Note:
- This tutorial requires access to Oracle Cloud. To sign up for a free account, see Get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
- It uses example values for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure credentials, tenancy, and compartments. When completing your lab, substitute these values with ones specific to your cloud environment.
Authenticate Oracle Database 23ai with Microsoft Entra ID
Introduction
Oracle Database can be integrated with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Microsoft Azure Active Directory) to enable secure, passwordless access to the database. With this setup, users and services can connect to the database using their Microsoft Entra ID credentials through Single Sign-On (SSO).
Authentication is handled through an OAuth2 access token issued by Microsoft Entra ID. This token, which includes the user’s identity and access details, is passed to the Oracle Database. The database client validates the token’s format and expiration before allowing access, ensuring a secure and streamlined connection process.
Why We Need This?
As organizations increasingly prioritize security, managing access to sensitive data becomes critical. Oracle Database, in collaboration with Microsoft Entra ID, allows for secure authentication without passwords, leveraging modern identity management systems for seamless, scalable, and robust access control. This integration supports a wide range of Oracle deployments, including Oracle Autonomous Database, Oracle Exadata, and Oracle Base Database Service, ensuring consistent and secure access across different environments.
Database Clients and Tools
Applications and tools that support Microsoft Entra ID tokens can authenticate users directly through Microsoft Entra ID and pass the database access token to the Oracle Database instance through the client API. Existing database tools, such as SQL*Plus, can be configured to use a Microsoft Entra ID token stored in a file. The token can be retrieved using helper tools like Microsoft PowerShell, Azure CLI, or libraries like Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) and saved in a specified file location. Later, SQL*Plus references this token when establishing the connection.
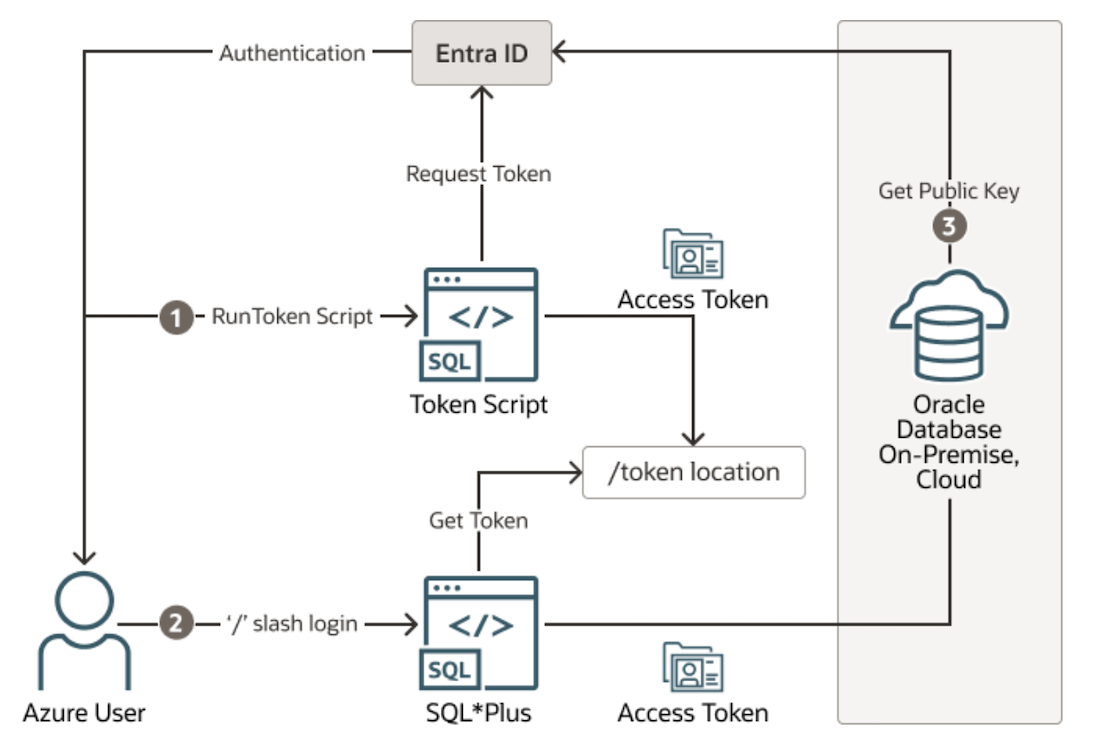
Note: This tutorial uses a Python script leveraging MSAL to acquire security tokens. For more information, see Overview of the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL).
This tutorial guides you through configuring Microsoft Entra ID authentication for Oracle Base Database 23ai, including TLS setup. Please refer to the documentation specific to your database type: on-premises, Exadata, DBaaS, or Autonomous. Note that TLS is pre-configured for Autonomous Database, so you may skip that step.
Audience
Oracle Database administrators and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (OCI IAM) administrators.
Objectives
-
Set up Transport Layer Security (TLS) for the database.
-
Register the Database Server with Microsoft Azure.
-
Register the Database Client with Microsoft Azure.
-
Configure the Database for Microsoft Azure integration.
-
Configure the Client using a helper script.
-
Test the connection using SQL*Plus.
Prerequisites
-
A Microsoft Azure account with administrative privileges.
-
Oracle Database 23ai on Oracle Base Database service.
-
Network Settings:
-
The Oracle Database server must be able to request the Microsoft Entra ID public key to validate the authenticity and validity of issued tokens, and to confirm they were issued by a trusted authority.
-
Depending on the network connectivity setup, appropriate routing and security rules must be configured. A NAT gateway can be used to route outbound traffic and egress rules should be restricted to only Microsoft Azure public IP ranges over port 443.
-
-
TLS Configuration:
- When sending Microsoft Entra ID tokens from the database client to the database server, a TLS connection must be established. In this tutorial, we will set up one-way TLS (configuring TLS with a self-signed root certificate), where only the server provides a certificate to the client to authenticate itself. The client does not need to have a separate client certificate to authenticate itself to the server.
-
Set up an Oracle client software 23ai running on Oracle Linux.
-
Install Python 3.6 or later, with the MSAL module. Even though Python 3.6 will work, the recommended version is
3.7+. Usepipto install the required module.
Task 1: Set up TLS for Oracle Database 23ai
Task 1.1: Prepare the Operating System (OS) for TLS Configuration
-
Log in to the database server and switch to the
rootuser to set up the directory.[opc@db23aigrid ~]$ sudo su - [root@db23aigrid ~]# mkdir -p /etc/ORACLE/WALLETS/oracle [root@db23aigrid ~]# cd /etc/ [root@db23aigrid etc]# chown -R oracle:oinstall ORACLE/ -
Get hostname as the
oracleuser.[root@db23aigrid etc]# su - oracle [oracle@db23aigrid admin]$ hostname -fSample output:
db23aigrid.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com -
Connect to the database.
[oracle@db23aigrid admin]$ sqlplus "/as sysdba" -
Verify the wallet root directory.
SQL> show parameter wallet_root;Sample output:
NAME TYPE VALUE ---------- ------ ---------------------------------------------------- wallet_root string /opt/oracle/dcs/commonstore/wallets/DB23GRID_w54_iad -
Check the Pluggable Database (PDB) name and GUID.
SQL> show pdbs;Sample output:
CON_ID CON_NAME OPEN MODE RESTRICTED ----- -------- --------- ---------- 2 PDB$SEED READ ONLY NO 3 DB23GRIDPDB READ WRITE NOSQL> select guid from v$containers where name = 'DB23GRIDPDB';Sample output:
GUID -- ----------------------------- 32435DD0A1EC55xxx0639400000A7225 -
Create local directories for wallet and certificates.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ mkdir -p /home/oracle/wallet_tls/certificates/rootCA [oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ mkdir -p /home/oracle/wallet_tls/certificates/db_wallet -
Create the database TLS directory under the wallet root path using the PDB GUID.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ mkdir -p /opt/oracle/dcs/commonstore/wallets/DB23GRID_w54_iad/32435DDxxxxxx7E0639400000A7225/tls -
Update
.bashrcwith TLS-related environment variables.[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ vi ~/.bashrcAdd the following and adjust the values according to your environment.
export DBUSR_SYSTEM=system export DBUSR_PWD=QAZxswedc123## # Wallet and Database Administrator (sys) password export ORA_TLS_DIR=/etc/ORACLE/WALLETS/oracle export TLS_DIR=/opt/oracle/dcs/commonstore/wallets/DB23GRID_w54_iad/32435DD0A1EC55E7E0639400000A7225/tls export ROOT_TLS_DIR=/home/oracle/wallet_tls/certificates/rootCA export DB_TLS_DIR=/home/oracle/wallet_tls/certificates/db_wallet export TLS_DN=CN=db23aigrid.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com,O=oracle,L=Austin,ST=Texas,C=US export TLS_SAN=DNS:db23aigrid,DNS:db23aigrid.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com, IPV4Address:143.47.117.99 -
Apply the changes.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ . ~/.bashrc
Task 1.2: Configure TLS Wallet and Certificate
-
Create and configure the root wallet.
-
Create the root wallet.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki wallet create -wallet ${ROOT_TLS_DIR} -pwd ${DBUSR_PWD} -auto_login -
View the contents of the wallet, it should be empty.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki wallet display -wallet ${ROOT_TLS_DIR} -
Create the self-signed certificate for the root CA wallet.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki wallet add -wallet ${ROOT_TLS_DIR} -dn $TLS_DN -keysize 2048 -sign_alg sha256 -self_signed -validity 3652 -pwd ${DBUSR_PWD} -addext_san $TLS_SAN -
The directory should now have
cwallet.ssoandewallet.p12files.ls -l ${ROOT_TLS_DIR} -
View the contents of the wallet, it should have a user and a trusted certificate.
orapki wallet display -wallet ${ROOT_TLS_DIR} -
Export the root CA trusted certificate for use in creating the database wallet.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki wallet export -wallet ${ROOT_TLS_DIR} -dn $TLS_DN -cert ${ROOT_TLS_DIR}/rootCA.crt -pwd ${DBUSR_PWD} -
View the contents of the
rootCA.crtfile.cat ${ROOT_TLS_DIR}/rootCA.crt
-
-
Create and configure the server (database) wallet.
-
Create the database wallet.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki wallet create -wallet ${DB_TLS_DIR} -pwd ${DBUSR_PWD} -auto_login -
Add the trusted root certificate to the wallet (get this from your certificate administrator).
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki wallet add -wallet ${DB_TLS_DIR} -trusted_cert -cert ${ROOT_TLS_DIR}/rootCA.crt -pwd ${DBUSR_PWD} -
Create a private key and certificate request in the wallet.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki wallet add -wallet ${DB_TLS_DIR} -keysize 2048 -dn $TLS_DN -pwd ${DBUSR_PWD}-addext_san $TLS_SAN -
Export the certificate request to get it signed.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki wallet export -wallet ${DB_TLS_DIR} -dn $TLS_DN -request ${DB_TLS_DIR}/db23gridpdb.csr -pwd ${DBUSR_PWD} -
Display the contents of the wallet, there will be an entry under Requested Certificates.
orapki wallet display -wallet ${DB_TLS_DIR} -
View the contents of the certificate signing request (CSR) file.
cat ${DB_TLS_DIR}/db23gridpdb.csr
-
-
Sign and import the server certificate.
-
Sign the CSR using the self-signed root wallet.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki cert create -wallet ${ROOT_TLS_DIR} -request ${DB_TLS_DIR}/db23gridpdb.csr -cert ${DB_TLS_DIR}/db23gridpdb-signed.crt -validity 3652 -sign_alg sha256 -pwd ${DBUSR_PWD} -
View the signed server user certificate.
cat ${DB_TLS_DIR}/db23gridpdb-signed.crt -
Import the signed database server user certificate into the database wallet.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki wallet add -wallet ${DB_TLS_DIR} -user_cert -cert ${DB_TLS_DIR}/db23gridpdb-signed.crt -pwd ${DBUSR_PWD} -
Display the contents of the wallet, ensure that the database server user certificate is now displayed under User Certificates. The wallet you will use for the database server and listener is now ready to be deployed for use.
orapki wallet display -wallet ${DB_TLS_DIR}
-
-
Deploy wallet files.
-
Copy the database server wallet files.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ cp -v ${DB_TLS_DIR}/ewallet.p12 ${TLS_DIR} [oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ cp -v ${DB_TLS_DIR}/cwallet.sso ${TLS_DIR} [oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ cp -v ${DB_TLS_DIR}/ewallet.p12 ${ORA_TLS_DIR} [oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ cp -v ${DB_TLS_DIR}/cwallet.sso ${ORA_TLS_DIR} -
Export the certificate.
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ orapki wallet export -wallet ${ROOT_TLS_DIR} -dn $TLS_DN -cert ${ROOT_TLS_DIR}/rootCA.crt -pwd ${DBUSR_PWD}
-
-
Trust the root CA system-wide as the
rootuser.-
Run the
[root@db23ailvm etc]# cp -v /home/oracle/wallet_tls/certificates/rootCA/rootCA.crt /etc/pki/catrust/source/anchors/command. -
Run the
[root@db23ailvm etc]# update-ca-trust extractcommand. -
Set appropriate file permissions.
cd /etc/ORACLE/WALLETS/ chmod -R 755 oracle/
-
Task 1.3: Configure Oracle for TLS Communication
-
Edit
sqlnet.orafor one-way TLS and append the following lines.[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin [oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ vi sqlnet.oraSSL_CLIENT_AUTHENTICATION = FALSE -
Edit
tnsnames.oraand ensure that entries for both TCP and TCPS are added for the PDB database.Adjust the values as per your environment:
[oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin [oracle@db23aigrid ~]$ vi tnsnames.oraDB23GRIDPDB=(DESCRIPTION=(CONNECT_TIMEOUT=5)(TRANSPORT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT=3)(RETRY_COUNT=3) (ADDRESS_LIST=(LOAD_BALANCE=on)(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=db23aigrid)(PORT=1521))) (CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=DB23GRIDPDB.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com))) DB23GRIDPDB_TLS=(DESCRIPTION=(CONNECT_TIMEOUT=5)(TRANSPORT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT=3)(RETRY_COUNT=3) (ADDRESS_LIST=(LOAD_BALANCE=on)(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCPS)(HOST=db23aigrid)(PORT=1522))) (CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=DB23GRIDPDB.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com)))
Task 1.4: Configure Listener with TLS
-
If you are using Oracle Grid Infrastructure, follow the steps:
-
Run the following commands.
sudo su - grid srvctl stop listener srvctl modify listener -p "TCP:1521/TCPS:1522" srvctl config listener | grep "End points" -
Edit the
listener.orafile.$ vi listener.ora LISTENER= (DESCRIPTION= (ADDRESS_LIST= (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=IPC)(KEY=LISTENER)) (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=db23aigrid.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com)(PORT=1521)) (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCPS)(HOST=db23aigrid.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com)(PORT=1522)) ) ) SSL_CLIENT_AUTHENTICATION = FALSE WALLET_LOCATION=(SOURCE=(METHOD=file) (METHOD_DATA=(DIRECTORY=/etc/ORACLE/WALLETS/oracle))) TRACE_LEVEL_LISTENER = support -
Restart the listener.
``` $ srvctl start listener ```Or
-
-
If you are using Oracle Linux Volume Manager, follow the steps:
-
Run the following command.
cd $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin lsnrctl stop -
Edit
listener.ora.$ vi listener.ora LISTENER = (DESCRIPTION_LIST = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST =db23ailvm.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com)(PORT = 1521)) (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC1521)) (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCPS)(HOST = db23ailvm.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com)(PORT = 1522)) (SECURITY=(WALLET_LOCATION=/home/oracle/wallet_tls/certificates/rootCA)) ) ) SSL_CLIENT_AUTHENTICATION = FALSE ADR_BASE_LISTENER = /u01/app/oracle/product/23.0.0 -
Restart the listener.
lsnrctl start
-
Task 1.5: Validate TLS Connectivity
-
Test the TCP (non-TLS).
$ sqlplus system/QAZxswedc123##@DB23GRIDPDB SQL> SELECT sys_context('USERENV', 'NETWORK_PROTOCOL') as network_protocol FROM dual; NETWORK_PROTOCOL Tcp -
Test the TCPS (TLS enabled)
$ sqlplus system/QAZxswedc123##@DB23GRIDPDB_TLS SQL> SELECT sys_context('USERENV', 'NETWORK_PROTOCOL') as network_protocol FROM dual; NETWORK_PROTOCOL Tcps
Task 1.6: Configure Client Host for TLS
Note: Prerequisites for this task.
OCI Compute instance running Oracle Linux 8.
Oracle Database client 23ai for Linux. For detailed information, see Oracle 23ai client installation.
Copy the Certificate files from the database server.
Follow the steps to configure the client host:
-
Copy the certificate and wallet files from the database server. You may use any preferred file transfer tool to move these files from database server to the client.
cd /home/oracle/wallet_tls/certificates/ tar -cvf rootCA.tar rootCA chmod 755 rootCA.tar cp rootCA.tar /tmp/ -
Set up client directories.
[opc@bastion-server8-8 ~]$ sudo su - oracle [oracle@bastion-server8-8 ~]$ mkdir wallet_db23aigrid_tls [oracle@bastion-server8-8 ~]$ mkdir -p network/admin [oracle@bastion-server8-8 ~]$ export TNS_ADMIN=/home/oracle/network/admin -
Transfer the certificate and wallet files from database server onto the client instance.
[oracle@bastion-server8-8 ~]$ cp rootCA.tar wallet_db23aigrid_tls / [oracle@bastion-server8-8 ~]$ cd wallet_db23aigrid_tls / [oracle@linuxclient23:~/wallet_db23aigrid_tls]$ cp /tmp/rootCA.tar -
Extract certificate files.
[oracle@linuxclient23:~/wallet_db23aigrid_tls]$ tar -xvf rootCA.tar -
Configure
tnsnames.ora.[oracle@bastion-server8-8 ~]$ cd ~/network/admin [oracle@linuxclient23:~/instantclient_23_7/network/admin]$ vi tnsnames.ora DB23GRIDPDB= (DESCRIPTION=(CONNECT_TIMEOUT=5)(TRANSPORT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT=3)(RETRY_COUNT=3) (ADDRESS_LIST=(LOAD_BALANCE=on)(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=143.47.117.99)(PORT=1521))) (CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=DB23GRIDPDB.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com))) DB23GRIDPDB_TLS=(DESCRIPTION=(CONNECT_TIMEOUT=5)(TRANSPORT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT=3)(RETRY_COUNT=3) (ADDRESS_LIST=(LOAD_BALANCE=on)(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCPS)(HOST=db23aigrid.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com)(PORT= 1522))) (CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=DB23GRIDPDB.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com)) (SECURITY = (SSL_SERVER_DN_MATCH=TRUE))) -
Configure
sqlnet.ora.[oracle@linuxclient23:~/instantclient_23_7/network/admin]$ vi sqlnet.ora SSL_CLIENT_AUTHENTICATION = FALSE WALLET_LOCATION = (SOURCE =(METHOD = FILE) (METHOD_DATA =(DIRECTORY =/home/oracle/wallet_db23aigrid_tls/rootCA)))
Task 1.7: Test the Connection from Client Instance
-
Test the TCP (non-TLS).
$ sqlplus system/QAZxswedc123##@DB23GRIDPDB SQL> SELECT sys_context('USERENV', 'NETWORK_PROTOCOL') as network_protocol FROM dual; NETWORK_PROTOCOL Tcp -
Test the TCPS (TLS enabled).
$ sqlplus system/QAZxswedc123##@DB23GRIDPDB_TLS SQL> SELECT sys_context('USERENV', 'NETWORK_PROTOCOL') as network_protocol FROM dual; NETWORK_PROTOCOL Tcps
Task 2: Set up Microsoft Azure and Database Integration
Task 2.1: Register Database Server in Microsoft Azure
-
Log in to the Microsoft Azure portal as an administrator who has Microsoft Entra ID privileges to register applications.
-
In the Azure Active directory admin center page, select Microsoft Entra ID.
-
Click App registrations and New registration.
-
Enter the following information.
-
Name: Enter
BaseDB-Server. -
Who can use this application or access this API?: Select Accounts in this organizational directory only.
-
-
Click Register.
-
Under Registered App, click Expose an API.
-
Click Add next to Application ID URI and Save. Leave the other values as default.
-
Click Add a scope and enter the following information.
-
Scope name: Enter
session:scope:connect. -
Who can consent?: Enter Admins and users.
-
Admin consent display name: Select Connect to database.
-
Admin consent description: Select Connect to database.
-
User consent display name: Select Connect to database.
-
User consent description: Select Connect to database.
-
State: Select Enabled.
Click Add scope. Once added, make sure to copy the value of Scope.

-
-
Under Token configuration, add Claim as upn with Token type as Access.
Note: This is required as part of enabling Microsoft Entra ID v2 token. For more information about v2 tokens, see Enabling Microsoft Entra ID v2 Access Tokens.
You might also be required to change the application’s manifest in Microsoft Entra ID to get a v2 token.

-
Under App roles, add the following app roles.

-
In Overview, copy Application ID URI, Directory (tenant) ID and Application (client) ID.
-
Navigate to Home, Enterprise applications, BaseDB-Server and Click Add user/group to assign users.
-
Under Users, select your user. While generating the access token, this assigned user will be used for single sign-on.
-
Under Select a role, select pdb.users, click Select and Assign.
-
Repeat step 13 and 14 for the same user and assign dba.role.
Task 2.2: Register Database Client in Microsoft Azure
-
Register the database client app with the following information.
-
Name: Enter
BaseDB-Client. -
Supported Account types: Select Accounts in this organizational directory only.
-
Redirect URI: Enter Public client/native -
<http://localhost>.
-
-
Under Manage, click API Permissions and Add a permission. Select APIs my organization uses, BaseDB-Server, Delegated permissions, Permission as session:scope:connect and click Add permissions.
-
In Overview, copy Application ID URI and Directory (tenant) ID.
Task 2.3: Configure Database Server for Microsoft Azure
Run the following queries to configure Microsoft Azure AD as the identity provider, and to create database global users and roles.
-
Check current identity provider in PDB database.
SELECT NAME, VALUE FROM V$PARAMETER WHERE NAME='identity_provider_type'; -
Set Microsoft Azure as the identity provider.
ALTER SYSTEM SET IDENTITY_PROVIDER_TYPE=AZURE_AD SCOPE=BOTH; -
Validate updated identity provider.
SELECT NAME, VALUE FROM V$PARAMETER WHERE NAME='identity_provider_type'; -
Set identity provider configuration. Replace
application_id_uri,tenant_idandapp_idwith values copied in Task 2.1.11.ALTER SYSTEM SET IDENTITY_PROVIDER_CONFIG = '{ "application_id_uri": "api://b7ae5060-667c-47b7-83f8-71283df2a2f6" , "tenant_id": "ef2b4271-9238-4dcd-8c56-d3e915e37c6f", "app_id": "b7ae5060-667c-47b7-83f8-71283df2a2f6" }' SCOPE=BOTH; -
Create global users and role in database.
CREATE USER allusers IDENTIFIED GLOBALLY AS 'AZURE_ROLE=pdb.users'; CREATE USER hrapp IDENTIFIED GLOBALLY AS 'AZURE_ROLE=hr.app'; CREATE ROLE dba_azure IDENTIFIED GLOBALLY AS 'AZURE_ROLE=dba.role'; -
Grant privileges to users and roles.
GRANT CREATE SESSION TO allusers; GRANT CREATE SESSION TO hrapp; GRANT pdb_dba TO dba_azure;
Task 2.4: Configure Helper Utility to Generate Microsoft Azure Access Token
In this task, we will make use of a Python utility to generate an access token which would be saved in a file, and later referred to by SQL*Plus. This utility requires the MSAL module to run.
-
Save the Python utility from here: Get-Token.py.
-
In the following Python code, replace the value of
scopewith the value copied in Task 2.1.8. Similarly, update the values ofclient_idandtenant_idwith values from Task 2.2.3. -
Run the Python code using the following command.
python ./get-token.py -
If everything is configured correctly, this should trigger a browser redirect to the Microsoft Azure portal for user authentication. Upon authentication, a token file will be generated in the directory where the Python command was run, which contains the access token. Access token and Refresh token will also be printed on the terminal window.
-
(Optional), You can validate the generated token by navigating here: jwt.io and pasting the token string into the Encoded field. The Decoded field displays information about the token string.
Task 2.5: Log in using SQL*PLUS
-
Test Microsoft Azure token login using SQL*PLUS.
sqlplus /nologconn /@(description= (retry_count=20) (retry_delay=3) (address= (protocol=tcps) (port=1522) (host=db23aigrid.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com)) (connect_data=(service_name=DB23GRIDPDB.sub10121249210.dbsecvcn.oraclevcn.com))(security=(SSL_SERVER_DN_MATCH=TRUE)(TOKEN_AUTH=OAUTH)(TOKEN_LOCATION=/home/oracle))) -
Verify the logged in user.
Note: Once logged in, you can run the following queries to retrieve user’s session specific information.
- CURRENT_USER variable returns the current user that’s active.
- ALLUSERS is the shared schema user which was assigned through Microsoft Entra ID app roles.
- AUTHENTICATED_IDENTITY represents the authenticated user from Microsoft Entra ID.
- ENTERPRISE_IDENTITY returns the GUID of the authenticated user from Microsoft Entra ID.
- SESSION_ROLES returns the combined list of roles granted locally and granted via global mappings through Microsoft Entra ID app roles.
-
Run the following query to verify the current user.
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT ('USERENV','CURRENT_USER') FROM DUAL;Output:
SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','CURRENT_USER') ALLUSERS -
Run the following query to verify the authenticated user.
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT ('USERENV','AUTHENTICATED_IDENTITY') FROM DUAL;Output:
SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','AUTHENTICATED_IDENTITY') <anujtrip.ai@gmail.com> -
Run the following query to verify the GUID of the authenticated user.
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT ('USERENV','ENTERPRISE_IDENTITY') FROM DUAL;Output:
SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','ENTERPRISE_IDENTITY') 7eb35b90-dcxxx5-bc0b-48789368e9cf -
Run the following query to verify the app roles.
SELECT * FROM SESSION_ROLES;Output:
ROLE DBA_AZURE PDB_DBA CONNECT
Next Steps
With Microsoft Entra ID-based authentication successfully implemented, you can align user roles and access policies through centralized identity governance. By leveraging global mappings for shared schema users and roles, you can streamline access control and reduce administrative complexity. Additionally, it is essential to monitor user sessions and access patterns to enhance security and ensure compliance with organizational policies. You should also consider extending this integration to other databases or applications to maintain consistent identity management across the enterprise.
Related Links
-
Use Azure Active Directory Authentication with Base Database Service
-
Authenticating and Authorizing Microsoft Azure Users for Oracle Databases
Acknowledgments
- Authors - Anuj Tripathi (Principal Cloud Architect, NA Solutions Engineering), Alex Kovuru (Principal Cloud Architect, NA Solutions Engineering)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Authenticate Oracle Database 23ai with Microsoft Entra ID
G33182-02
Copyright ©2025, Oracle and/or its affiliates.