Note:
- This tutorial requires access to Oracle Cloud. To sign up for a free account, see Get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
- It uses example values for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure credentials, tenancy, and compartments. When completing your lab, substitute these values with ones specific to your cloud environment.
Migrate Bare Metal GPU Nodes to OKE as Self-Managed Nodes using an OCI Stack
Introduction
In this tutorial, we will walk through the process of migrating bare metal (BM) GPU nodes to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Kubernetes Engine (OKE) self-managed nodes using an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) stack.
Let us first understand what self-managed nodes are, and why they are an ideal fit for running GPUs on OKE.
What are OKE Self-Managed Nodes?
As the name implies, self-managed nodes are fully controlled and maintained by the customer. This includes provisioning, scaling, configuration, upgrades, and maintenance tasks such as Operating System (OS) patching and node replacement. While this approach requires more manual management, it provides maximum flexibility and control, making it suitable for specialized workloads like those running on GPUs.
Key Features of Self-Managed Nodes:
-
Full Control: Customer has complete control over the node lifecycle, including provisioning, OS updates, scaling, and termination.
-
Custom Configurations: Customer can use custom images, install specific software, configure networking, or use alternative instance types.
-
Manual Upgrades: Unlike OKE-managed node pools, customer must manually upgrade Kubernetes versions, security patches, and OS updates.
-
Bring Your Own Nodes (BYON): Customer can use existing OCI Compute instances as worker nodes in an OKE cluster.
-
No Automatic Node-cycling: If a node fails, customer needs to manually replace/cycle it.
This tutorial covers a use case where BM A100 GPU workloads are currently running on a Slurm cluster in OCI, with the goal of migrating them to an OKE cluster. This can be achieved using the High Performance Computing (HPC) OKE stack to deploy an empty OKE cluster and then add the existing GPU nodes to it.
Objectives
- Migrate BM A100 GPU nodes to OKE as self-managed nodes using HPC OKE stack.
Prerequisites
-
Administrator access to an OCI tenancy and OKE cluster running.
-
Install NVIDIA Run:ai on BM A100 nodes to containerize the applications. For more information, see NVIDIA Run:ai.
-
Run Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) GPU workloads on OKE. For more information, see Running RDMA (remote direct memory access) GPU workloads on OKE.
Task 1: Migrate BM A100 GPU Nodes to OKE using HPC OKE Stack
-
Log in to the OCI Console and create the necessary policies as mentioned in this GitHub page: Running RDMA (remote direct memory access) GPU workloads on OKE.
-
Click Deploy to Oracle Cloud and review the terms and conditions.
-
Select the region where you want to deploy the stack.
-
In the Stack information page, enter Name for your stack.
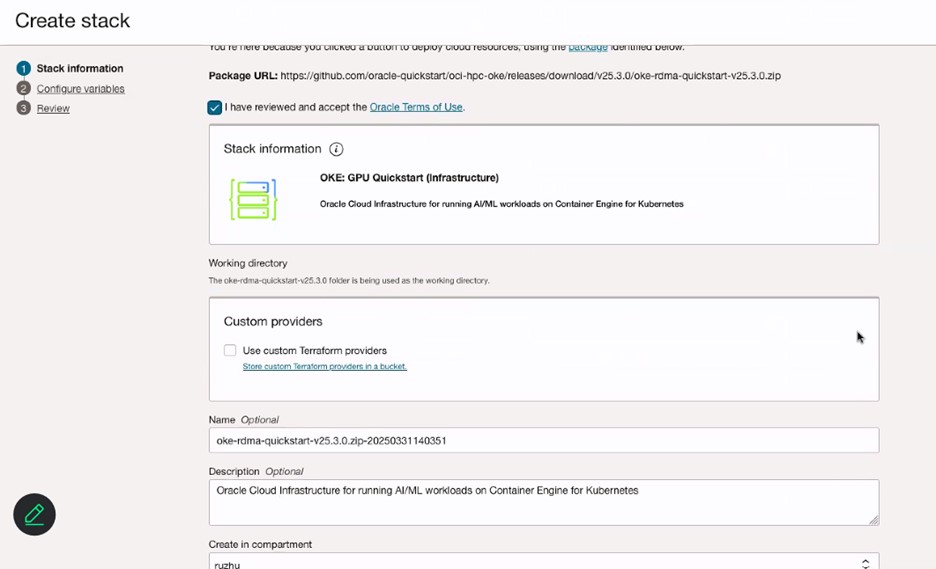
-
In the Configure variable page, enter Name for your VCN.

-
In the Bastion & Operator section, enter the information of Bastion instance and add SSH key for the Bastion instance.
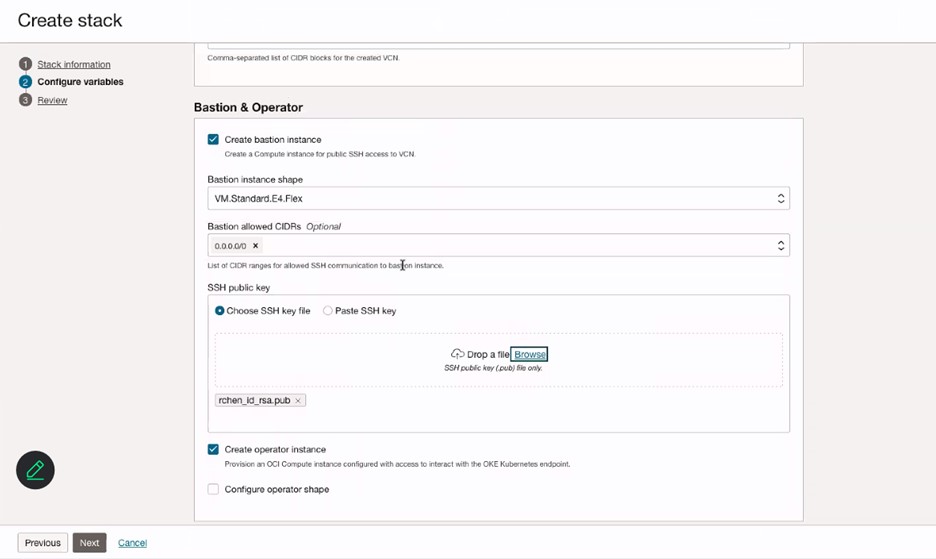
-
(Optional) Select Configure operator shape to create operator node for monitoring or running jobs.
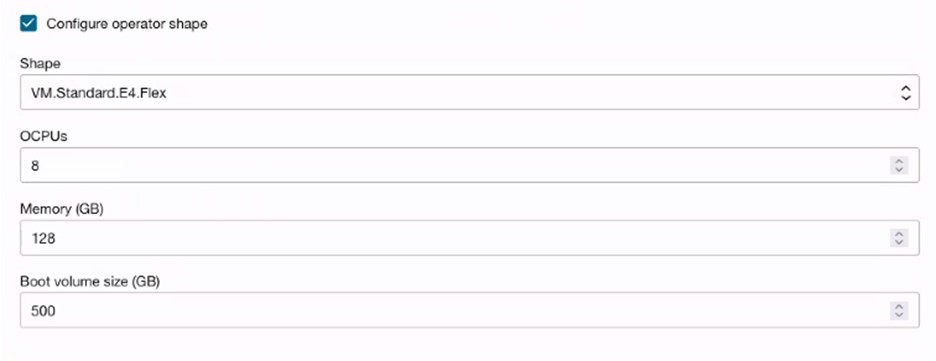
-
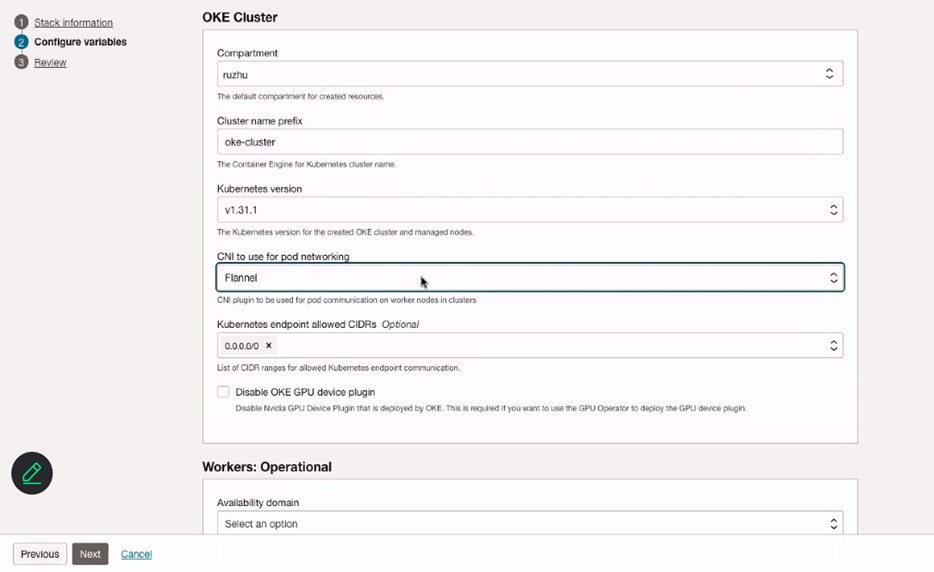
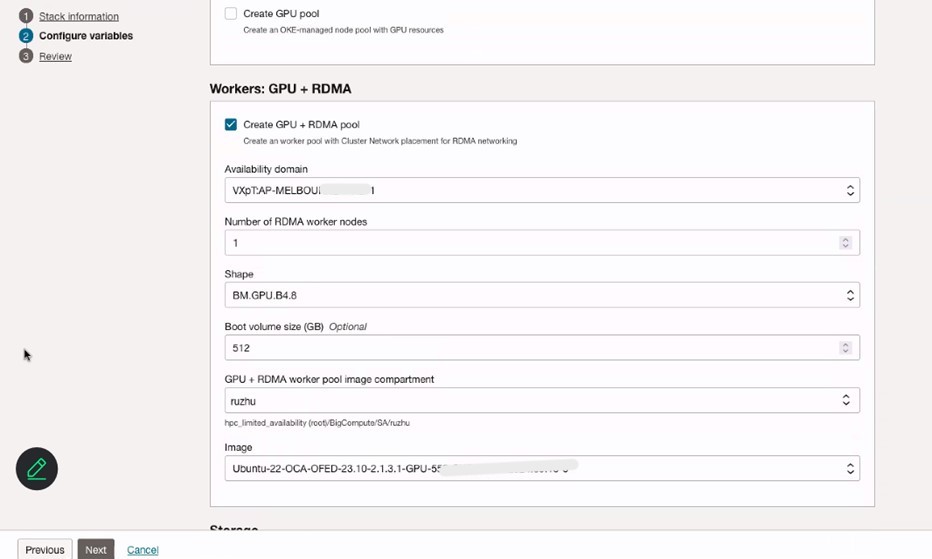
Configure variables of OKE Cluster, Workers: Operational nodes and Workers: GPU + RDMA nodes. Make sure to select Flannel CNI to use for pod networking.

-
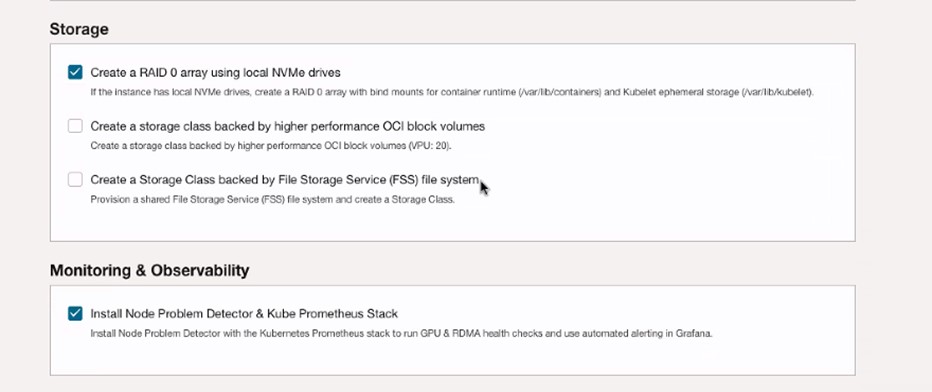
Select Create a RAID 0 array using local NVMe drives and Install Node Problem Detector & Kube Prometheus Stack.
-
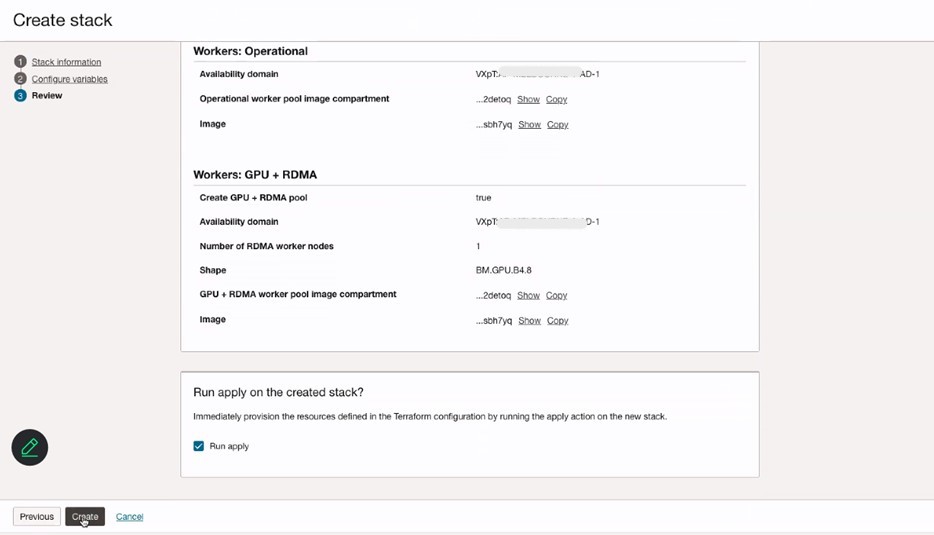
Review stack information and click Create.
-
Review the Stack details in Resource Manager and verify the OKE cluster under the Kubernetes section in the OCI Console.
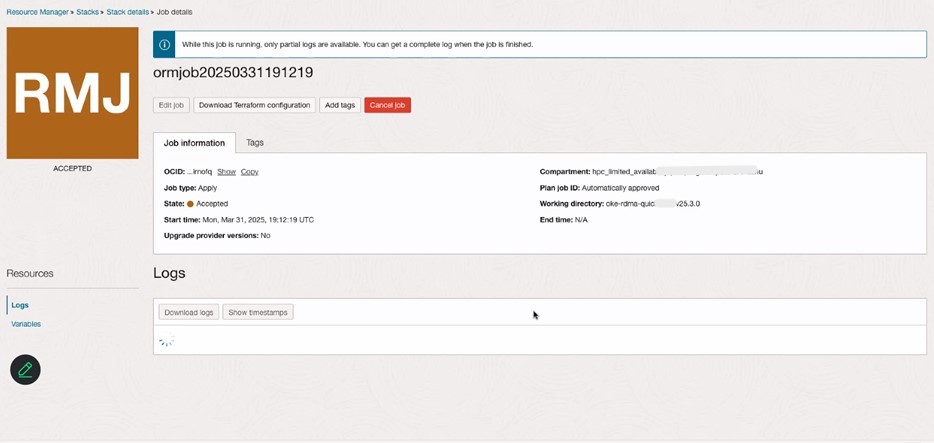
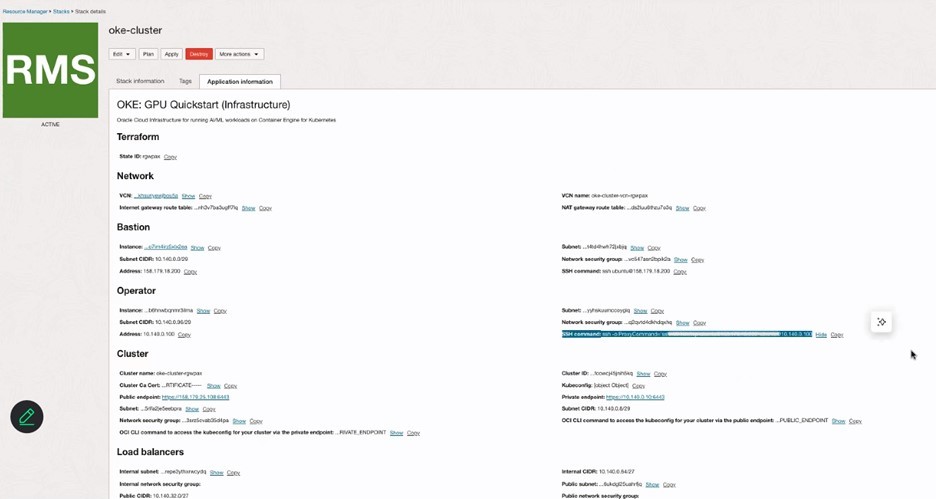
-
Log in to the OKE cluster using the access cluster through OCI Console and proceed to add new GPU nodes to it.
-
Follow all the steps mentioned here: Creating a Dynamic Group and a Policy for Self-Managed Nodes.
-
Follow step 1 and step 2 mentioned here: Creating Cloud-init Scripts for Self-managed Nodes.
-
Run the following script to add the GPU nodes to the OKE cluster.
sudo rm archive_uri-https_objectstorage_ap-osaka-1_oraclecloud_com_p_ltn5w_61bxynnhz4j9g2drkdic3mwpn7vqce4gznmjwqqzdqjamehhuogyuld5ht_n_hpc_limited_availability_b_oke_node_repo_o_ubuntu-jammy.list sudo apt install -y oci-oke-node-all* sudo oke bootstrap --apiserver-host <API SERVER IP> --ca <CA CERT> --manage-gpu-services --crio-extra-args " -
Run the following command to verify that the nodes have been successfully added to the OKE cluster.
kubectl get nodes
Related Links
-
Creating a Dynamic Group and a Policy for Self-Managed Nodes
-
Introducing the best platform for AI workloads – OCI Kubernetes Engine (OKE)
Acknowledgments
- Authors - Ruzhu Chen (Master Principal Enterprise Cloud Architect), Payal Sharma (Senior Enterprise Cloud Architect)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Migrate Bare Metal GPU Nodes to OKE as Self-Managed Nodes using an OCI Stack
G31632-01
Copyright ©2025, Oracle and/or its affiliates.