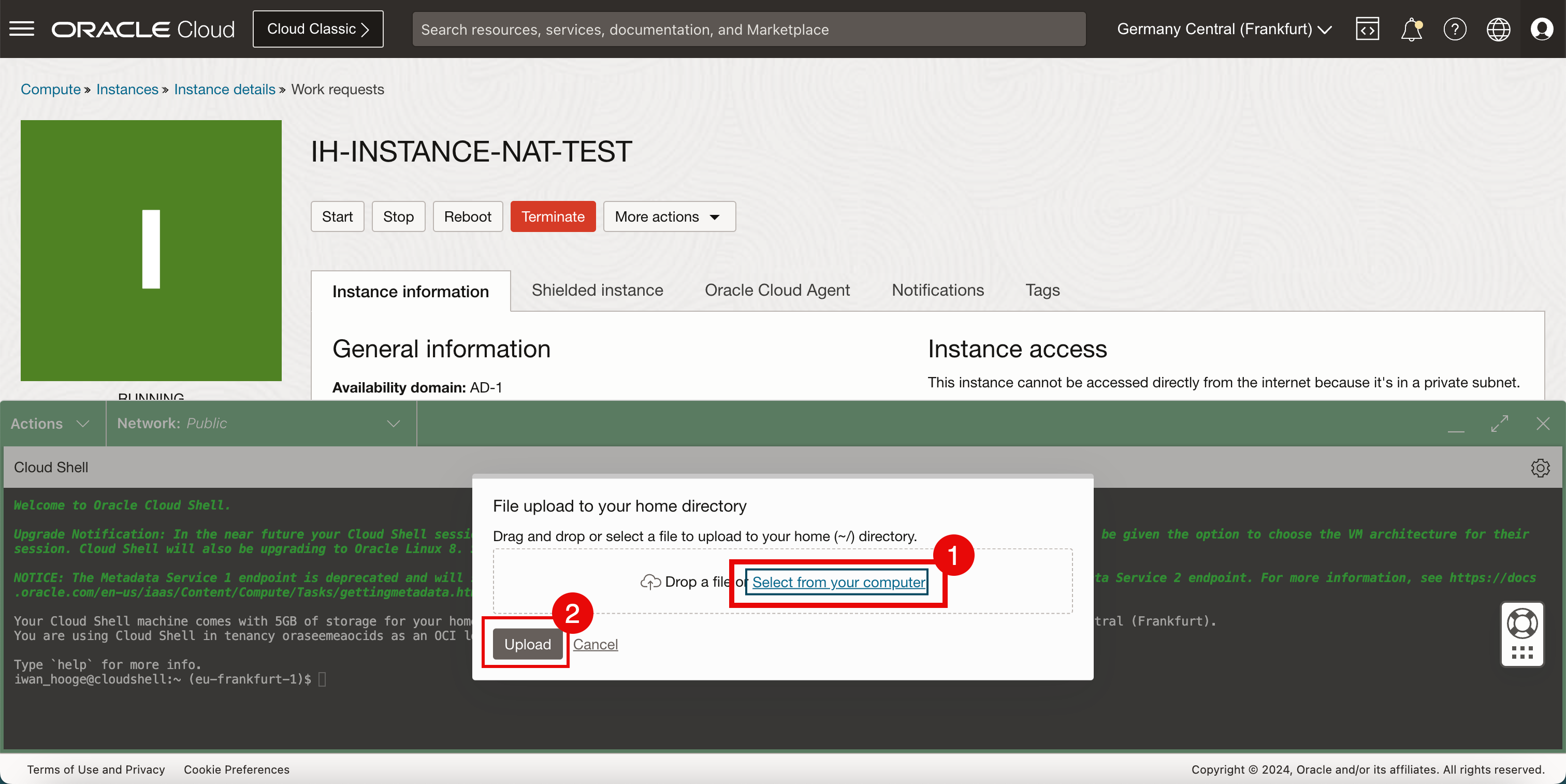
Select Upload.
- Click Select from your computer.
- Click Upload.
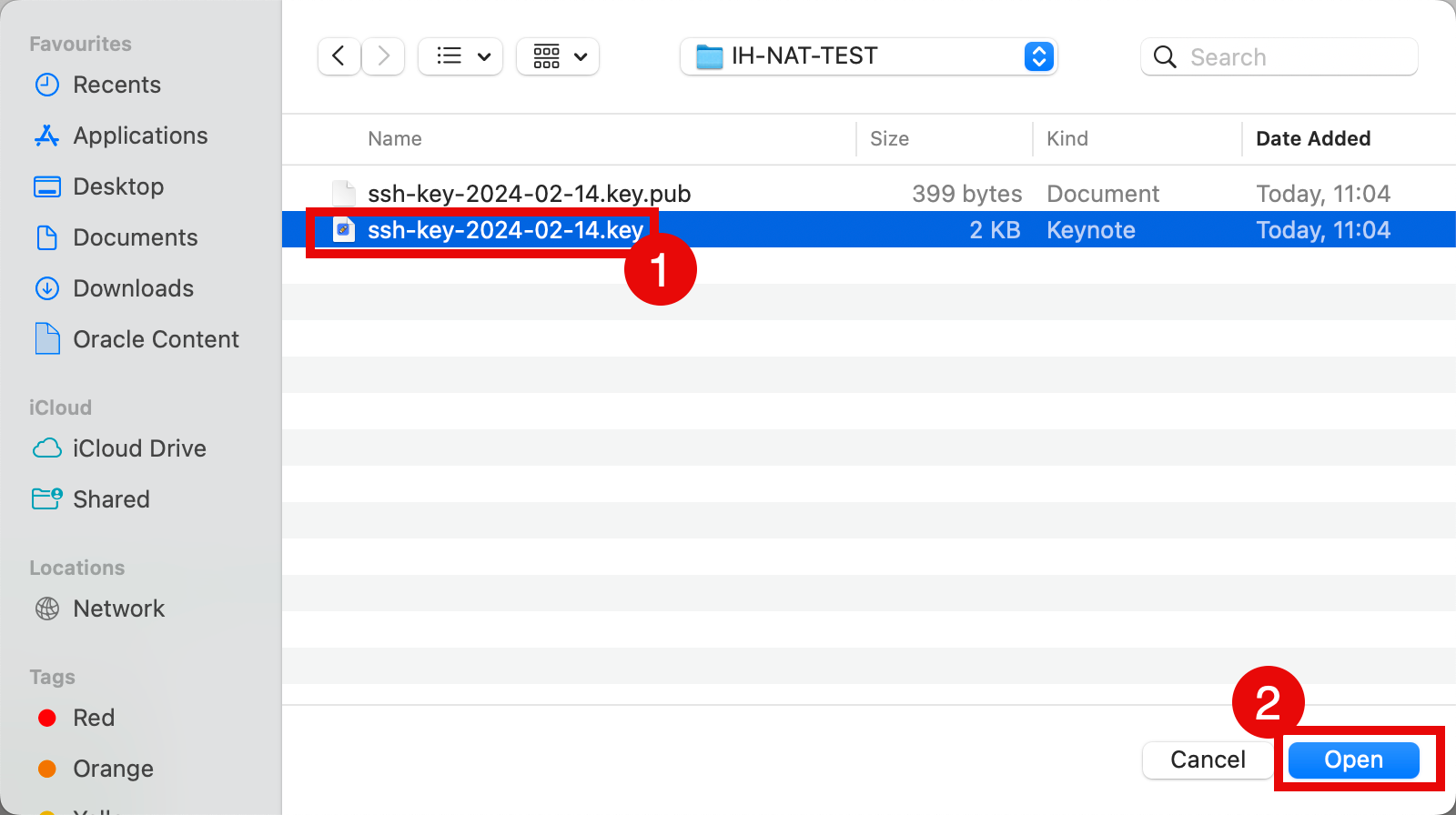
- Select the private key from your local computer.
- Click Open.
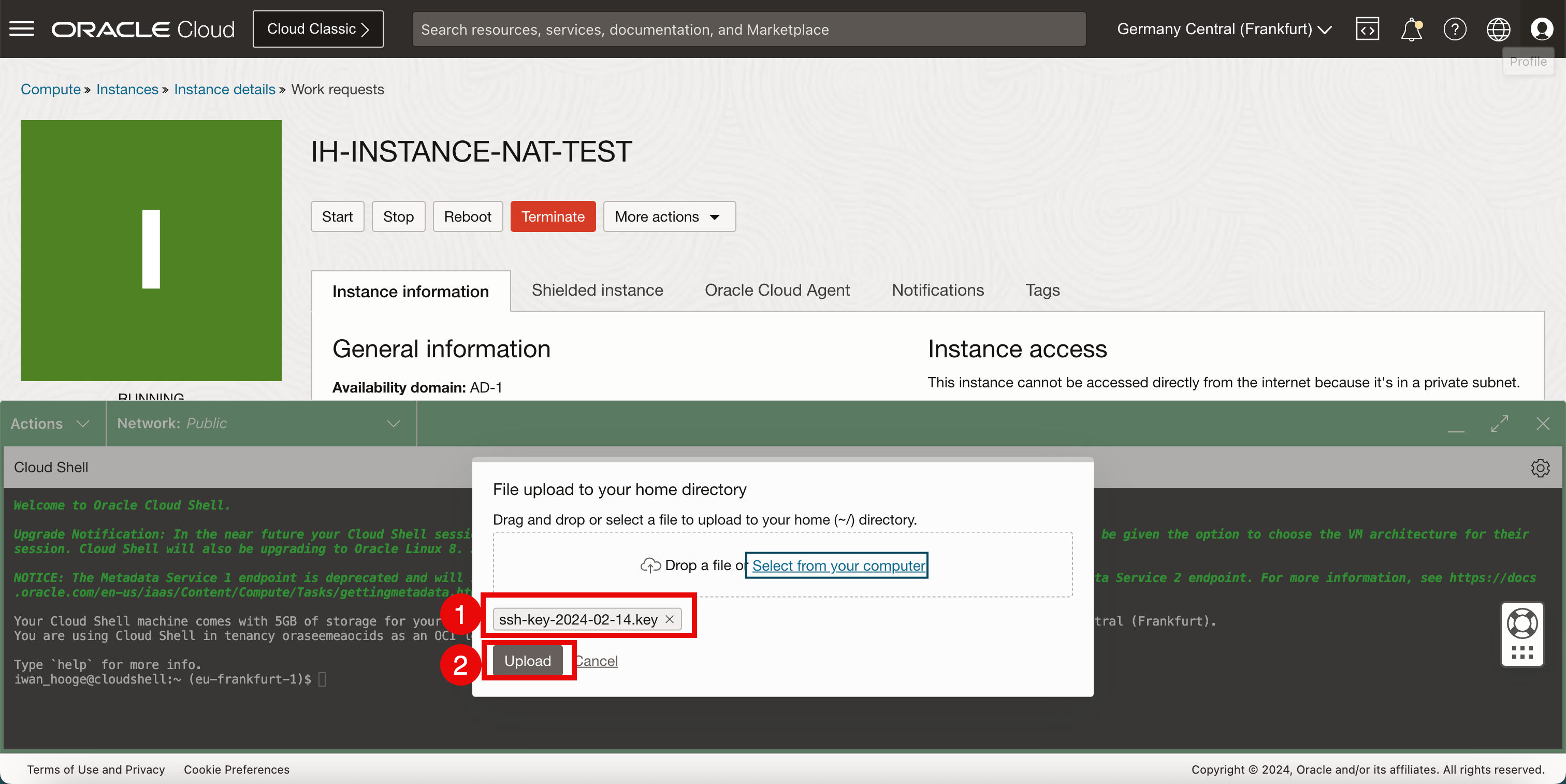
- Verify the private key that you selected.
- Click Upload.
- Click Hide.
-
Run the
ls-lcommand to verify the private key.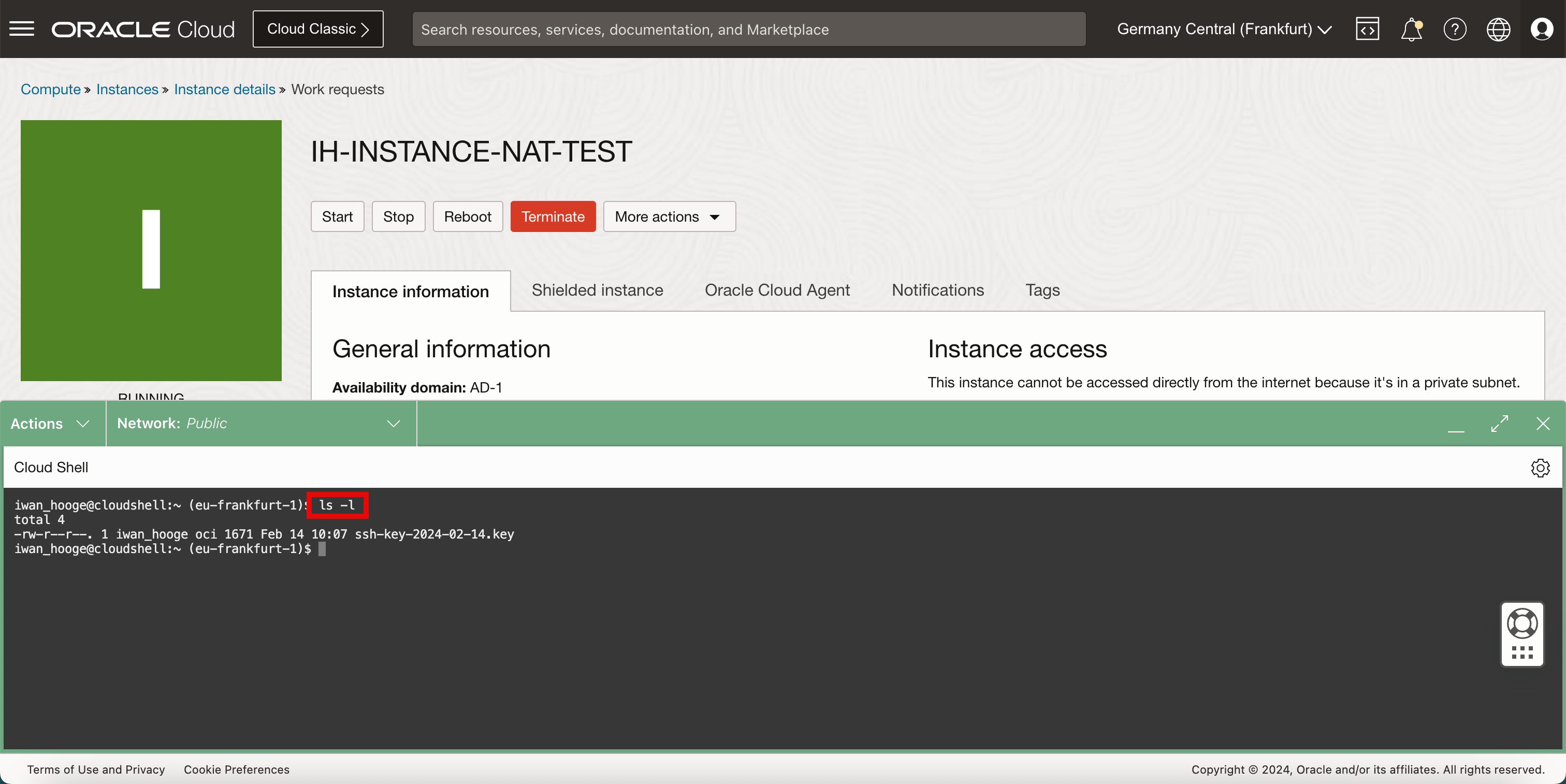
- Connect to the instance using the SSH command where you specify the private key.
- Notice that the connection is timing out.
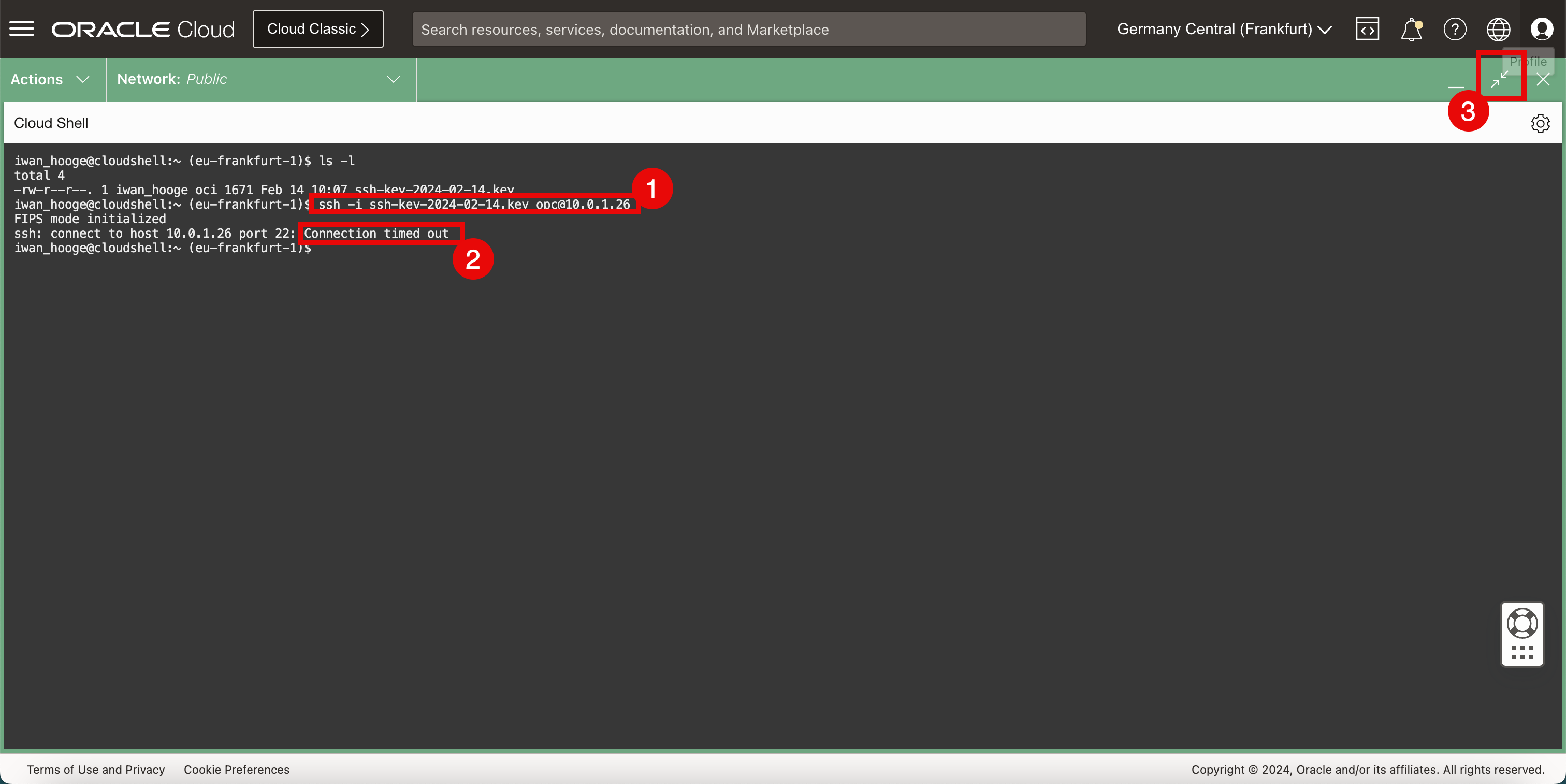
-
In order to connect to the Linux instance using the private IP address, it is important that the Cloud Shell gets access to the same subnet to which the Linux instance is connected.
We can do this by plugging the Cloud Shell into the same VCN and subnet containing the Linux instance. By default the network is set to Public, but we are going to change this by creating a new private network on the fly.
- Click Network.
- Select Private network definition list.
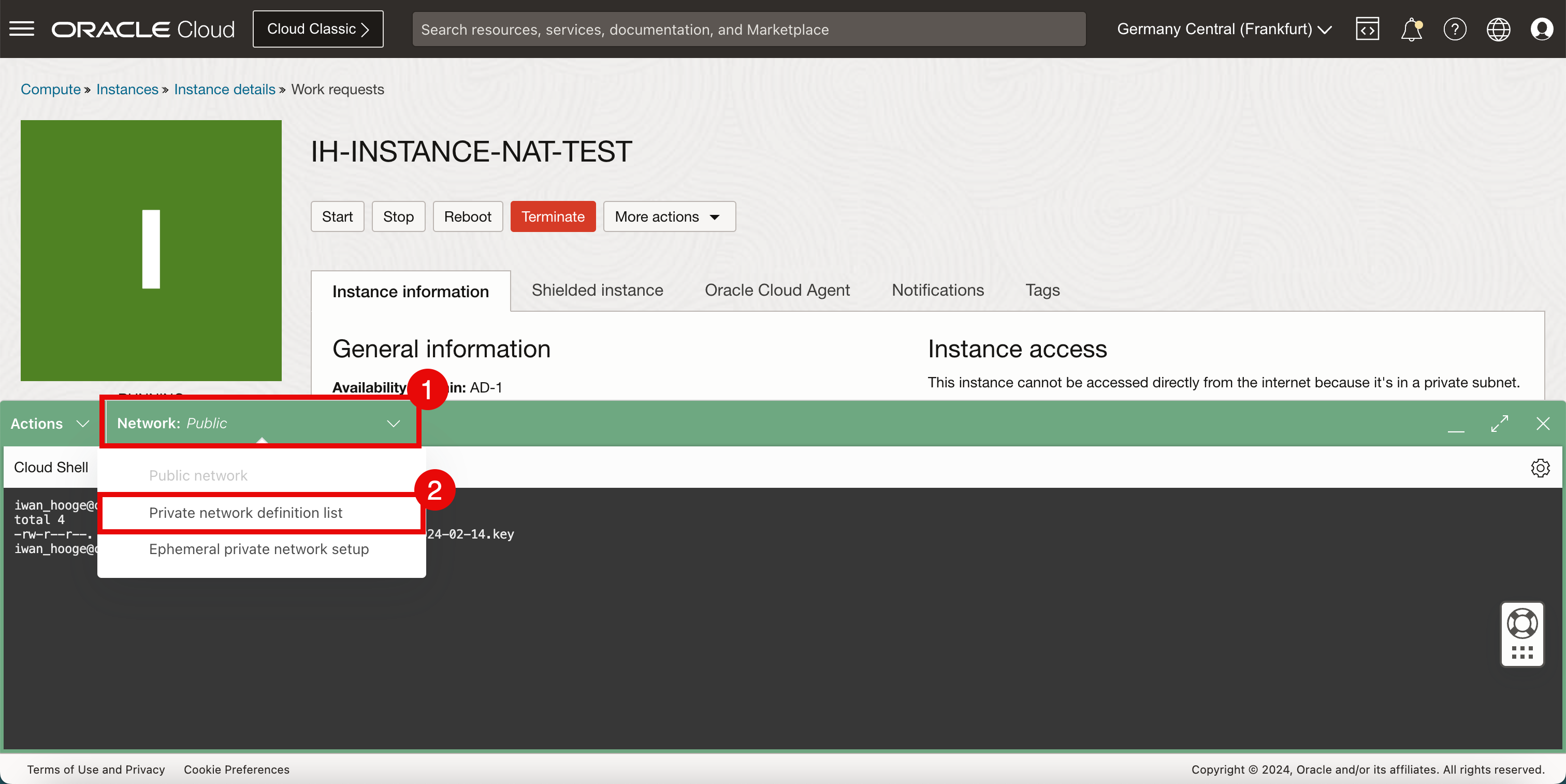
-
Click Create private network definition.
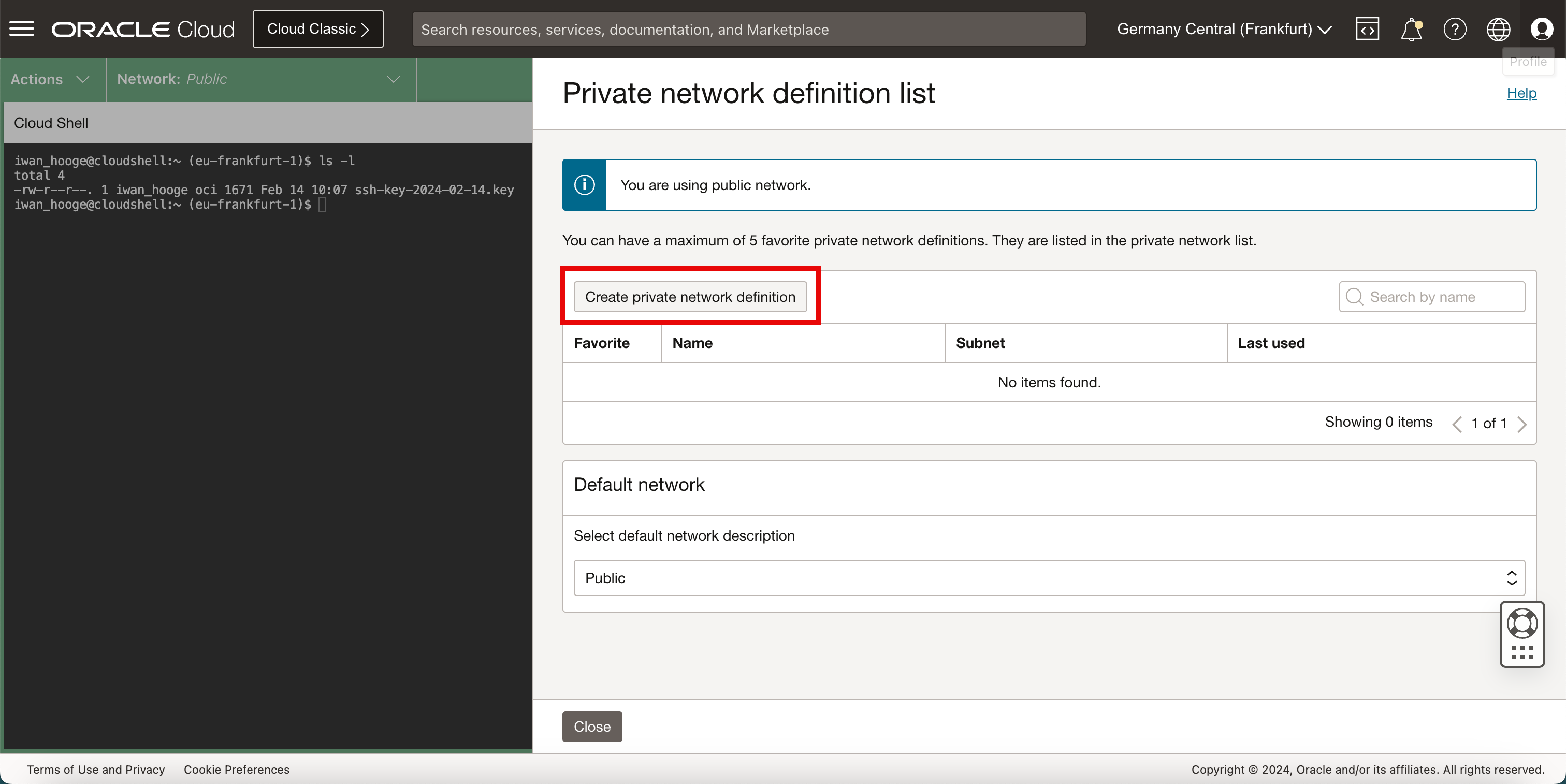
-
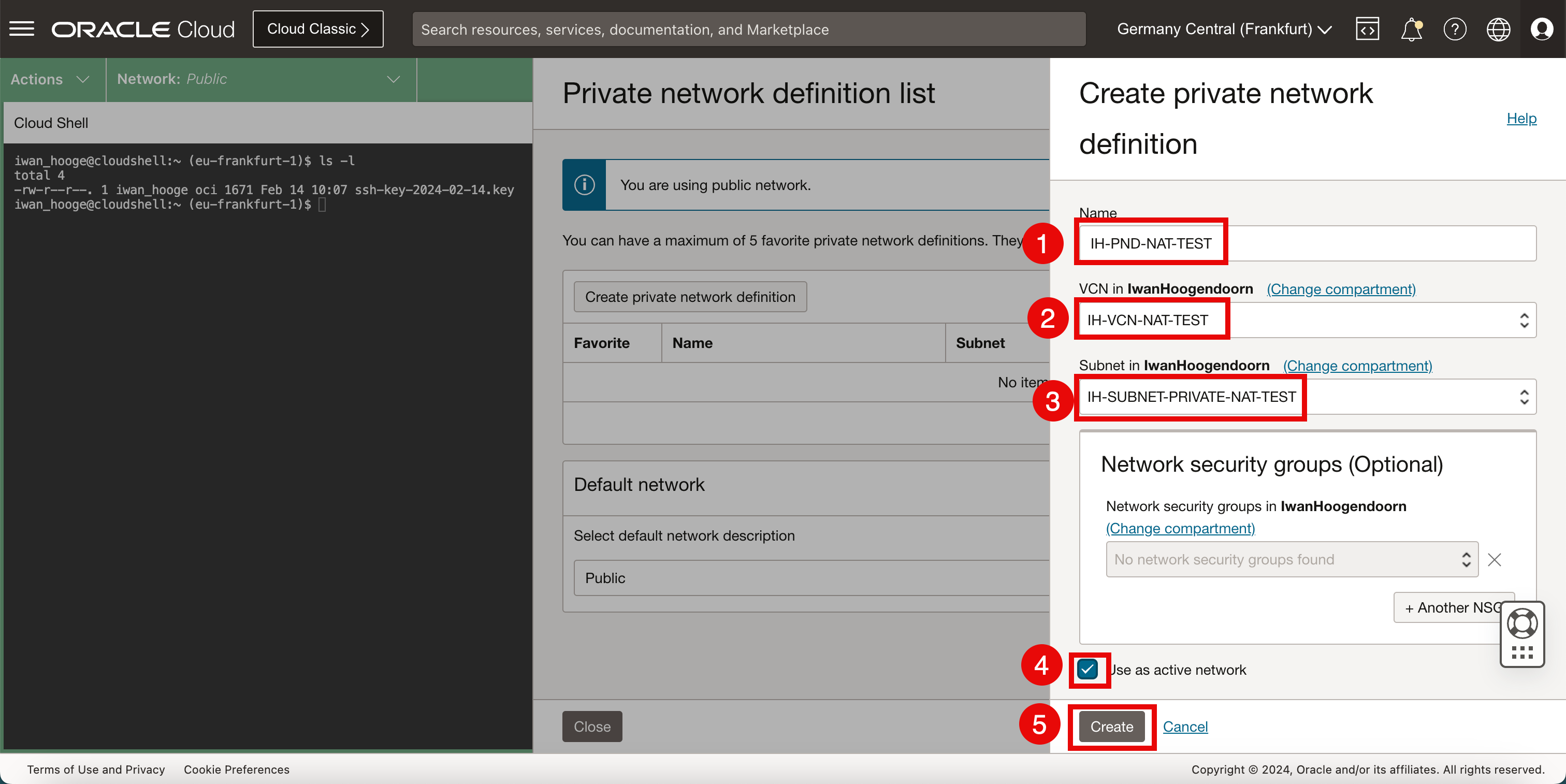
In Create private network definition, enter the following information.
- Enter a Name.
- Select the corresponding VCN with the Linux instance.
- Select the Subnet with the Linux instance.
- Select Use active network to activate the private network right away.
- Click Create.
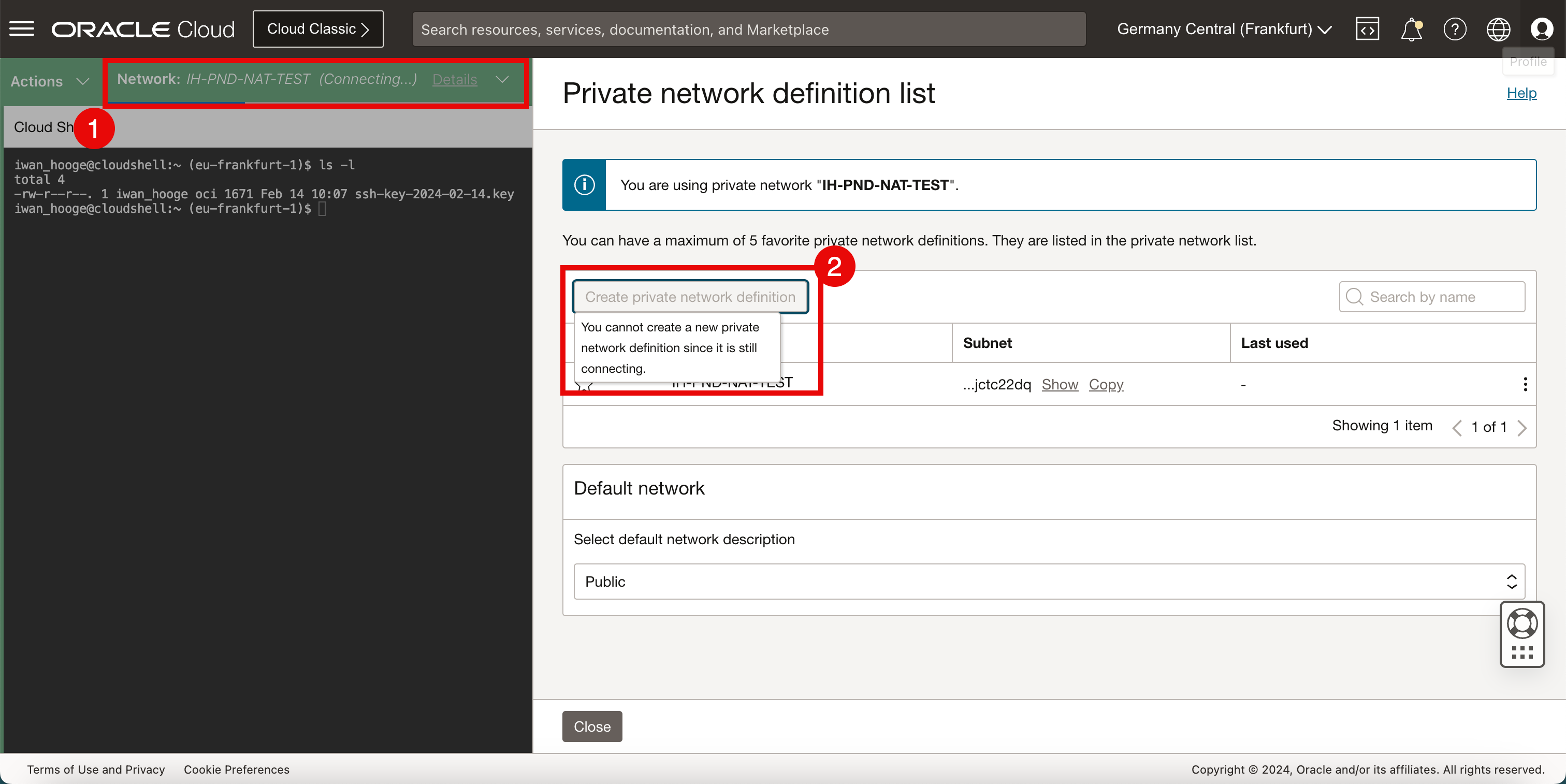
- Notice that the status of the network will change to the newly created private network with Connecting. This will take a few seconds to complete.
- Notice the message that; it is not possible to create a private network definition when the Cloud Shell is connecting to a new network.
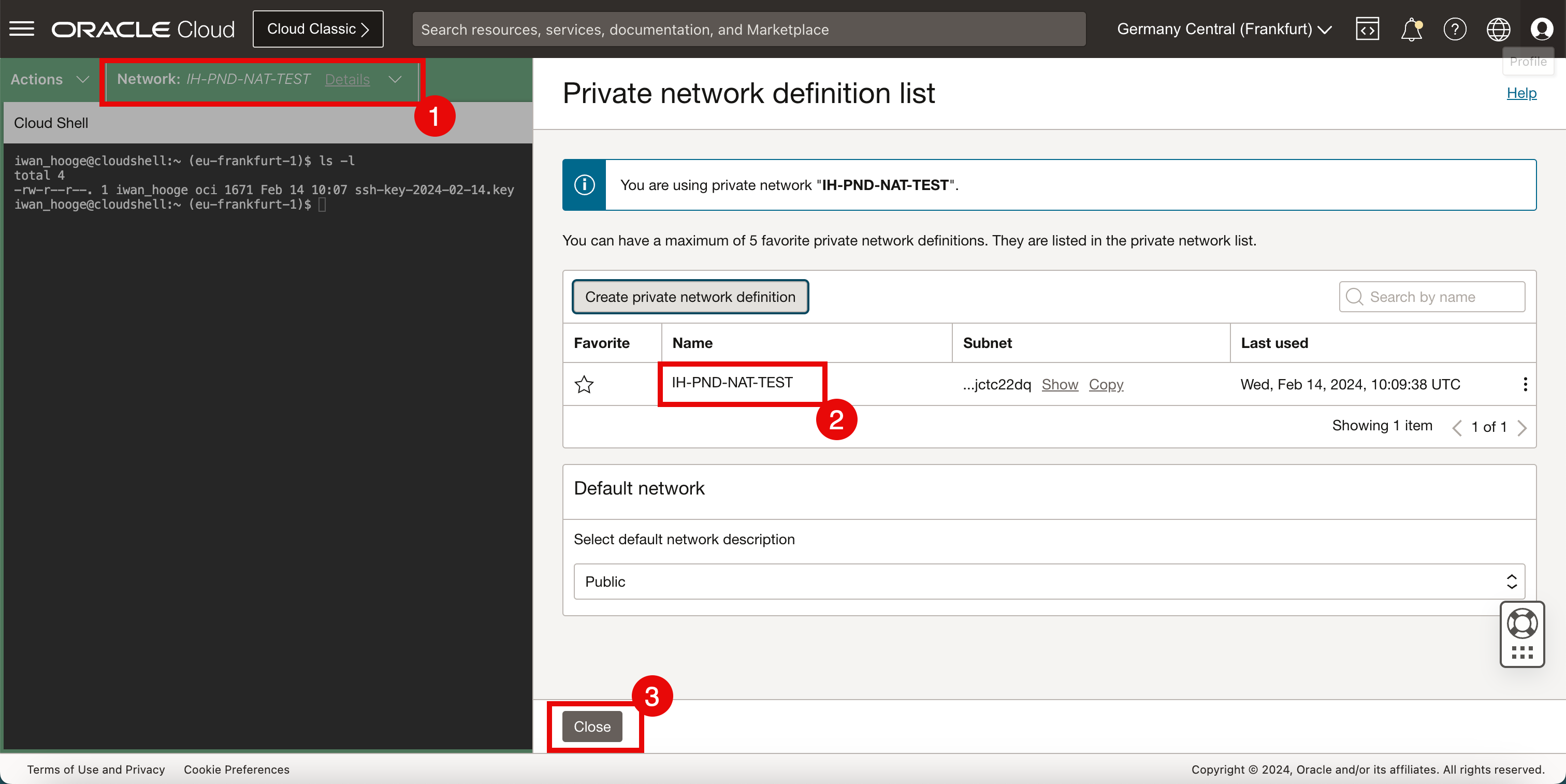
- After a few minutes, the private network is connected.
- Notice that the private network is also listed.
- Click Close to close the private network definition list.
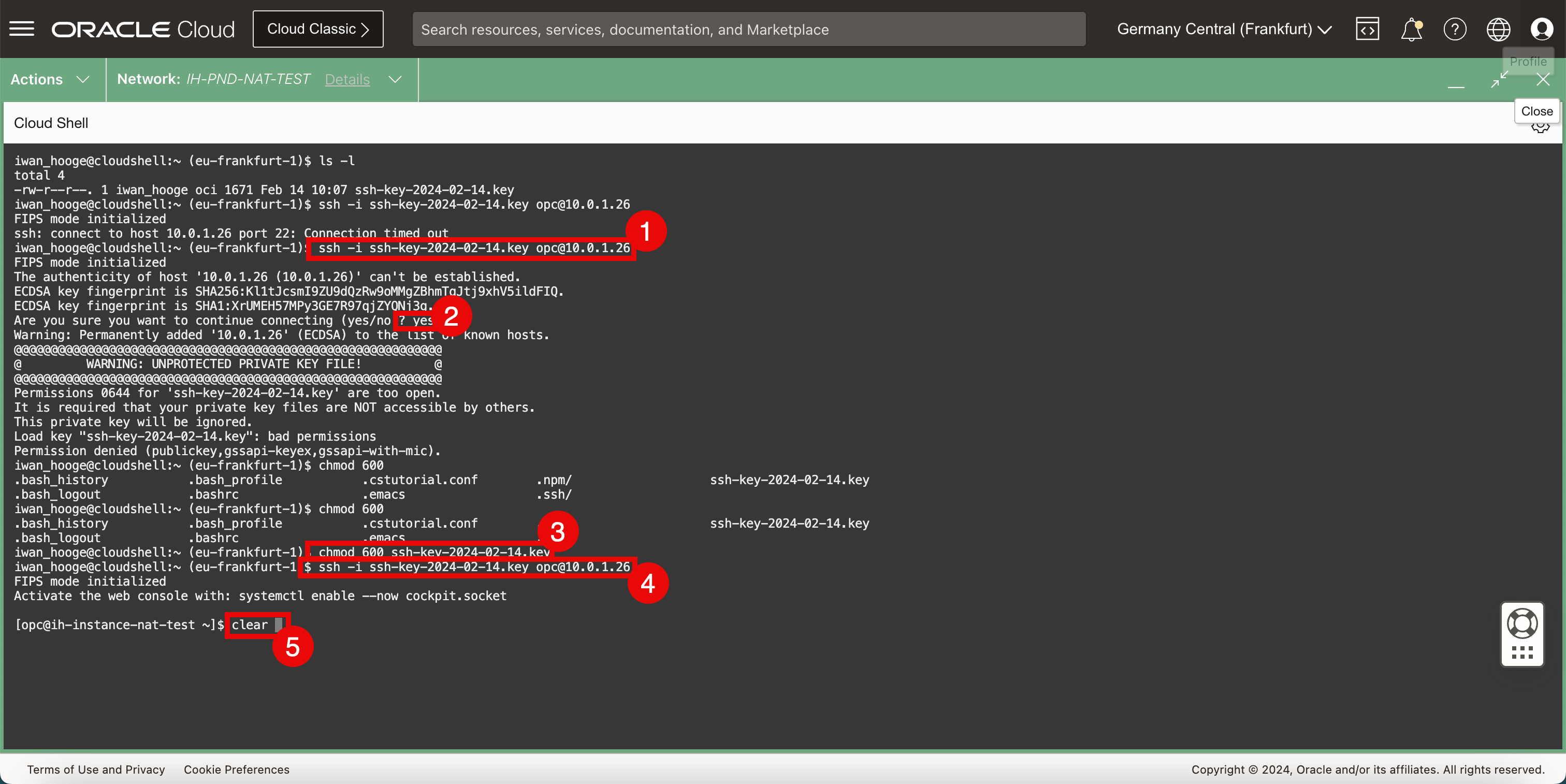
- Connect to the instance using the SSH command where you specify the private key.
- Enter yes.
- Restrict the permissions of the private key and make sure the access is restricted before it can be used.
- Connect to the instance using the SSH command where you specify the private key.
- Enter clear to clean the terminal.
Task 5: Verify Internet Connectivity on the Instance
-
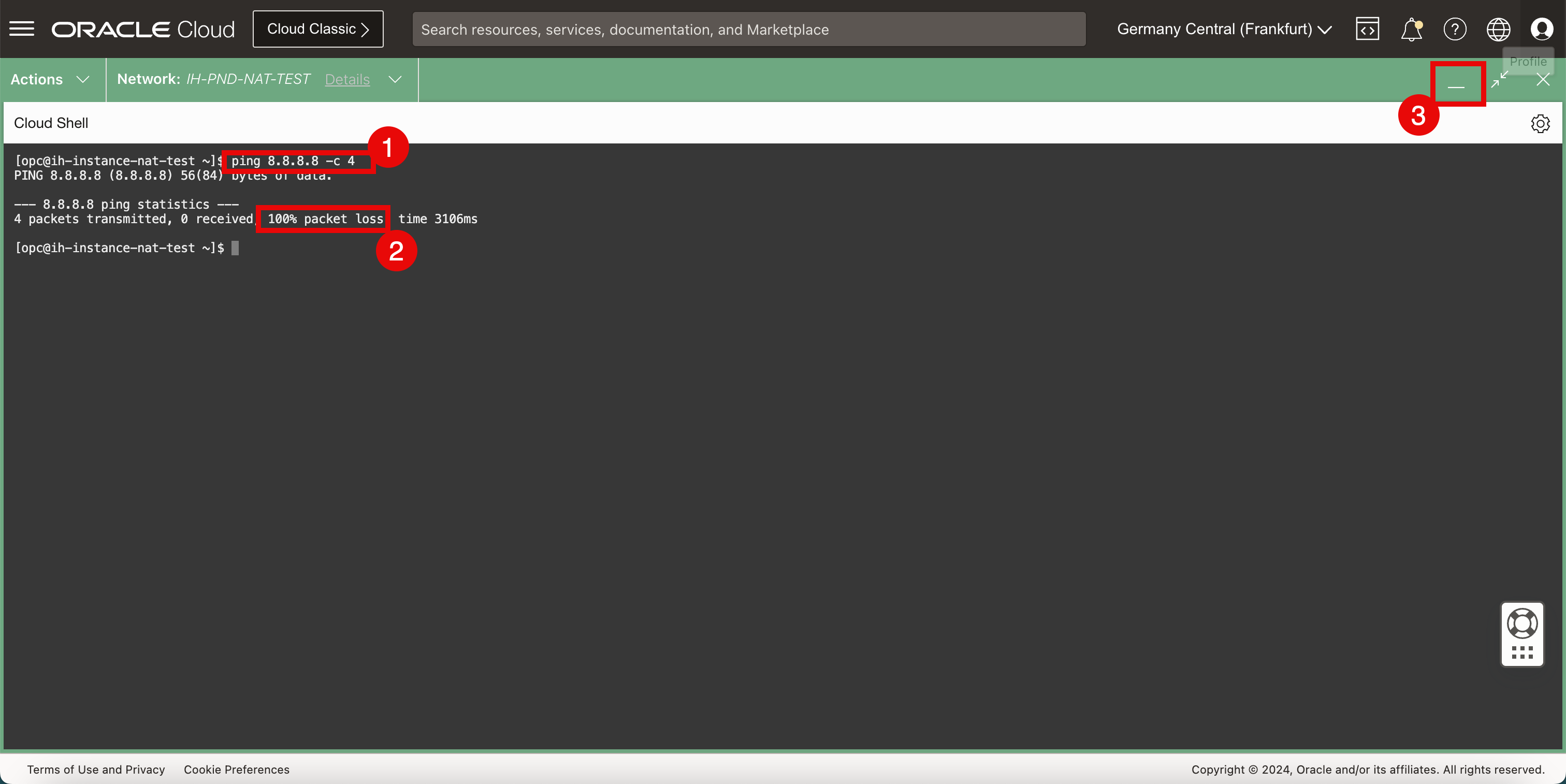
To check connectivity, follow the steps.
- To verify connectivity to the internet, we will do a simple ping to Google’s DNS server.
- Notice that ping is not working and we have a 100% packet loss.
- Click the minimize icon of the Cloud Shell terminal.
-
Click the hamburger menu in the top left corner.
Task 6: Create a NAT Gateway and Route the Internet Traffic to the NAT Gateway
-
Click Virtual Cloud Networking.
-
Scroll down.
-
We can see there are no NAT gateways available. Click NAT Gateways.
-
Click Create NAT Gateway.
-
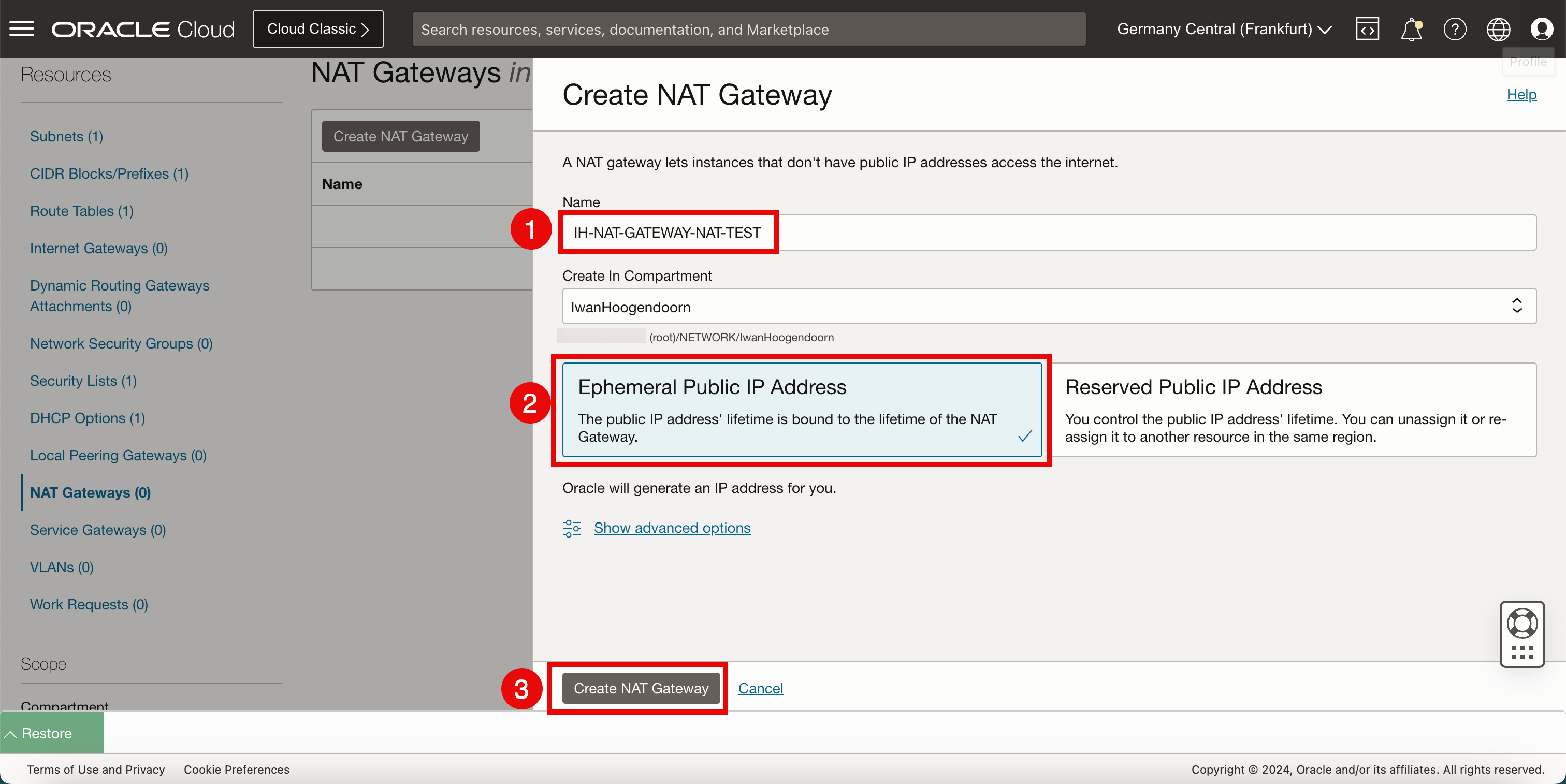
In Create NAT Gateway, enter the following information.
- Enter the Name of the NAT gateway.
- Select Ephemeral Public IP address.
- Click Create NAT Gateway.
- Notice that the status of the NAT gateway is Available.
- Click Route Tables.
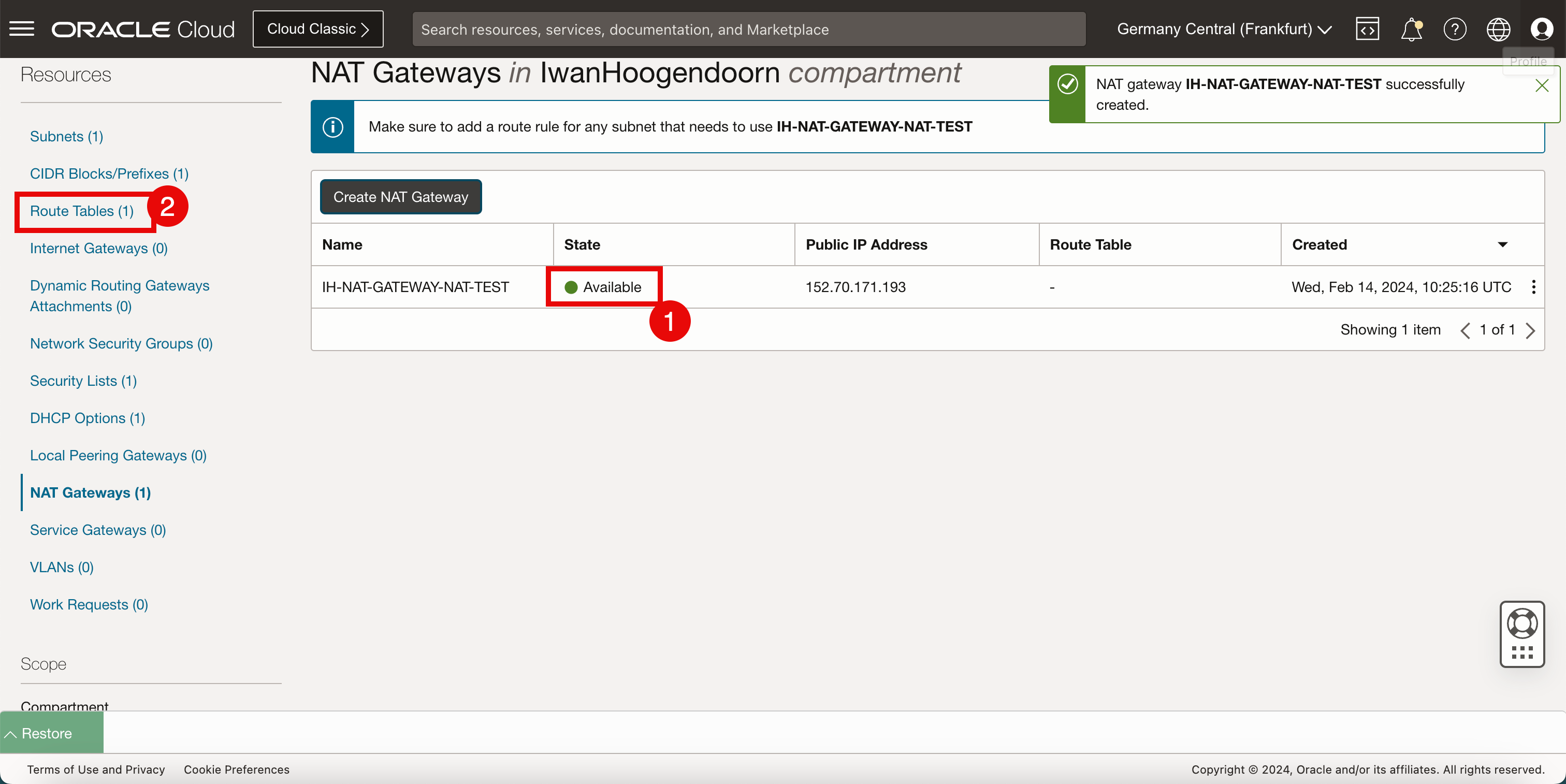
-
Route the traffic from the private subnet to the NAT gateway so that the internet is reachable and a static route needs to be created. Click Default Route Table.
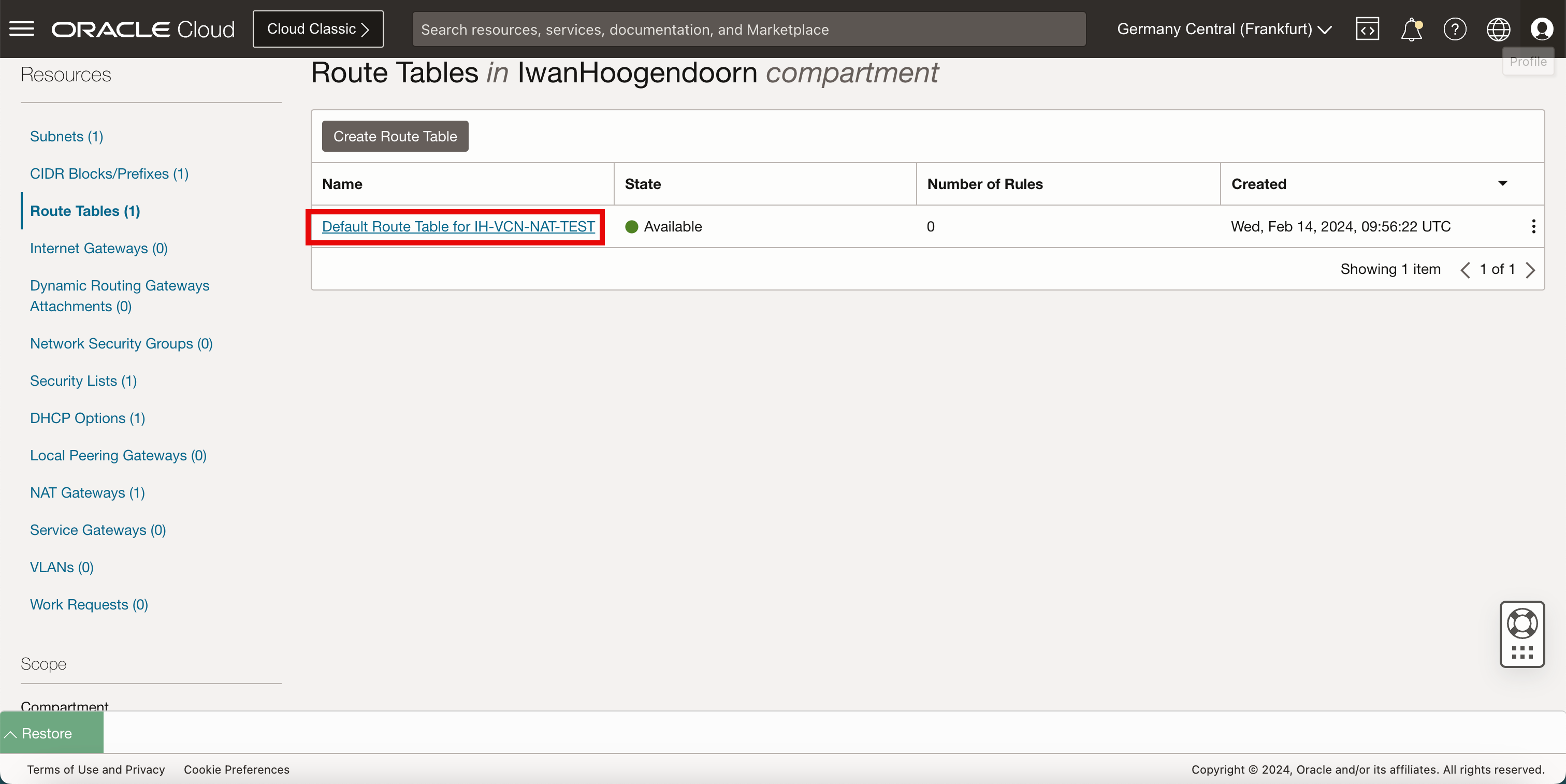
-
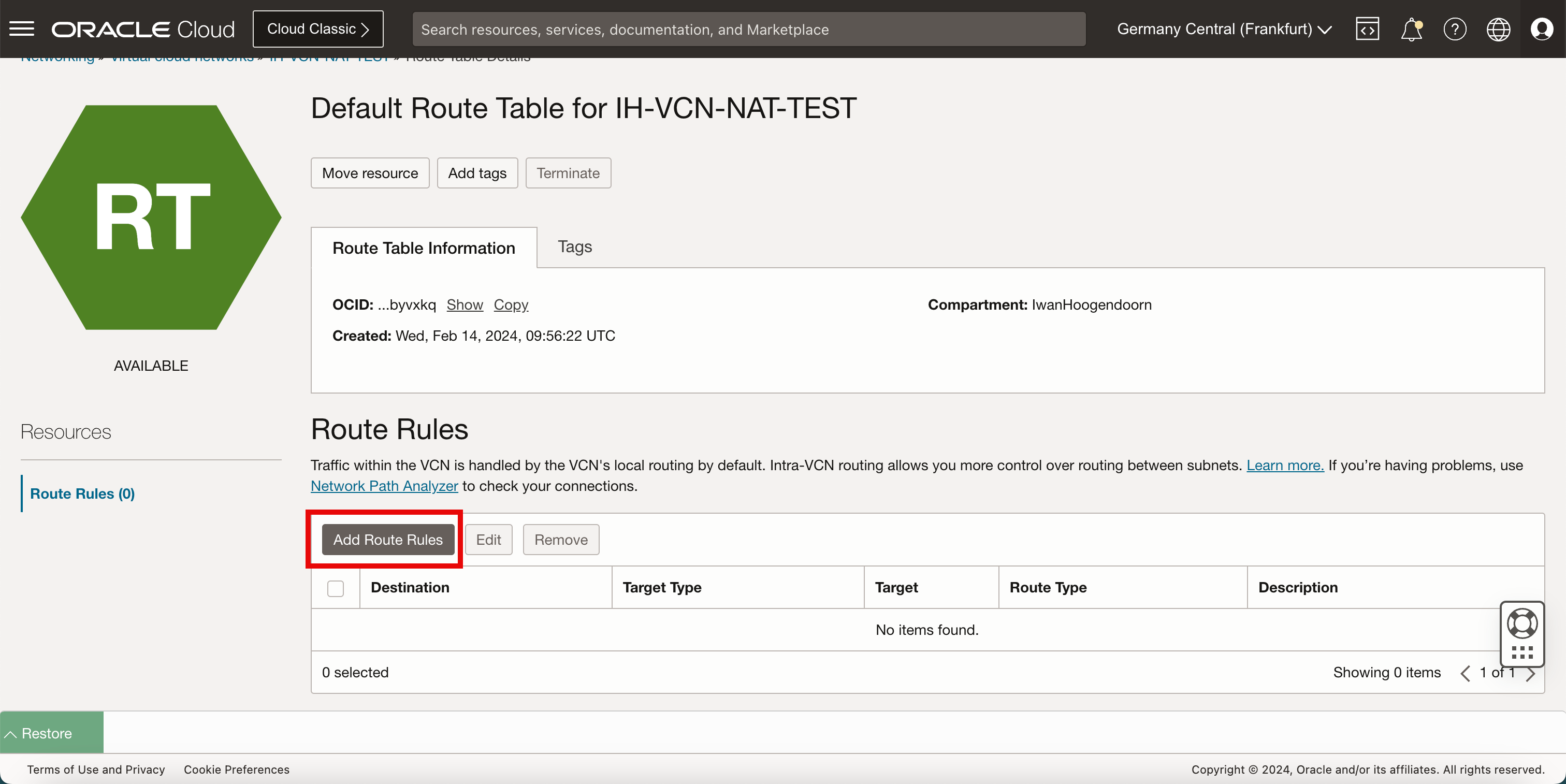
Click Add Route Rules.
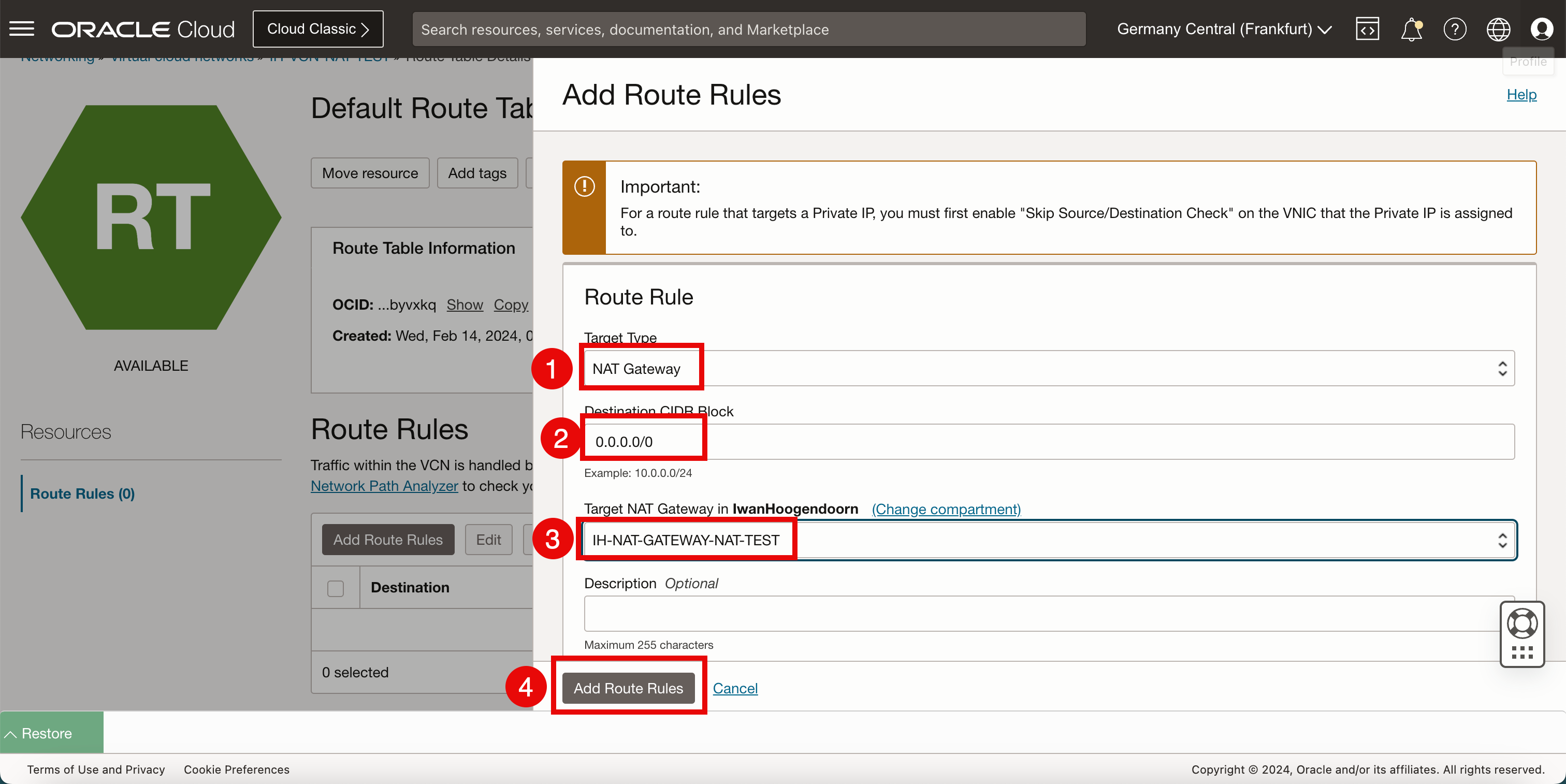
- Select the Target Type as NAT Gateway.
- Enter the Destination CIDR Block as
0.0.0.0/0(all network traffic). - Select the target NAT gateway created in Task 5.
- Click Add Route Rules.
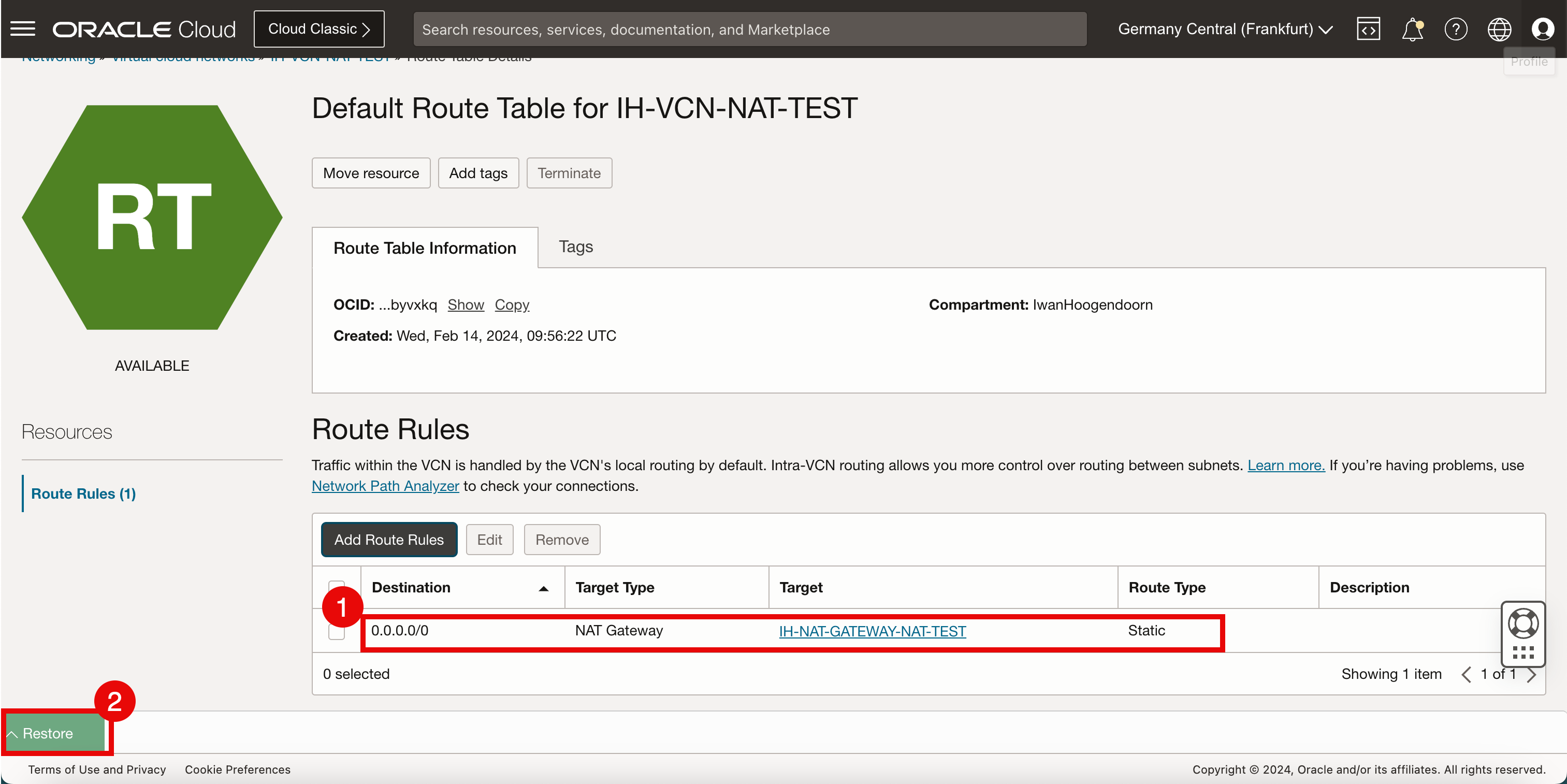
- Notice that the new route rule has been created.
- Click Restore to restore the Cloud Shell terminal.
- To verify connectivity to the internet we will do a simple ping to Google’s DNS server.
- Notice that ping is working and we have a 0% packet loss.
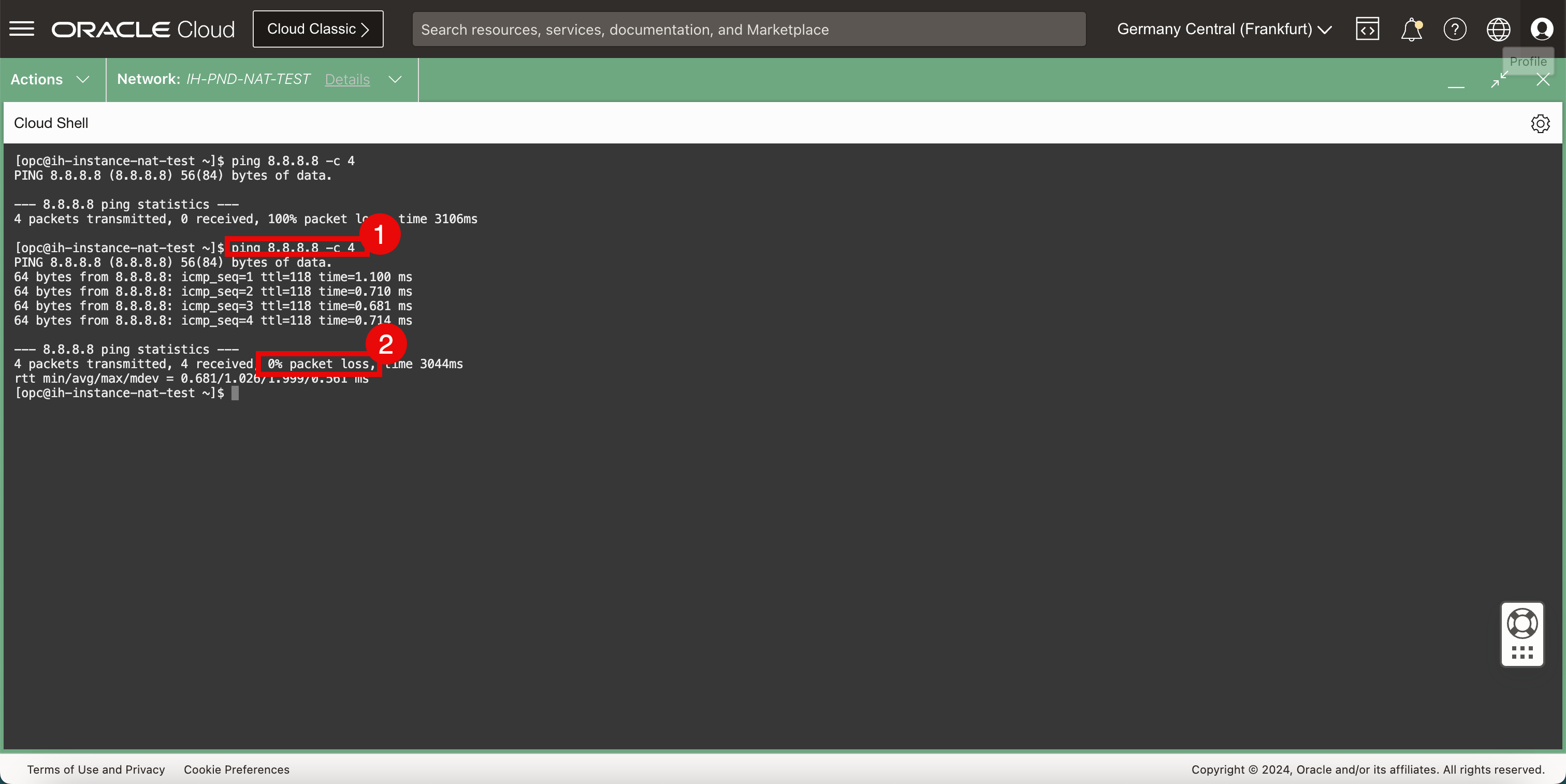
We can now access the internet with an instance that is connected to a private subnet with a RFC1981 IPv4 address.
Acknowledgments
- Author - Iwan Hoogendoorn (OCI Network Specialist)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Use NAT Gateway to allow Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Instances to Access the Internet
F93981-01
March 2024
Copyright © 2024, Oracle and/or its affiliates.