Note:
- This tutorial requires access to Oracle Cloud. To sign up for a free account, see Get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
- It uses example values for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure credentials, tenancy, and compartments. When completing your lab, substitute these values with ones specific to your cloud environment.
Deploy Microsoft SQL Server Always On Availability Groups for HA and DR on OCI
Introduction
The deployment of Microsoft SQL Server is a common use case in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). As is often the case in an OCI deployment, customers look for highly resilient architectures that address their business continuity requirements. Therefore, understanding how to deploy SQL Server for high availability and disaster recovery becomes an imperative for these customers.
There are several SQL Server business continuity solutions. The solution discussed in this tutorial is widely adopted by SQL Server administrators Always On availability groups. Solutions like SQL Server Always On Failover Cluster Instances (FCI) can also be deployed on OCI, but are excluded from this tutorial.
This tutorial is inspired by customer use cases and differentiates itself by centralizing three key elements of SQL Server Always On availability groups deployment on OCI in a single document.
-
The architecture needed for deploying SQL Server Always On availability groups. There are some specifics to deploying SQL Server on OCI that customers need to be aware of to make sure their SQL Server Always On availability groups deployment is successful.
-
The prerequisites that need to be in place for deploying SQL Server Always On availability groups.
-
The step-by-step procedures for deploying a two-node SQL Server Always On availability group. This constitutes the bulk of the tutorial. The same procedures can be used for deployments that use more than two nodes. This tutorial documents the procedures using the Windows Operating System graphical interface, which makes it adequate for non-advanced users. If you are an advanced user, you can implement the configuration using Windows PowerShell.
Architecture
This tutorial uses the following architecture:
-
Single Region: The deployment comprises a single OCI region. The deployment could be extended to other OCI regions, but such configurations fall outside the scope of this tutorial.
-
Private Subnets: With the exception of an OCI Bastion virtual machine (VM), all resources are placed in private regional subnets.
-
SQL Server Nodes on Multiple Subnets: Each of the two nodes of the SQL Server deployment is placed in a different subnet as per Microsoft recommendations. For more information, see Prerequisites for availability groups in multiple subnets (SQL Server on Azure VMs). SQL Server Always On availability groups could be deployed in a single subnet but this is not a recommended architecture by Microsoft. Additionally, it will require the use of a load balancer and functionality not supported by OCI (direct server return).
-
Windows Server Failover Cluster Quorum Witness: Always On availability groups runs on a Windows Server Failover Cluster (WSFC). WSFC requires the use of a cluster quorum witness, for which there are several deployment options. This tutorial uses a file share witness, as it is optimal for an OCI deployment. To achieve this, a quorum witness VM is provisioned as per the architecture diagram.
-
SQL Server IPs needed: Each of the SQL Server VMs needs the following IPs in the primary Virtual Network Interface Cards (VNIC).
- Primary IP: Operating System access (created automatically upon VM provisioning).
- Secondary IP 1: Windows Server Failover Cluster IP. To be created in this tutorial.
- Secondary IP 2: SQL Server Always On availability groups listener. To be created in this tutorial.
-
Accounts needed
- Domain Administrator: Domain administrator performs all configuration tasks in this tutorial. This account also needs to be configured both as a local administrator on each SQL Server VM and as a member of SQL Server sysadmin fixed server role for each SQL Server instance.
- Service Account: It is used for SQL Server service to operate on both SQL Server nodes.

Objectives
Create and configure the following:
-
Users and accounts needed for SQL Server Always On availability groups.
-
A Windows Server Failover Cluster for Always On availability groups.
-
A SQL Server Always On availability group.
Prerequisites
-
Networking
-
Access to an OCI tenancy and a compartment for placing all the resources.
-
Networking configured according to the architecture diagram.
- 1 VCN.
- 1 public subnet and 4 private subnets.
-
Security list rules configured for implementing SQL Server Always On availability groups -
1433and5022ports open. -
Security list rules configured for implementing Active Directory in OCI as described in the OCI white paper Creating Active Directory Domain Services in OCI.
-
We can use the Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) blocks shown in this tutorial, or you can select CIDR blocks following your cloud networking team advice.

-
-
Servers
-
1 Bastion VM in a public subnet to make sure you can connect to the VMs running on private subnets.
-
1 Domain controller VM in a private subnet.
-
1 Quorum VM in a private subnet.
-
2 SQL Server VMs, each in a different private subnet.
-
There are 2 ways to run SQL Server in OCI: OCI Marketplace Image and Bringing Your Own Microsoft License (BYOL). You can use whichever you prefer. This tutorial just assumes, we have a SQL Server default instance installation (a single SQL Server installation per VM).
-
If we use the OCI Marketplace image, the provisioning process will install SQL Server with the opc user. When we join each of the nodes to the domain, we will then need to make sure that the domain administrator is part of the local administrators so that we can connect to each of the SQL Server database instances on SQL Server Management Studio.
-
Install SQL Server Management Studio on the SQL Server node VMs.

-
-
Active Directory Domain prerequisites
-
Domain controller features and roles added to the domain controller VM.
-
Domain configured by the OS administrator. The domain controller in the present tutorial has the root domain name
mssql.acme. We can configure the domain with a root domain name of your choice. -
You can consult the OCI white paper on Creating Active Directory Domain Services in OCI.
-
SQL Server VMs and Quorum VM added to the domain.
-
Exclusions for this Tutorial
-
Multi Region: A multi region deployment is possible but is outside the scope of this tutorial. For more information, see Configure a multi-subnet availability group across Azure regions - SQL Server on Azure VMs.
-
Storage: For this tutorial, the boot volume of each VM is used as the SQL Server repository for the database, backups and logs (they all map to the
C:\drive). Depending on the requirements, you might need to use and configure separate volumes for the database, backups and logs. We need to be aware that WSFC uses an IP from the169.254.\*address space for internal communication, which overlaps with OCI address space for exposing iSCSI block devices. This will require to create static IP routes to expose iSCSI target portals in each of the SQL Server node VMs. Such configuration is out of the scope of this tutorial. For more information, see Failover Clustering Networking Basics and Fundamentals. -
Highly Available Witness File Share: This tutorial uses a single VM for the quorum witness file share. A highly available witness file share is outside the scope of this tutorial. For more information on how to deploy, see Deploying a Highly Available Windows File Server on OCI.
Task 1: Configure the Secondary IPs
For each SQL Server node VM, create the secondary IP needed for the Windows Server Failover Cluster and for the Always On availability groups listener.
-
In the OCI Console, go to the SQL Server node 1 VM, and select the Attached VNICs in the Resources menu.

-
Select the primary VNIC and then select IPv4 Addresses in the Resources menu.


-
Select Add Secondary Private IP Address and enter the details for adding a new private IP to the VNIC. Click Create and we will see a new secondary IP associated with this VNIC. This is the WSFC IP.

-
Repeat steps 1 to 3 in the same VNIC for creating another secondary IP for the Always On availability groups listener.
-
Repeat steps 1 to 4 for the other SQL Server node VM.
Task 2: Create a SQL Server Service Account
SQL Server needs to use a dedicated domain account. In this task, we will create this account. Later in the tutorial, we use this account to configure the SQL Server service at each of the nodes.
-
Log in to the Domain Controller using the domain administrator account, and navigate to Active Directory Users and Computers.

-
Expand the domain you configured for this tutorial.

-
Right-click on Users and select New User to create a new user.

-
Enter the following details and click Next.

-
Enter the password for this domain account and click Next.

-
Review the details and click Finish.

Task 3: Configure a Witness File Share
As mentioned, the architecture in this tutorial uses a file share witness to implement the quorum witness. In this task, we will create a shared folder. In a subsequent task, we will use this shared folder to configure the Windows Server Failover Cluster.
-
Log in to the Quorum VM using the domain administrator account and create a witness folder.

-
Right-click on the folder you created and select Properties. On the Sharing tab, click Share and select Everyone to share the folder. If you prefer to be more strict, select the SQL Server service account created in Task 2.

-
We will see that the folder has been shared, click Done.

Task 4: Configure a Windows Server Failover Cluster
SQL Server Always On availability groups runs on Windows Server Failover Cluster (WSFC) technology. In this task, we will:
-
Add WSFC roles to the SQL Server VMs.
-
Create and configure a cluster using the secondary IPs created in Task 1 and the quorum file share witness created in Task 3. This cluster will be used in a subsequent task by the Always On availability groups capability.
Task 4.1: Add WSFC Roles to the SQL Server VMs
-
Log in to SQL Server node 1 VM using the domain administrator, open Server Manager and on the Dashboard, click Add roles and features.

-
Click Next to proceed to the Installation Type.

-
Select Role-based or feature-based installation and click Next.

-
In Select destination server, select the server from the server pool and the SQL Server node 1, and click Next to proceed.

-
In Features, select Failover Clustering. When you do, a window will appear, then click Add Features.


-
In Confirm installation selection, review the details and click Install to confirm the installation.

-
When the installation is finished, close the wizard.

-
To confirm the installation, type Failover Cluster Manager on the search bar. You can open it and see it contains no clusters yet.


-
Repeat steps 1 to 8 in the other SQL Server node VM.
Task 4.2: Create a Cluster
-
Log in to the SQL Server node 1 VM using the domain administrator account, and open the Failover Cluster Manager. You will find there are no clusters running.

-
Right-click on Failover Cluster Manager and select Create Cluster…, this will open a Create Cluster Wizard.

-
Once the Create Cluster Wizard opens, click Next to proceed.

-
Click Browse and select the SQL Server node 1 and SQL Server node 2 VMs.

-
Confirm that you have selected the appropriate nodes and then click Next.

-
Select Yes, When I click Next, run the configuration tests, and then return to the process of creating the cluster and click Next.

-
Select Run all tests and click Next.

-
In the Confirmation window, click Next.

Wait till all tests are finished.

-
Click Finish.

-
Enter a Cluster Name and consider the NetBIOS constraints.

-
Confirm the cluster before creating and then click Next.

-
When the cluster is successfully created, click Finish.

-
Open the Failover Cluster Manager and you will be able to see the newly created cluster.

-
Notice that the status of the cluster is Offline in Cluster Core Resources section. Expand the resources and find the cluster IP addresses not yet configured. We will do it in a few steps from now.

Task 4.3: Configure a Cluster
-
Before setting up the cluster IPs, we will configure the quorum witness. Right-click on the cluster name, select More Actions and Configure Cluster Quorum Settings…. This will open up a configuration wizard.

-
In the Configure Cluster Quorum Wizard window, click Next to proceed.

-
Select the Select the quorum witness and click Next.

-
Select the Configure a file share witness and click Next.
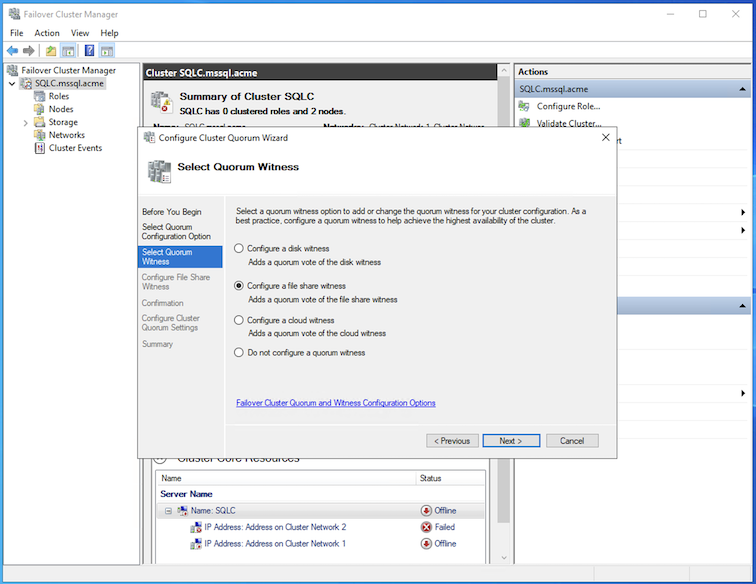
-
Enter the File Share Path configured in Task 3 and click Next.

-
Review the quorum configuration settings and click Next.

-
The quorum witness will be configured. When the configuration is successfully completed, click Finish to close the wizard.

-
We will associate the IPs created in Task 1 to the cluster. This will bring the cluster up and make it operational. On the Failover Cluster Manager, expand the Cluster Core Resources and right-click on the IP address with Failed status and then click Properties.

-
In the General tab, specify the Static IP Address configured for this node in Task 1 and click Apply.

-
Repeat steps 8 and 9 for the other IP. You will have the cluster properly set up. When the cluster name resource comes online, it updates the domain controller server with a new Active Directory computer object. We are now ready to move on to the Always On availability groups configuration.

Task 5: Configure an Always On Availability Groups for a sample database
In this task, we will:
-
Grant the appropriate permissions to the virtual computer object account created in the domain by the cluster, this will allow the cluster to create the resources Always On availability groups needs.
-
Enable Always On availability groups capability in the nodes.
-
Configure an Always On availability groups for a sample database.
-
Create a listener for the Always On availability groups.
Task 5.1: Grant permissions to the Cluster Domain Computer Object
-
Log in to the Domain Controller using the domain administrator account, and open the Active Directory Users and Computers.

-
Click View and select Advanced Features to view advanced features.

-
Right-click on Computers and select Properties.

-
Go to the Security tab and click Add.

-
In the Users, Computers, Service Accounts, or Groups wizard, click Object Types….

-
Select Computers and click OK.

-
Enter the name of the cluster and click OK. We will now see the cluster computer object in the list of groups or user names.

-
Select the cluster computer object and click Advanced to configure permissions.

-
On the Permissions tab, select your cluster computer object and click Edit.

-
Select the Create Computer objects permission entry and click OK.

-
We are now back at the Advanced Security Settings for Computers and click Apply and then OK. With this, the computer account of the cluster has the necessary permissions for Always On availability groups to work.


Task 5.2: Enable Always On availability groups in the nodes
-
Log in to the SQL Server node 1 VM using the domain administrator account, and open the SQL Server Configuration Manager.
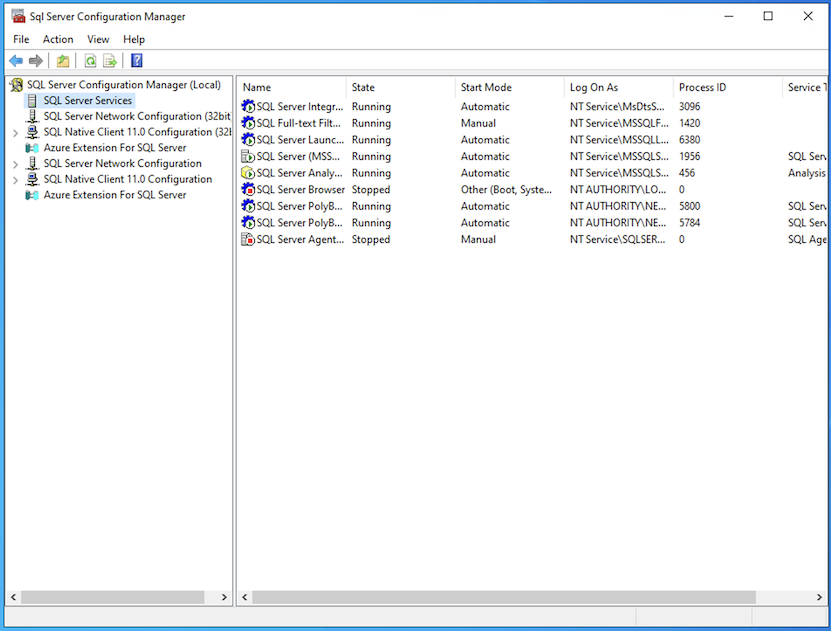
-
Click SQL Server Services, right-click on the SQL Server (MSSQL SERVER) and select Properties.

-
On the Always On Availability Groups tab, select Enable Always On Availability Groups. Notice the name of the cluster already created in Task 4.2, the Windows Server Failover Cluster and click Apply. A warning message to restart the service is displayed. Click OK to apply the changes. The service will be restarted.

-
If the SQL Server service is not restarted automatically, we can restart it manually, right-click on the SQL Server service and click Restart.

-
Right-click on the SQL Server service, select Properties and go to the Log On tab. Select This account and enter the SQL Server account details created in Task 2. Click Apply and then click OK.

-
Repeat steps 1 to 5 for the SQL Server node 2 VM.
Task 5.3: Create and Back up a Sample Database for Always On Availability Groups
-
Log in to the SQL Server node 1 VM using the domain administrator account, open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to the SQL Server instance in that node.

-
Select NEW Query and create a sample database using a create database query as shown in the following image.


-
Expand Databases on the Object Explorer and we will find the sample database created in the step 2. Right-click on it, click Tasks and then click Backup….

-
Select Full as the Backup Type. Review and confirm the backup destination and click OK.

-
We will see a message informing the successful completion of the backup. Click OK.

Task 5.4: Create an Availability Groups for the Sample Database
-
The backup is created, we are ready to start configuring an availability group. Right-click on Always On High Availability and select New Availability Group Wizard….

-
In Create a new availability group, click Next to proceed.

-
Enter an Availability group name, select Windows Server Failover Cluster as the Cluster Type and click Next.

-
Select the sample database created in Task 5.3 and click Next.

-
In the Specify Replicas window, click Specify Replicas and Add Replica… to select the node 2 replica. On the window, enter the name of the node 2 server VM, then click Connect.

-
We will now see both replicas, one with the primary role and the other with the secondary role. We can change the availability mode depending on requirements. Click Next and we will notice the Listener tab. For now skip it. We will configure a listener later in this tutorial.

-
In Select Data Synchronization, select Automatic seeding and click Next.

-
A validation of the configurations will be run. We can see that all the validation results are successful except the listener configuration. Click Next.

-
In Summary, click Finish to complete the creation and configuration of the availability group.

-
In Results, we will see a message informing you of the successful completion of the availability group configuration. Click Close.

The availability group is created and we can see its details on the Object Explorer.

Task 5.5: Create an Availability Group Listener
In this task, we will create a Listener for the availability group created in Task 5.4. The listener is a virtual network name that provides connectivity to the database on an Always On availability groups configuration. It allows a client to connect to a replica without having to know the physical instance name of the SQL Server. Since the listener routes traffic, the client connection string does not need to be modified after a failover occurs.
-
On the Object Explorer, expand the Availability Groups and the availability group created in Task 5.4 and right-click on Availability Group Listener and select Add Listener….

-
Enter a Listener DNS Name for the Listener, specify port
1433and Static IP in the Network Mode. Click Add… to add the listener IPs created in Task 1.
-
Make sure the subnet of the node you are connected to is the selected subnet and enter the IPv4 Address with the secondary IP created for the listener in Task 1 and click OK.

-
To add the second IP, click Add… again. Make sure the subnet selected is the subnet of the other node and enter the IP address of the secondary IP created for the other node in Task 1. Click OK.
-
Confirm that you can see both IPs configured and click OK to finish the listener creation.

-
Go to the Object Explorer and confirm the listener appears on the Availability Group Listeners folder.

In SQL Server Management Studio, we can now connect to the listener just as you will to any of the SQL Server nodes. Your Always On availability groups configuration is finished and you have a listener to facilitate application connectivity. Your deployment is now ready for failover, which you can perform manually.

Related Links
Acknowledgments
- Authors - Ricardo Malhado (Principal Cloud Solution Architect), Raphael Teixeira (Principal Cloud Solution Architect)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Deploy Microsoft SQL Server Always On Availability Groups for HA and DR on OCI
F92624-01
February 2024
Copyright © 2024, Oracle and/or its affiliates.